Influence of Arch-Support Orthoses with Heel Lift Manipulation on Joint Moments and Forefoot Mechanics in Running
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
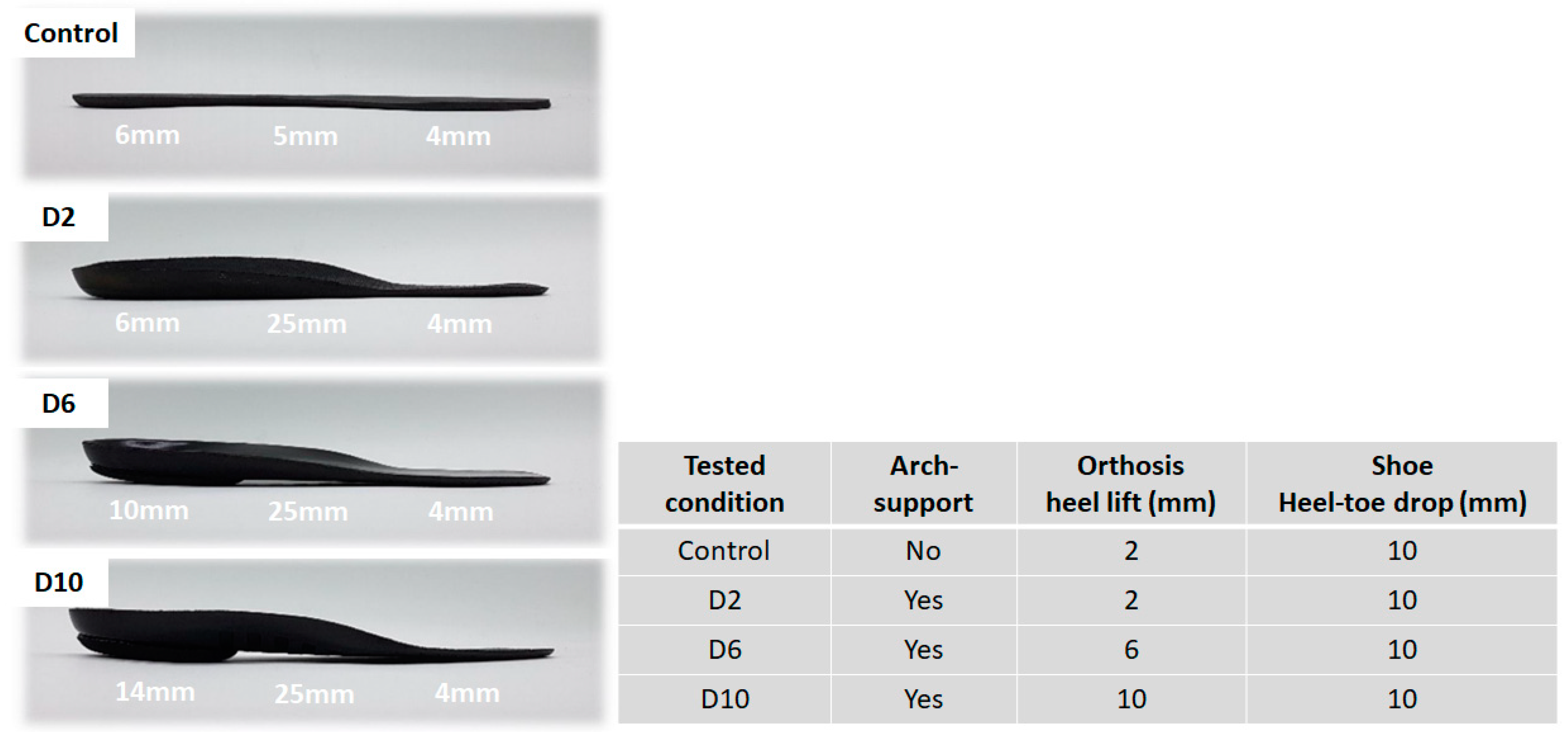
2.2. Experimental Conditions and Procedure
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal and GRF Variables
3.2. Sagittal Joint Kinematics Variables
3.3. Frontal Joint Kinematics Variables
3.4. Joint Moment Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filo, K.; Funk, D.C.; O’Brien, D. Examining motivation for charity sport event participation: A comparison of recreational-based and charity-based motives. J. Leis. Res. 2011, 43, 491–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, R.N.; Siem, D.; van Middeloop, M.; van Os, A.G.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Koes, B.W. Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredericson, M.; Misra, A.K. Epidemiology and aetiology of marathon-running injuries. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.D.; Hespanhol Junior, L.C.; Yeung, S.S.; Costa, L.O.P. What are the main running-related musculoskeletal injuries? Sports Med. 2012, 42, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Cuevas, A.G.; Perez-Soriano, P.; Llana-Belloch, S.; Macian-Romero, C.; Sanchez-Zuriaga, D. Effect of custom-made and prefabricated insoles on plantar loading parameters during running with and without fatigue. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, K.; Vorpahl, K.A.; Heiderscheit, B. Effect of Cushioned Insoles on Impact Forces During Running. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2008, 98, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Stergiou, P.; Worobets, J.; Nigg, B.; Stefanyshyn, D. Improved footwear comfort reduces oxygen consumption during running. Footwear Sci. 2009, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.M. Prefabricated insoles and modifications in sports medicine. In Athletic Footwear and Orthoses in Sports Medicine; Werd, M.B., Knight, E.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Hu, K.; Wan, Q.; Ding, Y.; Vanwanseele, B. Adding an arch support to a heel lift improves stability and comfort during gait. Gait Posture 2017, 58, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Preston, J.J.; Queen, R.M.; Byram, I.R.; Hardaker, W.M.; Gross, M.T.; Davis, J.M.; Taft, T.N.; Garrett, W.E. Effects of wearing foot orthosis with medial arch support on the fifth metatarsal loading and ankle inversion angle in selected basketball tasks. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2007, 37, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.W.; Chong, L.J.; Pan, J.W.; Lam, W.K.; Ho, M.; Kong, P.W. Effects of foot orthosis on ground reaction forces and perception during short sprints in flat footed athletes. Res. Sports Med. 2021, 29, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundermann, A.; Nigg, B.M.; Humble, R.N.; Stefanyshyn, D.J. Foot orthotics affect lower extremity kinematics and kinetics during running. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, G.F.; Solomonidis, S.E.; Paul, J.P. Biomechanics of longitudinal arch support mechanisms in foot orthoses and their effect on plantar aponeurosis strain. Clin. Biomech. 1996, 11, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabusin, C.L.; Menz, H.B.; McClelland, J.A.; Tan, J.M.; Whittaker, G.A.; Evans, A.M.; Munteanu, S.E. Effects of heel lifts on lower limb biomechanics and muscle function: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2019, 69, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinschmidt, C.; Nigg, B.M. Influence of heel height on ankle joint moments in running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, G.; Veer, F.; Verhulst, S.; Solomonidis, S.E.; Paul, J.P. The effect of heel elevation on strain within the plantar aponeurosis: In vitro study. Foot Ankle Int. 2001, 11, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.; Flowers-Johnson, J.; Bunnell, M.; Carter, L. The use of heel lifts and custom orthotics in reducing self-reported chronic musculoskeletal pain scores. AAO J. 2009, 19, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, S.J.; Kerwin, D.G. The influence of heel lift manipulation on Achilles tendon loading in running. J. Appl. Biomech. 1998, 14, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Kerwin, D.G. The influence of heel lift manipulation on sagittal plane kinematics in running. J. Appl. Biomech. 1999, 15, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisogono, V. Physiotherapy treatment for Achilles tendon injuries. Physiotherapy 1989, 75, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLellan, G.; Vyvyan, B. Management of pain beneath the heel and Achilles tendonitis with visco-elastic heel inserts. Br. Joint J. 1981, 63, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- James, A.; Williams, C.; Haines, T. Effectiveness of interventions in reducing pain and maintaining physical activity in children and adolescents with calcaneal apophysitis (sever’s disease): A systematic review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2013, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fabry, G.; Molenaers, G.; Lammens, J.; Moens, P. Kinematic and kinetic asymmetry in patients with leg-length discrepancy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1998, 18, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnanson, M.; Cooksey, A.; Hillier, C.; Kobbeman, H.; Stambaugh, A. Heel lifts and the stance phase of gait in subjects with limited ankle dorsiflexion. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, T.; Morio, C.; Millet, G.Y.; Rossi, J. Influence of shoe drop on running kinematics and kinetics in female runners. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvais, N.; Samozino, P. Effect of midsole geometry on foot-strike pattern and running kinematics. Footwear Sci. 2013, 5, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, D.E.; Venkadesan, M.; Werbel, W.A.; Daoud, A.I.; D’andrea, S.; Davis, I.S.; Mang’eni, R.O.; Pitsiladis, Y. Foot strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners. Nature 2010, 463, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, C.E.; Ferber, R.; Pollard, C.D.; Hamill, J.O.; Davis, I.S. Biomechanical factors associated with tibial stress fracture in female runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, S.; Lam, W.K.; Ching, E.C.K.; Chan, Z.Y.S.; Zhang, J.H.; Cheung, R.T.H. Effects of heel-toe drop on running biomechanics and perceived comfort of rearfoot strikers in standard cushioned running shoes. Footwear Sci. 2020, 12, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoitz, F.; Mohr, M.; Asmussen, M.; Lam, W.K.; Nigg, S.; Nigg, B. The effects of systematically altered footwear features on biomechanics, injury, performance and preference in runners of different skill level: A systematic review. Footwear Sci. 2020, 12, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honert, E.C.; Mohr, M.; Lam, W.K.; Nigg, S. Shoe feature recommendations for different running levels: A Delphi study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, F.C.; Stein, T.; Ringhof, S.; Stetter, B.J. The effect of heel-to-toe drop of standard running shoes on lower limb biomechanics. Footwear Sci. 2019, 11, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malisoux, L.; Chambon, N.; Urhausen, A.; Theisen, D. Influence of the heel-to-toe drop of standard cushioned running shoes on injury risk in leisure-time runners: A randomized controlled trial with 6-month follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 2933–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, I.S.; Bowser, B.J.; Hamill, J. Vertical impact loading in runners with a history of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, M.B.; Hamill, J.; Davis, I.S. Biomechanical and anatomic factors associated with a history of plantar fasciitis in female runners. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009, 19, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosonen, J.; Kulmala, J.P.; Müller, E.; Avela, J. Effects of medially posted insoles on foot and lower limb mechanics across walking and running in overpronating men. J. Biomech. 2017, 54, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.J.; Feger, M.A.; Hertel, J. Forefoot involvement in lateral ankle sprains and chronic ankle instability. Part 2: Clinical Considerations. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2016, 11, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferber, R.; Hettinga, B.A. A comparison of different over-the-counter foot orthotic devices on multi-segment foot biomechanics. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2016, 40, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nester, C.J. Lessons from dynamic cadaver and invasive bone pin studies: Do we know how the foot really moves during gait? J. Foot Ankle Res. 2009, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, J.; Taylor, P.J.; Hebron, J.; Chockalingam, N. Differences in multi-segment foot kinematics measured using skin and shoe mounted markers. Foot Ankle Online J. 2014, 7, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ojukwu, C.P.; Anyanwu, E.G.; Nwafor, G.G. Correlation between foot arch index and the intensity of foot, knee, and lower back pain among pregnant women in a south-eastern nigerian community. Med. Princ. Pr. 2017, 26, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinger, P.; Murley, G.S.; Barton, C.J.; Cotchett, M.P.; McSweeney, S.R.; Menz, H.B. A comparison of foot kinematics in people with normal- and flat-arched feet using the Oxford Foot Model. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbins, J.; Harrington, M.; Thompson, N.; Zavatsky, A.; Theologis, T. Repeatability of a model for measuring multi-segment foot kinematics in children. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.J.; Arnold, B.L.; Coffey, T.G.; Pidcoe, P.E. Repeatability of the modified Oxford foot model during gait in healthy adults. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, W.K.; Wong, C.K.; Park, L.Y.; Tan, M.F.; Leung, A.K.L. Effectiveness and reliability of foot orthoses on impact loading and lower limb kinematics when running at preferred and nonpreferred speeds. J. Appl. Biomech. 2020, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Jeon, H.M.; Lam, W.K.; Stefanyshyn, D.; Ryu, J. The effets of downhill slope on kinematics and kinetics of the lower extremity joints during running. Gait Posture 2018, 68, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, N.; Delattre, N.; Gueguen, N.; Berton, E.; Rao, G. Shoe drop has opposite influence on running pattern when running overground or on a treadmill. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.K.; Lee, W.C.C.; Lee, W.M.; Ma, C.Z.H.; Kong, P.W. Segmental forefoot plate in basketball footwear: Does it influence performance and foot joint kinematics and kinetics. J. Appl. Biomech. 2018, 34, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associate, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, T.; Morio, C.; Rossi, J. Effects of shoe drop on running mechanics in women. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, B. Influence of in-shoe heel lifts on plantar pressure and center of pressure in the medial-lateral direction during walking. Gait Poture 2014, 39, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrick, T.R.; Dereu, D.; McLean, S.P. Impacts and kinematic adjustments during an exhaustive run. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christina, K.; White, S.; Gilchrist, L. Effect of localized muscle fatigue on vertical ground reaction forces and ankle joint motion during running. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2001, 20, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Lam, W.-K.; Zhang, X.; Vanwanseele, B.; Liu, H. Influence of heel design on lower extremity biomechanics and comfort perception in overground running. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.-K.; Pak, L.-Y.; Wong, C.K.-K.; Tan, M.F.; Park, S.-K.; Ryu, J.; Leung, A.K.-L. Effects of arch-support orthoses on ground reaction forces and lower extremity kinematics related to running at various inclinations. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Wong, D.W.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.L.W.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, M. Immediate effects of medially posted insoles on lower limb joint contact forces in adult acquired flatfoot: A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatone, S.; Gard, S.A.; Malas, B.S. Effect of ankle-foot orthosis alignment and foot-plate length on the gait of adults with poststroke hemiplegia. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmyttere, G.; Hajizadeh, M.; Bleau, J.; Begon, M. Effect of foot orthosis design on lower limb joint kinematics and kinetics during walking in flexible pes planovalgus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 59, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Leung, A.K.-L.; Zhang, M. Biomechanical consequences of subtalar joint arthroereisis in treating posterior tibial tendon dysfunction: A theoretical analysis using finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, C.; Davis, I.S.; Hamill, J. Influence of a custom foot orthotic intervention on lower extremity dynamics in healthy runners. Clin. Biomech. 2016, 21, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbolue, U.C.; Yates, E.L.; Wearing, S.C.; Gu, Y.; Lam, W.K.; Valentin, S.; Baker, J.S.; Dutheil, F.; Sculthorpe, N.F. Sex differences in heel pad stiffness during in vivo loading and unloading. J. Anat. 2020, 237, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessery, Y.; Belzile, E.; Turmel, S.; Corbeil, P. Effects of foot orthoses with medial arch support and lateral wedge on knee adduction moment in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2017, 41, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.W.K.; Kong, P.W. Association between foot type and lower extremity injuries: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2013, 43, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, M.A.; Takacs, J.; Krowchuk, N.M.; Hatfield, G.L.; Hinman, R.S.; Chang, R. Lateral wedges with and without custom arch support for people with medial knee osteoarthritis and pronated feet: An exploratory randomized crossover study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2017, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Orthosis Condition | ANOVA Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat (Control) | D2 | D6 | D10 | F-Value | p-Value | Partial Eta Squared (ηp2) | |
| Max loading rate (BW/s) | 871.4 (321.0) * | 881.7 (307.1) * | 801.7 (275.4) | 737.4 (266.4) | 11.49 | <0.001 | 0.45 |
| Contact time (ms) | 262.0 (31.5) | 263.2 (33.3) | 262.0 (30.5) | 263.6 (34.3) | 0.19 | 0.901 | 0.01 |
| Stride length (m) | 1.33 (0.12) | 1.38 (0.11) | 1.32 (0.11) | 1.36 (0.11) | 2.41 | 0.080 | 0.15 |
| Stride frequency (Hz) | 2.08 (0.45) | 1.95 (0.26) | 2.10 (0.42) | 1.99 (0.32) | 2.37 | 0.084 | 0.15 |
| Orthosis Condition | ANOVA Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat (Control) | D2 | D6 | D10 | F-Value | p-Value | Partial Eta Squared (ηp2) | |
| Total RoM (o) | |||||||
| Forefoot-sagittal | 17.6 (4.8) | 19.7 (6.7) | 18.0 (6.2) | 20.7 (9.7) | 1.60 | 0.224 | 0.10 |
| Rearfoot-sagittal | 29.5 (5.6) | 31.5 (6.4) | 31.5 (5.5) | 33.2 (8.9) | 2.06 | 0.152 | 0.13 |
| Knee-sagittal | 25.3 (3.2) | 25.7 (3.0) | 25.3 (2.8) | 25.9 (2.8) | 0.82 | 0.493 | 0.06 |
| Angle at touchdown (o) | |||||||
| Forefoot dorsiflexion | 12.9 (5.4) | 14.3 (5.8) | 10.7 (6.1) | 10.5 (8.9) | 2.67 | 0.090 | 0.16 |
| Rearfoot dorsiflexion | 2.2 (5.6) *^ | 3.3 (8.1) * | 7.3 (7.1) | 9.5 (9.5) | 8.96 | <0.001 | 0.39 |
| Knee flexion | −18.3 (4.2) | −18.4 (4.3) | −18.6 (4.2) | −17.6 (4.7) | 1.44 | 0.093 | 0.09 |
| Peak angle during stance (o) | |||||||
| Peak forefoot dorsiflexion | 17.4 (5.2) | 18.0 (5.9) | 17.7 (5.5) | 16.5 (7.9) | 0.39 | 0.671 | 0.03 |
| Peak forefoot plantarflexion | −0.2 (3.7) | −1.7 (4.7) | −0.3 (4.9) | −4.2 (7.4) | 2.81 | 0.051 | 0.17 |
| Peak rearfoot doriflexion | 21.3 (6.5) * | 23.6 (7.3) * | 23.7 (7.4) * | 27.9 (8.8) | 5.29 | 0.003 | 0.27 |
| Peak rearfoot plantarflexion | −8.6 (6.8) | −7.7 (7.7) | −7.8 (6.0) | −5.3 (8.1) | 1.69 | 0.183 | 0.11 |
| Peak knee flexion | −42.9 (3.6) | −43.0 (3.7) | −43.1 (3.6) | −42.6 (4.1) | 0.34 | 0.797 | 0.02 |
| Min knee flexion | −17.5 (4.0) | −17.2 (4.5) | −17.8 (4.1) | −16.7 (4.2) | 1.36 | 0.267 | 0.09 |
| Joint angles at push-off (o) | |||||||
| Forefoot dorsiflexion | 9.5 (5.8) | 10.3 (5.1) | 11.4 (5.7) | 8.8 (9.1) | 1.25 | 0.302 | 0.08 |
| Rearfoot plantarflexion | −6.6 (8.5) | −5.7 (8.1) | −6.1 (8.0) | −3.0 (8.9) | 1.82 | 0.159 | 0.12 |
| Knee flexion | −23.1 (4.9) | −22.3 (5.9) | −23.3 (6.3) | −22.4 (5.1) | 0.93 | 0.435 | 0.06 |
| Orthosis Condition | ANOVA Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat (Control) | D2 | D6 | D10 | F-Value | p-Value | Partial Eta Squared (ηp2) | |
| Total RoM (o) | |||||||
| Forefoot-frontal | 4.4 (1.3) | 5.3 (2.1) ^ | 4.1 (1.2) | 5.7 (2.8) ^ | 3.50 | 0.024 | 0.20 |
| Rearfoot-frontal | 13.2 (3.5) | 12.8 (3.1) * | 13.2 (2.2) | 13.9 (2.9) | 2.87 | 0.048 | 0.17 |
| Angle at touchdown (o) | |||||||
| Forefoot inversion | 1.2 (2.5) | −0.03 (4.6) | 0.4 (2.9) | −0.8 (2.2) | 1.53 | 0.220 | 0.10 |
| Rearfoot eversion | 1.3 (4.2) | 0.6 (2.6) | 0.5 (3.8) | 0.01 (4.1) | 0.61 | 0.613 | 0.04 |
| Peak angle during stance (o) | |||||||
| Peak forefoot eversion | −1.5 (1.7) * | −3.4 (4.7) | −1.2 (2.5) * | −3.6 (2.9) | 3.35 | 0.028 | 0.19 |
| Peak forefoot inversion | 2.8 (2.0) | 1.8 (4.5) | 2.9 (2.0) | 2.1 (2.6) | 0.65 | 0.590 | 0.04 |
| Peak rearfoot eversion | −7.8 (5.0) | −7.9 (4.1) | −8.4 (4.7) | −9.6 (3.9) | 1.74 | 0.173 | 0.11 |
| Peak rearfoot inversion | 5.4 (4.1) | 4.9 (2.6) | 4.8 (3.6) | 4.3 (3.2) | 0.50 | 0.683 | 0.04 |
| Joint angles at push-off (o) | |||||||
| Forefoot eversion | 0.4 (2.1) | −1.3 (4.2) | 1.1 (2.1) | −1.1 (3.1) | 2.69 | 0.058 | 0.16 |
| Rearfoot inversion | 4.9 (4.2) | 4.7 (2.9) | 4.4 (3.5) | 3.6 (3.5) | 0.77 | 0.520 | 0.05 |
| Orthosis Condition | ANOVA Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat (Control) | D2 | D6 | D10 | F-Value | p-Value | Partial Eta Squared (ηp2) | |
| Peak moment (Nm/BW) | |||||||
| Rearfoot plantarflexion | −2.75 (0.50) | −2.67 (0.52) | −2.69 (0.57) | −2.78 (0.54) | 1.56 | 0.215 | 0.10 |
| Rearfoot eversion | 0.18 (0.25) | 0.11 (0.23) | 0.08 (0.26) # | 0.11 (0.22) | 3.03 | 0.040 | 0.18 |
| Knee extension | 2.07 (0.42) | 2.20 (0.42) # | 2.19 (0.46) | 2.19 (0.44) # | 3.24 | 0.031 | 0.19 |
| Knee adduction | −1.05 (0.37) | −1.04 (0.40) | −1.00 (0.31) | −1.05 (0.34) | 0.41 | 0.748 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, J.-X.; Lam, W.-K.; Lung-Wai Sze, P.; Tan, M.F.; Leung, A.K.-L. Influence of Arch-Support Orthoses with Heel Lift Manipulation on Joint Moments and Forefoot Mechanics in Running. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041613
Pan J-X, Lam W-K, Lung-Wai Sze P, Tan MF, Leung AK-L. Influence of Arch-Support Orthoses with Heel Lift Manipulation on Joint Moments and Forefoot Mechanics in Running. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041613
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Jun-Xiang, Wing-Kai Lam, Peter Lung-Wai Sze, Mohammad Farhan Tan, and Aaron Kam-Lun Leung. 2021. "Influence of Arch-Support Orthoses with Heel Lift Manipulation on Joint Moments and Forefoot Mechanics in Running" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041613
APA StylePan, J.-X., Lam, W.-K., Lung-Wai Sze, P., Tan, M. F., & Leung, A. K.-L. (2021). Influence of Arch-Support Orthoses with Heel Lift Manipulation on Joint Moments and Forefoot Mechanics in Running. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041613






