Configuration Design of an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot with a Generalized Shoulder Joint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Human Upper Limb Kinematics
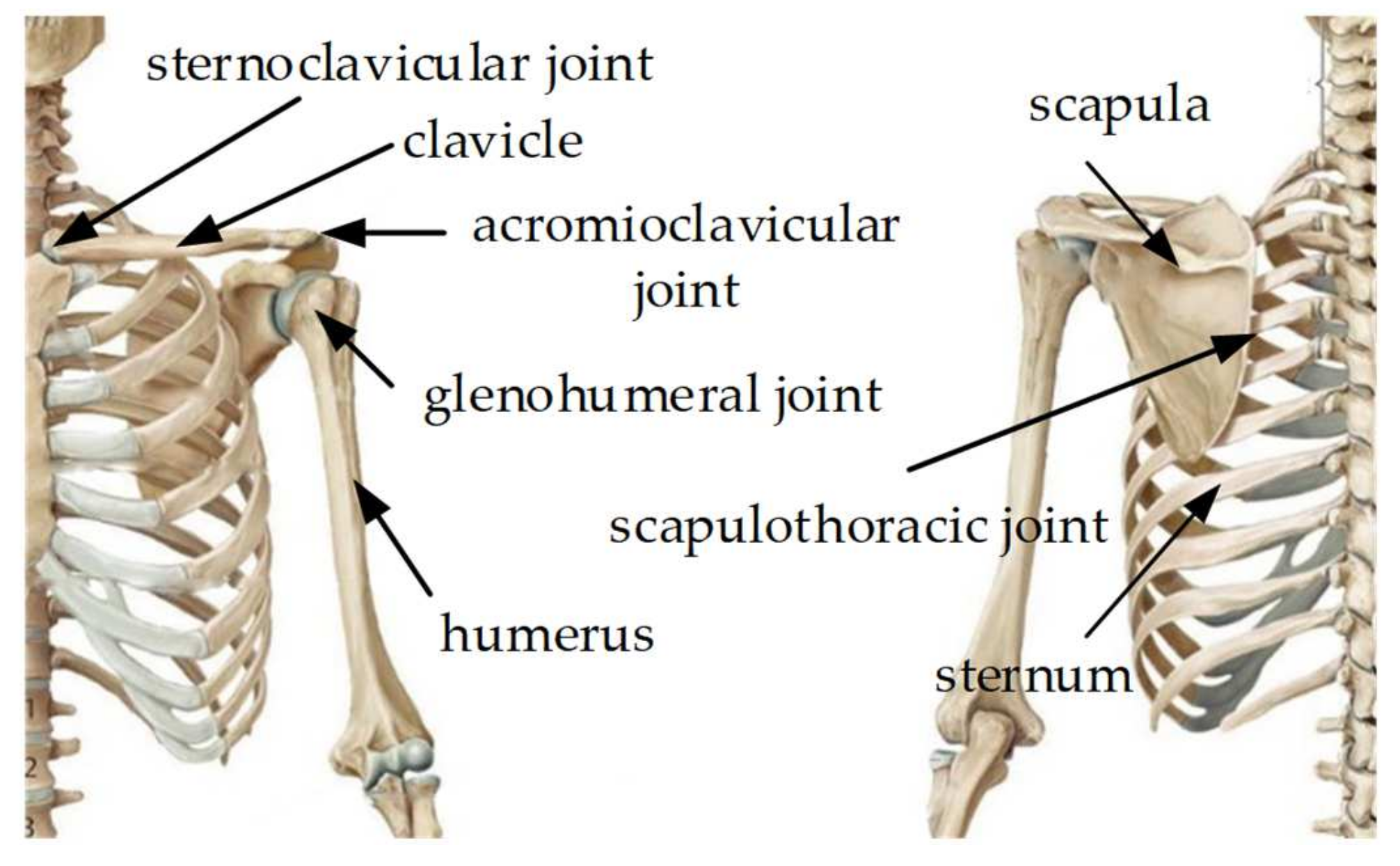
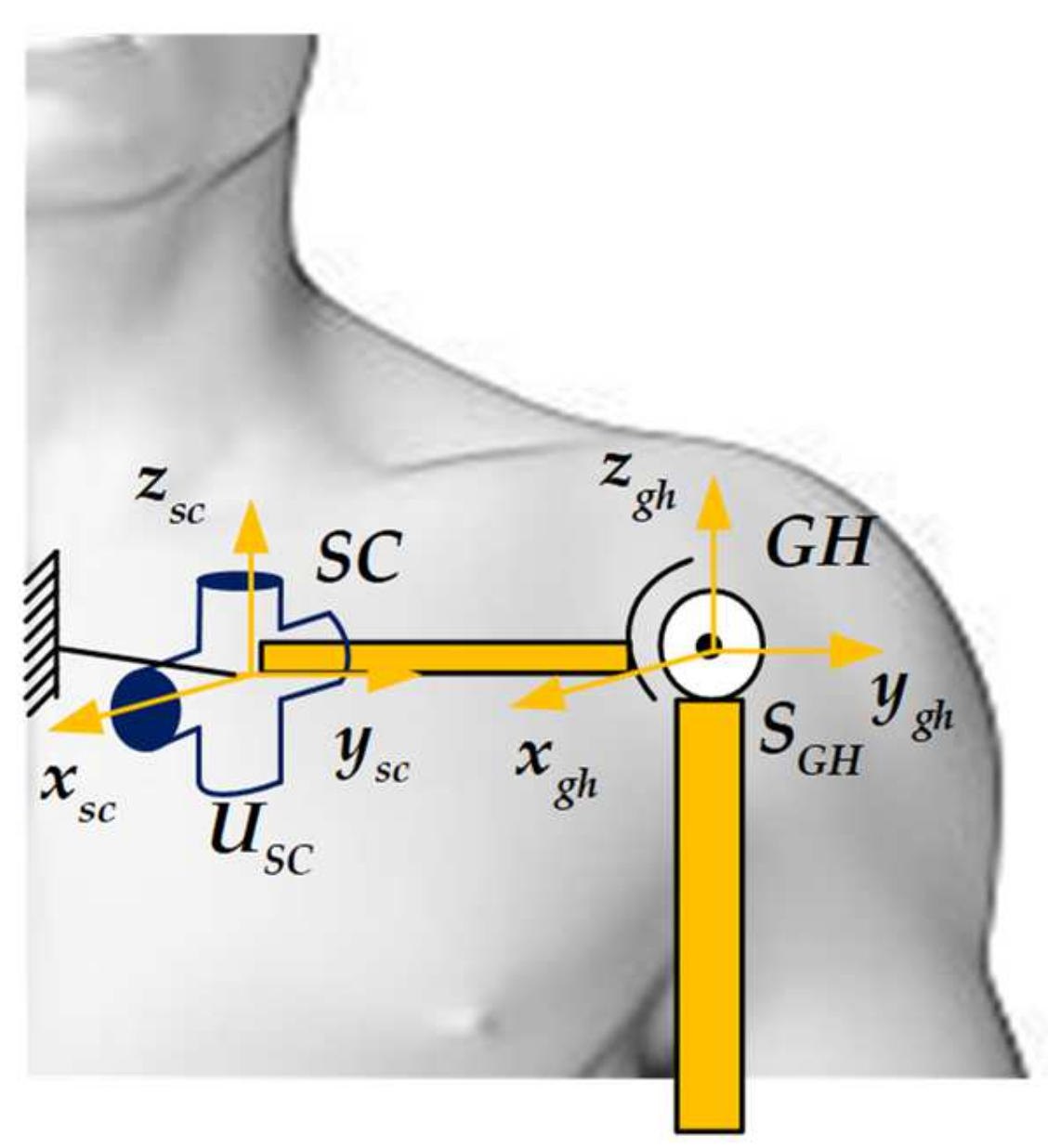
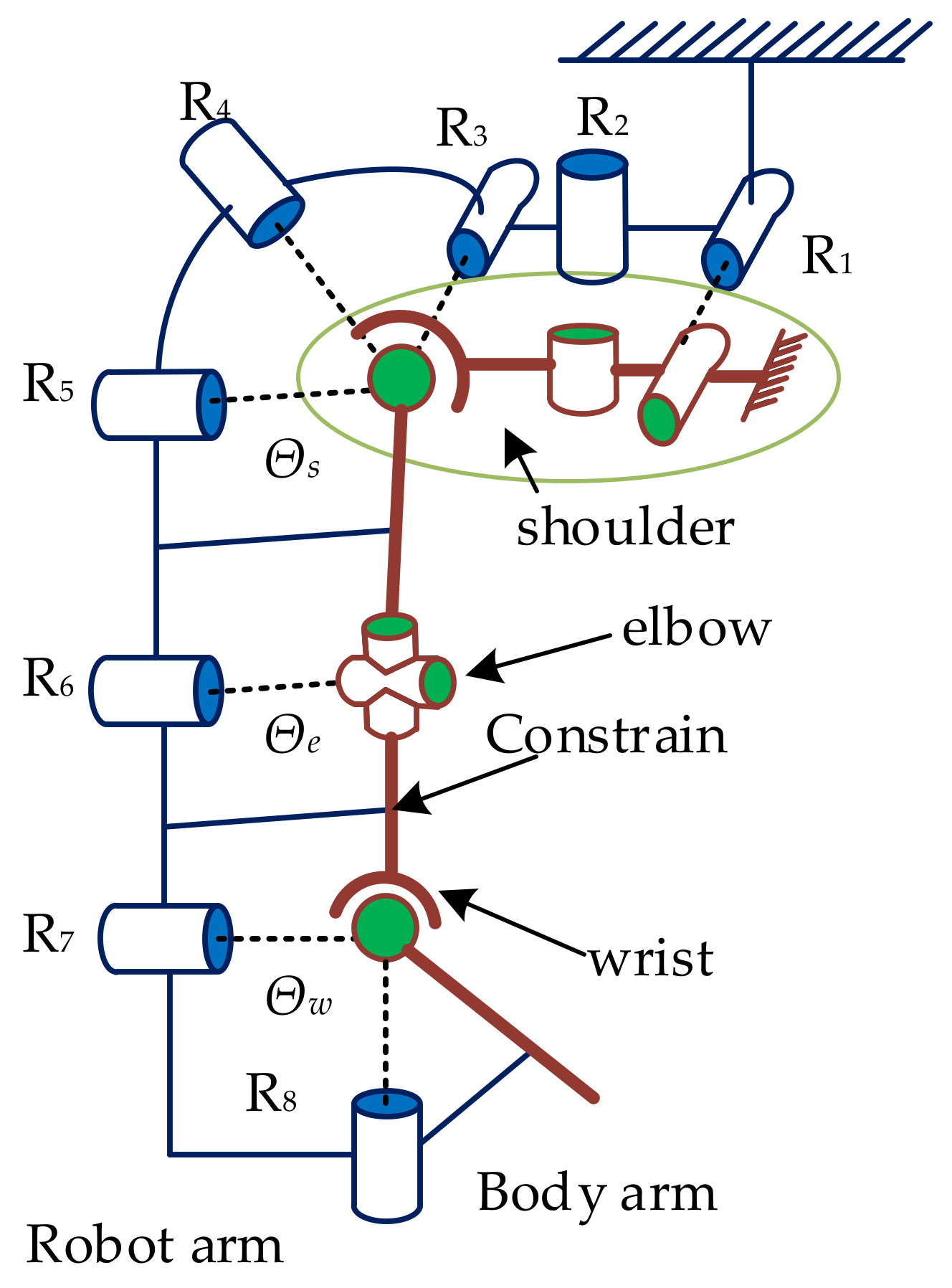
2.1. Human Upper Limb Anatomical Structure and Equivalent Mechanism Model
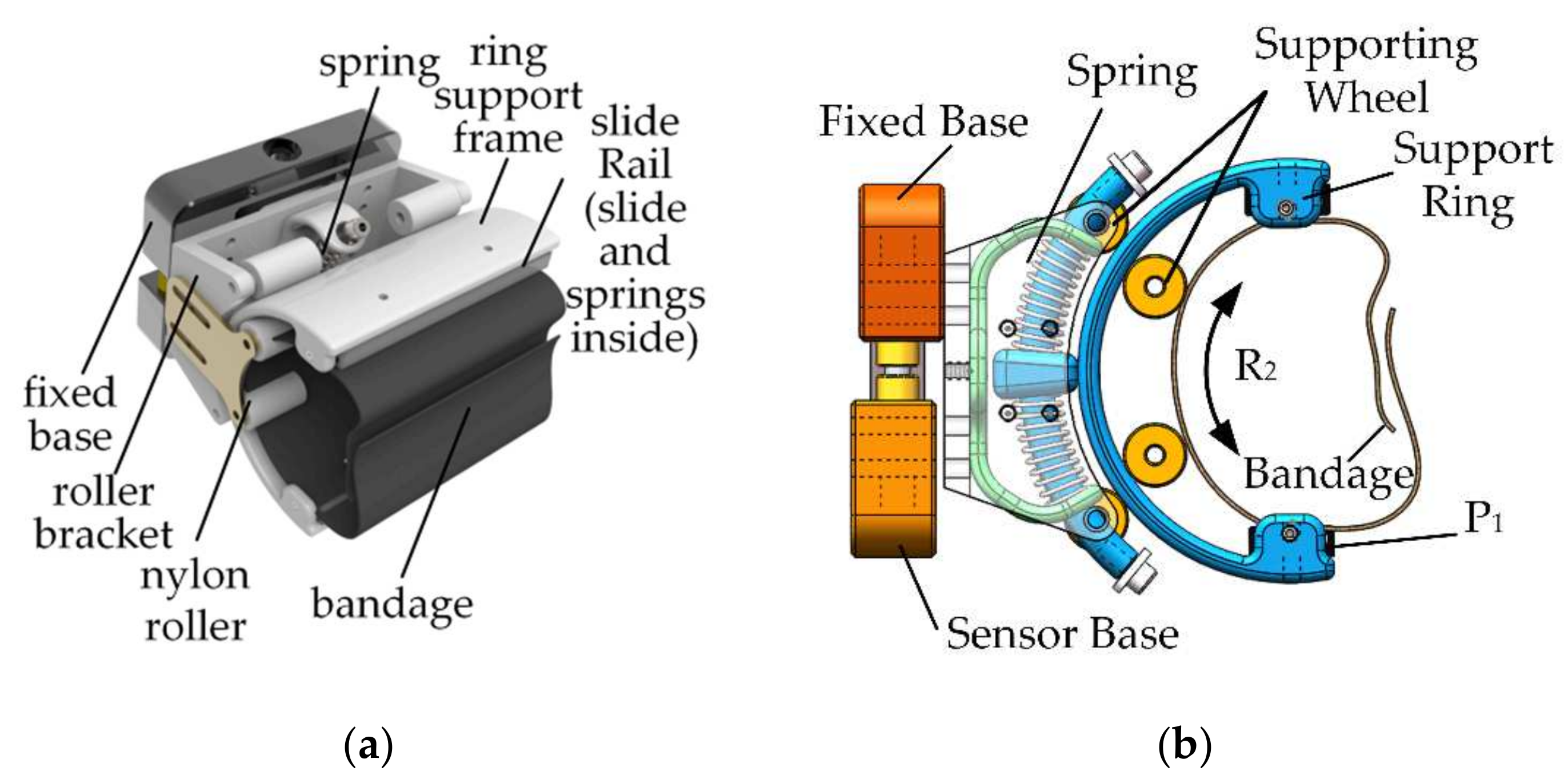
2.2. Human–Machine Compatible Configuration Design of the Shoulder Joint
3. Kinematics Analysis of the Equivalent Mechanism
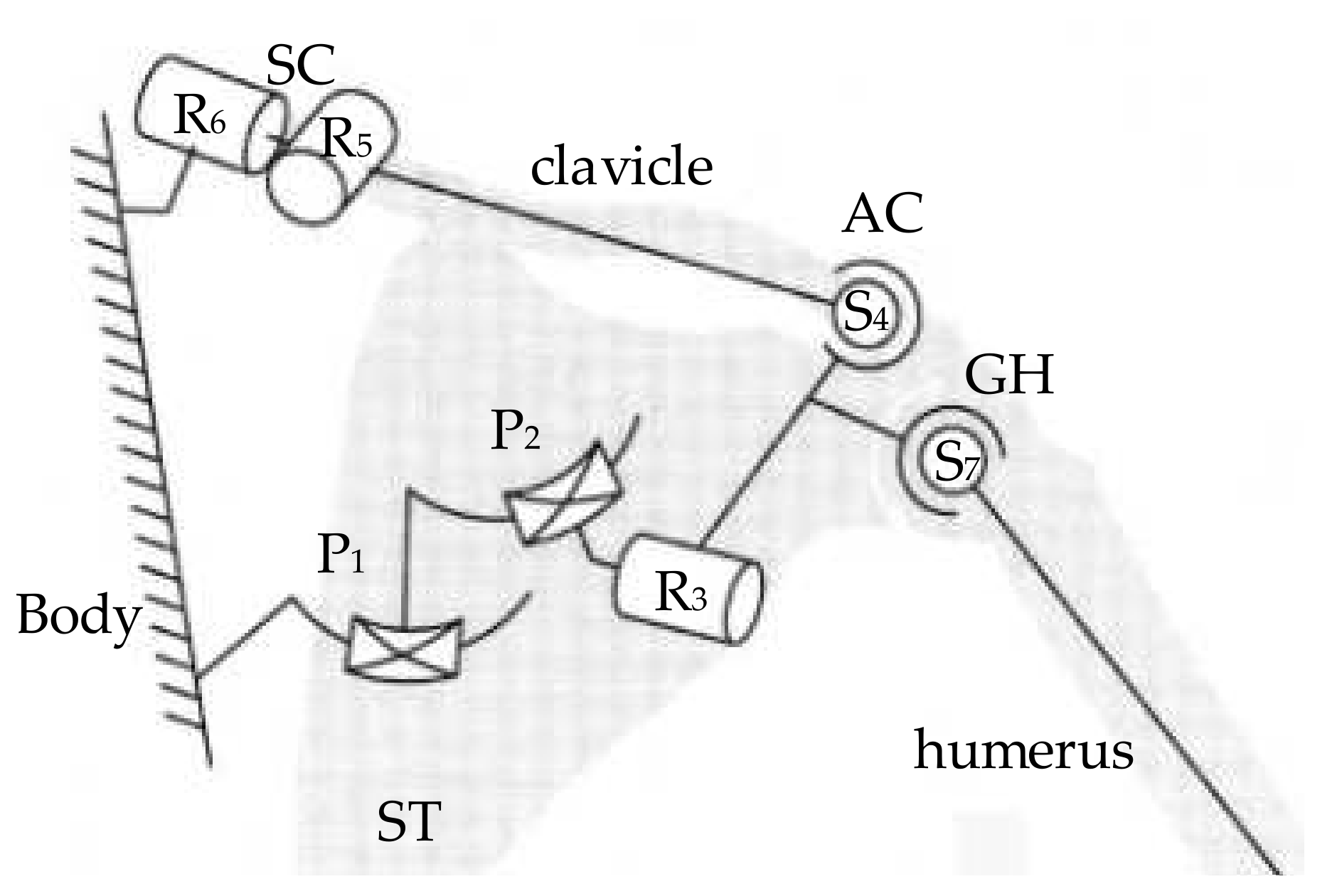
3.1. 2Pa1P3Ra Shoulder Joint Mechanism Configuration
3.2. 5Ra1P Shoulder Joint Mechanism Configuration
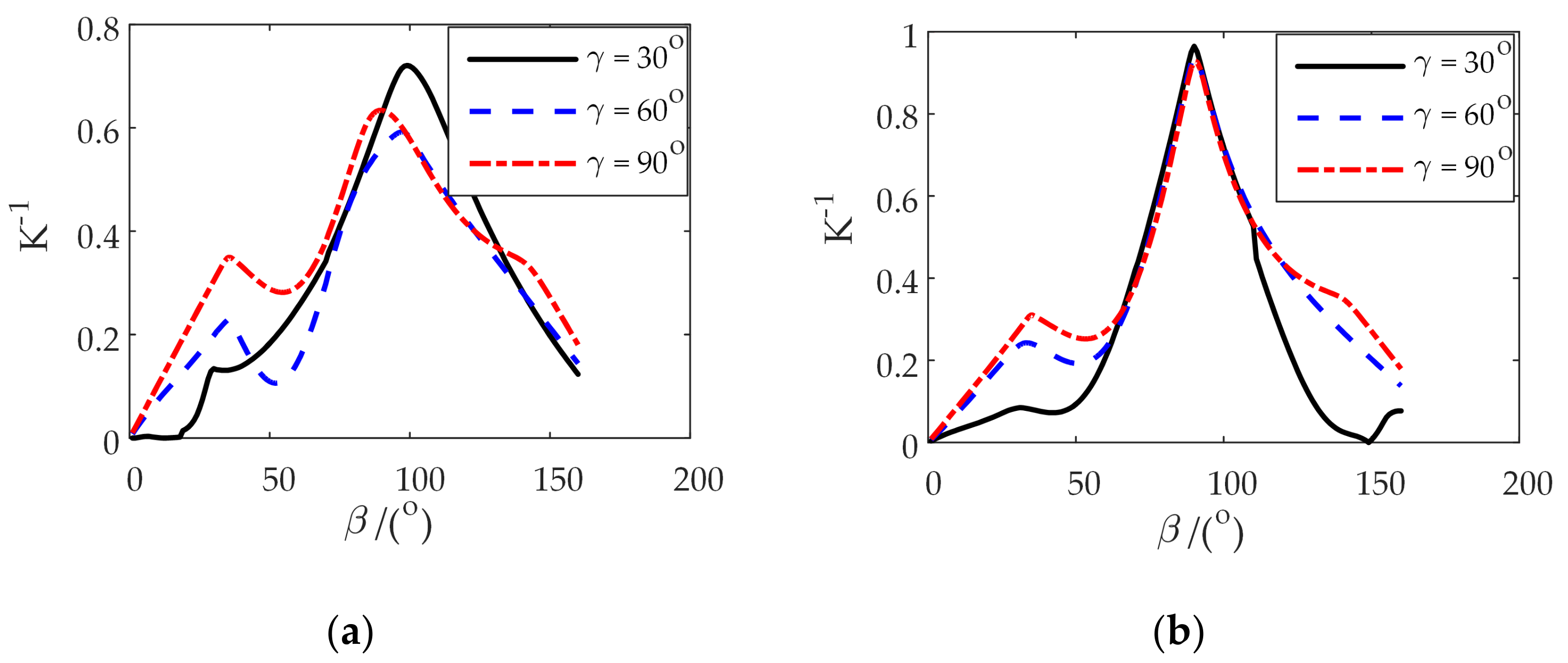
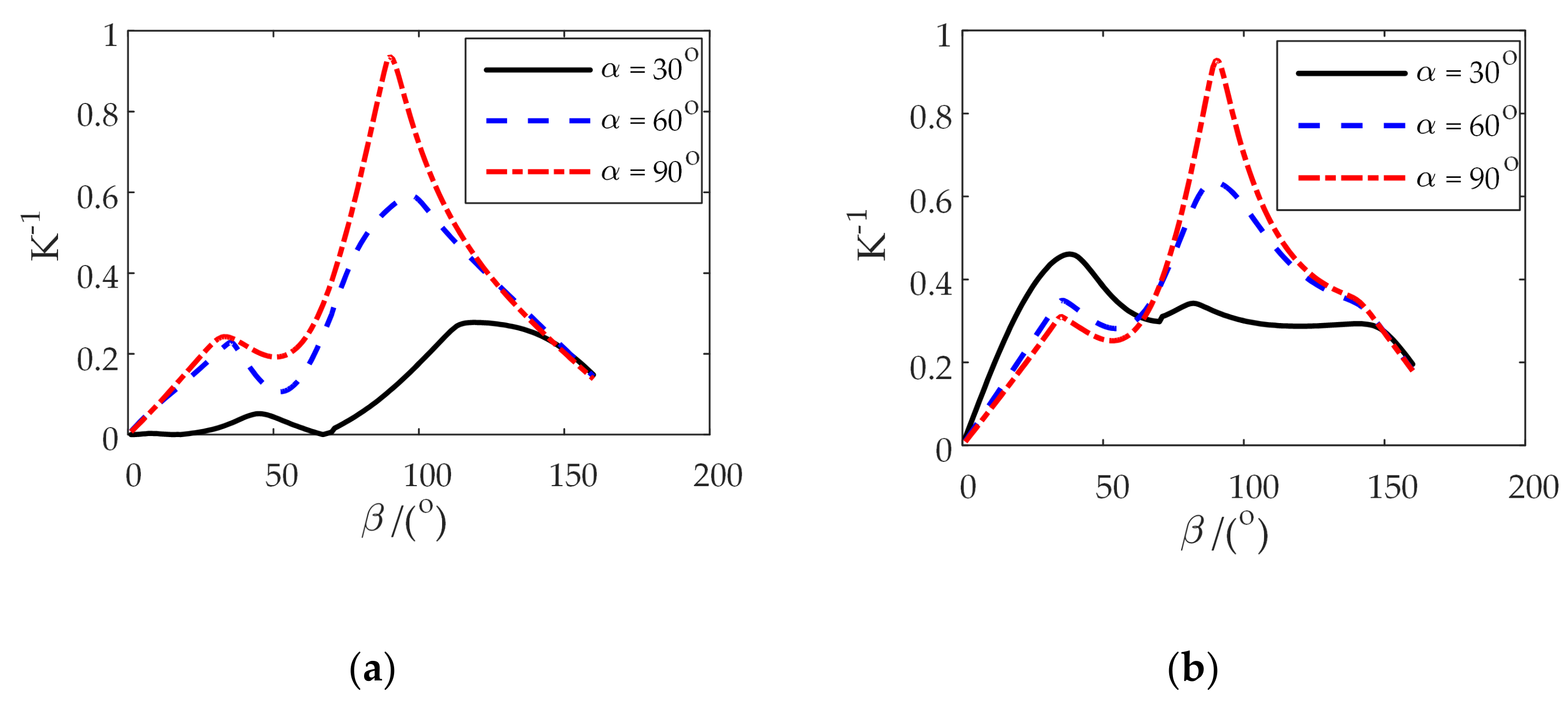
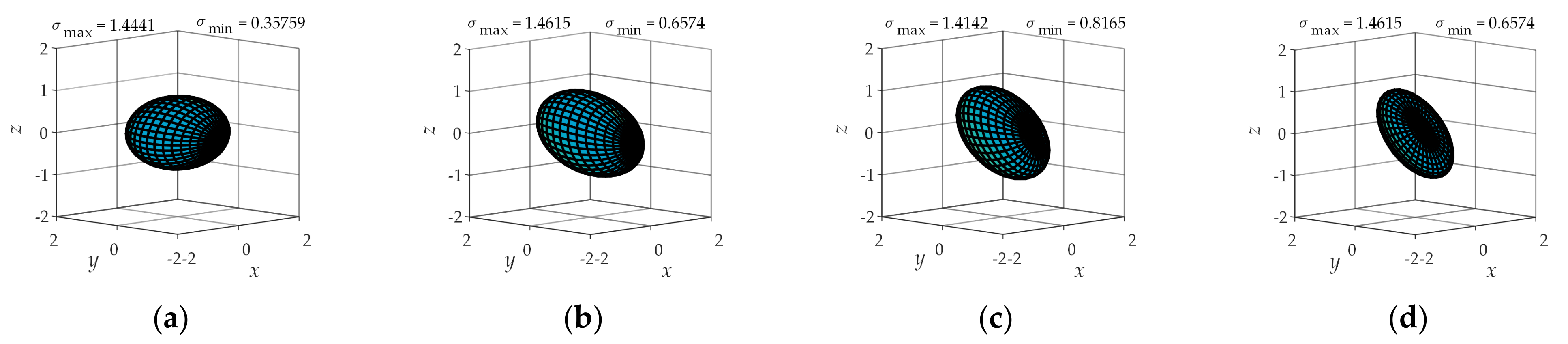
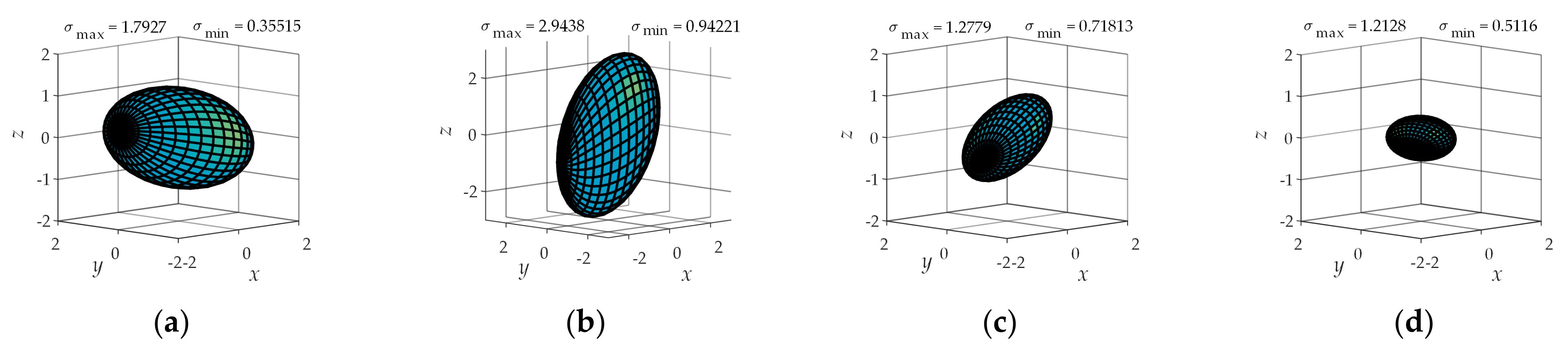
4. Comprehensive Kinematic Performance Analysis of the Shoulder Joint Configuration
4.1. Inverse Kinematic Solution and Flexibility Analysis of Two Configurations
4.2. Operational Ellipsoid Analysis
5. Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Q.; Guo, Q.; Luo, B.; Xu, Y. Expert consensus on post-stroke cognitive management. Chin. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 519–531. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, C.H.; Ya, Z.; Wei, W.L.; Teng, Y.Z. Prospects for intelligent rehabilitation techniques to treat motor dysfunction. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 2, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.; Truelsen, T. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2014, 383, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, Z.M.; Wu, D.L.; Su, L.J.; Zheng, Y.D.; Chen, P.R.; Zhang, Y.W.; Dou, Z.L.; Li, K.; Hoseinbeyki, A. Analysis of the Positive Effect of Robot-Assisted Virtual Reality Technology on Rehabilitation of Motor Function and Nerve Function in Cerebral Stroke Patients. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2021, 2, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B. Human Upper Limb Kinematics Analysis and Humanoid Body Design and Movement Planning. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, WuHan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Karduna, A.R.; McClure, P.W.; Michener, L.A. Scapular kinematics: Effects of alterning the Euler angle sequence of rotations. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borstad, J.D.; Ludewig, P.M. Comparison of scapular kinematics between elevation and lowering of the arm in the scapular plane. Clin. Biomech. 2002, 17, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, M.; Kato, S.; Barrance, P.J.; Elias, J.J.; McFarland, E.G.; Nobuhara, K.; Chao, E.Y. Scapular and clavicular kinematics during humeral elevation: A study with cadavers. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2001, 10, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, P.W.; Michener, L.A.; Sennett, B.J.; Karduna, A.R. Direct 3-dimensional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2001, 10, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nef, T.; Guidali, M.; Riener, R. ARMinIII-arm therapy exoskeleton with an ergonomic shoulder actuation. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2015, 6, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klamrothmarganska, V.; Blanco, J.; Campen, K. Three-dimensional, task-specific robot therapy of the arm after stroke: A multicentre, parallel-group randomisedtrial. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry B, E.; Evans E, K.; Stokic, D.S. Weight compensation characteristics of Armeo Spring exoskeleton: Implications for clinical practice and research. J. Neuro Eng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Rosen, J. A novel linear PID controller for an upper limb exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 December 2010; pp. 3548–3553. [Google Scholar]
- Pignolo, L.; Lucca, L.F.; Basta, G.; Serra, S.; E Pugliese, M.; Sannita, W.G.; Dolce, G. A new treatment in the rehabilitation of the paretic upper limb after stroke: The ARAMIS prototype and treatment protocol. Annali dell’Istituto Superiore di Sanità 2016, 52, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, S.J.; Brown, I.E.; Scott, S.H. Medarm: A rehabilitation robot with 5-DOF at the shoulder complex. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Zurich, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Deshpande, A.D. An upper-body rehabilitation exoskeleton Harmony with an anatomical shoulder mechanism: Design, modeling, control, and performance evaluation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36, 414–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, A.; Voort, C.; Stienen, A. Limpact: A hydraulically powered self-aligning upper limb exoskeleton. IEEE/Asme Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Park, H.S.; Zhang, L.Q. Developing a whole-arm exoskeleton robot with hand opening and closing mechanism for upper limb stroke rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Tokyo, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 761–765. [Google Scholar]
- Gaeblerspira, D.; Peri, E.; Lunardini, F. Rehabilitation Technologies for Cerebral Palsy; Emerging Therapies in Neurorehabilitation II: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Jin, X.; Scholz, J.P. Human movement training with a cable driven arm exoskeleton (CAREX). IEEE Trans. Nat. Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, S.E. Robotic-Assisted Shoulder Rehabilitation Therapy Effectively Improved Poststroke Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Jia, M.P. Human-machine compatibility and dynamic analysis of a novel unpowered and self-adaptive shoulder rehabilitation exoskeleton. J. Southeast Univ. 2020, 36, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J. Analysis of Kinematic Performance of Spherical Scissor Type Shoulder Joint Rehabilitation Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, North University of China, Tai Yuan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.F.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Tao, C.J.; Ji, R.; Zhao, P.B. Kinematics and flexibility analysis of human-machine compatible shoulder rehabilitation exoskeleton mechanism. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 54, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, T.; Yu, S.R. Developing Conceptual PSS Models of Upper Limb Exoskeleton based Post-stroke Rehabilitation in China. Procedia Cirp 2019, 80, 750–755. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, S.R. Design of an active strength training device for upper limb exoskeleton for patients with stroke recovery. Mech. Des. Res. 2019, 35, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.Z. Design and Research of Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot. Master’s Thesis, Hubei University of Technology, Wu Han, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.H.; Bai, Y.L. Differential diagnosis and rehabilitation treatment of frozen shoulder. Shanghai Med. 2017, 38, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.D. Human Anatomy; Peking Union Medical College Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wu, T.H.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.K.; Ge, J.H.; Bai, R.; Xiang, F.F.; Sun, Y.L. Anatomical and biomechanical characteristics of the sternoclavicular joint. Chin. Tissue Eng. Res. 2018, 22, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Van Der Helm, F.C.; Veeger, H.D.; Makhsous, M.; Van Roy, P.; Anglin, C.; Nagels, J.; Karduna, A.R.; McQuade, K.; Wang, X.; et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate systems of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion—Part II: Shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopcar, N.; Lenarcc, J. Bilateral and unilateral shoulder girdle kinematics during humeral elevation. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, S20–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhu, L.Y.; Gou, X.F. Kinematics analysis of lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton mechanism based on human-machine closed chain. J. Eng. Des. 2019, 26, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zhao, T.S. Advanced Spatial Mechanism; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.F.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tao, C.J. Structure design of lower limb exoskeletons for gait training. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2015, 28, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 10,000-19.8. Human Dimensions of Chinese Adults; China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.G.; Zhang, J. Manipulator flexibility analysis based on SVD maneuverability index. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 2019, 682, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, T. Manipulability of Robotic Mechanisms. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1985, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



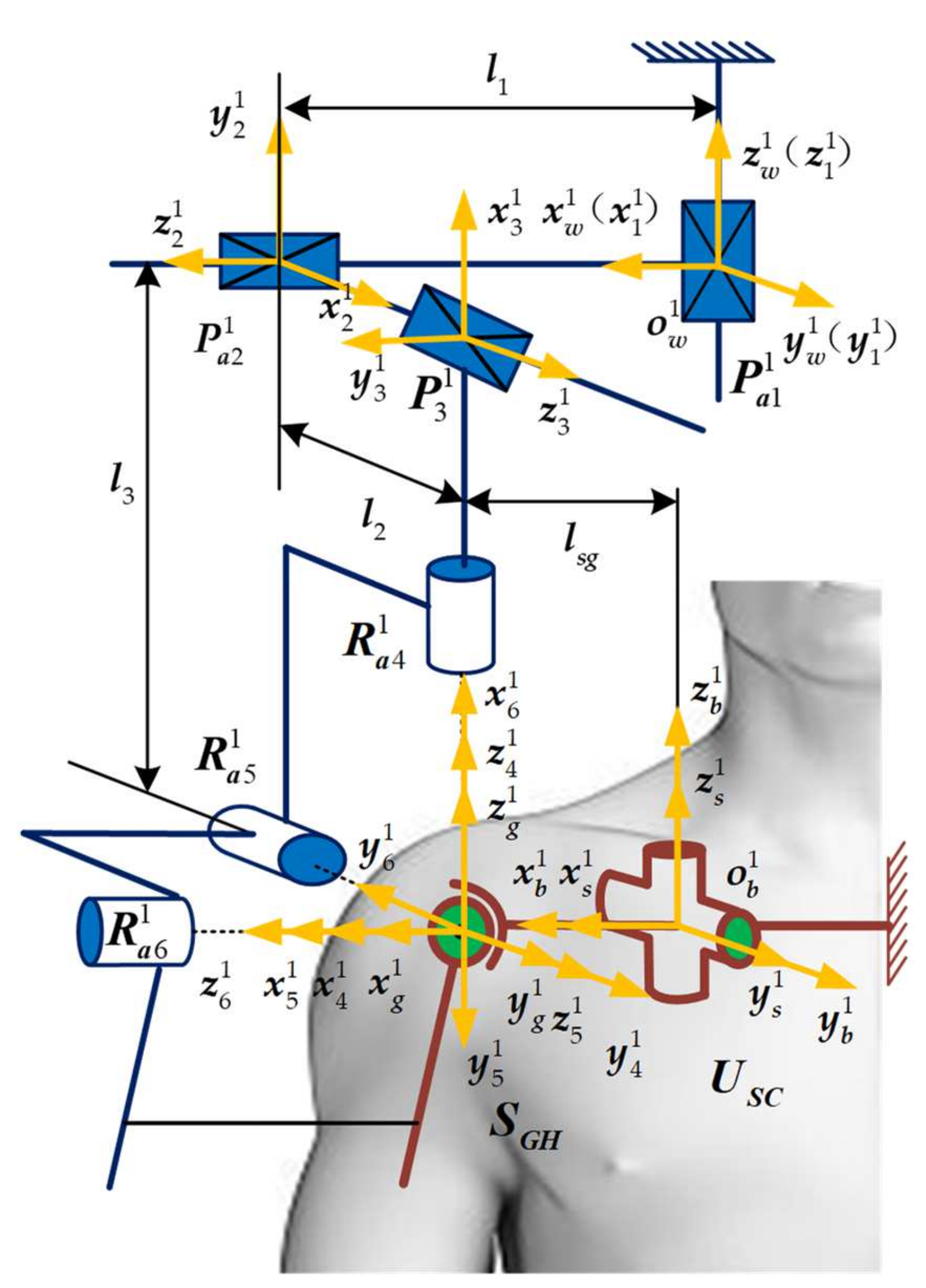
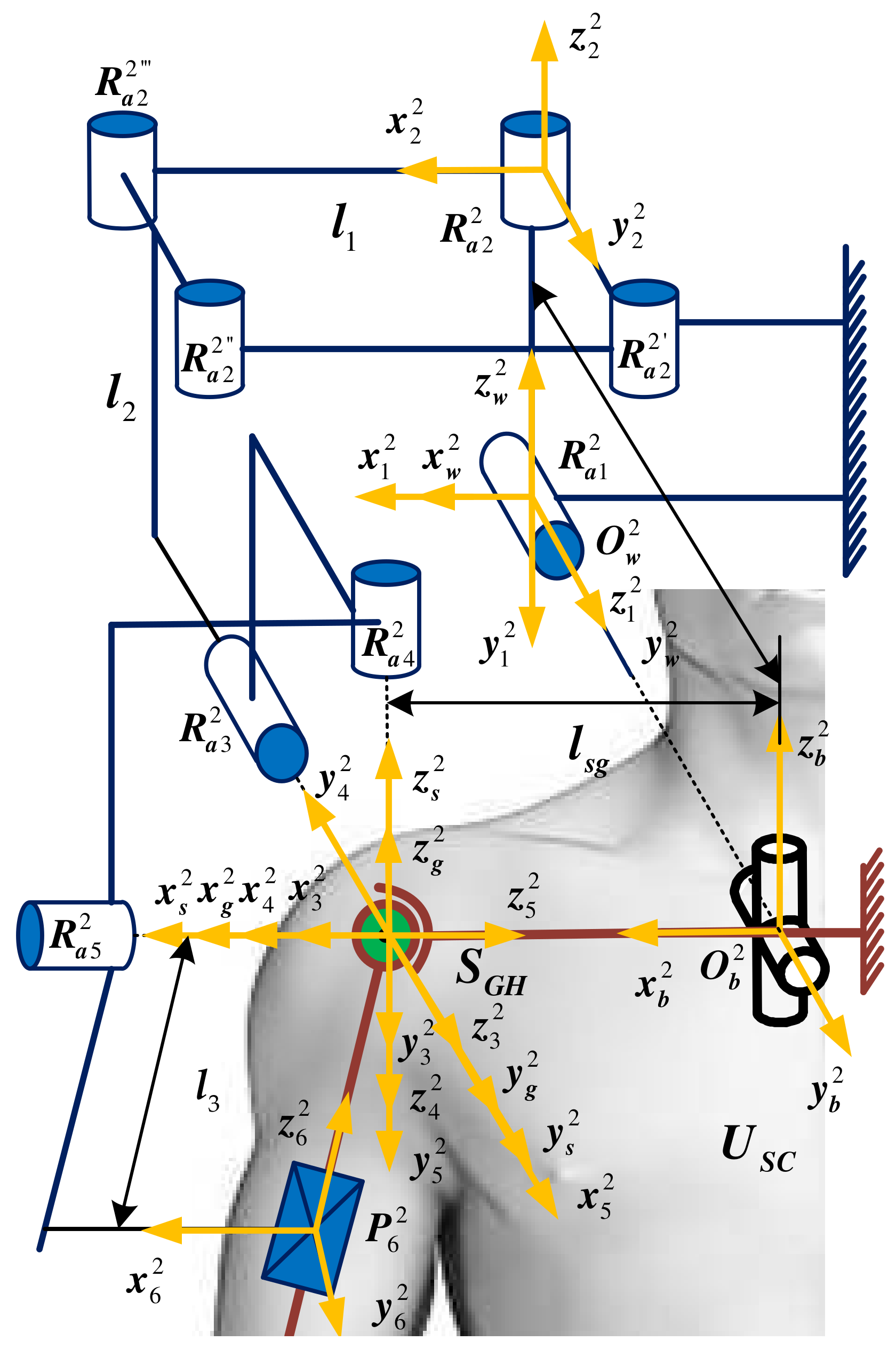
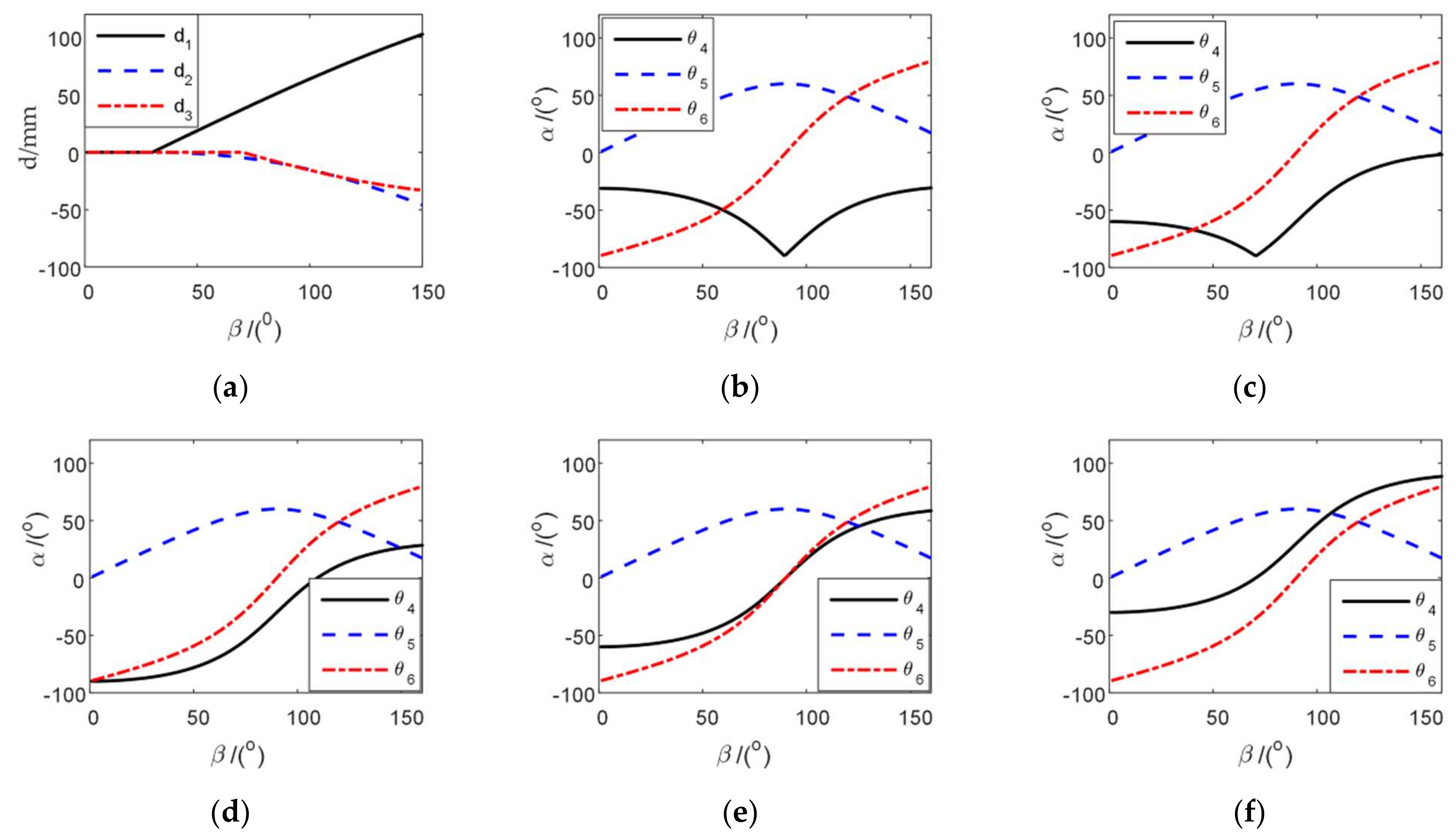

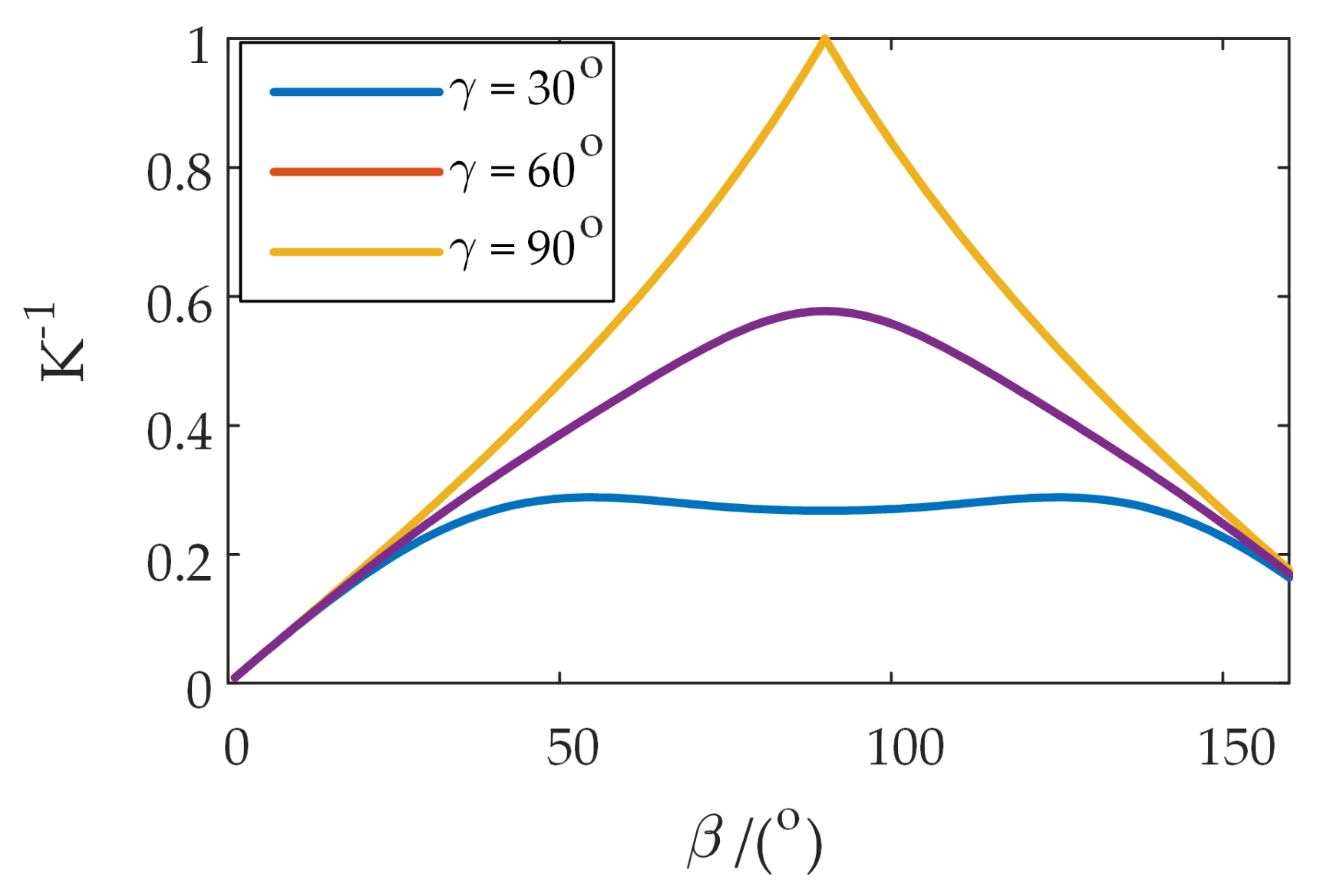

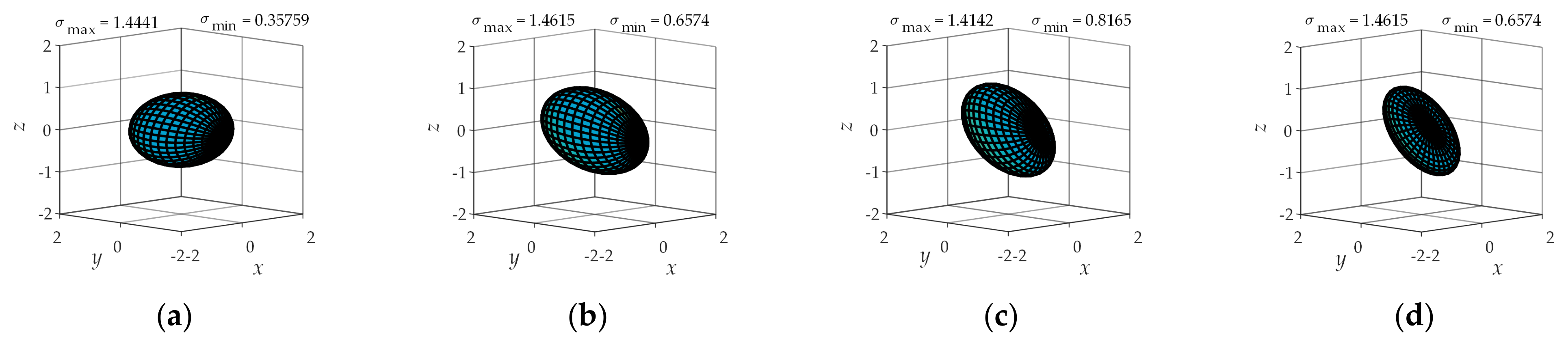
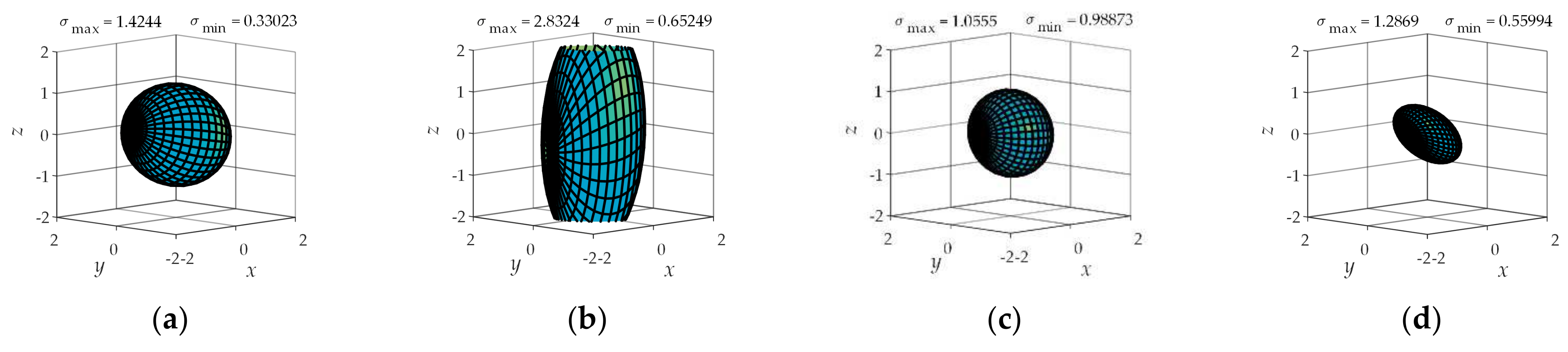
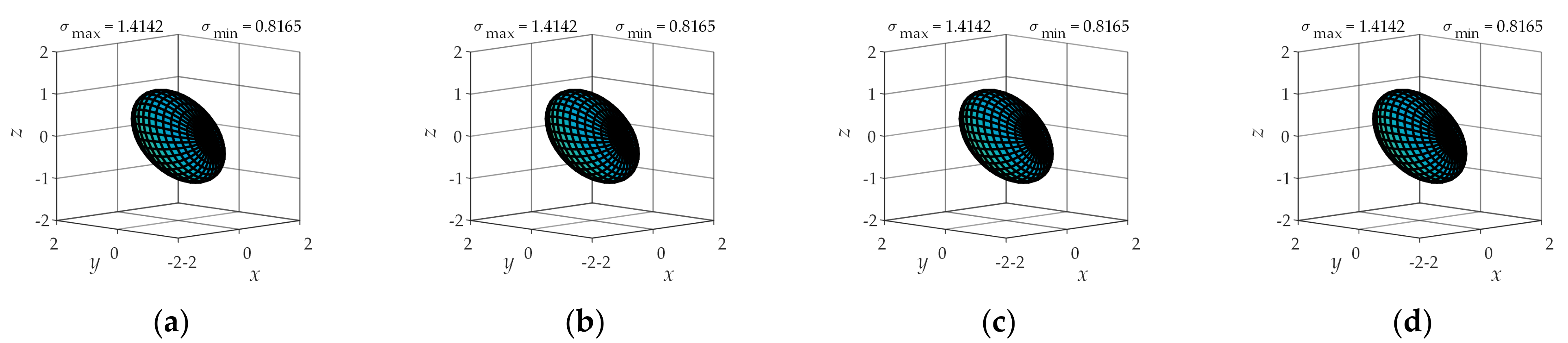
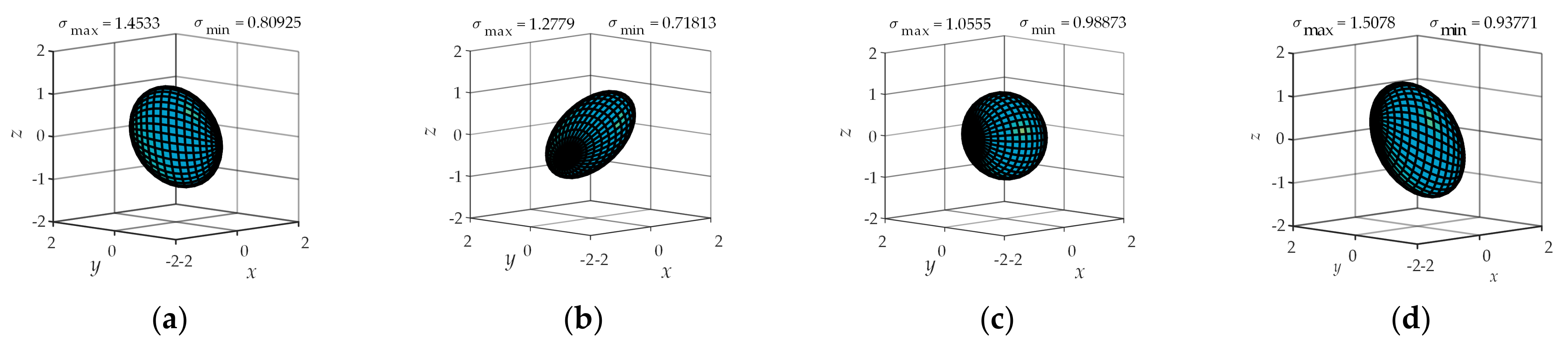


| Types of Sports Pair | Joint Number | Number of Combinations | Branch Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-DOF | 3 | 8 | RRR, RRP, RPR, PRR, PPP, PPR, PRP, RPP |
| With 2-DOF | 2 | 8 | RU, PU, RC, PC, UR, UP, CR, CP |
| With 3-DOF | 1 | 1 | S |
| Parameter | Value/(mm) | Parameter | Value/(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scapula belt length | 150 | Distance from human sternum to rotation pair | 300 |
| Distance from P1 to P2 | 200 | Distance from to | 100 |
| Distance from P2 to P3 | 200 | Length of parallel four-bar mechanism | 150 |
| Distance from P3 to R4 | 200 | Distance from to | 150 |
| Plane | 2Pa1P3Ra | 5Ra1P | Dominant Proportion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | ||
| 30° coronal plane | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.2 | 0.32 | 0.56 | 0.42 | −0.21 |
| sagittal plane | 0.25 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.94 | 0.44 | 0.12 |
| horizontal plane | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.94 | 0.62 | 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Niu, J.; Ning, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Configuration Design of an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot with a Generalized Shoulder Joint. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052080
Yan H, Wang H, Chen P, Niu J, Ning Y, Li S, Wang X. Configuration Design of an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot with a Generalized Shoulder Joint. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052080
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hao, Hongbo Wang, Peng Chen, Jianye Niu, Yuansheng Ning, Shuangshuang Li, and Xusheng Wang. 2021. "Configuration Design of an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot with a Generalized Shoulder Joint" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052080
APA StyleYan, H., Wang, H., Chen, P., Niu, J., Ning, Y., Li, S., & Wang, X. (2021). Configuration Design of an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot with a Generalized Shoulder Joint. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052080







