Debris Flow Characteristics in Flume Experiments Considering Berm Installation
Abstract
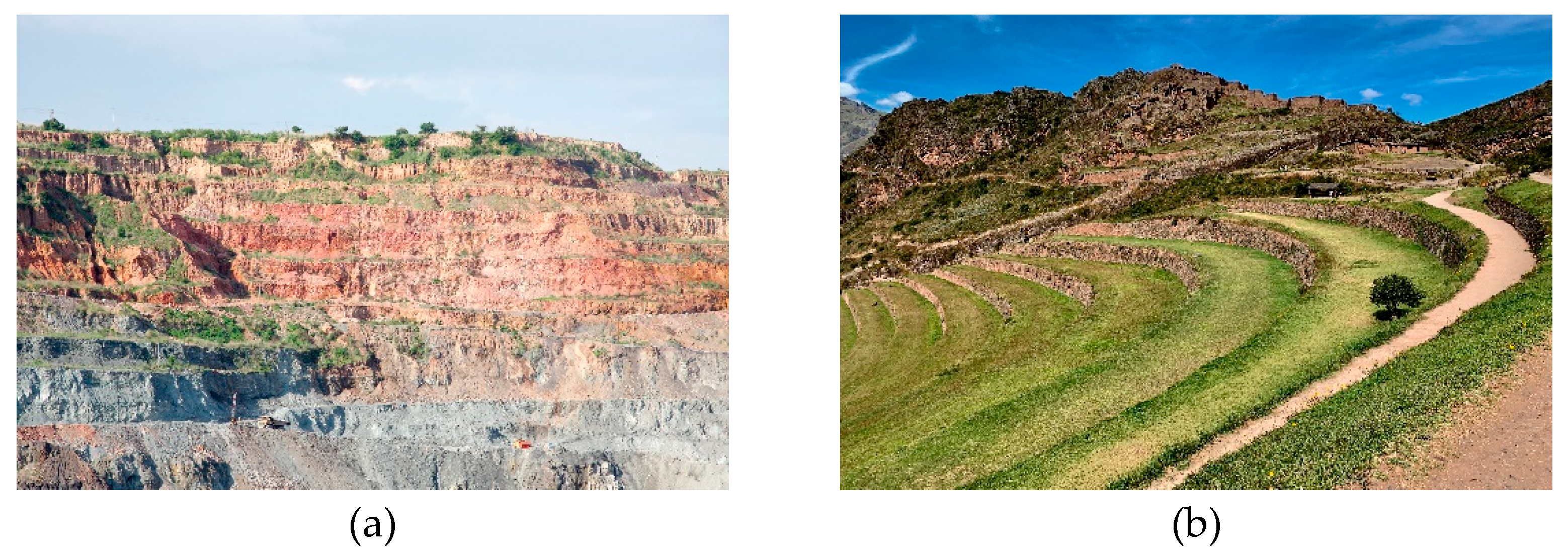
:1. Introduction
2. Methods for Assessing Debris Flow Characteristics
2.1. Flow Velocity
2.2. Froude Number
2.3. Mobility Ratio
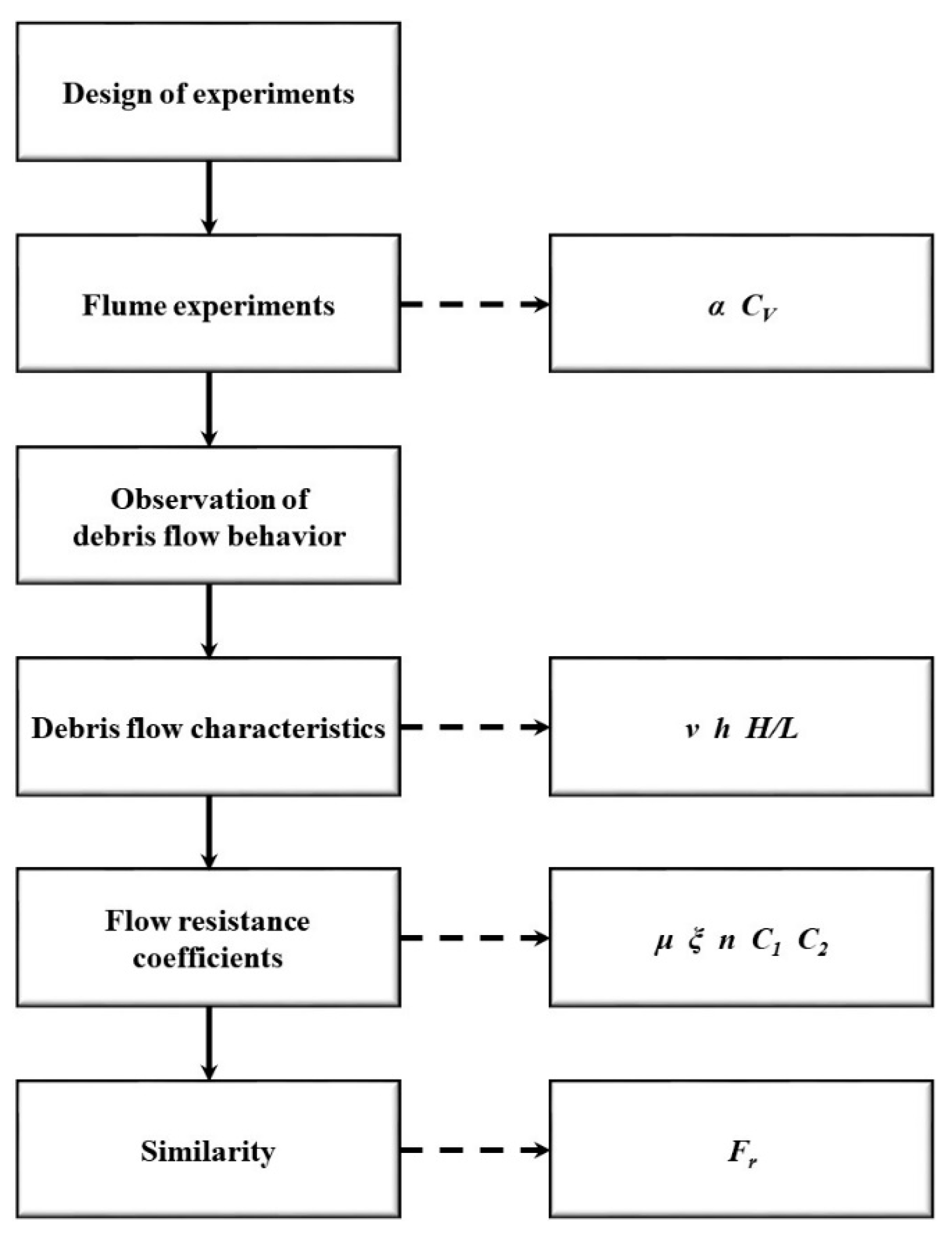
3. Flume Experiments
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Experimental Conditions
3.3. Sample Properties
3.4. Experimental Method
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Debris Flow Characteristics
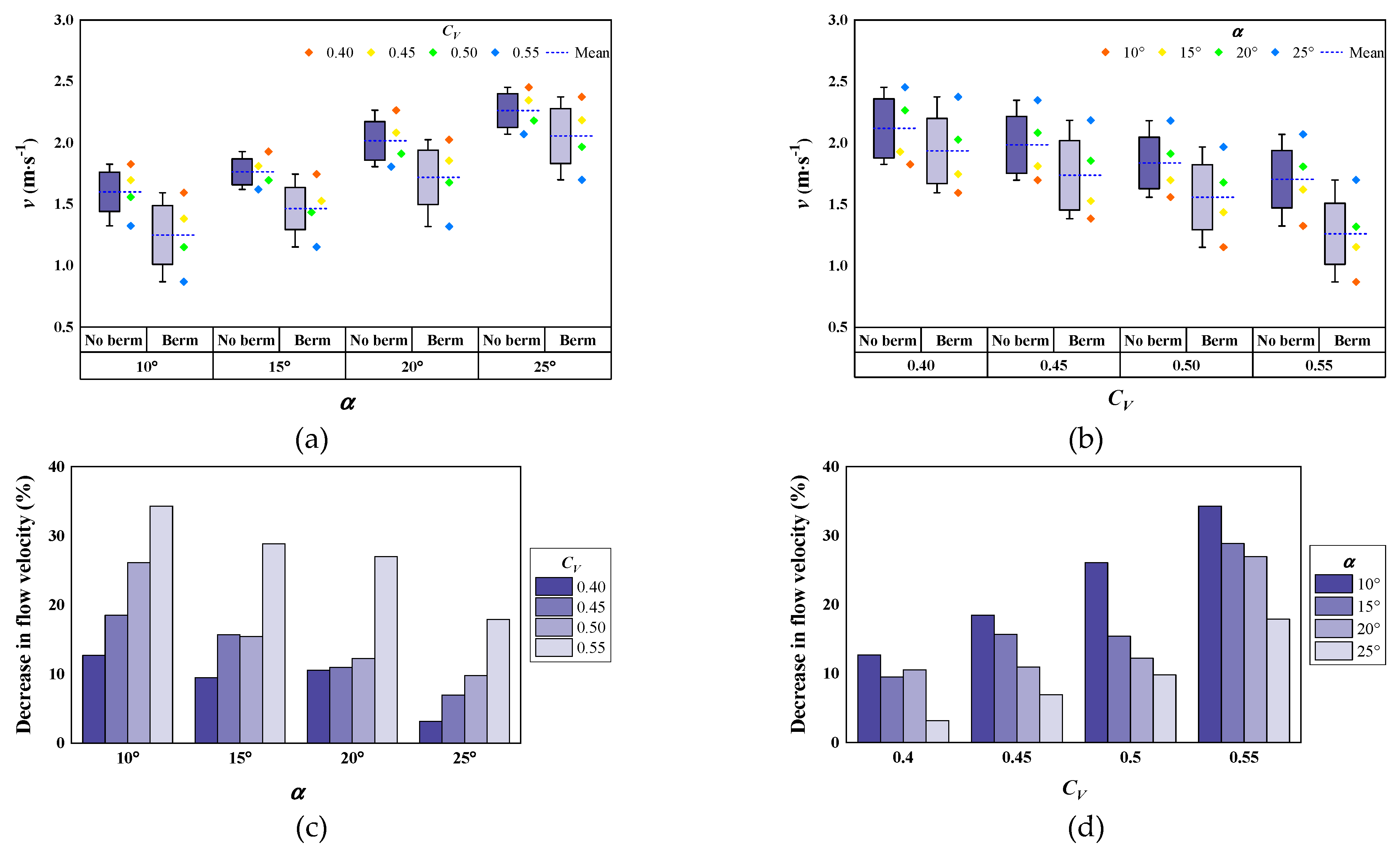
4.1.1. Flow Velocity
4.1.2. Flow Depth
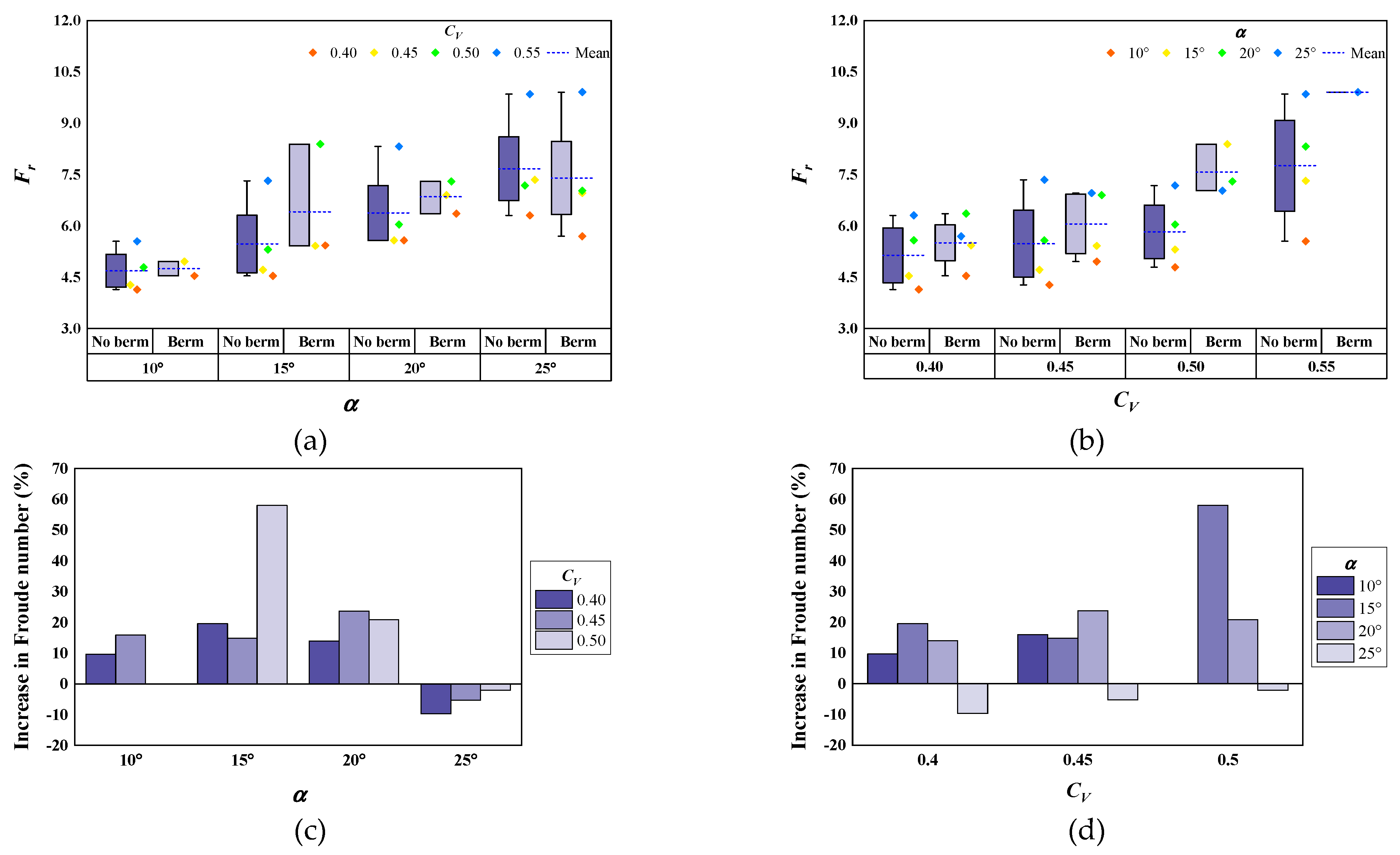
4.1.3. Froude Number
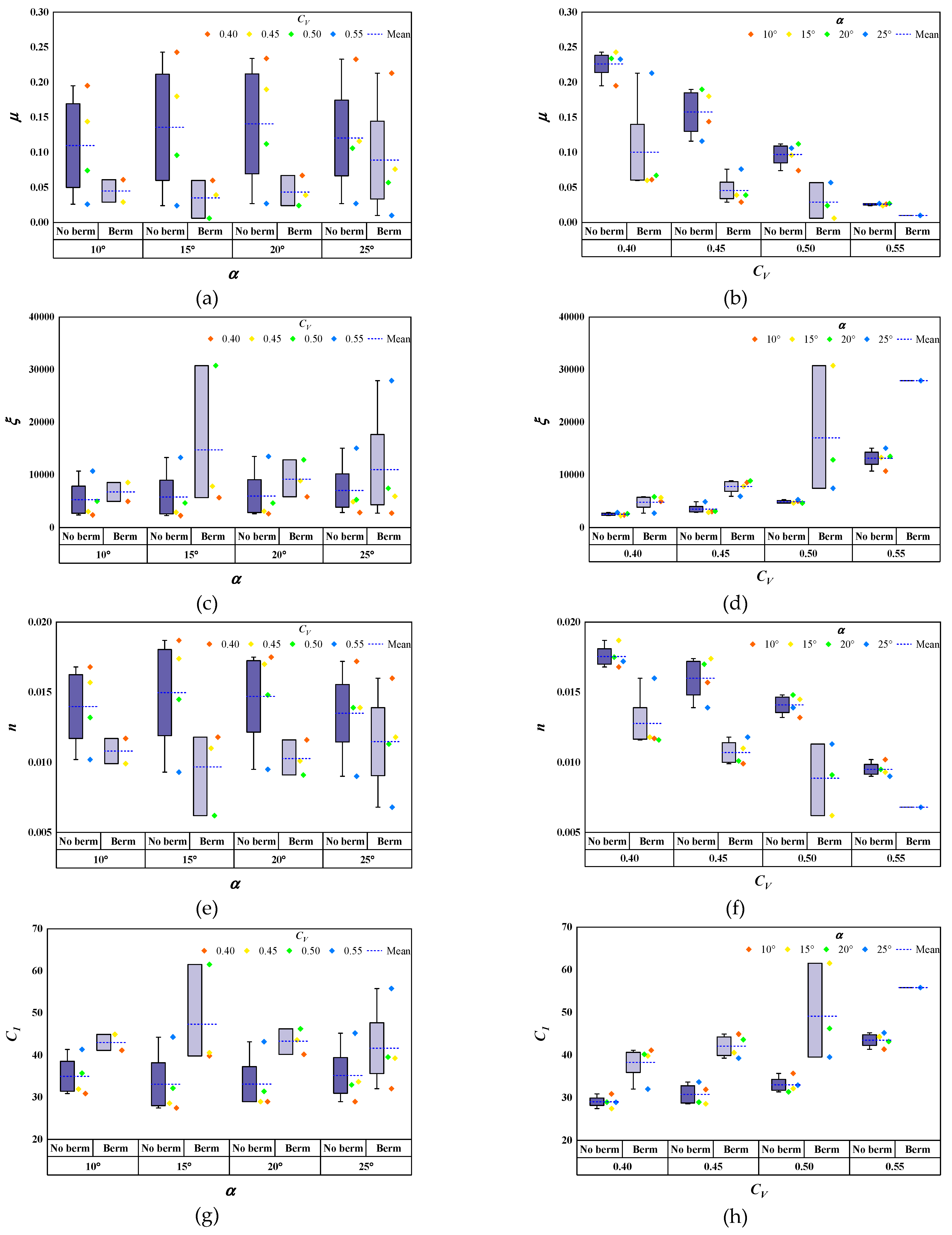
4.1.4. Flow Resistance Coefficients
4.1.5. Mobility Ratio
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eu, S.; Im, S.; Kim, D.; Chun, K.W. Flow and deposition characteristics of sediment mixture in debris flow flume experiments. For. Sci. Technol. 2017, 13, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eu, S.; Im, S.; Kim, D. Development of debris flow impact force models based on flume experiments for design criteria of soil erosion control dam. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.E. Physical geomorphology of debris flows. In Developments and Applications of Geomorphology; Costa, J.E., Fleisher, P.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 268–317. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Kim, Y. The physical vulnerability of different types of building structure to debris flow events. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1475–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eu, S.; Im, S. Examining the impact force of debris flow in a check dam from small-flume experiments. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation, Golden, CO, USA, 10–13 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Coussot, P.; Meunier, M. Recognition, classification and mechanical description of debris flows. Earth Sci. Rev. 1996, 40, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archetti, R.; Lamberti, A. Assessment of risk due to debris flow events. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2003, 4, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, V.; Cesca, M.; Marchi, L. Field and laboratory investigations of runout distances of debris flows in the Dolomites (Eastern Italian Alps). Geomorphology 2010, 115, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Das, D.K. Debris Flow: Mechanics, Prediction and Countermeasures, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Hübl, J.; Suda, J.; Proske, D.; Kaitna, R.; Scheidl, C. Debris flow impact estimation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering, Ohrid, Macedonia, 1–5 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- de Haas, T.; Braat, L.; Leuven, J.R.F.W.; Lokhorst, I.R.; Kleinhans, M.G. Effects of debris flow composition on runout, depositional mechanisms, and deposit morphology in laboratory experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1949–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, P.; Zeng, C.; Lei, Y. Experimental analysis on the impact force of viscous debris flow. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, F.; McArdell, B.W.; Huggel, C.; Vieli, A. The importance of entrainment and bulking on debris flow runout modeling: Examples from the Swiss Alps. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iverson, R.M. The physics of debris flows. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hungr, O.; Morgan, G.C.; Kellerhals, R. Quantitative analysis of debris torrent hazards for design of remedial measures. Can. Geotech. J. 1984, 21, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenmann, D. Empirical relationships for debris flows. Nat. Hazards 1999, 19, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDine, D.F. Debris Flow Control Structures for Forest Engineering; BC Ministry of Forests: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1996; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska, A.B.; Santi, P.M.; Higgins, J.D. Debris basin and deflection berm design for fire-related debris-flow mitigation. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2008, 14, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H. A study of the debris flow activity on the one-stepped channel slope. Soil Water Res. 2015, 10, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Raju, P.T.; Sreedhar, V.; Mahiyar, H. Slope stability analysis of steep reinforced soil slopes using finite element method. In Geotechnical Applications; Anirudhan, I.V., Maji, V.B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Proske, D.; Suda, J.; Hübl, J. Debris flow impact estimation for breakers. Georisk Assess. Manag. Risk Eng. Syst. Geohazards 2011, 5, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Debris flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1981, 13, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Tian, M.; Li, Y. Influence of flow width on mean velocity of debris flows in wide open channel. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidl, C.; Chiari, M.; Kaitna, R.; Müllegger, M.; Krawtschuk, A.; Zimmermann, T.; Proske, D. Analysing debris-flow impact models, based on a small scale modelling approach. Surv. Geophys. 2013, 34, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iverson, R.M. Scaling and design of landslide and debris-flow experiments. Geomorphology 2015, 244, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T. Testing various constitutive equations for debris flow modelling. In Hydrology, Water Resources and Ecology in Headwaters; Kovar, K., Tappeiner, U., Peters, N.E., Craig, R.G., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 1998; pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, D.O.K. Review of Natural Terrain Landslide Debris-Resisting Barrier Design: Geo Report No. 104; Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, The Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Kowloon, Hong Kong, China, 2000; p. 92.
- Prochaska, A.B.; Santi, P.M.; Higgins, J.D.; Cannon, S.H. A study of methods to estimate debris flow velocity. Landslides 2008, 5, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenmann, D. Debris flows 1987 in Switzerland: Modelling and fluvial sediment transport. In Hydrology in Mountainous Regions II; Sinniger, R.O., Monbaron, M., Eds.; IAHS: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1990; pp. 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnold, R.A. Experiments on a Gravity-Free Dispersion of Large Solid Spheres in a Newtonian Fluid under Shear; Proceedings of the Royal Society: London, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuyama, T.; Ishikawa, Y. Technical Standard for the Measures against Debris Flow (Draft); Sabo (Erosion Control) Division, Sabo Department, Public Works Research Institute, Ministry of Construction: Tokyo, Japan, 1988; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, A. Der Bergsturz von Elm. Z. Der Dtsch. Geol. Ges. 1882, 34, 74–115. [Google Scholar]
- Toyos, G.; Dorta, D.O.; Oppenheimer, C.; Pareschi, M.T.; Sulpizio, R.; Zanchetta, G. GIS-assisted modelling for debris flow hazard assessment based on the events of May 1998 in the area of Sarno, Southern Italy: Part I. Maximum run-out. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, J.C.; Burton, A.; Ward, T.J. Debris flow run-out and landslide sediment delivery model tests. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfield, G. Assessing the dynamic influences of slope angle and sediment composition on debris flow behaviour: An experimental approach. Master’s Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Im, S.; Eu, S.; Kim, D. Understanding debris flow characteristics using flume experiments. In Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides; Mikos, M., Tiwari, B., Yin, Y., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, R.P. Debris flows in the southern Coast Mountains, British Columbia: Dynamic behaviour and physical properties. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hürlimann, M.; Rickenmann, D.; Graf, C. Field and monitoring data of debris-flow events in the Swiss Alps. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Su, F.; Xie, J.; Wang, B. Relationship between grain composition and debris flow characteristics: A case study of the Jiangjia Gully in China. Landslides 2015, 12, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnion, L.; McArdell, B.W.; Bartelt, P.; Wendeler, C. Measurements of hillslope debris flow impact pressure on obstacles. Landslides 2012, 9, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheidl, C.; McArdell, B.W.; Rickenmann, D. Debris-flow velocities and superelevation in a curved laboratory channel. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wendeler, C.; Volkwein, A. Laboratory tests for the optimization of mesh size for flexible debris-flow barriers. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, R.; Fei., W.; Zhou, H.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J. Experimental and numerical study on the load and deformation mechanism of a flexible net barrier under debris flow impact. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 2213–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

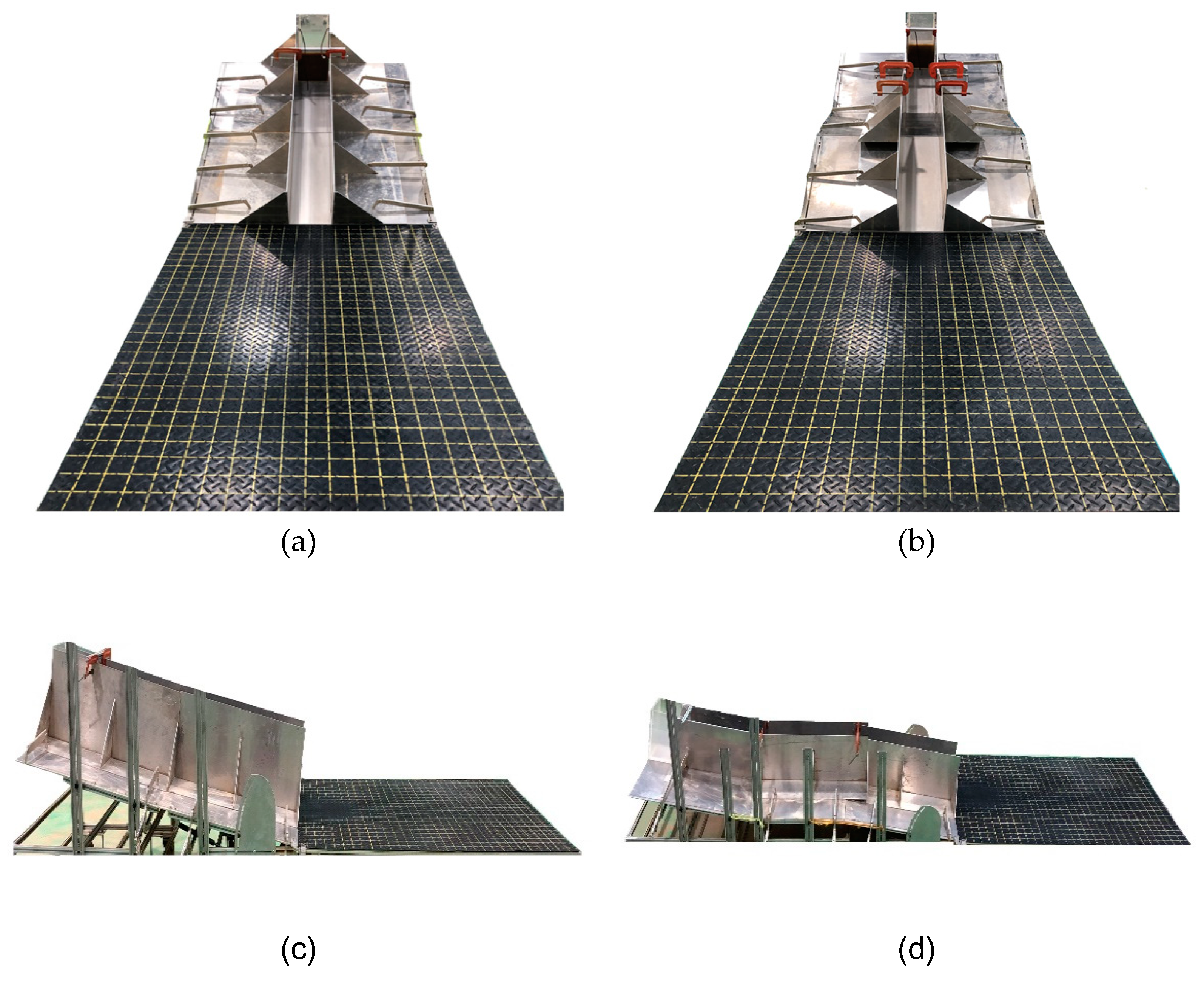
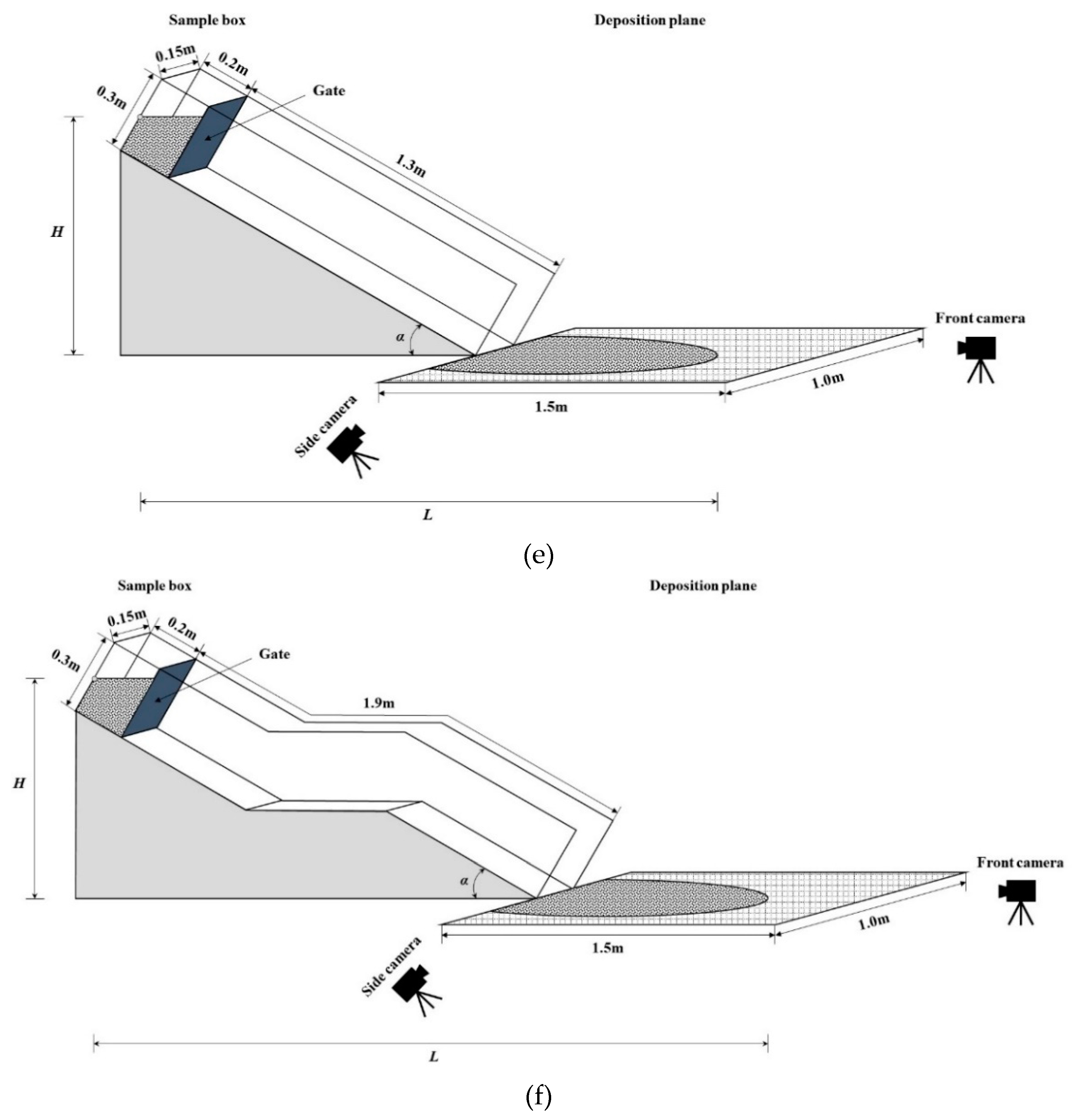






| Test Type | Length (m) | Width (m) | Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straight channel test | 1.3 | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| Single-berm channel test | 1.9 | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| Straight Channel Test | Single-Berm Channel Test | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Slope α (°) | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| Volumetric concentration CV | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | |
| 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | |
| 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | |
| 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | |
| Particle Size (mm) | Weight Ratio (%) |
|---|---|
| 4.750–9.500 | 25.00 |
| 2.000–4.750 | 25.00 |
| 0.850–2.000 | 10.67 |
| 0.425–0.850 | 20.63 |
| 0.250–0.425 | 13.57 |
| 0.150–0.250 | 3.63 |
| 0.075–0.150 | 1.00 |
| <0.075 | 0.50 |
| CV | < 2 mm (kgf) | 2–4.75 mm (kgf) | 4.75–9.5 mm (kgf) | Water (kgf) | W (kgf) | ρ (kg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.40 | 2.200 | 1.100 | 1.100 | 2.700 | 7.100 | 1578 |
| 0.45 | 2.475 | 1.238 | 1.238 | 2.475 | 7.425 | 1650 |
| 0.50 | 2.750 | 1.375 | 1.375 | 2.250 | 7.750 | 1722 |
| 0.55 | 3.025 | 1.513 | 1.513 | 2.025 | 8.075 | 1794 |
| 0.60 | 3.300 | 1.650 | 1.650 | 1.800 | 8.400 | 1867 |
| Test Type | N | α (°) | CV | v (m·s−1) | h (m) | Fr | H (m) | L (m) | H/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight channel | 1 | 10 | 0.40 | 1.826 | 0.0198 | 4.14 | 0.391 | 2.459 | 0.159 |
| 2 | 10 | 0.45 | 1.697 | 0.0160 | 4.28 | 0.391 | 2.340 | 0.167 | |
| 3 | 10 | 0.50 | 1.559 | 0.0108 | 4.79 | 0.391 | 2.194 | 0.178 | |
| 4 | 10 | 0.55 | 1.324 | 0.0058 | 5.55 | 0.391 | 2.105 | 0.186 | |
| 5 | 10 | 0.60 | 1.169 | - | - | 0.391 | 1.780 | 0.220 | |
| 6 | 15 | 0.40 | 1.929 | 0.0184 | 4.54 | 0.507 | 2.630 | 0.193 | |
| 7 | 15 | 0.45 | 1.811 | 0.0150 | 4.72 | 0.507 | 2.541 | 0.200 | |
| 8 | 15 | 0.50 | 1.697 | 0.0104 | 5.31 | 0.507 | 2.339 | 0.217 | |
| 9 | 15 | 0.55 | 1.621 | 0.0050 | 7.32 | 0.507 | 2.098 | 0.242 | |
| 10 | 15 | 0.60 | 1.231 | 0.0038 | 6.38 | 0.507 | 1.763 | 0.288 | |
| 11 | 20 | 0.40 | 2.265 | 0.0168 | 5.58 | 0.620 | 2.661 | 0.233 | |
| 12 | 20 | 0.45 | 2.083 | 0.0142 | 5.58 | 0.620 | 2.560 | 0.242 | |
| 13 | 20 | 0.50 | 1.912 | 0.0102 | 6.04 | 0.620 | 2.417 | 0.256 | |
| 14 | 20 | 0.55 | 1.806 | 0.0048 | 8.32 | 0.620 | 2.176 | 0.285 | |
| 15 | 20 | 0.60 | 1.629 | 0.0034 | 8.92 | 0.620 | 1.765 | 0.351 | |
| 16 | 25 | 0.40 | 2.453 | 0.0154 | 6.31 | 0.728 | 2.739 | 0.266 | |
| 17 | 25 | 0.45 | 2.347 | 0.0104 | 7.35 | 0.728 | 2.613 | 0.278 | |
| 18 | 25 | 0.50 | 2.181 | 0.0094 | 7.18 | 0.728 | 2.429 | 0.300 | |
| 19 | 25 | 0.55 | 2.070 | 0.0045 | 9.85 | 0.728 | 2.187 | 0.333 | |
| 20 | 25 | 0.60 | 1.912 | 0.0032 | 10.79 | 0.728 | 1.817 | 0.400 | |
| Single-berm channel | 21 | 10 | 0.40 | 1.594 | 0.0125 | 4.55 | 0.391 | 2.907 | 0.134 |
| 22 | 10 | 0.45 | 1.383 | 0.0079 | 4.97 | 0.391 | 2.587 | 0.151 | |
| 23 | 10 | 0.50 | 1.152 | - | - | 0.391 | 2.349 | 0.166 | |
| 24 | 10 | 0.55 | 0.870 | - | - | 0.391 | 2.255 | 0.173 | |
| 25 | 10 | 0.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 26 | 15 | 0.40 | 1.746 | 0.0106 | 5.41 | 0.507 | 2.969 | 0.171 | |
| 27 | 15 | 0.45 | 1.527 | 0.0078 | 5.52 | 0.507 | 2.791 | 0.182 | |
| 28 | 15 | 0.50 | 1.435 | 0.0030 | 8.36 | 0.507 | 2.602 | 0.195 | |
| 29 | 15 | 0.55 | 1.153 | - | - | 0.507 | 2.252 | 0.225 | |
| 30 | 15 | 0.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 31 | 20 | 0.40 | 2.026 | 0.0104 | 6.34 | 0.620 | 3.089 | 0.201 | |
| 32 | 20 | 0.45 | 1.855 | 0.0074 | 6.88 | 0.620 | 2.873 | 0.216 | |
| 33 | 20 | 0.50 | 1.678 | 0.0054 | 7.29 | 0.620 | 2.617 | 0.237 | |
| 34 | 20 | 0.55 | 1.319 | - | - | 0.620 | 2.280 | 0.272 | |
| 35 | 20 | 0.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 36 | 25 | 0.40 | 2.375 | 0.0178 | 5.68 | 0.728 | 3.159 | 0.230 | |
| 37 | 25 | 0.45 | 2.184 | 0.0100 | 6.97 | 0.728 | 2.938 | 0.248 | |
| 38 | 25 | 0.50 | 1.967 | 0.0080 | 7.02 | 0.728 | 2.647 | 0.275 | |
| 39 | 25 | 0.55 | 1.699 | 0.0030 | 9.90 | 0.728 | 2.380 | 0.306 | |
| 40 | 25 | 0.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Flow Resistance Coefficient | Range | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| μ (Pa·s) | 0.006–0.243 | 0.089 | 0.075 |
| ξ (m−1/2·s−1) | 2240–30,764 | 9152 | 7514 |
| n (m−1/3·s) | 0.006–0.019 | 0.012 | 0.003 |
| C1 (m1/2·s−1) | 27.47–61.53 | 38.87 | 8.132 |
| C2 (m0.78·s−1) | 6.48–9.05 | 8.00 | 0.639 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.; Ryou, K.; Lee, H. Debris Flow Characteristics in Flume Experiments Considering Berm Installation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052336
Chang H, Ryou K, Lee H. Debris Flow Characteristics in Flume Experiments Considering Berm Installation. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052336
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Hyungjoon, Kukhyun Ryou, and Hojin Lee. 2021. "Debris Flow Characteristics in Flume Experiments Considering Berm Installation" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052336
APA StyleChang, H., Ryou, K., & Lee, H. (2021). Debris Flow Characteristics in Flume Experiments Considering Berm Installation. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052336








