Abstract
The review describes the main methods of obtaining hydroxides and aluminium oxides (AO) of various structures from gibbsite. The promising techniques of obtaining AO adsorbents are discussed, namely the technique of thermal activation in the mode of pneumatic transport with gibbsite by heated air (TCA Gb) and the technique of thermal activation of gibbsite in centrifugal flash reactors (CTA Gb). The main methods of improving the adsorbent properties of AO, such as the optimisation of texture characteristics and phase composition, as well as the influence of the modification of aluminium oxide adsorbents, obtained using CTA and TCA technologies with cations of alkaline metals, are considered. It is shown that the modification allows a controlled variation of the characteristics of donor and acceptor active sites on the surface of adsorbents and, thus, a substantial increase in their adsorption activity, in particular, with respect to water vapour.
1. Introduction
Adsorbents-desiccants of the air are successfully applied in different fields of industry, particularly in mechanical engineering and for the elimination of excessive moisture in amenity premises. As a rule, they are also used at a dewpoint for compressed air below 0 °C. The adsorption method is applied in processes in which a high degree of air dehydration is required (pharmaceutics, chemical and petrochemical plants, textile factories, food and electronic industry, etc.) [1,2,3].
The following requirements are imposed on industrial adsorbents-desiccants [4,5]:
- -
- Interaction processes between adsorbents and water vapours must be fast. Adsorbents must have high absorption capacity, which will allow the gas to pass through adsorbers at a high rate and use compact adsorption plants for dehydration.
- -
- Adsorbents must have gigh stability after multiple regenerations.
- -
- Adsorbent grains must have high mechanical compression, (crushing) and abrasion strength.
- -
- Adsorbents must be inexpensive and easily regenerated.
- -
- Adsorbents must not react chemically during adsorption and regeneration.
To meet the abovementioned requirements for the efficiency of the adsorbent, it must have the following characteristics:
- -
- Large internal pore volume
- -
- Large value of specific surface
- -
- Controlled pore-size distribution, preferably in the micropore range
- -
- Controlled properties of the surface, owing to selected functional groups
- -
- Weak interactions between an adsorbate and an adsorbent (in general, physical adsorption)
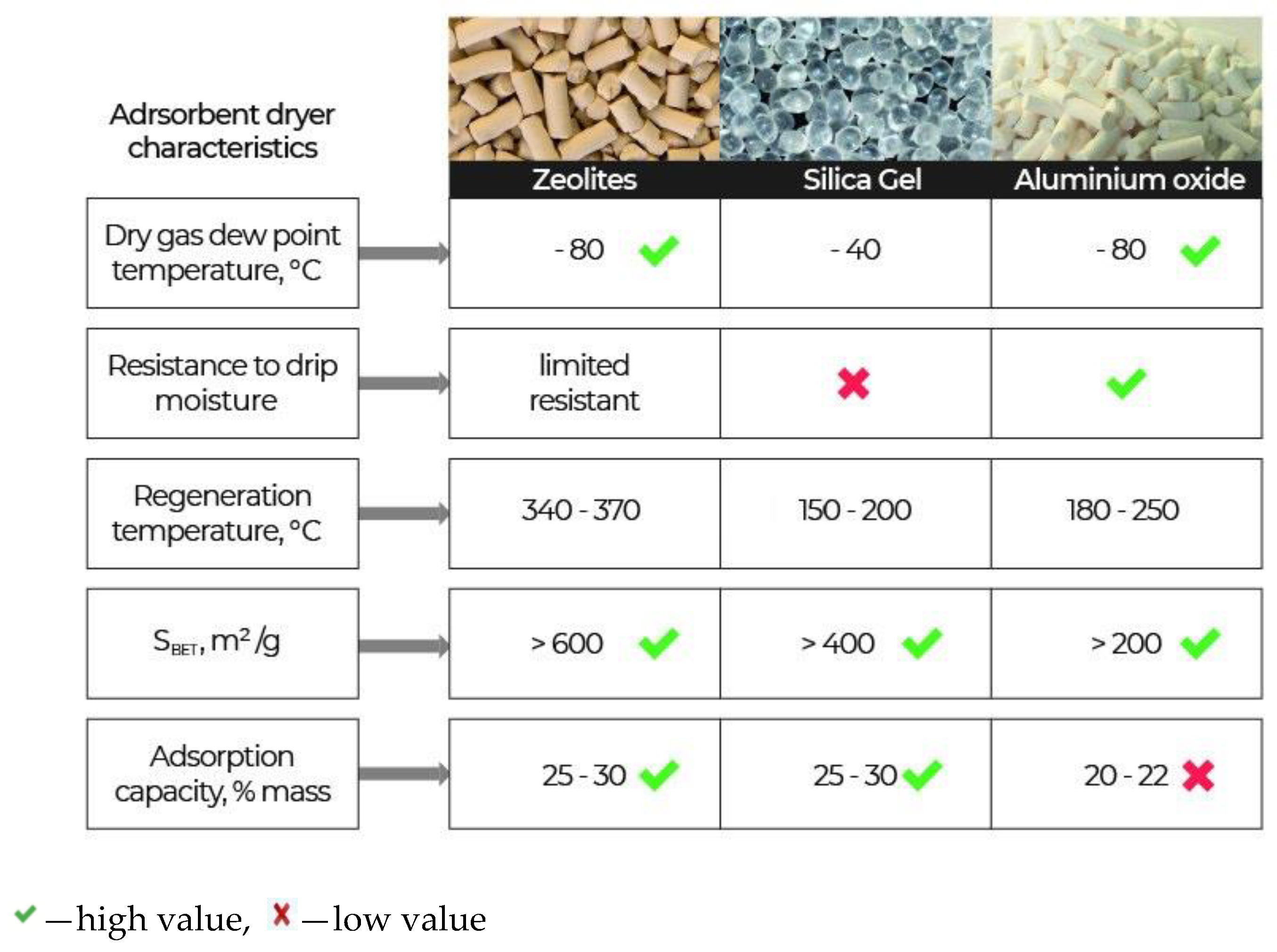
Molecular sieves (zeolites), silica gels, and activated aluminium oxide are usually used as adsorbents-desiccants. These adsorbents have their own advantages and disadvantages [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13], as shown in Figure 1.
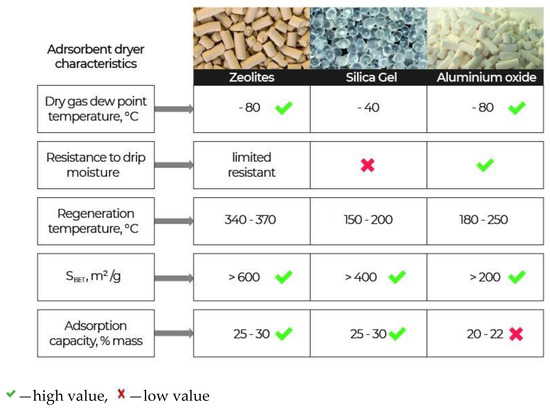
Figure 1.
Characteristics of the basic adsorbents-desiccants.
Zeolites have sufficiently large adsorption capacity by water, but they are costly and difficult to regenerate. Prolonged time and temperatures above 340 °C are required for their regeneration. A distinctive feature of zeolites is a high adsorption rate of water vapour (steep rise of isotherms) in the area of low concentrations of water vapour. The amount of the absorbed water reaches a maximum value with a relative humidity equal to 20% and practically remains constant with a subsequent increase in the air humidity [14]. The second distinctive feature of adsorption of water vapour on zeolites is a weak dependence of its adsorption capacity on the temperature. At a temperature of 100 °C and a pressure of 10 mm of mercury, the adsorption capacity of zeolites reaches 15 ÷ 16 g/100 g of the adsorbent. Even at 200 °C, it is still significant at—3.6 g/100 g of the adsorbent [14].
The absorption capacity of silica gel depends on the temperature of humid air and partial pressure of vapour: When the temperature increases and the partial pressure of vapour decreases, this capacity decays. It is expedient to use silica gel, having a low regeneration temperature 150–200 °C (see in Table 1 [5,14]), in desiccants of compressed air with hot regeneration at an adsorption temperature not higher than 35 °C and content of water vapour in the dehumidified air not lower than 0.02 vol.%. The main disadvantage of silica gels is low water resistance [14], which leads to their destruction when in contact with water.

Table 1.
Titles, scope and references of the main review, focusing on the topics of the adsorbents based on aluminium oxide.
The advantages of active aluminium oxide (AO), providing its wide application for gas dehydration, are high adsorption capacity as compared to zeolites with high relative humidity; thermal stability; a possibility of multiple regeneration, which determines its good indicators under operation conditions; water resistance, especially resistance to condensed moisture; and relative ease of production, as well as availability of raw materials. These are data based on the fact that granules of aluminium oxide are stronger than the granules of the majority of other desiccants, as they are not grained and abraded in rather harsh operating conditions of the pressure swing adsorption process [15].
The AO properties are determined by the structural peculiarities of its numerous polymorphic modifications (γ-, η-, χ-, δ-, θ-, κ-, α-, ρ-) and depend on the structure and properties of their precursors—aluminium hydroxides. Aluminium hydroxides also exist in the form of various modifications that differ in the chemical composition and crystal structure. Therefore, the thermal transformations of each aluminium hydroxide have their own peculiarities [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Depending on the preparation method, adsorbents can have different crystal structures and a wide range of pores [23,24]. Among the known series of aluminium oxide modifications, gamma (γ), eta (η) and chi (χ)-Al2O3 are the most widely used.
In the last few years, a number of reviews have been published, in which aluminium oxide has been used as a desiccant in desiccant coated heat exchangers [25] and in desiccant cooling systems [26], as well as for water purification [27,28,29] from different organic and inorganic contaminants (see references with their corresponding scope, given in Table 1).
Another important field of application of aluminium oxide is its use for deep air dehumidification from water vapour. Therefore, the improvement of its phase and chemical composition (modification of the surface properties) to enhance its adsorption capacity and stability is a relevant task. The techniques of its obtainement, influencing the structure, surface acidity, mechanical strength of the obtained material and, ultimately, its adsorption activity, are considered in this review.
2. Methods of Obtainment of Aluminium Oxide Used in Industry
As a rule, bauxite, alunite and nepheline are used as raw materials for obtaining aluminium oxide. If the content of aluminium oxide in them is more than 6−7%, the production is carried out by the main method—the Baeyer method. If the content of the substance is lower, the method of sintering ore with lime or soda is used. The main raw-material source of Al2O3 is bauxite, which mainly consists of hydrated forms of Al2O3 (gibbsite, boehmite, diaspore). On average, bauxite contains from 45 wt.% to 60 wt.% of Al2O3 (in conversion from hydroxides), 10–30 wt.% of Fe2O3 and varying amounts of SiO2, CaO, TiO2 and H2O.
2.1. Methods of Alumina Obtainment
2.1.1. Bauxite Ore Treatment by the Baeyer Method
As of today, about 90–95% of the world’s aluminium hydroxide is extracted using the Baeyer process, which was proposed in 1887 [30]. The Baeyer method is a hydrochemical method of obtaining alumina from bauxites. Large pieces of bauxite, supplied from the mines, are first crushed, and then wet-ground in ball mills. Bauxite, caustic alkali and recycled liquor are fed to ball mills. Sometimes, a little lime is added to bauxite to facilitate their breakability. The pulp from the mills is collected in collectors, where the remaining amount of the recycled liquor with a concentration of Na2O = 300 g/l is fed. Then, it is heated there by separation steam to 90–100 °C and soaked for 4–8 h while stirring for preliminary bauxite desiliconization, i.e., there is a transfer of the most part of the active silica from bauxite to the liquor. The mixture of the ground bauxite and the recycled liquor (raw pulp) is sent to one of the main operations. This process is called the leaching or cooking of bauxite, which is carried out in autoclaves at a temperature of 230–240 °C. The purpose of this operation is to dissolve the aluminium oxide contained in bauxite, avoiding the transfer of other components of bauxite (silica, iron oxides, etc.) to the liquor. The silica is removed by subsequent slow heating when Na2Si(OH)6 precipitates. The remaining pure liquor of NaAl(OH)4 is cooled, diluted with water and neutralized with carbon dioxide. As a result, aluminium trihydrate Al(OH)3 (gibbsite) is selectively deposited from the liquor without the residues of the dissolved silica.
2.1.2. Sintering Technique
The technique of sintering ore with lime or soda involves mixing high-silica finely ground ore (nepheline and others) with soda and limestone and sintering in rotating furnaces at 1250−1300 °C. The obtained mass is leached with an aqueous alkaline solution. The solution of sodium aluminate, obtained in this way, is separated from the sludge, then it is released from SiO2, precipitating it in an autoclave at a pressure of about 0.6 MPa and then with lime under atmospheric pressure, and the aluminate is decomposed with gaseous CO2 along with the formation of Al(OH)3.
Both described methods are multistage. They include both the main technological stages of production and auxiliary operations related to waste disposal and to the repeated return of mother liquors to the circulating cycle [31]. The main product when using the abovementioned methods of ore processing is gibbsite (hydrargillite).
2.2. Methods of AO Obtainment
To obtain active aluminium oxide, various methods of processing gibbsite are used [24,32], as described in the following subsection.
2.2.1. Aluminate Technology with Alkali Treatment
- (a)
- Dissolution of gibbsite in alkali, accompanied by the formation of sodium aluminate:
Al(OH)3 + H2O + NaOH → NaAlO2 + 2H2O;
- (b)
- Reprecipitation with acid:
NaAlO2 + HNO3 + H2O → Al(OH)3 (bayerite) + NaNO3 pH = 10–12;
NaAlO2 + HNO3 → AlO(OH) (pseudoboehmite) + NaNO3 pH < 9.
A continuous process based on the reaction of HNO3 with NaAlO2 was described by the authors of [32]. The principle is as follows: In the first reactor, HNO3 and NaAlO2 are mixed at a temperature of 30 °C to 75 °C. Then, the resulting suspension is sent to the second reactor where it is converted into pseudoboehmite. The suspension fraction is recycled in the first reactor with a ratio of 0.1 to 3 of slurry volume per volume of mixing (NaAlO2 + HNO3). Pseudoboehmite is then removed from the second reactor. After drying, it has a specific surface area in the range of 200 m2/g to 300 m2/g.
This method is the most common for producing aluminium gel for catalysis. Precipitation is carried out from alkaline solutions (aluminates) with acids (sulfuric, nitric, hydrochloric) or acidic solutions of salts. Various structural and texture characteristics of the resulting hydroxide are determined by the pH, temperature and nature of the anion. The crystallisation rate of pseudoboehmite is determined largely by the temperature of deposition, and bayerite is primarily determined by the pH.
To increase the dissolution velocity, gibbsite is preliminary ground to the particle size of 10 µm and/or the temperature of the reacting mixture is raised.
There are various techniques of precipitation—with a variable and constant value of pH, two-stage (cold and hot precipitation), etc. For example, cold precipitation from the sodium aluminate solution with the sulphuric acid solution is carried out at 20–25 °C and pH = 9.3–9.5. Hot precipitation is performed at 90–95 °C and pH = 9.3–9.5. Then, both modifications of aluminium oxide are mixed, and a precipitate consisting of pseudoboehmite and boehmite is obtained, which can be rinsed and filtered very well. Granules of active aluminium oxide of high mechanical strength can be obtained using this technique.
The drawback of this method is the high cost of removing sodium due to the difficulty of rinsing the gel. The aluminium hydroxide precipitate is filtered, rinsed on a filter press and moulded into granules, which are later dried and calcined at 670–820 K to obtain η- or γ-Al2O3.
2.2.2. Acid Technology
- (a)
- Dissolution of gibbsite in acid:
Al(OH)3 + 3HNO3 → Al(NO3)3 + 3H2O;
- (b)
- Precipitation with alkali or ammonia water:
Al(NO3)3+ 3NaOH → Al(OH)3 + 3NaNO3,
Al(NO3)3+ 3NH4OH → AlOOH + 3NH4NO3 + H2O.
The aluminium hydroxide precipitate is filtered, rinsed on a filter press and moulded into granules, which are later dried and calcined.
Acid technology also makes it possible to obtain a wide range of products depending on the conditions of the process. Precipitation of aluminium hydroxide at low temperatures and pH > 10 contributes to the formation of bayerite, while precipitation at pH = 7–9 and elevated temperature contributes to the formation of pseudoboehmite. Precipitation is carried out from acidic solutions of aluminium salts (sulphate, nitrate, chloride) with solutions of bases (ammonia, ammonium carbonate). However, this method is more expensive, since in this case, three moles of acid and, respectively, three moles of alkali are consumed per mole of the obtained product. On the other hand, when using ammonia as a precipitator, the sodium impurity in the oxide is excluded.
Aluminium hydroxides of the pseudoboehmite type (Al2O3·1.5H2O) and, much less often, of the bayerite type (Al(OH)3), are usually obtained from aluminium-containing solutions using aluminate and acid technologies of “deposition.” Sodium aluminate, as a raw material for obtaining η-Al2O3, is undesirable. When obtaining bayerite (pH > 10), the precipitate is always heavily contaminated with the sodium admixture (0.2–0.5% Na2O).
The deposition conditions—the temperature, pH, time and the temperature of the subsequent aging of the precipitate—have a direct impact on the properties of the resulting product: The chemical and phase composition, porous structure and dispersion [17]. To obtain aluminium oxide, hydroxides are subjected to calcination. Adsorbents-desiccants based on γ-Al2O3 are most frequently obtained through the precipitation technology. A common drawback of precipitation methods is the high consumption of reagents and a significant number of chemically contaminated effluents [24].
Some companies have made significant advances in the development of alumina obtaining methods based on acidic process. Canadian company Orbite Aluminae Inc. presented technological methods of using HCl for the production of aluminium oxide and a number of by-products, such as silica, hematite and rare earth metals with HCl regeneration, thus increasing the profitability of alumina production [33].
2.2.3. Rapid Calcination of Baeyer Hydrate (Gibbsite)
Method of Thermochemical Activation (TCA)
Gibbsite can be calcined rapidly by pulsed heating at the dehydration temperature in apparatuses (the method of thermochemical activation by flue gases—thermochemical activation and thermochemical decomposition in catalytic heat generators) or by mechanochemical activation (MCA) in mills with high power rating. The essence of the TCA method is that the initial material—gibbsite—is activated by heated air in the pneumatic transport mode within a few seconds. The best result is achieved when combining TCA with MCA, as the TCA product is subjected to additional fine grinding. The resulting amorphous product has a large specific surface and is characterised by high reactivity. In the presence of water, it hydrolyses easily, and is accompanied by the formation of pseudoboehmite in the neutral environment and bayerite in the alkaline environment. The amorphized powder can be formed in advance before the crystallisation stage by pelletising on plate granulators into spherical particles, which then crystallise in a steam-air medium into high-strength balls of pseudoboehmite and then into those of aluminium oxide of mainly the γ-phase [34,35].
2Al(OH)3 → Al2O3 + 3H2O.
The TCA method is widely used, including for the multi-tonnage production of the so-called flash product (thermally activated aluminium hydroxide), which is a raw material for the preparation of aluminium oxide materials of various applications. However, it has serious drawbacks:
- -
- Dusty gas emissions
- -
- Probability of contamination of TCA products due to impurities in the fuel and products of its incomplete combustion
- -
- Instability of the operating mode, resulting in poor reproducibility of the physical and chemical properties of the flash product
- -
- Low efficiency of energy use of the heat carrier and, consequently, high specific energy consumption—more than 10 kJ/g of raw materials
Centrifugal Thermal Activation (CTA)
In the light of the disadvantages of the CTA method, a new energy-saving technology has been developed to increase the reactivity of powder materials under the action of centrifugal force in centrifugal flash reactors [36,37,38], which is called centrifugal thermal activation (CTA). The appearance of the centrifugal reactor “TSEFLARTM” of the drum type is shown in Figure 2.
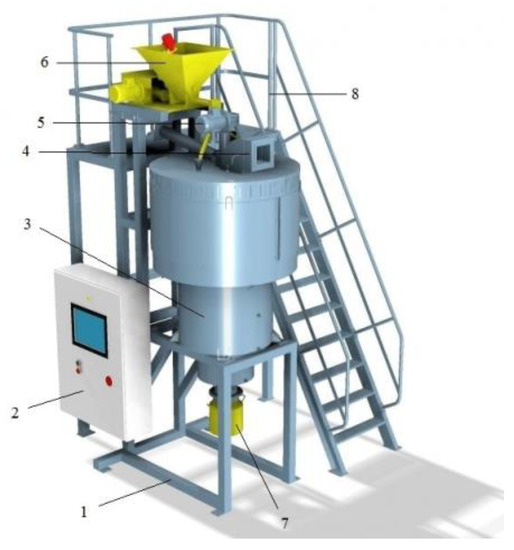

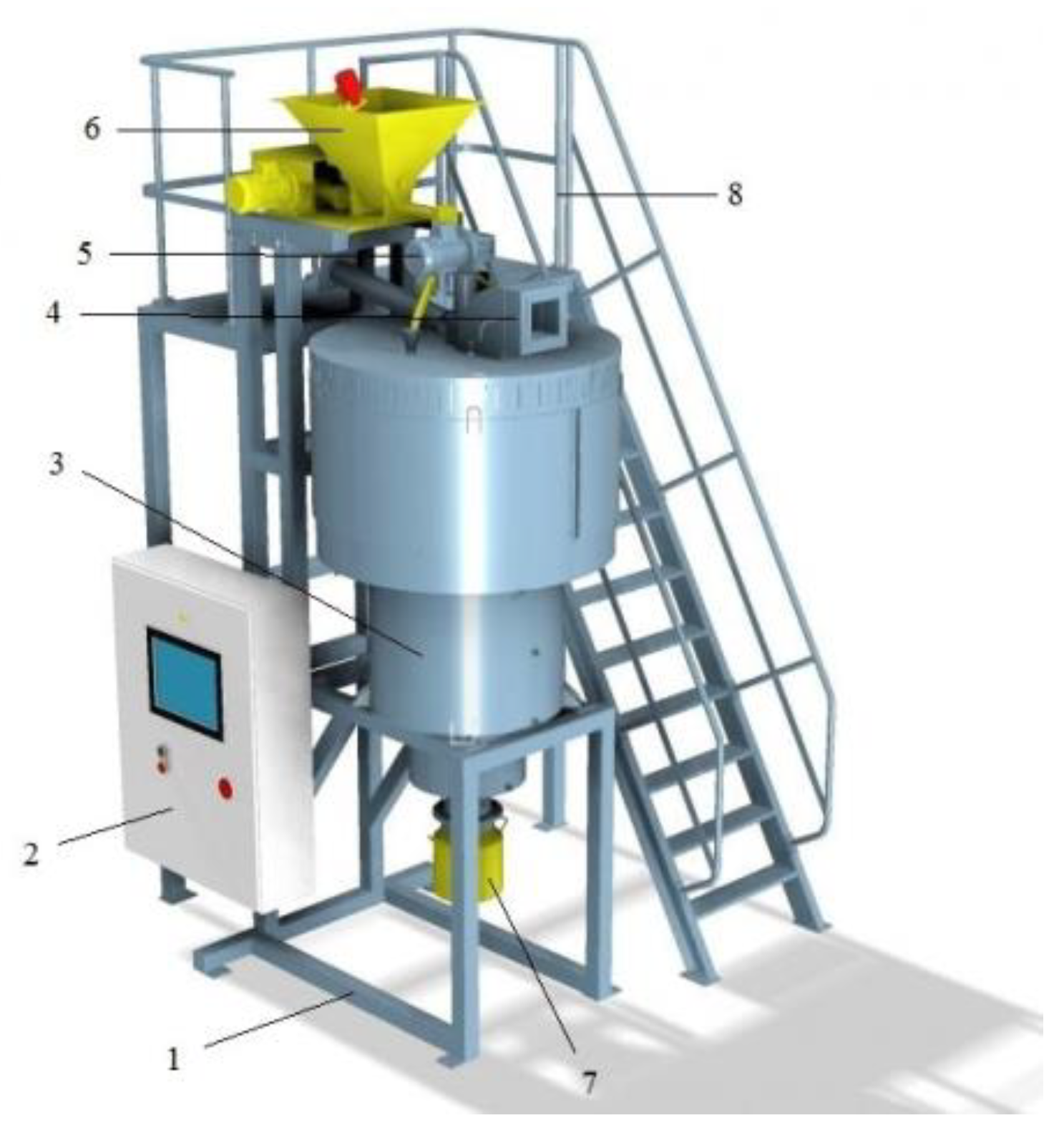
Figure 2.
Experimental-industrial centrifugal reactor “TSEFLARTM” of the drum type: 1—frame; 2—control board; 3—cooler; 4—air duct; 5—drum drive; 6—tank for raw material; 7—tank for the thermally treated product; 8—processing area.
The main difference between CTA and TCA processes is that, during thermal activation, the powder is in contact for 1–2 s with a rotating and heated solid heat-transfer agent under the action of centrifugal forces. Conditions of the CTA process such as temperature, contact time, etc. can be varied in a wide range, thereby changing the decomposition depth of gibbsite and the properties of the obtained products. CTA products have a developed surface and disordered and heterogeneous mesoporous structure from which hydroxides and oxides of aluminium of different modifications can be formed, including during its subsequent hydration and heat treatment.
The authors of [39] showed that the flash product, calcined at 400 °C, represents an almost amorphous phase and contains only a small amount of crystallised boehmite. An increase in the temperature during processing of this material leads to the crystallisation of the amorphous phase, accompanied by the formation of η-Al2O3, whose proportion increases and reaches 60% at 900 °C.
The phase composition of the CTA product of gibbsite at T > 400 °C and the contact time of ~1.5 s is approximately as follows: Gibbsite (0–20%) + boehmite (0–10%) + pseudoboehmite (0–20%) + amorphous phase (the rest is up to 100%). As a result of the thermal shock treatment, the content of chemically bound water in the samples decreases to 5–15%, and the specific surface increases from 2–5 to 100–250 m2/g (T = 300 °C) due to the formation of a branched system of micropores. The mentioned characteristics of the adsorbent vary depending on the processing conditions, namely the eat carrier temperature, time of contact, fraction composition of the reagent, mass flow rate of the powder, its initial temperature, pressure and steam-air mixture in the water-vapour removal system. The specific energy consumption at 300 °C is about 4 kJ/g of gibbsite. The CTA process parameters (temperature, contact time) are easily controlled, which provides good reproducibility of the physical and chemical properties of the resulting products.
The hydration process of the CTA product can be divided into stages: An intensive period of prehydration, an acceleration period that passes through the maximum of the heat release rate and a final period of dissipation of a certain amount of released heat [40]. The phase composition of the samples shows that the acceleration period is associated with the crystallisation of amorphous gels, which is accompanied by the bayerite formation. This period is also characterised by large changes in the morphology of particles. When the temperature increases, the period of crystallisation is shortened. A peculiarity of bayerite-containing aluminium hydroxide is the formation of low-temperature phases of aluminium oxide (primarily η-modification) at a calcination temperature of >300 °C, which makes it possible to obtain samples with a more developed specific surface, a large number of micropores and, accordingly, with a larger statistic capacity as compared to desiccants based on γ-Al2O3.
The study of the rehydration process of the CTA gibbsite product under mild conditions at a temperature of 15–35 °C, using aqueous solutions of electrolytes (pH of 5–11) and applying X-ray phase analysis, thermal analysis (TA), electron microscopy methods, etc., has shown that significant morphological and phase changes of the CTA product occur as a result of the interaction. These changes depend on the pH of the electrolyte, temperature and hydration time. In an alkaline and aqueous environment, up to 50% of the pseudoboehmite phase is formed in less than 24 h. An increase in the temperature, pH and hydration time leads to the formation of mainly (80%) the bayerite phase. A rengenoamorphic hydroxide is formed in an acidic environment [41]. The influence of the particle size of the products of pulsed thermal activation of gibbsite on the hydration process has already been noted in the earliest research. The authors of [42] specifically showed that the grinding accelerates the hydration process, and even at room temperature, up to 60% of pseudoboehmite can be formed in 1 h. It has been found that during the hydration of thermal activation products in slightly alkaline media, bayerite is formed. The amount of bayerite depends on the temperature, and in strongly alkaline solutions, on nordstrandite. The formation of pseudoboehmite was observed in hot (130 °C) acid solutions [43].
The CTA product of gibbsite is somewhat analogous to the abovementioned flash product, but the special designation has been introduced on the grounds that the properties of CTA and TCA products differ on a number of points. In this way, during hydration under mild conditions (room temperature and atmospheric pressure) in the aqueous medium of the CTA product, in contrast to TCA, there is no accumulation of pseudoboehmite, and the low-temperature aluminium oxides, formed during calcination, are characterised by changed lattice parameters [44]. It has been found that during hydration of the CTA product of gibbsite in the temperature range of 75–80 °C, pseudoboehmite is predominantly formed in a slightly acidic medium (acid modulus for HNO3 = 0.04), and bayerite is formed in an alkaline medium (solution: KOH, pH: 12–13, alkaline modulus: 0.1) [45,46].
In this way, depending on the hydration conditions (temperature, electrolyte type, time, etc.) of the CTA product, aluminium hydroxides with different phase compositions can be formed.
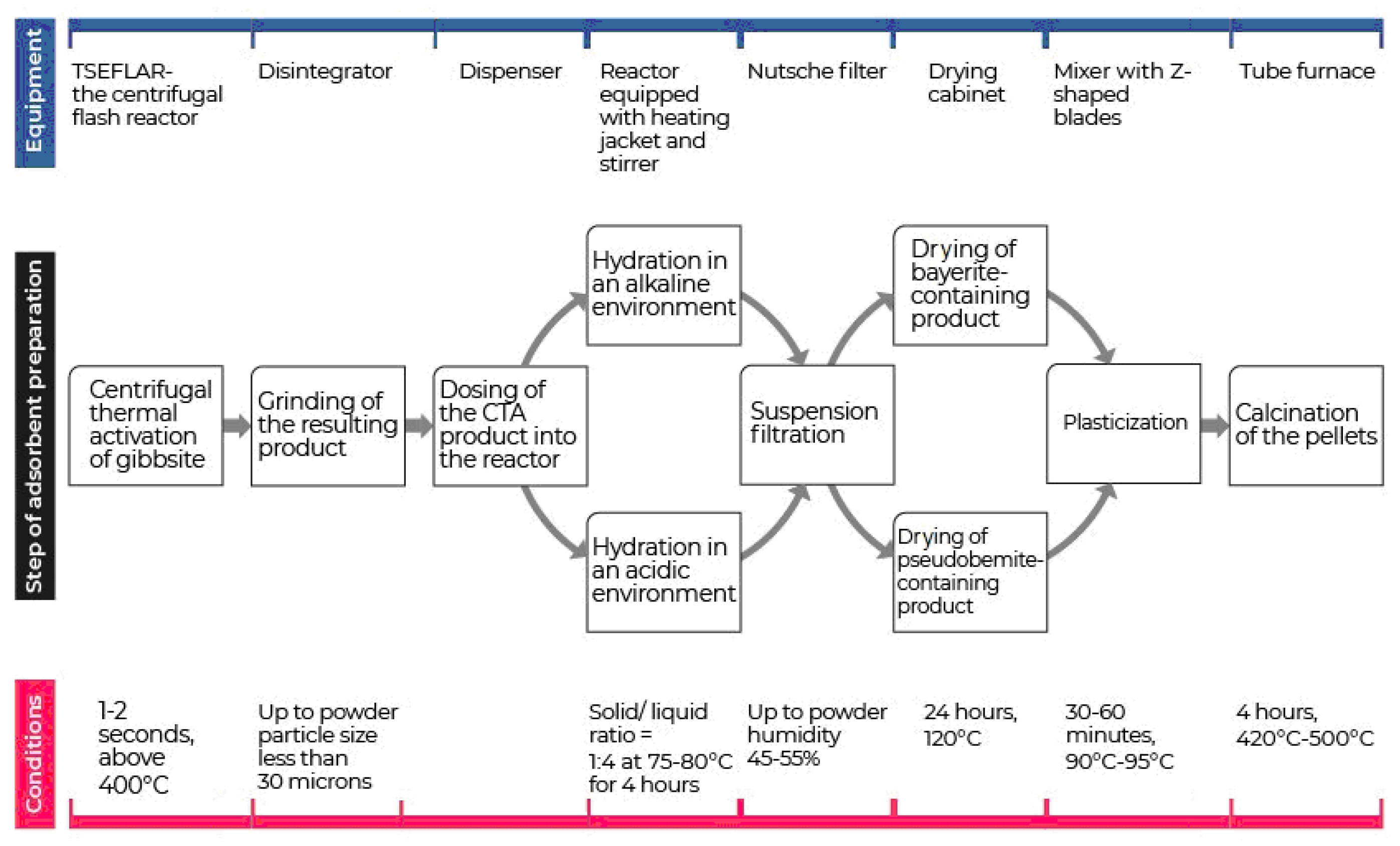
An important stage in the preparation of aluminium oxides which can dramatically influence its composition and characteristics is the calcination stage. Depending on the type of aluminium hydroxide at the heat treatment stage at temperatures < 600 °C, low-temperature aluminium oxides (mainly η-, γ- χ-forms) are formed which have different properties. The sequence of technological stages for obtaining an adsorbent-desiccant using the CTA product is shown in Figure 3.
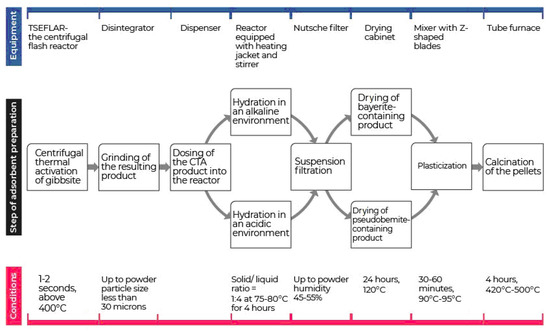
Figure 3.
Technological stages of obtaining aluminium oxide adsorbents using the centrifugal thermal activation (CTA) method.
It has been found that aluminium oxide, obtained from amorphized gibbsite (TCA and CTA products), has a higher adsorption activity with respect to water vapour than that of γ-Al2O3 obtained by precipitation from pseudoboehmite [45,46].
The comparison of the adsorption properties of Al2O3 samples obtained by the CTA method from a bayerite-containing product (Figure 3) and containing η-Al2O3 has shown that they have a higher adsorption capacity with respect to water vapour than that of AO obtained from pseudoboehmite and containing γ-Al2O3.
2.2.4. Synthesis of Aluminium Oxide from the Basic Aluminium Salt Al2(OH)5Cl or from Alcoholates Al(OR)3
Schemes for the synthesis of aluminium oxide from the main aluminium salt Al2(OH)5Cl or from alcoholates Al(OR)3, obtained by dissolving aluminium in acid or by the reaction of direct interaction of aluminium with alcohol, respectively, are characterised by the use of a large number of aggressive and expensive reagents. They have a large number of stages and a high cost.
In the Honeywell UOP (Universal Oil Products) process, the main aluminium salt, Al2(OH)5Cl obtained during the interaction of hydrochloric acid with metallic aluminium, is mixed with hexamethylenetetraamine ((CH2)6N4). This solution is fed through the filter to the heated column, whereby balls are formed. These balls gelatinise during the decomposition of (CH2)6N4 according to the equation:
(CH2)6N4 +4H+ + 6H2O → 6CH2O + 4NH4+.
After removing the balls from the bottom of the column and crystallising them, a narrow size distribution of crystallites and, as a consequence, uniform pores are obtained [24].
The process of obtaining aluminium oxide from alcoholates is based on the Ziegler reaction [47], which was originally used for the production of higher linear alcohols. Using aluminium of standard quality, hydrogen and ethylene, a number of reactions can be performed:
Synthesis of triethylaluminium:
2Al + H2 + 6C2H4 → 2Al(C2H5)3
Chain propagation:
Al(C2H5)3 + 3nC2H4 → Al[(C2H4)nC2H5]3
Oxidation of trialkylaluminium:
2AlR3 + 3O2 → 3Al(OR)3
Hydrolysis of alcoholate to form alcohol and aluminium oxide:
3Al(OR)3 + 3H2O → Al(OH)3 + 3ROH
In view of the high selectivity of the reaction, the impurities, contained in Al remain as insoluble mud, which is removed by filtration and centrifugation. In this case, pure hydroxides of the boehmite and bayerite structure are obtained, which also have a highly developed surface.
In this way, it can be noted that the procedure of obtaining active aluminium oxide usually consists in the synthesis of aluminium hydroxide and its subsequent drying, calcination and granulation. The analysis of the literature shows that the physicochemical properties of aluminium oxide are determined by the properties of the hydroxide precursor, which are naturally transformed during heat treatment according to the mechanism of phase transitions [21]. Only an intentional synthesis of the hydroxide precursor can guarantee obtainment of the aluminium oxide adsorbent or carrier with desired properties.
3. Basic Methods of Moulding of Adsorbent Granules
Adsorption dehydration of gases and liquids is usually carried out in fixed granular layers of the adsorbent. When obtaining catalysts and sorbents with a developed geometric surface, the moulding stage becomes crucial. The sorbent granules of the desired size, shape, type and strength are produced by several moulding methods. In general, the methods of disk granulation, extrusion and moulding in a liquid medium of high-molecular hydrocarbons are used. These methods account for 40%, 50% and 10%, respectively, of 120,000 tons of aluminium oxide that enters the world market and is used in adsorption and catalytic processes. Tableting and spray drying are mainly used for the moulding of massive catalysts and cracking catalysts in a suspended layer, respectively [48].
3.1. Method of Disk Granulation of Adsorbents
The moulding of aluminium hydroxides on the disk represents an agglomeration in the form of balls after powder humidification. This operation is performed using a granulator that rotates around an inclined axis. The powder is continuously fed to the granulator and continuously wetted with various electrolytes. The already-formed aluminium hydroxide grains are continuously fed there. They are gradually covered with the wetted powder, and the grain diameter increases. As the grains grow, they move from the centre of the granulator disk to its edges. Then, starting from a certain size, they are thrown off the disk using the action of centrifugal force. The granulation operation is followed by the activation of the granules. The disk granulation method is more preferable for the agglomeration of aluminium oxide, which is obtained by rapid calcination. The properties of the granules, obtained by this method, depend on the physicochemical characteristics of the initial powder and the conditions of the granulation process (the feed rate of the powder, grains, water, type and amount of the binder, etc.) [24].
3.2. Liquid Moulding Method
The principle of production of granulated alumina, using the method of moulding in oil, often called as the oil-dripping moulding, is to create drops of the aqueous layer of alumina by means of the sprayer. These drops fall into the column, filled with a solvent (oil) that does not mix with water. The surface tension, created in this column on sol droplets, leads to the formation of ideally spherical particles, which are neutralized and, if necessary, crystallised, and then dried and calcined [24,49].
3.3. Extrusion Moulding Method
The method of extrusion moulding has, as a rule, two stages: Mixing the raw material and extrusion. The paste, obtained at the mixing stage, is extruded (for example, in a single- or twin-screw extruder), and subsequently dried and calcined. The normal form of extrudates is cylinders with diameters of 1–4 mm. Some manufacturers supply extrudates with different forms of section (multilobate), which have theoretically better properties in some applications [50,51].
3.4. Comparison of Moulding Methods
The three moulding methods described above differ in the AO concentration in the resulting system “aluminium oxide—water.” The mass content of aluminium oxide, amounting to ~60% in the case of disk moulding, decreases to approximately 45% in the case of extrusion and up to 25% in the case of liquid moulding. The extrusion of the boehmite gel, as well as the oil-dripping coagulation process, leads to the formation of granules that already have the required characteristics for final use. The oil-dripping method for gelatinisation-crystallisation of the basic salts of aluminium oxide and disk moulding during rapid calcination are processes in which moulding precedes the stage of final crystallisation of aluminium oxide [24].
The main advantage of disk moulding is its higher productivity and, therefore, lower cost of the granules. The disadvantages of this method include the fact that aluminium oxide granules of different sizes are formed as a result, which subsequently requires their dispersion through sieves to the desired size, which is accompanied by the separation of defective granules. The advantage of the oil-dripping moulding method is that balls of the same size are formed, but this method is significantly more expensive than disk granulation [47]. Among all the described methods, the most optimal method is extrusion moulding, since this method is technologically simple and makes it possible to obtain granules of a required size at the moulding stage with a minimum quantity of spoiled products. In addition, the method of extrusion moulding allows for the easy moulding of pastes, consisting of several components (composite pastes), which makes it possible to vary the properties of the resulting adsorbent within a sufficiently large range.
The product, obtained by “rapid dehydration,” is usually processed by two methods: Rolling-up the powders on the disk granulator [48,52] or rehydration, obtaining pseudoboehmite or bayerite, with subsequent processing into oxide products of the required modification using extrusion moulding [35,53].
4. Industrial Adsorbents-Desiccants and Their Characteristics
The most famous manufacturers of aluminium oxide desiccants are companies such as Axens, Alcoa, Alumac, Albemarle and BASF. The main method of obtaining active aluminium oxide is currently the “flash process.” The simplified technology for obtaining active aluminium oxide is as follows. The raw material–bauxite ore—is transformed into the solution by means of sodium carbonate (Baeyer process). Solid impurities are removed, and alumina is isolated by crystallisation of trihydroxide (Baeyer hydrate), which is actually gibbsite. Then, the gibbsite is calcined for a very short time (from 1 s to 10 s) in an air flow (gas flow velocity: from 8 m/s to 25 m/s) at a gas temperature from 400 °C to 1000 °C, followed by the separation of the reacted powder from the gas flow and cooling (quenching) to a temperature less than 60 °C. The result is active aluminium oxide, which has a high specific surface area, high specific pore volume and high adsorption capacity, determining its widespread use in the petrochemical industry.
In the Russian industry, active aluminium oxide is produced using a similar “flash process” by means of the TCA method [54]. The initial material—gibbsite—is activated by the air, which is heated by the heat generator, in the pneumatic transport mode for 5–8 s. The latter is heated at the expense of thermal energy, generated by burning diesel fuel. The air temperature in the reaction zone can reach ~550 °C. Depending on the TCA conditions, active aluminium oxide can be obtained with different sets of physicochemical properties.
Table 2 shows the characteristics of some industrial adsorbents based on aluminium oxide.

Table 2.
Characteristics of some industrial adsorbents based on aluminium oxide.
In this way, technological schemes are currently being implemented in the industry that allow for the production of granulated active aluminium oxides of various low-temperature modifications (η-Al2O3, γ-Al2O3 or χ-Al2O3) without precipitation stages. They include materials with the specific surface from 200 m2/g to 400 m2/g that have both monodisperse and bidisperse porous structures. Spherical granules based on χ-Al2O3 are obtained by disk granulation of the gibbsite thermal activation product, and granules of cylindrical or more complex shape based on γ-Al2O3 or η-Al2O3 are obtained by extrusion moulding of hydrated thermal activation products. The catalogue [58] presents a wide range of brands of active aluminium oxide used as adsorbents or catalysts whose granules have a spherical, cylindrical and ring shape. The widespread use of AO as an adsorbent is determined, along with good adsorption properties, by a possibility of geometric and chemical modification, rather high mechanical strength and stability in the cyclic operation.
5. Physicochemical Properties of the Surface and Sorption Characteristics of Aluminium Oxide Adsorbents
5.1. Aluminium Oxide Surface Characteristics
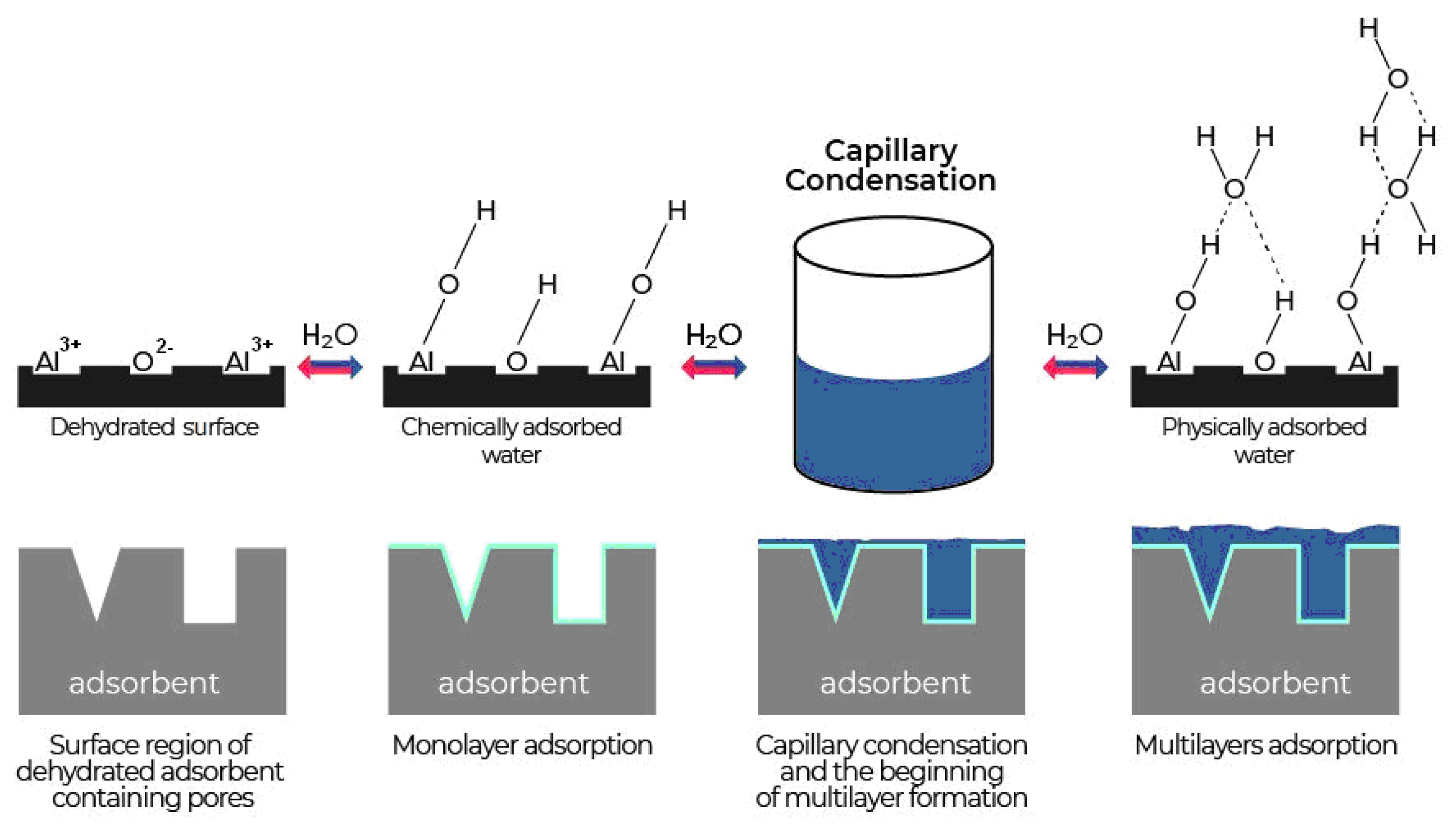
Active sites and hydroxyls on the AO surface largely determine its physicochemical and adsorption properties. The increased chemical activity and active adsorption sites on the surface appear as a result of the formation of a defective structure during the transition from the amorphous to crystalline state during thermal dehydration [8]. The interaction of water vapour with the AO surface is complex and proceeds under the influence of several different types of forces. Water adsorption by aluminium oxide desiccants is the result of three processes (Figure 4). The first is chemisorption or dissociative adsorption of water molecules on the active sites of the aluminium oxide surface, which leads to the formation of the first layer. The second is physical adsorption, leading to the formation of multilayers due to hydrogen bonds. The third is capillary condensation in pores [8,14,56].
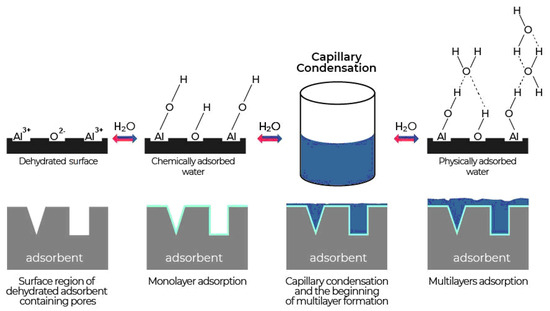
Figure 4.
Stages of water vapour adsorption on aluminium oxide.
The efficiency of adsorbents and their static and dynamic capacity depend on the structural modification of aluminium oxide (η-Al2O3, γ-Al2O3, χ-Al2O3), as well as the preparation conditions that determine the donor-acceptor properties of the oxide surface and their textural characteristics: Specific surface, pore volume and size distribution [46,57,59]. In addition, the adsorption properties also depend on the size and shape of the granules [14,60].
According to modern concepts, the surface of a solid body represents a combination of Lewis and Brønsted sites of the acid and basic type [61]. The surface of aluminium oxide is generally amphoteric. Oxygen atoms are strong basic sites, and aluminium ions act as strong Lewis sites. Four types of Lewis acid sites have been identified, differing in the structure of the second coordination sphere of aluminium [62]. As for the basic Lewis sites, two sites are most clearly shown: Strong and weak sites, associated with the bridging oxygen atoms of Al-O-Al and oxygen atoms of OH groups, respectively. A comparison of the Brønsted acidity and basicity of OH groups conducted by the authors of [62] showed that AO hydroxyls are more basic than acidic. Using spin probes, it has been shown that aluminium oxides have electron-acceptor and electron-donator sites on their surface that are capable of reducing (oxidizing) the molecules adsorbed on them due to the transfer of a single electron (Single Electron Transfer (SET) mechanism) [63,64,65]. It is logical to assume that changes in the concentration or strength of the abovementioned sites can influence the physicochemical properties of the surface. The authors of [66] showed that the number of Lewis acid sites (LAS), determined from the FT-IR spectra after pyridine adsorption, decreases in the series of η-Al2O3 > γ-Al2O3 > (χ + γ)-Al2O3 and correlates well with the catalytic activity in the reaction of methanol dehydration into dimethyl ether.
There is a close relationship between the structure of the initial hydroxides and oxides Al3+ obtained from them during heat treatment: Gibbsite → (χ + γ)- Al2O3; bayerite → η-Al2O3; boehmite → γ-Al2O3; pseudobemite → pseudocubic γ-Al2O3. The last two γ-modifications of Al2O3 differ significantly in their structural peculiarities, distribution of Al3+ ions over tetra-(Td) and octa-(Oh) oxygen positions and, consequently, in their acidic properties. Thus, the choice of the structural modification of Al3+ hydroxide can regulate not only the specific surface area (Ssp) and texture of desiccants, but also their acidity, which can influence the sorption properties of desiccants.
The acid-base properties of the surface of aluminium oxides obtained by thermal activation differ from the acid-base properties of homogeneous in their phase composition oxides obtained by precipitation. For example, the authors of [67] established that γ-Al2O3 obtained by thermal activation and subsequent autoclaving is characterised by a higher content and strength of Lewis acid sites and a lower content of basic sites than those of γ-Al2O3 obtained by precipitation, approaching η-Al2O3, obtained by precipitation. The authors of [68] found that, for oxides obtained by thermal activation and subsequent hydration under mild conditions, γ-Al2O3 is characterised by a larger number and strength of Lewis acid sites than those of γ-Al2O3 obtained by precipitation. η-Al2O3, on the contrary, is characterised by a significantly higher surface basicity than that of γ-Al2O3.
A relatively simple method which makes it possible to change the specific surface value, pore-size distribution, total pore volume, strength and concentration of active surface sites is the controlled heat treatment of AO [16].
Dehydrogenation and dehydroxylation of the surface, proceeding during thermal and chemical transformations of aluminium oxides, lead to the appearance of coordination-unsaturated oxygen atoms (Lewis base) and aluminium (Lewis acid). On the surface of the oxide, there are bridge and terminal hydroxyl groups that are Brønsted acid sites. During dehydration of two neighbouring OH- groups of this type, a water molecule is formed and released, and the Lewis acid (Al3+) and basic (O2) sites remain on the surface [61,66]. Usually, the surface of aluminium oxide manifests strong acidity after calcination in vacuum at temperatures above 470 °C [69]. At temperatures up to 973 K, the number of Lewis sites increases with the decrease in the OH- group content. It has been found that the acidity of aluminium oxide is mainly determined by aprotonic sites, and Brønsted acidity is weakly expressed. Tendencies to increase the acidity and to decrease the basicity of the aluminium oxide surface with increasing temperature during its thermal activation were also noted by the authors of [16].
The comparison of aluminium oxides of various modifications has shown that the set of OH- groups for them is approximately the same [61], and OH- groups on the surface of aluminium oxide have different acidity. At the same time, the concentration of OH- groups significantly depends on the crystal structure and on the conditions of heat treatment of the initial hydroxides. According to the concepts available in the literature, the sorption characteristics of desiccants based on active AO can directly depend on the acid-base properties of AO and on the nature of its acid sites (acceptor/donor, weak/strong, Lewis/Brønsted) [59,61]. The authors of [59] established that the dependence of the static capacity value of aluminium oxide sorbents at low relative humidity (1.0–1.5%) on the concentration of electron-acceptor sites (presumably associated with Brønsted acidity), and suggested that the presence of a hydroxylated surface contributed to the sorption of water vapour at low relative humidity. At the same time, individual aluminium oxides that do not have strong Brønsted acid sites [70] also sorb water well, which indicates that other sites may also participate in the water sorption process.
5.2. Modification of Adsorbents Based on Aluminium Oxide with the Cations of Alkaline Metals
An increase in the efficiency of aluminium oxide adsorbents can be achieved by changing the strength and the concentration of acid-base sites on their surface. The acid-base properties of the surface can be changed by modification with inorganic acids (HF, H2SO4, H3PO4, H3BO3), bases (alkalis, carbonates) or bifunctional additives (salts of various acids) [62].
As the aluminium oxide surface is impregnated with alkali, the total surface basicity increases [16]. At the same time, Lewis and Brønsted acidity increases with a low content of the alkaline cation. However, it then decreases with an increase in the alkali content.
Modification with small amounts of alkali metal (Li, Na, K) does not lead to a significant change in the specific surface of γ-Al2O3 in the phase composition, and it affects only the near-surface layer [71,72]. When the content of sodium and potassium cations increases from 0.3 mmol/g to 0.9 mmol/g of Al2O3, the concentration of coordination-unsaturated Al3+ cations on the surface decreases, and the strength of Lewis acid sites (LAS) decreases significantly. The increase in the strength of the sites is due to an increase in the electron density throughout the entire AO lattice. It has been noted that with an increase in the cation radius, the strength of electron-acceptor sites weakens [73], which supports the assumption of electronic suppression of the acidic properties of AO with the introduction of alkali metals. In some cases, with an increase in the content of modifying components, the formation of new phases, in particular, aluminates of alkali metals, has been noted. It has been found that Lewis acidic properties of lithium aluminates correlate with the presence of aluminium cations in their crystal structure in the tetrahedral coordination. The impregnation of γ-Al2O3 with NaOH solutions with an alkali content from 0.1 wt.% to 3.0 wt.%, as noted by the authors of [74]. Impregnation also leads to a decrease in the total and local LAC concentration, and the strongest LAS disappears first. When AO is modified with alkalis, the concentration and the strength of weak basic sites increases. When the sodium content is high, strong sites appear due to the appearance of oxygen atoms, which are bound directly to sodium [75].
The authors of [68,76] studied the influence of acid and alkaline modification on the adsorption characteristics of aluminium oxide desiccants prepared from amorphized gibbsite (products of CTA and THA). The authors established that the introduction of the sulphuric acid solution at the stage of obtaining the plastic paste from pseudoboehmite- and bayerite-containing hydroxides makes it possible to increase the dynamic capacity of desiccants based on γ-Al2O3 to the level of η-Al2O3 both by reducing the average pore diameter and by increasing the surface acidity. These processes practically do not influence the phase composition, texture and adsorption characteristics of adsorbents based on bayerite. When aluminium oxides are modified with sulphate ions on the surface, as shown by the authors of [76], strong LAS are formed, the water adsorption on which is accompanied by the formation of strong Brønsted acid sites (BAS), which leads to an increase in the sorption capacity of the desiccants modified with sulphate ions by water. During alkaline modification, by introducing the solution of KOH or NaOH at the stage of obtaining the plastic paste based on pseudoboehmite-containing hydroxides, the static capacity of the adsorbent is not changed. However, the dynamic capacity increases against the background of the increased average pore diameter, reduction in the number and strength of LAS, appearance of new super strong basic sites and increase in the total number of the basic sites of varying force. For desiccants prepared on the basis of bayerite-containing hydroxide, the introduction of alkaline cations at the stage of obtaining the plastic paste has not led to an improvement in sorption characteristics. At the same time, an increase in the average pore diameter, a decrease in the number of acid sites and an increase in the number of super strong basic sites was also observed, but the total concentration of all basic sites decreased during modification [68]. The dynamic capacity of the obtained adsorbents, measured at the gas moisture content at the inlet of the adsorber of 15.6–16.6 g/m3 (dewpoint: 18.5–19.5 °C), ranged from 3.9 g/100 cm3 to 5.9 g/100 cm3. The static capacity at 60% humidity of the synthesized adsorbents was in the range of 17.5% to 23.1%. The content of the χ-phase in aluminium oxide adsorbents significantly increased during acid modification, but practically did not change during alkaline modification, which allowed the authors of the work to associate the increase in the moisture capacity only with the process of the chemical modification with alkalis. A correlation was found between the change in the total concentration of the basic sites during modification of desiccants and the change in their dynamic capacity.
The study of the acid-base characteristics, modified with K and Na ions at the stage of obtaining the plastic paste of adsorbents by removing the curves of influence of the aqueous suspension pH of desiccant samples on the time, was carried out by the authors of [77]. The authors showed that a sharp alkalinization of the solution occurred in the first seconds of contact of the sample with distilled water. The location of the kinetic curves above the level of neutrality and the high rate of the pH change indicate the presence of strong basic sites of the aprotic type on the surface of these adsorbents. It has been noted [78] that when metal cations are introduced during peptization, there is a natural decrease in the total number of LAS and an increase in the number of basic ones. The values of the adsorption capacity of the samples correlate well with the concentrations of both types of sites and their total number.
The life tests of such adsorbents, based on pseudoboehmite and performed on a pilot plant at an increased pressure of 3 MPa, showed [79] that the sample of the desiccant, modified with potassium (~2 wt.%), was not inferior in terms of dynamic capacity under low load to the sample, which was obtained on the basis of bayerite-containing hydroxide. After conducting nine cyclic tests (adsorption-desorption), the phase composition, content of alkaline impurities, specific surface area and crushing strength of the samples did not change within the margin of error of determination.
Another way to increase the concentration of the basic sites on the surface of aluminium oxides is to introduce alkaline ions by impregnation of calcined AO granules [80]. It was shown that the impregnation of the initial aluminium oxide granules (γ-Al2O3) with alkaline solutions of sodium or potassium led to an increase in the dynamic capacity of the modified desiccants, while the impregnation of the initial aluminium oxide granules with carbonate solutions of sodium or potassium resulted in a decrease in the dynamic capacity. The static capacity by water of the obtained samples practically did not change. There was a decrease in the specific surface of the modified desiccants and an increase in the average pore diameter and strength of granules (during modification with carbonates, the strength practically did not change).
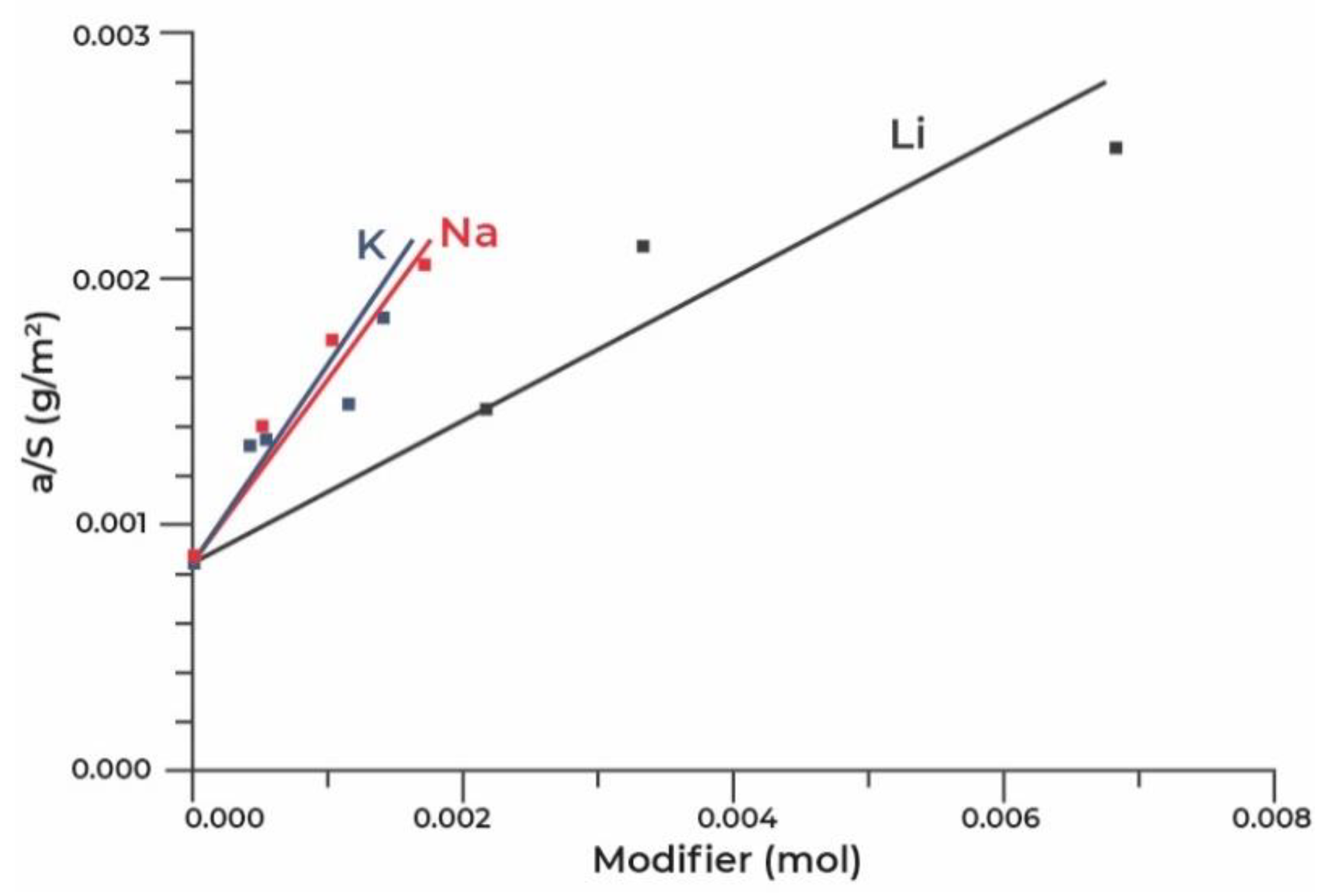
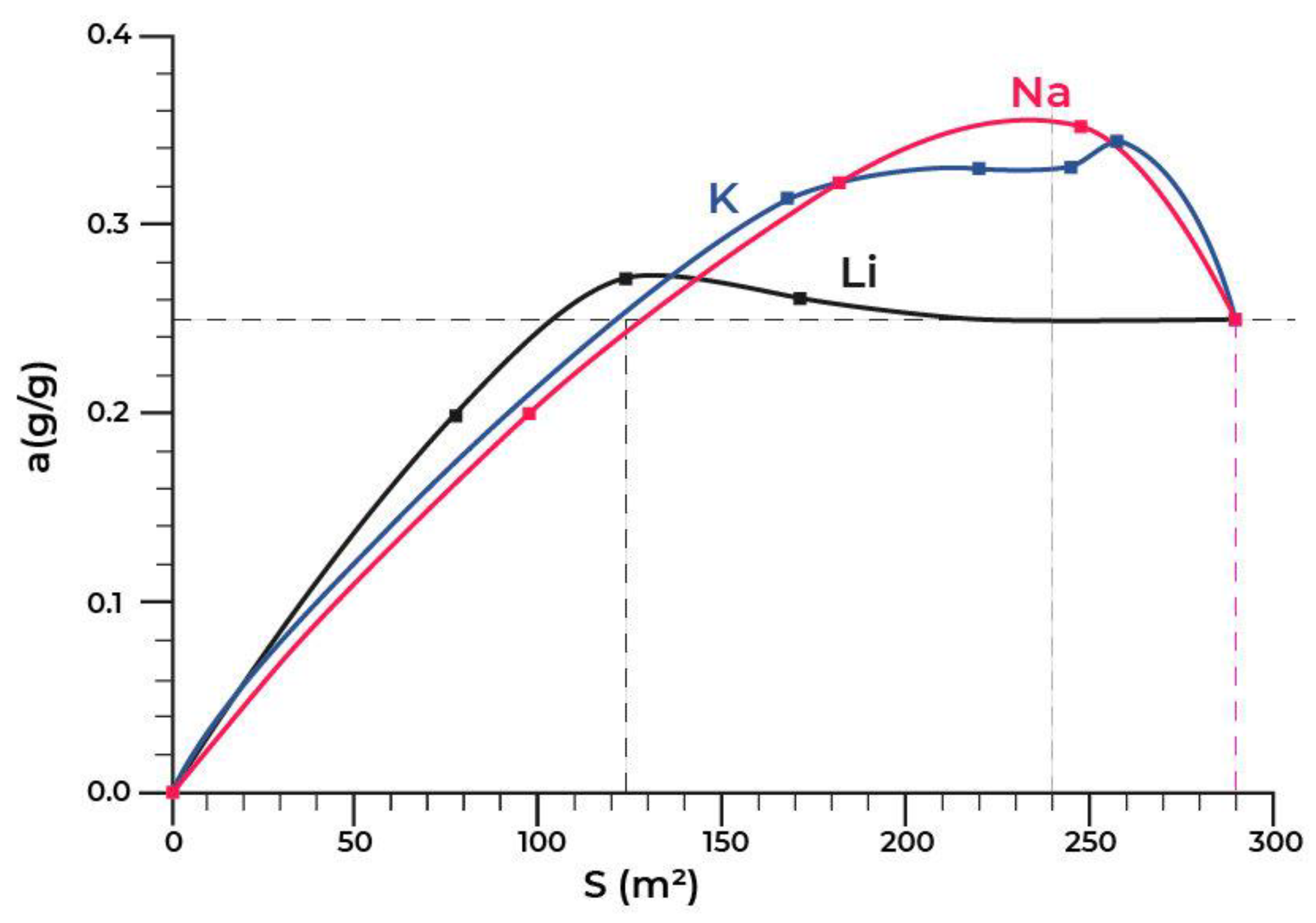
The analysis of acidic and basic properties of the surface of desiccants, performed by the authors of [80], by means of IR spectroscopy using CO and CDCl3 probe molecules, respectively, showed that the surface modification was accompanied by a decrease in Lewis and an almost complete disappearance of Brønsted acidity, appearance of super strong ones and significant increase in the concentration of strong basic sites, associated apparently with bridged oxygen atoms near alkaline ions. According to the authors, the formation of super strong sites can take place when a proton at the end of the OH group is replaced by a sodium or potassium ion with the formation of a bridged oxygen atom between Na+ and Al3+ ions. In this work, a linear correlation has been found between the concentration of strong basic sites on the surface and the dynamic capacity of desiccants, which allowed for the conclusion that the dynamic capacity is related to the strengthening of the main properties of the samples. The best sorption and strength characteristics have been demonstrated by a sample, which was obtained by the impregnation with potassium hydroxide with a potassium content of 3 mass.%. It has been assumed that during modification from carbonate solutions, the carbonates deposited on the surface block both strong and weak basic sites, which leads to a decrease in the dynamic capacity of water. The authors of [81] studied the properties of aluminium oxide granules modified with Li, K and Na cations by the impregnation from an excess of an alkali solution of pseudoboehmite-based aluminium oxide granules. In addition, for the modified adsorbents obtained by the water capacity impregnation, these samples have demonstrated a decrease in the specific surface and an increase in the average pore size against the background of an increase in the specific adsorption capacity of the samples, with an increase in the content of alkali metal cations (Figure 5).
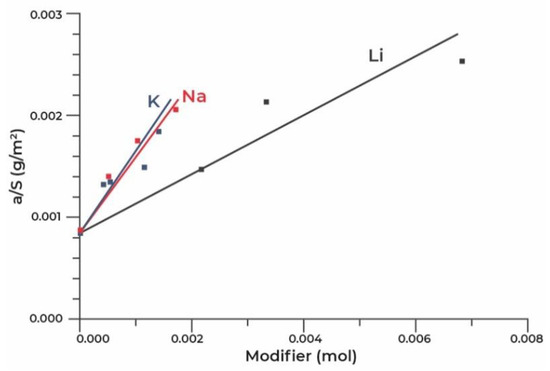
Figure 5.
Dependence of the capacity of the adsorbent surface unit on the mole content of the modifier.
Figure 6 shows the dependence of the equilibrium adsorption capacity of the modified materials (a) on the specific surface (Ssp).
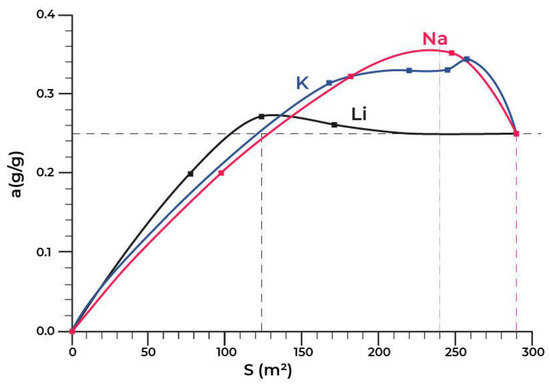
Figure 6.
Dependence of the adsorption capacity of the modified materials (a) on the specific surface (Ssp).
Figure 6 shows that the lithium modification has almost no effect on the adsorption capacity. At the same time, the dependence of the capacity of the samples modified with potassium and sodium on the specific surface is extreme in the range of changes in the specific surface of Ssp = 125–290 m2/g. The maximum value of the equilibrium adsorption capacity has been observed in the range of Ssp = 240 ± 10 m2/g. This value of the specific surface corresponded to the modification of the initial material in the amount of 1.2 wt.% of sodium or 2.6 wt.% of potassium.
Besides, the introduction of the controlled number of alkali metal cations into AO is possible at the stage of CTA product hydration during the synthesis of an adsorbent-desiccant, consisting of the mixture of low-temperature modifications of aluminium oxide of 60–70% (γ + η)-Al2O3 + 30–40% χ-Al2O3 [77]. It was shown that changes in the preparation conditions (alkaline modulus and the type of alkali at the hydration stage, the value of the acid modulus at the peptization stage) practically did not influence the static capacity of the desiccants, while an increase in the alkali content at the hydration stage or the use of NaOH instead of KOH increased the dynamic capacity of the desiccant granules.
In this way, alkaline cations can be introduced at different stages of desiccant preparation: By the impregnation of finished granules, using alkalis at the stage of preparation of plastic pastes, and in the case of desiccants based on n η-Al2O3, using solutions of alkalis with different concentrations at the hydration stage of the thermal activation product [82]. In the first case, the number of preparation stages increases. When the modifier content is higher than 2–3%, the specific surface area significantly decreases, which is undesirable. In the second case, there is a decrease in the strength of granules as compared to the granules, which are prepared using nitric acid for plasticization, which is consistent with the literature data and may be conditioned by the lower solubility of aluminium hydroxides in alkalis as compared to nitric acid [44]. Negative phenomena, typical of the first two methods, can be avoided, and the content of alkaline cations in η-Al2O3 can be increased by increasing the concentration of alkali at the hydration stage of the thermal activation product. Obtaining strong granules is achievable by optimizing the amount of nitric acid, which is used to prepare the moulded paste [82]. The data, presented by the authors of [82], indicate that the samples, modified with potassium and sodium, have a specific surface of more than 300 m2/g. The surface size, pore volume and average pore size of the samples modified with potassium are higher. Meanwhile, they are lower in samples modified by sodium, mainly due to a decrease in the volume of mesopores, since the volume of micropores in the samples is almost the same. An increase in the potassium content at the hydration stage leads to a decrease in the strength of the granules. A similar decrease in the strength of granules was observed earlier when using KOH at the stage of preparation of the moulded paste [68]. The use of NaOH instead of KOH during hydration, as well as an increase in the sodium content, on the contrary, led to an increase in strength. Comparing the characteristics of the adsorbents obtained during modification by the introduction of alkaline cations at the paste preparation stage and the introduction of alkaline cations at the hydration stage of the gibbsite thermal activation product, it can be noted that the previously achieved dynamic capacity and mechanical strength indicators (5.9 g/100 cm3 and 5.7 MPa) were exceeded [68]. These indicators in the latter case were 7.5 g/100 cm3 of the desiccant and 8.4 MPa, respectively [82].
The conducted test of the developed modified adsorbent-desiccant in comparison with well-known Russian and foreign analogues [82] has shown that industrial adsorbents, obtained by thermal activation technology, contain mainly χ-Al2O3 or γ-Al2O3, while the proposed desiccant contains η-Al2O3. The texture characteristics of the foreign desiccant based on aluminium oxide [82] and the proposed adsorbent have been shown to be quite similar. The higher efficiency of the developed desiccant has been associated by the authors of this work with a higher content of the basic sites, conditioned by the introduction of alkaline cations. It has been shown that the obtained values of the dynamic capacity of desiccants based on AO (industrial and developed) correlate well with the content of sodium cations in them. With an increase in the content of sodium cations, an increase in the dynamic capacity of desiccants was observed, despite the fact that the structural modification of aluminium oxides in these desiccants differs.
The study of the dynamic capacity of the developed highly efficient sample of an aluminium oxide adsorbent, as well as the comparison of its adsorption characteristics with those of a commercial adsorbent based on NaX zeolite under similar conditions were presented by the authors of [83]. The grain size of the aluminium oxide adsorbent was characterized by a diameter of 3.55 mm, height of 5.2 mm and NaX dimensions of 4.2 × 4.4 mm. In this way, the equivalent diameter of the adsorbents (proportional to the ratio of the grain volume to its outer surface) was approximately the same at dэ = 4.0 ÷ 4.2 mm. It has been noted that as the layer height of the studied adsorbents increases, their dynamic capacity with respect to water vapour and the time of protective action naturally increases. At atmospheric pressure up to 0.3 MPa, the adsorption characteristics of the NaX adsorbent are higher than those of the aluminium oxide adsorbent, and the protective action time of the layers of these adsorbents is comparable. However, at a higher pressure (0.3 ÷ 0.6 MPa), the situation changes, and the adsorption capacity and protective action time of the developed Al2O3 adsorbent become higher. Under these conditions, the use of the developed aluminium oxide adsorbent, considering its higher resistance to moisture, lower cost and lower regeneration temperature, is preferable as compared to zeolite-based analogues during dehydration under pressure.
Along with the equilibrium characteristics of adsorbents (adsorption capacities), an important role belongs to the adsorption kinetics, which take into account the dynamics of adsorption and diffusion of water vapour in individual granules of the absorbent and the rate of filling the volume of these granules. Since the adsorbent granules used in industrial conditions are usually shaped like cylinders and spheres of various sizes, it is important to study the influence of the grain size on the adsorption kinetics. The experimental results on the kinetics of water vapour adsorption on active aluminium oxide have been described by the authors of [84,85,86].
The influence of the granule size on the water vapour absorption kinetics for the fractions of the studied sample of highly efficient aluminium oxide (0.25–0.5 mm and 0.5–1.0 mm and a granule size of 3.7 × 6.0 mm) was studied by the authors of [86]. It has been shown that when the fraction size is more than 0.25–0.5 mm, the rate of water vapour adsorption decreases, which is due to the influence of internal diffusion. This happens due to the presence of small mesopores (3 ÷ 7 nm) in the aluminium oxide adsorbent. Mathematical simulation of mass transfer rates based on a quasi-homogeneous model has been performed. The mathematical simulation made it possible to obtain a quantitative assessment of parameters such as the absorption rate constants and to obtain the efficient water diffusion coefficient inside the grain, the value of which was 1.2·10−6 m2/s. The proposed mathematical model describes quite well the experimental data on the kinetics of water vapour adsorption on a highly active aluminium oxide adsorbent and can be used for modelling the absorber.
In this way, the data presented in this section indicate the important role of the acid-base sites of the surface of aluminium oxides in their adsorption characteristics. By means of methods such as heat treatment or chemical modification, it is possible to control the variations in the strength and concentration of active surface sites and other characteristics of AO. As a rule, this type of impact changes the specific surface value, pore size distribution, total pore volume and adsorption characteristics of the material. The adsorption capacity of aluminium oxide in relation to water vapour can be increased by introducing up to 3 mass.% of alkaline cations (Na, K), increasing the concentration of strong basic sites on the surface.
6. Conclusions
The abovementioned method of thermal activation of gibbsite (TCA Gb) has a number of economic and environmental advantages over traditional methods of reprecipitation and hydrolysis of aluminium alcoholates due to lower production costs and less waste. As a result of TCA, a product is obtained that is suitable for further processing into aluminium hydroxides, from which, in turn, aluminium oxide adsorbents, carriers and catalysts can be synthesized. However, this method also has a number of disadvantages, mentioned in the review. A more promising method is its improved version—thermal activation of gibbsite powder for 1–2 s in contact with a rotating and heated solid heat carrier under the action of centrifugal forces in flash reactors (CTA Gb, TSEFLARTM). The reduction of energy consumption and harmful emissions as compared to the TCA method is achieved by eliminating the use of combustion gases and intensifying the heat supply to the reagent layer due to the contact with a solid rotating surface.
Based on the advantages and disadvantages of industrial adsorbents-desiccants mentioned in the review, it can be concluded that the main dehydration of gases with a significant water vapour content should be carried out with aluminium oxide, which is resistant to condensed moisture, and a deep final dehumidification with zeolite.
Varying the conditions for the preparation of adsorbents-desiccants based on aluminium oxide and modifying them with the introduction of alkaline cations (Na and K) makes it possible to control the change in the characteristics of donor and acceptor active sites on the surface of adsorbents and thereby significantly increase their adsorption activity, in particular, with respect to water vapour. It has been shown that the preparation of adsorbents-desiccants based on η-Al2O3 should rather be carried out by regulating the concentration of alkali at the stage of hydration of the thermal activation product during synthesis. This makes it possible to obtain adsorbents with high values of static and dynamic water vapour capacity and mechanical strength. The adsorption properties (adsorption rate and adsorption capacity) of adsorbents obtained by this method, with a sodium content of 2.3 mass.% (adsorption rate and adsorption capacity), are quite similar to the characteristics of the zeolite-based adsorbents, which are widely used for deep air dehumidification. In this way, such adsorbents have a good potential for industrial use not only as a protective layer, but also as a main layer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P.M. and I.A.K.; methodology, S.I.R.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P.M.; writing—review and editing, E.P.M., S.I.R. and M.P.S.; visualization, M.P.S.; funding acquisition, I.A.K. and A.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- White, D.H. Compressed Air and Gas Purification and Fractionation for High Purity Applications by Improved PSA Processes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, K. Dehumidification. Planning Guidelines for Technical Building Services and Specialist Planners. 2016. Available online: https://www.condairgroup.com/m/0/planningbrochure-dehumidification-161202-en.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Atlas Copco. White Paper—Compressed Air Drying. 2016. Available online: https://www.atlascopco.com/content/dam/atlas-copco/compressor-technique/oil-free-air/documents/Compressed_air_drying_whitepaper_EN_Antwerp_2937016013.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Stewart, M. Dehydration. In Surface Production Operations: Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 279–373. ISBN 9780123822086. [Google Scholar]
- Shuguang, D. Sorbent Technology. Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267778978_Sorbent_Technology (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Ciahotný, K.; Hlinčík, T.; Vagenknechtová, A.; Prokeš, O. Adsorbents for the natural gas drying at CNG stations. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2016, 21, 306–313. Available online: https://actamont.tuke.sk/pdf/2016/n4/6ciahotny.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Linsen, B. Physical and Chemical Aspects of Adsorbents and Catalysts; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1970; ISBN 0124511503. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, R.; Hussain, M.; Ruthven, D.M. Adsorption of water vapour on activated alumina: I—Equilibrium behaviour. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1992, 70, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudisill, E.N.; Hacskaylo, J.J.; LeVan, M.D. Coadsorption of hydrocarbons and water on BPL activated carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, S.U.; Yang, R.T.; Buzanowski, M.A. Sorbents for air prepurification in air separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 4827–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, W.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, J.-T.; Suh, J.-K.; Lee, J.-M. Adsorption of water vapour on alumina, zeolite 13X and a zeolite X/activated carbon composite. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2003, 48, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbezov, A. Adsorption equilibrium of water vapour on F-200 activated alumina. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2003, 48, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CECA. Molecular Sieves. General Technical Information. 2015. Available online: https://www.cecachemicals.com/export/sites/ceca/.content/medias/downloads/products/dtm/brochure-gti-siliporite-2015_bdef.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Keltsev, N.V. Fundamentals of Adsorption Technology; Chemistry: Moscow, Russia, 1984; p. 595. [Google Scholar]
- Ruthven, D.M.; Farooq, S.; Knaebel, K.S. Pressure Swing Adsorption; VCH: Weinheim, Germany; Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 352. ISBN 3527895175. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, H.L. Adsorption on aluminas—Current applications. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1999, 120, 561–585. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, A.S. Aluminium oxide and systems based on it: Properties and applications. Kinet. Catal. 2012, 53, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, A.; Livanova, A.; Kosova, N.; Godymchuk, A.; Mamontov, G. Aluminium oxide-hydroxides obtained by hydrothermal synthesis: Influence of thermal treatment on phase composition and textural characteristics. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 98, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, J.F.; Doremus, R.H. (Eds.) Ceramic and Glass Materials; Springer Science and Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 201. ISBN 978-0-387-73362-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram-Jones, V.J.; Slade, R.C.T.; Davies, T.W.; Southem, J.C.; Salvador, S. Dehydroxylation sequences of gibbsite and boelumite: Study of differences between soak and flash calcination and of particle-size effects. J. Mater. Chem. 1996, 6, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wefers, K.; Misra, C. Oxides and Hydroxides of Aluminium; Alcoa Laboratories: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1987; Volume 19, p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, K.; Harato, T.; Hamano, S.; Horinouchi, K. Dehydration products of gibbsite by rotary kiln and stational calciner. Light Met. 1984, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neymark, I.E. Synthetic Mineral Adsorbents and Catalyst Supports; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1982; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Stiles, A.B. Catalyst Supports and Supported Catalysts: Theoretical and Applied Concepts; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; p. 270. ISBN 9780409951486. [Google Scholar]
- Bhabhor, K.K.; Jani, D.B. Progressive development in solid desiccant cooling: A review. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2019, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekh, P.; Kumja, M.; Bui, D.T.; Chua, K.J. Recent developments in solid desiccant coated heat exchangers—A review. Appl. Energy 2018, 229, 778–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabia, A.R.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Zulkepli, N.N. Activated alumina preparation and characterisation: The review on recent advancement. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Wang, L.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J. Rational design, synthesis, adsorption principles and applications of metal oxide adsorbents: A review. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 4790–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hami, H.K.; Abbas, R.F.; Eltayef, E.M.; Mahdi, N.I. Applications of aluminium oxide and nano aluminium oxide as adsorbents: Review. Samarra J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Abuzov, A.M. Aluminium Oxide and Alumina Ceramics (review). Part 1. Properties of Al2O3 and Commercial Production of Dispersed Al2O3. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2019, 60, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, I.M. Chemical Deposition from Solutions; Chemistry: Leningrad, Russia, 1980; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Schüth, F.; Sing, K.S.W.; Weitkamp, J. Handbook of Porous Solids; Wiley-Vch: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 1591–1677. ISBN 9783527302468. [Google Scholar]
- Senyuta, A.; Panov, A.; Suss, A.; Layner, Y. Innovative technology for alumina production from low-grade raw materials. In Light Metals 2013; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotovsky, B.P.; Bukhtiyarova, G.A.; Buyanov, R.A.; Murin, V.I.; Grunvald, V.R.; Efremova, L.V. Method for Obtaining Spherical Aluminium Oxide. R.U. Patent RU2096325C1, 20 November 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Icaev, B.N.; Kuyazev, V.M.; Moroz, E.M.; Murin, V.I.; Grunvald, V.R.; Efremova, L. Method of Preparing Granulated Activated Alumina. G.B. Patent GB1599374A, 30 September 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhmostov, V.S.; Tanashev, Y.Y.; Sokolov, D.N.; Danilevich, V.V.; Zolotarskij, I.A.; Parmon, V.N. Method and Device for Pulse Heat Treatment of Loose Materials. R.U. Patent RU2264589C1, 20 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhmostov, V.S.; Tanashev, Y.Y.; Sokolov, D.N.; Danilevich, V.V.; Zolotarskij, I.A.; Parmon, V.N. Device for Pulsed Heat Treatment of Bulk Materials. R.U. Patent RU2360196C2, 27 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pinakov, V.I.; Stoyanovsky, O.I.; Tanashev, Y.Y.; Pikarevsky, A.A.; Grinberg, B.E.; Dryab, V.N.; Kulik, K.V.; Danilevich, V.V.; Kuznetsov, D.V.; Parmon, V.N. TSEFLARTM—the centrifugal flash reactor for rapid thermal treatment of powdered materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 107, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul’ko, E.V.; Ivanova, A.S.; Kruglyakov, V.Y.; Moroz, E.M.; Shefer, K.I.; Litvak, G.S.; Kryukova, G.N.; Tanashev, Y.Y.; Parmon, V.N. Synthesis of aluminium oxides from the products of the rapid thermal decomposition of hydrargillite in a centrifugal flash reactor: II. Structural and textural properties of aluminium hydroxide and oxide obtained from the product of the centrifugal thermal activation of hydrargillite (CTA product). Kinet. Catal. 2007, 48, 316–326. [Google Scholar]
- Mista, W.; Wrzyszcz, J. Rehydration of transition alumina obtained by flash calcination of gibbsite. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 331, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharina, I.V.; Isupova, L.A.; Litvak, G.S.; Moroz, E.M.; Kryukova, G.N.; Rudina, N.A.; Tanashev, Y.Y.; Parmon, V.N. Synthesis of aluminium oxides from the products of the rapid thermal decomposition of hydrargillite in a centrifugal flash reactor: III. Properties of aluminium hydroxides and oxides obtained via the mild rehydration of the products of the centrifugal thermal activation of hydrargillite. Kinet. Catal. 2007, 48, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, U.; Becker, K.; Berger, H.-J.; Birke, P.; Engels, S.; Gruhn, G.; Jancke, K.; Kraak, P.; Lange, R.; Steinike, U. On preparation and reactivity of partial-crystalline aluminas. Cryst. Res. Technol. 1988, 23, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkrabina, R.A.; Moroz, E.M.; Kambarova, T.D.; Khomyakova, L.G.; Bychkova, T.G.; Levitskii, E.A. Synthesis of various forms of aluminium hydroxide catalyst components from the thermal dispersion products of gibbsite. Kinet. Catal. 1981, 22, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Isupova, L.A.; Tanashev, Y.Y.; Kharina, I.V.; Moroz, E.M.; Litvak, G.S.; Boldyreva, N.N.; Paukshtis, E.A.; Burgina, E.B.; Budneva, A.A.; Shmakov, A.N.; et al. Physico-chemical properties of TSEFLARTM-treated gibbsite and its reactivity in rehydration process under mild conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 107, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isupova, L.A.; Kharina, I.V.; Parmon, V.N. Granulated Active Aluminium Oxide and Preparation Method Thereof. R.U. Patent RU2390495C2, 27 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Danilevich, V.V.; Isupova, L.A.; Kagyrmanova, A.P.; Kharina, I.V.; Zyuzin, D.A.; Noskov, A.S. Highly Effective Water Adsorbents Based on Aluminium Oxide. Kinet. Catal. 2012, 53, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, K. Linked polymerization of ethylene and its homologs. Brennstoff Chem. 1954, 35, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Poisson, R.; Brunelle, J.-P.; Nortier, P. Alumina. In Catalysts Supports Supported Catalysts; Stiles, A.B., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 11–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jacques, R.; Poisson, R. Production of Spheroidal Alumina Shaped Articles. U.S. Patent US4273735A, 16 June 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Banta, F. Demetalation, Desulfurization, and Decarbonization of Petroleum Oils by Hydrotreatment in a Dual Bed System Prior to Cracking. U.S. Patent US4447314A, 8 May 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, K.R. Large Pore Shaped Hydroprocessing Catalysts. U.S. Patent US4489173, 18 December 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic, N.; Novakovic, T.; Janacovich, J.; Terlecki-Baricevic, A. Properties of activated alumina obtained by flash calcination of gibbsite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 150, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoyakova, L.G.; Vorobev, Y.K.; Shkrabina, R.A.; Levutskij, E.A. Method of Producing Active Granulated Aluminium Oxide. S.U. Patent SU615645A1, 23 December 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotovskii, B.P.; Buyanov, R.A.; Bukhtiyarova, G.A.; Taraban, E.A.; Murin, V.I.; Grunval’d, V.R.; Demin, V.V.; Saifullin, R.A. Production and properties of spherical alumina supports, adsorbents, and catalysts. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 1997, 70, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Activated Alumina F200 Data Sheet—PSB Industries Inc. Available online: http://www.psbindustries.com/pdf/Activated%20Alumina%20F200%20Data%20Sheet.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Ducreux, O.; Lavigne, C.; Nedez, C. Air and Gas Drying with Activated Aluminas. Available online: http://www.cabestisrl.com.ar/AirGas%20Drying%20Brochure.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Sircar, S.; Rao, M.B.; Golden, T.C. Drying of gases and liquids by activated alumina. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1996, 99, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katalizator, J.S.C. Dryers and Supports. Available online: https://www.katcom.ru/upload/buklet_eng.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Zotov, R.A.; Glazyrin, A.A.; Danilevich, V.V.; Kharina, I.V.; Zyuzin, D.A.; Volodin, A.M.; Isupova, L.A. Influence of the Temperature of Calcination of Bayerite-Containing Aluminium Hydroxide Pellets on the Water Vapour Adsorption Capacity and Acid-Base Properties of Alumina. Kinet. Catal. 2012, 53, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotarskii, I.A.; Voennov, L.I.; Zudilina, L.Y.; Isupova, L.A.; Zotov, R.A.; Medvedev, D.A.; Stepanov, D.A.; Livanova, A.V.; Meshcheryakov, E.P.; Kurzina, I.A. Theoretical Optimization of the Shape and Size of Adsorbent Grains for Associated Petroleum Gas Drying. Catal. Ind. 2018, 10, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Misono, M.; Hattori, H.; Ono, Y. New Solid Acids and Bases: Their Catalytic Properties; Elsevier Science: Tokyo, Japan, 1990; Volume 51, p. 364. [Google Scholar]
- Paukshtis, E.A. Infrared Spectroscopy in Heterogeneous: Acid Catalysis; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1992; p. 255. ISBN 5-02-029281-8. [Google Scholar]
- Volodin, A.M.; Bolshov, V.A.; Konovalova, T.A. Photostimulated Formation of Radicals on Oxide Surfaces. Molec. Eng. 1994, 4, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedilo, A.F.; Volodin, A.M. Radical Cations of Aromatic Molecules with High Ionization Potentials on the Surfaces of Oxide Catalysts: Formation, Properties, and Reactivity. Kinet. Catal. 2009, 50, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedilo, A.F.; Ivanova, A.S.; Pahomov, N.A.; Volodin, A.M. Development of an ESR Technique for Testing Sulfated Zirconia Catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A. 2000, 158, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, D.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, E.D. Correlation between acidity and catalytic activity for the methanol dehydration over various aluminium oxides. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2010, 36, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulko, E.V.; Ivanova, A.S.; Budneva, A.A.; Paukshtis, E.A. Acid-base properties of alumina prepared from a hydrated product of centrifugal thermal activation of hydrargillite (CTA-product). React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2006, 88, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilevich, V.V.; Isupova, L.A.; Danilova, I.G.; Zotov, R.A.; Ushakov, V.A. Characteristics optimization of activated alumina desiccants based on product of a centrifugal thermal activation of gibbsite. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2016, 89, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K. Solid Acids and Bases—Their Catalytic Properties; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1970; p. 184. ISBN 9780323160582. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, O.V. Heterogeneous Catalysis; IKC Academkniga: Moscow, Russia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Burova, M.V. Donor-Acceptor and Catalytic Properties of Systems Based on Aluminium and Zirconium Oxides. Ph.D. Thesis, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fionov, A.V.; Burova, M.V.; Tveritinova, E.A.; Krylova, I.V. Donor-acceptor properties, catalytic activity, and negative charge exoemission from the alumina surface modified with lithium cations. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2006, 55, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morterra, C.; Bolis, V.; Magnacca, G. IR spectroscopic and microcalorimetric characterisation of lewis acid sites on (transition phase) AI2O3 using adsorbed CO. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, G.G.; Miguel, S.R.; Scelza, O.A.; Castro, A.A. Study of the Poisoning of y-Al2O3 by alkali metals addition. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1992, 53, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, R.G.; Petrova, E.V. Acid-base surface properties of aluminium oxides. Bull. Kazan Technol. Univ. 2006, 6, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Danilevich, V.V.; Isupova, L.A.; Paukshtis, E.A.; Ushakov, V.A. Effect of modifying desiccants with sulfuric acid on their physiochemical properties. Kinet. Catal. 2014, 55, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotov, R.; Meshcheryakov, E.; Livanova, A.; Minakova, T.; Magaev, O.; Isupova, L.; Kurzina, I. Influence of the Composition, Structure, and Physical and Chemical Properties of Aluminium-Oxide-Based Sorbents on Water Adsorption Ability. Materials 2018, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnikov, S.I.; Livanova, A.V.; Meshcheryakov, E.P.; Kurzina, I.A.; Isupova, L.A. Kinetic Aspects of the Adsorption on Aluminium Oxide Drying Agents Doped with Alkali Metal Ions. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotov, R.A.; Isupova, L.A.; Danilevich, V.V.; Babina, A.A.; Sinelnikov, A.N.; Meshcheryakov, E.P.; Kurzina, I.A. Dynamic capacity dryers based on modified alumina at elevated pressures. Catal. Ind. 2017, 9, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isupova, L.A.; Danilova, I.G.; Danilevich, V.V.; Ushakov, V.A. Enhancement of the Sorption Ability of Aluminium Oxide Desiccants by Alkaline Modification. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnikov, S.; Kurzina, I.; Livanova, A.; Meshcheryakov, E.; Isupova, L. Effect of Li, Na and K Modification of Alumina on its Physical and Chemical Properties and Water Adsorption Ability. Materials 2019, 12, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruglyakov, V.Y.; Glazyrin, A.V.; Mescheryakov, E.P.; Kurzina, I.A.; Isupova, L.A. A High-Performance Alumina Desiccant. Catal. Ind. 2020, 12, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshcheryakov, E.; Kozlov, M.; Reshetnikov, S.; Isupova, L.; Livanova, A.; Kurzina, I. Studies of Water-Vapour Adsorption Dynamics of High-Efficiency Desiccant Based on Aluminium Oxide and NaX Zeolite. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Hussain, M.; Ruthven, D.M. Adsorption on Activated Alumina: I1—Kinetic Behaviour. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1992, 70, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcussen, L. The influence of temperature on effective diffusivity and adsorption kinetics for humid air-porous alumina. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1974, 29, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnikov, S.I.; Kurzina, I.A. Investigation of adsorption of water vapour on porous aluminium oxide material. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 597, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).