Experimental Assessment of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Non-Contact Tonometer Airflows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
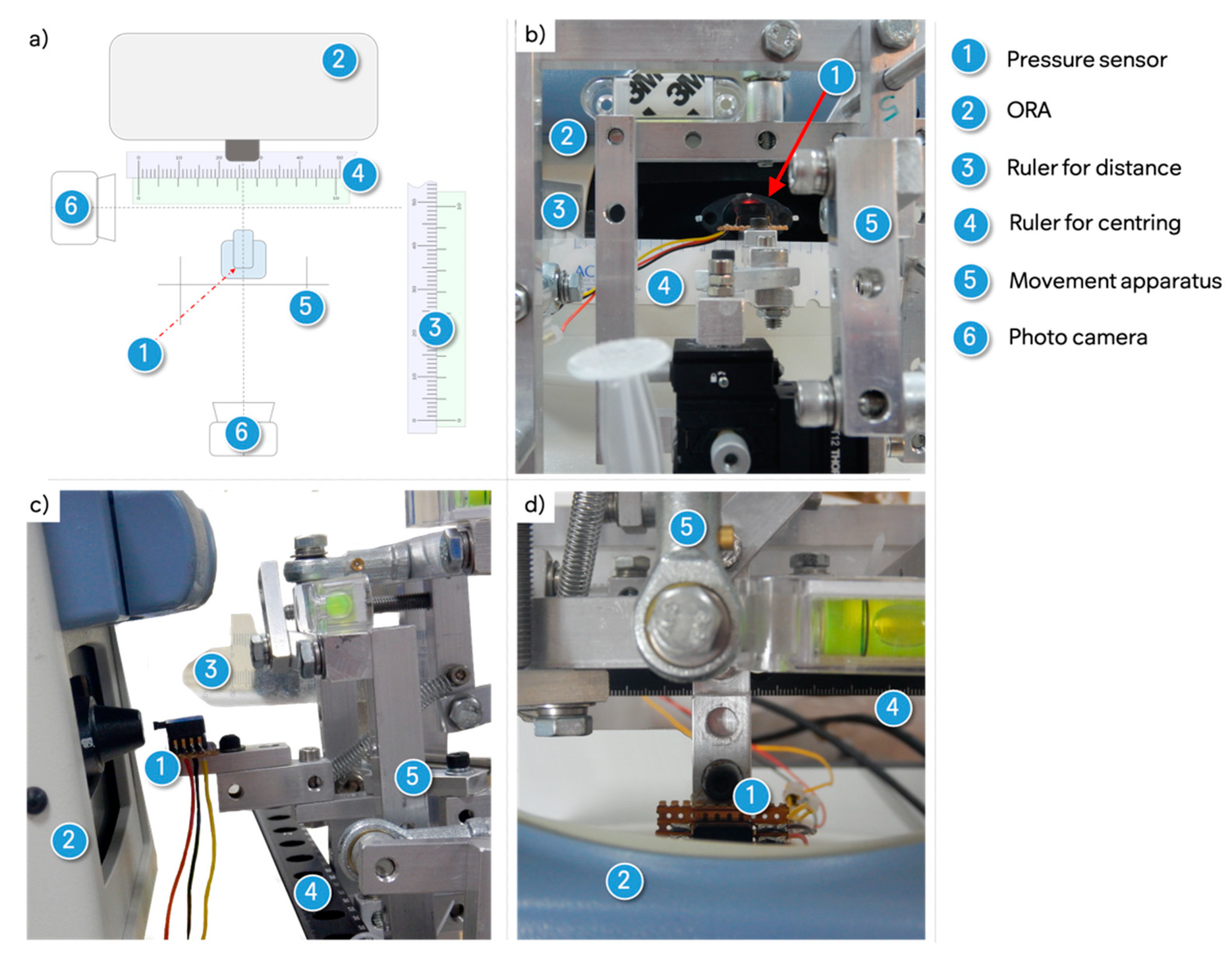
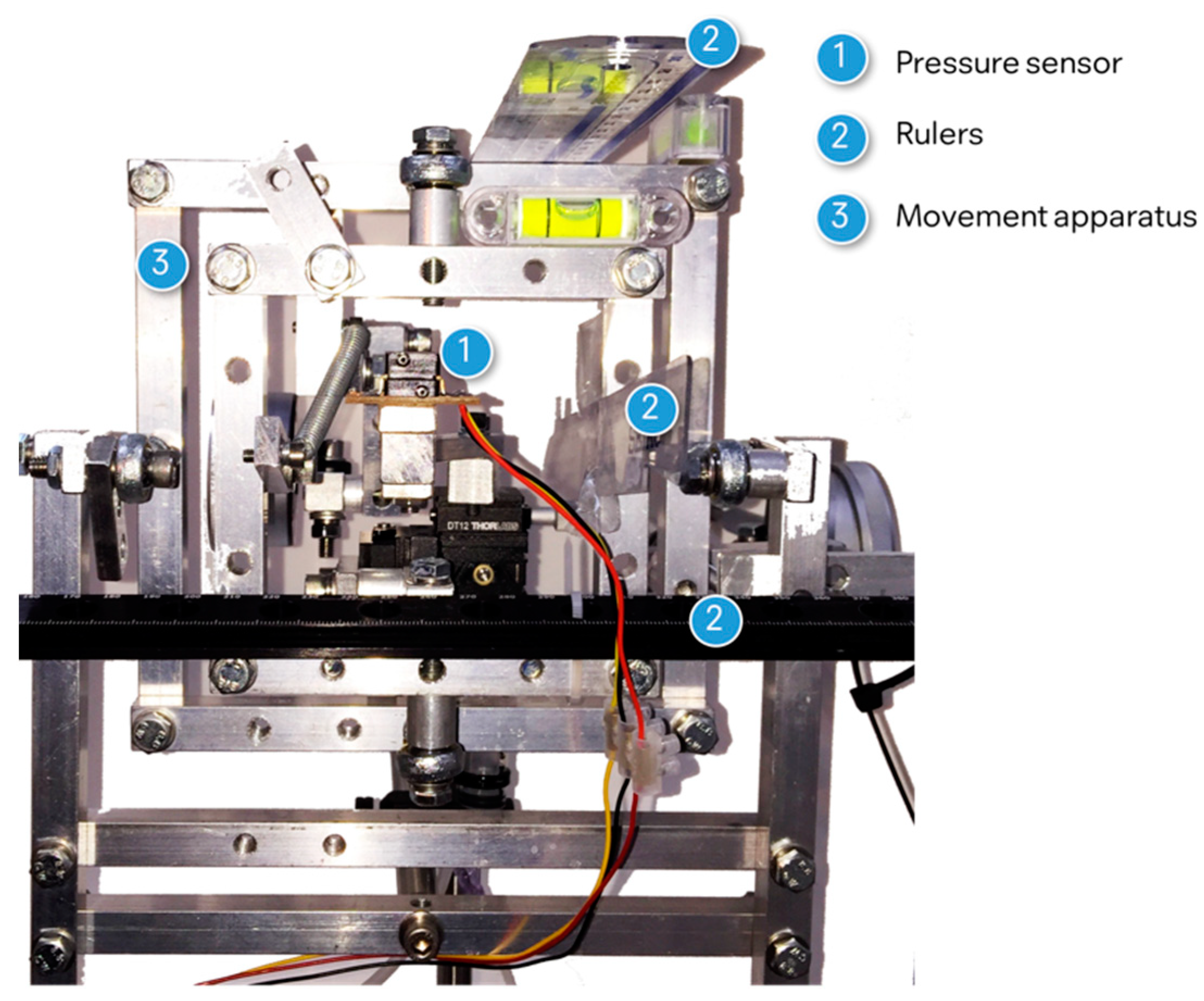
2.1. Experimental Set Up
2.1.1. Pressure Sensor
2.1.2. Mapping Grids
2.1.3. Pressure Recording
2.2. Mapping Procedure
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Outcome Measures and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Experimental Set Up
3.1.1. Sensor Noise and Signal-to-Noise Ratio
3.1.2. Mapping Procedure
3.2. CorvisST Airflow Pressure
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution
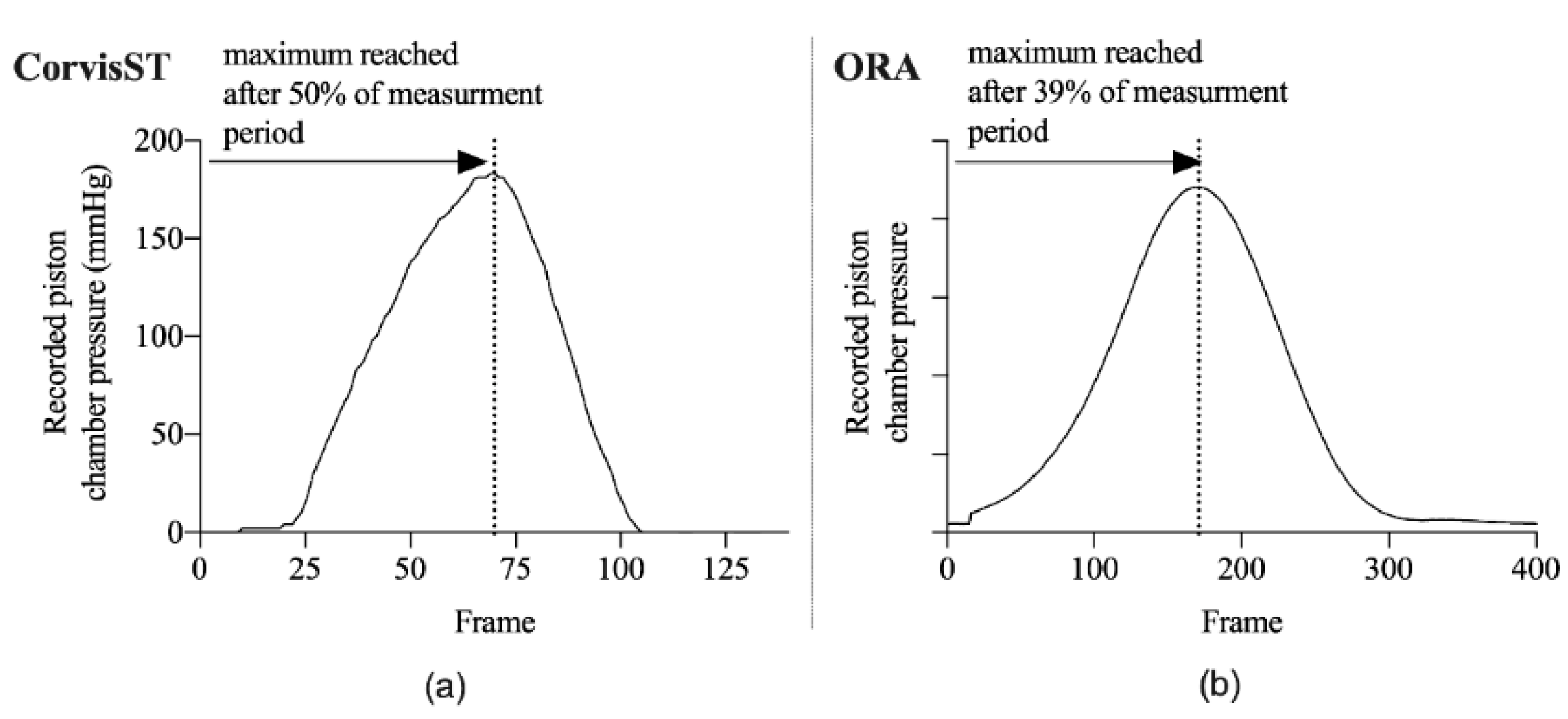
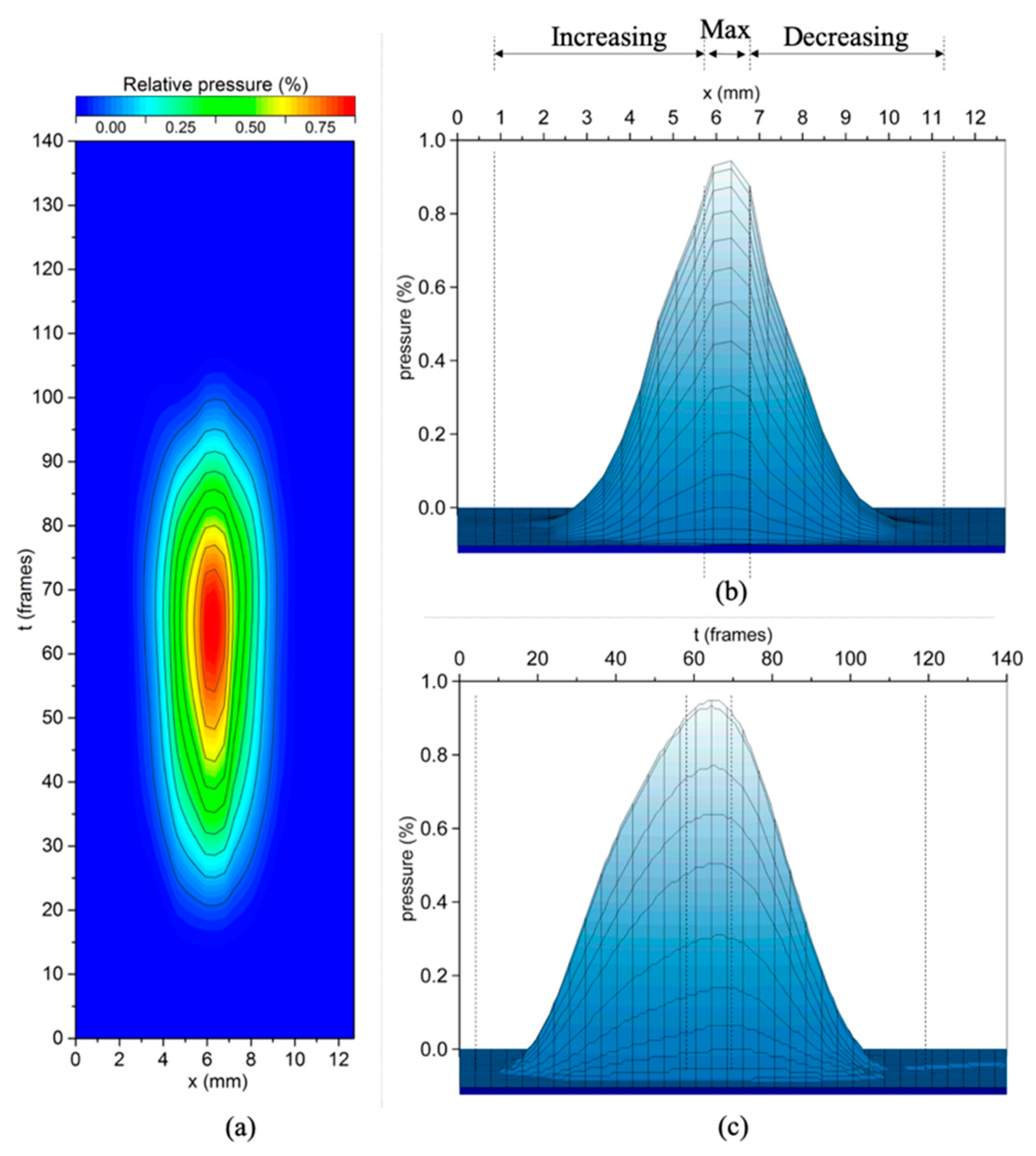
3.2.2. Temporal Distribution
3.2.3. Airflow Profile at the Object Plane of the CorvisST Scheimpflug Camera System
3.2.4. Comparison to Piston-Chamber Pressure
3.3. ORA Airflow Pressure
3.4. Analytical Modelling
- CorvisST Δp((px − py)/average(px, py)) = (0.6 ± 0.45)%;
- ORA Δp((px − py)/average(px, py)) = (−0.4 ± 1.19)%.
3.5. Comparison between the Central CorvisST and ORA Airflow Pressures
4. Discussion
4.1. CorvisST Airflow Pressure
4.2. ORA Airflow Pressure
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Comparison between the Airflow Pressures of the CorvisST and ORA
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hon, Y.; Lam, A.K. Corneal deformation measurement using Scheimpflug noncontact tonometry. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esporcatte, L.P.G.; Salomao, M.Q.; Lopes, B.T.; Vinciguerra, P.; Vinciguerra, R.; Roberts, C.; Elsheikh, A.; Dawson, D.G.; Ambrosio, R., Jr. Biomechanical diagnostics of the cornea. Eye Vis. (Lond.) 2020, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasy, A.; Chen, K.J.; Vinciguerra, R.; Lopes, B.T.; Abass, A.; Vinciguerra, P.; Ambrosio, R., Jr.; Roberts, C.J.; Elsheikh, A. Determination of Corneal Biomechanical Behavior in-vivo for Healthy Eyes Using CorVis ST Tonometry: Stress-Strain Index. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, D.A. Determining in vivo biomechanical properties of the cornea with an ocular response analyzer. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2005, 31, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantomme, M.; Pourjavan, S.; Detry-Morel, M. The range of the waveform score of the ocular response analyzer (ora) in healthy subjects. Bull. Soc. Belg. Ophtalmol. 2013, 332, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Tian, M.; Zhao, J. Relationship among corneal stiffness, thickness, and biomechanical parameters measured by Corvis ST, Pentacam and ORA in keratoconus. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Dou, R.; Wang, Y. Comparisons of the corneal biomechanics between low and high myopic eyes–a meta-analysis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 207, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Corneal Biomechanical Properties Characterization Using Air-jet Indentation Based Optical Coherence Tomography System (AIOCT). MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 256, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wallace, H.; Misra, S.; Li, S. Biomechanical changes in the cornea following cataract surgery: A prospective assessment with the Corneal Visualisation Scheimpflug Technology. Clin. Exp. 2019, 47, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, H.; McKelvie, J.; Green, C. Corneal Curvature: The Influence of Corneal Accommodation and Biomechanics on Corneal Shape. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Safeen, S.; Shah, S.; Laiquzzaman, M. Changes of corneal biomechanics with keratoconus. Cornea 2012, 31, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinciguerra, R.; Ambrosio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A.; Roberts, C.J.; Lopes, B.; Morenghi, E.; Azzolini, C.; Vinciguerra, P. Detection of Keratoconus With a New Biomechanical Index. J. Refract. Surg. 2016, 32, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziskin, M.C. Fundamental physics of ultrasound and its propagation in tissue. Radiographics 1993, 13, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatt, I.; Weissman, B.A. Physiology of the Eye: An. Introduction to the Vegetative Functions; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Grolman, B. A new tonometer system. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1972, 49, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorronsoro, C.; Pascual, D.; Perez-Merino, P.; Kling, S.; Marcos, S. Dynamic OCT measurement of corneal deformation by an air puff in normal and cross-linked corneas. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, A.; Joda, A.; Abass, A.; Garway-Heath, D. Assessment of the Ocular Response Analyzer as an Instrument for Measurement of Intraocular Pressure and Corneal Biomechanics. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonini, I.; Angelillo, M.; Pandolfi, A. Theoretical and numerical analysis of the corneal air puff test. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 93, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonini, I.; Pandolfi, A. The influence of intraocular pressure and air jet pressure on corneal contactless tonometry tests. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 58, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza-Gracia, M.Á.; Wu, W.; Calvo, B.; Malvè, M.; Büchler, P.; Matas, J.F.R. Fluid–structure simulation of a general non-contact tonometry. A required complexity? Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 340, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, S.; Bekesi, N.; Dorronsoro, C.; Pascual, D.; Marcos, S. Corneal viscoelastic properties from finite-element analysis of in vivo air-puff deformation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzler, K.; Roberts, C.; Whitaker, S.; Lawrence, M.; Malik, J.; Bons, J. Modeling corneal response to an air puff using deformation data to derive Young’s modulus. In ARVO; Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science: Seatle, WA, USA, 2013; p. 1629. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, K.; Roberts, C.; Whitaker, S.; Lawrence, M.; Malik, J.; Bons, J. The Influence of IOP, Corneal Stiffness, and Sclera on Corneal Deformation Response to an Air Puff Using the CorVis ST; The Ohio State University, Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science: Seatle, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, N.; Ali, N.; Patel, D.; McGhee, C.; Hunter, P.; Ho, H. Modelling the Deformation of the Human Cornea Produced by a Focussed Air Pulse. Comput. Biomech. Med. 2015, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Luce, D. Air–jet temporal and spatial pressure properties of the reichert ocular response analyzer (ORA). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 5009. [Google Scholar]
- Asaoka, R.; Nakakura, S.; Tabuchi, H.; Murata, H.; Nakao, Y.; Ihara, N.; Rimayanti, U.; Aihara, M.; Kiuchi, Y. The Relationship between Corvis ST Tonometry Measured Corneal Parameters and Intraocular Pressure, Corneal Thickness and Corneal Curvature. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haustein, M.; Spoerl, E.; Pillunat, L. Correlation of Biomechanic Parameters Measured by Corvis ST (Oculus®) and by Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA, Reichert®). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 1626. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, M.; Hirasawa, K.; Murata, H.; Yanagisawa, M.; Nakao, Y.; Nakakura, S.; Kiuchi, Y.; Asaoka, R. The Relationship between Corvis ST Tonometry and Ocular Response Analyzer Measurements in Eyes with Glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejwani, S.; Shetty, R.; Kurien, M.; Dinakaran, S.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, A.S. Biomechanics of the cornea evaluated by spectral analysis of waveforms from ocular response analyzer and Corvis-ST. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmanson, J.P.; Martinez, J.G. Size does matter: What is the corneo-limbal diameter? Clin. Exp. Optom. 2017, 100, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbelman, M.; Sicam, V.A.; Van der Heijde, G.L. The shape of the anterior and posterior surface of the aging human cornea. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D.; Haouat, M.; Hoang-Xuan, T. A review of mathematical descriptors of corneal asphericity. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2002, 25, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, M.; Matalia, H.; Nuijts, R.; Haex, B.; Shetty, R.; Sinha Roy, A. Corneal Viscous Properties Cannot Be Determined From Air-Puff Applanation. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.; Roberts, C.J.; Lopes, B.; Eliasy, A.; Vinciguerra, R.; Ambrósio, R.; Vinciguerra, P.; Elsheikh, A. Can the Corvis ST Estimate Corneal Viscoelasticity? J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Mendes, J.; Lopes, B.T.; Faria-Correia, F.; Salomao, M.Q.; Rodrigues-Barros, S.; Ambrosio, R., Jr. Enhanced Ectasia Detection Using Corneal Tomography and Biomechanics. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 197, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, M.R.; Momeni-Moghaddam, H.; Yekta, A.; Elsheikh, A.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Ambrosio, R., Jr.; Maddah, N.; Danesh, Z. Biomechanically-Corrected Intraocular Pressure Compared To Pressure Measured With Commonly Used Tonometers In Normal Subjects. Clin. Optom. (Auckl.) 2019, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abitbol, O.; Bouden, J.; Doan, S.; Hoang-Xuan, T.; Gatinel, D. Corneal hysteresis measured with the Ocular Response Analyzer in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2010, 88, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Buey, M.A.; Cristobal, J.A.; Ascaso, F.J.; Lavilla, L.; Lanchares, E. Biomechanical properties of the cornea in Fuchs' corneal dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3199–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Lam, A.K.; Cho, P. A pilot study on the corneal biomechanical changes in short-term orthokeratology. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2009, 29, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, S.; Lira, M. Biomechanical properties of the cornea measured by the Ocular Response Analyzer and their association with intraocular pressure and the central corneal curvature. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2009, 92, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, C.; O’Keefe, M. Corneal hysteresis using the Reichert ocular response analyser: Findings pre-and post-LASIK and LASEK. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008, 86, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Laiquzzaman, M.; Bhojwani, R.; Mantry, S.; Cunliffe, I. Assessment of the biomechanical properties of the cornea with the ocular response analyzer in normal and keratoconic eyes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 3026–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Meijome, J.M.; Queiros, A.; Jorge, J.; Diaz-Rey, A.; Parafita, M.A. Intraoffice variability of corneal biomechanical parameters and intraocular pressure (IOP). Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2008, 85, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohmoto, F. Effect of aging on corneal biomechanical parameters using the ocular response analyzer. J. Refract. Surg. 2009, 25, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Pandav, S.S.; Banger, A.; Aggarwal, K.; Gupta, A. Relationship between corneal biomechanical properties, central corneal thickness, and intraocular pressure across the spectrum of glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 153, 840–849.e842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, C.; O’keefe, M.; Lanigan, B. Corneal hysteresis and intraocular pressure measurement in children using the Reichert ocular response analyzer. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 142, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, A.; Chen, D.; Chiu, R.; Chui, W.-S. Comparison of IOP measurements between ORA and GAT in normal Chinese. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2007, 84, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.; Gazzard, G.; Chan, Y.-H.; Fong, A.; Kotecha, A.; Sim, E.-L.; Tan, D.; Tong, L.; Saw, S.-M. Cornea biomechanical characteristics and their correlates with refractive error in Singaporean children. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3852–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Xu, S.; Qu, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Wang, J. Central corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis during corneal swelling induced by contact lens wear with eye closure. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Qu, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Lu, F. Diurnal variation of ocular hysteresis, corneal thickness, and intraocular pressure. Optom Vis. Sci. 2008, 85, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Congdon, N.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Choi, K.; Lam, D.S.; Pang, C.P.; Xie, Z.; Liu, X.; Sharma, A. Corneal hysteresis and axial length among Chinese secondary school children: The Xichang Pediatric Refractive Error Study (X-PRES) report no. 4. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 145, 819–826. e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touboul, D.; Roberts, C.; Kérautret, J.; Garra, C.; Maurice-Tison, S.; Saubusse, E.; Colin, J. Correlations between corneal hysteresis, intraocular pressure, and corneal central pachymetry. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramm, L.; Herber, R.; Spoerl, E.; Raiskup, F.; Pillunat, L.E.; Terai, N. Intraocular pressure measurement using Ocular response analyzer, dynamic contour tonometer, and scheimpflug analyzer Corvis ST. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 3879651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salouti, R.; Razeghinejad, R.; Masihpour, N.; Ghoreyshi, M.; Nowroozzadeh, M.H. Agreement in central corneal thickness measurement between Corvis ST and ocular response analyzer. Int. Ophthalmol. 2020, 40, 2563–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishiro, T.; Matsuura, M.; Fujino, Y.; Murata, H.; Tokumo, K.; Nakakura, S.; Kiuchi, Y.; Asaoka, R. The relationship between corvis ST tonometry parameters and ocular response analyzer corneal hysteresis. J. Glaucoma 2020, 29, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annette, H.; Kristina, L.; Bernd, S.; Mark-Oliver, F.; Wolfgang, W. Effect of central corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis on tonometry as measured by dynamic contour tonometry, ocular response analyzer, and Goldmann tonometry in glaucomatous eyes. J. Glaucoma 2008, 17, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

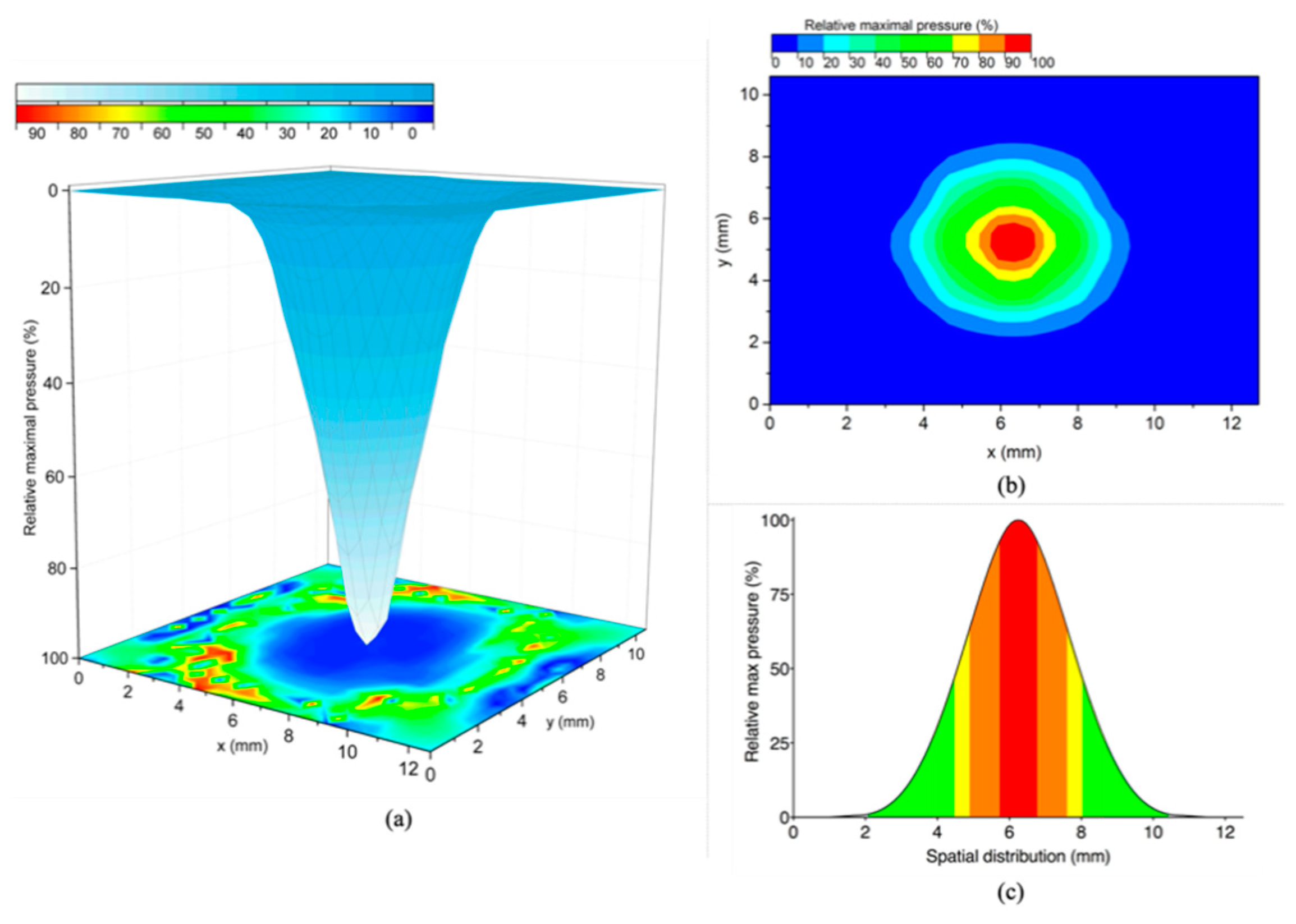
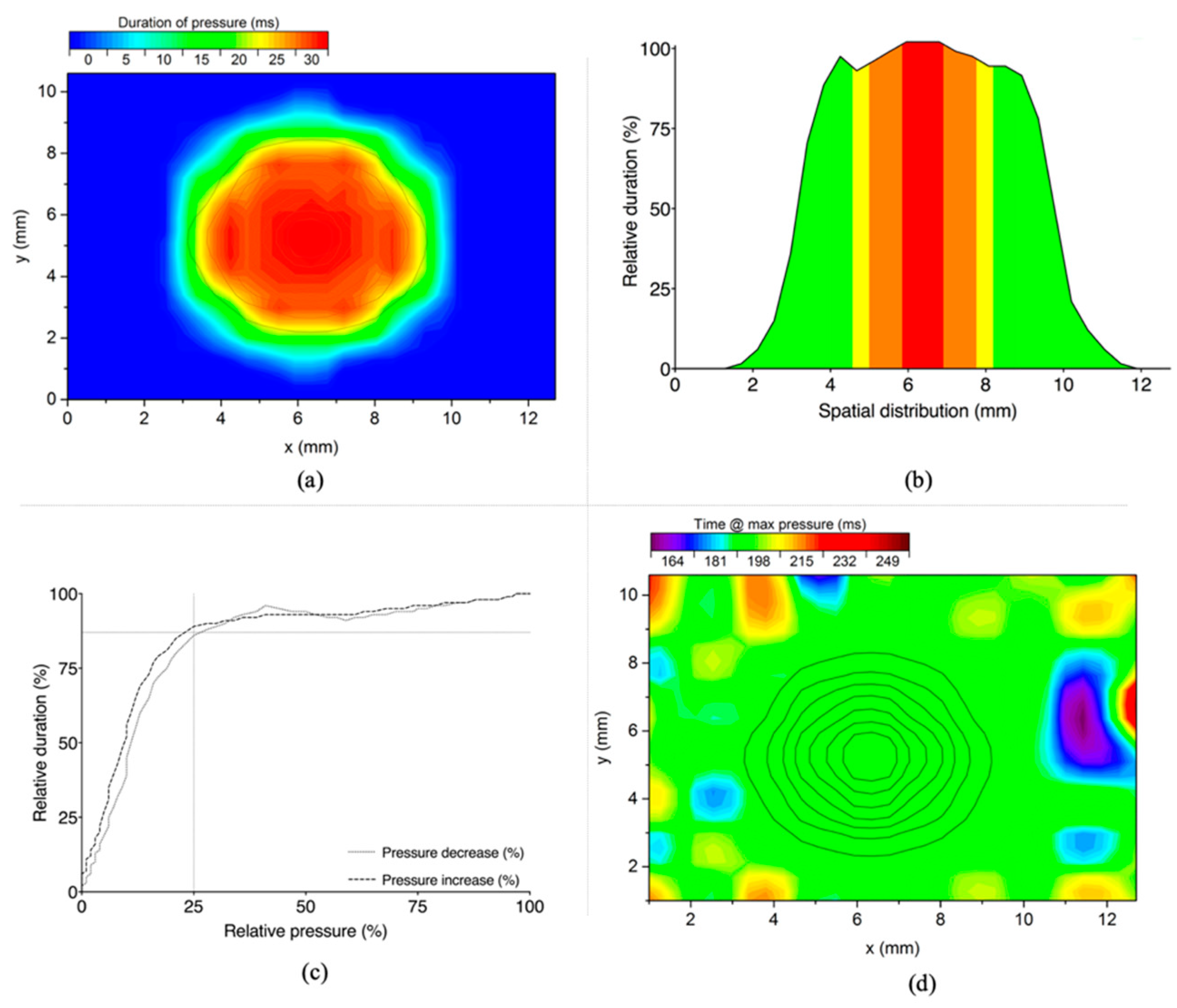

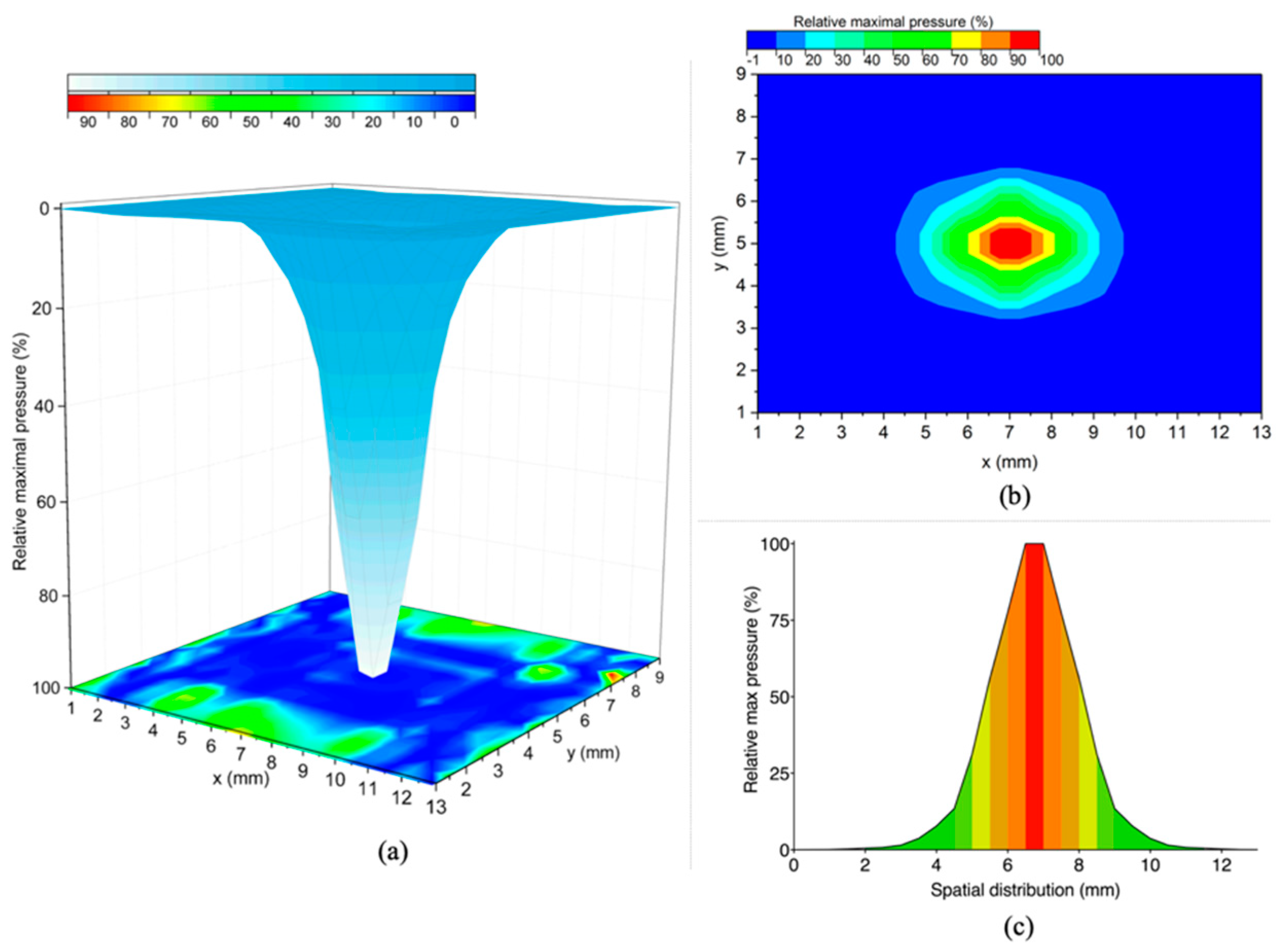

| Airflow Pressure (%) | Area (mm2) | Slope * (%/mm) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90–100% ** | 0.8 | - | - |
| 80–89% | 1.9 | −29.5 | 0.999 |
| 70–79% | 3.5 | −26.1 | 0.999 |
| 60–69% | 5.7 | −27.9 | 0.999 |
| 50–59% | 7.5 | −30.1 | 0.995 |
| 40–49% | 10.2 | −35.9 | 0.999 |
| 30–39% | 13.8 | −31.1 | 0.995 |
| 20–29% | 20.4 | −25.5 | 0.994 |
| 10–19% | 45.2 | −15.6 | 0.991 |
| Phase * | Airflow Pressure (%) | Duration (Frames) | Slope (%) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure free | 0.01 to 0.09 | 8 (1–9) | >0.000 | 0.949 | |
| (1) Increasing | Slow | 0.09 to 4.52 | 8 (10–18) | 0.70 | 0.928 |
| Sharp | 5.80 to 98.14 | 42 (19–61) | 2.39 | 0.988 | |
| Maximum | 99.51 ± 0.456 | 6 (62–68) | <0.000 | 0.002 | |
| (2) Decreasing | Sharp | 98.89 to 5.54 | 31 (69–100) | −3.13 | 0.995 |
| Slow | 4.37 to 0.22 | 8 (101–109) | −0.96 | 0.973 | |
| Pressure free | 0.22 to 0.00 | 30 (110–140) | >0.000 | 0.974 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oehring, D.; Jenkins, D.; Buckhurst, P.J.; Buckhurst, H. Experimental Assessment of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Non-Contact Tonometer Airflows. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062499
Oehring D, Jenkins D, Buckhurst PJ, Buckhurst H. Experimental Assessment of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Non-Contact Tonometer Airflows. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062499
Chicago/Turabian StyleOehring, Daniela, David Jenkins, Phillip Jonathan Buckhurst, and Hetal Buckhurst. 2021. "Experimental Assessment of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Non-Contact Tonometer Airflows" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062499
APA StyleOehring, D., Jenkins, D., Buckhurst, P. J., & Buckhurst, H. (2021). Experimental Assessment of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Non-Contact Tonometer Airflows. Applied Sciences, 11(6), 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062499









