Evaluation of the Nasolabial Angle in Orthodontic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
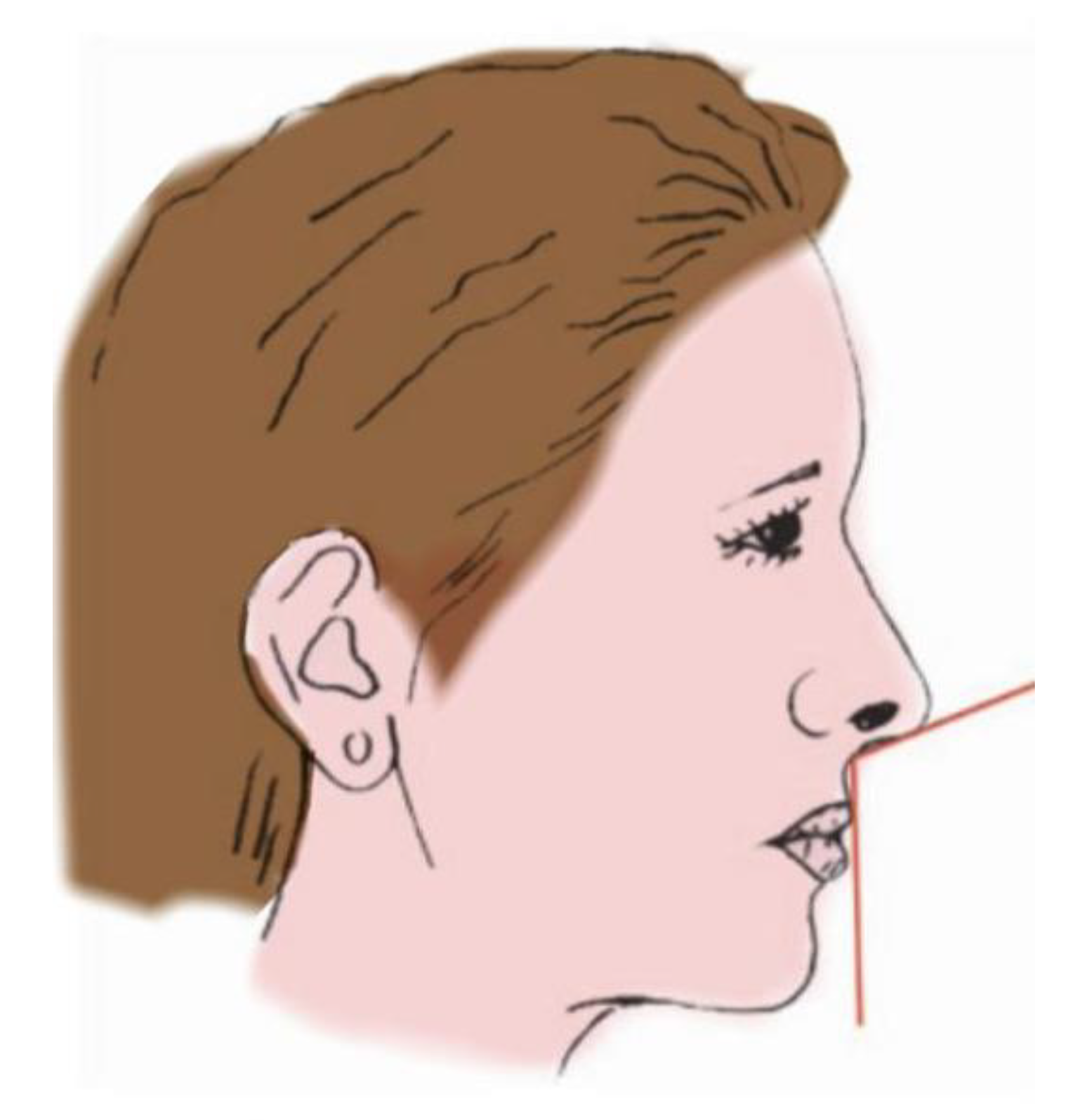
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources, Search Strategy, and Study Selection
2.4. Data Items
2.5. Summary Measures and Approach to Synthesis
3. Results
- 10 articles focused on NLA in extractive cases.
- 5 articles analyzed the NLA in cases of class II malocclusion.
- 2 articles studied the NLA in class III malocclusion cases.
- 1 article focused on the NLA in cases of rapid palatal expansion.
- 4 articles analyzed the NLA in cases of orthognathic surgery.
- 4 articles studied the variation of the NLA in relation to the treatment of non-surgical rhinoplasty with a hyaluronic acid filler.
4. Discussion
4.1. NLA in Extraction vs. Non-Extraction Cases
4.2. NLA in Treatment of Class II Malocclusion
4.3. NLA in Treatment of Class III Malocclusion
4.4. NLA after Rapid Palatal Expansion
4.5. NLA after Orthognatic Surgery
4.6. NLA and Hyaluronic Acid Fillers
5. Conclusions
- -
- with a class I and extractive treatments of the first or second four premolars,
- -
- with a class II and maxillary protrusion,
- -
- with maxillary biprotrusion, except in cases of severe crowding where the extraction spaces are not used for retraction of the anterior sector,
- -
- undergoing non-surgical rhinoplasty with a hyaluronic acid filler
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rho, N.K.; Park, J.Y.; Youn, C.S.; Lee, S.-K.; Kim, H.S. Early Changes in Facial Profile Following Structured Filler Rhinoplasty: An Anthropometric Analysis Using a 3-Dimensional Imaging System. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.Y.; Bayome, M.; Park, J.; Lim, H.J.; Kook, Y.-A.; Han, S.H. Comparison of treatment effects between four premolar extraction and total arch distalization using the modified C-palatal plate. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMurtadha, R.H.; Alhammadi, M.S.; Fayed, M.M.; Abou-El-Ezz, A.; Halboub, E. Changes in Soft Tissue Profile After Orthodontic Treatment With and Without Extraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Évid. Based Dent. Pract. 2018, 18, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantonis, D.; Vasileiou, D.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Eliades, T. Soft tissue changes following extraction vs. nonextraction orthodontic fixed appliance treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashwant, V.A.; Arumugam, E. Comparative evaluation of soft tissue changes in Class I borderline patients treated with extraction and nonextraction modalities. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2016, 21, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirschneck, C.; Proff, P.; Reicheneder, C.; Lippold, C. Short-term effects of systematic premolar extraction on lip profile, vertical dimension and cephalometric parameters in borderline patients for extraction therapy—a retrospective cohort study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourfar, J.; Lisson, J.A.; Gross, U.; Frye, L.; Kinzinger, G.S.M. Soft tissue profile changes after Functional Mandibular Advancer or Herbst appliance treatment in class II patients. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 22, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, L.; Janson, G.; Patel, M.P.; Reis, R.S.; Castillo, A.A.-D.; Henriques, J.F.C. Class II malocclusion treatment effects with Jones Jig and Distal Jet followed by fixed appliances. Angle Orthod. 2017, 88, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celikoglu, M.; Yavuz, I.; Ünal, T.; Oktay, H.; Erdem, A. Comparison of the soft and hard tissue effects of two different protraction mechanisms in class III patients: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-Y.; Kwon, T.-G.; Rong, H.; Kyung, H.-M.; Bing, L.; Wu, X.-P. Morphological Changes of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion in Mixed Dentition with Protraction Combined Activities. Int. J. Morphol. 2018, 36, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghassemi, M.; Hilgers, R.-D.; Fritz, U.; Modabber, A.; Ghassemi, A. Maxillary advancement versus mandibular setback in class III dentofacial deformity: Are there any differences in aesthetic outcomes? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [Updated March 2011]. Available online: http://handbook.cochrane.org/ (accessed on 11 November 2012).
- Alqahtani, N.D.; Alshammari, R.; Almoammar, K.; Almosa, N.; Almahdy, A.; AlBarakati, S.F. Post-orthodontic cephalometric variations in bimaxillary protrusion cases managed by premolar extraction—A retrospective study. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.-J.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.-T. Soft Tissue Changes in Patients With Dentoalveolar Protrusion Treated With Maximum Anchorage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Évid. Based Dent. Pract. 2019, 19, 101310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, B.V.; Rodrigues, V.P.; Rodrigues, M.F.; De Melo, H.V.; Dos Santos, P.C. Soft tissue facial profile changes after orthodontic treatment with or without tooth extractions in Class I malocclusion patients: A comparative study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2019, 9, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iared, W.; Da Silva, E.M.K.; Iared, W.; Macedo, C.R. Esthetic perception of changes in facial profile resulting from orthodontic treatment with extraction of premolars. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2017, 148, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Z.; Short, L.; Banting, D.W.; Saltaji, H. Profile changes following extraction orthodontic treatment: A comparison of first versus second premolar extraction. Int. Orthod. 2018, 16, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, J.; Bing, L.; Li, S.-F.; Ma, Y.-N.; Kwon, T.-G.; Wu, X.-P. Morphological Characteristics of Soft Tissue Profile of Angle’s Class II Division I Malocclusion before and after Orthodontic Treatment. Int. J. Morphol. 2018, 36, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Kutschera, E.; Memmert, S.; Gölz, L.; Jäger, A.; Bourauel, C.; Eliades, T. Effectiveness of early orthopaedic treatment with headgear: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2016, 39, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.O.; Sa’Aed, N.L.; Bayome, M.; Park, J.H.; Kook, Y.-A.; Park, Y.-S.; Han, S.H. Comparison of treatment effects between the modified C-palatal plate and cervical pull headgear for total arch distalization in adults. Korean J. Orthod. 2017, 47, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torun, G.S. Soft Tissue Changes in the Orofacial Region after Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study. J. Orofac. Orthop. Fortschr. Kieferorthopädie 2017, 78, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuly, T.; Chaushu, G.; Allon, D.M. Does Maxillary Advancement Influence the Nasolabial Angle? J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, e408–e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allar, M.L.; Movahed, R.; Wolford, L.M.; Oliver, D.R.; Harrison, S.D.; Thiesen, G.; Kim, K.B. Nasolabial Changes Following Double Jaw Surgery. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 2560–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassemi, M.; Hilgers, R.-D.; Jamilian, A.; Shokatbakhsh, A.; Hölzle, F.; Fritz, U.; Ghassemi, A. Effect of maxillary advancement on the change in the soft tissues after treatment of patients with class III malocclusion. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santorelli, A.; Marlino, S. Non-surgical Rhinoplasty with Hyaluronic acid Fillers: Predictable Results Using Software for the Evaluation of Nasal Angles. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, K. Midline Volume Filler Injection for Facial Rejuvenation and Contouring in Asians. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.H.; Seo, K.K. Filler Rhinoplasty Evaluated by Anthropometric Analysis. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (A) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Article Title | Year | Author | Result | NLA Average Value | |
| Extractions | Changes In Soft Tissue Profile After Orthodontic Treatment With And Without Extraction: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [3] | 2018 | Rian H. Almurtadha Et Al. | NLA Increase (4.92° Average Value) In Extractive Group Compared To Non-Extractive Group | Not Reported |
| Extractions | Post-Orthodontic Cephalometric Variations In Bimaxillary Protrusion Cases Managed By Premolar Extraction—A Retrospective Study [13] | 2019 | Nd Alqahtani Et Al. | Significant NLA Increase (6.6°) In Extractive Group Compared To Non-Extractive Group | 104.7° ± 18.4° |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Changes Following Extraction Vs. Nonextraction Orthodontic Fixed Appliance Treatment: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [4] | 2018 | Konstantonios D Et Al. | Significant NLA Increase (2.4–4.3°) In Extractive Group Compared To Non-Extractive Group | Not Reported |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Change In Patients With Dentoalveolar Protrusion Treated With Maximum Anchorage: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [14] | 2019 | Yan Liu Et Al. | Higher NLA Increase Miniscrew Anchorage (3.52°) Compared To Traditional Anchorage (0.68°) | Not Reported |
| Extractions | Comparison Of Treatment Effects Between Four Premolar Extraction And Total Arch Distalization Using The Modified C-Palatal Plate [2] | 2018 | Sung Young Jo Et Al. | Significant NLA Increase In Both Study Groups | Extr. 109.21° ± 11.72° Distalization 104.53° ± 11.55° |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Facial Profile Changes After Orthodontic Treatment With Or Without Tooth Extractions In Class I Malocclusion Patients: A Comparative Study [15] | 2019 | Benedito V. Freitas Et Al. | No Statistically Significant Variations On Average NLA Values Between Extractive And Non-Extractive Group | Extr. 106.4° No Extr. 97.1° |
| Extractions | Esthetic Perception Of Changes In Facial Profile Resulting From Orthodontic Treatment With Extraction Of Premolar [16] | 2017 | Walter Iared Et Al. | 1.4° NLA Increase In Extractive Group And 3° Decrease In Non-Extractive Group | Not Reported |
| Extractions | Comparative Evaluation Of Soft Tissue Changes In Class I Borderline Patient Treated With Extraction And Nonextraction Modalities [5] | 2016 | Aniruddh Yashwant V. Et Al. | Significant NLA Increase (9.410°) In Extractive Group Compared To Non-Extractive Group | Extr. 102.77° No Extr. 98.23° |
| Extractions | Profile Changes Following Extraction Orthodontic Treatment: A Comparison Of First Versus Second Premolar Extraction [17] | 2018 | Ziad Omar Et Al. | Significant NLA Increase (2.2°) In Extractive Group Compared To Non-Extractive Group | Pm1 112.81° ± 8.01° Pm2 113.13° ± 7.76° |
| Extractions | Short-Term Effects Of Systematic Premolar Extraction On Lip Profile, Vertical Dimension And Cephalometric Parameters In Borderline Patients For Extraction Therapy—A Retrospective Cohort Study [6] | 2016 | Christian Kirschneck Et Al. | No Statistically Significant Variations In NLA Values Between Extractive And Non-Extractive Group | Extr. 113.2° No Extr. 112.7° |
| (B) | |||||
| Class II Malocclusion | Morphological Characteristics Of Soft Tissue Profile Of Angle’s Class II Division I Malocclusion Before And After Orthodontic Treatment [18] | 2018 | Jing Xuan Et Al. | Increase In NLA Values After Treatment, But Values Are Not Statistically Significant | Not Reported |
| Class II Malocclusion | Soft Tissue Profile Changes After Functional Mandibolar Advancer Or Herbst Appliances Treatment In Class II Patients [7] | 2017 | Jan Hourfar Et Al. | No Statistical Differences Were Detected Between Both Ffas And Rfa, NLA Showed More Pronounced Changes In Herbst Appliance Patients. | 114.78° Fma 118.64° Herbst |
| Class II Malocclusion | Class II Malocclusion Treatment Effects With Jones Jig And Distal Jet Followed By Fixed Appliances [8] | 2018 | Lorena Vilanova Et Al. | Better NLA Values In Control Group (Untreated Patients) | 107.25° |
| Class II Malocclusion | Effectiveness Of Early Orthopaedic Treatment With Headgear: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [19] | 2017 | Spyridon N. Papageorgiou Et Al. | Short-Term Decrease In NLA Values | 81.6° |
| Class II Malocclusion | Comparison Of Treatment Effects Between The Modifies C-Palatal Plate And Cervical Pull Headgear For Total Arch Distalization In Adults [20] | 2017 | Chong Ook Park Et Al. | Significant Increase In NLA And Upper Lip Retraction | 81.31° |
| (C) | |||||
| Class III Malocclusion | Comparison Of The Soft And Hard Tissue Effects Of Two Different Protraction Mechanisms In Class III Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial [9] | 2015 | Mevlut Celikoglu Et Al. | No Statistically Significant Difference In Both Study Groups | Rme/Fm 98.33° Mmp 106.24° |
| Class III Malocclusion | Morphological Changes Of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion In Mixed Dentition With Protraction Combined Activities [10] | 2018 | Fan-Yu Xu Et Al. | Significant NLA Decrease 5.629° | Not Reported |
| (D) | |||||
| Rapid Maxillary Expansion | Soft Tissue Changes In The Orofacial Region After Rapid Maxillary Expansion [21] | 2016 | Gulsilay Sayar Torun | No Statistically Significant Difference In Both Study Groups | 117.5° |
| (E) | |||||
| Orthognatic Surgery | Does Maxillary Advancement Influence The Nasolabial Angle? [22] | 2019 | Tom Shmuly Et Al. | No Statistically Significant Difference In Both Study Groups NLA Decrease 3.78° | 98.68° ± 12.10° |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Nasolabial Changes Following Double Jaw Surgery [23] | 2019 | Michelle L. Allar Et Al. | NLA Decrease Correlated With Maxillary And Mandibular Advancement | Not Reported |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Maxillary Advancement Versus Mandibular Setback In Class III Dentofacial Deformity:Are There Any Differences In Aesthetic Outcomes? [11] | 2016 | M. Ghassemi Et Al. | NLA Increase After Mandibular Setback NLA Decrease After Upper Maxillary Advancement | Mandibular Setback 106.585° Upper Maxillary Advanement 102.075° |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Effect Of Maxillary Advancement On The Changes In The Soft Tissues After Treatment Of Patients With Class III Malocclusion [24] | 2015 | M. Ghassemi Et Al. | No Statistically Significant Difference In Both Study Groups | 100.6° |
| (F) | |||||
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty With Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Predictable Results Using Software For The Evaluation Of Nasal Angles [25] | 2020 | Adriano Santorelli Et Al. | Significant Increase In NLA | 88.5° ± 6.1° |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Midline Volume Filler Injection For Facial Rejuvenation And Countouring In Asians [26] | 2019 | Zhezhen Xiong Et Al. | NLA Increase 3.2° ± 2.6° | 107.93° ± 9.01° |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Early Changes In Facial Profile Following Structured Filler Phinoplasty: An Anthropometric Analysisi Using A 3-Dimensional Imaging System [1] | 2017 | Nark Kyoung Rho Et Al. | NLA Increase 3.79° ± 8.71° | 95.97° |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Filler Rhinoplasty Evaluated By Anthropometric Analysis [27] | 2016 | Sung Hwan Youn Et Al. | NLA Increase 9.4° ± 4.5° | Increase: Tip Rotation 93.3° ± 9.3° Total Nose 96.9° ± 10° Hump Correction 96.8° ± 10° |
| (A) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Article Title | Number and Age of Reported Patients | Gender | Average Age | |
| Extractions | Changes In Soft Tissue Profile After Orthodontic Treatment With And Without Extraction: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [3] | 305 Patients 12.26–24.49 Years Old | Extr 102f 18m No Extr. 77f 16m Not Reported: 92 Patients | 18.375 Years Old |
| Extractions | Post-Orthodontic Cephalometric Variations In Bimaxillary Protrusion Cases Managed By Premolar Extraction—A Retrospective Study [13] | 46 Patients 18–30 Years Old | 30f 16m | 24 Years Old |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Changes Following Extraction Vs. Non Extraction Orthodontic Fixed Appliance Treatment: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [4] | 1876 Patients. 14 Years Old | 1291f 585m | 14 Years Old |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Change In Patients With Dentoalveolar Protrusion Treated With Maximum Anchorage: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [14] | 99 Patients. 13.55–29.25 Years Old | Not Reported | 21.4 Years Old |
| Extractions | Comparison Of Treatment Effects Between Four Premolar Extraction And Total Arch Distalization Using The Modified C-Palatal Plate [2] | 40 Patients 16.1–32.2 Years Old | 4pe 19f 1m Mcpp 16f 4m | 24.15 Years Old |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Facial Profile Changes After Orthodontic Treatment With Or Without Tooth Extractions In Class I Malocclusion Patients: A Comparative Study [15] | 20 Patients. 12.3 Years Old | Extr. 6f 4m No Extr. 5f 5m | 12.3 Years Old |
| Extractions | Esthetic Perception Of Changes In Facial Profile Resulting From Orthodontic Treatment With Extraction Of Premolar [16] | 195 Patients Average Age Not Reported | Not Reported | Not Reported |
| Extractions | Comparative Evaluation Of Soft Tissue Changes In Class I Borderline Patient Treated With Extraction And Non Extraction Modalities [5] | 150 Patients Average Age Not Reported | Not Reported | Not Reported |
| Extractions | Profile Changes Following Extraction Orthodontic Treatment: A Comparison Of First Versus Second Premolar Extraction [17] | 81 Patients 10–16 Years Old | Pm1 28f 20m Pm2 22f 11m | 13 Years Old |
| Extractions | Short-Term Effects Of Systematic Premolar Extraction On Lip Profile, Vertical Dimension And Cephalometric Parameters In Borderline Patients For Extraction Therapy—A Retrospective Cohort Study [6] | 50 Patients 9–15 Years Old | Extr. 15f 10m No Extr. 14f 11m | 12 Years Old |
| 345 Patients Not Included In The Calculations Of Average Values, Due To Incomplete Data (Patients’ Average Age) Provided By The Authors | Total Average Age Total Patients Reported 2517 | 15.07 Years Old | ||
| (B) | ||||
| II Class Malocclusion | Morphological Characteristics Of Soft Tissue Profile Of Angle’s Class II Division I Malocclusion Before And After Orthodontic Treatment [18] | 20 Patients 14.3 Years Old | Not Reported | 14.3 Years Old |
| II Class Malocclusion | Soft Tissue Profile Changes After Functional Mandibular Advancer Or Herbst Appliances Treatment In Class II Patients [7] | 42 Patients 12.1–16.2 Years Old | Fma 10f 11m Herbst 10f 11m | 14.15 Years Old |
| II Class Malocclusion | Class II Malocclusion Treatment Effects With Jones Jig And Distal Jet Followed By Fixed Appliances [8] | 45 Patients 12.90 Years Old | 16f 29m | 12.9 Years Old |
| II Class Malocclusion | Effectiveness Of Early Orthopaedic Treatment With Headgear: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [19] | 930 Patients 7.6–12.9 Years Old | 379f 479m | 10.25 Years Old |
| II Class Malocclusion | Comparison Of Treatment Effects Between The Modifies C-Palatal Plate And Cervical Pull Headgear For Total Arch Distalization In Adults [20] | 44 Patients. Mcpp 24.7 ± 7.7 Years Old Headgear 23.0 ± 7.7 Years Old | 32f 12m | 23.85 Years Old |
| Total Average Age Total Patients Reported 1081 | 11.14 Years Old | |||
| (C) | ||||
| III Class Malocclusion | Comparison Of The Soft And Hard Tissue Effects Of Two Different Protraction Mechanisms In Class III Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial [9] | 32 Patients 12 ± 0.89 Years Old | Mmp 9f 7m Fm/Rme 10f 6m | 12 Years Old |
| III Class Malocclusion | Morphological Changes Of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion In Mixed Dentition With Protraction Combined Activities [10] | 30 Patients 6–10 Years Old | 15f 15m | 8 Years Old |
| Total Average Age Total Patients Reported 62 | 10.6 Years Old | |||
| (D) | ||||
| Rapid Maxillary Expansion | Soft Tissue Changes In The Orofacial Region After Rapid Maxillary Expansion [21] | 28 Patients. 13.91 ± 1.8 Years Old | 18f 10m | 13.91 Years Old |
| Total Average Age Total Patients Reported 28 | 13.91 Years Old | |||
| (E) | ||||
| Orthognatic Surgery | Does Maxillary Advancement Influence The Nasolabial Angle? [22] | 32 Patients 21 ± 3.4 Years Old | 20f 12m | 21 Years Old |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Nasolabial Changes Following Double Jaw Surgery [23] | 37 Patients 32.2 ± 14.6 Years Old | 29f 8m | 32.2 Years Old |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Maxillary Advancement Versus Mandibular Setback In Class III Dentofacial Deformity: Are There Any Differences In Aesthetic Outcomes? [11] | 34 Patients 16–51 Years Old | Not Reported | 33.5 Years Old |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Effect Of Maxillary Advancement On The Changes In The Soft Tissues After Treatment Of Patients With Class III Malocclusion [24] | 48 Patients 28 Years Old | 29f 24m | 28 Years Old |
| Total Average Age Total Patients Reported 151 | 28.78 Years Old | |||
| (F) | ||||
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty With Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Predictable Results Using Software For The Evaluation Of Nasal Angles [25] | 62 Patients 29 ± 9.2 Years Old | 57f 5m | 29 Years Old |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Midline Volume Filler Injection For Facial Rejuvenation And Countouring In Asians [26] | 40 Patients 31.55 ± 6.43 Years Old | 37f 3m | 31.55 Years Old |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Early Changes In Facial Profile Following Structured Filler Rhinoplasty: An Anthropometric Analysis Using A 3-Dimensional Imaging System [1] | 40 Patients 28.5 Years Old | 40f 0m | 28.5 Years Old |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Filler Rhinoplasty Evaluated By Anthropometric Analysis [27] | 242 Patients 31 ± 9 Years Old | Not Reported | 31 Years Old |
| Total Average Age Total Patients Reported 384 | 30.47 Years Old | |||
| Total Number of Patients Reported | Total Number of Patients by Gender | Total Average Age | Not Classified by Gender | Not Classified by Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4568 | 2336 F 1333 M | 14.62 Years old | 897 | 345 |
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NLA Extr. | Nasolabial Angle Patients Treated With Extraction |
| No Extr. | Patients Treated Without Extraction |
| Pm1 | Patients Treated With Extraction Of First Four Premolars |
| Pm2 | Patients Treated With Extraction Of Second Four Premolars |
| Rfa | Patients Treated With Removable Functional Appliances |
| Herbst | Patients Treated With Herbst Appliance |
| Ffas | Patients Treated With Fixed Functional Appliances |
| Fma | Patients Treated With Functional Mandibular Advancer |
| Rme/Fm | Face Mask And Rapid Maxillary Expansion |
| Mmp | Mini Maxillary Protractor |
| F | Female Patients |
| M | Male Patients |
| 4pe | Four Premolar Extraction |
| Mcpp | Total Arch Distalization Using The Modified C-Palatal Plate |
| Article Title | Year | Author | NLA Variations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extractions | Changes In Soft Tissue Profile After Orthodontic Treatment With And Without Extraction: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [3] | 2018 | Rian H. Almurtadha Et Al. | Increase With Extractions |
| Extractions | Post-Orthodontic Cephalometric Variations In Bimaxillary Protrusion Cases Managed By Premolar Extraction—A Retrospective Study [13] | 2019 | Nd Alqahtani Et Al. | Increase With Extractions |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Changes Following Extraction Vs. Nonextraction Orthodontic Fixed Appliance Treatment: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [4] | 2018 | Konstantonios D Et Al. | Increase With Extraction |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Change In Patients With Dentoalveolar Protrusion Treated With Maximum Anchorage: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [14] | 2019 | Yan Liu Et Al. | Increase With Extraction And Miniscrew Anchorage |
| Extractions | Comparison Of Treatment Effects Between Four Premolar Extraction And Total Arch Distalization Using The Modified C-Palatal Plate [2] | 2018 | Sung Young Jo Et Al. | Increase With Extractions |
| Extractions | Soft Tissue Facial Profile Changes After Orthodontic Treatment With Or Without Tooth Extractions In Class I Malocclusion Patients: A Comparative Study [15] | 2019 | Benedito V. Freitas Et Al. | Unaffected |
| Extractions | Esthetic Perception Of Changes In Facial Profile Resulting From Orthodontic Treatment With Extraction Of Premolar [16] | 2017 | Walter Iared Et Al. | Increase With Extractions |
| Extractions | Comparative Evaluation Of Soft Tissue Changes In Class I Borderline Patient Treated With Extraction And Nonextraction Modalities [5] | 2016 | Aniruddh Yashwant V. Et Al. | Increase With Extractions |
| Extractions | Profile Changes Following Extraction Orthodontic Treatment: A Comparison Of First Versus Second Premolar Extraction [17] | 2018 | Ziad Omar Et Al. | Increase With Extractions |
| Extractions | Short-Term Effects Of Systematic Premolar Extraction On Lip Profile, Vertical Dimension And Cephalometric Parameters In Borderline Patients For Extraction Therapy—A Retrospective Cohort Study [6] | 2016 | Christian Kirschneck Et Al. | Unaffected |
| Class II Malocclusion | Morphological Characteristics Of Soft Tissue Profile Of Angle’s Class II Division I Malocclusion Before And After Orthodontic Treatment [18] | 2018 | Jing Xuan Et Al. | Increase After Treatment |
| Class II Malocclusion | Soft Tissue Profile Changes After Functional Mandibolar Advancer Or Herbst Appliances Treatment In Class II Patients [7] | 2017 | Jan Hourfar Et Al. | Unaffected |
| Class II Malocclusion | Class II Malocclusion Treatment Effects With Jones Jig And Distal Jet Followed By Fixed Appliances [8] | 2018 | Lorena Vilanova Et Al. | Unaffected |
| Class II Malocclusion | Effectiveness Of Early Orthopaedic Treatment With Headgear: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis [19] | 2017 | Spyridon N. Papageorgiou Et Al. | Decrease After Treatment |
| Class II Malocclusion | Comparison Of Treatment Effects Between The Modifies C-Palatal Plate And Cervical Pull Headgear For Total Arch Distalization In Adults [20] | 2017 | Chong Ook Park Et Al. | Increase After Treatment |
| Class III Malocclusion | Comparison Of The Soft And Hard Tissue Effects Of Two Different Protraction Mechanisms In Class III Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial [9] | 2015 | Mevlut Celikoglu Et Al. | Unaffected |
| Class III Malocclusion | Morphological Changes Of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion In Mixed Dentition With Protraction Combined Activities [10] | 2018 | Fan-Yu Xu Et Al. | Decrease After Treatment |
| Rapid Maxillary Expansion | Soft Tissue Changes In The Orofacial Region After Rapid Maxillary Expansion [21] | 2016 | Gulsilay Sayar Torun | Unaffected |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Does Maxillary Advancement Influence The Nasolabial Angle? [22] | 2019 | Tom Shmuly Et Al. | Decrease After Treatment |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Nasolabial Changes Following Double Jaw Surgery [23] | 2019 | Michelle L. Allar Et Al. | Decrease After Treatment |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Maxillary Advancement Versus Mandibular Setback In Class III Dentofacial Deformity:Are There Any Differences In Aesthetic Outcomes? [11] | 2016 | M. Ghassemi Et Al. | Increase After Mandibular Setback Decrease After Maxillary Advancement |
| Orthognatic Surgery | Effect Of Maxillary Advancement On The Changes In The Soft Tissues After Treatment Of Patients With Class III Malocclusion [24] | 2015 | M. Ghassemi Et Al. | Unaffected |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty With Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Predictable Results Using Software For The Evaluation Of Nasal Angles [25] | 2020 | Adriano Santorelli Et Al. | Increase After Filler Injection |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Midline Volume Filler Injection For Facial Rejuvenation And Countouring In Asians [26] | 2019 | Zhezhen Xion Et Al. | Increase After Filler Injection |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Early Changes In Facial Profile Following Structured Filler Phinoplasty: An Anthropometric Analysisi Using A 3-Dimensional Imaging System [1] | 2017 | Nark Kyoung Rho Et Al. | Increase After Filler Injection |
| Hyaluronic Acid Filler | Filler Rhinoplasty Evaluated By Anthropometric Analysis [27] | 2016 | Sung Hwan Youn Et Al. | Increase After Filler Injection |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinzi, V.; Paskay, L.C.; D’Andrea, N.; Albani, A.; Monaco, A.; Saccomanno, S. Evaluation of the Nasolabial Angle in Orthodontic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062531
Quinzi V, Paskay LC, D’Andrea N, Albani A, Monaco A, Saccomanno S. Evaluation of the Nasolabial Angle in Orthodontic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062531
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinzi, Vincenzo, Licia Coceani Paskay, Nicola D’Andrea, Arianna Albani, Annalisa Monaco, and Sabina Saccomanno. 2021. "Evaluation of the Nasolabial Angle in Orthodontic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062531
APA StyleQuinzi, V., Paskay, L. C., D’Andrea, N., Albani, A., Monaco, A., & Saccomanno, S. (2021). Evaluation of the Nasolabial Angle in Orthodontic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 11(6), 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062531








