Optimizing Support Locations in the Roof–Column Structural System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Optimal Column Locations
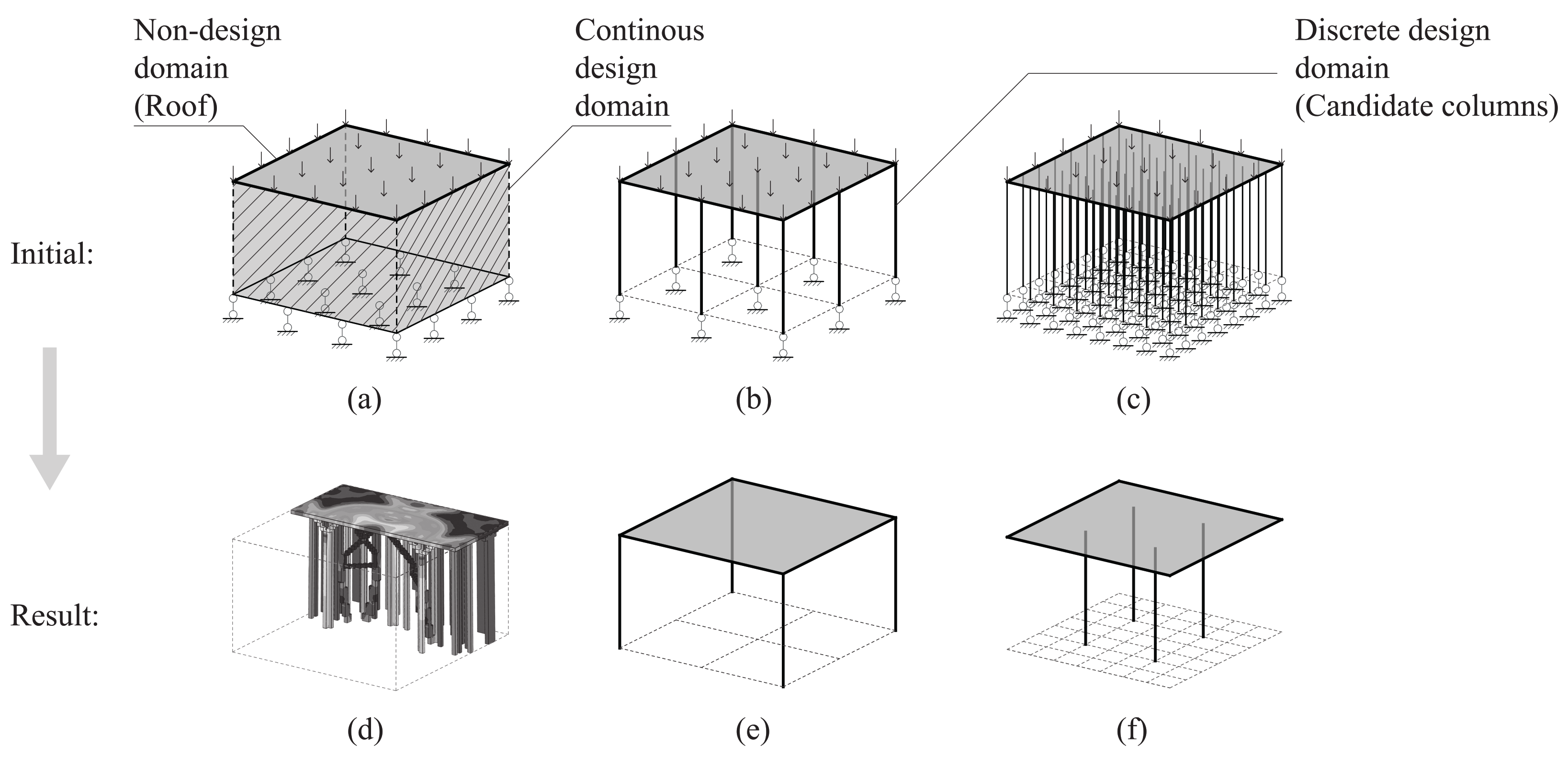
2.1. Problem Definition
2.2. Problem Statement
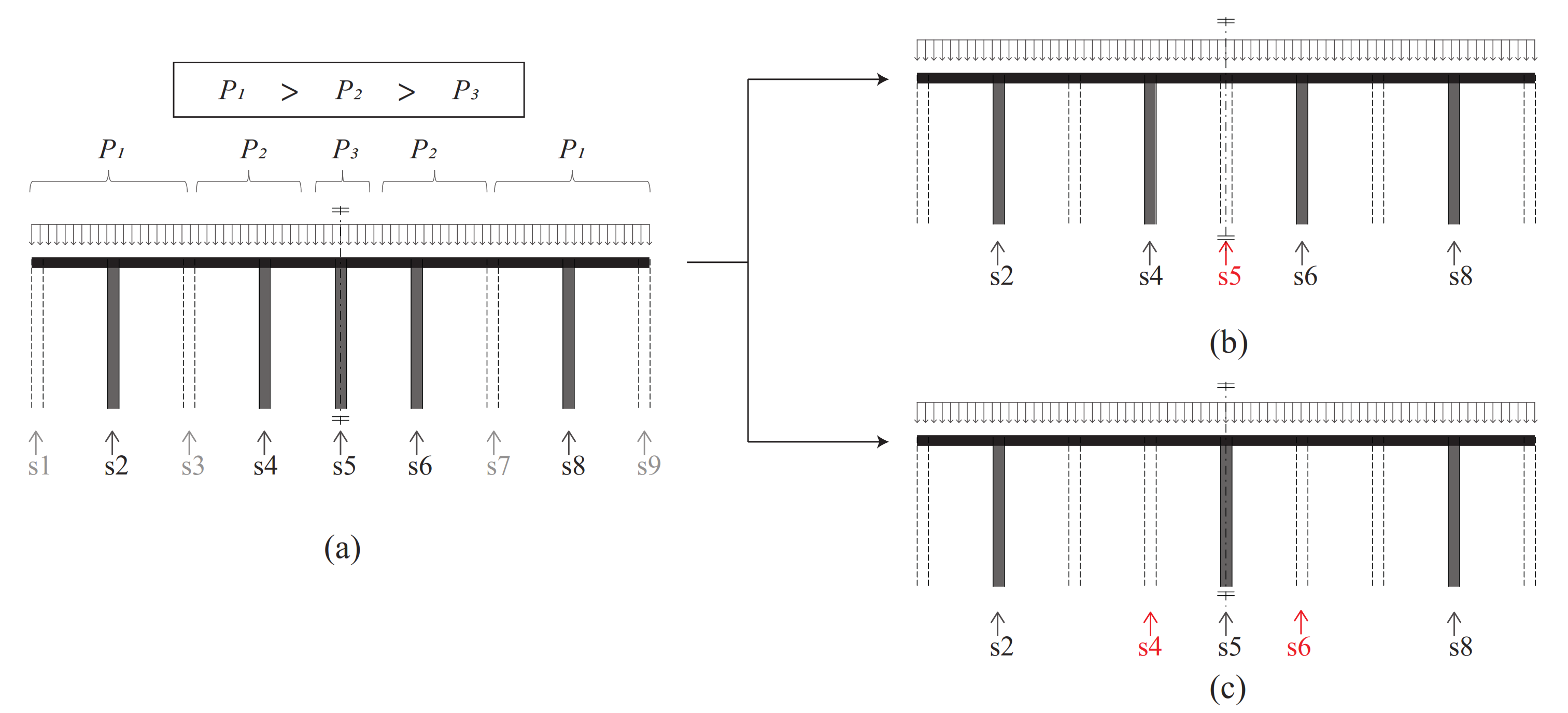
2.3. Optimization Algorithm
3. Controlling Optimization Tendency
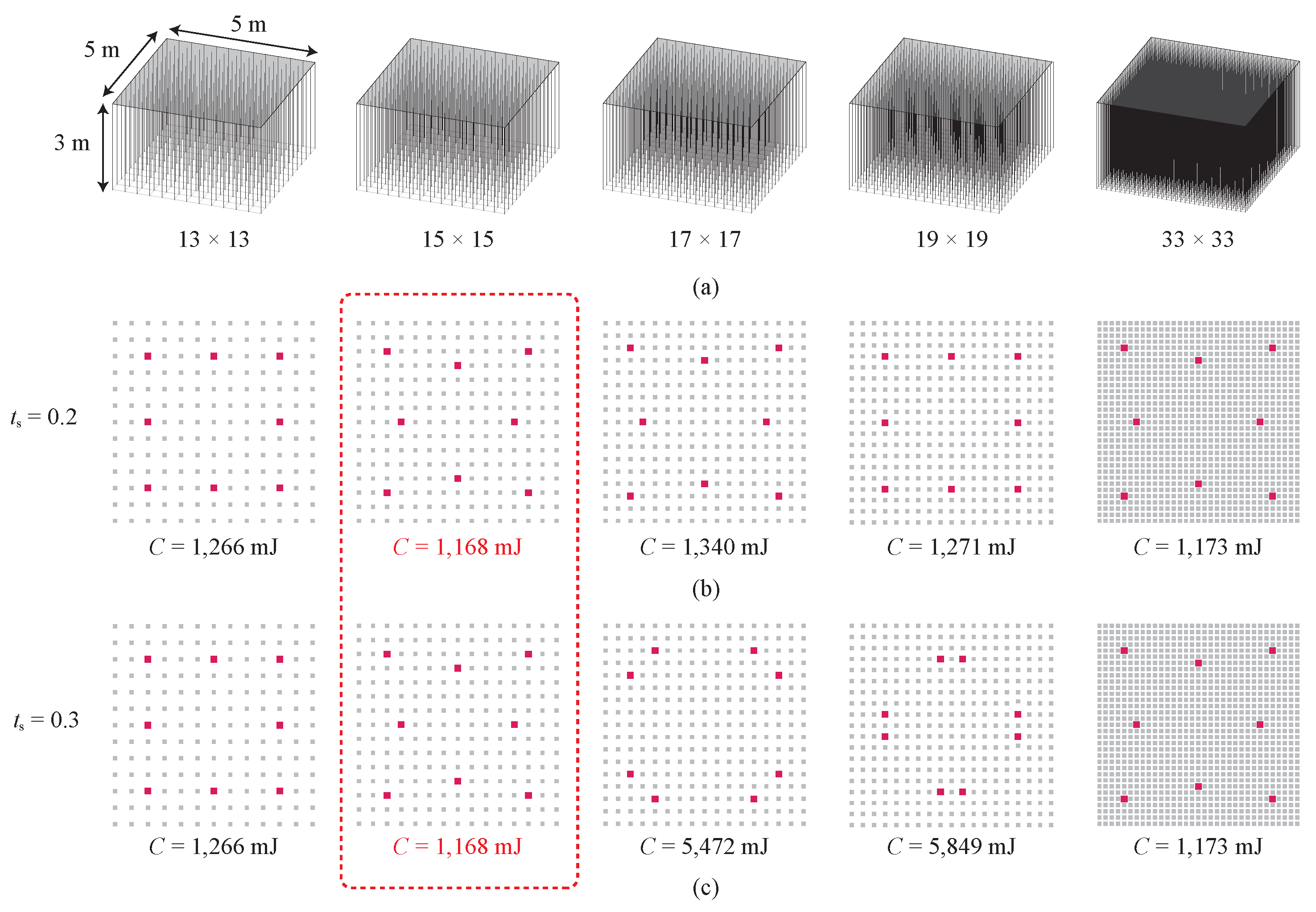
3.1. Initial Discrete Candidates
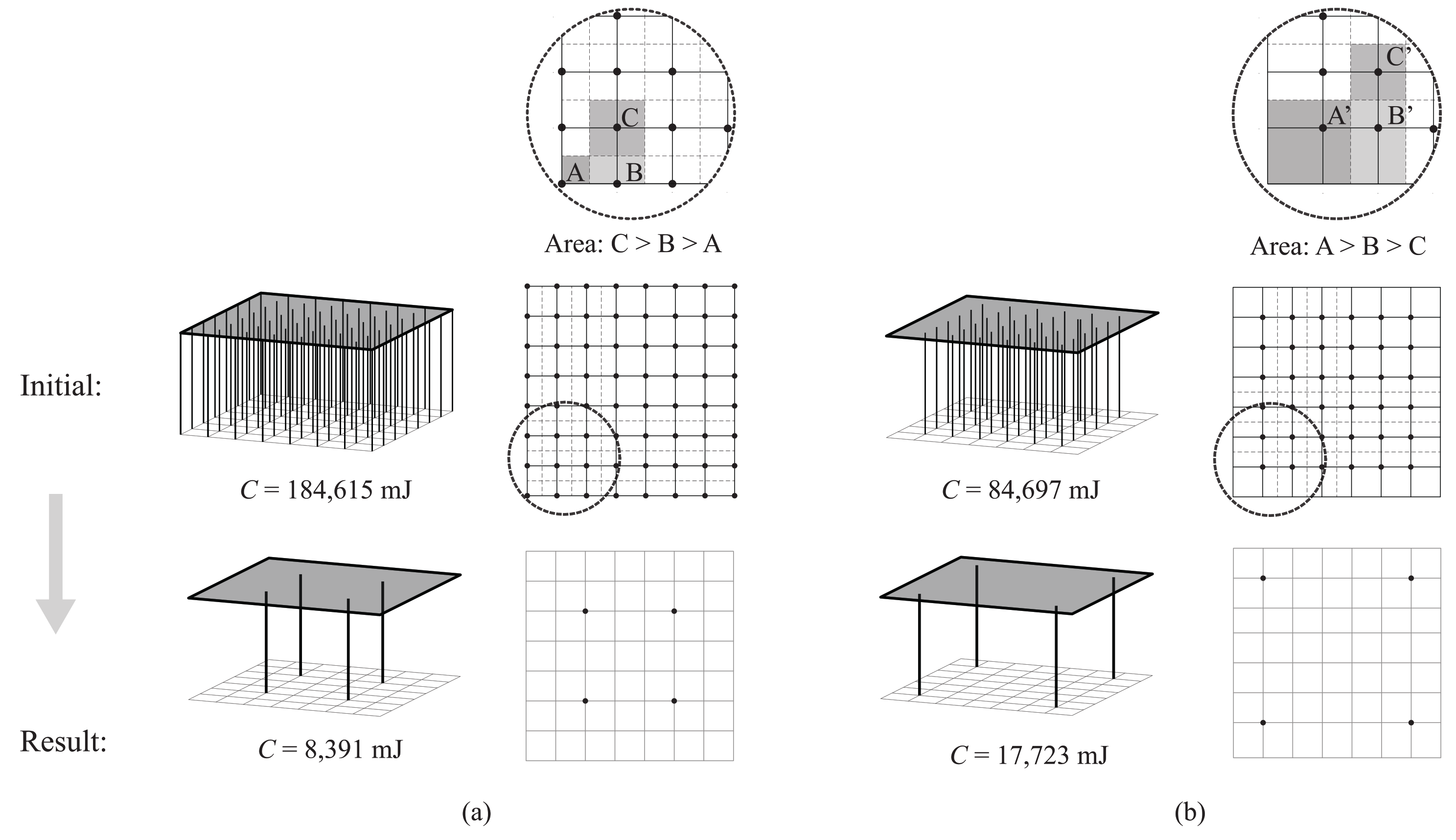
3.2. Roof–Column Relative Stiffness
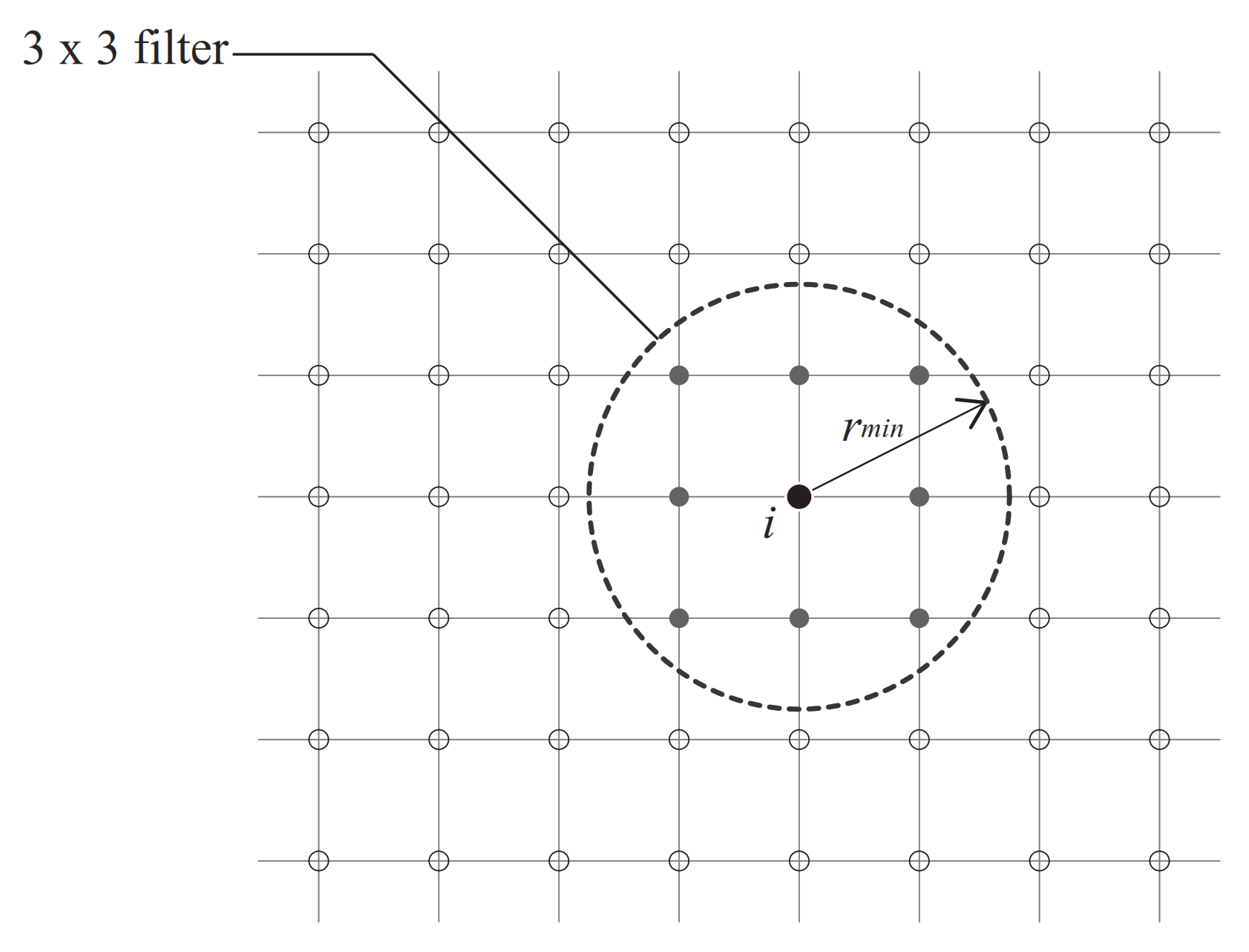
3.3. Filtering Scheme
4. Numerical Analysis
4.1. Method
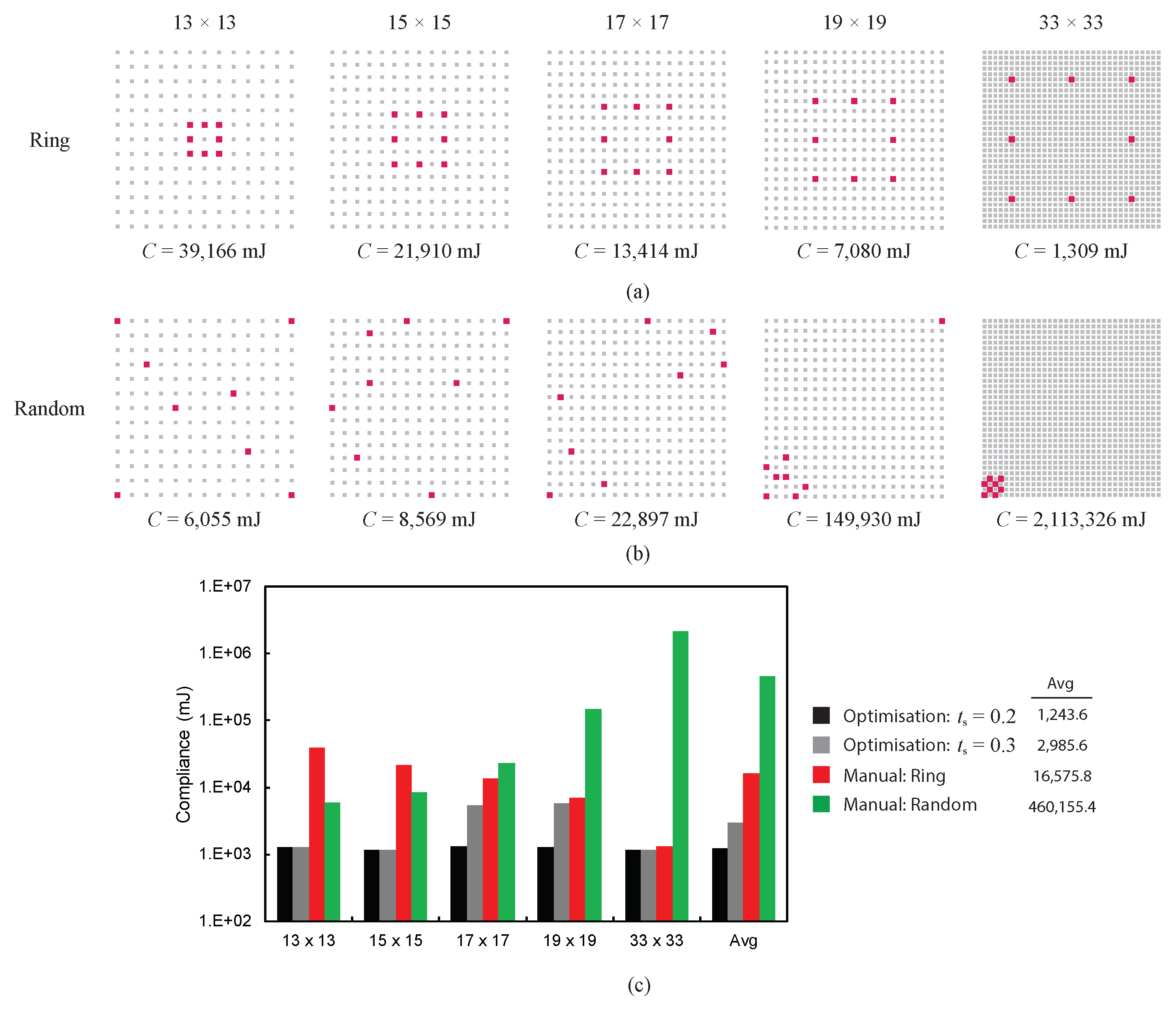
4.2. Optimization Results
4.3. Result Validation
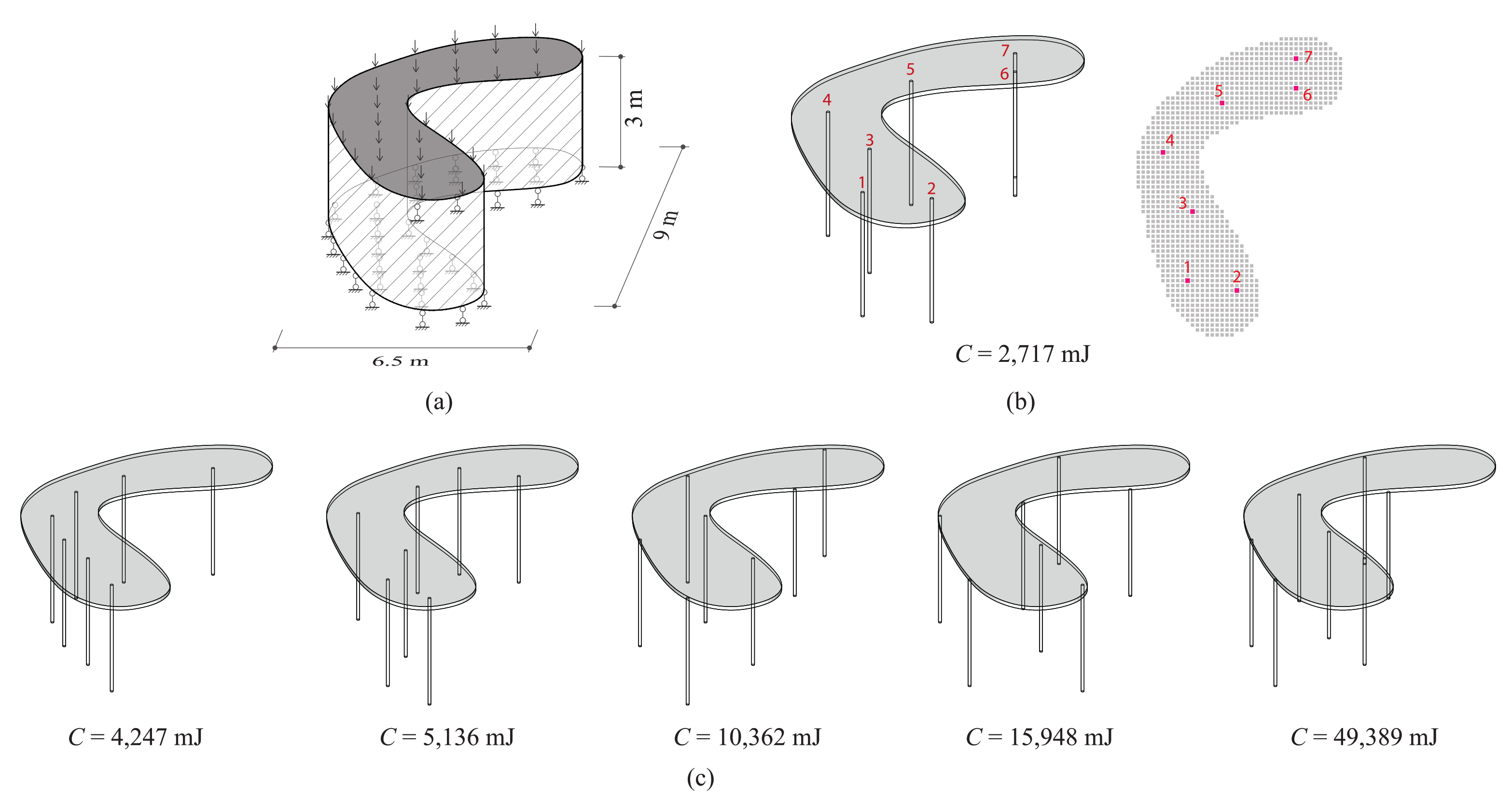
5. Extended Designs
5.1. Eye-Shaped Roof
5.2. Bean-Shaped Roof
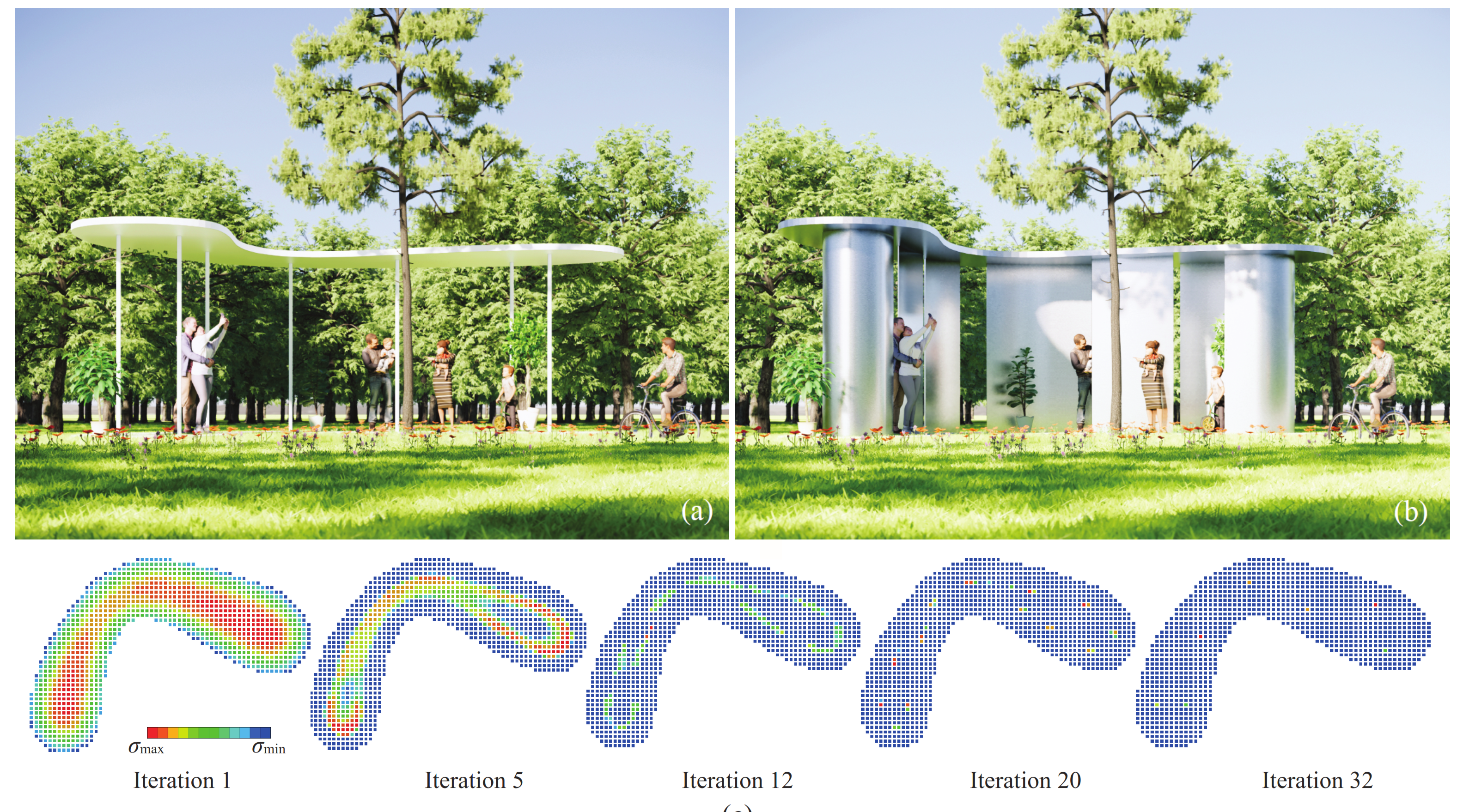
5.3. Pavilion with Bean-Shaped Roof
5.4. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charleson, A. Structure as Architecture; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adriaenssens, S.; Block, P.; Veenendaal, D.; Williams, C. (Eds.) Shell Structures for Architecture: Form Finding and Optimization; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Michell, A.G.M. The limits of economy of material in frame-structures. Philos. Mag. 1904, 8, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Y.M. Evolutionary Topology Optimization of Continuum Structures: Methods and Applications; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg, L.L.; Beghini, A.; Baker, W.F.; Paulino, G.H. Application of layout and topology optimization using pattern gradation for the conceptual design of buildings. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2011, 43, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnbull, J. Toyo Ito: Forces of Nature; Princeton Architectural Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Optim. 1989, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Rozvany, G.I.N. The COC algorithm, part II: Topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1991, 89, 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 1999, 69, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Steven, G.P. A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput. Struct. 1993, 49, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querin, O.M.; Steven, G.P.; Xie, Y.M. Evolutionary structural optimisation (ESO) using a bidirectional algorithm. Eng. Comput. 1998, 15, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Xie, Y.M.; Steven, G.P.; Querin, O.M. Bidirectional evolutionary method for stiffness optimization. AIAA J. 1999, 37, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Y.M. Convergent and mesh-independent solutions for the bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2007, 43, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethian, J.A.; Wiegmann, A. Structural Boundary Design via Level Set and Immersed Interface Methods. J. Comput. Phys. 2000, 163, 489–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, D. A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2003, 192, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tong, L.; Kang, Z. A level set method for structural shape and topology optimization using radial basis functions. Comput. Struct. 2009, 87, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Ito, T.; Isozaki, A. Morphogenesis of Flux Structure; AA Publications: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dorn, W.; Gomory, R.; Greenberg, M. Automatic design of optimal structures. J. Mec. 1964, 3, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.Q.; Zhu, B.; Hu, C.; Wang, X. Simulation of nonlinear behavior of beam structures based on discrete element method. Int. J. Steel. Struct. 2019, 19, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.D.; Gu, X. ε-relaxed approach in structural topology optimization. Struct. Optim. 1997, 13, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ohsaki, M. Adaptive force density method for form-finding problem of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 5658–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohsaki, M. Genetic algorithm for topology optimization of trusses. Comput. Struct. 1995, 57, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, L. An efficient simulated annealing algorithm for design optimization of truss structures. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 1936–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, T.; Liew, K.M. A swarm metaphor for multiobjective design optimization. Eng. Optim. 2002, 34, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, F.; Frost, K.S.; Fisher, A.; Witt, A.; Tourre, V.; Koren, B. Concurrent geometric, structural and environmental design: Louvre Abu Dhabi. In Advances in Architectural Geometry 2012; Hesselgren, L., Sharma, S., Wallner, J., Baldassini, N., Bompas, P., Raynaud, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund, O. A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 21, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, K. The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1987, 24, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremicker, M.; Papalambros, P.Y.; Loh, H.T. Solution of mixed-discrete structural optimization problems with a new sequential linearization algorithm. Comput. Struct. 1990, 37, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Zhou, S.; Feng, X.Q.; Xie, Y.M. On the internal architecture of emergent plants. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2018, 119, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodidio, P.; Calatrava, S. Calatrava: Santiago Calatrava, Complete Works, 1979–2009; Taschen: Cologne, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sejima, K. Yu-xi garden. El. Croquis 2018, 139, 268–273. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Lee, T.-U.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.M. Optimizing Support Locations in the Roof–Column Structural System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062775
Meng X, Lee T-U, Xiong Y, Huang X, Xie YM. Optimizing Support Locations in the Roof–Column Structural System. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062775
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xianchuan, Ting-Uei Lee, Yulin Xiong, Xiaodong Huang, and Yi Min Xie. 2021. "Optimizing Support Locations in the Roof–Column Structural System" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062775
APA StyleMeng, X., Lee, T.-U., Xiong, Y., Huang, X., & Xie, Y. M. (2021). Optimizing Support Locations in the Roof–Column Structural System. Applied Sciences, 11(6), 2775. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062775






