Pulmonary Effects Due to Physical Exercise in Polluted Air: Evidence from Studies Conducted on Healthy Humans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Alteration of Ventilatory Function and Appearance/Exacerbation of Respiratory Symptoms during Physical Exercise with Polluted Air: Short- and Medium-Term Effects
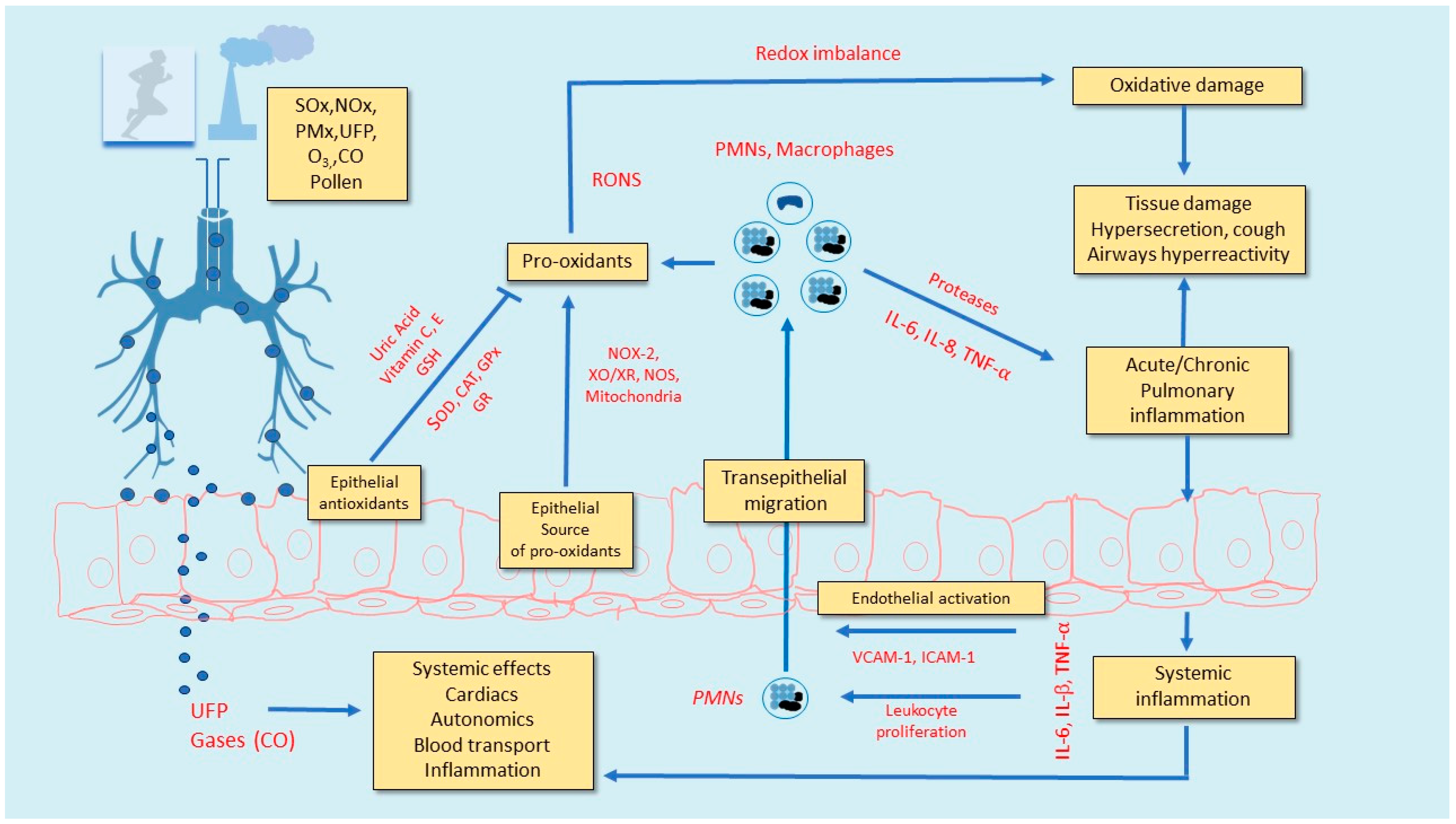
3. Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Due to Exercise in Polluted Air
4. Recommendations to Consider When Prescribing Exercise in Areas with Low Air Quality
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J. Particulate matter in the atmosphere: Which particle properties are important for its effects on health? Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F.; Curriero, F.C.; Coursac, I.; Zeger, S.L. Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Mortality in 20 U.S. Cities, 1987–1994. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Air Pollution and Daily Mortality: A Review and Meta Analysis. Environ. Res. 1994, 64, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, O.K.; Zhang, J.; Pinkerton, K.E. Pulmonary health effects of air pollution. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 22, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- First WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, 30 October–1 November 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/airpollution/events/conference/ (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Tan, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. A review of current air quality indexes and improvements under the multi-contaminant air pollution exposure. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Ren, D.; Li, C. Study on clean heating based on air pollution and energy consumption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 6549–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, C.E.; Valacchi, G.; Schock, B.; Wilson, M.; Weber, S.; Eiserich, J.; van der Vliet, A. Environmental oxidant pollutant effects on biologic systems: A focus on micronutrient antioxidant-oxidant interactions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166 Pt 2, S44–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, V. Environmental Air Pollution. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, S44–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, C.C.; Chalupa, D.C.; Gibb, F.R.; Morrow, P.E.; Oberdörster, G.; Utell, M.J.; Frampton, M.W. Ultrafine Particle Deposition in Humans During Rest and Exercise. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.E.; Li, Q.; Gingrich, S.E.; Macfarlane, R.G.; Cheng, S. Should People Be Physically Active Outdoors on Smog Alert Days? Can. J. Public Health 2005, 96, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrufello, P.T.; Smoliga, J.; Rundell, K.W. Small things make a big difference: Particulate matter and exercise. Sports Med. 2012, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, J.E. Clinicians prescribing exercise: Is air pollution a hazard? Med. J. Aust. 2005, 182, 606–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, L.V.; Koehle, M.S. The Health Effects of Exercising in Air Pollution. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.C. Effects of Ozone Exposure at Ambient Air Pollution Episode Levels on Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 1987, 4, 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.C.; Schelegle, E.S. Ozone and high ventilation effects on pulmonary function and endurance per-formance. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1983, 55, 805–812. [Google Scholar]
- Foxcroft, W.J.; Adams, W.C. Effects of ozone exposure on four consecutive days on work performance and VO2max. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 61, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonfeld, B.R.; Adams, W.C.; Schelegle, E.S. Duration of Enhanced Responsiveness upon Re-Exposure to Ozone. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1989, 44, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmes, J.R.; Chen, L.L.; Scannell, C.; Tager, I.; Christian, D.; Hearne, P.Q.; Kelly, T.; Aris, R.M. Ozone-induced decre-ments in FEV1 and FVC do not correlate with measures of inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundell, K.W. High Levels of Airborne Ultrafine and Fine Particulate Matter in Indoor Ice Arenas. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.B.; Ljungman, P.L.; Wilker, E.H.; Dorans, K.S.; Gold, D.R.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P.; Washko, G.R.; O’Connor, G.T.; Mittleman, M.A. Long-Term Exposure to Traffic Emissions and Fine Particulate Matter and Lung Function Decline in the Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avol, E.L.; Linn, W.S.; Venet, T.G.; Shamoo, D.A.; Hackney, J.D. Comparative respiratory effects of ozone and am-bient oxidant pollution exposure during heavy exercise. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1984, 34, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H., Jr.; Bradley, P.W.; Simmons, M.S.; Tashkin, D.P. Impaired exercise performance and pulmonary function in elite cyclists during low-level ozone exposure in a hot environment. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 134, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, W.F.; Stewart, P.W.; Smith, M.V.; Pan, W.K.; Pan, J. Ozone-induced respiratory symptoms: Expo-sure-response models and association with lung function. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folinsbee, L.J.; McDonnell, W.F.; Horstman, D.H. Pulmonary Function and Symptom Responses after 6.6-Hour Exposure to 0.12 ppm Ozone with Moderate Exercise. JAPCA 1988, 38, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linder, J.; Herren, D.; Monn, C.; Wanner, H.U. Effect of ozone on physical performance capacity. Int. J. Public Health 1987, 32, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Morales Cardona, T. Performance of athletes exercising in ozone polluted air. Bol. Asoc. Med. Puerto Rico 1990, 82, 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, W.C. Ozone dose–response effects of varied equivalent minute ventilation rates. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2000, 10, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brant, T.C.S.; Yoshida, C.T.; Carvalho, T.D.S.; Nicola, M.L.; Martins, J.A.; Braga, L.M.; De Oliveira, R.C.; Leyton, V.; De André, C.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; et al. Mucociliary clearance, airway inflammation and nasal symptoms in urban motorcyclists. Clinics 2014, 69, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sa, M.C.; Nakagawa, N.K.; Saldiva de Andre, C.D.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; de Santana Carvalho, T.; Nicola, M.L.; de Andre, P.A.; Nascimento Saldiva, P.H.; Vaisberg, M. Aerobic exercise in polluted urban environments: Effects on airway defense mechanisms in young healthy amateur runners. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 046018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubesch, N.J.; De Nazelle, A.; Westerdahl, D.; Martinez, D.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Bouso, L.; Guerra, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Respiratory and inflammatory responses to short-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution with and without moderate physical activity. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 72, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauner, E.V.; Mortensen, J.; Moller, P. Effects of ambient airparticulate exposure on blood–gas barrier permeability and lung function. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardot, S.P.; Ryan, P.B.; Smith, S.M.; Davis, W.T.; Hamilton, C.B.; Obenour, R.A.; Renfro, J.R.; Tromatore, K.A.; Reed, G.D. Ozone and PM 2.5 Exposure and Acute Pulmonary Health Effects: A Study of Hikers in theGreat Smoky Mountains National Park. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilliland, F.D.; Berhane, K.; Rappaport, E.B.; Thomas, D.C.; Avol, E.; Gauderman, W.J.; London, S.J.; Margolis, H.G.; McConnell, R.; Islam, K.T.; et al. The effects of ambient air pollution on school absenteeism due to respir-atory illnesses. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomis, D.; Castillejos, M.; Gold, D.R.; McDonnell, W.; Borja-Aburto, V.H. Air Pollution and Infant Mortality in Mexico City. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Avol, E.; Gilliland, F.; Vora, H.; Thomas, D.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Kuenzli, N.; Lurmann, F.; Rappaport, E.; et al. The Effect of Air Pollution on Lung Development from 10 to 18 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Urman, R.; Avol, E.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Rappaport, E.; Chang, R.; Lurmann, F.; Gilliland, F. Association of Improved Air Quality with Lung Development in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilliland, F.D.; McConnell, R.; Peters, J.; Gong, H., Jr. A theoretical basis for investigating ambient air pollution and children’s respiratory health. Environ Health Perspect. 1999, 107 (Suppl. S3), 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun-Fahrlander, C.; Kunzli, N.; Domenighetti, G.; Carell, C.F.; Ackermann-Liebrich, U. Acute effects of ambient ozone on respiratory function of Swiss schoolchildren after a 10-min heavy exercise. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1994, 17, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timonen, K.L.; Pekkanen, J.; Tiittanen, P.; Salonen, R.O. Effects of air pollution on changes in lung function induced by exercise in children with chronic respiratory symptoms. Occup. Environ. Med. 2002, 59, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McConell, G.K.; Lee-Young, R.S.; Chen, Z.-P.; Stepto, N.K.; Huynh, N.N.; Stephens, T.J.; Canny, B.J.; Kemp, B.E. Short-term exercise training in humans reduces AMPK signalling during prolonged exercise independent of muscle glycogen. J. Physiol. 2005, 568, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Hoek, G.; Breugelmans, O.; Leentvaar, M. Respiratory effects of low-level photochemical air pollution in amateur cyclists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korrick, S.A.; Neas, L.M.; Dockery, D.W.; Gold, D.R.; Allen, G.A.; Hill, L.B.; Kimball, K.D.; Rosner, B.A.; Speizer, F.E. Effects of ozone and other pollutants on the pulmonary function of adult hikers. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H., Jr.; Linn, W.S.; Clark, K.W.; Anderson, K.R.; Sioutas, C.; Alexis, N.E.; Cascio, W.E.; Devlin, R.B. Exposures of healthy and asthmatic volunteers to concentrated ambient ultrafine particles in Los Angeles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, W.F.; Stewart, P.W.; Smith, M.V.; Kim, C.S.; Schelegle, E.S. Prediction of lung function response for populations exposed to a wide range of ozone conditions. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Alexis, N.E.; Rappold, A.G.; Kehrl, H.; Hazucha, M.J.; Lay, J.C.; Schmitt, M.T.; Case, M.; Devlin, R.B.; Peden, D.B.; et al. Lung Function and Inflammatory Responses in Healthy Young Adults Exposed to 0.06 ppm Ozone for 6.6 Hours. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, C.R.; Colebatch, H.J.H.; Mebel, P.E.; Nadel, J.A.; Staub, N.C. Motor control of pulmonary airways studied by nerve stimulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1965, 20, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnarine, S.I.; Haddad, E.B.; Khawaja, A.M.; Mak, J.C.; Rogers, D.F. On muscarinic control of neurogenic mucus secretion in ferret trachea. J. Physiol. 1996, 494, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.A.; Wald, J.A.; Doran, S.; Soda, D. Endogenous nitric oxide in expired air: Effects of acute exercise in humans. Life Sci. 1994, 55, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, V.; Svartengren, M.; Rak, S.; Barck, C.; Bylin, G. Repeated exposure to an ambient level of NO2 enhances asthmatic response to a nonsymptomatic allergen dose. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulstrunk, M.; Bohni, B. Comparison of lung function parameters in healthy non-smokers following exertion in urban environmental air and in air-conditioned inside air. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1992, 122, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jörres, R.; Nowak, D.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W.; Oldigs, M.; Magnussen, H. The effect of 1 ppm nitrogen dioxide on bronchoalveolar lavage cells and inflammatory mediators in normal and asthmatic subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 1995, 8, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogel, J.A.; Gleser, M.A. Effect of carbon monoxide on oxygen transport during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1972, 32, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, A.; Wasserman, K.; Armon, Y.; Weiler-Ravell, D. The work-rate-dependent effect of carbon monoxide on ventilatory control during exercise. Respir. Physiol. 1991, 85, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.A.; McNicol, M.W. The effect of nicotine and carbon monoxide on exercise performance in normal subjects. Respir. Med. 1993, 87, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpino, P.; Tomei, F.; La Valle, C.; Tomao, E.; Rosati, M.V.; Ciarrocca, M.; De Sio, S.; Cangemi, B.; Vigliarolo, R.; Fedele, F. Respiratory and cardiovascular function at rest and during exercise testing in a healthy working population: Effects of outdoor traffic air pollution. Occup. Med. (Lond.) 2004, 54, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, H., Jr.; Bedi, J.F.; Horvath, S.M. Inhaled albuterol does not protect against ozone toxicity in nonasthmatic athletes. Arch. Environ. Health 1988, 43, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinney, P.L.; Nilsen, D.; Lippmann, M.; Brescia, M.; Gordon, T.; McGovern, T.; El-Fawal, H.; Devlin, R.B.; Rom, W.N. Biomarkers of lung inflammation in recreational joggers exposed to ozone. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aris, R.M.; Christian, D.; Hearne, P.Q.; Kerr, K.; Finkbeiner, W.E.; Balmes, J.R. Ozone-induced Airway Inflammation in Human Subjects as Determined by Airway Lavage and Biopsy. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, E.C.; Stone, V.; Florida-James, G. Impact of heat and pollution on oxidative stress and CC16 secretion after 8 km run. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2011, 111, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.R.; Cardellach, F.; López, S.; Casademont, J.; Miró, O. Carbon monoxide specifically inhibits cytochrome c oxidase of human mitochondrial respiratory chain. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, K.; Brito, J.M.; Silva, L.F.; Lino-Dos-Santos-Franco, A.; Frias, D.P.; ESilva, R.C.R.; Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; de Fátima Lopes Calvo Tibério, I.; Mauad, T.; et al. The effects of particulate matter on inflammation of respiratory system: Differences between male and female. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, J.; Brancher, E.A.; Costa, C.; de Pinho, R.A.; Teixeira, J.P. Cardio-respiratory health effects of exposure to traffic-related air pollutants while exercising outdoors: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R. Oxidative stress and the cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudway, I.S.; Kelly, F.J. An Investigation of Inhaled Ozone Dose and the Magnitude of Airway Inflammation in Healthy Adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garey, K.W.; Neuhauser, M.M.; Robbins, R.A.; Danziger, L.H.; Rubinstein, I. Markers of inflammation in exhaled breath condensate of young healthy smokers. Chest 2004, 125, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghio, A.J.; Kim, C.; Devlin, R.B. Concentrated Ambient Air Particles Induce Mild Pulmonary Inflammation in Healthy Human Volunteers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, B.-M.; Sehlstedt, M.; Grunewald, J.; Sköld, C.M.; Lundin, A.; Blomberg, A.; Sandström, T.; Eklund, A.; Svartengren, M. Road tunnel air pollution induces bronchoalveolar inflammation in healthy subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaoli, A.P.; Frampton, M.W.; Hyde, R.W.; Morrow, P.E.; Oberdörster, G.; Cox, C.; Speers, D.M.; Frasier, L.M.; Chalupa, D.C.; Huang, L.-S.; et al. Pulmonary Function, Diffusing Capacity, and Inflammation in Healthy and Asthmatic Subjects Exposed to Ultrafine Particles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, L.G.; Santos, J.M.B.; Foster, R.; Rossi, M.; Luna Junior, L.A.; Katekaru, C.M.; de Sá, M.C.; Jonckheere, A.-C.; Almeida, F.M.; Amaral, J.B.; et al. The Effect of Particulate Matter Exposure on the Inflammatory Airway Response of Street Runners and Sedentary People. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartoli, M.L.; Novelli, F.; Costa, F.; Malagrinò, L.; Melosini, L.; Bacci, E.; Cianchetti, S.; Dente, F.L.; Di Franco, A.; Vagaggini, B.; et al. Malondialdehyde in Exhaled Breath Condensate as a Marker of Oxidative Stress in Different Pulmonary Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witten, A.; Solomon, C.; Abbritti, E.; Arjomandi, M.; Zhai, W.; Kleinman, M.; Balmes, J. Effects of Nitrogen Dioxide on Allergic Airway Responses in Subjects with Asthma. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 47, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, R.B.; Horstman, D.P.; Gerrity, T.R.; Becker, S.; Madden, M.C.; Biscardi, F.; Hatch, G.E.; Koren, H.S. Inflammatory response in humans exposed to 2.0 ppm nitrogen dioxide. Inhal. Toxicol. 1999, 11, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, C.J.; Ozemek, C.; Carbone, S.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Blair, S.N. Sedentary Behavior, Exercise, and Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, A.P.; Andersen, L.B.; Byrne, N.M. Physical activity and obesity in children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.C.; Winters-Stone, K.; Lee, A.; Schmitz, K.H. Cancer, Physical Activity, and Exercise. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 2775–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandola, A.; Vancampfort, D.; Herring, M.; Rebar, A.; Hallgren, M.; Firth, J.; Stubbs, B. Moving to Beat Anxiety: Epidemiology and Therapeutic Issues with Physical Activity for Anxiety. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.Y.; Han, L.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Luo, S.; Hu, J.W.; Sun, K. The influence of physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marker, A.M.; Steele, R.G.; Noser, A.E. Physical activity and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2018, 37, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Lawson, K.D.; Kolbe-Alexander, T.L.; A Finkelstein, E.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; van Mechelen, W.; Pratt, M. The economic burden of physical inactivity: A global analysis of major non-communicable diseases. Lancet 2016, 388, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs-Balcom, H.M.; Grant, B.J.B.; Muti, P.; Sempos, C.T.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Browne, R.W.; Trevisan, M.; Iacoviello, L.; Cassano, P.A.; Schünemann, H.J. Oxidative Stress and Pulmonary Function in the General Population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grievink, L.; De Waart, F.G.; Schouten, E.G.; Kok, F.J. Serum Carotenoids, α-Tocopherol, and Lung Function among Dutch Elderly. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Cassano, P.A. Antioxidant nutrients and pulmonary function: The Third National Health and Nutri-tion Examination Survey (NHANES III). Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samet, J.M.; Hatch, G.E.; Horstman, D.; Steck-Scott, S.; Arab, L.; Bromberg, P.A.; Levine, M.; McDonnell, W.F.; Devlin, R.B. Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Ozone-Induced Lung Injury in Human Subjects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schünemann, H.J.; McCann, S.; Grant, B.J.B.; Trevisan, M.; Muti, P.; Freudenheim, J.L. Lung Function in Relation to Intake of Carotenoids and Other Antioxidant Vitamins in a Population-based Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherrie, J.W.; Apsley, A.; Cowie, H.; Steinle, S.; Mueller, W.; Lin, C.; Horwell, C.J.; Sleeuwenhoek, A.; Loh, M. Effec-tiveness of face masks used to protect Beijing residents against particulate air pollution. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, D.; Korytny, A.; Isenberg, Y.; Marcusohn, E.; Zukermann, R.; Bishop, B.; Minha, S.; Raz, A.; Miller, A. Return to training in the COVID-19 era: The physiological effects of face masks during exercise. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, H.; Salthammer, T.; Morawska, L. Human exposure to air contaminants in sports environments. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 1109–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqua, L.A.; Damasceno, M.V.; Cruz, R.; Matsuda, M.; Martins, M.G.; Lima-Silva, A.E.; Marquezini, M.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Bertuzzi, R. Exercising in Air Pollution: The Cleanest versus Dirtiest Cities Challenge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tainio, M.; de Nazelle, A.J.; Götschi, T.; Kahlmeier, S.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; de Sá, T.H.; Kelly, P.; Woodcock, J. Can air pollution negate the health benefits of cycling and walking? Prev. Med. 2016, 87, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whyand, T.; Hurst, J.R.; Beckles, M.; Caplin, M.E. Pollution and respiratory disease: Can diet or supplements help? A review. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araneda, O.F.; Kosche-Cárcamo, F.; Verdugo-Marchese, H.; Tuesta, M. Pulmonary Effects Due to Physical Exercise in Polluted Air: Evidence from Studies Conducted on Healthy Humans. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072890
Araneda OF, Kosche-Cárcamo F, Verdugo-Marchese H, Tuesta M. Pulmonary Effects Due to Physical Exercise in Polluted Air: Evidence from Studies Conducted on Healthy Humans. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072890
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraneda, Oscar F., Franz Kosche-Cárcamo, Humberto Verdugo-Marchese, and Marcelo Tuesta. 2021. "Pulmonary Effects Due to Physical Exercise in Polluted Air: Evidence from Studies Conducted on Healthy Humans" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072890
APA StyleAraneda, O. F., Kosche-Cárcamo, F., Verdugo-Marchese, H., & Tuesta, M. (2021). Pulmonary Effects Due to Physical Exercise in Polluted Air: Evidence from Studies Conducted on Healthy Humans. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11072890





