Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution in Lightweight Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- It extracts useful spatial information in proportion to the interval of all feature maps to remove spatial features with similar features to reduce redundancy and the amount of calculation.
- It maintains the useful information when downsampling compared to the existing method of reducing spatial information to a one-dimensional vector.
- Through the verification of different types of networks of different widths, it was found that our method effectively reduced the value of floating-point operations per second (FLOPs) and improved the accuracy of the standard lightweight network and dynamic network.
2. Related Works
2.1. Efficient Work
2.2. Dynamic Neural Networks (DyNet)
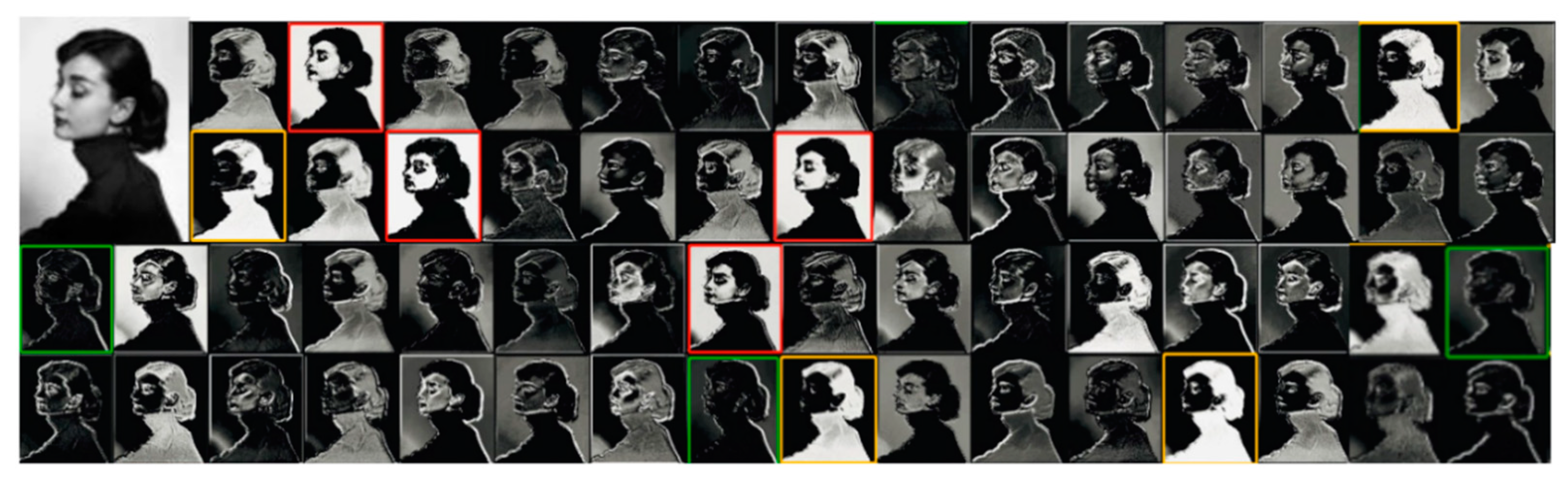
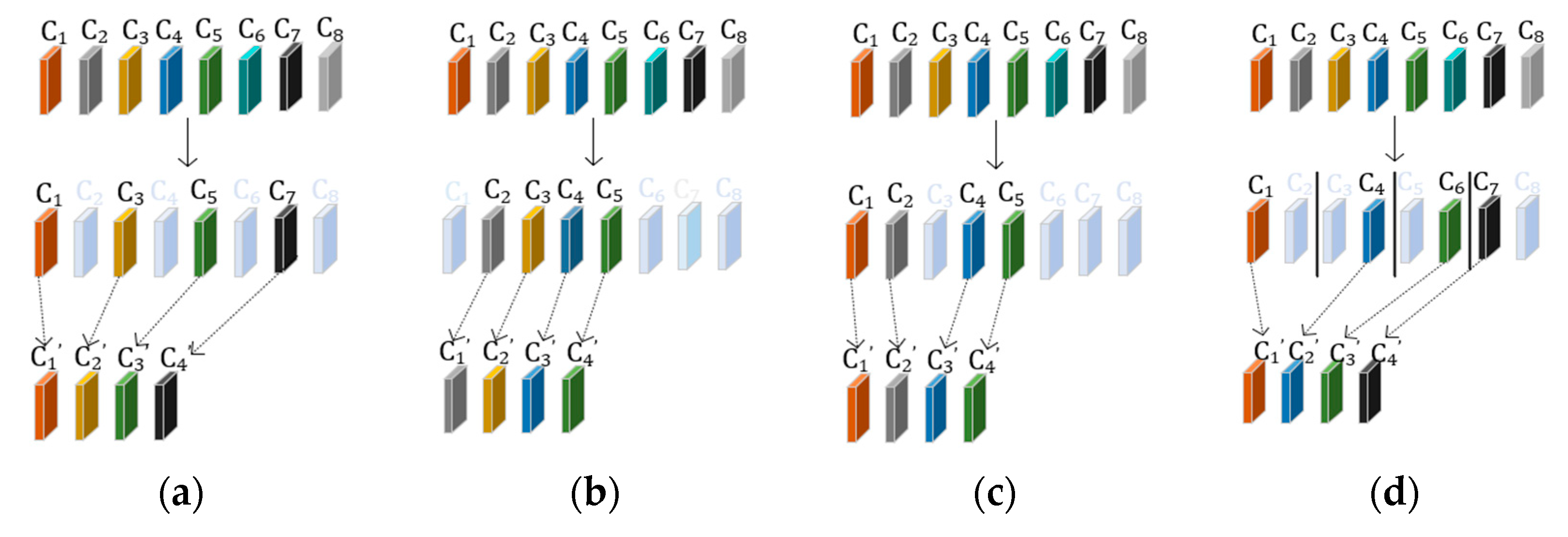
2.3. The Channel Redundancy in Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
3. Proposed Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution Network (EAM-DyNet)
3.1. Lightweight Neural Networks
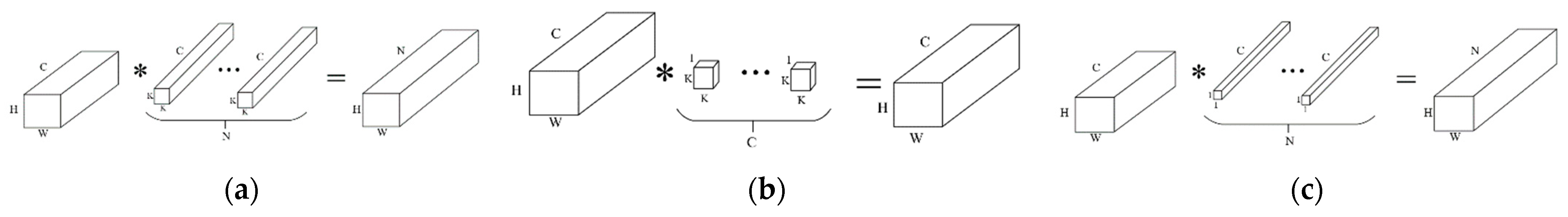
3.2. The Standard Model of Dynamic Network
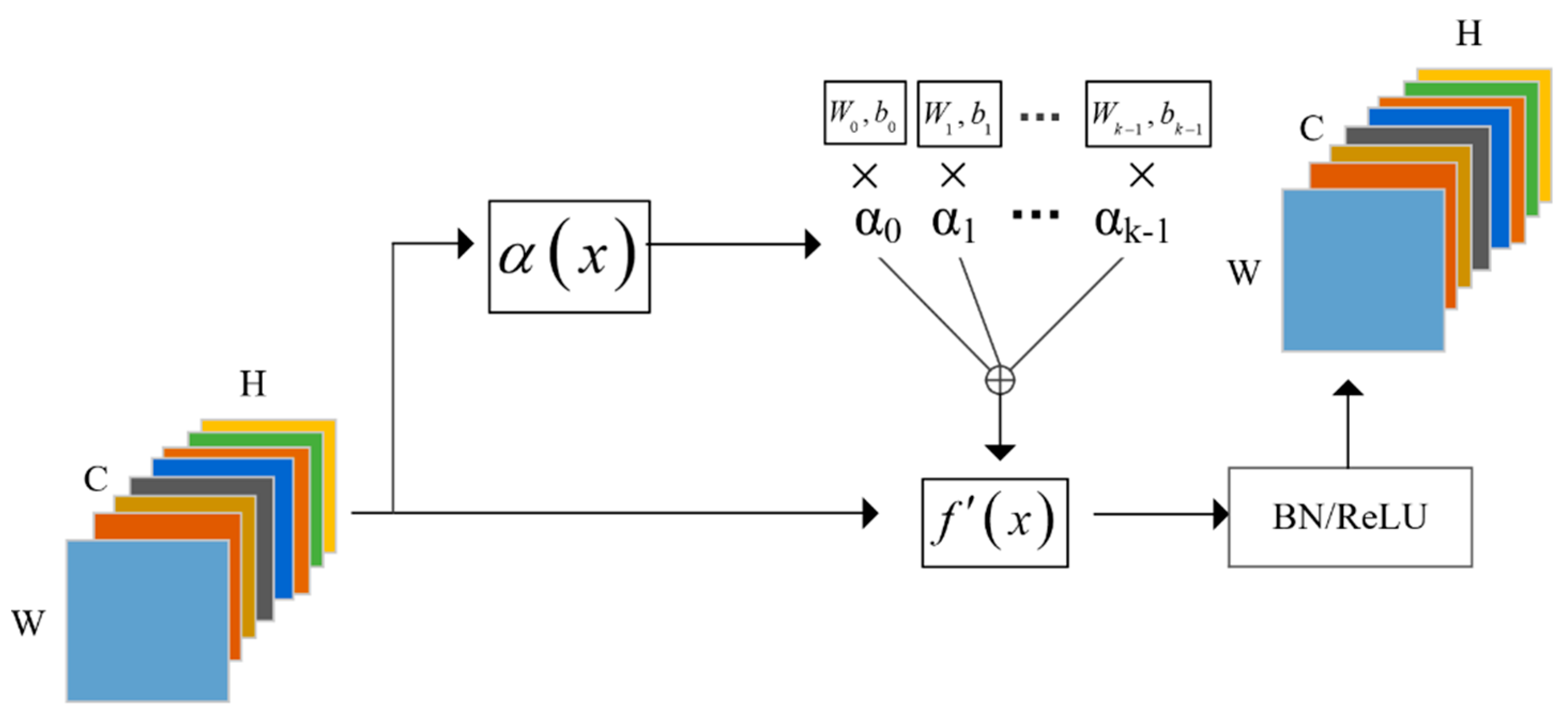
3.3. Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution Network (EAM-DyNet)
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. CIFAR10 and CIFAR100
4.1.2. ImageNet100
4.1.3. Baseline
4.1.4. Model
4.2. Numerous Results
4.2.1. Baseline Results
4.2.2. Ablation Studies Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, W.; Ding, E.; Garcia-Ortiz, A. EPKF: Energy efficient communication schemes based on Kalman filter for IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 6201–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–4 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.L.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Bender, G.; Le, Q.V.; Ngiam, J. CondConv: Conditionally parameterized convolutions for efficient inference. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32, Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, NeurIPS 2019, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alche-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R., Eds.; NeurIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Z. DyNet: Dynamic convolution for accelerating convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10694. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Dynamic convolution: Attention over convolution kernels. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.03458. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50× fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Wan, A.; Yue, X.; Jin, P.; Zhao, S.; Golmant, N.; Gholaminejad, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Keutzer, K. Shift: A zero FLOP, zero parameter alternative to spatial convolutions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.08141. [Google Scholar]
- Sifre, L.; Mallat, S. Rigid-motion scattering for texture classification. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1403.1687. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Le, Q.V. MnasNet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2815–2823. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Le, Q.V. Neural architecture search with reinforcement learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01578. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.-J.; Howard, A.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Go, A.; Sandler, M.; Sze, V.; Adam, H. NetAdapt: Platform-aware neural network adaptation for mobile applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Zhu, L.; Han, S. ProxylessNAS: Direct neural architecture search on target task and hardware. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.00332. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mu, H.; Heng, W.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Single path one-shot neural architecture search with uniform sampling. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.00420. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8697–8710. [Google Scholar]
- Real, E.; Aggarwal, A.; Huang, Y.P.; Le, Q.V. Regularized evolution for image classifier architecture search. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2019), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January 27–1 February 2019; pp. 4780–4789. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Simonyan, K.; Yang, Y. DARTS: Differentiable architecture search. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.09055. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Zheng, H.; Liu, C.; Lin, L. SNAS: Stochastic neural architecture search. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.09926. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, D.; Amthor, M. Rethinking depthwise separable convolutions: How intra-kernel correlations lead to improved MobileNets. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14588–14597. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Rao, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J. Runtime neural pruning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, NeurIPS 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; NeurIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Deng, J. Dynamic deep neural networks: Optimizing accuracy-efficiency trade-offs by selective execution. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-18), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, F.; Dou, Z.-Y.; Darrell, T.; Gonzalez, J.E. SkipNet: Learning dynamic routing in convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 420–436. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Nagarajan, T.; Kumar, A.; Rennie, S.; Davis, L.S.; Grauman, K.; Feris, R. BlockDrop: Dynamic inference paths in residual networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8817–8826. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Chen, D.; Li, T.; Wu, F.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Multi-scale dense networks for resource efficient image classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09844. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Huang, T. Universally slimmable networks and improved training techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–4 November 2019; pp. 1803–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Gan, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Han, S. Once-for-all: Train one network and specialize it for efficient deployment. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.09791. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Graves, A.; Antonoglou, I.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M. Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.5602. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, M.-T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.04025. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1577–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Han, J.n.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, S.-h.; Men, A. Split to be slim: An overlooked redundancy in vanilla convolution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.12085. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Wide residual networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.07146. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Wei, L.; Yangqing, J.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]


| Network | CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | ImageNet100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | |
| MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 93.83 | 74.41 | 75.27 |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 93.99 | 74.76 | 75.94 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 + RCR | 93.61 | 74.83 | 76.37 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 + CGR | 93.93 | 75.21 | 76.11 |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.75 | 93.50 | 73.54 | 74.14 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.75 + RCR | 93.49 | 73.88 | 74.67 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.75 + CGR | 93.55 | 74.04 | 74.51 |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.5 | 93.15 | 72.31 | 72.27 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.5 + RCR | 92.70 | 72.85 | 72.93 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.5 + CGR | 92.78 | 72.42 | 72.15 |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.25 | 91.14 | 68.30 | 66.76 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.25 + RCR | 91.01 | 68.61 | 68.50 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 0.25 + CGR | 91.12 | 68.71 | 67.25 |
| MobilenetV2 × 1.0 | 93.60 | 74.90 | 77.66 |
| DyNet MobilenetV2 × 1.0 | 94.09 | 75.50 | 78.11 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV2 × 1.0 + RCR | 94.07 | 75.23 | 78.67 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV2 × 1.0 + CGR-MAX | 94.22 | 75.44 | 78.26 |
| DyNet MobilenetV3_small × 1.0 | 91.97 | 73.10 | 69.22 |
| EAM-DyNet MobileneV3_small × 1.0 + RCR | 91.93 | 72.14 | 69.65 |
| EAM-DyNet MobileneV3_ small × 1.0 + CGR-MAX | 92.13 | 72.42 | 70.64 |
| MobilenetV3_large × 1.0 | 93.70 | 75.20 | 76.36 |
| DyNet MobilenetV3_large × 1.0 | 94.15 | 75.03 | 76.37 |
| EAM-DyNet MobileneV3_large × 1.0 + RCR | 94.00 | 74.77 | 76.62 |
| EAM-DyNet MobileneV3_large × 1.0 + CGR-MAX | 94.20 | 75.15 | 76.37 |
| Network | ImageNet100 Top-1 (%) | Parameters | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 75.94 | 14.27M | 589.70M |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 + RCR | 76.37 (+0.43) | 12.89M (−9.6%) | 583.55M |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 + CGR | 76.11 | 12.89M (−9.6%) | 583.55M |
| DyNet MobilenetV2 × 1.0 | 78.11 | 11.25M | 336.34M |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV2 × 1.0 + RCR | 78.67 (+0.56) | 8.98M (−20.17%) | 327.42M |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV2 × 1.0 + CGR | 78.26 | 8.98M (−20.17%) | 327.42M |
| The Number of Channels (RCR) | CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | ImageNet100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 93.99 | 74.76 | 75.94 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (2 channels) | 93.95 | 74.50 | 75.78 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (4 channels) | 93.61 | 74.83 | 76.37 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (8 channels) | 94.07 | 74.70 | 75.45 |
| The Methods of Channels Selection | CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | ImageNet100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 93.99 | 74.76 | 75.94 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 (take every 4 channels) | 93.72 | 74.84 | 76.58 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (0~1/4C) | 93.79 | 74.38 | 75.92 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (1/4C~1/2C) | 93.90 | 75.18 | 75.20 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (1/2C~3/4C) | 93.62 | 75.03 | 75.80 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (3/4C~C) | 94.03 | 74.99 | 76.23 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0(RCR) | 93.61 | 74.83 | 76.37 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0(CGR) | 93.93 | 75.21 | 76.11 |
| Network | ImageNet100 Top-1 (%) | Parameters | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (1/4C) | 76.58 | 13.48M | 585.17M |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 + RCR | 76.37 | 8.98M | 583.55M |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 + CGR | 76.11 | 8.98M | 583.55M |
| The Selection of Pooling | CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | ImageNet100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 93.99 | 74.76 | 75.94 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (AdaptAvgPool) | 93.61 | 74.83 | 76.37 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (AdaptMaxPool) | 93.89 | 74.91 | 76.50 |
| The Output Size of AdaptAvgPool | CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | ImageNet100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | Top-1 (%) | |
| DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 | 93.99 | 74.76 | 75.94 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (3 × 3) | 94.08 | 74.56 | 75.84 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (5 × 5) | 93.61 | 74.83 | 76.37 |
| EAM-DyNet MobilenetV1 × 1.0 (7 × 7) | 93.73 | 74.27 | 76.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, E.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, W. Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution in Lightweight Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073111
Ding E, Cheng Y, Xiao C, Liu Z, Yu W. Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution in Lightweight Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073111
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Enjie, Yuhao Cheng, Chengcheng Xiao, Zhongyu Liu, and Wanli Yu. 2021. "Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution in Lightweight Neural Network" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073111
APA StyleDing, E., Cheng, Y., Xiao, C., Liu, Z., & Yu, W. (2021). Efficient Attention Mechanism for Dynamic Convolution in Lightweight Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073111





