Numerical Control Machine Optimization Technologies through Analysis of Machining History Data Using Digital Twin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Cutting Condition and Machining Quality
2.2. Cutting Dynamics
2.3. Chatter Diagnosis
2.4. Digital Twin
3. Design and Implementation
3.1. Manufacturing Digital Twin for Dedicated Equipment
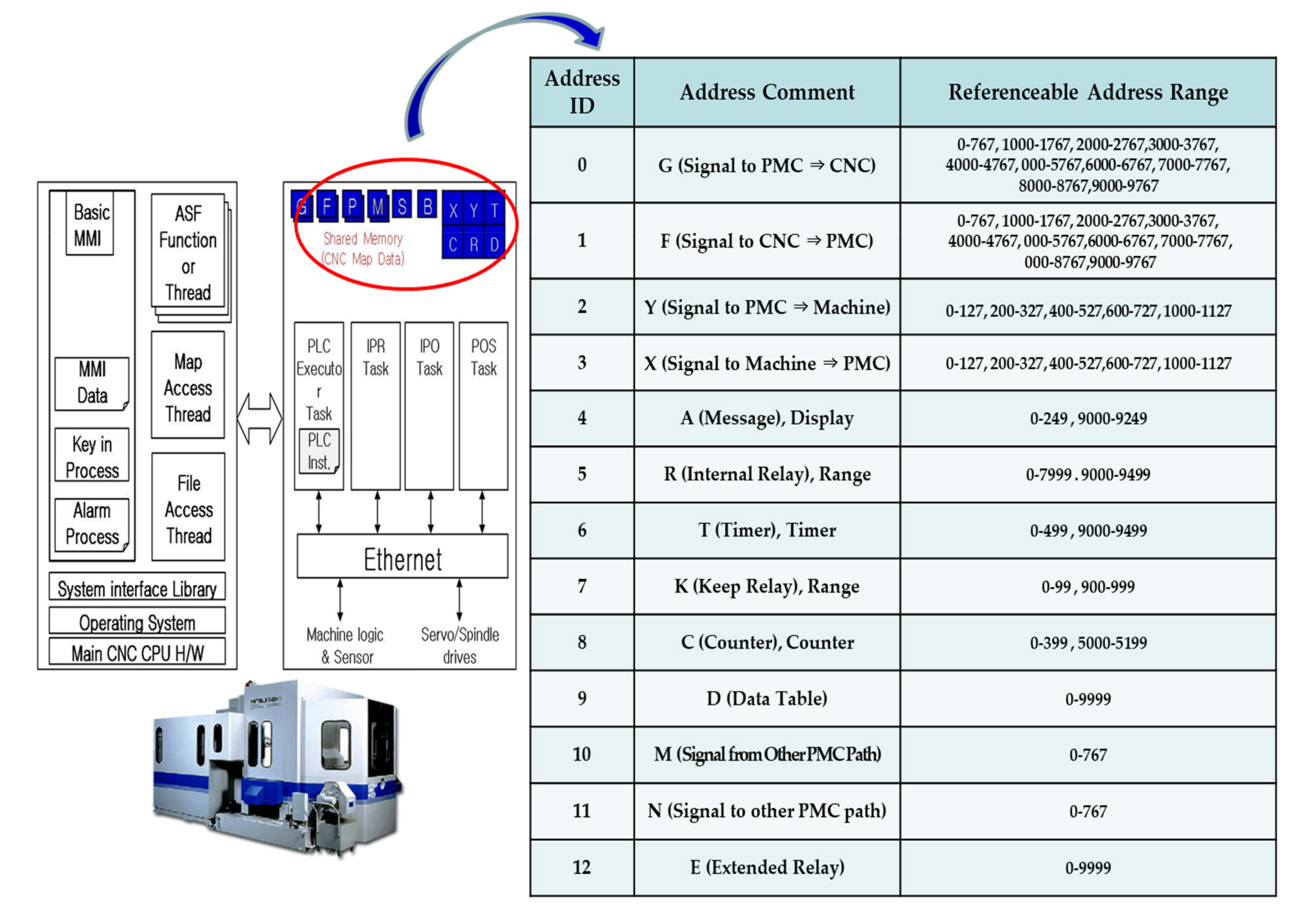
3.2. Sensor Data Synchronization
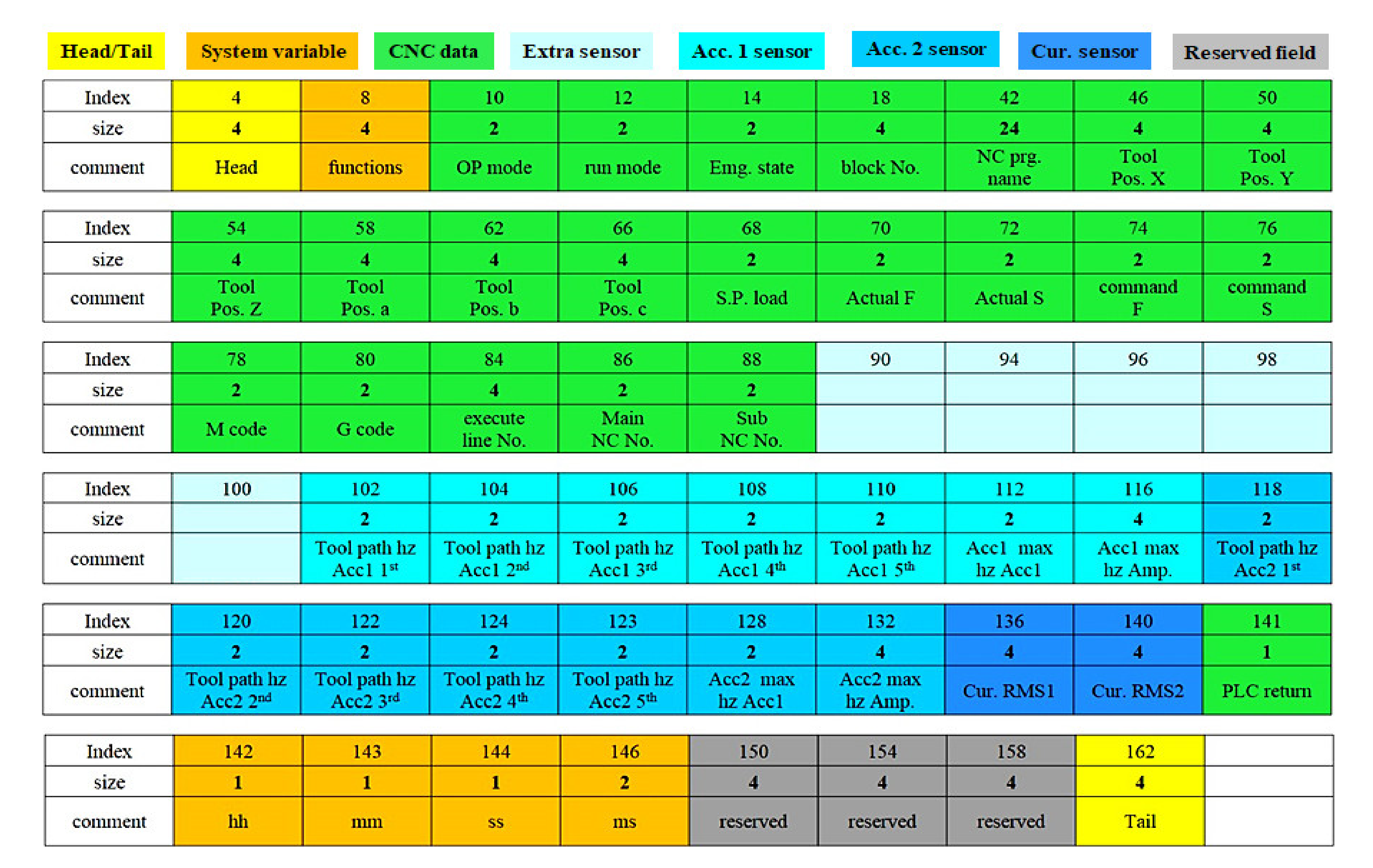
3.3. CNC Information and Acceleration Sensor
3.4. CNC Information and Current Sensor
3.5. Storage of Machining History File
4. Machining History Analysis and Optimization
4.1. Linear Interpolation Based on User-Input Maximum Load
4.2. Machining History-Based Optimization Flowchart
5. Experiments and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yusuf, A. Manufacturing Automation: Metal Cutting Mechanics, Machine Tool Vibration and CNC Design, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.K.; Yoon, M.C.; Ha, M.K.; Sim, S.B. A Study on the Behaviors of Chatter in Milling Operation. J. Korean Soc. Manuf. Technol. 2002, 1, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, W. Chatter Stability of Micro end Milling by Considering Process, Nonlinearities and Process Damping. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 2785–2796. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, M.C.; Chin, D.H. Time Series Modeling and Spectrum Analysis for Chatter Mode in Endmilling Dynamics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 20, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Signal Acquisition for Effective Prediction of Chatter Vibration in Milling Processes. J. Korean Soc. Manuf. Technol. Eng. 2014, 23, 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Mahr, F.; Wagner, U.; Uhlmann, E. Chatter Frequencies of Micromilling Processes: Influencing Factors and Online Detection via Piezoactuators. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2012, 56, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, N.S.; Yang, M.Y. Analytical Prediction of Chatter Vibration in Milling Process. J. Korean Soc. Mech. Eng. 2009, 33, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VERICUT. Available online: https://www.cgtech.com/ (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- MACHPRO. Available online: https://www.malinc.com/products/machpro/ (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Altintas, Y.; Kersting, P.; Biermann, D.; Budak, E.; Denkena, B.; Lazoglu, I. Virtual Process System for Part Machining Operations. Cirp Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 63, 585–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Coma, O.; Paul, J. Reverse Engineering for NC Machining Simulation. In Proceedings of the IDMME 2010-Visaul Concept 2010, Bordeaux, France, 20–22 October 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Nassehi, A.; Newman, S.T. Feature Recognition from CNC Part Programs for Milling Operations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, H.; Guan, L.; Hua, Y.; Wang, X. Study on the Technology of Cutting Force Simulation for NC Machining Process Based on the Secondary Development of VERICUT. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2012, 5, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Research and Development of Optimization of NC Machining Parameters. Aeronaut. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 22, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cus, F. The Inclusion of Geometrical Shape of the Cutter into the Optimization of the Milling Process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2000, 16, 392–403. [Google Scholar]
- Dolinsek, S. Interrelation between Cutting Mechanics and Machinability Parameters. Drill. Austenitic Stainl. Steels Met. 2000, 54, 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Vajde Horva, R.; Welzer Druzovec, T.; Rozman, I.; Sokovic, M. An Evaluation of Process Complexity. Stroj. Vestn. 2001, 47, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Altintas, Y.; Budak, E. Analytical Prediction of Stability Lobes in Milling. Ann. CIRP 1995, 44, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Industry 4.0 and the Digital Twin. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/focus/industry-4-0/digital-twin-technology-smart-factory.html (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Agnusdei, G.P.; Elia, V.; Gnoni, M.G. A Classification Proposal of Digital Twin Applications in the Safety Domain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 107–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, M. Digital Twin Shop-Floor: A New Shop-Floor Paradigm towards Smart Manufacturing. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20418–20427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Liu, J.; Xiong, H. Digital Twin-based Smart Production Management and Control Framework for the Complex Product Assembly Shop-Floor. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Qi, Q. Digital Twin and Big Data towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar]
- Botkina, D.; Hedlind, M.; Olsson, B.; Henser, J.; Lundholm, T. Digital Twin of a Cutting Tool. Procedia CIRP 2018, 72, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, J.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, M.; Sui, F. Digital Twin-Driven Product Design, Manufacturing and Service with Big Data. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 3563–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzinber, W.; Karner, M.; Traar, G.; Henjes, J.; Sihn, W. Digital Twin in Manufacturing: A Categorical Literature Review and Classification. IFAC-Pap. 2018, 51, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao., F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, A.; Nee, A.Y.C. Digital Twin in Industry: State-of-the-Art. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenov, Y.; Bustillo, A.; Mikolajczyk, T. Artificial Intelligence for Automatic Prediction of Required Surface Roughness by Monitoring Wear on Face Mill Teeth. J. Intell. Manuf. 2018, 29, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, A.; Pimenov, Y.; Mia, M.; Kaplonek, W. Machine-learning for Automatic Prediction of Flatness Deviation Considering the Wear of the Face Mill Teeth. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Shin, G.S.; Hong, S.D.; Yoo, N.H. A Study on the Control System of Lower Ram Operation by the Upper Ram Position of Powder Molding Press. In Proceedings of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers Spring Conference, Yeosu-si, Korea, 19–20 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, N.H. Design and Implementation of OPC-Based Intelligent Precision Servo Control Powder Forming Press System. J. Korean Inst. Electron. Commun. Sci. 2018, 13, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, N.H. A Heat Shock Simulation System for Testing Performance of EWP. J. Korean Inst. Electron. Commun. Sci. 2019, 14, 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Gwon, D.H.; Lee, J.S.; Yoo, N.H. An Automotive Industry Vision Inspection System using Big Data Analytic System. In Proceedings of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering Spring Conference, Daejeon-si, Korea, 23–25 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, N.H. A Study of Leakage Inspection System for EWP. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Electrical Engineering Technology, Penang, Malaysia, 25–27 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, C.S.; Heo, E.Y.; Moon, D.H.; Park, C.S. A Study on the Monitoring Method of Internal Barrel Temperature in Injection Molding Machine. In Proceedings of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering Spring Conference, Jeju-si, Korea, 29–31 May 2013; pp. 699–700. [Google Scholar]





















| Tool Index | Specification | Cutting Condition |
|---|---|---|
| D100 | Helix Angle 30°, 6-tooth insert face cutter, Carbide insert, Korloy insert | RPM 4000/Feed rate 2500 |
| D25 | Helix Angle 30°, 2-tooth insert end mill, Carbide insert, Korloy insert | RPM 4000/Feed rate 3000 |
| D16 | Corner radius 3.0, Helix angle 30°, Round end mill, 2-flute, Carbide | RPM 4000/Feed rate 3500 |
| D16R3 | Helix Angle 30°, Flat end mill, 2-Flute, Carbide | RPM 4000/Feed rate 3000 |
| Sensor | Input | Output | Sensitivity | Sampling Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current | 24 V | 0~5 [V]/0–20 [mA] | 100 [mV/A] | 2 K[Hz] |
| Accelerometer | 5 V | ±5 V | 100 [mV/g] | 51 K[Hz] |
| Parameters | D100 | D25 | D16 | D16R3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Speed Override [%] | 80% ≤ S ≤ 120% | |||
| Min feed rate [mm/min] | 500 | |||
| Max feed rate [mm/min] | 2500 | 3000 | 3500 | 3500 |
| Non-cutting feed rate | 5000 [mm/min] | |||
| Max. Cutting Load [%] | 60 | |||
| Min. Cutting Load [%] | 6 | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| Tool Index | Chatter Frequency [Hz] | Recommend Spindle Speed [RPM] | Adopted Spindle Speed [RPM] |
|---|---|---|---|
| D100 | 366.7 | 5500.0 3667.7, 2750.0, 2200.0 | 4800 |
| D25 | 366.7 3476.7 3210.0 2120.0 … | 5500.0, 3666.7, 2750.0, 2200.0 4345.9, 3863.0, 3476.7, 3160.6 4012.5, 3566.7, 3210.0, 2918.2 5300.0, 4542.9, 2650.0, 2355.6 … | 4800 |
| D16 | 216.7 430.0 | 6500.0, 3250.0, 2166.7, 1625.0 4300.0, 3225.0, 2580.0, 2150.0 | 4800 |
| D16R3.0 | 216.7 432.0 253.3 | 6500.0, 3250.0, 2166.7, 1625.0 4275.0, 3800.0, 3420.0, 3109.1 7599.0, 3799.5, 2533.0, 1899.8 | 3600 |
| Tool | Machining Time | Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original NC Data [min] | Proposed NC Data [min] | ||
| D100 | 5:38 | 5:14 | 0.929 |
| D25 | 32:4 | 22:59 | 0.717 |
| D16R3 | 9:52 | 5:11 | 0.525 |
| D16 | 10:44 | 5:5 | 0.474 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, E.; Yoo, N. Numerical Control Machine Optimization Technologies through Analysis of Machining History Data Using Digital Twin. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073259
Heo E, Yoo N. Numerical Control Machine Optimization Technologies through Analysis of Machining History Data Using Digital Twin. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073259
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Eunyoung, and Namhyun Yoo. 2021. "Numerical Control Machine Optimization Technologies through Analysis of Machining History Data Using Digital Twin" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073259
APA StyleHeo, E., & Yoo, N. (2021). Numerical Control Machine Optimization Technologies through Analysis of Machining History Data Using Digital Twin. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073259






