Abstract
The rapid development of smart technologies and data analytics empowers most industries to evolve their systems and introduce innovative applications. Consequently, smart metering technology, an internet of things-based application service, is diffusing rapidly in the energy sector. Regardless of its associated benefits, smart meters continue to struggle from consumers’ acceptance. To promote smart meters’ successful deployment, research is needed to better understand consumers’ acceptance of smart metering. Motivated by these concerns, a smart meter acceptance model is developed to evaluate the moderation role of experience and personal innovativeness factors among residential consumers. A cross-sectional research design was used in this study. Data were collected using a self-administrated questionnaire from 318 smart meters consumers who have had experience in using it. Hypothetical relationships were assessed and validated using partial least squares structural equation modelling. The empirical findings exert the moderating role of experience and personal innovativeness of smart meter acceptance that achieved an acceptable fit with the data, and specifically, five out of nine hypotheses were supported.
1. Introduction
Smart metering technology has been used for the development of smart grids [1], in which power grid components are connected through communication networks (e.g., internet or sensor networks). Smart metering is one of the key elements of the smart grid, which can provide a solution for climate change and energy efficiency. Therefore, it was presented to the consumers as an alternative to the conventional electricity meters. Traditional electricity meters must be read by the metering worker from utility companies, while smart metering uses the Internet of things (IoT) technology which enables consumers to remotely monitor, track, control and automate the energy consumption more accurately [2,3,4,5].
Apart from just recording and tracking energy consumption, smart metering systems also have enormous advantages, including easy processing of bills, automated reading and data processing, energy loss detection, early warning for blackouts, rapid detection of energy supply interruption, potential real-time pricing schemes, energy-saving demand/response, and efficient use of generated energy [6]. Therefore, the adoption of this technology is rapidly gaining momentum, and businesses are facing various technological, social, and competitive pressures to transform and adapt. As this technology progresses and the number of adoptions increases, the smart metering technology acceptance becomes subject of great interest.
Due to the high cost and technological investments involved in smart metering technology, companies have to understand the challenges of its implementation to ensure that their resources are spent wisely. However, these companies may face negative responses due to the fact that while many innovations are beneficial to society, new risks may also be introduced [7]. As a result of these trends, public controversy and concerns are also influenced [8]. For instance, a consumer backlash against the acceptance of smart metering due to breach of privacy, health risks regarding frequency radiation and higher cost might be occurring [9]. One of the key problems that energy service providers may face and suffer from, is the low consumer acceptance, as the smart meter was reported to be one of the IoT applications that has received low acceptability from different industries in several countries in Europe and the United States [10,11,12]. Likewise, TNB, Malaysia’s largest electric utility firm, announced a low smart meter application use rate in their smart billing project, with statistics from device logs indicating that only 10% of users actively and regularly use the service [13,14]. The low usage rate of the application is indicative of the low acceptance level of using smart meter systems. A limited number of studies have determined that consumers have misperceptions about smart meters, which contributed to their low level of acceptance [9,15].
Energy efficiency and savings are among the priorities of smart meters, and these objectives are unlikely to be reached unless the problem of customer acceptance is addressed. The success of smart meter systems’ implementation is attributed to consumer acceptance that leads to actual utilisation of the system. All of the possible advantages of smart meters will only be realised if customers are able to embrace and use them. As a result, before smart meters are widely spread and installed in homes, it is critical to resolve customer concerns that may limit their adoption and usage of the technology. This could save utility providers money by avoiding the expensive effects of customer rejection and backlash after implementation, which could hinder the adoption of this new technology.
In previous work, we have evaluated the direct impact of several factors on the behavioral intention to use the smart metering system. These factors include eco-effective feedback, privacy concerns, and technology awareness, which were assessed in [16]. Furthermore, environmental awareness and electricity saving knowledge factors were investigated in [17]. The current study aims to investigate the moderation role of experience and personal innovativeness on the acceptance of smart metering technology by evaluating smart meters users who have had experience in using it. Many studies have found that previous experience with a particular technology is a key factor in evaluating technology acceptance [18,19]. This demonstrates that user’s acceptance of technology is affected by user’s experience with it. Therefore, familiarity with the intended or related technology will predict technology acceptance, whereby a user’s experience will determine if the technology is useful and simple to use. On the other hand, users with low personal innovativeness, knowledge, and involvement with the new technology do not pay attention to the effect of the new technology in achieving a task. The work of [20] found that individuals who are more innovative are likely to adopt innovation more readily than others. This confirms the fact that an innovative individual is more capable of cultivating positive attitudes towards the perceptions of using the innovation compared to a less innovative individual. The findings of this extended model will result in a greater understanding of the acceptance of smart meters from the perspective of the users. In addition, the results of this study emphasize the experience and personal innovativeness related to the use of smart meters.
The remaining of this paper is organized as the following. Section 2 explains the theoretical concept and choices behind this study, followed by Section 3, which reviews the related work, and Section 4 evaluates the research models and hypothesis. The research methodology is assessed in Section 5. The findings of the analysis are summarized in Section 6, followed by Section 7, where the results of the analysis are discussed. The implication of the findings is summarized in Section 8, and Section 9 concludes the article. Here, the study’s shortcomings are discussed, and future directions for work are proposed.
2. Theoretical Background and Concept
The main focus of this study is on users’ acceptance of smart metering technology. Hence, we found that the constructs of UTAUT2 are more appropriate because they are more closely related to consumer use, while other models, such as TAM, TAM2, and UTAUT, were not considered because they were primarily developed to demonstrate technology acceptance in an organisational context. However, the proposed technology acceptance model of smart meter is more personalized and focuses on the available services made by the smart meter system. This section introduces the UTAUT2 model and highlights its role in investigating users’ acceptance of similar technology.
2.1. The Extended Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT2)
The current literature suggests that there is a controversy surrounding the applicability of technology acceptance model (TAM) and UTAUT within the customer context [21], which contributes to its the growth. The UTAUT2 was introduced by Venkatesh et al. [18] in response to the ongoing upgrades regarding the initial model, and with the aim of catering new constructs that provide a better explanation of the latest emerging technology adoption within the context of consumer. Centered on the outcomes of a Hong Kong study, the original UTAUT model was modified by Venkatesh et al. [18], and three new constructs were used to propose the UTAUT2. These constructs are habit, price and hedonic motivation. UTAUT2 clarified 74% of the variance in the behavioral intent of customers to use a technology and 52% of the variance in the use of consumer technology [22,23].
Due to its parsimonious structure and higher explanatory power (R2), UTAUT2 was commonly used in different studies that were related to technology acceptance and use (see Table 1). These studies involve applications, replications and extensions of the whole model or part of the model that help to expand the understanding of technology adoption. The findings are shown in Table 1 which demonstrates all the studies have explanatory power (R2) greater than 50%, suggesting that the proposed factors of UTAUT2 match the model in multiple contexts.

Table 1.
Applications of UTAUT2 in different sectors.
2.2. Critiques of Technology Acceptance Models
The technology acceptance models include TAM, TAM2, and UTAUT, each model has its own limitations. For example, TAM has been tested in numerous empirical work such as [18,33,34], it was criticized for not providing an adequate information on user’s opinion regarding specific technologies and thus, requires further investigations. Another two major limitations were found in TAM related studies, including (i) the explanatory power of TAM (at an average of 40%) and (ii) the mixed relationship results between constructs, with only few studies showing significant relationships, while others were insignificant. For instance, inconsistent findings were reported in the work of [21,35] regarding the PEOU influence towards attitude, behavioural intention and actual use of technology. Hence, more models were then proposed with extensions, including human and social variables (e.g., TAM2 and UTAUT).
Regarding UTAUT, in spite of having high explanatory power as mentioned earlier, a few limitations still exist. For instance, Bagozzi [36] stated that UTAUT has not explored direct effects that could expose new relationships. In another research, it was criticised that the high coefficient of determination value of UTAUT was obtained only when the moderating key variables are present [37]. However, Dwivedi et al. [38] suggested that the proposed moderators in UTAUT should be reconsidered. They clarify the reasons behind not utilizing all the moderators by prior studies as there may not be any variation in the moderator for the adoption and use context. For example, the adoption of a particular technology may have been required by the organization in which all the individuals should use it. In this case, the voluntariness moderator may not be applicable. Another critical element missing from the UTAUT model is the individual behaviour engagement [38]. For instance, the personal characteristics that express the tendency of the individuals may be influential in showing their behaviours. The literature outlines a few personal characteristics involving computer self-efficacy, attitude, and personal innovativeness (e.g., [39,40]). UTAUT2 on the other hand is different from UTAUT, because it is developed to adapt to the context of customer use, while UTAUT is based on the organizational context. UTAUT2 has been widely accepted and used in other contexts, such as the context of consumer technologies which involve a high cost of implementation in view of the large number of technology devices, applications, and services that targeting consumers [18]. In addition, the constructs which were provided by UTAUT2 are more appropriate for consumer technology acceptance. For example, the theoretical constructs that were found to be significant for consumer decision-making in the use of technology include hedonic motivation, cost (i.e., price), and habit, which were not provided by TAM nor UTAUT.
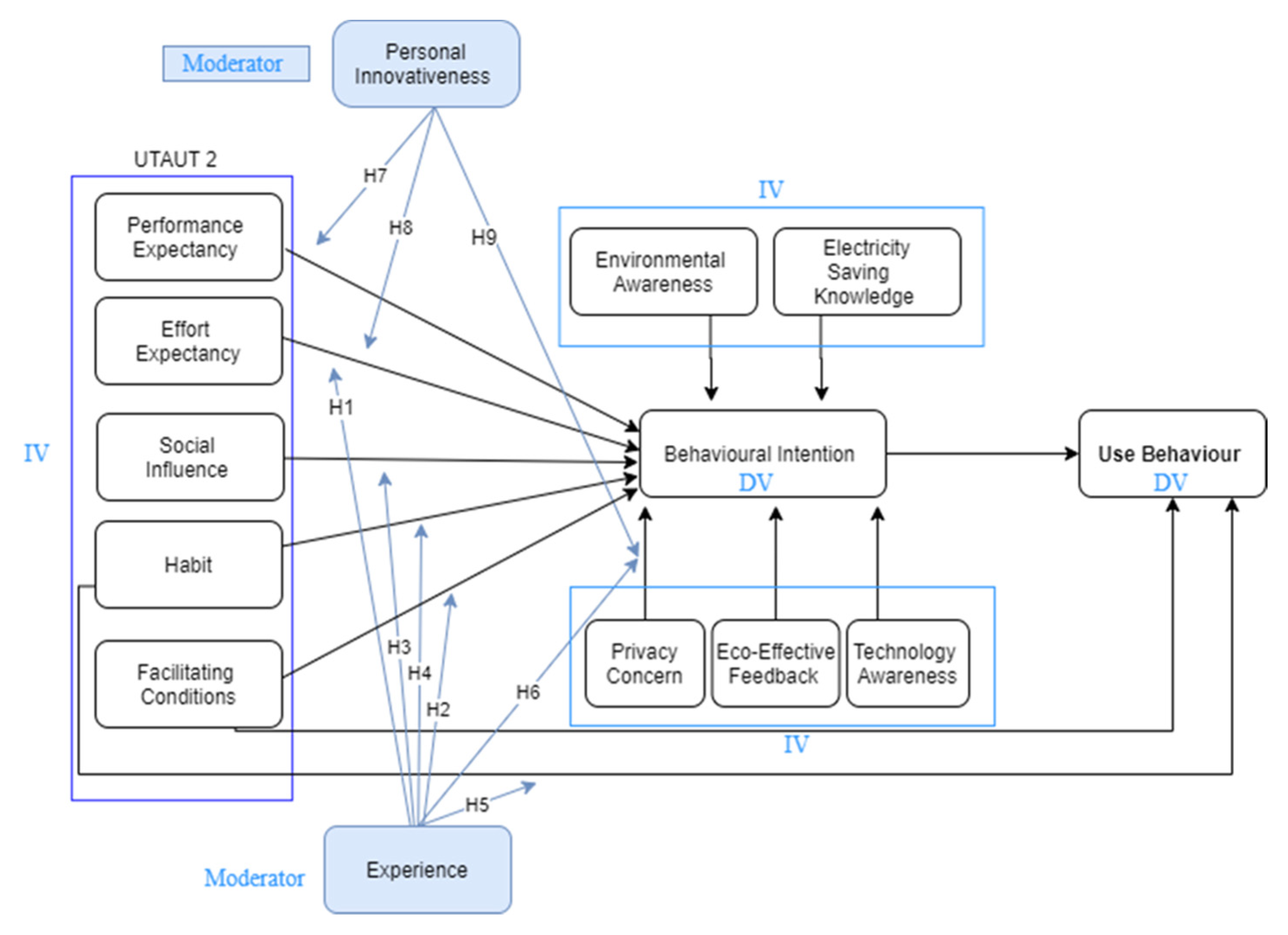
Considering the above, UTAUT2 was selected as the theoretical base for this study, where the moderating role of personal innovativeness and experience factors and their influence on consumers’ acceptance toward smart metering technology are investigated. It is worth mentioning that the UTAUT2 requires further modifications in order to suit the smart metering context as shown in our proposed model (see Figure 1).
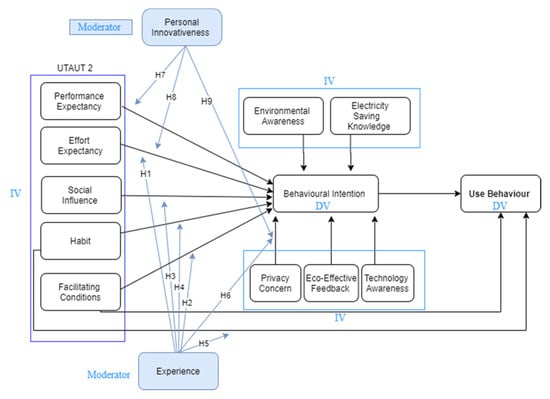
Figure 1.
Research model.
3. Related Works
The determinants of smart metering technology were thoroughly examined in recent years. However, on the basis of reviewing the related literature, it was noticed that only a limited understanding exists on the factors that influence the acceptance of smart meters. In an online survey-based research, Kranz et al. [41] applied TAM and included additional variable, such as subjective control (which refers to the ability to control a technology), in addition to perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use. This work found that perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and subjective control had a significant influence on attitude toward the use of technology. In another study, 1365 households were polled about the smart gas meter deployment [42]. The aim of the study is linking end-user characteristics (age, education, social class, and employment status) to their views on saving resources, improving home behaviour, and lowering carbon emissions. When this research was conducted, it discovered a statistically significant correlation between certain attributes of end-users and using the smart meter. The data indicate that the households’s employment status, age, and social class have statistical significance on the end-users’ variance, particularly when it comes to lowering their bill and changing their behaviour around the house.
The authors of [43] investigated the determinants of consumers’ intention to continue using smart metering technology through TAM as well. They conducted a survey to 212 smart meter customers in Southern Germany and found that perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and subjective control, and attitude toward use had a significant influence on intention to use the smart metering. Furthermore, the authors of [44] took a quantitative approach and performed several experiments to determine the motives, processes and outcomes of the development of smart grid in the South Korean context and also to identify the relationships between macroeconomic policy and the government role. The study showed that smart grid systems are being adopted by participants as a solution to climate change and energy problems. They preferred renewable energy and energy saving to address these concerns. In the same line of work, behavioural decision-making experiments to assess the perceptions of consumers in Korea was conducted by Krishnamurti et al. [9], who found that participants preferred the smart meters. However, the participants expected instant savings to be achieved. Some threats were also viewed by them, including less control over their use of electricity, privacy breaches, and higher costs. Regarding the aforementioned theories and models used in smart meters, TAM was frequently cited by several authors (e.g., [45,46]). Meanwhile, other scholars such as Tohir [32] used UTAUT2 to explore smart meters acceptance in Indonesia. The authors have not examined the experience and habit factors, as their primary concern was about the behavioural intention towards the use of smart meters rather than its actual use.
The literature review indicates that there are several opportunities for improvement in various domains. Many studies on smart meters have investigated the acceptance of individuals, yet there are limited studies that examine the exogenous factors that determine its acceptance. Table 2 illustrates and summarizes additional studies regarding the smart meter acceptance, the extracted data from these studies are based on their targeted case, observed behaviour, models used and main findings. Firstly, the targeted case represents the type of participants involved in these studies. Most of the participants were electricity consumers who were users of smart meters. However, no study has examined the users of smart meters. Secondly, the observed behaviour describes the outcome variables. Several behaviours were observed, such as intention, support, acceptance, attitude, and adoption. Furthermore, the intention to use was the dominant variable among these studies. However, no study has examined the actual use of the smart meter system. Considering the most important factors shaping smart meter acceptance, privacy, ease of use and usefulness are frequently investigated. Other significant factors that influence the behavioural intention to use smart meters, such as attitude, satisfaction, behavioural control, personal norm, energy price, health, affordability, social influence, and environmental concern, did not receive much attention. It was noticed that a few studies did not apply any theoretical base related to technology acceptance rather than just general concepts. for example, Karlin [47] reviewed reports gathered from 20 utilities in USA that were either undergoing deployment of smart meters or in the planning phase. It was concluded that effective feedback is very important for the consumer to react and use of smart meters.

Table 2.
Related studies on smart meter acceptance.
The results in [48] showed, on the other hand, a lack of understanding of energy efficiency solutions and potential for more visual, mobile, engaging, and target-driven energy data interfaces.
Addition, the findings showed the importance of technology awareness for consumers to get engage with smart meters. In the same line of study, Vassileva and Campillo [49] showed essential role of feedback in accepting the smart meter.
4. Research Model and Hypothesizes
In a prior discussion, a well-known technology acceptance theory, i.e., UTAUT2, was introduced as a theoretical base for the smart meter technology acceptance model. The semantic of the model was also discussed previously in light of the smart meter system in the energy context. The smart meter is an example of the energy sector’s IoT-based device, which is still being installed on a small scale. The device was subjected to an in-depth study of elicit variables that could have a negative effect on the acceptance of smart meter by consumers. In our previous work [16,17], in order to examine its shortcomings and benefits, an in-depth study of the smart meter system was carried out. The process resulted in a number of constraints (challenges) and advantages (benefits) that influenced the acceptance and usage of this technology by consumers. The set of identified challenges and benefits of smart meter system were translated into acceptance factors. These factors were used to extend the UTAUT2 model to fit the smart meter acceptance model and achieve a comprehensive view of the individuals regarding the IoT-based smart meter. The composition of the identified challenges and benefit factors and UTAUT2 factors are adopted in this study.
The current study investigates the moderating role of personal innovativeness and user experience toward smart meter acceptance model. This study can help to understand if these two moderators are suited for this technology acceptance within the energy domain. This will also assist in discovering the consumer’s opinion and behaviour on the system itself and explore the impact of these moderators on the acceptance factors of smart metering. This section presents the moderating variables and provide a discussion in terms of their content. The justification of the model is done based on the viewpoint of its enhancement from the base model, namely UTAUT2 [18], and its adaptation to suit the smart meter (see the work of [16,17]). However, this work does not include all moderators involved in UTAUT2, as it only uses the experience moderator from UTAUT2 and the personal innovativeness as an external moderator.
4.1. Experience
Many studies found that the use of experience in investigating a specific technology serve as an important factor to determine its acceptance. This indicates that technological acceptance is influenced by experiences. In other words, experience will say whether any technology is useful and easy to use. Hence, experience of expected or related technologies will lead to the estimation of their acceptance. Other research has shown that greater technology usage contributes to greater familiarity and that “people with more computer experience tend to have fewer negative feelings towards the technology” [60]. Venkatesh et al. [21] confirmed that new technology experience has affected the intensity of the effects of effort expectancy, social influence and the facilitating conditions of the intention to use new technology [21]. The ease of use becomes less important in predicting the user’s behavioral intentions after many years of technology experience. This led to the first hypothesis of this study:
H1.
The user’s experience of using the smart meter negatively moderates the influence of effort expectancy on behavioural intention to use the smart meter.
A meta-analysis study confirmed that users with low experience of using the technology need conditions that are more favourable than users with higher experience levels. [61]. However, in the work of [18] the moderating role of experience on the influence of facilitating conditions on behavioral intention was not found to be significant., the facilitating conditions is the degree to which a user believes that the technical infrastructure exists to support the use of smart meter. Nevertheless, in this study, since the smart meters were mounted and used for two years, the experience will be evaluated at once. Hence, it is anticipated that the influence of the experience moderator on the whole research model will be significant, especially on the effect of facilitating conditions on behaviour intention. This led to the second hypothesis of this study:
H2.
The user’s experience of using the smart meter positively moderates the influence of facilitating conditions on behavioural intention to use the smart meter.
Venkatesh et al. [21] reported that users with good experience of using the technology are less impacted by the social influence. Instead of social influence, users with a greater degree of experience are practically driven. [18]. Hence, the effect of social influence on behavior intention will decrease if the experience increases. Thus, the proposed third hypothesis of this study is as follows:
H3.
The user’s experience of using the smart meter negatively moderates the impact of social influence on behavioural intention to use the smart meter.
It was noticed that experience strengthens the habit. Limayem et al. [62] stated that due to the repeated behaviour, the relationship between experience and habit is shaped and improved [63]. The work of [64] has also reported the greater impact of habit on behavioural intention and actual use of smart metering with customers who have more experience. Hence, the experience moderator is hypothesized as follows:
H4.
The user’s experience of using the smart meter positively moderates the impact of habit on behavioural intention to use the smart meter.
With more experience, behavioral intention to use a particular technology would be decreased. Jasperson et al. [65] pointed out that having extensive experience in the use of technology would contribute to automatic routine behaviour. As experience increases, the effect of habit on the use of technology can decrease. [18]. Therefore, the experience moderator is hypothesized as follows:
H5.
The user’s experience of using the smart meter negatively moderates the impact of habit on smart meter use behaviour.
Experience develops sense of knowledge and risk awareness. Several studies have shown that more experienced consumers have greater confidence in online technology, as they know the anticipated risks involved in such technology [66,67]. Consequently, a consumer with a high degree of smart meter device experience would have a greater effect of privacy concerns on behavioral intention. Thus, the experience moderator is hypothesized as follows:
H6.
The user’s experience of using the smart meter positively moderates the influence of privacy concerns on behavioural intention to use the smart meter.
4.2. Personal Innovativeness
Many researchers have concluded that personal innovativeness can influence conception through the use of new technology [68]. The work of [69,70] suggested that in the IT sense, personal innovativeness may play the role of a moderating variable on the factors which form the perception to adopt a specific technology, and they concluded that there is a need for further studies to examine the personal innovativeness as a moderator with different samples and IT innovations. Xu and Gupta [20] found that people who are more innovative are likely to accept technology more quickly than others. This reinforces the fact that an innovative person is more capable of cultivating optimistic attitudes relative to others towards the expectations of using innovation. Thus, the effect of performance expectancy on behavioural intention is more visible among innovative individuals. Similarly, effort expectancy has greater effects on behavioural intention to use smart meter among innovative individuals compared to less innovative individuals. This has led us to the following hypotheses:
H7.
The user’s personal innovativeness positively moderates the influence of performance expectancy on behavioural intention to use smart meter.
H8.
The user’s personal innovativeness positively moderates the influence of effort expectancy on behavioural intention to use smart meter.
A number of studies have shown that risk and uncertainty are related to any innovation [69,71]. For example, Xu and Gupta [20] believed that “personal innovativeness characterizes the risk-taking tendency of some individuals and not others”. However, we believe, there are some risks when using smart meters, in particular with regard to user’s personal data, which may be made available without permission to other parties. There is a greater likelihood that more knowledgeable users are more likely to face higher privacy threats in a way that will impact the perception of the service provider. Therefore, the impact of privacy on the behavioral intention of using the smart meter system tends to be more apparent to innovative people relative to less innovative people. Thus, the personal innovativeness moderator is hypothesized as follows:
H9.
The user’s personal innovativeness positively moderates the influence of privacy concern on behavioural intention to use smart meter.
The current research model for investigating the moderating role of experience and personal innovativeness of smart meter acceptance (see Figure 2) is developed by incorporating the constructs from UTAUT2 and the constructs originating from our previous work, which examined the benefit factors [17], and explored the challenge factors related to smart meters acceptance [16].
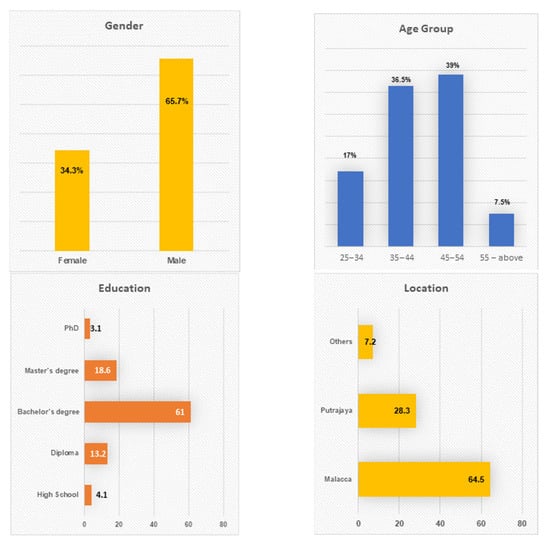
Figure 2.
Descriptive analysis.
5. Method and Materials
5.1. Development of Measures
In the proposed research model, the initial items for the scales were adopted from the literature and modified to suit the smart meter system context.
Hence, before the development of theinstrument’s measurements for the research model, a review of literature was carried out to gather an extensive list of measures to include in the form of scales that were generated and validated previously. Measures were adapted from UTAUT2.
5.2. Survey Design
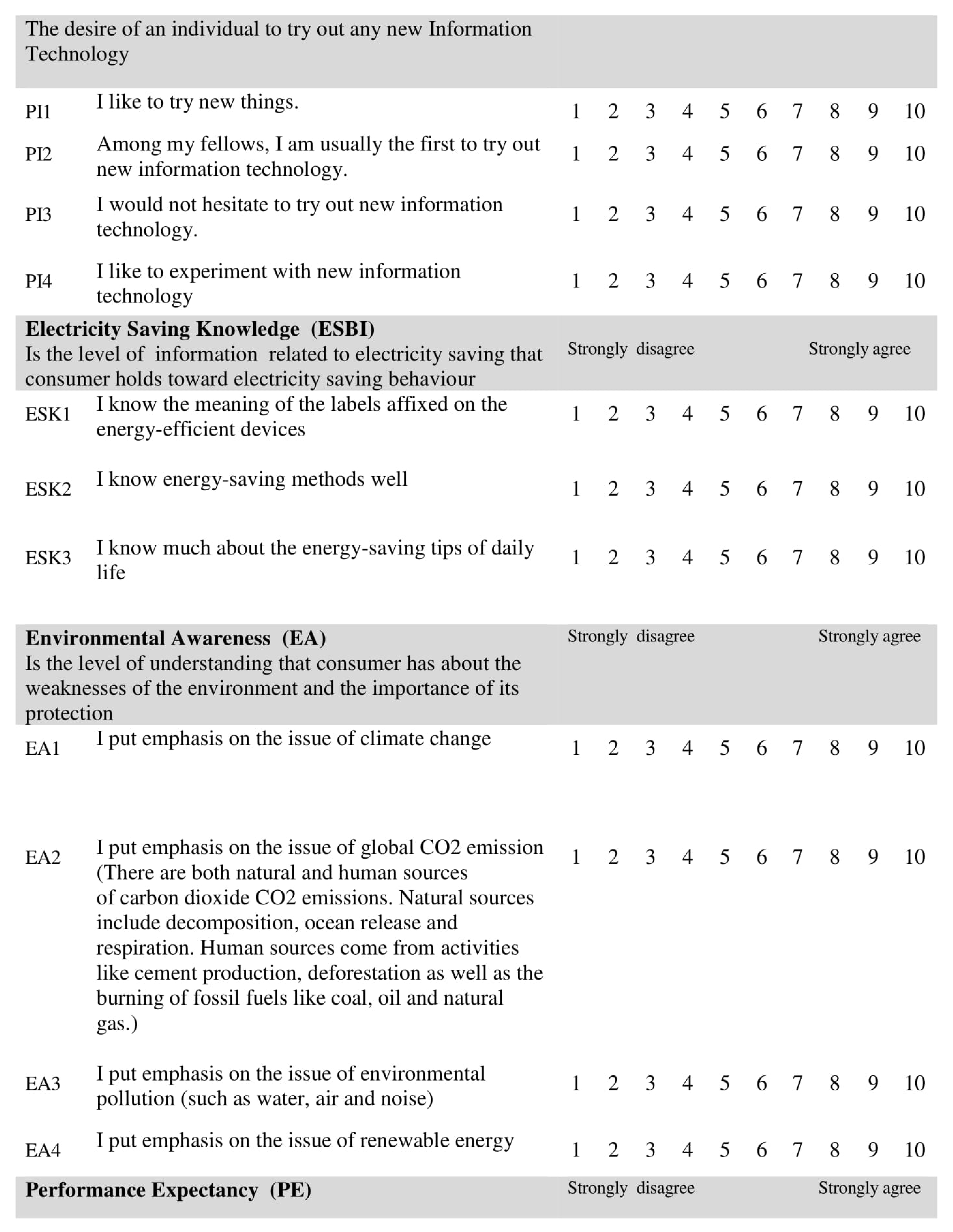
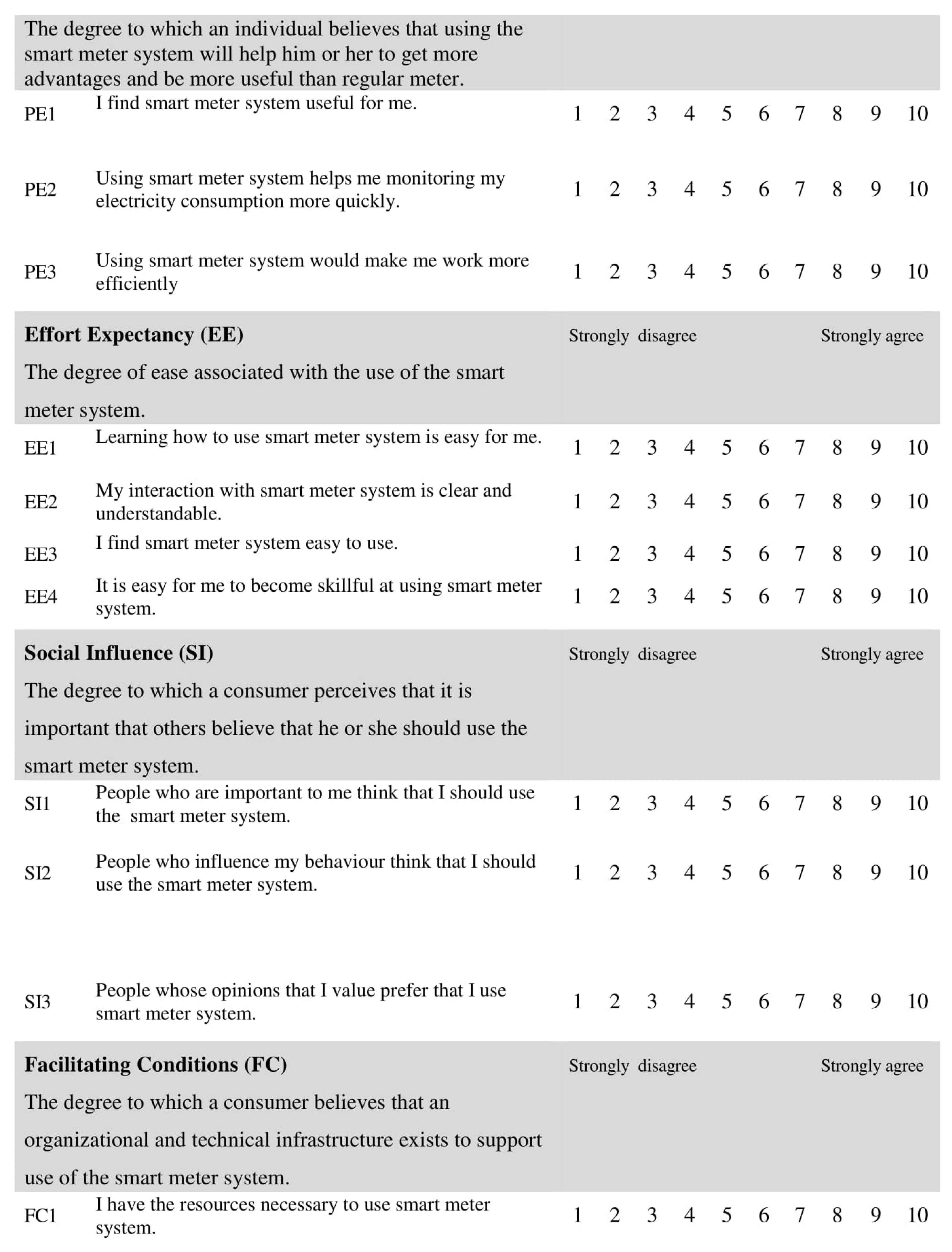
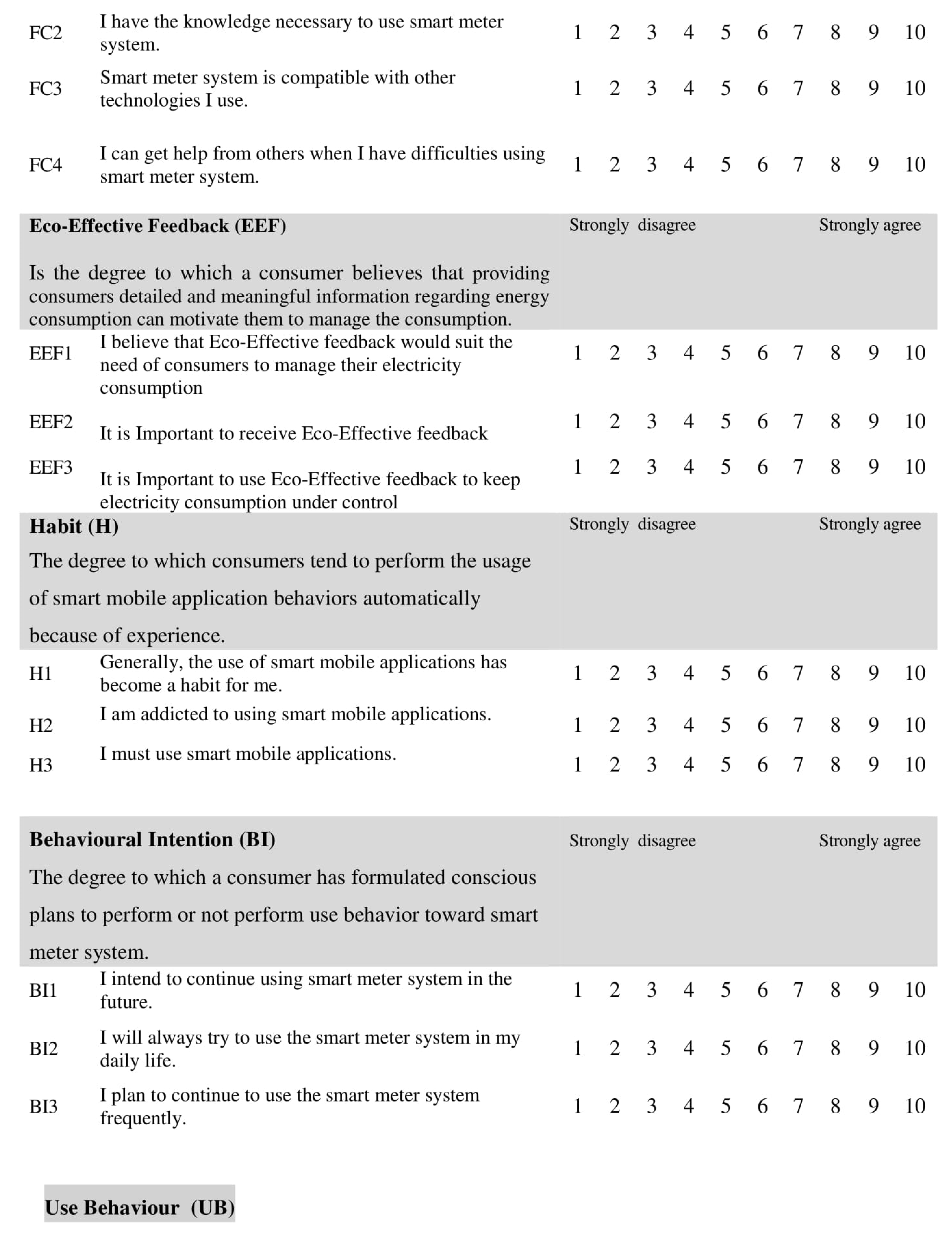
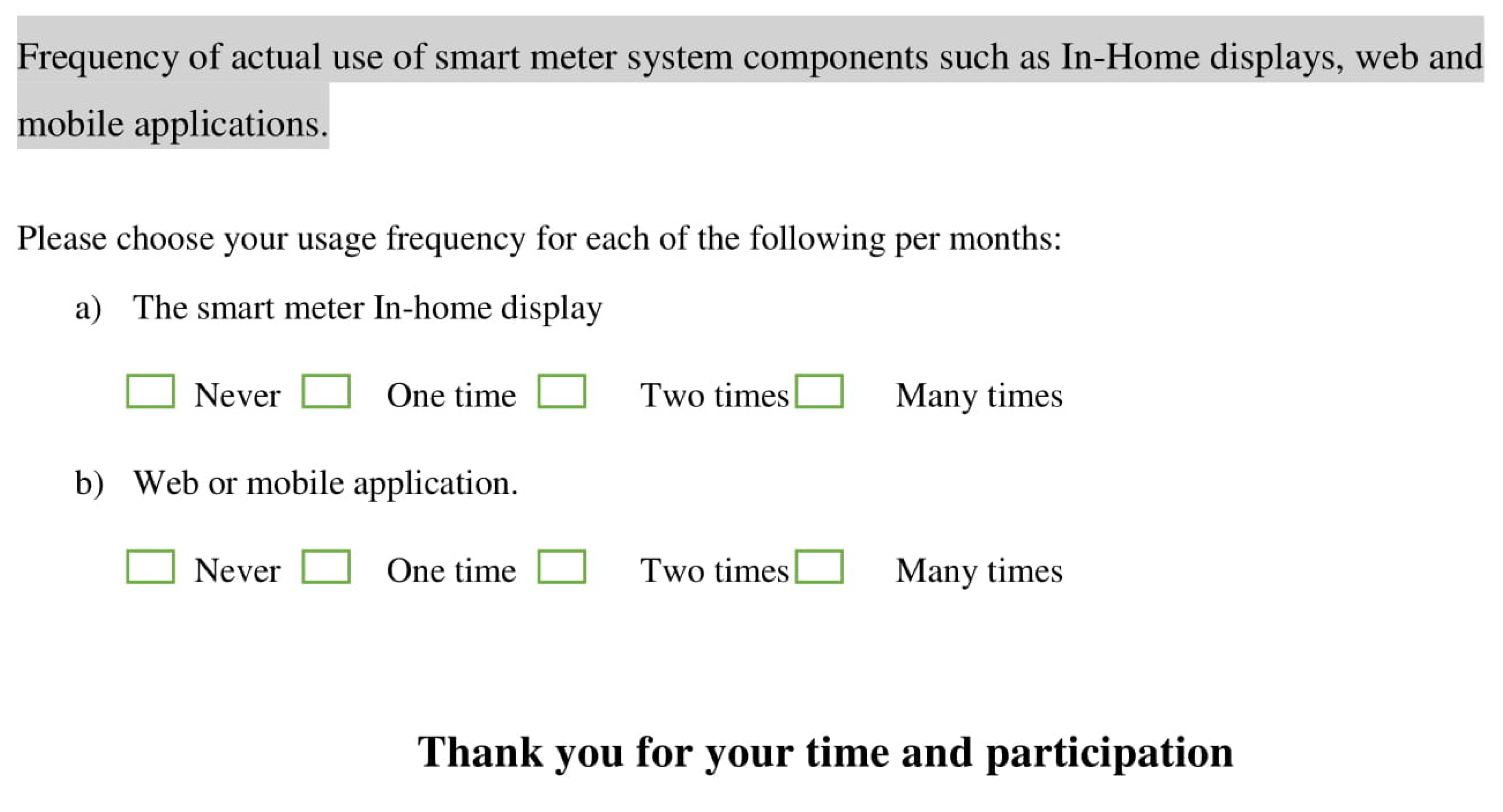
Most of the items, used a ten-point Likert scale ranging from (1) “strongly disagree” to (10) “strongly agree,” to assess the independent variables (IV) and behavioral intention. Related scales of the five-point and seven point Lickert were used in IS research primarily in the adoption and acceptance of IS/IT. In the work of [72], the 10-point Likert scale has been found to be more preferable than others because both measurement and structural models can expect more success in evaluating the validity of the construct.
In addition, a 10-point Likert provides better opportunity to detect changes, and provides more variance than a smaller Likert scale [73]. The questionnaire included closed questions only. Each construct was enclosed with its definition to guarantee that the participants interpret the questionnaire items correctly (see Appendix A).
Four academic experts and one expert from the industry were involved to verify if the items represent the variables correctly and their degree of redundancy. The experts’ validations results stated that all the items had a congruency percentage (ACP) for the constructs higher than 90%, hence the acceptability standard was achieved.
To ensure that the instruments reached most of targeted participants this research tended to give choices to answer in two languages (English and local language). An academic translator translated the instrument from English to the local language to ensure the accuracy of the translations. A pilot analysis was performed in the last stage of the instrument development process to test the validity of measurement items in the survey.
In the survey instrument, the reliabilities scales were examined. A sample of 40 electricity consumers from Malaysia was surveyed in this pilot study, with the help of Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB). Using the internal consistency test Cronbach’s alpha (CA), the reliability of the measured items used in the survey was tested and composite reliability (CR), which show an excellent value that indicates an acceptable level and ideal internal quality of the model.
5.3. Sampling
In this study, each individual who uses the smart meter system is a part of the population. Thus, the individual customer or user who was currently using the smart meter system was selected. The management of smart meter project had the lists and other related information about customers. TNB launched the smart metering project to handle implementation program of smart meter systems. The management of smart meter project had the lists and other related information about customers. According to the users’ data provided by TNB, there were 698 users registered in the smart meter systems. The provided list consisted of 954 consumers. However, upon checking the list, 256 records were removed due to the duplication of records. This appeared because some consumers had more than one unit registered under their same name.
In deciding on the minimum sample size required to fit this research, a few issues were discussed and set as conditions to define the sample size. First, this research used the structural equation modelling (SEM) technique to analyze the data, which requires careful attention to the sample size [74]. Several researchers argued that in studies where SEM was used, the average sample size should be around 200 cases [75], which reflects the approximate median sample size in published studies up to 2006 [76].
Secondly, on the basis of population size, Saunders et al. [77] further noted that the study requires 217 research participants as the minimum sample size obtained from the population of 698 in order to achieve a 5% error margin and a 95% degree of certainty. Finally, based on the findings above and comparing to the previous studies related to technology acceptance, it was concluded that the sample size required to fit this study should be greater than 220 cases.
5.4. Data Collection
The TNB Smart Meter Project provided information that only contained the consumer name and email. Addresses and contact numbers were not provided. Hence, postal and telephone surveys were not suitable in this particular case–only personal administered questionnaire, and electronic questionnaires survey were possible given the information provided.
The Smart Meter Project set out several initiatives in various states to promote the smart metering awareness among the consumers and these initiatives called for personally administered questionnaire with participants.
The questionnaire administration was started through an email survey on October 2017 and was completed by March 2018. This was conducted during the TNB Smart Meter Project’s public events in two states. Upon questionnaire distribution, some of the participants filled them in and submitted them, while others dropped their emails for later contact. To ensure that the smart meters existed in their houses, prior to the responding to the questionnaires, the participants were first checked. From the 898 questionnaires distributed, 698 were through email among registered consumers and 200 through personally administered distribution. A further 85 questionnaires remained undelivered owing to wrong email addresses or invalid email accounts. Email responses returned 179 after the follow-ups, with the rate of response increasing after every follow-up. With regards to the personal-administered survey, 159 responses were received.
The total retrieved questionnaires were 338 with 20 returned blank or had missing information, making the answer rate 318 (usable questionnaires). The collected data yield a rate of response of 39.1%. According to Cornford & Smithson [78], in IS studies, a response rate of 20% or greater is acceptable.
6. Results
6.1. Descriptive Analysis of the Sample
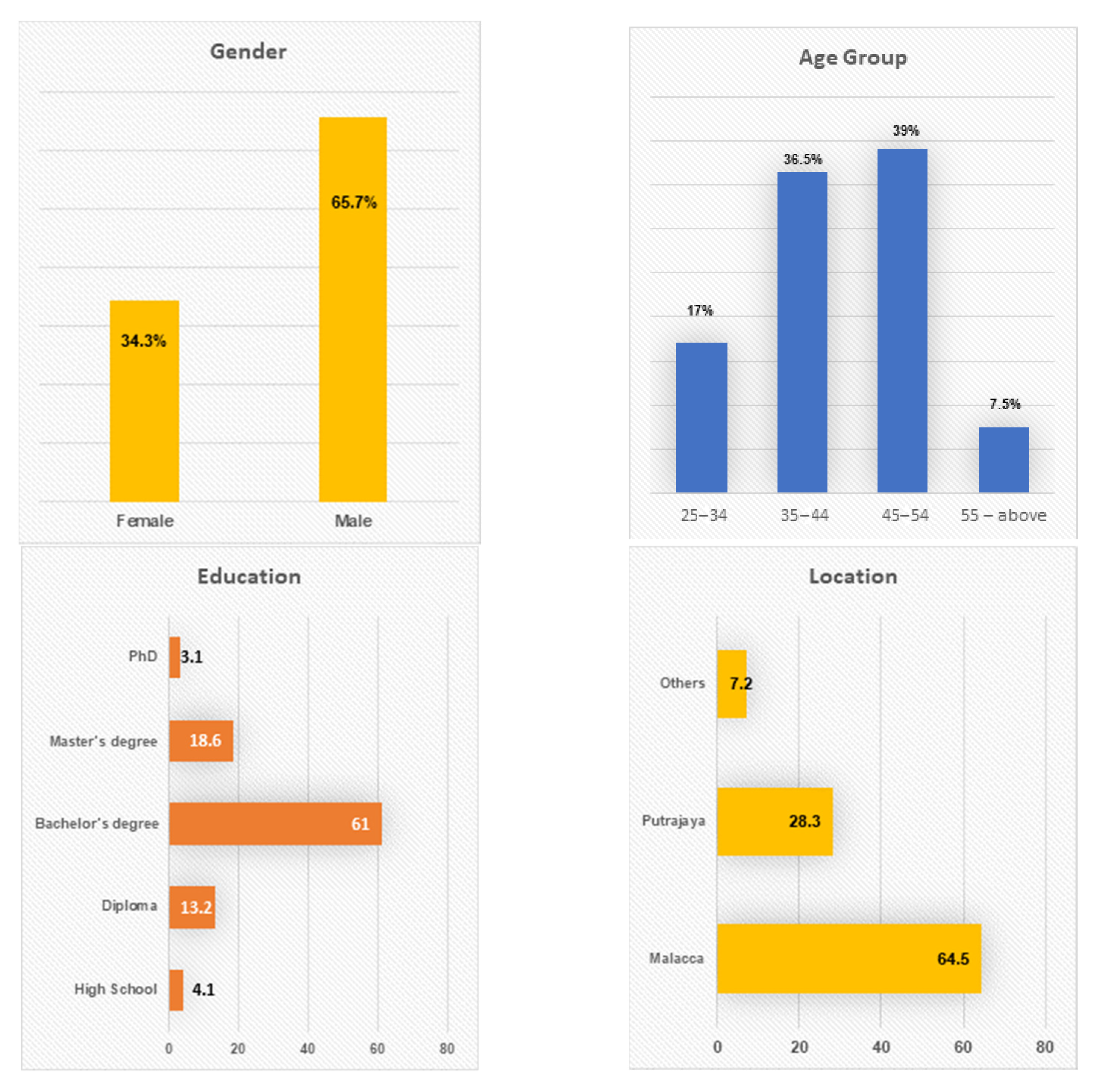
A descriptive analysis to explain the demographic characteristics of the respondents was conducted on the basis of the final results. Data such as gender, age, education, location and experience with smart metering technology were collected.
As shown in Figure 2 (the gender), 109 of the participants were females (34.3%) while 209 were males (65.7%). Furthermore, Figure 2 (the age group) shows that most of the respondents (39%) were in the age group between 45 and 54, followed by the group of 35 and 44 (36.5%) and group “25–34” is (17%). The rest of the participants were above 55 and above (7.5%).
As shown in Figure 2 (education), the majority of the respondents (61%) had a bachelor’s degree, followed by a master’s degree (18.6%) and diploma (13.2%). The remainders were the respondents with PhD (3.1%) and high school (4.1%). Based on Figure 2 (location), most of the respondents were from Malacca (64.5%) while only 28.3% were from Putrajaya. The rest were from various locations.
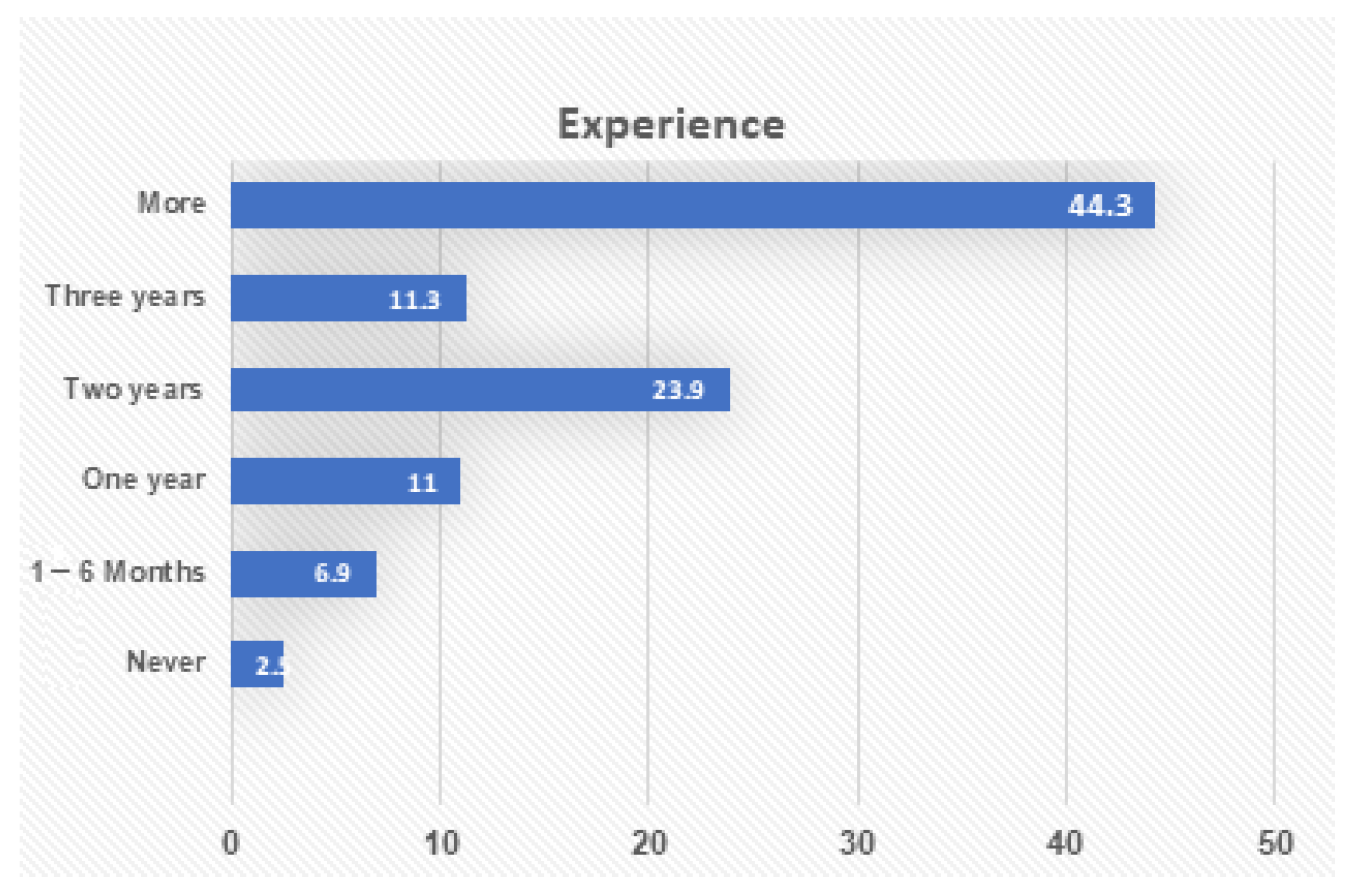
Finally, Figure 3 shows the period of experience of using applications, with the mean of experience in using applications is 4.7 years (SD = 1.43 years). This shows that almost all the participants have been experiencing the use of smart metering technology.
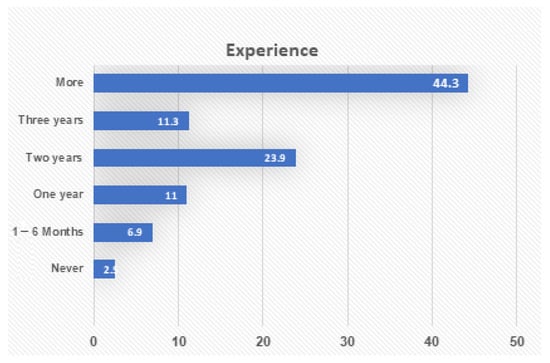
Figure 3.
Respondents by experience.
6.2. Assessment of the Research Model
For data analysis, the PLS-SEM method was used, as this research is an extension of an established theory [79]. Chin [80] indicates that less constraints on measurement scales, sample size, data distribution, and normality are the benefits of PLS. Accordingly, the sample size and the response rate have to be sufficient. The response rate gained in this study iwas 39.1% that is more than the minimum response rate (20%) established by [81]. This study had a good sample size of respondents, higher than the minimum sample size required for PLS. It was explained that 217 is the number of participants needed for the proposed model by heuristics [77]. In relation to this, the responses obtained were 318, which is obviously higher than 217.
6.2.1. Assessment of the Measurement Model
Hulland [82] stated that the measurement model adequacy could be specified by obtaining item reliability, internal consistency reliability, convergent validity, and discriminant validity.
Item Reliability
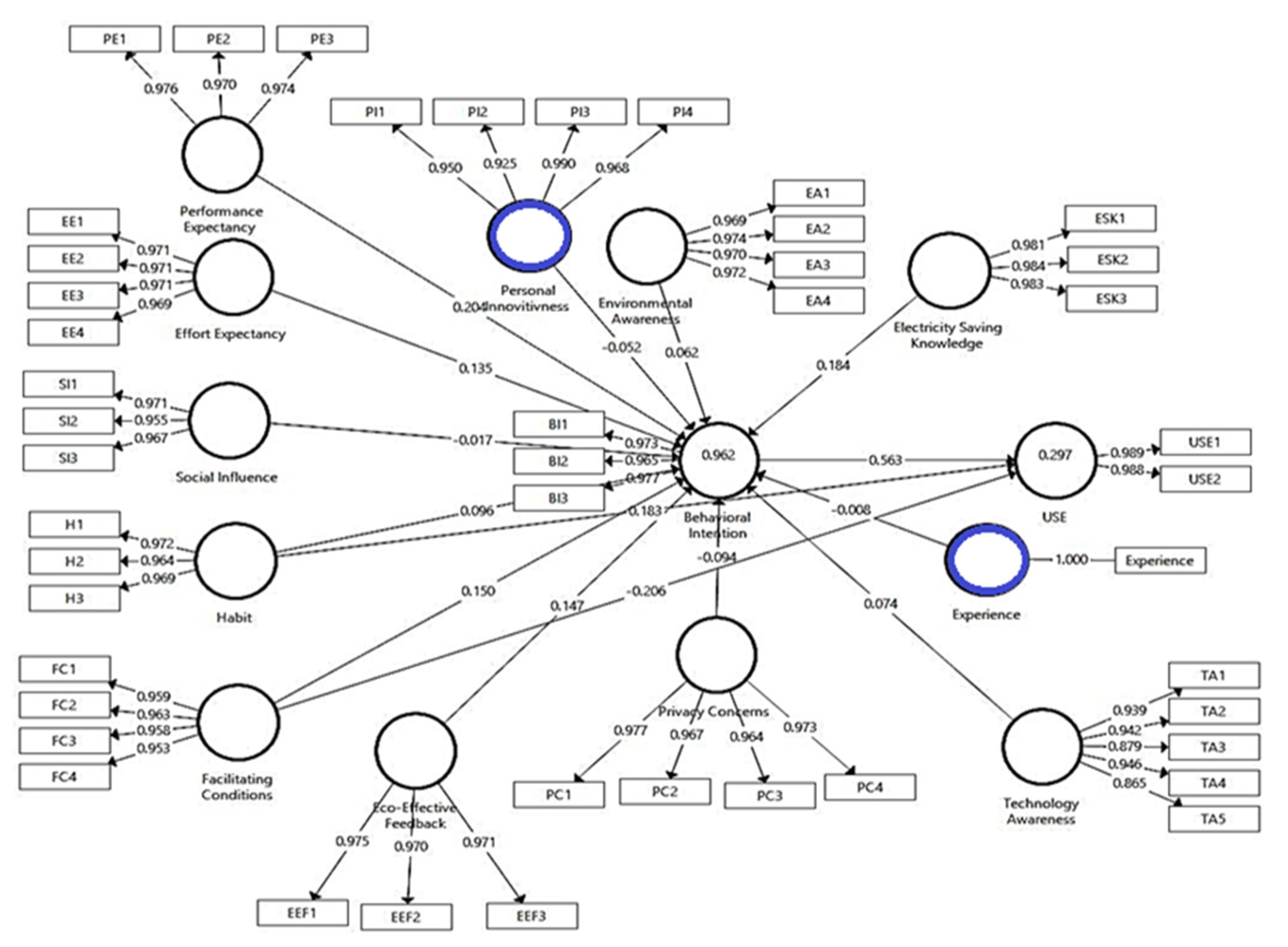
According to [80], the threshold value for individual item loadings should be above 0.7 to determine item reliability. In this study, all the items (46 items) exceeded the threshold value indicating that the survey instrument was adequate for measuring each construct individually. Therefore, all 46 items were kept for further analysis. Their item loadings, as presented in Figure 4, ranged from 0.865 to 1 and all indicated statistical significance.
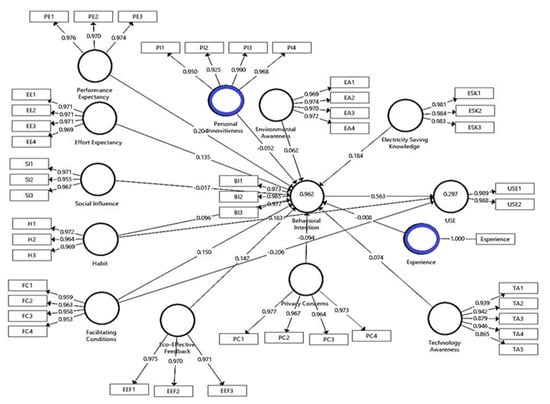
Figure 4.
Measurement model.
Internal Consistency Reliability
The internal consistency reliability was examined by determining the composite reliability (CR) values. In this study, the CR values were all above 0.9 (over the minimum 0.80) (See Table 3), which indicated that the constructs measures had high internal consistency reliability.

Table 3.
Results of PLS Analysis: Measurement Model.
Convergent Validity
The three conditions laid down by Fornell & Larcker [83] concerning the measures, convergent validity was used. First, the item factor loadings have to be over 0.70 (item reliability) and second, each construct should have composite reliability (CR) value of over 0.80 (internal consistency reliability). Lastly, the construct’s average variance extracted (AVE) should be more than 0.50. Previous sections confirmed that the entire items factor loadings exceeded 0.70 and the entire composite reliability values exceeded 0.80. With regards to AVE values, they ranged from 0.83 (over 0.50) as presented in Table 3, which confirmed their convergent validity.
Discriminant Validity
Discriminant validity was evaluated for each construct by observing the AVE square root (diagonal line in Table 4), which must be higher compared to the correlations between the construct and other model constructs. The discriminant validity of the constructs is presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Correlations between constructs compared to square roots of AVE.
6.2.2. Assessment of the Structural Model
Bootstrapping was performed using 500 samples to determine the significance of the paths within the structural model. Aside from the single path tests, the amount of variance explained by the independent variables, gauged using R2 of the dependent ones, which revealed that independent variables collectively explained 86% of the variance in behavioural intention towards smart meter system use. The next section discusses the hypotheses results one by one. The results of the hypotheses testing for each hypothesis are interpreted in relation to the relevant studies in the literature.
Moderating Effect of Experience
This study made use of the PLS-SEM indicator method to conduct an estimation of the strength of the moderating effects of experience on effort expectancy, facilitating conditions, social influence, eco-effective feedback, habit, and privacy concerns. In order to determine such moderating effects, Cohen’s [84] guidelines were followed for effect size. The proceeding figures and table presents the moderating effect on the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Under the moderating effects hypotheses, the experience was hypothesized to moderate the effects of effort expectancy, facilitating conditions, habit and privacy concerns on behavioural intention, and the effects of habit on technology use. Hypothesis H1 was supported by the results in that experience moderated the effort expectancy-behavioural intention relationship (β = −0.027, p = 0.003). Along a similar line of findings, experience also moderated the habit-behavioural relationship (β = 0.019, p = 0.006) in H4, and the habit-technology use relationship (β = −0.072, p = 0.011) in H5. The findings of the privacy concerns–behavioural intention relationship (β = −0.017, p = 0.000) in H6 was supported. In contrast, the experience did not moderate effect of facilitating conditions on behavioural intention, and the result was found insignificant. Practically, the magnitude and effect size of the moderating effects were small. In H3, the moderation effect was not considered since the social influence-behavioural intention relationship was not significant. The hypotheses results (H1–H6, excluding H3) are provided in Table 5.

Table 5.
Moderating effect of experience.
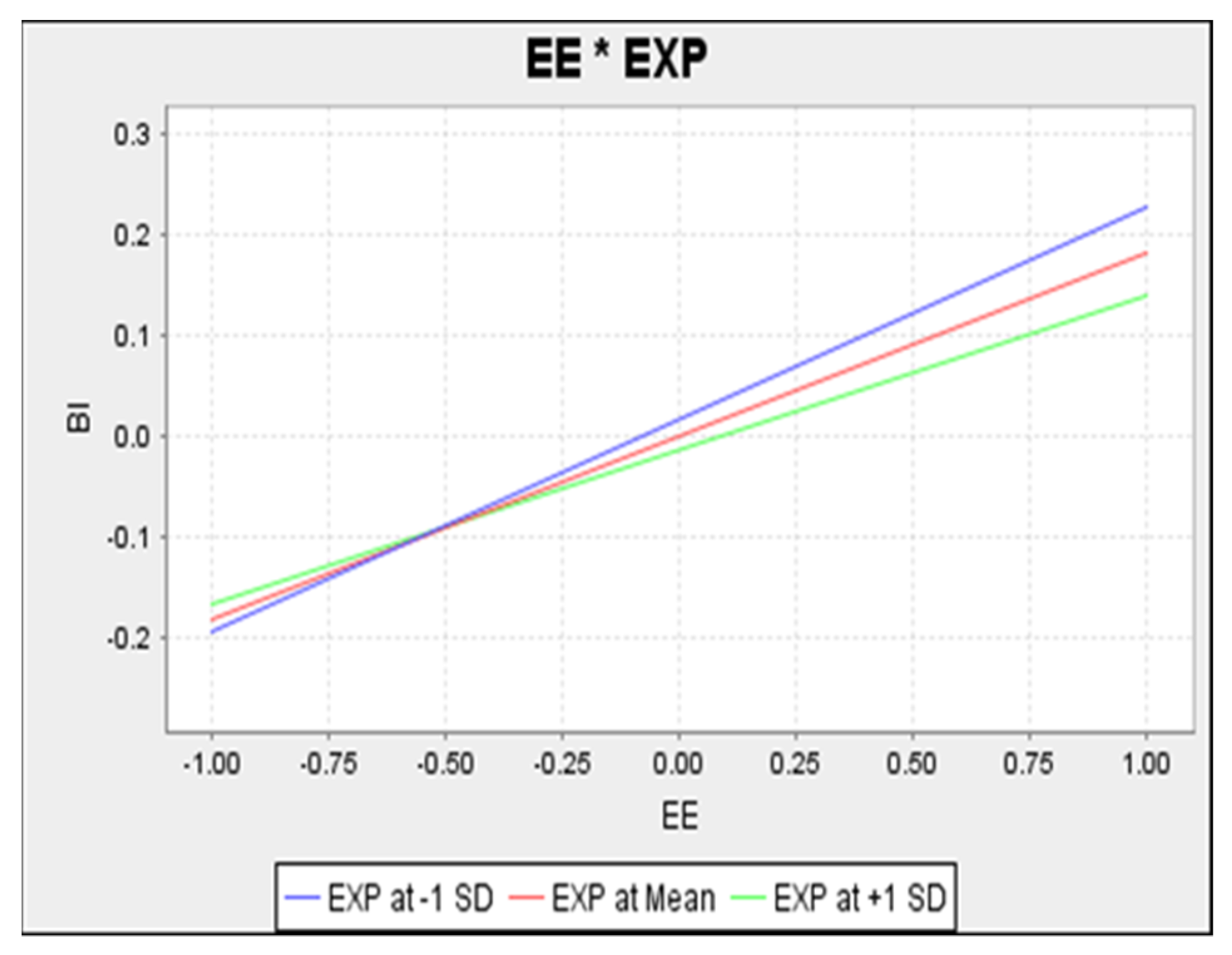
In Figure 5, it is evident that the effort expectancy-behavioural intention relationship is direct with higher levels of the former expected to lead to higher levels of the latter. Added to this, the moderating effect scope was examined in detail. The upper blue line represents low level of moderator construct (experience), while the green line represents a high level of experience, with a steeper slope. This is logical with a negative interaction effect. Therefore, the simple plot supports the prior discussion on the negative interaction term, where higher levels of experience are expected to lead to lower relationship strength between effort expectancy and behavioural intention.
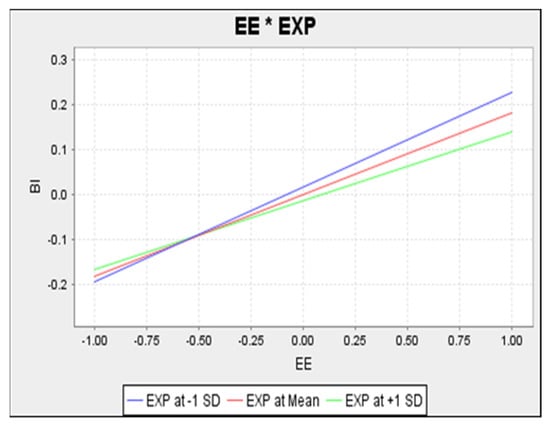
Figure 5.
Simple Slope Analysis of Effort Expectancy on Behavioural Intention.
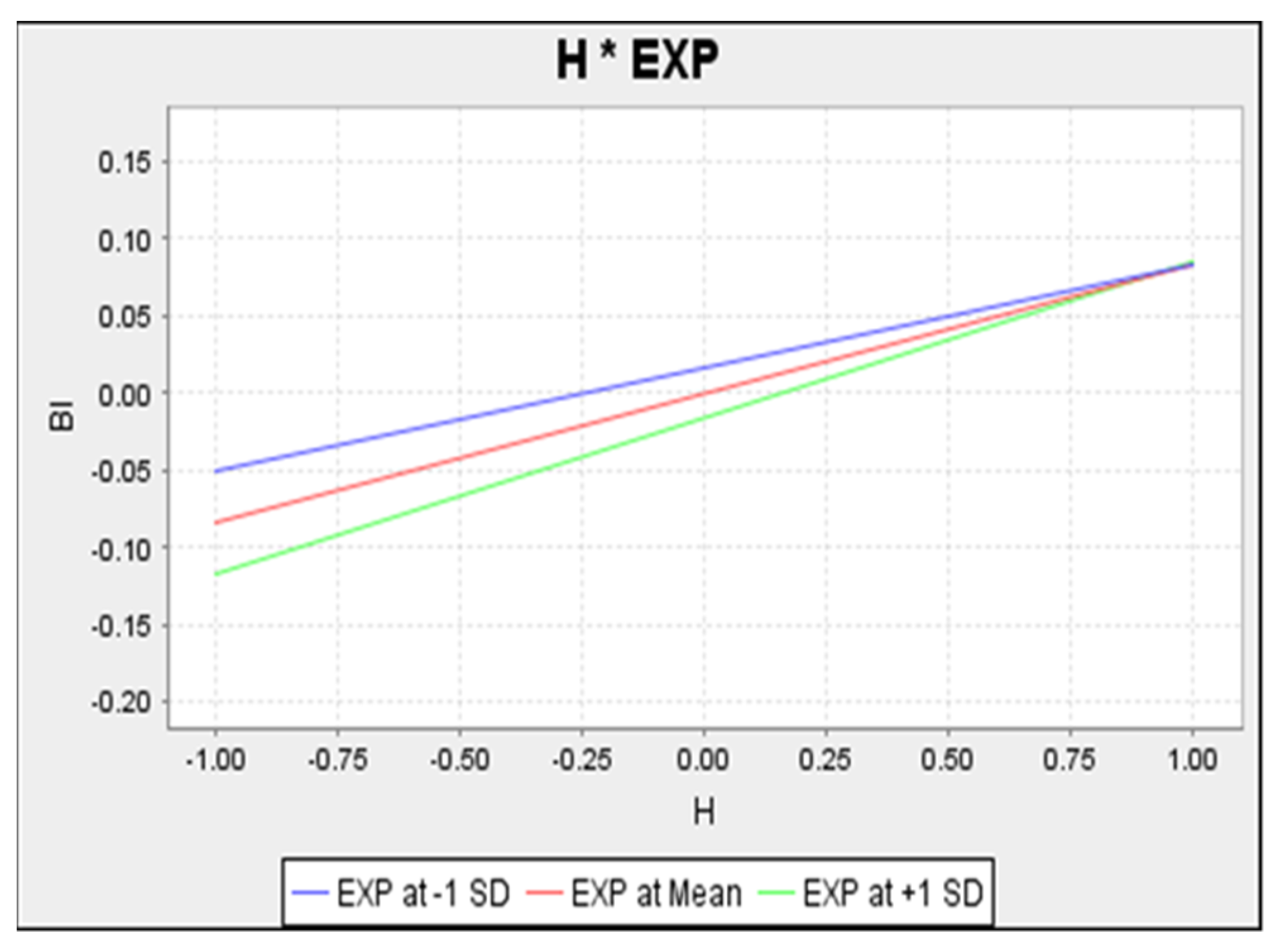
Figure 6 shows that the upper line, representing a low level of moderation (experience), is flatter in slope, whereas the lower line, representing a high level of moderation (experience), takes on a steeper slope. The positive relationship shows that the relationship is less positive among users with high experience compared to users with low experience.
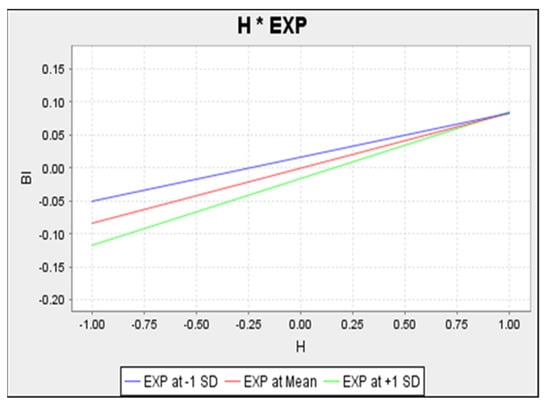
Figure 6.
Simple Slope Analysis of Habit on Behavioural Intention.
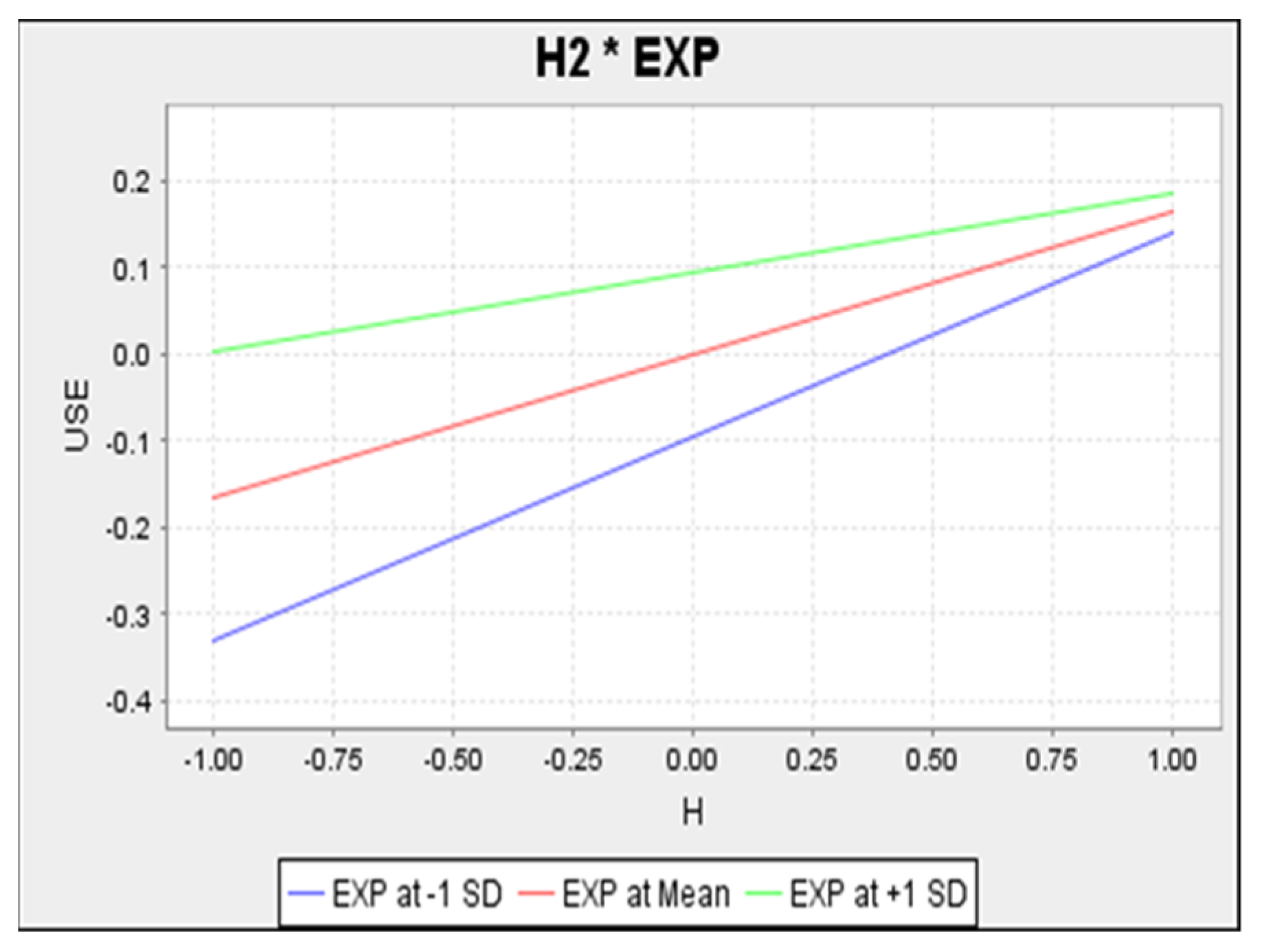
Figure 7 presents the privacy concerns-behavioural intention inverse relationship. High privacy concerns, therefore, correspond to low behaviour intention levels. The lower line, representing high experience level, indicates a steeper slope and this is attributed to the negative interaction effect. Therefore, the relationship was more negative among high-experienced users compared to low-experienced ones. Experience had a negative moderating effect on habit and technology use (See Table 5), with the plot in Figure 8 showing that high experience corresponds to a lower habit–technology use relationship.
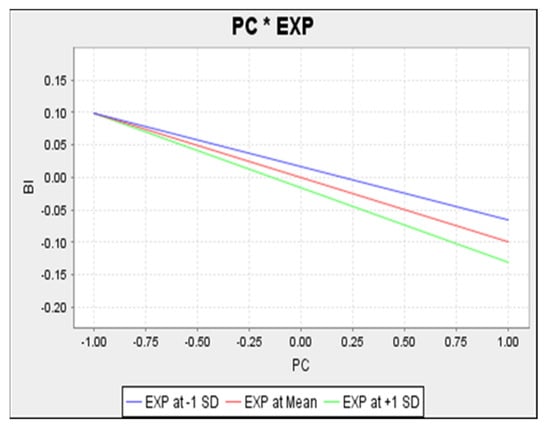
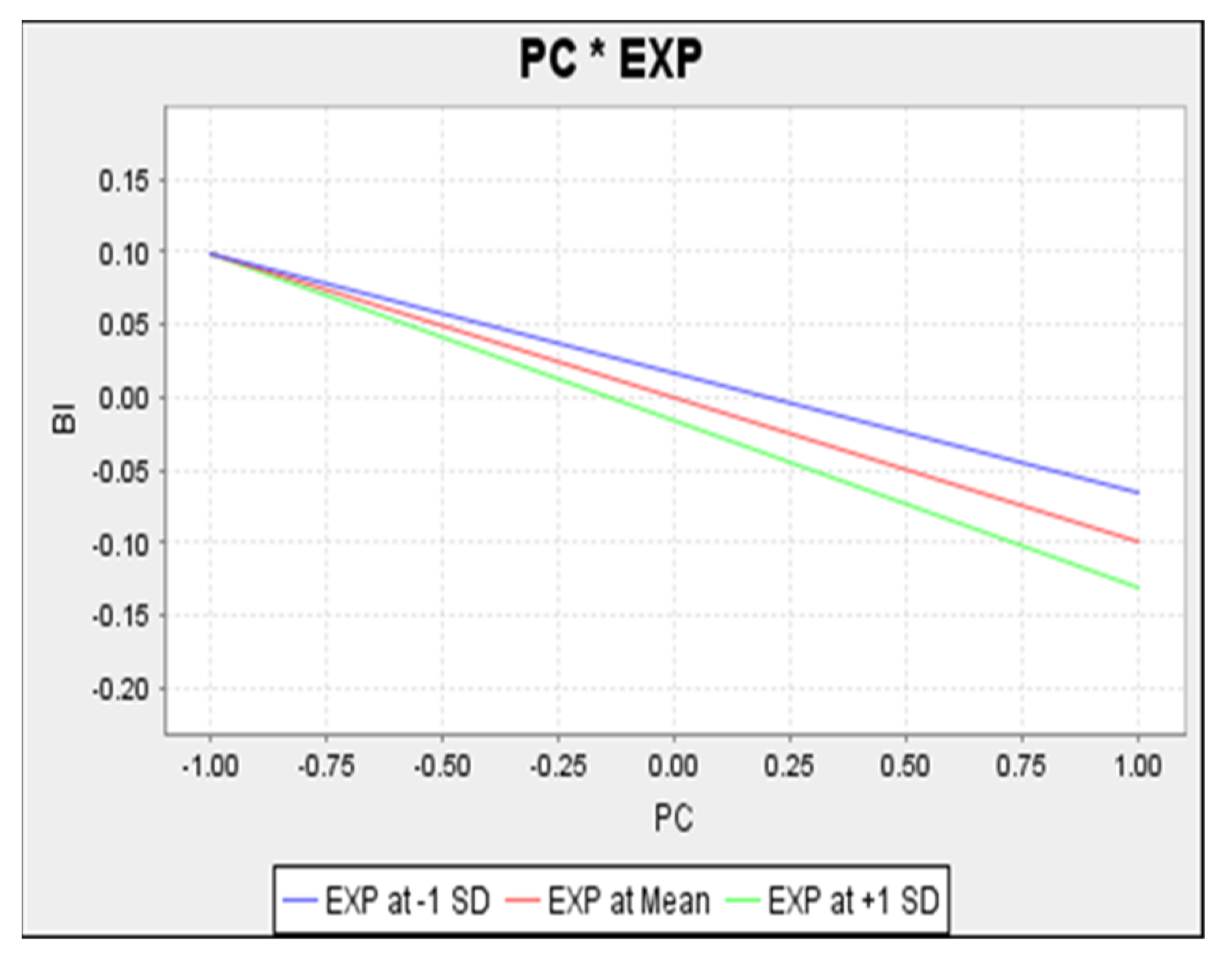
Figure 7.
Simple Slope Analysis of Privacy Concern on Behavioural Intention.
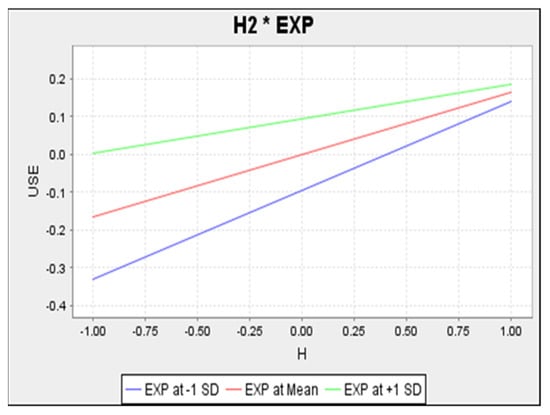
Figure 8.
Simple Slope Analysis of Habit on Technology Use.
Moderating Effect of Personal Innovativeness
This study proposed the significant and moderating effect of personal innovativeness on the effects of performance expectancy, effort expectancy, and privacy concerns on behavioural intention. All the hypotheses in this line were not supported, with the exception of H9 (privacy concern-behavioural intention relationship, β = 0.009, p = 0.001). Practically, the magnitude and effect size of the moderating effect was low. Table 6 illustrates the results of hypotheses H7 to H9.

Table 6.
Moderating effect of personal innovativeness.
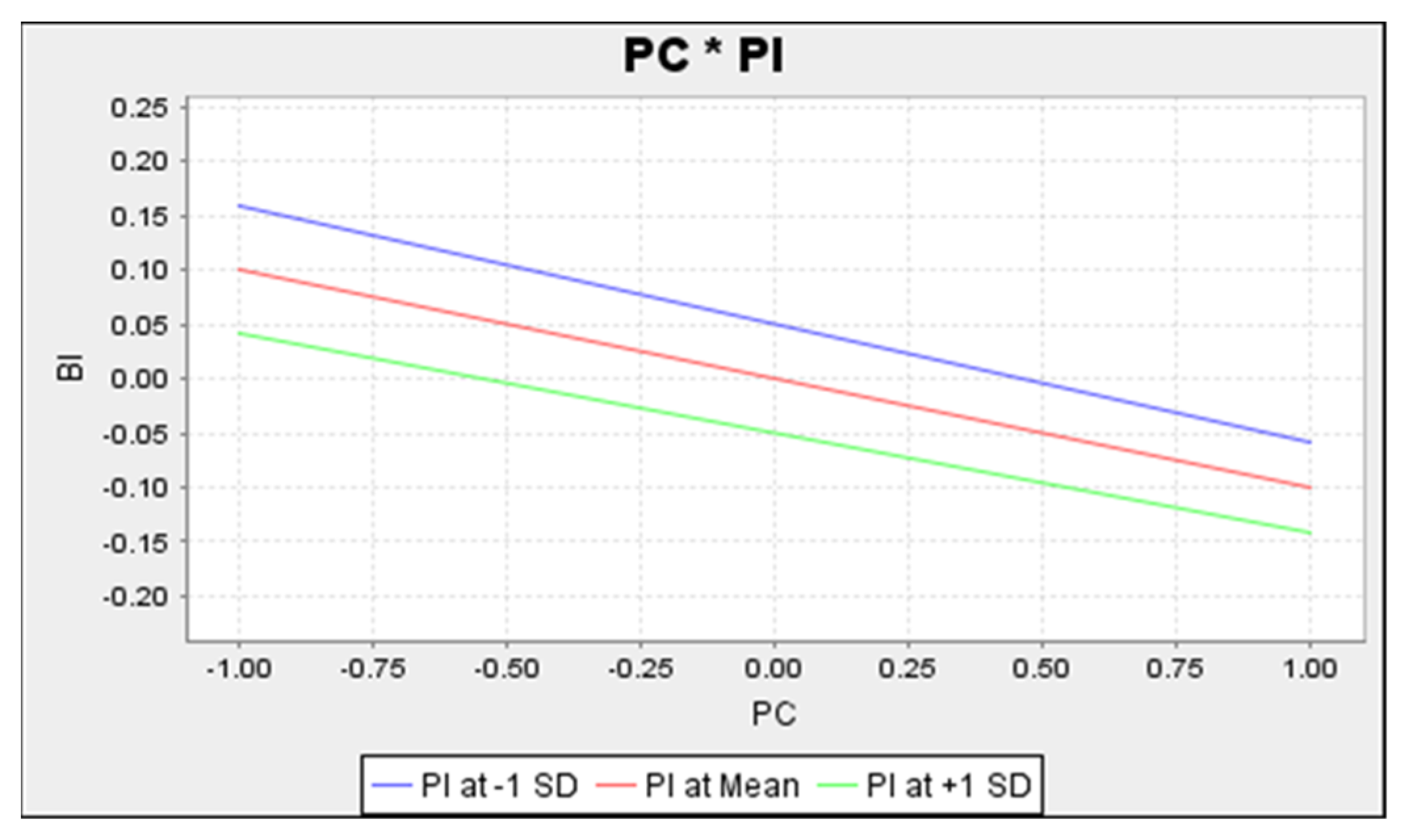
Figure 9 presents the inverse relationship between privacy concerns and behaviour intention, with high privacy concerns among users expected to lead to lower behavioural intention levels. The lower line represents a high level of personal innovativeness and it has a steeper slope. Thus, the relationship was less positive for those with high personal innovativeness compared to their counterparts with low ones.
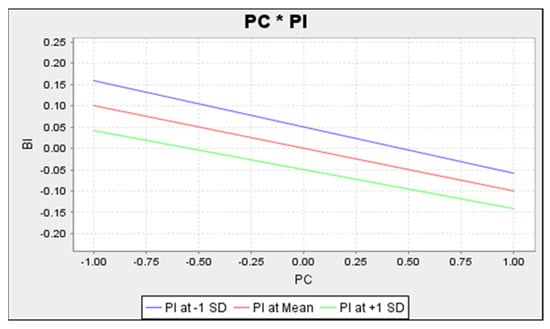
Figure 9.
Simple Slope Analysis of Personal Innovativeness on Behavioral Intention.
7. Assessment and Discussions
The moderators adopted in this study were the experience and personal innovativeness. The experience was proven to moderate the effects of effort expectancy, social influence, eco-effective feedback, habit and privacy concerns on behavioural intention, along with the effect of habit on technology use. By contrast, personal innovativeness was found to moderate the effect of privacy concerns on behavioural intention but not the effects of performance expectancy and effort expectancy on behavioural intention.
7.1. Experience Moderation
The findings of this study indicated that increased experience in using smart meter systems will boost relationships with the constructs and increase consumer intention to use such systems. The positive values of interaction in terms of the moderating variable indicated that the experience moderates relationships positively, which is in line with the hypothesis (H4) developed in this study. The relationship between habit towards behavioural intention was confirmed to be stronger amongst experienced users. By contrast, the negative values of interaction imply that a higher level of experience results in reduced relationship strength. This study indicated that the relationships between effort expectancy towards behavioural intention is weaker amongst experienced users. Similarly, the relationship between habit and use behaviour was weaker amongst experienced users. This study is consistent with prior studies that show higher level of experience negatively influences relationship strength of effort expectancy on behavioural intention, and habit on use behaviour by Venkatesh et al. [18]. The negative value of interactions can be explained by the fact that consumers who are more experienced in using smart meter systems will be more engaged in the systems and find effort expectancy, and habit less important because of the simplicity of such systems. This study found the moderating effect of experience on privacy concern toward behavioural intention was significant. This indicated that higher experience consumers have a stronger concern of privacy when tended to use smart meter system. These findings were in line with prior studies by [66,67]. Furthermore, the moderating effect of experience was not found significant to facilitating conditions when accepting smart meters. This finding implied that the moderating effect of experience on the relationship between the facilitating conditions and behavioural intention was insignificant. Hence, H2 was not supported in accordance with our empirical analysis. Although it was not empirically supported, the results of the moderating impact of experience are in line with those of previous studies, that is, people with experience are more likely to adopt technologies [85,86].
7.2. Personal Innovativeness Moderation
Personal innovativeness was the second moderator investigated in this study. The results indicated that the relationship between privacy concerns and behavioral intention was stronger amongst consumers with high personal innovativeness. This suggested that a more innovative person was likely to face higher privacy risks inherent in the use of smart meters. It is also fair to argue that personal innovativeness characterizes the potential for risk-taking that occurs in some people and not in others. In particular, the risks associated with the use of LBS relates to privacy, whereby one’s personal details could be exchanged without permission with other parties or used for any other nefarious purposes. Rogers [87] argued that higher levels of ambiguity should be dealt with by innovators and early adopters. It is probable that the insignificant outcome can be clarified by the IoT context. The considerable attention received by the widely available information regarding IoT’s ‘effort expectancy’ and ‘performance expectancy’ may result in knowledge and awareness levels for consumers, thereby rendering the moderating effects of personal innovativeness insignificant.
8. Implications
8.1. Implications for Research
The feasibility of UTAUT2 was tested in this study by evaluating the established model in the context of energy saving. UTAUT2 was extended by testing new moderators and introducing other constructs from the energy-saving perspective to study the consumers’ use of smart meters and their decision to accept this technology. One of the first research to use UTAUT2 to investigate smart meter acceptance was this study. This study adopted personal innovativeness as a new moderator in addition to experience in the UTUAT2 model. This step was taken after conducting the literature review, in which the personal innovativeness of the respondents was determined to be a good moderator. The proposed model could successfully be generalized to the acceptance of similar technologies from the same context (energy), such as a gas smart meter or smart grid applications, or from the same domain (IoT), such as a water smart meter. In addition, this research can be extended to other developing countries, which are planning to deploy the smart meters. The following justifies generalizability of the proposed model.
8.2. Implications for Practice
Developers must understand user requirements. The smart meter acceptance variables defined in this study provide developers with useful information. Developers need to consider consumer views of smart meters at this early stage and how these systems are viewed within the energy and IoT sectors. The proposed model will also enable the development of new approaches or update their strategies for managing and implementing the service in order to increase the degree of acceptance. For example, this study shows influence of identified factors on consumers’ intention of use. These variables can encourage developers to design functions and interfaces that provide insightful feedback and eco-wages or icons that can sustain usage and allow connected devices or neighbors to compare the use of electricity. Also, they can design interfaces that include saving plans, tricks, and forecast scenarios.
Governments must ensure that the implementation of smart meter systems does not affect personal data and human rights. The privacy concern factor that was identified in this study confirms the finding of a comparative study among five countries including leading countries in adopting smart meters by Zhou & Brown [52], which demonstrated that countries with a range of policy initiatives that introduce multiple barriers to smart meters appear to be pioneers, while laggards frequently ignore or refuse to implement policies to address key barriers. Thus, public policy makers and government regulators can direct authorities to monitor and control privacy frameworks, to ensure the protection of privacy. The standard use of consumer data will protect privacy and reduce concerns regarding smart meter use.
9. Conclusions and Future Work
This study investigated the moderation role of experience and personal innovativeness on the acceptance of IoT-based smart metering technology. The results of this extended model will lead to a deeper understanding of smart meter acceptance from the customer’s perspective. In addition, the results of this study emphasized the experience and personal innovativeness related to the use of smart meters. The implications for practice indicated that electricity suppliers use the smart meter acceptance model to update the requirements of customers in their schemes, hence increasing the rate of acceptance.
Smart meter manufacturers can be guided by following the proposed model to create products with better user specifications, which will improve user interaction. Two UTAUT2 moderators were excluded in light of the limitations of this study: gender and age. Although this omission is justified and in accordance with previous literature, investigating further and determining the effect of different groups on the proposed model will be interesting.
For future direction, studies can further determine the group comparison of technology acceptance by assessing groups. For example, electricity consumers can be grouped into different categories, such as type (residential or commercial), location (urban or rural), and lifestyle (lavish or normal). Future studies can compare these categories and assess group differences or similarities in accepting smart meter systems. This study confirms a statistical difference between two groups, namely high-experience and low-experience users, in terms of their behavioral intention to use smart meter systems. Such assessments are expected to provide a deeper understanding of the consumer acceptance of smart meter systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A. and N.A.; methodology, G.A. and N.A.; software, G.A. and Y.B.; formal analysis, G.A. and Y.B.; investigation, G.A.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.B.; writing—review and editing, G.A. and Y.B.; visualization, Y.B; supervision, N.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universiti Tenaga Nasional under the BOLDREFRESH2025 Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
This study does not report any data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
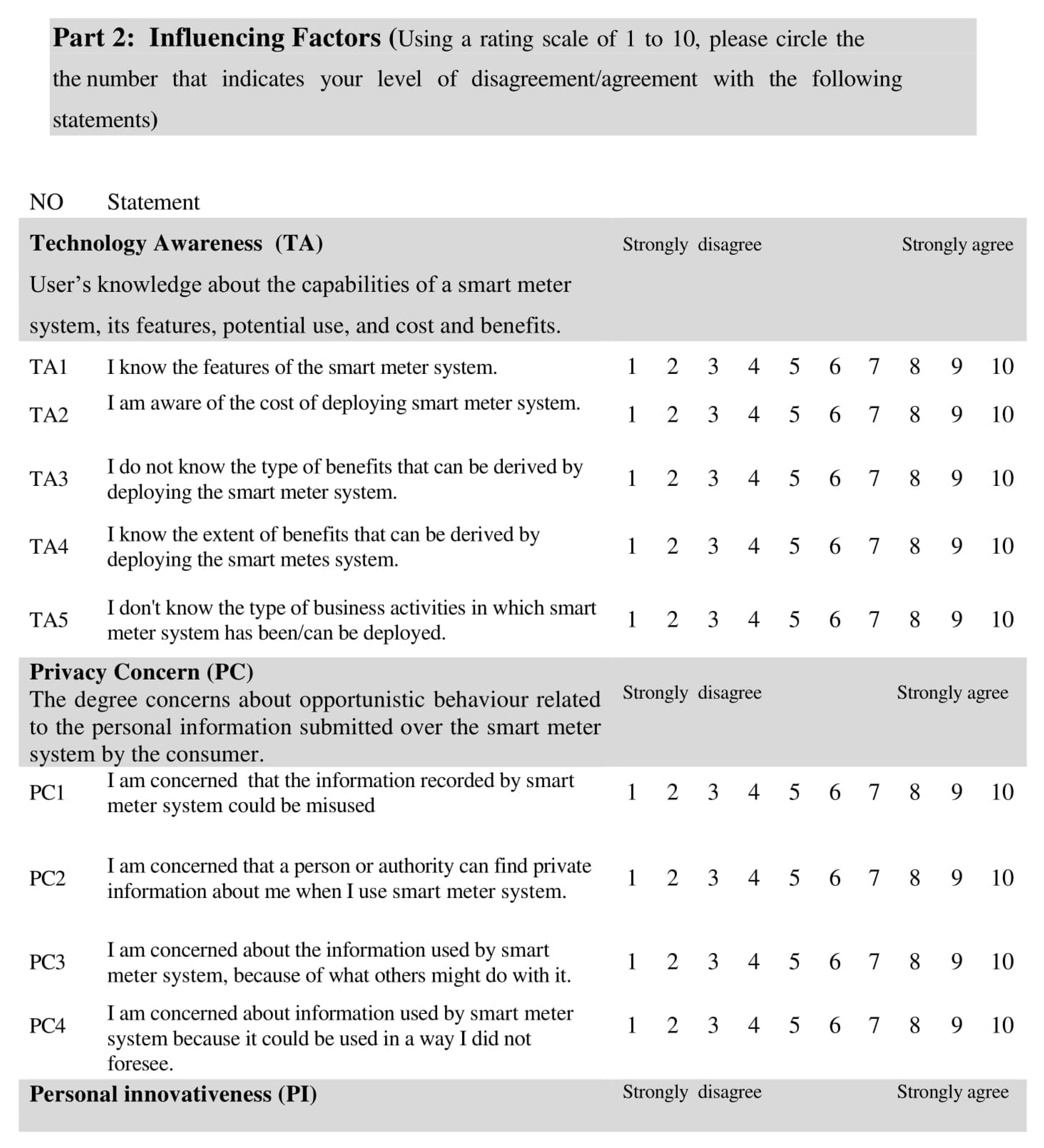
Appendix A. Research Questionnaire Sample
References
- Avancini, D.B.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Rabêlo, R.A.L.; Das, A.K.; Kozlov, S.; Solic, P. A new IoT-based smart energy meter for smart grids. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Yaqoob, I.; Gani, A.; Imran, M.; Guizani, M. Internet-of-things-based smart environments: State of the art, taxonomy, and open research challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.; Tomas, J.; Canovas, A.; Parra, L. An Integrated IoT architecture for smart metering. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.; Sarker, M.T.; Haque, M.E.; Jahid, A. A smart IoT based system for monitoring and controlling the sub-station equipment. Internet Things 2019, 7, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokan, A.B.; Kotb, Y. Towards a real IoT-based smart meter system. In First International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Computational Intelligence; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadharshini, S.; Subramani, C.; Roselyn, J.P. An IOT based smart metering development for energy management system. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 9, 3041–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, V.J.; Harris, C.K. Noisy Winter: The DDT controversy in the years before silent spring. Rural. Sociol. 1998, 63, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, H. A road map to integration: Perspectives on smart grid development. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2014, 12, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, T.; Schwartz, D.; Davis, A.; Fischhoff, B.; de Bruin, W.B.; Lave, L.; Wang, J. Preparing for smart grid technologies: A behavioral decision research approach to understanding consumer expectations about smart meters. Energy Policy 2012, 41, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preeti, S. Why IoT Opportunities Are High, Adoption Rates Low. 2015. Available online: Cxotoday.com (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Castro, D.; New, J.; McQuinn, A. How Is the Federal Government Using the Internet of Things; Center for Data Innovation: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, M. Study: IoT Adoption Still Slow for Government Agencies. Washington Technology, 26 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alkawsi, G.A.; Ali, N.A.B.; Alghushami, A. Toward understanding individuals’acceptance of internet of things-based services: Developing an instrument to measure the acceptance of smart meters. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 4265–4281. [Google Scholar]
- Alkawsi, G.A.; Ali, N.A.B. A systematic review of individuals’ acceptance of IOT-based technologies. Int. J. Eng. Technol. (UAE) 2018, 7, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wolsink, M. The research agenda on social acceptance of distributed generation in smart grids: Renewable as common pool resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawsi, G.A.; Ali, N.; Mustafa, A.S.; Baashar, Y.; Alhussian, H.; Alkahtani, A.; Tiong, S.K.; Ekanayake, J. A hybrid SEM-neural network method for identifying acceptance factors of the smart meters in Malaysia: Challenges perspective. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawsi, G.A.; Baashar, Y. An empirical study of the acceptance of IoT-based smart meter in Malaysia: The effect of electricity-saving knowledge and environmental awareness. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 42794–42804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivumäki, T.; Ristola, A.; Kesti, M. The effects of information quality of mobile information services on user satisfaction and service acceptance–empirical evidence from Finland. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2008, 27, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gupta, S. The effects of privacy concerns and personal innovativeness on potential and experienced customers’ adoption of location-based services. Electron. Mark. 2009, 19, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.; Don, Y. Preservice teachers’ acceptance of learning management software: An application of the UTAUT2 model. Int. Educ. Stud. 2013, 6, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, L.E.; Williams, M.D.; Dwivedi, Y. Extending UTAUT2 to explore consumer adoption of mobile payments. In Proceedings of the 23rd UK Academy for Information Systems Conference (UKAIS), Milan, Italy, 15–18 December 2013; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas-Gaitán, J.; Peral-Peral, B.; Ramón-Jerónimo, M.A. Elderly and internet banking: An application of UTAUT2. J. Internet Bank. Commer. 2015, 20, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Alalwan, A.A.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P. Factors influencing adoption of mobile banking by Jordanian bank customers: Extending UTAUT2 with trust. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2017, 37, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwan, A.A.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P.; Algharabat, R. Examining factors influencing Jordanian customers’ intentions and adoption of internet banking: Extending UTAUT2 with risk. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 40, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Masri, M.; Tarhini, A. Factors affecting the adoption of e-learning systems in Qatar and USA: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 (UTAUT2). Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2017, 65, 743–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.H.; San Martín Gutiérrez, H.; de los Salmones, M.D.G. Explaining the adoption of social networks sites for sharing user-generated content: A revision of the UTAUT2. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 71, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.; Thomas, M.; Baptista, G.; Campos, F. Mobile payment: Understanding the determinants of customer adoption and intention to recommend the technology. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 61, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dogra, N.; George, B. What determines tourist adoption of smartphone apps? J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2018, 9, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopdar, P.K.; Korfiatis, N.; Sivakumar, V.; Lytras, M.D. Mobile shopping apps adoption and perceived risks: A cross-country perspective utilizing the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 86, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrawati; Tohir, L.M. Predicting smart metering acceptance by residential consumers: An Indonesian perspective. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT), Bandung, Indonesia, 25–27 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Kozar, K.A.; Larsen, K.R. The technology acceptance model: Past, present, and future. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2003, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momani, A.M.; Jamous, M. The evolution of technology acceptance theories. Int. J. Contemp. Comput. Res. 2017, 1, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, P. The role of moderating factors in user technology acceptance. Int. J. Human Comput. Stud. 2006, 64, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P. The legacy of the technology acceptance model and a proposal for a paradigm shift. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2007, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raaij, E.M.; Schepers, J.J. The acceptance and use of a virtual learning environment in China. Comput. Educ. 2008, 50, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P.; Jeyaraj, A.; Clement, M.; Williams, M.D. Re-examining the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): Towards a revised theoretical model. Inf. Syst. Front. 2019, 21, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, A.Y.-L. Predicting m-commerce adoption determinants: A neural network approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.; Schaupp, L.C. Efficacy and acceptance in e-file adoption. In Proceedings of the 14th Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2008), Toronto, ON, Canada, 14–17 August 2008; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Kranz, L.; Gallenkamp, J.; Picot, A.O. Exploring the role of control–smart meter acceptance of residential consumers. In Proceedings of the 16th Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2010), Lima, Peru, 12–15 August 2010; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, W.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Kotze, B. Perceptions on smart gas meters in smart cities for reducing the carbon footprint. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, P.; Veit, D.; Sarker, S. Examination of the determinants of smart meter adoption: An user perspective. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2012), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, D.N.-Y.; Van Der Vleuten, J.M.; Ip, J.C.-M.; Hills, P.R. Governing the transition of socio-technical systems: A case study of the development of smart grids in Korea. Energy Policy 2012, 45, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Yeh, C.-F. Factors affecting adoption of smart meters in the post-Fukushima era in Taiwan: An extended protection motivation theory perspective. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2017, 36, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, L.; Gallenkamp, J.; Picot, A. Power control to the people? Private consumers’ acceptance of smart meters. In Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2010), Pretoria, South Africa, 7–9 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Karlin, B. Public acceptance of smart meters: Integrating psychology and practice. In Proceedings of the ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Buildings, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 12–17 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fredericks, D.; Fan, Z.; Woolley, S.; De Quincey, E.; Streeton, M. A decade on, how has the visibility of energy changed? Energy feedback perceptions from UK focus groups. Energies 2020, 13, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, I.; Campillo, J. Consumers’ perspective on full-scale adoption of smart meters: A case study in Vasteras, Sweden. Resources 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Xu, X.; Arpan, L. Between the technology acceptance model and sustainable energy technology acceptance model: Investigating smart meter acceptance in the United States. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2017, 25, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimi, K.T.; Carrico, A.R. Understanding and beliefs about smart energy technology. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2016, 12, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Brown, M.A. Smart meter deployment in Europe: A comparative case study on the impacts of national policy schemes. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, M.B.; Schuitema, G.; Thøgersen, J. Responsible technology acceptance: Model development and application to con-sumer acceptance of Smart Grid technology. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, H.; Zo, H. User acceptance of smart home services: An extension of the theory of planned behavior. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2017, 117, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerpott, T.J.; Paukert, M. Determinants of willingness to pay for smart meters: An empirical analysis of household customers in Germany. Energy Policy 2013, 61, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugden, D.; Stedman, R. A synthetic view of acceptance and engagement with smart meters in the United States. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 47, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuhaiber, A. The role of perceived control, enjoyment, cost, sustainability and trust on intention to use smart meters: An empirical study using SEM-PLS. In World Conference on Information Systems and Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, K.; Banks, N.; Preston, I.; Russo, R. The British public’s perception of the UK smart metering initiative: Threats and opportunities. Energy Policy 2016, 91, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-K.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-S. A study of factors enhancing smart grid consumer engagement. Energy Policy 2014, 72, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, N.E.; Dornisch, M.M. When is trust not enough? The role of perceived privacy of communication tools in comfort with self-disclosure. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2010, 26, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notani, A.S. Moderators of perceived behavioral control’s predictiveness in the theory of planned behavior: A meta-analysis. Consum. Psychol. Rev. 1998, 7, 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limayem, M.; Hirt, S.G.; Cheung, C.M.K. How habit limits the predictive power of intention: The case of information systems continuance. MIS Q. 2007, 31, 705–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.B.; Häubl, G. Explaining cognitive lock-in: The role of skill-based habits of use in consumer choice. J. Consum. Res. 2007, 34, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, G.; Oliveira, T. Understanding mobile banking: The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology combined with cultural moderators. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 50, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasperson, S.J.; Carter, P.E.; Zmud, R.W. A comprehensive conceptualization of post-adoptive behaviors associated with information technology enabled work systems. MIS Q. 2005, 29, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, F. Consumer response to the Internet: An exploratory tracking study of on-line home users. J. Bus. Res. 2002, 55, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liébana-Cabanillas, F.; Sánchez-Fernández, J.; Muñoz-Leiva, F. The moderating effect of experience in the adoption of mobile payment tools in virtual social networks: The m-payment acceptance model in virtual social networks (MPAM-VSN). Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2014, 34, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tung, L.L. How individual differences influence technology usage behavior? Toward an integrated framework. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2005, 46, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Prasad, J. A conceptual and operational definition of personal innovativeness in the domain of information technology. Inf. Syst. Res. 1998, 9, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabholkar, P.A.; Bagozzi, R.P. An attitudinal model of technology-based self-service: Moderating effects of consumer traits and situational factors. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2002, 30, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiesse, F. RFID, privacy and the perception of risk: A strategic framework. J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 2007, 16, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, Z.; Afthanorhan, A.; Mamat, M. The Likert scale analysis using parametric based Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Comput. Methods Soc. Sci. 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Wittink, R.D.; Bayer, L.R. The measurement imperative. Mark. Res. 1994, 6, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, B.M. Structural Equation Modeling with EQS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R.; Goldstein, S.M. Use of structural equation modeling in operations management research: Looking back and forward. J. Oper. Manag. 2005, 24, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, N.M.; Lewis, P.; Thornhill, A. Research Methods for Business Students EBook; Pearson Australia Pty Limited: Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cornford, T.; Smithson, S. Project Research in Information Systems: A Student’s Guide; Macmillan International Higher Education: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Mod. Methods Bus. Res. 1998, 295, 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Cooper, H. A quantitative review of research design effects on response rates to questionnaires. J. Mark. Res. 1983, 20, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulland, J. Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: A review of four recent studies. Strateg. Manag. 1999, 20, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, S.; Rajan, P. Modeling intermediary satisfaction with mandatory adoption of e-government technologies for food distribution. Inf. Technol. Int. Dev. 2016, 12, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wamatu, A.K. Moderating Factors in Adoption of Mobile Financial Services in Kenya. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).