Integrated User-Oriented Service for 3D Printing Environments with Recycled Material from Maritime Plastic Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Searching for an Open Technology Strategy for Marine Plastic Recycling
2.1. CircularSeas Project and Main Results of Plastic Waste Survey
2.2. Open 3D Printing Technologies
3. Integrated User-Oriented Framework
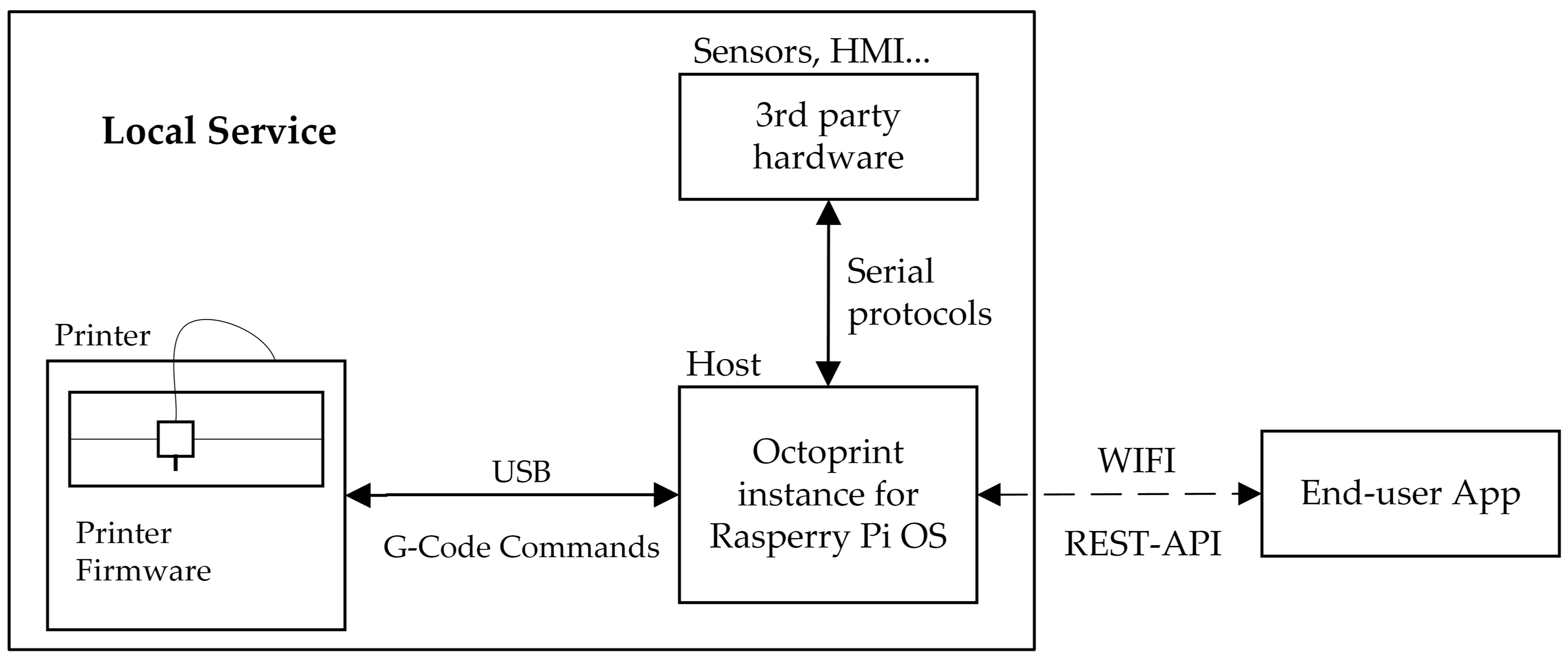
- Local Service—performs the 3D printed job of the object, so it is a local service for the end-user; consists of a commercial 3D printer connected to a print host (Raspberry Pi with Octoprint) that allows remote management (as illustrated in Figure 1).
- Cloud Service—the service in charge of the CAM process and the management of material data and filament stock at the node; a back-end service running in the cloud by the service provider.
- End-user App—the user application, with a user-friendly interface, having just the selection of the model to be printed and its requirements as well as basic operation management on the 3D printer.
3.1. Local Service: 3D Printing Manufacturing
3.2. Cloud Service: CAM and Materials Management
- to provide the tools for automatic and customised G-code generation;
- to serve as a link to the material database where the stock at the user nodes and the properties of standard and recycled filaments are stored. All this information is intended to help in material selection, detailed in Section 3.3.1.
- 3D printer configuration, related to the machine: nozzle diameter, accelerations, print volume, etc.;
- filament configuration, related to material: hot-end and hot-bed temperature, cooling settings, etc.;
- quality profile configuration, related to the process: layer height, top and bottom solid layers, wall thickness, etc.
3.3. End-User Application
- Control panel page: the current status of the manufacturing process is periodically monitored. It contains the most basic functional actions (start, stop, etc.) and access to successive pages.
- Slicing page: new print job setup page. Figure 5 specifies the activities carried out. When the user plans to make a new part, the first step is to configure the process in A0, based on the available materials and quality profiles. Subsequently, after attaching the STL of the part, this data is sent to the Cloud Service, which will carry out activity A1 (detailed in Figure 3, d A1.1 and A1.2 activities). The Local Service is responsible for carrying out the manufacture of the final part from the G-code generated (action A2).
- Printing page: direct printing without using the Cloud Service. This is possible for 3D printing parts that have already been sliced, as the G-code files are stored in the Local Service once they have been generated.
- Material selection page: available from the slicing page. It launches a material selection wizard to aid the user to select the most suitable material, as detailed below.
3.3.1. Helping User to Select the Printing Material
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Material Development Experiment: Strapping Tape Recycling
4.2. Classic vs. Integrated Printing Framework for Working with Non-Standard Recycled Filaments
- Standard/Classic 3D printing environment. The steps are as follows: select part file; create a new profile configuration; set—at least—temperature, cooling, deposition rate, retraction, layer height, infill density, brim and print speed configurations; slice; save file to flash memory, insert it in 3D printer, search the machine code file; and print. More than 38 variables have to be set, which often requires expert knowledge (first row in Table 6).
- Integrated 3D printing environment. The material and quality configurations are carried out by the service provider through the Cloud Service, externalizing the most technical steps for the user. The user steps consist of filing part, material and qualities selection, and printing (Figure 7c), consisting of about four steps (second row in Table 6).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, S.-J.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Yoo, S.-H. Economic Valuation of Reducing Submerged Marine Debris in South Korea. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics Europe: Association of Plastics Manufacturers; Plastics Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Law, K.L. Plastics in the Marine Environment. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, B.; Guillaume, B.; Eleonora, S.; João, S. The Marine Plastic Footprint: Towards a Science-Based Metric for Measuring Marine Plastic Leakage and Increasing the Materiality and Circularity of Plastic; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9782831720289. [Google Scholar]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalansa, S.; El Mahrad, B.; Vondolia, G.K.; Icely, J.; Newton, A. The Marine Plastic Litter Issue: A Social-Economic Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, W.C.; TSE, H.F.; FOK, L. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blettler, M.C.M.; Abrial, E.; Khan, F.R.; Sivri, N.; Espinola, L.A. Freshwater plastic pollution: Recognizing research biases and identifying knowledge gaps. Water Res. 2018, 143, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Mendoza, L.M.; Balcer, M. Microplastics in freshwater environments: A review of quantification assessment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozar, A.; Echevarria, F.; Gonzalez-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Ubeda, B.; Hernandez-Leon, S.; Palma, A.T.; Navarro, S.; Garcia-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence that the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is rapidly accumulating plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinold, S.; Herrera, A.; Hernández-González, C.; Gómez, M. Plastic pollution on eight beaches of Tenerife (Canary Islands, Spain): An annual study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Gardfeldt, K.; Krumpen, T.; Thompson, R.C.; O’Connor, I. Microplastics in sea ice and seawater beneath ice floes from the Arctic Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Institute of Marine Engineering Science & Technology. Steering towards an Industry Level Response to Marine Plastic Pollution: Roundtable Summary Report; The Institute of Marine Engineering Science & Technology: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, A.P.M.; Morrison, A.E.; Preston, V.L.; Marx, C.T.; Colson, B.C.; White, H.K. Rapid Identification of Marine Plastic Debris via Spectroscopic Techniques and Machine Learning Classifiers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10630–10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, L.; Andrady, A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmerik, T.; Schwarz, A. Plastic debris in rivers. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winton, D.J.; Anderson, L.G.; Rocliffe, S.; Loiselle, S. Macroplastic pollution in freshwater environments: Focusing public and policy action. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Cózar, A.; Gimenez, B.C.G.; Barros, T.L.; Kershaw, P.J.; Guilhermino, L. Macroplastics Pollution in the Marine Environment. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 305–328. ISBN 9780128050521. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, F.; Saini, C.; Potter, G.; Galgani, F.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Hagmann, P. An evaluation of surface micro- and mesoplastic pollution in pelagic ecosystems of the Western Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12190–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, J.; Booth, A.M.; Tiller, R.; Maes, T.; Larreta, J. Microplastics Pollution and Regulation. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Frias, J.P.G.L.; Booth, A.M.; Vieira, L.R.; Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics Pollution in the Marine Environment. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 329–351. ISBN 9780128050521. [Google Scholar]
- Gigault, J.; Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic, D.; Aoustin, E.; Buclet, N.; Brandt, N. Plastic waste management in the context of a European recycling society: Comparing results and uncertainties in a life cycle perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 55, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, J.; Schlögel, K.; Lechthaler, S.; Plaster, J.; Bitter, K.; Blank, L.M.; Quicker, P. Comparative Analysis of the Behaviour of Marine Litter in Thermochemical Waste Treatment Processes. Processes 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkl, A.; Stuchtey, M. Stemming the Tide: Land-Based Strategies for a Plastic- Free Ocean; Ocean Conservancy and McKinsey Center for Business and Environment. 2015, pp. 1–47. Available online: https://oceanconservancy.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/full-report-stemming-the.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issifu, I.; Sumaila, U.R. A Review of the Production, Recycling and Management of Marine Plastic Pollution. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, A.; Savelli, H.; Beunen, R.; Kalz, M.; Ragas, A.; Van Belleghem, F. Solutions for global marine litter pollution. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 28, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syberg, K.; Nielsen, M.B.; Westergaard Clausen, L.P.; van Calster, G.; van Wezel, A.; Rochman, C.; Koelmans, A.A.; Cronin, R.; Pahl, S.; Hansen, S.F. Regulation of plastic from a circular economy perspective. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 29, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyns, Z.O.G.; Shaver, M.P. Mechanical Recycling of Packaging Plastics: A Review. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, W.; Kitaw, D. Conceptualizing reverse logistics to plastics recycling system. Soc. Responsib. J. 2020. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular Economy; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- OCEANETS. Technological Approaches for Circular Economy Solutions in Terms of Prevention, Recover, Re-Use and Recycle of Fishing Gears to Obtain Added-Value Products in the Textile Industry. Available online: http://oceanets.eu/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- marGnet. Mapping and Recycling of Marine Litter and Ghost Nets on the Sea-Floor. Available online: http://www.margnet.eu/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- NetTag. Tagging Fishing Gears and Enhancing on Board Best-Practices to Promote Waste Free Fisheries. Available online: https://net-tag.eu/?lang=en (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- CleanAtlantic. Tackling Marine Litter in the Atlantic Area. Available online: http://www.cleanatlantic.eu/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- CircularSeas. Turning Ocean Plastic Waste into Green Products for Maritime Industries. Available online: https://circularseas.com/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Kostidi, E.; Nikitakos, N. Exploring the Potential of 3D Printing of the Spare Parts Supply Chain in the Maritime Industry. In Safety of Sea Transportation; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 171–178. ISBN 978-1-315-09908-8. [Google Scholar]
- Aurrekoetxea, J.; Sarrionandia, M.A.; Urrutibeascoa, I.; Maspoch, M.L. Effects of recycling on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of isotactic polypropylene. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 2607–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlantic Area. Projects. Available online: https://www.atlanticarea.eu/page/48 (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Kostidi, E.; Nikitakos, N. Is It Time for the Maritime Industry to Embrace 3d Printed Spare Parts? TransNav Int. J. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2018, 12, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizon, J.R.C.; Valino, A.D.; Souza, L.R.; Espera, A.H.; Chen, Q.; Advincula, R.C. Three-dimensional-printed molds and materials for injection molding and rapid tooling applications. MRS Commun. 2019, 9, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguella-Canela, J.; Planas, S.M.; Ayats, J.R.G.; de los Santos López, M.A. Study and comparison of the different costs’ schema associated to geometry, material and processing between 3D printing, injection molding and machining manufacturing technologies. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 41, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkanen, J.; Manfredi, D.; Minetola, P.; Iuliano, L. About the Use of Recycled or Biodegradable Filaments for Sustainability of 3D Printing. In Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2017; Campana, G., Howlett, R.J., Setchi, R., Cimatti, B., Eds.; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 68, pp. 776–785. ISBN 978-3-319-57077-8. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Part 2: Overview of Process Categories and Feedstock; ISO 17296-2:2015; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, O.A.; Masood, S.H.; Bhowmik, J.L. Optimization of fused deposition modeling process parameters: A review of current research and future prospects. Adv. Manuf. 2015, 3, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtchnell, T.; Urry, J. A Brief History of 3D Printing. In A New Industrial Future? 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 18–42. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Automation Systems and Integration—Numerical Control of Machines—Program Format and Definitions of address Words—Part 1: Data Format for Positioning, Line Motion and Contouring Control Systems; ISO 6983-1:2009; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.C.; de Beer, D. Development of a stereolithography (STL) slicing and G-code generation algorithm for an entry level 3-D printer. In Proceedings of the 2013 Africon, Pointe-Aux-Piments, Mauritius, 9–12 September 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ranellucci, A. Reprap, Slic3r and the Future of 3D Printing. In Low-cost 3D Printing for Science, Education & Sustainable Development; ICTP—The Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics: Trieste, Italy, 2013; pp. 75–82. ISBN 92-95003-48-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Ariffin, M.K.A.; Sukindar, N.A.; Baharudin, B.T.H.T.; Jaafar, C.N.A.; Ismail, M.I.S. Slicer Method Comparison Using Open-source 3D Printer. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 114, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, F.; Bugdayci, H.; Grunert, J.; Keller, F.; Roller, D. Influence of slicing tools on quality of 3D printed parts. Comput.-Aided Des. Appl. 2016, 13, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmani, M.A.A.; Jaywant, S.A.; Arif, K.M. Study of Microchannels Fabricated Using Desktop Fused Deposition Modeling Systems. Micromachines 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, F.W.; Kopp, O.; Roller, D. Abstract API for 3D printing hardware and software resources. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 1519–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.F.; Abreu, P.; Restivo, M.T.; Chouzal, M.F.; Santos, B.F.; Rodrigues, J. Enhancing a 3D Printer with Online Access. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. IJIM 2017, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußge, G. OctoPrint. Available online: https://octoprint.org/ (accessed on 18 February 2021).
- Horvath, J. Driving Your Printer: G-code. In Mastering 3D Printing; Apress: Berkeley, CA, UAA, 2014; pp. 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Free and Open-source Control Software for 3-D Motion and Processing. J. Open Res. Softw. 2016, 4, e2. [CrossRef]
- Kostidi, E.-E.; Nikitakos, N. Additive manufacturing of Spare parts in the Maritime Industry in the digital era. In Proceedings of the Annual conference of the International Association of Maritime Economists (IAME), Athens, Greece, 25–28 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, J.; Zhang, L.; Tao, F.; Ren, L. Customized production based on distributed 3D printing services in cloud manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 84, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszkiewicz, A.; Bolanowski, M.; Budzik, G.; Przeszłowski, Ł.; Oleksy, M. Process of Creating an Integrated Design and Manufacturing Environment as Part of the Structure of Industry 4.0. Processes 2020, 8, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chou, W.; Zhou, W.; Luo, M. Design Patterns and Extensibility of REST API for Networking Applications. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2016, 13, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußge, G. REST API. Available online: https://docs.octoprint.org/en/master/api/index.html (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Petzold, C. Creating Mobile Apps with Xamarin.Forms; Microsoft Press: Redmond, WA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-5093-0297-0. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.-M.; Edwards, K.L. The role of materials identification and selection in engineering design. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikula, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Izydorczyk, G.; Warchoł, J.; Moustakas, K.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. 3D printing filament as a second life of waste plastics—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 12321–12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, S.B.; Bhowmik, S.; Ray, A. Multi Criteria Decision Making For Selection Of Material Composition For Powder Metallurgy Process. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 4615–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Khan, S.A.; Alhems, L.M. Application of TOPSIS Approach to Multi-Criteria Selection of Wind Turbines for On-Shore Sites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attributes Decision Making Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, B.; Lamata, M.T.; Pelta, D.; Sanchez, J.M. El método topsis relativo vs. Absoluto. Rev. Electrón. Comun. Trab. ASEPUMA 2013, 14, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- The Waste and Resources Action Programme. Plastics Market Situation Report 2019; The Waste and Resources Action Programme: Banbury, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, F.; Roller, D. Additive Manufacturing, Cloud-Based 3D Printing and Associated Services—Overview. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2017, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Waste | Quantity (Tn) | Plastic Type | Current Waste Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nets | 1681.34 | HDPE, PP | Sale to plastic recycling company |
| Containers | 454.10 | PET, HDPE, PP, LDPE | Contract with private company for collection, transport and management of the waste |
| Films | 135.73 | LDPE | MSW 1 or sale to plastic recycling company |
| Bags | 130.00 | LDPE | Compacted and managed as MSW 1 |
| Ropes | 100.00 | HDPE, PP | Sale to company for reuse |
| Fragile packaging | 31.28 | EPS (Expanded PolyStyrene) | Collection by the port manager |
| Strapping tapes | 29.56 | PP | MSW 1 or sale to plastic recycling company |
| Plastic Type | Quantity (Tn) |
|---|---|
| HDPE | 1429.04 |
| PP | 365.83 |
| LDPE | 265.73 |
| PET | 62.04 |
| EPS | 31.28 |
| Part | Quantity in Demand (by Year) | Manufacturing Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Prototypes | - | 3D Printing |
| Pallets | 3545 items | Injection |
| Spare parts (Bearing carriers) | - (44 items) | 3D Printing |
| Film | 60,480 kg | Other |
| Bags | 1500 items | Other |
| Roller stops | 300 items | 3D Printing |
| Rack tubes | 50 items | 3D Printing |
| Special parts of a jetty, such as curved or trim elements | - | 3D Printing |
| Bottles | 270 items | Injection |
| Containers | 1800 items | Injection/Other or 3D Printing |
| Support components | 1000 items | 3D Printing |
| Plastic pipes | - | Injection |
| Criterion 1 | Criterion 2 | … | Criterion n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material 1 | … | |||
| Material 2 | … | |||
| … | … | … | … | … |
| Material m | … | |||
| Criterion weight | … |
| Criterion 1 | Criterion 2 | … | Criterion n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material 1 | … | ||||||
| Material 2 | … | ||||||
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Material m | … | ||||||
| Normalised weight | … | ||||||
| … | |||||||
| … |
| Steps | Variables | Time to Print (min) | User 3D Technology Knowledge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 15 | 38 | 15 | High |
| Integrated | 4 | 3 | 2 | Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrido, J.; Silva, D.; Portela, B.; Lekube, B. Integrated User-Oriented Service for 3D Printing Environments with Recycled Material from Maritime Plastic Waste. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093787
Garrido J, Silva D, Portela B, Lekube B. Integrated User-Oriented Service for 3D Printing Environments with Recycled Material from Maritime Plastic Waste. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093787
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrido, Julio, Diego Silva, Bruno Portela, and Blanca Lekube. 2021. "Integrated User-Oriented Service for 3D Printing Environments with Recycled Material from Maritime Plastic Waste" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093787
APA StyleGarrido, J., Silva, D., Portela, B., & Lekube, B. (2021). Integrated User-Oriented Service for 3D Printing Environments with Recycled Material from Maritime Plastic Waste. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093787







