The Role of Palynology in Archaeoecological Research: Reconstructing Human-Environment Interactions during Neolithic in the Western Mediterranean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
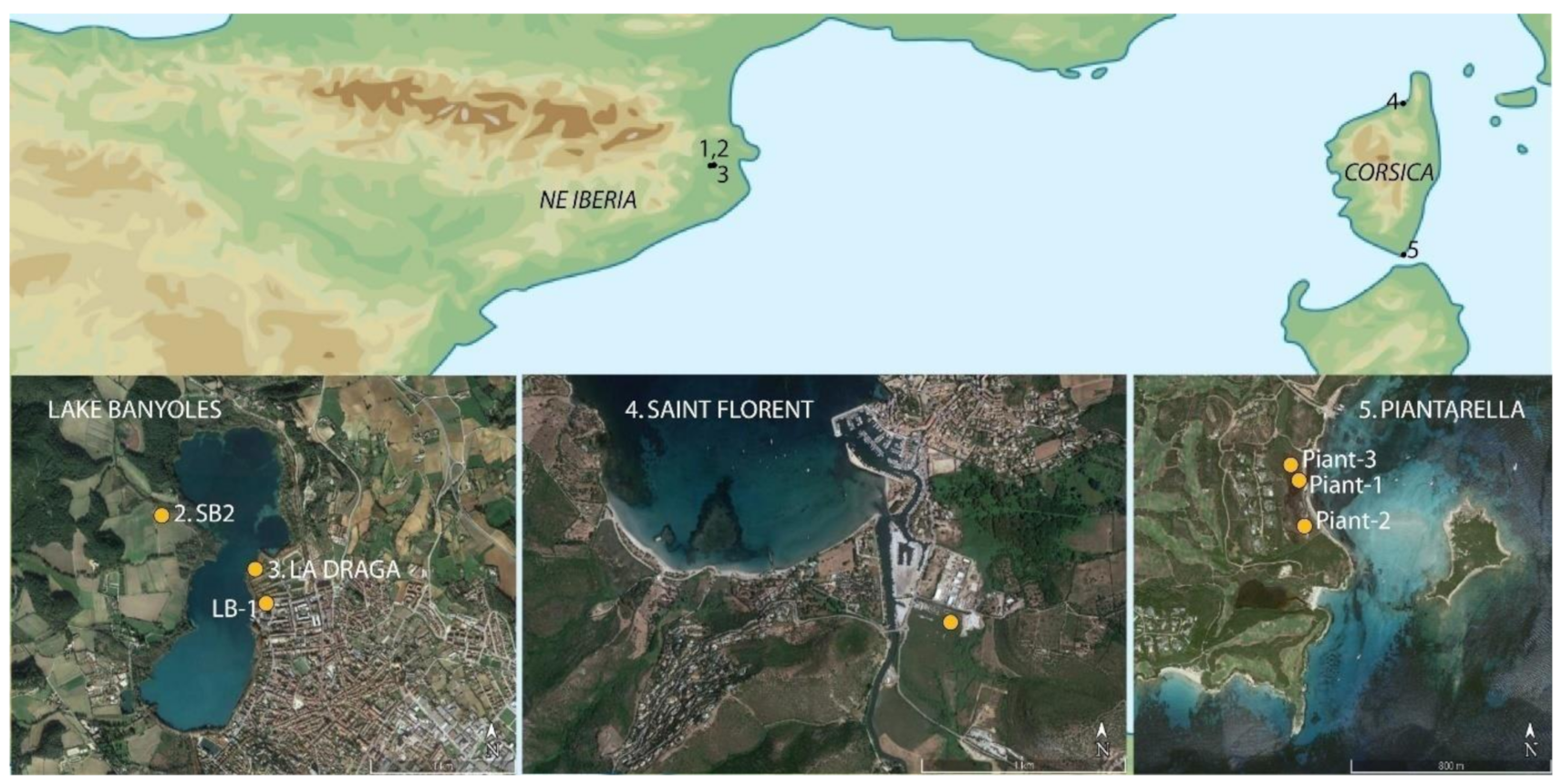
2. Study Area: Environmental Settings and Archaeological Background
2.1. Corsica
2.2. NE Iberia
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Cases
3.1.1. Piantarella (South Corsica)
3.1.2. Saint Florent (North Corsica)
3.1.3. Lake Banyoles (NE Iberia)
3.1.4. La Draga (NE Iberia)
3.2. Palynology, the Study of Pollen and Non-Pollen Palynomorphs (NPP)
3.3. Numerical Analysis
4. Results
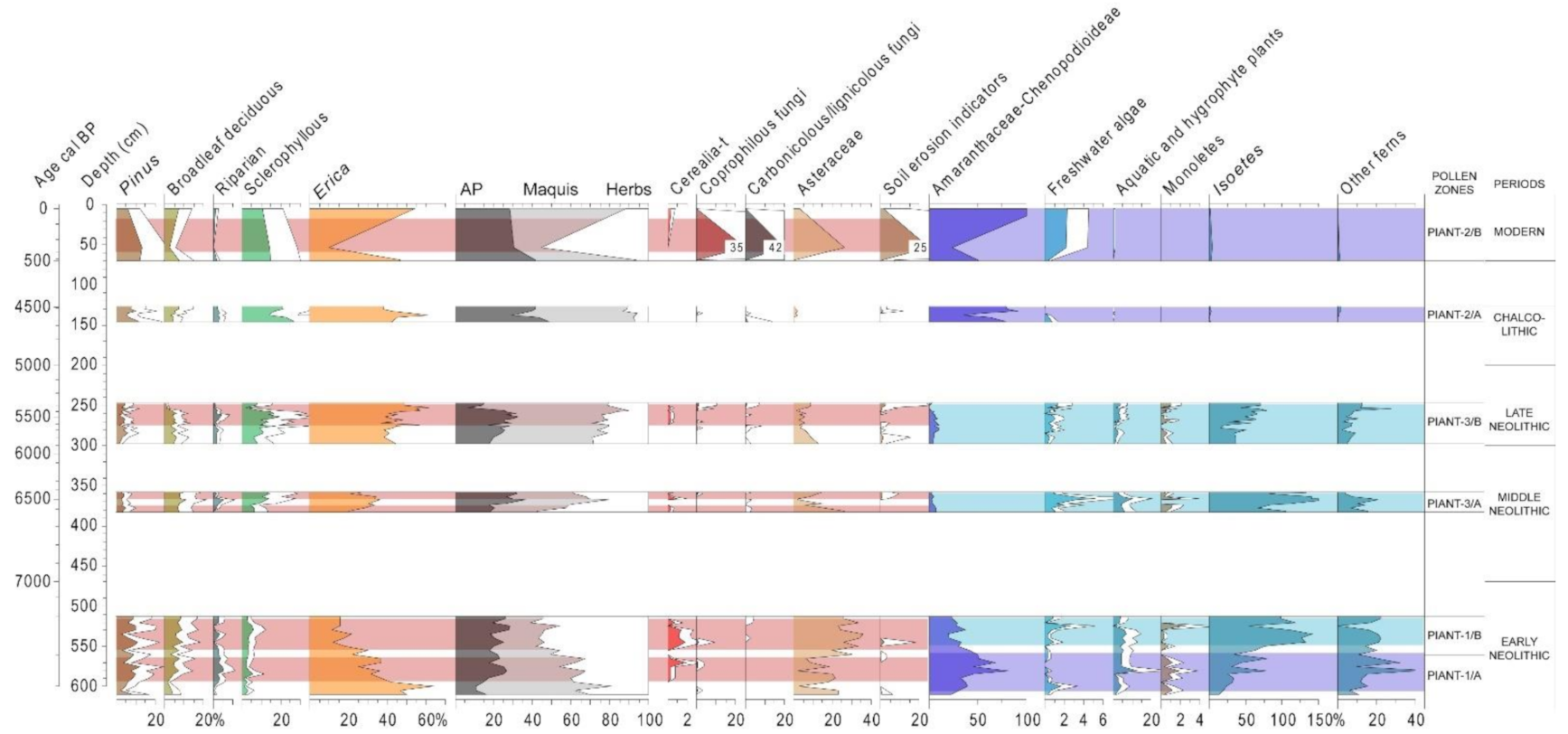
4.1. Piantarella (South Corsica, France)
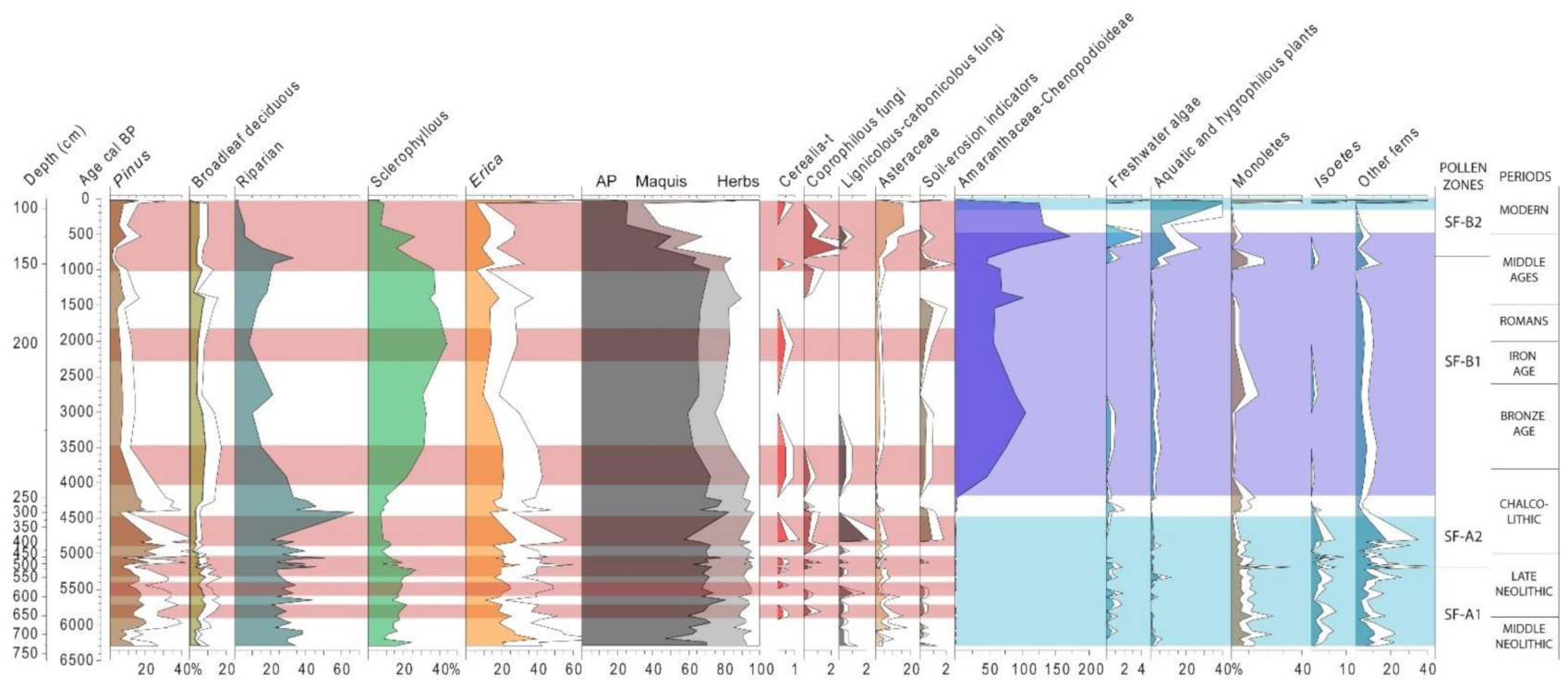
4.2. Saint Florent (North Corsica, France)
4.3. Lake Banyoles (Girona, NE Iberia)
4.4. La Draga (Girona, NE Iberia)
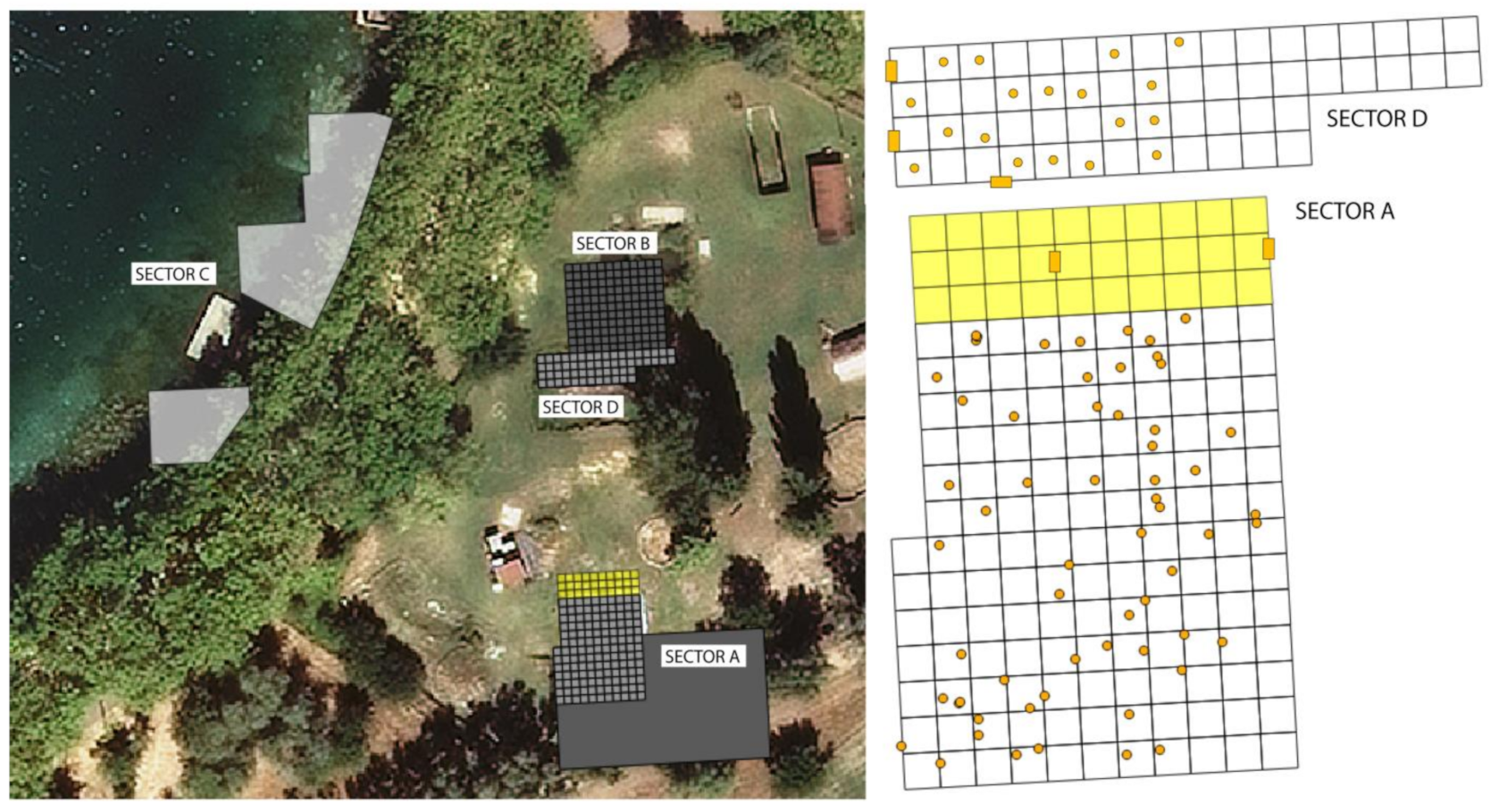
4.4.1. Archaeological Profiles
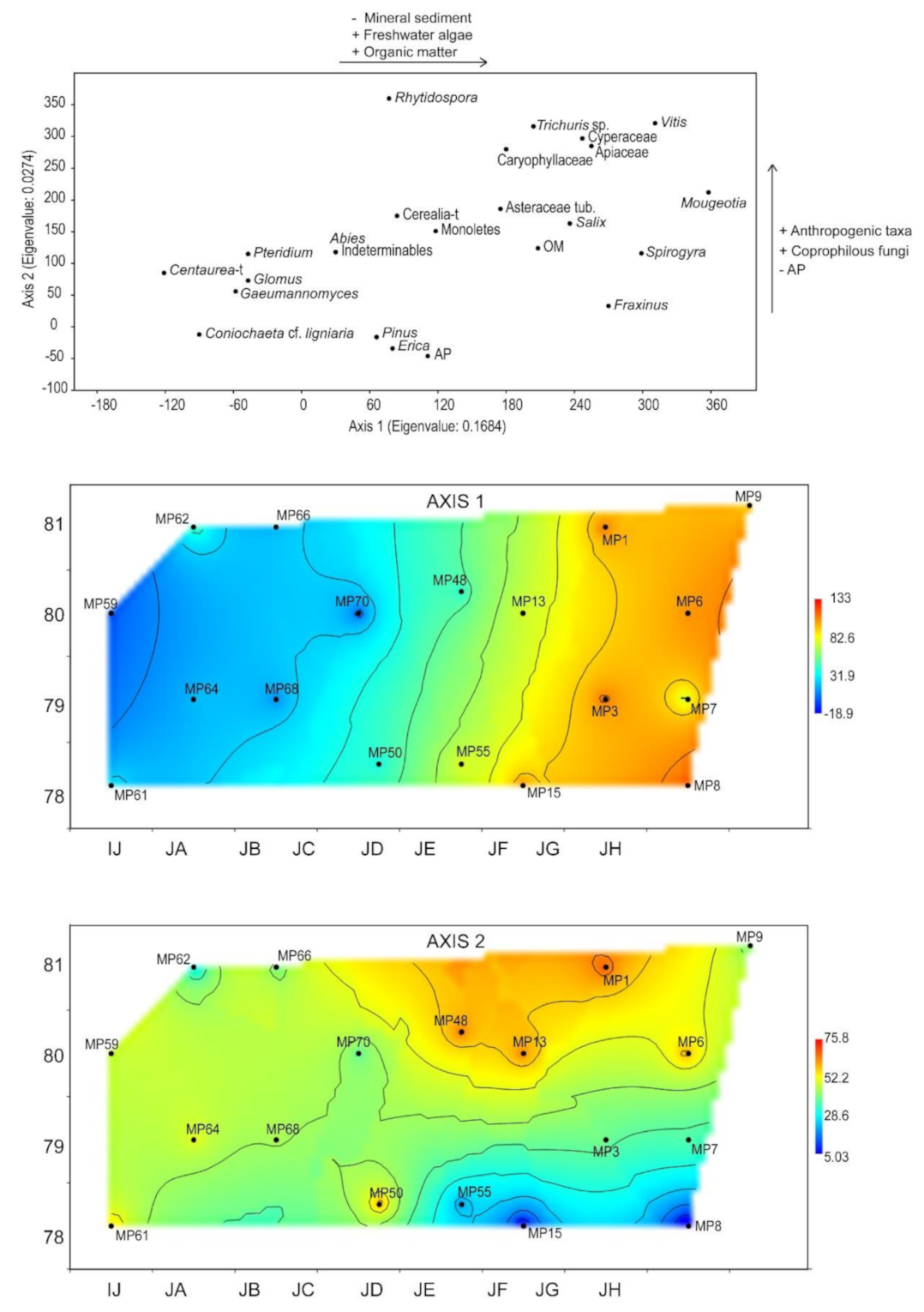
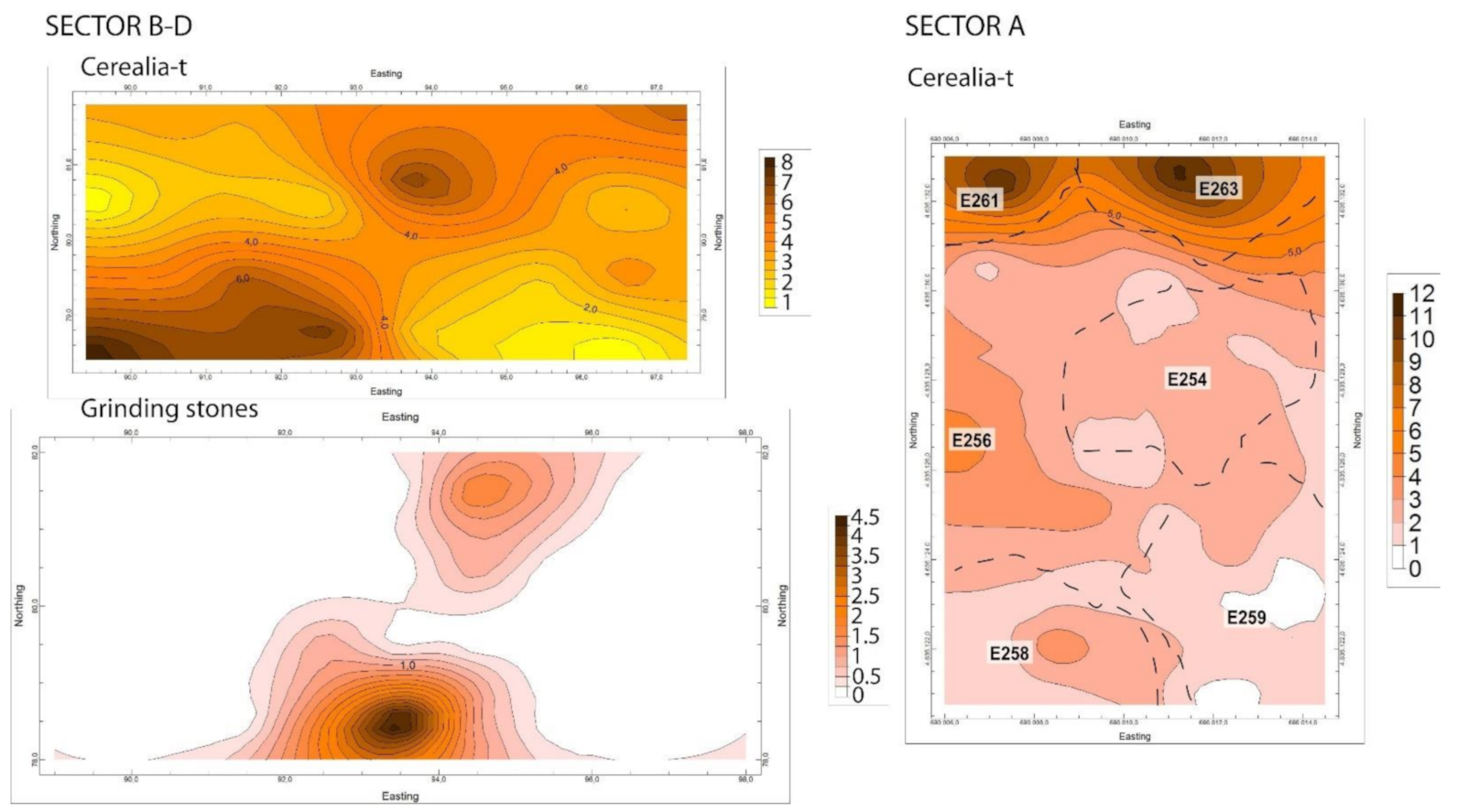
4.4.2. Spatial Distribution of Pollen and NPP
5. Discussion
5.1. Mid-Holocene Vegetation History and Neolithic Landscape Transformation in the Western Mediterranean
5.2. Local Palaeoenvironmental Evolution in Lakes and Wetlands, the Value of Non-Pollen Palynomorphs (NPP)
5.3. Archaeopalynology: How Pollen and NPP Can Provide Relevant Data for the Study of Plant Uses, Social Use of Space and Site Formation Processes
5.3.1. Site Formation Processes and Environmental Evolution
5.3.2. Social Use of Space
5.3.3. Plant and Fungi Uses
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruddiman, W.F. The Anthropocene. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 41, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D.; Zeder, M.A. The onset of the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2014, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.N.; Woodbridge, J.; Palmisano, A.; Bevan, A.; Fyfe, R.; Shennan, S. Mediterranean landscape change during the Holocene: Synthesis, comparison and regional trends in population, land cover and climate. Holocene 2019, 29, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beaulieu, J.L.; Miras, Y.; Andrieu-Ponel, V.; Guiter, F. Vegetation dynamics in north-western Mediterranean regions: In-stability of the Mediterranean bioclimate. Plant Biosyst. 2005, 139, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.; Meadows, M.E.; Dodson, J.R. The history of mediterranean-type environments: Climate, culture and landscape. Holocene 2001, 11, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, R.M.; Woodbridge, J.; Palmisano, A.; Bevan, A.; Shennan, S.; Burjachs, F.; Herrero, B.L.; Puchol, O.G.; Carrión, J.-S.; Revelles, J.; et al. Prehistoric palaeodemographics and regional land cover change in eastern Iberia. Holocene 2019, 29, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombaroli, D.; Vannière, B.; Emmanuel, C.; Magny, M.; Tinner, W. Fire-vegetation interactions during the Mesolithic-Neolithic transition at Lago dell’Accesa, Tuscany, Italy. Holocene 2008, 18, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannière, B.; Colombaroli, D.; Chapron, E.; Leroux, A.; Tinner, W.; Magny, M. Climate versus human-driven fire regimes in Mediterranean landscapes: The Holocene record of Lago dell’Accesa (Tuscany, Italy). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouli, K.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Natural and cultural landscape of the Neolithic settlement of Dispilio: Palynological results. Hell. J. Geosci. 2008, 43, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vescovi, E.; Ammann, B.; Ravazzi, C.; Tinner, W. A new Late-glacial and Holocene record of vegetation and fire history from Lago del Greppo, northern Apennines, Italy. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2010, 19, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinova, E.; Tonkov, S.; Bozilova, E.; Vajsov, I. Holocene anthropogenic landscapes in the Balkans: The palaeobotanical evidence from southwestern Bulgaria. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2012, 21, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbridge, J.; Roberts, N.; Fyfe, R. Pan-Mediterranean Holocene vegetation and land-cover dynamics from synthesized pollen data. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 2159–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, S.E.; Vannière, B.; Colombaroli, D.; Anderson, R.S.; Carrión, J.S.; Ejarque, A.; Romera, G.G.; González-Sampériz, P.; Hoefer, D.; Morales-Molino, C.; et al. Humans take control of fire-driven diversity changes in Mediterranean Iberia’s vegetation during the mid–late Holocene. Holocene 2019, 29, 886–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, A.M.; Allevato, E.; Arobba, D.; Mazzanti, M.B.; Bosi, G.; Caramiello, R.; Castiglioni, E.; Carra, M.L.; Celant, A.; Costantini, L.; et al. Pollen and macroremains from Holocene archaeological sites: A dataset for the understanding of the bio-cultural diversity of the Italian landscape. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2015, 218, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Revelles, J.; Burjachs, F.; Van Geel, B. Pollen and non-pollen palynomorphs from the Early Neolithic settlement of La Draga (Girona, Spain). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2016, 225, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, R.; Revelles, J.; Burjachs, F.; Fermé, L.C.; Pérez-Obiol, R. Interdisciplinary approach to the landscape and firewood exploitation during the Holocene at La Garrotxa (Girona, NE Iberia). Quat. Int. 2018, 463, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, A.M.; Florenzano, A.; Burjachs, F.; Giardini, M.; Kouli, K.; Masi, A.; Picornell-Gelabert, L.; Revelles, J.; Sadori, L.; Servera-Vives, G.; et al. From influence to impact: The multifunctional land use in Mediterranean prehistory emerging from palynology of archaeological sites (8.0–2.8 ka BP). Holocene 2019, 29, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillson, L.; Whitlock, C.; Humphrey, G. Resilience and fire management in the Anthropocene. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugliè, C. Your path led trough the sea … the emergence of Neolithic in Sardinia and Corsica. Quat. Int. 2018, 470, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Puchol, O.; Salazar-García, D.C. Timing the West Mediterranean Last Hunter-Gatherers and First Farmers. In Times of Neolithic Transition along the West Mediterranean, Fundamental Issues in Archaeology; Springer Int. Publ.: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 69–99. [Google Scholar]
- Weninger, B.; Alram-Stern, E.; Bauer, E.; Clare, L.; Danzeglocke, U.; Joris, O.; Claudia, K.E.; Gary, R.F.; Todorova, H.; van Andel, T. Climate forcing due to the 8200 cal yr BP event observed at Early Neolithic sites in the eastern Mediterranean. Quat. Res. 2006, 66, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.F.; Guilaine, J. The 8200 cal BP abrupt environmental change and the Neolithic transition: A Mediterranean perspective. Quat. Int. 2009, 200, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J. Archaeoecology of Neolithisation. Human-environment interactions in the NE Iberian Peninsula during the Early Neolithic. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 15, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Ghilardi, M.; Rossi, V.; Currás, A.; López-Bultó, O.; Brkojewitsch, G.; Vacchi, M. Coastal landscape evolution of Corsica island (W. Mediterranean): Palaeoenvironments, vegetation history and human impacts since the early Neolithic period. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 225, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramoni, P.; D’Anna, A. Le Néolithique moyen de la Corse revisité: Nouvelles données, nouvelles perceptions. In Le Chasséen, des Chasséens… Retour sur une Culture Nationale et ses Parallèles, Sepulcros de Fossa (Cortaillod, Lagozza); Société Préhistorique Française: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barceló, J.A. La seqüència crono-cultural de la prehistòria catalana. Anàlisi estadística de les datacions radiomètriques de l’inici de l’Holocè a la edat del ferro. Cypsela 2008, 17, 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Oms, F.X.; Terradas, X.; Morell, B.; Gibaja, J.F. Mesolithic-Neolithic transition in the northeast of Iberia: Chronology and socioeconomic dynamics. Quat. Int. 2018, 470, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilhao, J. Time is on my side…. In Dynamics of Neolithisation in Europe. Studies in Honour of Andrew Sherratt; Hadjikoumis, A., Robinson, E., Viner, S., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 46–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabeu, J.; Molina, L.L.; Esquembre, M.A.; Ortega, J.R.; Boronat, J. La cerámica impresa mediterránea en el origen del Neolítico de la Península Ibérica. In De Méditerranée et D’ailleurs. Melanges Offerts à Jean Guilaine; Archives d’Écologie Préhistorique: Toulouse, France, 2009; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Antolín, F. Of Cereals, Poppy, Acorns and Hazelnuts. Plant Economy Among Early Farmers (5400–2300 cal BC) in the NE of the Iberian Peninsula. An Archaeobotanical Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Antolín, F.; Jacomet, S.; Buxó, R. The hard knock life. Archaeobotanical data on farming practices during the Neolithic (5400–2300 cal BC) in the NE of the Iberian Peninsula. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 61, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilaine, J. A personal view of the neolithisation of the Western Mediterranean. Quat. Int. 2018, 470, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Ghilardi, M. 50. Piantarella (south Corsica, France). Grana 2021, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Ghilardi, M. 49. Saint Florent (north Corsica, France). Grana 2021, 60, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamitjana, X.; Colomer, J.; Roget, E.; Serra, T. Physical limnology in Lake Banyoles. Limnetica 2006, 25, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Höbig, N.; Weber, M.E.; Kehl, M.; Weniger, G.C.; Julià, R.; Melles, M.; Fülöp, R.H.; Vogel, H.; Reicherter, K. Lake Banyoles (northeastern Spain): A Last Glacial to Holocene multi-proxy study with regard to environmental variability and human occupation. Quat. Int. 2012, 274, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Obiol, R.; Julià, R. Climatic change on the Iberian Peninsula recorded in a 30,000-yr pollen record from Lake Banyoles. Quat. Res. 1994, 41, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Cho, S.; Iriarte, E.; Burjachs, F.; van Geel, B.; Palomo, A.; Piqué, R.; Peña-Chocarro, L.; Terradas, X. Mid-holocene vegetation history and Neolithic land-use in the Lake Banyoles area (Girona, Spain). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 435, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J. 42. Lake Banyoles SB2 core (Girona, north-eastern Iberia, Spain). Grana 2019, 58, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, A.; Piqué, R.; Terradas, X.; Bosch, A.; Buxó, R.; Chinchilla, J.; Tarrús, J. Prehistoric occupation of Banyoles Lakeshore: Results of recent Excavations at La Draga Site, Girona, Spain. J. Wetl. Archaeol. 2014, 14, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreaki, V.; Barceló-Álvarez, J.A.; Antolín i Tutusaus, F.; Bogdanovic, I.; Gassmann, P.; López-Bultó, O.; Morera, N.; Palomo, A.; Piqué, R.; Revelles, J.; et al. Un modelo bayesiano para la cronología del yacimiento neolítico de La Draga (Banyoles. Girona). Un caso de estudio con ChronoModel 2.0. In Métodos Cronométricos en Arqueología, Prehistoria y Paleontología; Dextra Editorial S.L.: Barcelona, Spain, 2020; pp. 403–418. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, A.; Buxó, R.; Chinchilla, J. El Poblat Lacustre Neolític de La Draga. Excavacions de 1990–1998. Monografies del Centre d’Arqueologia Subaquàtica de Catalunya 2; Girona, Museu d’Arqueologia de Catalunya-CASC: Girona, Spain, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, A.; Buxó, R.; Chinchilla, J. El Poblat Lacustre del Neolític Antic de La Draga. Excavacions 2000–2005. Monografies del Centre d’Arqueologia Subaquàtica de Catalunya 9; Girona, Museu d’Arqueologia de Catalunya-CASC: Girona, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Terradas, X.; Piqué, R.; Palomo, A.; Antolín, F.; López, O.; Revelles, J.; Buxó, R. Farming practices in the Early Neolithic according to agricultural tools: Evidence from La Draga site (Northeastern Iberia). In Times of Neolithic Transition along the Western Mediterranean); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 199–220. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Obiol, R. Análisis polínicos de sedimentos lacustres y de suelos de ocupación de la Draga (Banyoles, Pla de l’ Estany). In Trabajos de Palinología Básica y Aplicada; Mateu-Andrés, I., Dupré-Ollivier, M., Güemes-Heras, J., Burgaz-Moreno, M.E., Eds.; Universitat de València: València, Spain, 1994; pp. 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Revelles, J. Pollen Analysis Report from ‘La Draga’. Fieldwork Campaign 2018 (Sector A). Institut Català de Paleoecologia Humana i Evolució Social (IPHES); Unpublished report; 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burjachs, F. El paisatge del neolític antic. Les dades palinològiques. In El Poblat Lacustre Neolític de la Draga. Excavacions de 1990 a 1998; Bosch, À., Chinchilla, J., Tarrús, J., Eds.; Centre d’Arqueologia Subaquàtica de Catalunya: Girona, Spain, 2000; pp. 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Revelles, J.; Burjachs, F.; Morera, N.; Barceló, J.A.; Berrocal, A.; López-Bultó, O.; Maicher, C.; Bailly, M.L.; Piqué, R.; Palomo, A.; et al. Use of space and site formation processes in a Neolithic lakeside settlement. Pollen and non-pollen palynomorphs spatial analysis in La Draga (Banyoles, NE Iberia). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 81, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J. Informe de L’anàlisi Arqueopalinològica del Sector A del Jaciment de La Draga (Banyoles, Girona). Campanyes D’excavació Arqueològica 2013–2016. Laboratori d’Arqueobotànica. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona; Unpublished report; 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.B. On the theory of pollen analysis. Am. J. Sci. 1963, 261, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosimann, J.E.; Greenstreet, R.L. Representation-insensitive methods for paleoecological pollen studies. Stat. Ecol. 1971, 1, 23–58. [Google Scholar]
- Green, D.G. The ecological interpretation of fine resolution pollen records. New Phytol. 1983, 94, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burjachs, F.; López-Sáez, J.A.; Iriarte, M.J. Metodología arqueopalinológica. In La Recogida de Muestras en Arqueobotànica: Objetivos y Propuestas Metodológicas; Museu d’Arqueologia de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2003; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Revelles, J. Arqueoecología, Arqueobotánica y Arqueopalinología: Una relación dialéctica entre sociedad y medio. In Los Lugares de la Historia. Colección Temas y Perspectivas de la Historia; Museu d’Arqueologia de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2013; Volume 3, pp. 729–748. [Google Scholar]
- Faegri, K.; Iversen, J. Text-Book of Modern Pollen Analysis; Ejnar Munksgaard: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton, V.; Messager, E.; Marquer, L.; Renault-Miskovsky, J. A neotaphonomic experiment in pollen oxidation and its implications for archaeopalynology. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2010, 162, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doppler, T.; Schibler, J.; R€oder, B.; Pichler, S.; Jacomet, S. Archäobiologie Als Sozialgeschichtliche informations quelle: Ein Bislang Vernachläassigtes forschungs potential. In Familie–Verwandtschaft—Sozialstrukturen: SozialarchÄologische Forschungenzu Neolithischen Befunden; Classen, E., Doppler, T., Ramminger, B., Eds.; Berichte der AG Neolithikum 1; Welt und Erde Verlag: Loogh, NE, USA, 2010; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Goeury, C.; de Beaulieu, J.-L. À propos de la concentration du pollen à l’aide de la liqueur de Thoulet dans les sédiments minéraux. Pollen Spores XXI 1979, 21, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, M.; Renault-Miskovsky, J. Nouvelles techniques de préparation en Palynologie appliqués à trois sédiments du Quaternaire final de l’Abri Cornille (Istres-Bouches du Rhône). Bull. AFEQ 1969, 4, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Reille, M. Pollen et Spores d’Europe et d’Afrique du Nord; (URA, CNRS, Laboratoire de Botanique Historique et Palynologie); Laboratoire de Botanique Historique et Palynologie: Marseille, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geel, B. A palaeoecological study of Holocene peat bog sections in Germany and The Netherlands. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 1978, 25, 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geel, B. Non-pollen palynomorphs. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments: Terrestrial, Algal, and Siliceous Indicators; en Smol, J.P., Birks, H.J.B., Last, W.M., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 3, pp. 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geel, B.; Buurman, J.; Brinkkemper, O.; Schelvis, J.; Aptroot, A.; van Reenen, G.; Hakbijl, T. Environmental reconstruction of a Roman Period settlement site in Uitgeest (The Netherlands), with special reference to coprophilous fungi. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2003, 30, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Van Geel, B. Human impact and ecological changes in lakeshore environments. The contribution of non-pollen palynomorphs in Lake Banyoles (NE Iberia). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2016, 232, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, E.C. Tilia, Tilia∙Graph and TGView. Illinois State Museum, Springfield. 1991–2011. Available online: http://museum.state.il.us/pub/grimm/tilia/ (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Grimm, E.C. CONISS: A FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput. Geosci. 1987, 13, 13–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondelli, B.; Lancelotti, C.; Madella, M.; Pecci, A.; Balbo, A.; Ruiz Pérez, J.; Inserra, F.; Gadekar, C.; Cau Ontiveros, M.A.; Ajithprasad, P. Anthropic activity markers and spatial variability: An ethnoarchaeological experiment in a domesticunit of Northern Gujarat (India). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achino, K.F.; Barceló, J.A. Spatial Prediction: Reconstructing the “Spatiality” of Social Activities at the Intra-Site Scale. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2019, 26, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achino, K.F. From Micro to Macro Spatial Dynamics in the Villaggio Delle Macine between XIX-XVI Century BC. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Reille, M. New pollen-analytical researches in Corsica: The problem of Quercus ilex L. and Erica arborea L.; the origin of Pinus halepensis Miller forests. New Phytol. 1992, 122, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soula, F. Les Pierres Dress_ees de L’aire Corso-Sarde. Etude Systémique des Territoires. Le Pietre Fitte Dell’area Corso-Sarda. Studio Sistemico dei Territori. Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille Université, Marseille, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carrión, J.S.; Fuentes, N.; González-Sampériz, P.; Sánchez Quirante, L.; Finlayson, J.C.; Fernández, S.; Andrade, A. Holocene environmental change in a montane region of southern Europe with a long history of human settlement. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 26, 1455–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, M.J.; Pérez-Díaz, S.; Ruiz-Alonso, M.; Zapata-Peña, L. Paleobotanica del Epipaleolítico y Mesolítico vascos. Veleia 2008, 24–25, 629–642. [Google Scholar]
- López-Sáez, J.A.; González Cordero, A.; Cerrillo Cuenca, E. Paleoambiente y paleoeconomía durante el Neolítico antiguo y el Calcolítico en Extremadura: Análisis arqueopalinológico del yacimiento del Cerro de la Horca (Plasenzuela, Cáceres, España). Zephyrus 2007, 60, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- López-Sáez, J.A.; Galop, D.; Iriarte, M.J.; López-Merino, L. Paleoambiente y antropización en los Pirineos de Navarra durante el Holoceno medio (VI-IV milenios cal BC. Una perspectiva palinológica. Veleia 2008, 24–25, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- López-Merino, L. Paleoambiente y Antropización en Asturias Durante el Holoceno (Tesis Doctoral). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- López-Merino, L.; Martínez Cortizas, M.; López-Sáez, J.A. Early agriculture and palaeoenvironmental history in the North of the Iberian Peninsula: A multi-proxy analysis of the Monte Areo mire (Asturias, Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, S.; López-Sáez, J.A.; Galop, D. Vegetation dynamics and human activity in the Western Pyrenean Region during the Holocene. Quat. Int. 2015, 364, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogaard, A. Neolithic Farming in Central Europe; Routledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sugita, S. Theory of quantitative reconstruction of vegetation I: Pollen from large sites REVEALS regional vegetation composition. Holocene 2007, 17, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugny, C.; Mazier, F.; Galop, D. Modern and fossil non-pollen palynomorphs from the Basque mountains (western Pyrenees, France): The use of coprophilous fungi to reconstruct pastoral activity. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2010, 19, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, E.; Bichet, V.; Massa, C.; Petit, C.; Vannière, B.; Richard, H. Pollen and non-pollen palynomorph evidence of medieval farming activities in southwestern Greenland. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2010, 19, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Antolín, F.; Berihuete, M.; Burjachs, F.; Buxó, R.; Caruso, L.; López-Bultó, O.; Palomo, A.; Piqué, P.; Terradas, X. Landscape transformation and economic practices among the first farming societies in Lake Banyoles (Girona, Spain). Environ. Archaeol. 2014, 19, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisset, E.; Revelles, J.; Expósito, I.; Bernabéu-Aubán, J.; Burjachs, F. Socio-Ecological Contingencies with Climate Changes over the Prehistory in the Mediterranean Iberia. Quaternary 2020, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burjachs, F.; Schulte, L. El paisatge vegetal del Penedès entre la Prehistoria i el Món Antic. In Territoris Antics a la Mediterrània ia la Cossetània Oriental (Actes del Simposi Internacional d’Arqueologia del Baix Penedès); Generalitat de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2003; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Court-Picon, M.; Vella, C.; Chabal, L.; Bruneton, H. Paléoenvironnements littoraux depuis 8000 ans sur la bordure occidentale du Golfe du Lion: Le lido de l’étang de Thau (carottage Setif, Sète, Hérault). Quaternaire 2010, 21, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Rita, F.; Magri, D. The 4.2 ka event in the vegetation record of the central Mediterranean. Clim. Past 2019, 15, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Rita, F.; Melis, R.T. The cultural landscape near the ancient city of Tharros (central West Sardinia): Vegetation changes and human impact. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 4271–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejarque, A.; Julià, R.; Reed, J.M.; Mesquita-Joanes, F.; Marco-Barba, J.; Riera, S. Coastal evolution in a Mediterranean microtidal zone: Mid to Late Holocene natural dynamics and human management of the Castelló lagoon, NE Spain. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burjachs, F.; Pérez-Obiol, R.; Picornell-Gelabert, L.; Revelles, J.; Servera-Vives, G.; Expósito, I.; Yll, E.-I. Overview of environmental changes and human colonization in the Balearic Islands (Western Mediterranean) and their impacts on vegetation composition during the Holocene. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 12, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelles, J.; Burjachs, F.; Palomo, A.; Piqué, R.; Iriarte, E.; Pérez-Obiol, R.; Terradas, X. Human-environment interaction during the Mesolithic- Neolithic transition in the NE Iberian peninsula. Vegetation history, climate change and human impact during the early-middle Holocene in the Eastern pre-pyrenees. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 184, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Liberta, A.E.; Dickman, L.A. Interaction of vascular plants and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi across a soil moisture-nutrient gradient. Oecologia 1984, 64, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, R.; Revelles, J.; Berihuete-Azorín, M.; Lladó, J.G.; Palomo, A.; Terradas, X. Use of fungi for tinder at the Early Neolithic settlement of La Draga (NE Iberia). Quat. Int. 2020, 541, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicher, C.; Hoffmann, A.; Côté, N.M.; Palomo Pérez, A.; Saña Segui, M.; Le Bailly, M. Paleoparasitological investigations on the Neolithic lakeside settlement of La Draga (Lake Banyoles, Spain). Holocene 2017, 27, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitkute, E. Paleoparasitology and Its Application the Case of La Draga Lakeside Settlement and Fumiers Contexts of El Mirador and Can Sadurní Caves. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Tarragona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shumilovskikh, L.S.; Ferrer, A.; Schlütz, F. Non-pollen palynomorphs notes: 2. Holocene record of Megalohypha aqua-dulces, its relation to the fossil form genus Fusiformisporites and association with lignicolous freshwater fungi. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2017, 246, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Campo, M.; Leroi-Gourhan, A. Note préliminaire à l’étude des pollens fossiles de différents niveaux des grottes d’Arcy-sur-Cure. Bull. Muséum Soc. Préhistoire Française 1956, 28, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, H.; Gery, S. Variations in pollen proportions of Plantago lanceolata and P. major/media at a Neolithic lake dwelling, Lake Chalain, France. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 1993, 2, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, E.; Richard, H. Bronze Age at Lake Bourget (NW Alps, France): Vegetation, human impact and climatic change. Quat. Int. 2009, 200, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeraj, M.; Veluscek, A.; Jacomet, S. The diet of Eneolithic (Copper Age, Fourth millennium cal B.C.) pile dwellers and the early formation of the cultural landscape south of the Alps: A case study from Slovenia. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2009, 18, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovic, I.; López-Bultó, O.; Rosillo, R.; Revelles, J.; Geli, R.; Palomo, A.; Terradas, X.; Piqué, R.; Morera, N.; Andreaki, V.; et al. Les intervencions arqueològiques al jaciment neolític lacustre de la Draga 2016–2017. (Banyoles-Pla de l’Estany). In Catorzenes Jornades d’Arqueologia de les Comarques de Girona; Caldes de Malavella: Girona, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geel, B. Non-pollen palynomorphs. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Power, R.C.; Salazar-García, D.C.; Straus, L.G.; Morales, M.R.G.; Henry, A.G. Microremains from El Mirón Cave human dental calculus suggest a mixed plant–animal subsistence economy during the Magdalenian in Northern Iberia. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 60, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berihuete-Azorín, M.; Girbal, J.; Piqué, R.; Palomo, A.; Terradas, X. Punk’s not dead. Fungi for tinder at the Neolithic site of La Draga (NE Iberia). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Revelles, J. The Role of Palynology in Archaeoecological Research: Reconstructing Human-Environment Interactions during Neolithic in the Western Mediterranean. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4073. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094073
Revelles J. The Role of Palynology in Archaeoecological Research: Reconstructing Human-Environment Interactions during Neolithic in the Western Mediterranean. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):4073. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094073
Chicago/Turabian StyleRevelles, Jordi. 2021. "The Role of Palynology in Archaeoecological Research: Reconstructing Human-Environment Interactions during Neolithic in the Western Mediterranean" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 4073. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094073
APA StyleRevelles, J. (2021). The Role of Palynology in Archaeoecological Research: Reconstructing Human-Environment Interactions during Neolithic in the Western Mediterranean. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 4073. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094073





