Featured Application
Singular studies suggested some effectiveness of pump techniques; however, the differences for population, modalities, dosage, and outcome measures do not allow definite conclusions.
Abstract
Background: Osteopathic manual procedures called pump techniques include thoracic, abdominal, and pedal pumps. Similar techniques, called pompages, are also addressed to joints and muscles. Despite their widespread use, no systematic review has been published on their effectiveness. (2) Methods: CINAHL, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, ISI Web of Science, PEDro, PubMed, and Scopus databases were searched until July 2020. Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) on adults were included. Subjective (e.g., pain, physical function) and objective (e.g., pulmonary function, blood collection) outcomes were considered. The Risk of Bias tool (RoB 2) and the GRADE instrument were used to evaluate the quality of evidence. (3) Results: 25 RCTs were included: 20 concerning the pump techniques and five concerning pompages. Due to the extensive heterogeneity of such studies, it was not possible to perform a meta-analysis. The risk of bias resulted from moderate to high and the quality of the evidence was from very low to high. Singular studies suggested some effectiveness of pump techniques on pain and length of hospitalization. Pompage seems also to help improve walking distance and balance. (4) Conclusions: Although several studies have been published on manual pump techniques, the differences for population, modalities, dosage, and outcome measures do not allow definite conclusions of their effectiveness.
1. Introduction
Osteopathic manual techniques were first proposed by A. Taylor Still to correct somatic dysfunctions, increase blood and lymphatic flow and improve the individual’s self-healing capacity [1]. Starting from these bases, in 1920, C. Earl Miller developed a manual technique called “thoracic pump technique”, aiming to improve lymphatic flow via intrathoracic pressure changes [2]. By the manipulation of this lymphatic pump, Dr. Miller speculated that an increased lymphatic circulation of the entire body could be provoked [3]. A number of other lymphatic pump techniques have been developed and investigated since Dr. Miller’s time [4]. Some ancient lymphatic pump techniques already in use are abdominal and pelvic pumps and pedal pumps [5].
Other authors deepened the pump techniques, expanding their focus and studying their effects on connective tissues. In the 1970s, Angus Cathie studied the relationship between spinal mechanics and respiratory dynamics and between the fascia and venous, lymphatic and lacunar circulation [6]. The fascia was considered as an integrated system; therefore, a fascial restriction can be potentially extended to distant areas of the body and can provoke stress/malfunction on any structure that is enveloped by the fascia itself [7,8].
Based on the studies of Dr. Cathie, another variation of pump techniques was developed in France. In the 1980s, the physical therapist Marcel Bienfait proposed a technique called pompage and widened its use [9,10]. Recently, pompages have been further modified and updated according to the most recent developments in treating the connective tissues [11].
Globally, pump techniques aim at promoting the relaxation and elongation of soft tissues and fascia [12,13,14], reducing intra-fascial thickening and adhesions, decreasing joint load [15,16], reactivating joint metabolism, facilitating circulation, and finally, reducing pain and normalizing muscular tone [17,18,19]. More specifically, the lymphatic pump techniques are designed to facilitate venous, lymphatic and lacunar circulation, with an action mediated by the alternation of pressure/traction and decompression/relaxation [20].
Lymphatic pump techniques are carried out in two phases. In the first phase (pressure/traction), the clinician applies a tension reaching the “barrier” or limit of the physiological elasticity of the fascia, without causing defense reactions by the patient. This tensioning must therefore be painless, but at the same time, it must not be too light to adequately stimulate the fascial tissue [21]. In the second phase (decompression/relaxation), the clinician allows the fascia to return to the initial position without stopping the movement [22,23].
The alternation of these two phases is rhythmic; the frequency can be slow (e.g., suboccipital release, pectoral traction, doming of the diaphragm, and rib raising), at medium speed—20/30 cycles per minute (e.g., release of the thoracic inlet, abdominal or pelvic lymphatic pump), or at high speed—110/120 cycles per minute (e.g., thoracic lymphatic pump, and pumps applied to peripheral areas). Pompage techniques addressed to joints and muscles are generally slower, and a further phase of maintaining the tension is added [23].
These different modalities and frequencies depend on the treated area and the characteristics of the tissues addressed by each technique. The alternation of rhythmic pressures and decompressions can be applied on the joints (joint/articular pump), the muscles (muscular pump), the abdominal area (abdominal pump), the feet and the lower limbs (pedal pump), or on the patient’s chest (thoracic pump) [24,25]. The pump techniques are generally well tolerated and can be used easily and safely in many clinical presentations. Currently, both the American osteopathic pump techniques and French pompages are performed as a part of a wider family of pump techniques.
Despite the widespread use of these manual procedures in clinical practice by osteopaths and physical therapists, their effectiveness was not deeply studied. Narrative reviews were published in 2007 [26], 2011 [27], 2014 [28], 2016 [29], and 2020 [30]. However, no systematic review was conducted, including risk of bias (RoB) and quality of the evidence assessment.
This systematic review aims to investigate the effectiveness of pump techniques and pompages in adults on subjective (e.g., pain, physical function) and objective (e.g., pulmonary function) outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
We followed the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention as our methodological guidance [31]. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement for the reporting was used [32]. The protocol was registered in PROSPERO database (CRD42020180002).
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
The following databases were searched: MEDLINE, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, PEDro, CINAHL, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science. Searches were conducted by the two authors (M.G., G.P.) up to July 2020.
The search in the individual databases was given by the union of various combinations of specific keywords: “lymphatic”/”abdominal”/”thoracic”/”pedal”/”muscular”/”technique/”osteopathic “/” pump “; “pompage” and adapted for each database. The specific search strategy for MEDLINE is reported in the Supplement 1.
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) published in all languages were eligible for inclusion. A reference list of identified articles was also checked for any relevance together with other grey literature sources.
2.2. Studies Selection
2.2.1. Types of Studies
The search was limited only to full-text RCTs. Unpublished studies (e.g., conference abstracts; trial protocols) were excluded.
2.2.2. Types of Participants
We included only RCTs on adults (≥18 years old) of any sex. Studies on animals were also excluded.
2.2.3. Types of Interventions
RCTs describing the intervention as different types of pump techniques (e.g., articular pump, lymphatic pump, abdominal pump, thoracic pump, pedal pump, thoracic lymphatic pump) and pompages were included.
2.2.4. Types of Comparator (s)/Control
We included RCTs where the treatment with pump techniques was compared with placebo, no intervention, any other types of physical therapy intervention (e.g., Exercise; Manual Therapy; Relaxation; Biofeedback; Physical Modalities; Taping; Orthosis; Dry Needling; Acupuncture; Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy; Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation) or other interventions such as pharmacotherapies or surgery.
2.2.5. Types of Outcome Measures
Pain intensity measured with a Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) or a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS); blood collection; lung functions by FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC, oxygenation, residual lung volume, expiratory flow peak, Tiffeneau index; length of hospitalization were considered as primary outcomes.
Additional outcomes were: Range of Motion—ROM (measured, for example, with tape or goniometer); Global Perceived Effect (measured, for example, with Global Rating of Change); Quality of Life (measured, for example, with SF-36 or Euro-QoL); Change in Neurological function (measured, for example, with neurodynamic tests, neurological examination, or other measures as pressure pain, thermal or vibration threshold or H-reflex); Psychological condition (measured, for example, with Fear-avoidance, Catastrophizing, Kinesiophobia, Pain Self-Efficacy, Anxiety or Depression Questionnaires); Treatment adherence and Adverse events.
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
Search results were collected and imported to EndNote V.X9 (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA). Duplicates were automatically removed [33]. Two independent reviewers (M.G., G.P.) performed the review process using Rayyan QRCI online software (Rayyan Systems Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA) [34]. This consisted of two levels of screening: title and abstract review and full-text review. In case of disagreement, conflicts were resolved by a third author (C.V.).
Two reviewers (M.G., G.P.) independently extracted the following data: Total number of participants; Number of participants of treatment and control groups; Mean age of participants; Proportion of males/females; Mean/median pain duration; Taking drugs; Mean Pain intensity; Mean Physical functioning; Type of treatment; Treatment dosage (number of times the intervention was delivered; number and duration of sessions; total duration of the program; intensity or dose); Type of control; Primary measure used to recording each outcome; Means and standard deviations of each outcome at post-intervention for all treatment groups; Measurement scales/questionnaires and their direction for each outcome; Number of adverse events in study group and control group; Type of adverse events; Year of publication; Publication language; Country of publication; Setting. Study authors were contacted to obtain important missing data.
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
Two authors (A.P., L.T.) independently assessed the RoB through the Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for RCTs (RoB 2) [31,35]. A RoB graph was created through RobVis visualization tool [36].
To assess the certainty of evidence for the main outcomes, two authors (A.P., L.T.) used the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) approach classifying evidence as high, moderate, low, or very low quality based on considerations of RoB, consistency, directness, precision, and publication bias [37]. In case of disagreement, a third author (C.V.) was consulted.
2.5. Data Synthesis and Analysis
A descriptive summary of the results of the included studies was provided, commenting on the difference between treatments. The treatment effect was measured for each study using the mean differences. Whenever possible, the data were synthesized using meta-analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Results
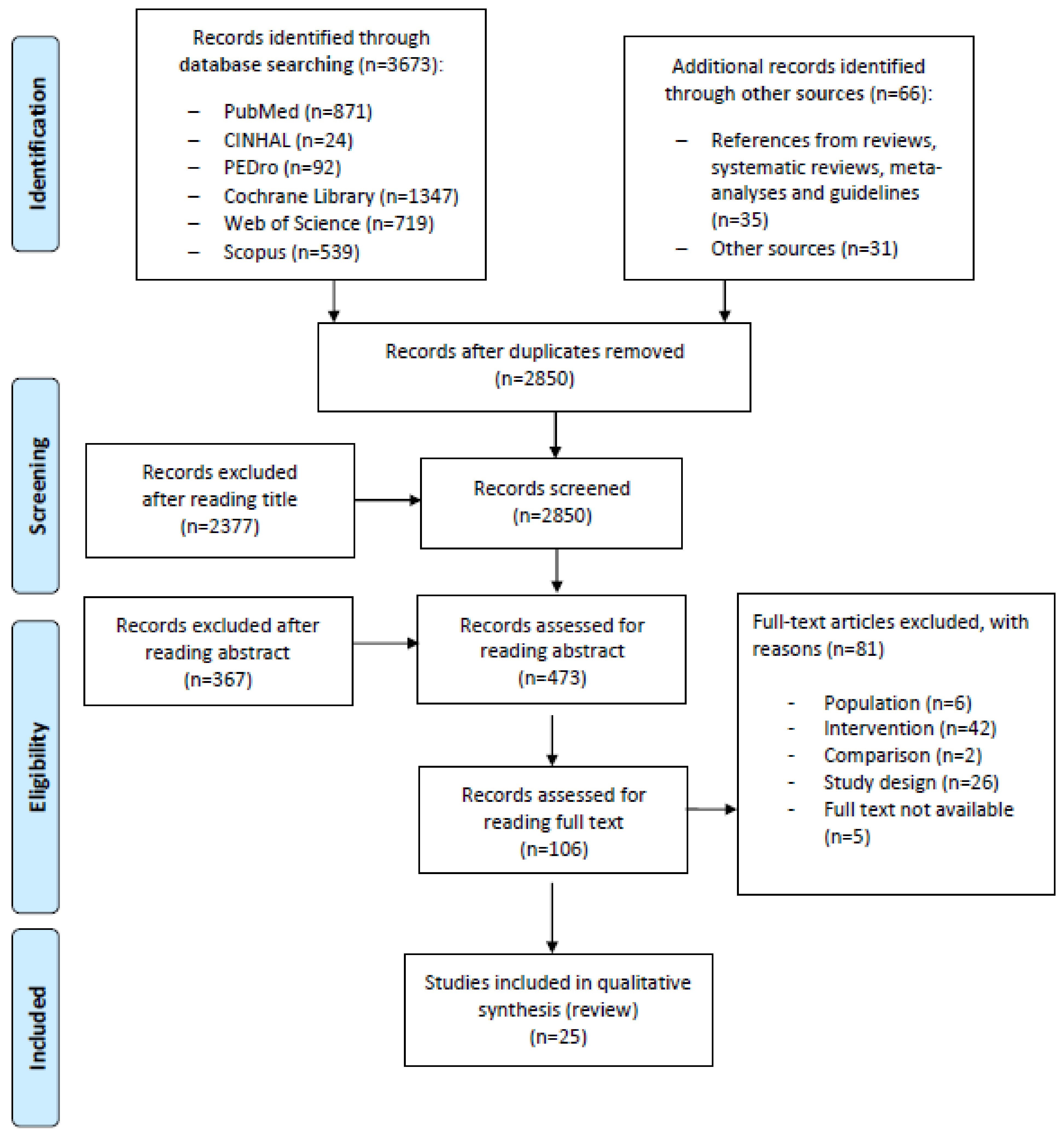
3673 studies were identified with the database search. Through other searches, a further 66 studies were added. After removing duplicates and excluding by title and abstract, 106 studies were eligible to be assessed by full-text reading to verify the eligibility for inclusion in this systematic review. Eighty-one articles were excluded for various reasons (Supplement 2), with 25 studies available for qualitative synthesis [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Flow chart of study selection.
Among these studies, 20 analyzed pump techniques [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56], and five concerned pompages [57,58,59,60,61]. The included studies were published from 1968 to 2019 and conducted in the USA [38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,54,55,56], Brazil [57,58,60,61], Italy [51,52,59], Egypt [37], Poland [53], and India [42]; the total number of patients who completed the assessments was 1632.
The treatment techniques used in the studies were osteopathic pump and pompage techniques. In 20 studies, thoracic lymphatic techniques were applied together with other techniques, such as pedal pump, abdominal pump, and sternal pump [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56]. In five studies, pompages were used [57,58,59,60,61]. The duration of the treatments ranged from one day to seven weeks and the duration of each treatment ranged from two to 50 min. The interventions with which the pump techniques were compared were no treatment [37,52], light touch [44,45,46,47,48,50,54,56,57], conventional rehabilitation [38,41,42,51,53,55,61], vaccination [39,40] stretching [58], muscle-tension headache program and electrotherapy program [59], and educational lectures [60]. Primary outcomes were pain intensity, lung functions, blood count cell, and length of hospitalization. Secondary outcome measures were ROM and psychological condition.
3.2. Quantitative Synthesis
We could only carry out one meta-analysis on two studies [51,53] similar for participants, interventions, comparison and outcomes. Nevertheless, due to the extensive heterogeneity (Chi2 = 9.97, I2 = 90%) of the included studies, meta-analysis was not reported and only a qualitative synthesis with a summary of the available evidence was conducted.
3.3. Qualitative Synthesis

Table 1.
Characteristics of the studies on pump techniques.

Table 2.
Characteristics of the studies on pompages.
3.3.1. Pump Techniques Versus Light Touch
Nine studies [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,56] were identified comparing osteopathic pump protocol versus light touch at short-term follow-up. Outcomes assessed were pulmonary function, blood collection, and length of hospitalization.
- Pulmonary function. Only one study [47] assessed this outcome on patients complaining of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). The OMT group showed a statistically significant decrease in Forced Expiratory Volume in the 1st second (FEV1), the Expiratory Reserve Volume and airway resistance. The OMT group also had a statistically significant increase in the residual volume, total lung capacity, and the ratio of those values compared with the control group.
- Blood collection. Two studies [49,56] assessed this outcome. No statistically significant changes emerged between the treatment groups and the control groups with regard to white and red blood cell count. In the first study [49] on subjects aged ≥ 60 years, an increase of platelets in the control group and a decrease in the treatment group was observed. In the second study [57] on adult males, a decreased level of monocytes was noted in both groups.
- Length of Hospitalization. Four studies [44,45,48,50] assessed this outcome on patients affected by pneumonia and patients operated on for heart surgery. All four studies showed no significant difference between the treatment groups and the control groups. A third group that received standard care was also compared in two studies [48,50]. In both studies, the length of hospitalization was shorter for the experimental groups than for the standard treatment groups.
- Cognitive status. Only one study [46] assessed this outcome on elderly subjects. In this study, comparing the subjects who responded to Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in the “normal” range, no differences occurred between the treatment group and the control group.
3.3.2. Pump Techniques Versus Conventional Rehabilitation
Six studies [38,41,42,51,53,55] were identified comparing osteopathic pump protocol versus standard rehabilitation at short-term follow-up. Conventional rehabilitation included treatments such as standard pulmonary rehabilitation (tapotement, pursed-lip breathing, saline nebulizer and rest) [41], supervised and unsupervised exercise (breathing, coordination and walking) [53], nebulization [38], standard cardiorespiratory rehabilitation [51], incentive spirometry [55], and drugs (bronchodilators, antibiotics, expectorants, sedatives, and parenteral fluids) [42]. The outcomes assessed were pain, pulmonary function, and length of hospitalization.
- Pain. Two studies [51,53] assessed this outcome in patients operated on for heart surgery at short-term follow-up. In both studies, there was a statistically significant decrease in mean pain intensity in the treatment group compared to the control group. In the first study [51] there was also a statistically significant decrease in breathing difficulty for the treatment group compared to the control group.
- Pulmonary function. Four studies [38,41,42,56] were identified comparing osteopathic pump protocol versus other conservative treatments, at short-term follow-up. In the first study [38] on patients with pulmonary pathology, a statistically significant increase in FVC appeared in both groups. No significant changes emerged for other lung functions. In the second study on healthy subjects [41], osteopathic techniques were compared with standard pulmonary rehabilitation [SPR]. In the treatment group, rib-raising and lymphatic pump led to a change in FEV1 and FVC although not statistically significant. In the control group, saline treatment was associated with significant decline in lung function. All other techniques did not significantly change lung function. In the third study on patients with pulmonary pathology [42], in the treatment group an osteopathic protocol was added to a nebulization, while the control group was submitted only to nebulization. Statistically significant post-treatment improvements in FEV1, FVC, VC, and FEV1/FVC emerged in the experimental group compared to the control group. In the fourth study [56] on patients operated on for cholecystectomy, an osteopathic pump protocol was compared with incentive spirometry. This study showed a significant increase in FVC and FEV1 in the treatment group compared to the control group at second and third postoperative days.
- Length of Hospitalization. Only one study in patients operated on for heart surgery [51] assessed this outcome. Hospitalization was significantly shorter for the treatment group compared with the control group.
- Functional capacity. Only one study in patients operated on for heart surgery [51] assessed this outcome. This study showed a statistically significant increase of walking distance for both groups, without significant difference between the treatment group and the control group.
3.3.3. Pump Techniques Added to Vaccination Versus Vaccination
Two studies [39,40] were identified comparing osteopathic pump protocol added to vaccination versus vaccination alone at short-term follow-up. The outcome assessed was blood collection.
- Blood collection. Two studies on healthy subjects [39,40] assessed this outcome. In the first study [39] there was no significant change in the anti-influenza immunoglobulin production in the treatment group compared to the control group. There was a significant increase in anti-influenza immunoglobulin in both groups for young subjects compared to elderly ones. In the second study [40], there was a significant increase in hepatitis B antibody in the treatment group compared to the control group at 13th week. No significant difference between the two groups emerged at the other follow-ups.
3.3.4. Pump Techniques Versus No Treatment
Two studies [37,52] were identified comparing osteopathic pump protocol versus no treatment, at short-term follow-up. Outcome assessed was blood collection.
- Blood collection. Two studies [37,52] assessed this outcome on healthy subjects. In the first study [37], two treatment groups (with different osteopathic pump protocols) were compared to a control group. Among the treatment groups and the control group, only the group submitted to thoracic lymphatic pump and splenic pump techniques showed a significant increase in CD4 lymphocytes.
In the second study [52], the only significant change was an increase in monocytes (white blood cells) in the treatment group compared to the control group. There were no significant changes in red blood cells.
3.3.5. Pump Techniques Versus Placebo
Saliva sampling. Only one study [54] assessed the salivary immunoglobulin A (sIgA) in highly stressed individuals. The experimental group received osteopathic protocol, whilst the control group sat relaxed in a separate area for 20 min. There was a significant increase in sIgA levels in both post-treatment groups, without any significant difference between groups.
3.3.6. Diaphragmatic Pompage (Manual Diaphragm Release Technique) Versus Light Touch
Functional capacity. Only one study [57] was identified comparing diaphragmatic pompage (Manual Diaphragm Release Technique) versus light touch in subjects with COPD, at short-term follow-up. Outcome assessed was functional capacity. This study showed a statistically significant improvement of walking distance measured with the 6-min Walking Test (6MWT) for the treatment group compared to the control group.
3.3.7. Pompages Added to Stretching and Aerobic Exercise Versus Stretching and Aerobic Exercise
Pain, fatigue and sleep quality. Only one study [58] on Myofascial Pain Syndrome was identified comparing Manual Diaphragm Release Technique added to stretching and aerobic exercise versus stretching and aerobic exercise in subjects with fibromyalgia, at short-term follow-up. Outcomes assessed were pain, fatigue and sleep quality. No significant differences emerged between the groups for all outcome measures.
3.3.8. Pompages Added to Sham Tension-Type Headache Program Versus Tension-Type Headache Program
Pain and ROM. Only one study [59] was identified comparing pompages added to sham total body electrode program versus total body electrode program, in subjects with chronic disabling tension headache, at short-term follow-up. Outcomes assessed were pain and ROM. A significant increase in flexion, extension and rotation ROM appeared in both groups, with ROM normalization. Furthermore, a significant reduction in perceived pain was recorded in both groups.
3.3.9. Knee Pompage Added to Exercise Versus Educational Lectures
Pain, postural balance and muscle strength. Only one study [60] was identified comparing knee pompage added to exercise versus educational lectures in knee osteoarthritis, at short-term follow-up. Outcomes assessed were pain, postural balance and muscle strength. The treatment group presented better results in pain, postural balance and muscle strength when compared to the control group. Pain reduction was not different between the treatment group and the control group. The only significant difference between groups was about better balance improvements for the experimental group at 12 weeks follow-up. A muscle strength increase was observed in symptomatic and less symptomatic knee, for both groups.
3.3.10. Pompages Added to Postural Treatment Versus Pulmonary Rehabilitation Protocol
Functional capacity. Only one study [61] was identified comparing pompages added to postural treatment versus pulmonary rehabilitation protocol in COPD patients at short-term follow-up. Outcome assessed was functional capacity. The patients of the treatment group increased the distance covered and had a better performance in the 6MWT after the intervention. On the contrary, the patients of the control group decreased the distance covered and had low performance in the 6MWT. A statistically significant difference between groups emerged.
3.4. Adverse Effects
Concerning side effects, one participant in a study from the treatment group reported stiffness and was unable to get out of bed the morning after the first treatment while in the control group, one participant reported “a little muscle soreness in the abdomen” [46]. In a second study [47], one subject in the treatment group reported generalized muscle soreness, and another reported “a little muscle soreness in the neck”, while in the control group, four instances of possible adverse effects were reported: “elevated blood pressure in the morning”, (164/90 mm Hg)“mild heart palpitations”, “a little [muscle] soreness”, and “back was a little sore”.
3.5. Risk of Bias and Quality of the Evidence Assessment
Table 3 and Table 4 show the synthesis of the RoB assessment for the selected studies. Globally, the RoB of the studies on pump techniques and pompages ranges from moderate to high.

Table 3.
Synthesis of the risk of bias assessment on pump techniques.

Table 4.
Synthesis of the risk of bias assessment on pump techniques.
The quality of evidence assessment through the GRADE instrument was made by consideration of the different comparisons between interventions explained in the previous paragraphs of the results. Table 5 and Table 6 show the quality of evidence for each comparison, which ranges from very low to high.

Table 5.
GRADE evaluation of the studies on pump techniques: quality of evidence and strength of recommendations.

Table 6.
GRADE evaluation of the studies on pompages: quality of evidence and strength of recommendations.
Effect size is not reported because meta-analysis was not performed. For the indirectness domain, we considered that the population generally investigated by clinical studies is not healthy, therefore the studies carried out on healthy subjects were rated as “serious”: Concerning the inconsistency domain, if the results were not statistically significant, we rated inconsistency as “serious”.
4. Discussion
This review aimed to investigate the effectiveness of pump techniques and pompages on subjective parameters (e.g., pain, physical function) and objective parameters (lung function, blood count cell, length of hospitalization) on adults.
The results of this review showed that pump techniques and pompages were applied in a wide spectrum of populations and using very different outcome measures. The studies on pump techniques were conducted both on healthy, young or elderly subjects, and in different clinical conditions as COPD, pneumonia, other pulmonary diseases, and patients submitted by surgery. The studies on pompages were done on pulmonary diseases, tension-type headache, fibromyalgia, and knee osteoarthritis.
All studies combined various pump techniques or added these techniques to other treatments, with different procedures. In example, the treatment performed by Noll and colleagues [48] included thoraco-lumbar soft tissue treatment, rib raising, diaphragm doming, cervical soft tissue treatment, suboccipital decompression, inlet relaxation, together with thoracic lymphatic pump and pedal pump. Instead, Racca and colleagues [51] performed chest wall and diaphragm manipulation, combined with manual compressions on the sternal, dorsal, and clavicular areas. On the other hand, these studies respected designs similar to common clinical practice, in which pump techniques are frequently adjunct to other therapeutic procedures, through the integration of different manual techniques [30].
Significant differences also appeared in sessions’ numbers, treatment length, and duration of each session: all these parameters seem to have been chosen arbitrarily. There is therefore a specific difficulty in measuring the single effects of the pump techniques with pragmatic studies, since they are usually applied within a multimodal program.
Singular studies seem to suggest a certain effectiveness of pump techniques in reducing pain and improving lung function in surgical and pulmonary diseases patients when compared to standard rehabilitation, and in reducing the length of hospitalization when compared to standard care. Only one study [47] showed worse results after having undergone thoracic pump with activation, compared to sham treatment. This specific pump technique, by facilitating the inspiration phase, may increase the residual volume and decrease the expiratory flow in old people with airflow obstruction.
No significant difference emerged when pump techniques were compared with light touch, and hematic exams results on healthy subjects were contradictory. The pompages techniques, alone or combined with exercise, seem effective in improving walking capacity in pulmonary disease and balance in knee osteoarthritis, nevertheless no significant difference emerged adding pompages techniques to stretching and exercise or sham tension-type headache program.
No serious adverse effect related to the application of pump techniques was reported in the selected studies.
These results must be taken with great caution, due to the heterogeneity of the studies and the small samples. The RoB and the quality of evidence assessment confirmed several limitations of the included studies.
A major strength of our study is an extensive search using many databases and careful consideration of all published reviews and guidelines on this topic. The selection and qualitative assessment were conducted independently by two authors. Only studies using explicit criteria for Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome (PICO) were included, while studies with important missing data were excluded, minimizing the reference bias. Studies in all languages, from every country and for any year of publication were searched, thereby reducing publication bias. Nevertheless, no study showed some evidence that favored controls, and we do not exclude the possibility that other negative studies were not published. Most of the included studies did not have a published protocol, and thus it is difficult to assess reporting bias.
The most important limitation of this review is related to the differences among studies related to populations, interventions and outcome measures, which did not allow us to perform a quantitative synthesis. Seven studies came from the same author, so we cannot exclude a publication bias. Even after attempting to contact authors, we were not able to retrieve five studies (detailed in Supplement 2), and some data from other studies were not found, forcing the elimination of them.
In the absence of any previous systematic reviews on this topic, we could not compare our results with other ones. Only an indirect comparison was made with a recent systematic review that challenged the validity of treating spinal dysfunctions with spinal manipulative therapy (manipulation, mobilization or traction) to obtain physiological effects [62].
The results of this systematic review may be interesting for clinical practice, because the use of pump techniques and pompages and outcome measures concerning pain, physical activity, and pulmonary function are common in clinical settings.
The quality of RCTs in this field should be significantly improved to reduce bias in future systematic reviews, especially by better standardization of techniques and dosages. In order to measure the real effectiveness of these procedures, the effects of pump techniques and pompages should be further investigated both as single treatment and as technique combined or integrated with other standardized treatments; finally, the clinical conditions better responding to pump techniques and pompages, and the most effective dosage should also be investigated.
5. Conclusions
This systematic review suggests the effectiveness of pump techniques and pompages on pulmonary, post-surgical and musculoskeletal conditions when comparing to standard rehabilitation but not to controls like light touch. These results emerged by single studies with moderate to high RoB. The quality of evidence, from very low to high, supports these results. Further research is likely to have an important impact in the estimation of the effects of these methods.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11094150/s1, Supplement 1: Search strategy for MEDLINE, Supplement 2: Details on the studies excluded from this review, with reasons.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.V., P.P. and S.G.; methodology, C.V. and S.G.; software, M.G., G.P. and S.G.; validation, M.G., G.P., A.P., L.T. and S.G.; formal analysis, M.G., G.P., A.P., L.T. and S.G.; investigation, C.V., M.G., G.P.; writing—original draft preparation, C.V., M.G., G.P., A.P., L.T. and S.G.; writing—review and editing, C.V., S.G., P.P.; supervision, C.V., S.G. and P.P.; project administration, C.V., P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Martina Ruggeri for her contribution to the literature search.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Still National Osteopathic Museum. Andrew Taylor Still: The Father of Osteopathic Medicine. Still National Osteopathic Museum Web Site. Available online: http://www.kcom.edu/newmuseum/atstill.htm (accessed on 22 November 2020).
- Miller, C.E. The lymphatic pump, its application to acute infections. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1926, 25, 443–445. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.E. Osteopathic principles and thoracic pump therapeutics proved by scientific research. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1927, 26, 910–914. [Google Scholar]
- Voyer, G. Articular Pumping—Practice Manual by Jane Stark; Somatotherapy Interactive Seminars, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, J.; Chikly, M. Manual techniques addressing the lymphatic system: Origins and development. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2005, 105, 457. [Google Scholar]
- Cathie, A.G. Textbook of Osteopathic Philosophy and Principles; American Academy of Osteopathy: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Greenman, P. Principles of Manual Medicine; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, T.W. Anatomy Trains: Myofascial Meridians for Manual and Movement Therapists, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bienfait, M. La Fascia, Il Pompage-Trattamento Della Fascia; Marrapese: Roma, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bienfait, M. Scoliosi e Terapia Manuale; Marrapese: Roma, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zanella, F.; Vanti, C. Tecnica Pompage; Il Release Mofasciale; Piccin: Padova, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cathie, A. American Academy of Osteopathy 1974 Year Book of Papers Selected from the Writings and Lectures of Angus G. Cathie; American Academy of Osteopathy: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Cathie, A.G. The Fascia of the Body in Relation to Function and Manipulative Therapy, in 1974 Year Book; American Academy of Osteopathy: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1974; pp. 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kumka, M. Fascia: A morphological description and classification system based on a literature review. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2012, 56, 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, H.; Schleip, R.; Zhiming, J. Three-dimensional mathematical model for deformation of human fasciae in manual therapy. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2008, 108, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleip, R.; Muller, D.G. Training principles for fascial connective tissues: Scientific foundations and suggested practical applications. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2012, 20, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.C.; Dalton, J.D., Jr.; Seaber, A.V.; Garrett, W.E., Jr. Viscoelastic properties of muscle-tendon units: The biomechanical effects of stretching. Am. J. Sports Med. 1990, 18, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, H.M.; Bouffard, N.A.; Badger, G.J.; Latridis, J.C.; Howe, A.K. Dynamics fibroblast cytoskeletal response to subcutaneous tissue stretch ex vivo and in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 288, C747–C756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, D.J.; Zachazewski, J.E.; Quillen, W.S. Scientific Foundation and Principles of Practice in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- David, O.D.; Kenneth, L.K. Therapeutic Modalities: The Art and Science; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- American Ostheopatic Association. Foundations of Osteopathic Medicine; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Grodin, A.J.; Cantu, R.I. Soft tissue mobilization. In Rational Manual Therapies; Basmajian, J.V., Nyberg, R., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bienfait, M. Bases Physiologiques de la Thérapie Manuelle et de L’ostéopathie; Speck: Paris, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Tozzi, P.; Davide, B.; Claudio, V. Fascial release effects on patients with non-specific cervical or lumbar pain. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2011, 15, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, C.; Ruggeri, M. The pompage technique, a narrative review. Sci. Riabil. 2016, 18, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Hruby, R.J.; Hoffman, K.N. Avian influenza: An osteopathic component to treatment. Osteopath. Med. Prim. Care 2007, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, L.M. Osteopathic Lymphatic pump techniques to enhance immunity and treat pneumonia. Int. J. Osteopath. Med. 2011, 15, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, Y.; John, H.; Wolfgang, G. Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment as a Useful Adjunctive Tool for Pneumonia. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 87, e50687. [Google Scholar]
- Minato Sagrillo, L.; Fernandez Frigo, L. The respiratory diaphragm in osteopathic vision: A literature review. Man. Ther. Posturology Rehabil. J. 2016, 14, 0414. [Google Scholar]
- Vanti, C.; Ruggeri, M. The “pump techniques”, new trends and evidence. Sci. Riabil. 2020, 22, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Furlan, A.D.; Malmivaara, A.; Chou, R.; Maher, C.G.; Deyo, R.A.; Schoene, M.; Bronfort, G.; Van, T.; Maurits, W. Updated Method Guideline for Systematic Reviews in the Cochrane Back and Neck Group. Spine 2015, 40, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. The PRISMA Group Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- End Note X9 Software. Available online: https://endnote.com (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Rayyan QCRI Software. Available online: https://rayyan.qcri.org (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for 511 visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A. Effect of selected osteopathic lymphatic techniques on immune system in healthy subjects: A randomized control trial. ACAM 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.W. The use of the thoracic pump in treatment of lower respiratory tract disease. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1967, 67, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breithaupt, T.; Ellis, J.; Purcell, E.; Weir, J.; Clothier, M.; Boesler, D. Thoracic lymphatic pumping and the efficacy of influenza vaccination in healthy young and elderly populations. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2001, 101, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, K. Effect of lymphatic and splenic pump techniques on the antibody response to the hepatitis B vaccine: A pilot study. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1998, 98, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, S. Assessment of Pulmonary Function After Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment vs Standard Pulmonary Rehabilitation in a Healthy Population. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2019, 119, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, S. Effect of Thoracic Lymphatic Pump Technique on Pulmonary Function in COPD Patients. Indian J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2013, 7, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, M.; Trubey, K.; Fernandez, M. Can Laypersons be Trained to Effectively Deliver Osteopathic Manual Therapy to Patients With HIV? A Pilot Study. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2011, 111, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Noll, D.R.; Shores, J.; Bryman, N.; Masterson, V. Adjunctive osteopathic manipulative treatment in the elderly hospitalized with pneumonia: A pilot study. J. Osteopath. Med. 1999, 99, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noll, D.R.; Gamber, G.; Herron, M.; Swift, J. Benefits of osteopathic manipulative treatment for hospitalized elderly patients with pneumonia. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2000, 100, 776–782. [Google Scholar]
- Noll, D.R.; Stuart, M.; McGovern, R. Effectiveness of a Sham Protocol and Adverse Effects in a Clinical Trial of Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment in Nursing Home Patients. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2004, 104, 107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noll, D.R.; Degenhardt, B.F.; Johnson, J.C.; Burt, S.A. Immediate Effects of Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment in Elderly Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2008, 108, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noll, D.R.; Degenhardt, B.F.; Morley, T.F.; Blais, F.X.; Hortos, K.A.; Hensel, K.; Johnson, J.C.; Pasta, D.J.; Stoll, S.T. Efficacy of osteopathic manipulation as an adjunctive treatment for hospitalized patients with pneumonia: A randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2010, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, D.R. The short-term effect of a lymphatic pump protocol on blood cell counts in nursing home residents with limited mobility: A pilot study. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2013, 13, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, D.R.; Degenhardt, B.F.; Johnson, J.C. Multicenter Osteopathic Pneumonia Study in the Elderly: Subgroup Analysis on Hospital Length of Stay, Ventilator-Dependent Respiratory Failure Rate, and In-hospital Mortality Rate. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2016, 116, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racca, V. Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment Improves Heart Surgery Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisanda, A.; Buscemi, A. Effect of osteopathy on haemochrome and blood pressure. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2015, 3, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Ratajska, M. Myofascial release in patients during the early postoperative period after revascularisation of coronary arteries. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 3327–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggio, G.; Docimo, S.; Pilc, J.; Norton, J.; Gilliar, W. Impact of Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment on secretory immunoglobulin a levels in a stressed population. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2011, 111, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Sleszynski, L. Comparison of thoracic manipulation with incentive spirometry in preventing postoperative atelectasis. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1993, 93, 834. [Google Scholar]
- Walkowski, S. Osteopathic manipulative therapy induces early plasma cytokine release and mobilization of a population of blood dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, T. The Manual Diaphragm Release Technique improves diaphragmatic mobility, inspiratory capacity and exercise capacity in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized trial. J. Physiother. 2015, 61, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correira, M.; Campos, G.; Santos, D.H.; Tenório, D.S. Effects of pompage associated with aerobic exercises on pain, fatigue, and sleep quality in female patients with fibromyalgia: A pilot study. Fisioter. Pesqui. 2016, 23, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Fidecicchi, G.; Pagliarini, S.; Lanciotti, C.; Provinciali, L.; Ceravolo, M.G. Studio randomizzato controllato dell’efficacia dell’horizontal therapy vs pompage cervicale in soggetti affetti da cefalea muscolo-tensiva invalidante. Eur. Med. Phys. 2008, 44 (Suppl. 1 to No. 3), 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Gondim, O.; De Lacerda, B.; Fernandes, K.; Do Couto, M.; Pedrosa, C. Effects of a therapeutic exercises program associated with pompage technique on pain, balance and strength in elderly women with knee osteoarthritis. Fisioter. Mov. 2017, 30, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.; De Carli, M.; Perini, M.; Steidl, E.; Antunes, V. Outcomes of Iso Stretching and Pompage techniques in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Rev. Saúde Santa Maria 2013, 39, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Coté, P.; Hartvigsen, J.; Axén, I.; Leboeuf-Yde, C.; Corso, M.; Shearer, H.; Wong, J.; Andrée-Anne Marchand, J.; Cassidy, D.; French, S.; et al. The global summit on the efficacy and effectiveness of spinal manipulative therapy for the prevention and treatment of non-musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review of the literature. CMT 2021, 29, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).