Underwater Excavation Records Using Underwater Acoustic Survey: A Case Study in South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background Information
3. Dangampo Site: Equipment Testing
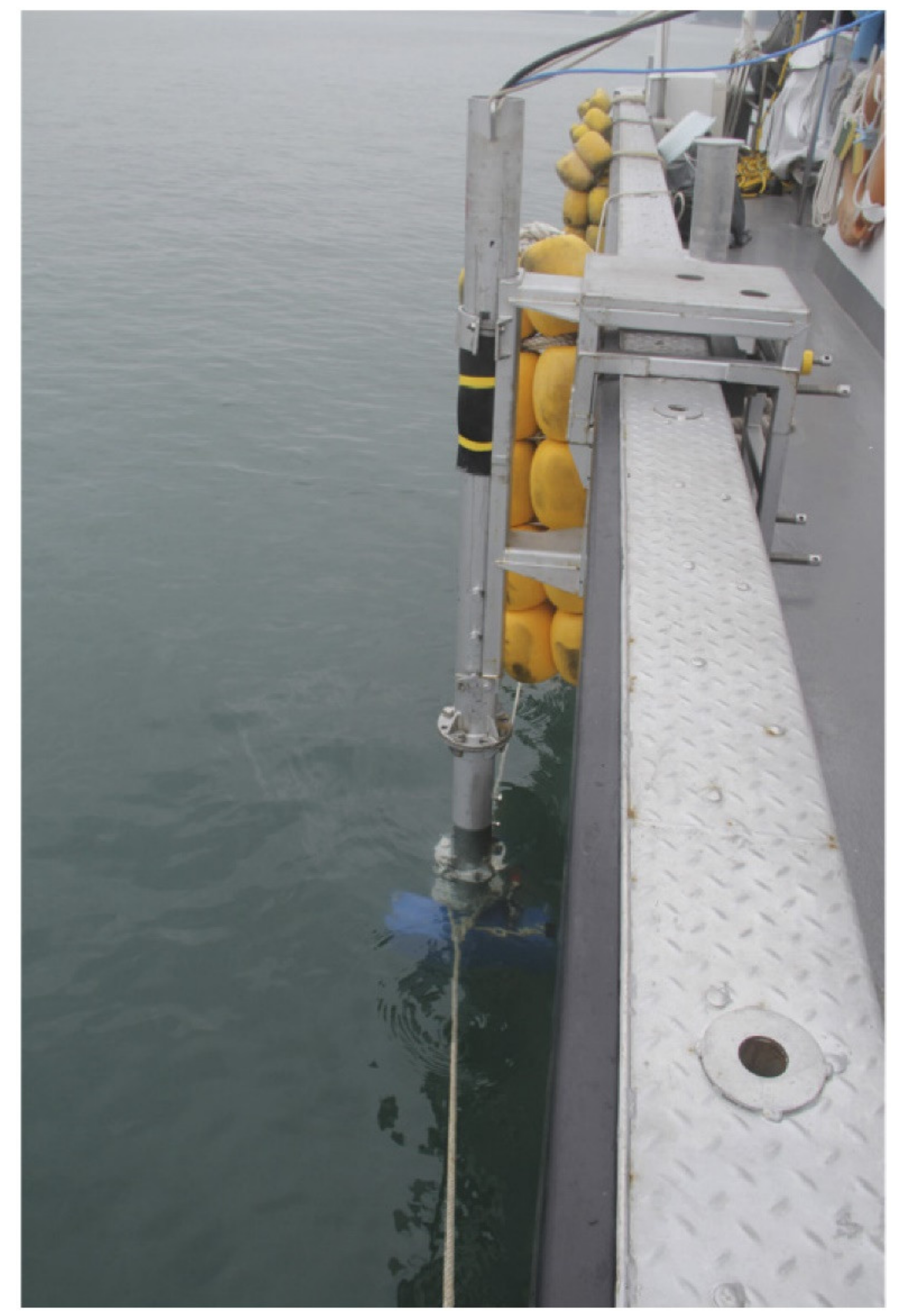
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.1.1. Side Scan Sonar
3.1.2. Echo Sounder
3.1.3. Scanning Sonar
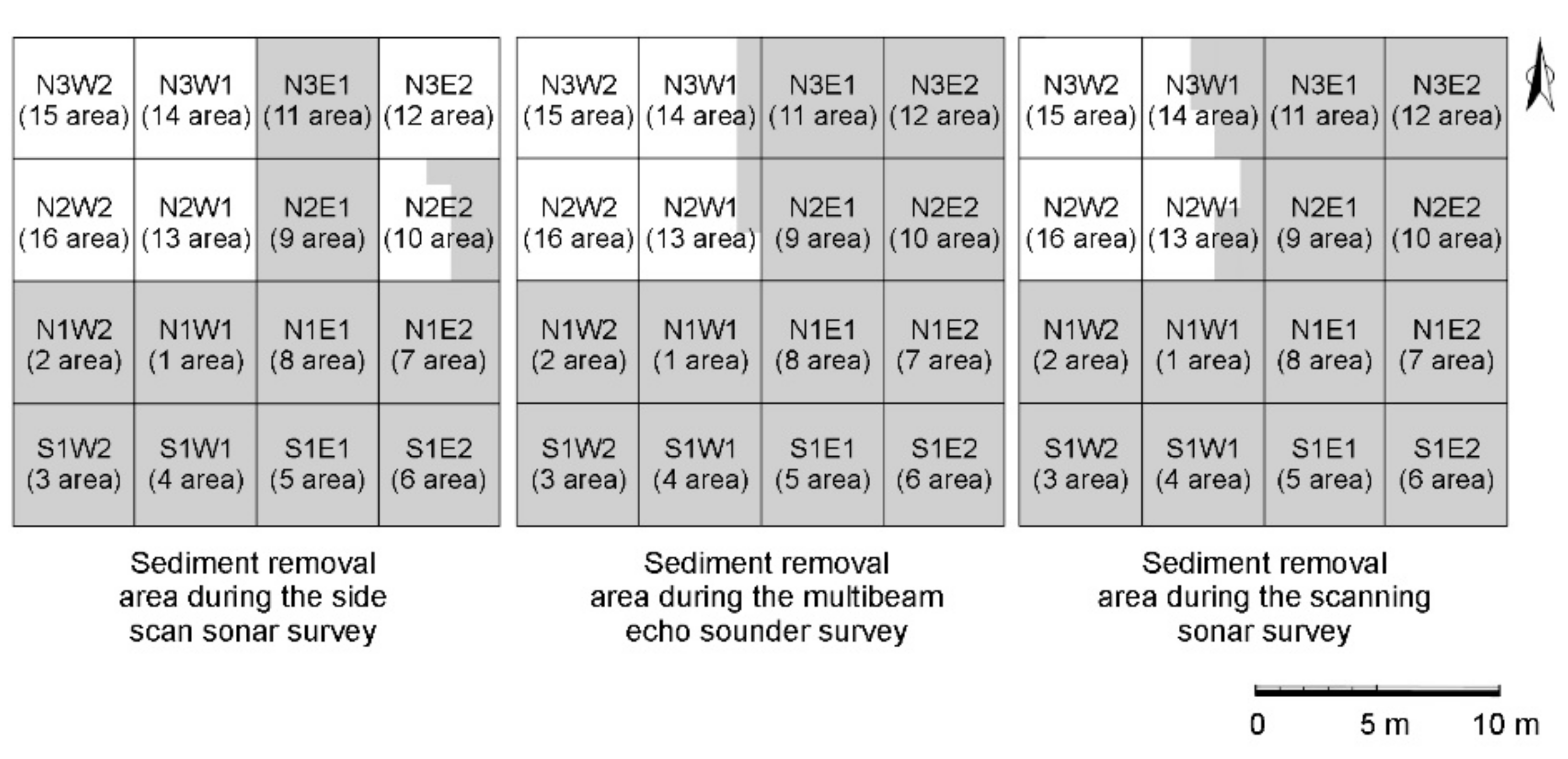
3.2. Results and Discussion
3.2.1. Side Scan Sonar
3.2.2. Echo Sounder
3.2.3. Scanning Sonar
3.2.4. Performance Evaluation
3.2.5. Second Excavation: Result Verification and Method Refinement
4. Application Case: Poor Underwater Visibility (Nakwoldo Site)
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Results and Discussion
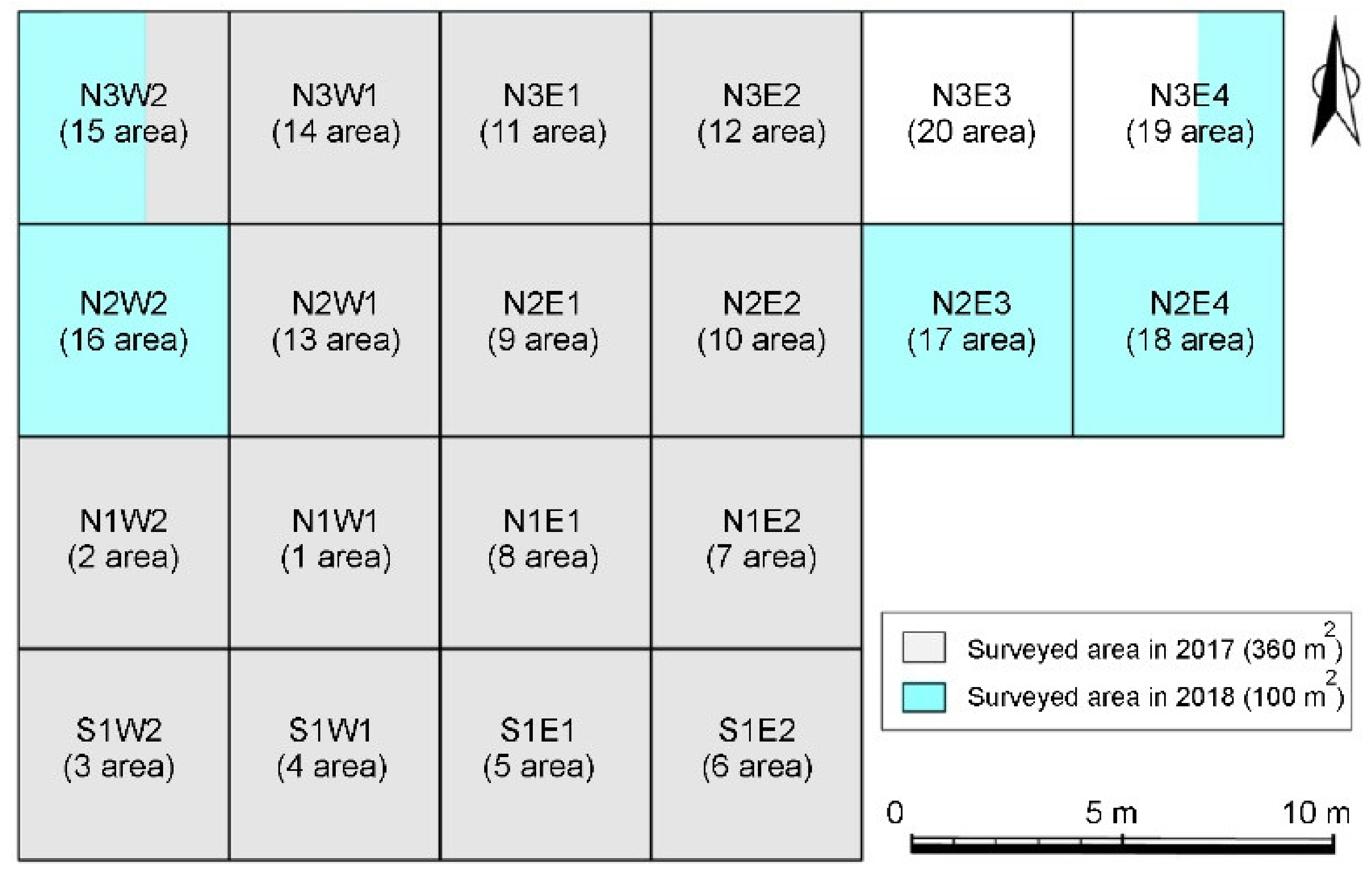
5. Application Case: Method Refinement (Myeongnyang Site)
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Report on the 1st exploration of Admiral Yi’s naval battle relics. Admiral Yi’s Naval Battle Relics Exploration Unit. In Cultural Heritage Administration; Ministry of Culture and Public Communication: Sejong, Korea, 1974.
- Report on the Underwater Excavation of Myeongnyang Site Near Jindo Island; National Research Institute of Maritime Cultural Heritage: Yonghae-dong, Korea, 2015.
- Report II on the Underwater Excavation of Myeongnyang Site Near Jindo Island; National Research Institute of Maritime Cultural Heritage: Yonghae-dong, Korea, 2018.
- Report on the Underwater Excavation near Nakwoldo Island, Yeonggwang; National Research Institute of Maritime Cultural Heritage: Yonghae-dong, Korea, 2019.
- Report on the Underwater Excavation Near Taean Dangampo; National Research Institute of Maritime Cultural Heritage: Yonghae-dong, Korea, 2019.
- Ferentinos, G.; Fakiris, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Gerage, M.; Dimas, X.; Georgiou, N.; Kordella, S.; Papatheodorou, G.; Prevenios, M.; Sotiropoulos, M. Optimal sidescan sonar and subbottom profiler surveying of ancient wrecks: The ‘Fiskardo’ wreck, Kefallinia Island, Ionian Sea. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2020, 113, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B. A Study on the MATLAB-based Chirp SBP Data Processing and Field Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, L.N.; Almeida, R.P.; Galeazzi, C.P.; Freitas, B.T.; Ianniruberto, M.; Prado, A.H. Upper-bar deposits in large Amazonrivers: Occurrence, morphology and internal structure. Sediment. Geol. 2019, 387, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Ko, E.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.H. Physical property analysis of sediments for development of maritime archaeological survey techniques. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Eng. 2014, 38, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plets, R.; Quinn, R.; Forsythe, W.; Westley, K.; Bell, T.; Benetti, S.; McGrath, F.; Robinson, R. Using multibeam echo-sounder data to identify shipwreck sites: Archaeological assessment of the Joint Irish Bathymetric Survey data. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2011, 40, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R. Marine geophysical investigation of Northern Ireland of the inshore coastal waters. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2000, 29, 249–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Breen, C.; Forsythe, W. Integrated geophysical surveys of the French Frigate La Surveillante (1797), Bantry Bay, Co. Cork, Ireland. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Forsythe, W.; Breen, C.; Dean, M.; Lawrence, M.; Liscoe, S. Comparison of the maritime sites and monuments record with side-scan sonar and diver surveys: A case study from Rathlin Island, Ireland. Geoarchaeology 2002, 17, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simyrdanis, K.; Papadopoulos, N.; Cantoro, G. Shallow off-shore archaeological prospection with 3-D electrical resistivity tomography: The case of Olous (modern Elounda), Greece. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, E.; Ginzburg, B.; Cohen, T.R.; Zafrir, H.; Alimi, R.; Salomonski, N.; Sharvit, J. High resolution marine magnetic survey of shallow water littoral area. Sensors 2007, 7, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhoop, T.; Stark, S.; Olaberria, J.P.; Whitewright, J. Quantifying ship shape in archaeology: Evaluating 3D geometric morphometrics. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2020, 49, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, R.; Katagiri, C.; Kan, H.; Nagao, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takemura, F.; Sakagami, N. Discovery of iron grapnel anchors in early modern Ryukyu and management of underwater cultural heritage in Okinawa, Japan. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2016, 45, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhong, G.; Lin, A.; Fang, X.; Wang, L. The target comparison from different sidescan sonar system. In International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers. In Proceedings of the 26th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 26 June–2 July 2016. ISOPE-I-16-553. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.; Benjamin, J.; Winton, T.; van Duivenvoorde, W. The rise of 3D in maritime archaeology. In 3D Recording and Interpretation for Maritime Archaeology; McCarthy, J., Benjamin, J., Winton, T., van Duivenvoorde, W., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Cheong, S.; Lee, C.; Riedel, M.; Kim, C.S.; Koo, N.H.; Kim, B.Y. Application of pseudo-3D Chirp sub-bottom profiler survey: A case study of ancient wooden shipwreck site, west coast of Korea. Explor. Geophys. 2021, 52, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, D.; Georgiou, P.; Mallios, A.; Kapsimalis, V. Searching for ancient shipwrecks in the Aegean Sea: The discovery of Chios and Kythnos Hellenistic wrecks with the use of marine geological-geophysical methods. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2007, 36, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreón-Freyre, D.; Cerca, M.; Hernández-Marin, M. Correlation of near-surface stratigraphy and physical properties of clayey sediments from Chalco basin, Mexico, using Ground Penetrating Radar. J. Appl. Geophy. 2003, 53, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.J.; Jang, I.S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.H. Performance analysis of sonar system applicable to underwater construction sites with high turbidity. J. Korea Acad. Industr. Coop. Soc. 2013, 14, 4507–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.-B. Underwater Excavation Records Using Underwater Acoustic Survey: A Case Study in South Korea. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094252
Lee Y-H, Kim J-H, Lee S-H, Kim S-B. Underwater Excavation Records Using Underwater Acoustic Survey: A Case Study in South Korea. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094252
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young-Hyun, Jin-Hoo Kim, Sang-Hee Lee, and Sung-Bo Kim. 2021. "Underwater Excavation Records Using Underwater Acoustic Survey: A Case Study in South Korea" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094252
APA StyleLee, Y.-H., Kim, J.-H., Lee, S.-H., & Kim, S.-B. (2021). Underwater Excavation Records Using Underwater Acoustic Survey: A Case Study in South Korea. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094252





