Hyper-Redundant Manipulator Capable of Adjusting Its Non-Uniform Curvature with Discrete Stiffness Distribution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
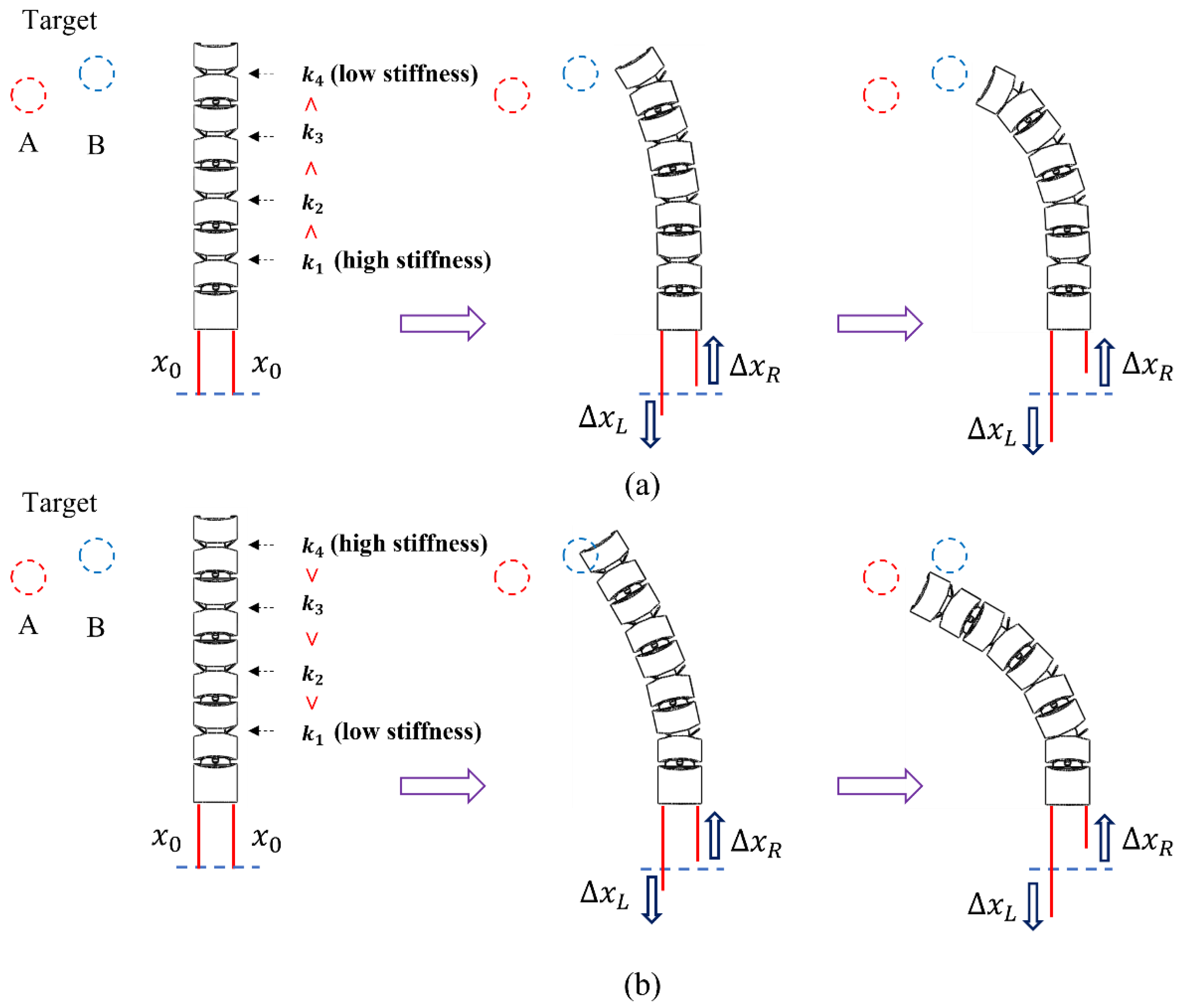
2. Method
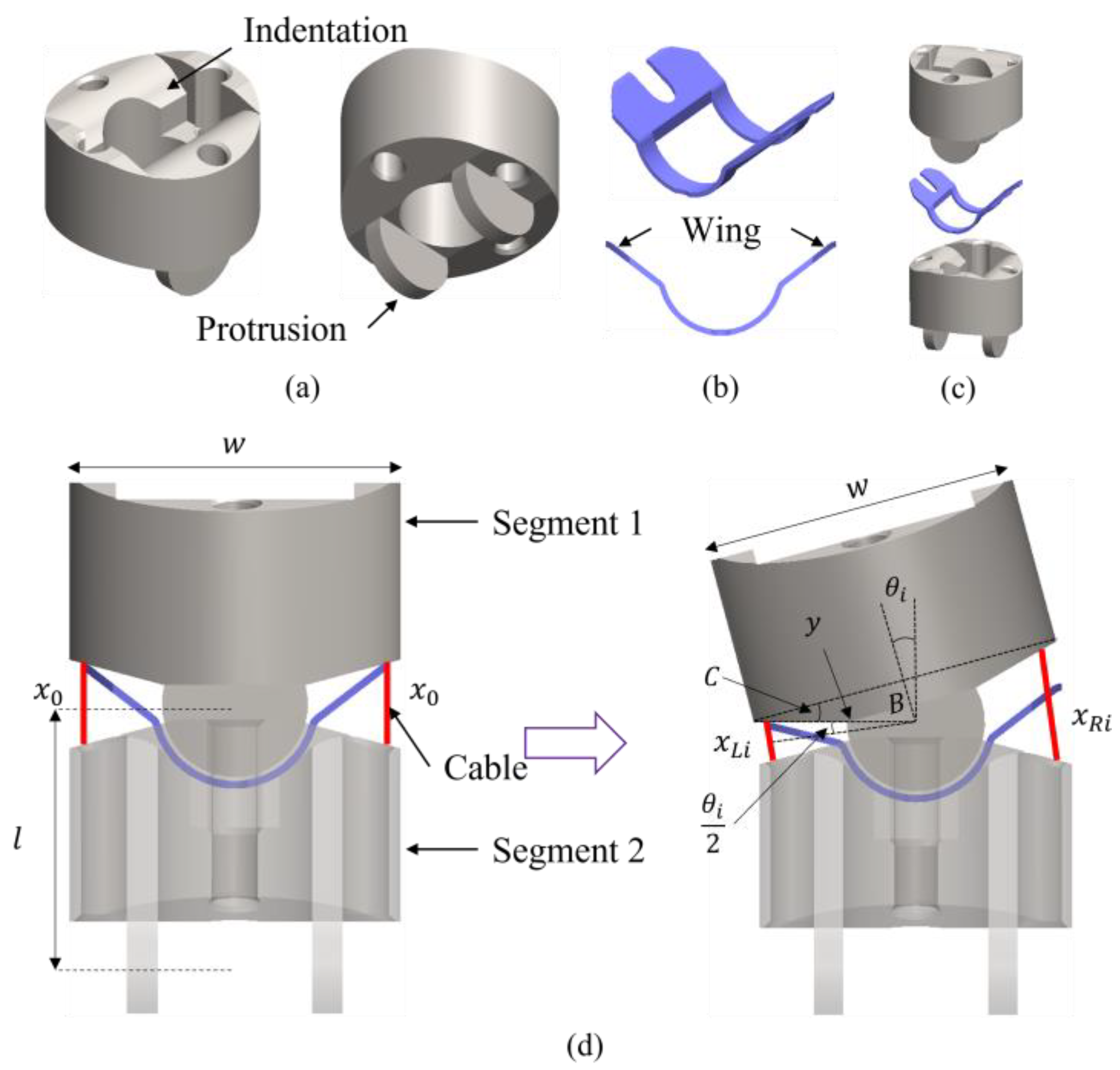
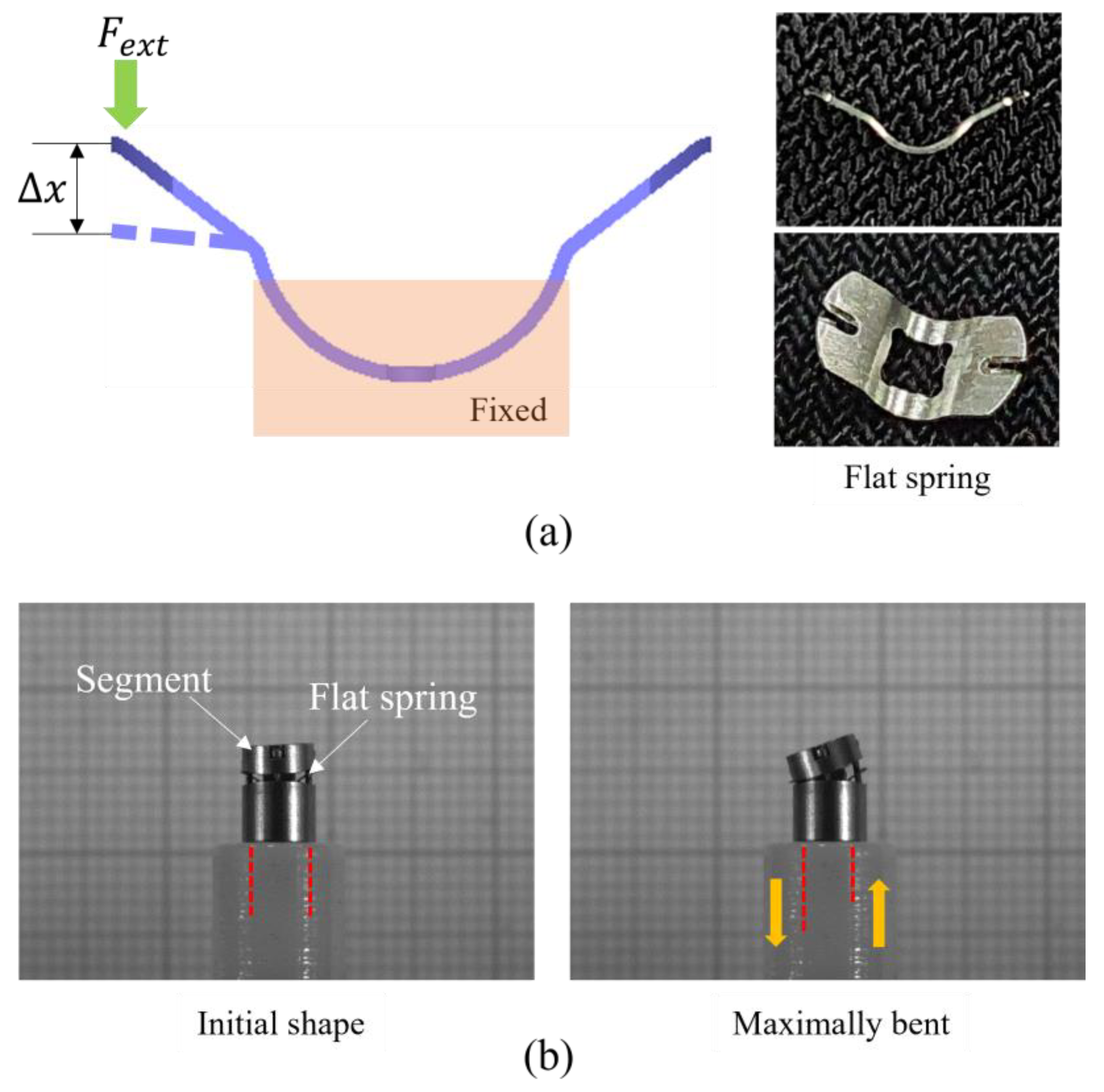
2.1. Design and Modeling for Bending Shape Prediction of Flat Spring Mechanism
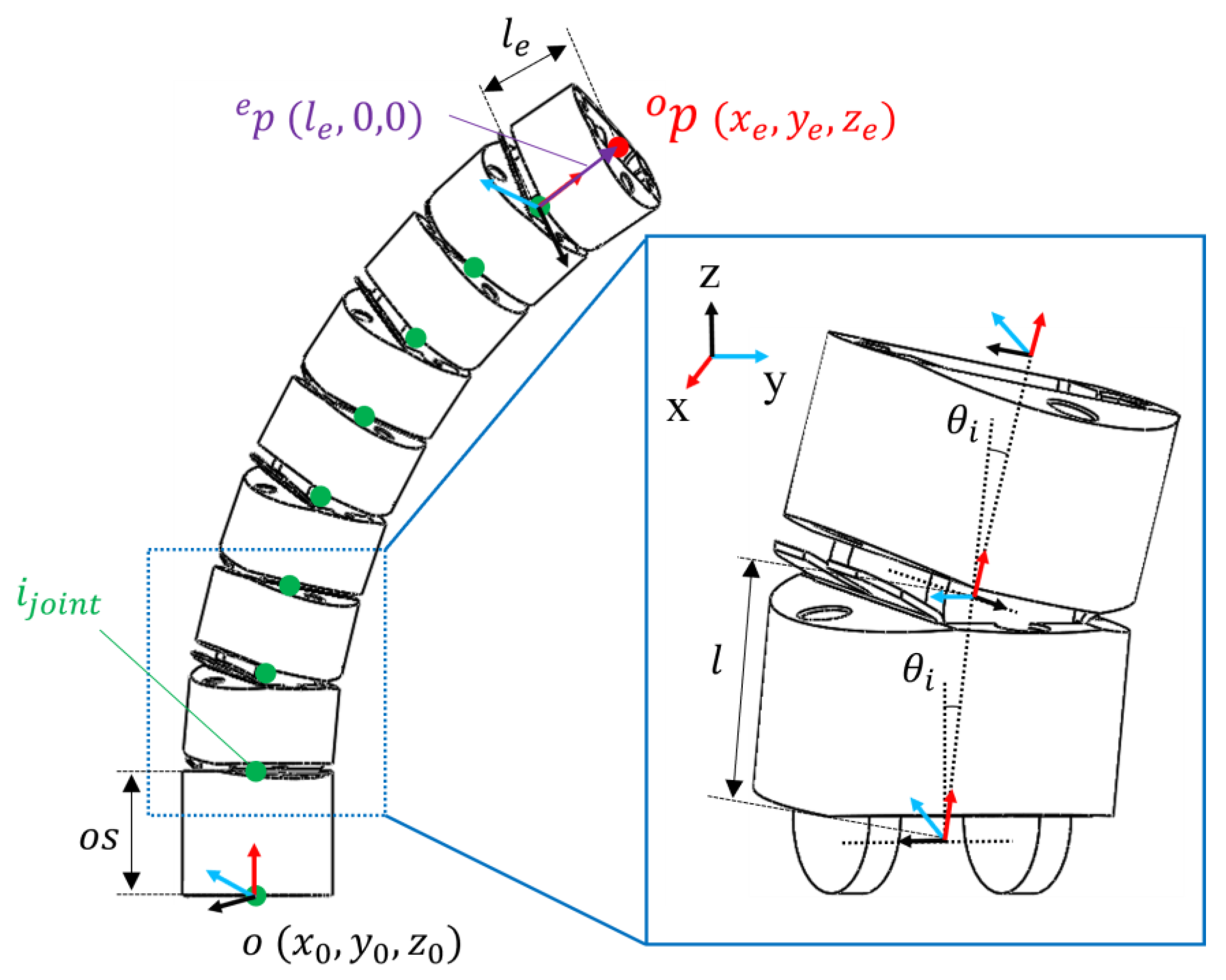
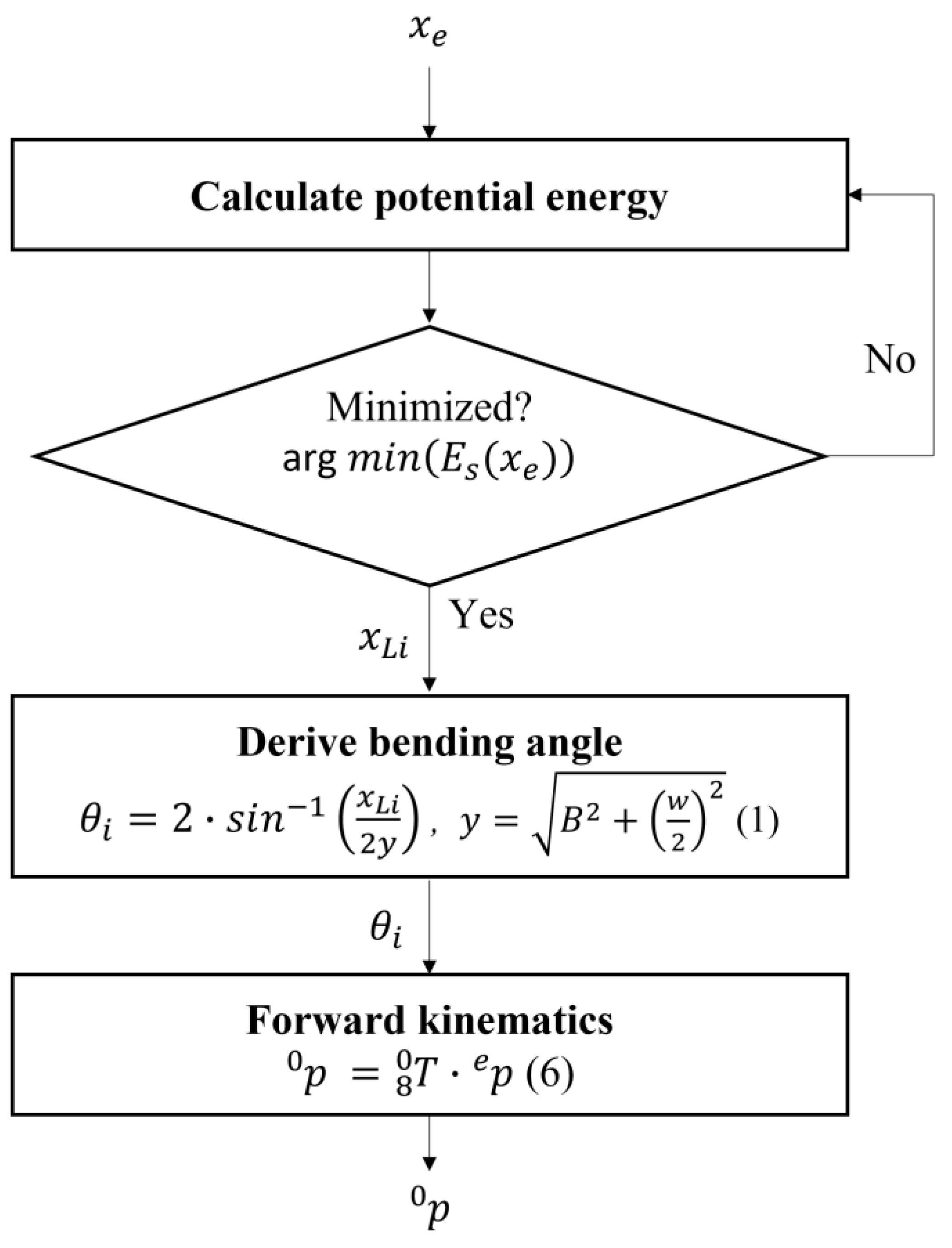
2.2. Kinematic Analysis and Prediction Process
3. Evaluation
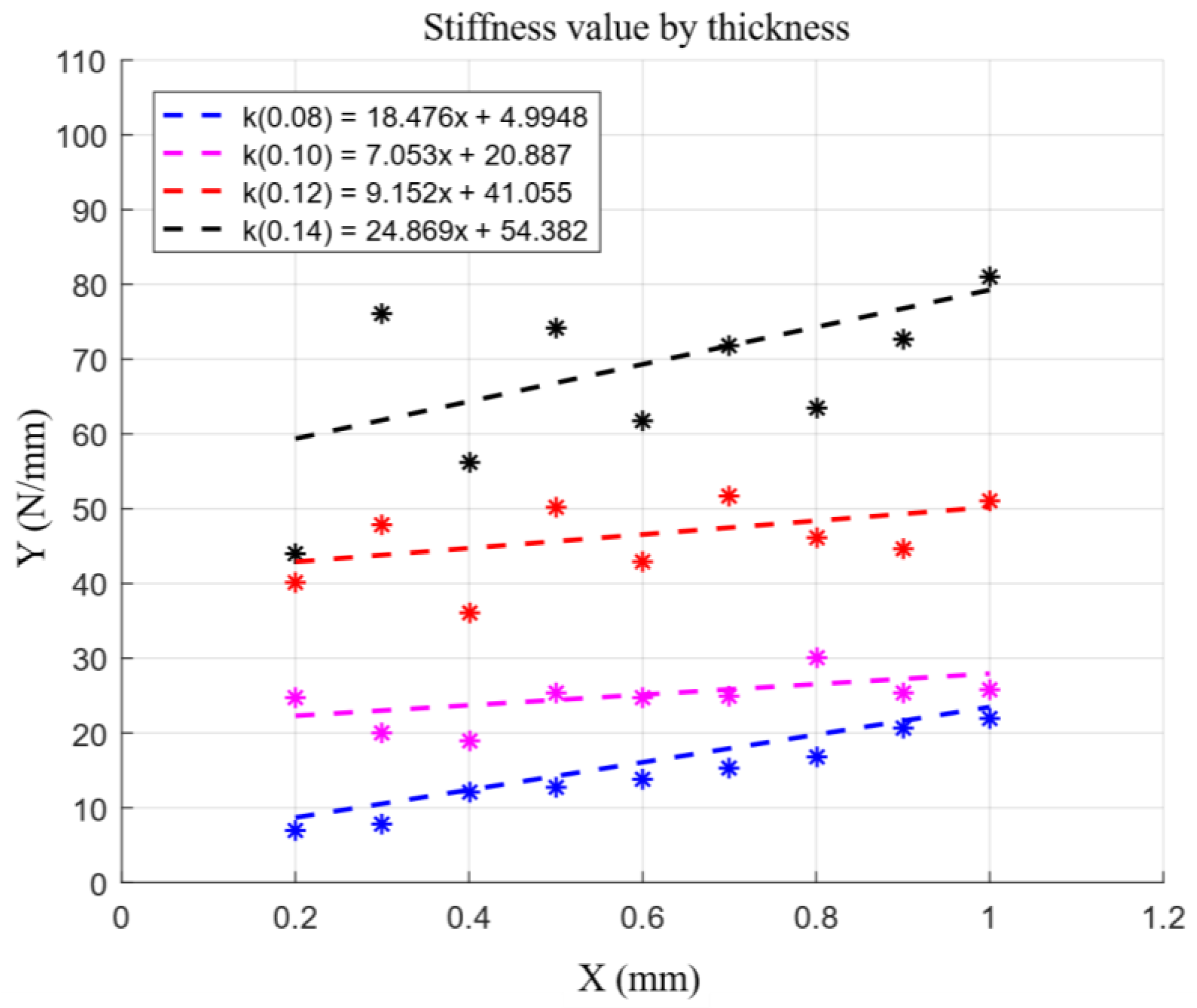
3.1. Flat Spring Stiffness Function
3.2. Prototype
3.3. Simulation
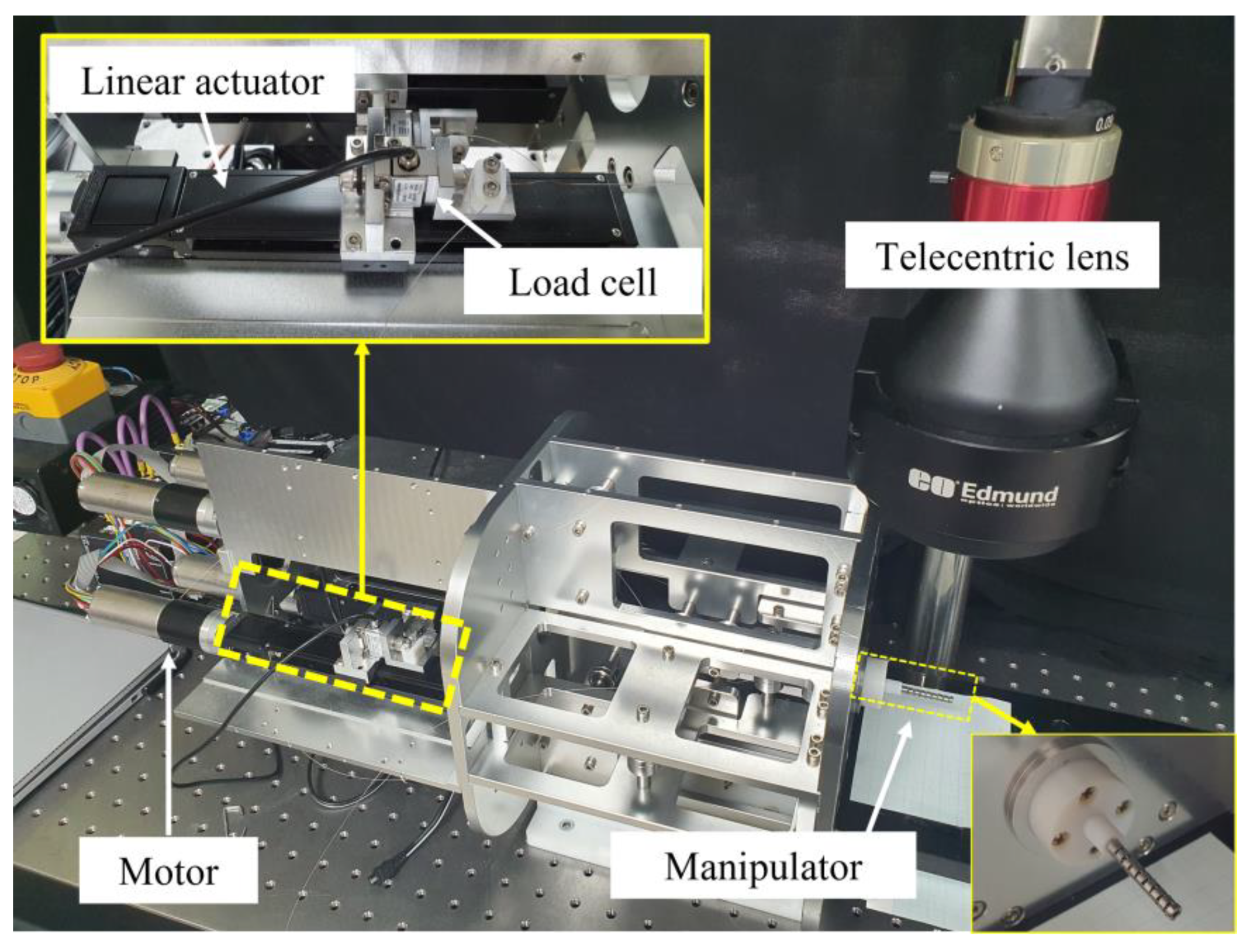
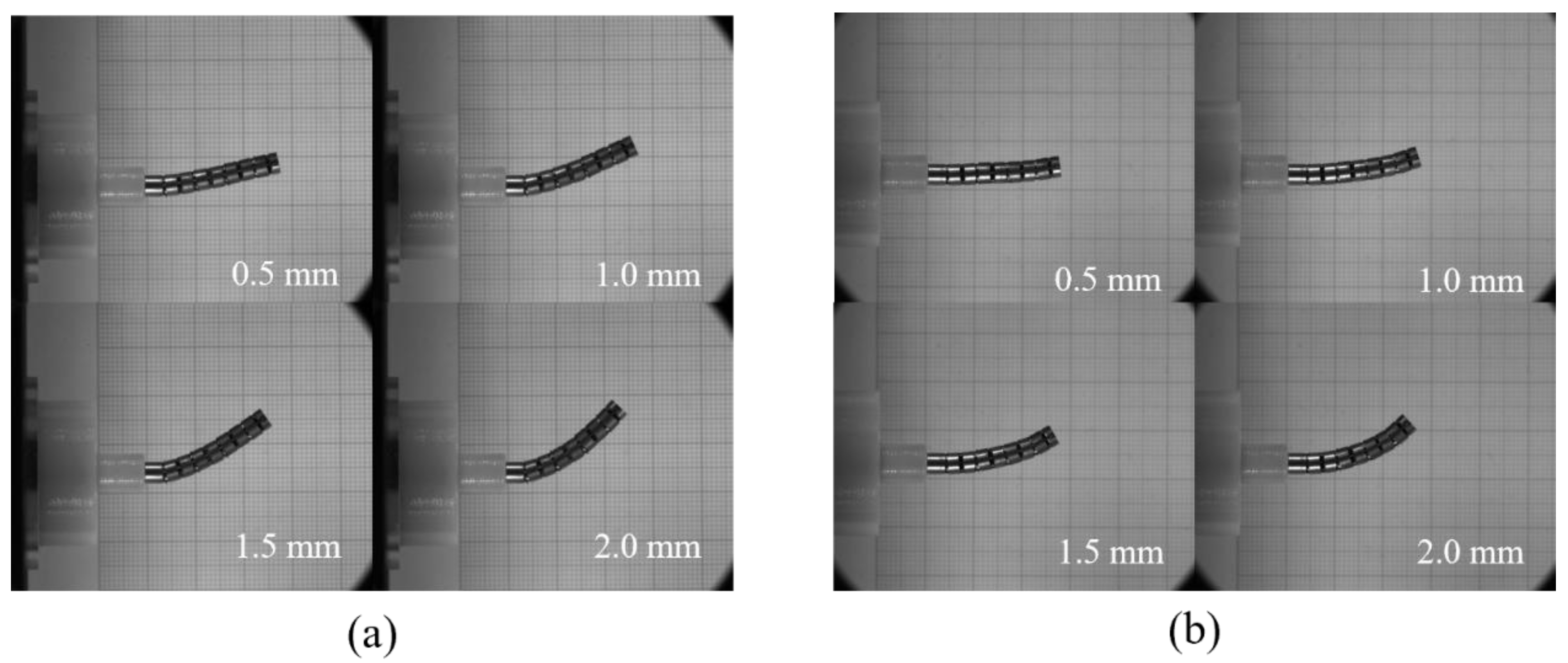
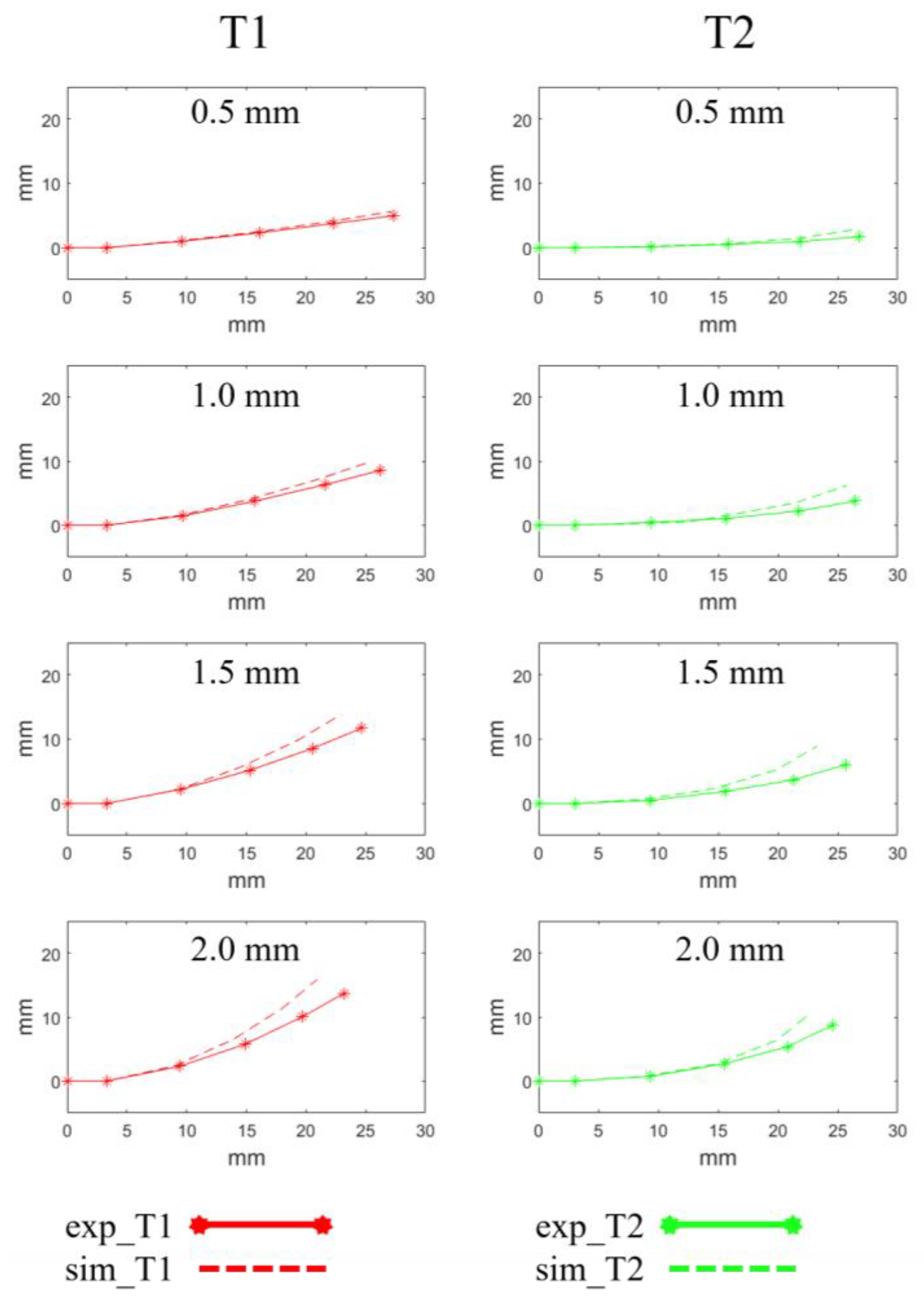
3.4. Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valentina, V.; Su-Lin, L.; Thomas, P.C.; Guang-Zhong, Y. Emerging robotic platforms for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 6, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Filip, J.; Ewout, A.A.; Paul, W.J.H.; Rob, P.; Paul, B. Classification of joints used in steerable instruments for minimally invasive surgery—A review of the state of the art. J. Med. Device 2015, 9, 010801. [Google Scholar]
- Brain, S.P.; Priscila, R.A.; Crystal, K.; Songita, A.C.; Dmitry, O. Review of emerging surgical robotic technology. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 1636–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaohua, H.; Ang, C.; Yigang, L.; Chris, Z.; Edwin, Z. Steerable catheters for minimally invasive surgery: A review and future directions. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2018, 23, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, B.; Konrad, L.; Kiyoung, K.; Carlo, A.S.; Jianzhong, S.; Guang-Zhong, Y. Rolling-joint design optimization for tendon driven snake-like surgical robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4964–4971. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, J.A.; Chris, B.; Richard, I.R.; William, J.P. Design of an endoluminal NOTES robotic system. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Brown, H.; Michael, S.; Shammas, E.; Choset, H. Design and control of a second-generation hyper-redundant mechanism. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 2603–2608. [Google Scholar]
- Arjo, L.; Paul, B.; Jenny, D. Scopes too flexible and too stiff. IEEE Pulse 2010, 1, 26–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hossein, D.; Shane, F.; Dmitry, O.; Benjamin, T. Automation of Suturing Path Generation for da Vinci-Like Surgical Robotic Systems. In Proceedings of the Design of Medical Devices Conference (DMD), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sahba, A.P.; Changyeob, S.; Peter, W.F.; Ji, M.; Erik, P.D.; Jacob, R. Autonomous Suturing Framework and Quantification Using a Cable-Driven Surgical Robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Changyeob, S.; Peter, W.F.; Sahba, A.P.; Ji, M.; Erik, P.D.; Jacob, R. Autonomous Tissue Manipulation via Surgical Robot Using Learning Based Model Predictive Control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QU, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 3875–3881. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, J.W.; Joseph, M.R.; Noah, J.C. Mechanics of precurved-tube continuum robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, M.D.; Saeid, N.; Robert, D.H. An Analytical Loading Model for n-Tendon Continuum Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Tobias, M.; Alexander, H.; Oliver, S. A variable curvature continuum kinematics for kinematic control of the bionic handling assistant. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 935–949. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyoung, K.; Hynsoo, W.; Jungwook, S. Design and evaluation of a continuum robot with discreted link joints for cardiovascular interventions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (Biorob), Enschede, The Netherlands, 26–29 August 2018; pp. 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Jeongryul, K.; Yonghwan, M.; Seong-il, K.; Keri, K. Accurate estimation of the position and shape of the rolling joint in hyper-redundant manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 3055–3060. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, J.W.; Kim, K.Y.; Jeong, J.W.; Lee, J.J. Design considerations for a hyper-redundant pulleyless rolling joint with elastic fixtures. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-jae, K.; Shanbao, C.; Sangbae, K.; Karl, I. A stiffness-adjustable hyperredundant manipulator using a variable neutral-line mechanism for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans. Robotics 2013, 30, 382–395. [Google Scholar]
- Minho, H.; Dong-Soo, K. K-FLEX: A flexible robotic platform for scar-free endoscopic surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot 2020, 16, e2078. [Google Scholar]
- Rucker, D.C. and Webster, R.J., III.Statics and Dynamics of continuum Robots with General Tendon Routing and External Loading. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeongjin, K.; Shing, S.C.; Jaydev, P.D. Active stiffness tuning of a spring-based continuum robot for MRI-guided neurosurgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 34, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yeongjin, K.; Shing, S.C.; Mahamadou, D.; Rao, P.G.; Simard, J.M.; Jaydev, P.D. Toward the development of a flexible mesoscale MRI-compatible neurosurgical continuum robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, J.; Haijie, Z.; Jianguo, Z. Kinematics and statics for soft continuum manipulators with heterogeneous soft materials. In Proceedings of the Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 12–14 October 2016; p. 50701. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.; Bei, L.; Lairong, Y.; Peng, Z.; Yuanhan, Y. Design and Validation of a Novel Cable-Driven Hyper-Redundant Robot Based on Decoupled Joints. Hindawi J. Robot. 2021, 2021, 5124816. [Google Scholar]
- Guodong, Q.; Aihong, J.; Yong, C.; Wenlong, Z.; Hongtao, P.; Shangshuang, S.; Yuntao, S. A Snake-Inspired Layer-Driven Continuum Robot. Soft Robot. 2021. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Haoyong, Y.; Hongliang, R.; Philip, W.Y.C.; Ruxu, D. A Novel Constrained Tendon-driven Serpentine Manipulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburga, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 5966–5971. [Google Scholar]
- Cristina, P.; Cristian, V.; Daniela, P.; Florina, B.; Stefan, C.; Andrei, T.; Ionut, R.; Nicu, B. Position control for hybrid infinite-continuous hyper-redundant robot. MATEC Int. Conf. Manuf. Sci. Educ. 2021, 343, 08009. [Google Scholar]
- Mingfeng, W.; Xin, D.; Weiming, B.; Abdelkhalick, M.; Dragos, A.; Andy, N. Design, modelling and validation of a novel extra slender continuum robot for in-situ inspection and repair in aeroengine. ELSEVIER Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 102054. [Google Scholar]
- Matteo, R.; Luca, R.; Xin, D.; Dragos, A.; James, K. Task-oriented optimal dimensional synthesis of robotic manipulators with limited mobility. ELSEVIER Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 102096. [Google Scholar]
- Seriani, S.; Gallina, P.; Scalera, L.; Lughi, V. Development of n-DoF Preloaded Structures for Impact Mitigation in Cobots. J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 051009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| i | di | θi | αi−1 | ri−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | θ1 | 0 | os |
| 2 | 0 | θ2 | 90° | l |
| 3 | 0 | θ3 | −90° | l |
| 4 | 0 | θ4 | 90° | l |
| 5 | 0 | θ5 | −90° | l |
| 6 | 0 | θ6 | 90° | l |
| 7 | 0 | θ7 | −90° | l |
| 8 | 0 | θ8 | 90° | l |
| Config. | Pulling Length (mm) | Difference of ith Joint and Endpoint (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd | 3rd | 4th | Endpoint | ||
| T1 | 0.5 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.39 | 0.66 |
| 1.0 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 1.02 | 1.61 | |
| 1.5 | 0.20 | 0.92 | 1.78 | 2.73 | |
| 2.0 | 0.35 | 0.99 | 4.62 | 2.27 | |
| T2 | 0.5 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.53 | 1.18 |
| 1.0 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 1.30 | 2.54 | |
| 1.5 | 0.47 | 0.99 | 2.12 | 3.75 | |
| 2.0 | 0.26 | 0.56 | 1.38 | 2.66 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Moon, Y.; Kim, K. Hyper-Redundant Manipulator Capable of Adjusting Its Non-Uniform Curvature with Discrete Stiffness Distribution. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010482
Kwon S, Kim J, Moon Y, Kim K. Hyper-Redundant Manipulator Capable of Adjusting Its Non-Uniform Curvature with Discrete Stiffness Distribution. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010482
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Seongil, Jeongryul Kim, Yonghwan Moon, and Keri Kim. 2022. "Hyper-Redundant Manipulator Capable of Adjusting Its Non-Uniform Curvature with Discrete Stiffness Distribution" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010482
APA StyleKwon, S., Kim, J., Moon, Y., & Kim, K. (2022). Hyper-Redundant Manipulator Capable of Adjusting Its Non-Uniform Curvature with Discrete Stiffness Distribution. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010482







