Towards Adaptive Gamification: A Method Using Dynamic Player Profile and a Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Previous Work
2.1. Player Modeling
2.2. Adaptation Strategy
3. Runtime Method for Adaptive Gamification
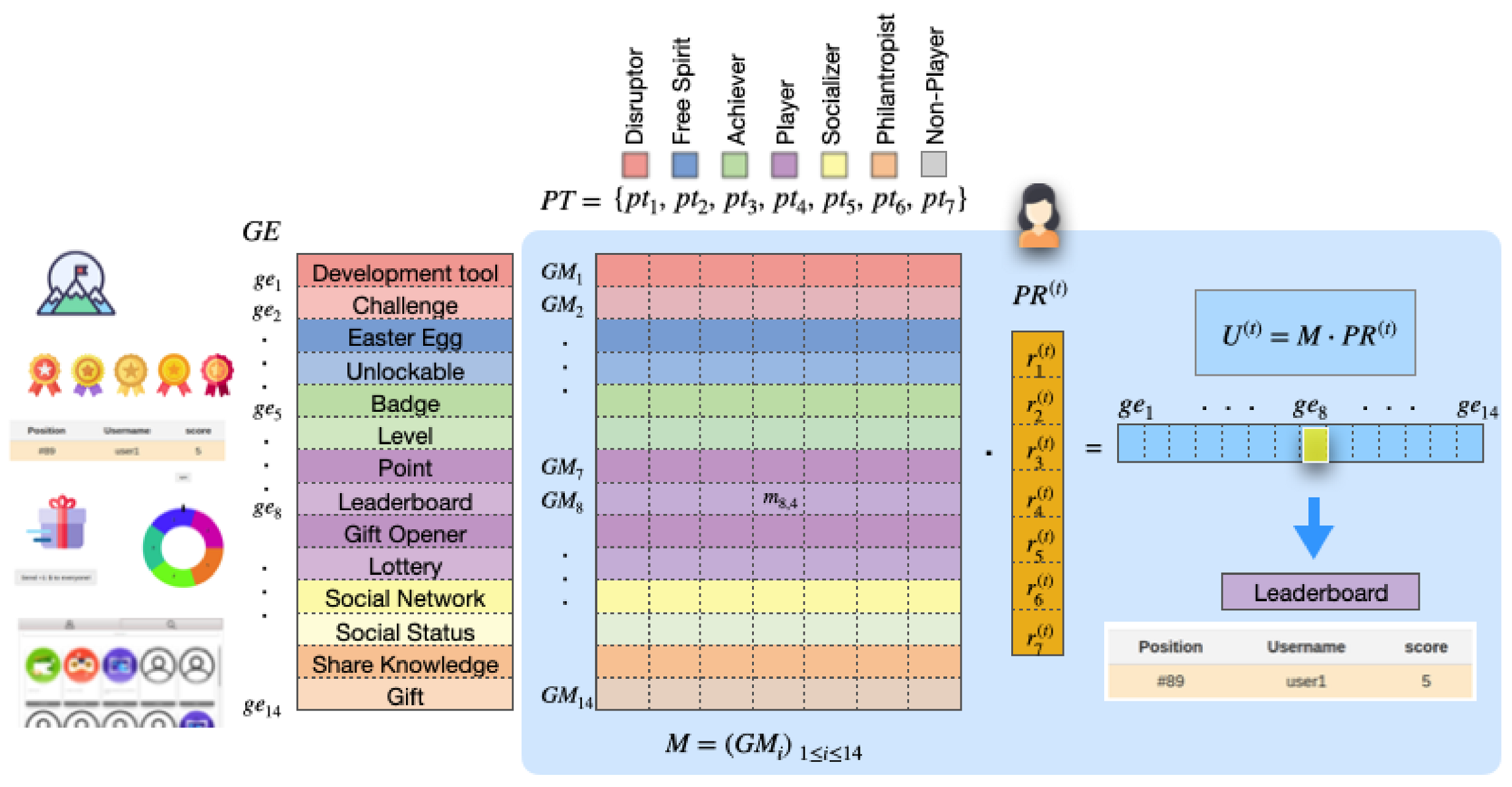
3.1. Previous Definitions
3.1.1. Player Type
- Disruptor: motivated by the ability to modify the system;
- Free spirit: motivated by the ability to freely explore the system;
- Achiever: motivated by the ability to win challenges and unlock hidden content.;
- Player: motivated by the game itself;
- Philanthropist: motivated by the ability to share goods and help other users;
- Socializer: motivated by social connections;
- Non-player: users who do not like to play.
3.1.2. Game Element
- Development tool: allows the player user to create certain gamification mechanics such as badges, challenges and unlockables.
- Challenge: the player must overcome a challenge, such as reaching a certain level and solving a problem in a certain time;
- Easter egg: the mechanism consists of an image which, when pressed five consecutive times, allows access to a mini-game;
- Unlockable: when a player overcomes a certain challenge, a hidden content is unlocked, which can be a message, a mini-game, etc.;
- Badge: awarded to the player when they manage to complete a difficult task;
- Level: shows the user’s progress in completing a task, subdivided into levels;
- Point: the player gains score, experience, virtual money, etc.;
- Leaderboard: displays a ranking of scores;
- Gift Opener: the player opens gifts they have received;
- Lottery: game of chance (roulette) that allows players to increase their scores;
- Social network: a small social network that allows players to create a profile, add friends and view their profiles;
- Social status: collection of rankings of players based on their scores, especially those related to social interactions, such as the number of followers, visitors, etc.;
- Share knowledge: the player sends help messages to everyone in a group;
- Gift: the player sends gifts to other users.
3.1.3. Interaction Index
- : the display time, i.e., the time interval for which the game element has been displayed until time t;
- : the number of interactions at time t;
- : the opinion, i.e., the user assessment of the game element. This is a value between 0 and 1. Opinions from 1 to 5 stars correspond to and 1, respectively.
3.1.4. Activities
3.2. Adaptive Method
- : the player type of the user at time t;
- : the interaction indexes;
- : to avoid extreme fluctuations between and , where —the value of this parameter should be tuned experimentally;
- : the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse matrix of M, needed in order to interpret and in the same space.
4. Case Study
4.1. Adaptive Gamification in Nanomoocs
4.2. Adaptive Gamification: Software Architecture
5. Adaptive Method Evaluation
5.1. Simulation System
- If the game element () fits the real bot’s profile (), the bot interacts more frequently than otherwise. Therefore, reflects this behavior by taking values from 0.5 (frequent interactions) to 10 (longer time between interactions);
- Regarding , we consider that the bot interacts once every ;
- The opinion can be calculated in a similar way using .
5.2. Results
- Method A—Constant : a constant player rating, , is assigned at any time. In this case, we use Equation (9) to calculate once and always use its maximal component.We calculate the error as follows. Since , the distance is simply calculated as . Note that if the user has accurately answered the questionnaire, we have ;
- Method B—Random dynamic : a dynamic player rating is randomly chosen at each time t and then, the game element selected to be shown is also the maximal component of . Note that this method is equivalent to picking a random game element.In this method, we compute the error as the average distance between and a random point using the average distance of random points in a unit hypercube (average distance of random points in a unit hypercube, https://martin-thoma.com/curse-of-dimensionality/, accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Method C—Our method, dynamic : a dynamic player rating is computed according the defined by Equation (6). The bot then simulates , , and using and . The game element selected to be shown is a weighted random choice of (see step 3 in Figure 2).In this method, we calculate the error based on the distances between and for all t from 1 to :
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapp, A.; Alessandro, M.; Simeoni, R.; Console, L. Playing while Testing: How to Gamify a User Field Evaluation. In Designing Gamification: Creating Gameful and Playful Experiences Held in Conjunction with SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’13); Gamification Research Network: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Vassileva, J. Adaptive Reward Mechanism for Sustainable Online Learning Community. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence in Education, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18–22 July 2005; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gené, O.; Núñez, M.; Blanco, A. Gamification in MOOC: Challenges, opportunities and proposals for advancing MOOC model. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality (TEEM’14), Salamanca, Spain, 1–3 October 2014; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoue, E.; Monterrat, B.; Desmarais, M.; George, S. Adaptive Gamification for Learning Environments. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2019, 12, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.; Black, M. Dynamic Player Modelling: A Framework for Player-centred Digital Games. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Games: Artificial Intelligence, Design and Education (CGAIDE’04), Microsoft Academic Campus, Reading, UK, 8–10 November 2004; pp. 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hallifax, S.; Serna, A.; Marty, J.; Lavoué, G.; Lavoué, E. Factors to consider for tailored gamification. In Proceedings of the CHI PLAY 2019 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play, Barcelona, Spain, 22–25 October 2019; pp. 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Puig, A.; Rodríguez, A. We Are Not the Same Either Playing: A Proposal for Adaptive Gamification. In Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications; Villaret, M., Alsinet, T., Fernández, C., Valls, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 339, pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallifax, S.; Serna, A.; Marty, J.; Lavoué, E. Adaptive Gamification in Education: A Literature Review of Current Trends and Developments. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2019, 11722, 294–307. [Google Scholar]
- Klock, A.C.T.; Gasparini, I.; Pimenta, M.S.; Hamari, J. Tailored gamification: A review of literature. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2020, 144, 102495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challco, G.C.; Moreira, D.A.; Mizoguchi, R.; Isotani, S. An ontology engineering approach to gamify collaborative learning scenarios. In CYTED-RITOS International Workshop on Groupware; Baloian, N., Burstein, F., Ogata, H., Santoro, F., Zurita, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Denden, M.; Tlili, A.; Essalmi, F.; Jemni, M. Does personality affect students’ perceived preferences for game elements in gamified learning environments? In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, ICALT 2018, Mumbai, India, 9–13 July 2018; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, L.S.; Walz, S.P.; Greuter, S. Towards personalised, gamified systems. In Proceedings of the 9th Australasian Conference on Interactive Entertainment Matters of Life and Death—IE ’13, Melbourne, Australia, 30 September–1 October 2013; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, S.; Mizoguchi, R.; Durelli, V.H.S.; Bittencourt, I.; Isotani, S. A link between worlds: Towards a conceptual framework for bridging player and learner roles in gamified collaborative learning contexts. In Advances in Social Computing and Digital Education, Croatia; Koch, F., Koster, A., Primo, T., Guttmann, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Knutas, A.; Ikonen, J.; Maggiorini, D.; Ripamonti, L.; Porras, J. Creating student interaction profiles for adaptive collaboration gamification design. Int. J. Hum. Cap. Inf. Technol. Prof. 2016, 7, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chtouka, E.; Guezguez, W.; Amor, N.B. Reinforcement learning for new adaptive gamified LMS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Economy, Mumbai, India, 9–13 July 2018; Jallouli, R., Bach Tobji, M., Bélisle, D., Mellouli, S., Abdallah, F., Osman, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Monterrat, B.; Lavoué, E.; George, S. Toward an Adaptive Gamification System for Learning Environments. In Computer Supported Education; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, C.; Tucker, C. Toward Personalized Adaptive Gamification: A Machine Learning Model for Predicting Performance. IEEE Trans. Games 2020, 12, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartle, R.A. Hearts, Clubs, Diamonds, Spades: Players Who Suit Muds. J. MUD Res. 1996, 1, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Nacke, L.E.; Bateman, C.; Mandryk, R.L. BrainHex: A neurobiological gamer typology survey. Entertain. Comput. 2014, 5, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczewski, A. Even Ninja Monkeys Like to Play: Gamification, Game Thinking and Motivational Design. In Game Thinking & Motivational Design; CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, Ed.; Blurb Inc.: London, UK, 2015; pp. 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sienel, N.; Münster, P.; Zimmermann, G. Player-Type-based Personalization of Gamification in Fitness Apps. In Proceedings of the HEALTHINF, Vienna, Austria, 11–13 February 2021; pp. 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, A.; Tondello, G.F.; Nacke, L.E.; Arnedo-Moreno, J. Effect of personalized gameful design on student engagement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference, EDUCON, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain, 17–20 April 2018; pp. 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmeyer, M.; Tondello, G.F.; Krüger, A.; Nacke, L.E. HexArcade: Predicting Hexad User Types by Using Gameful Applications. In Proceedings of the CHI PLAY 2020 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play, Virtual Event, 2–4 November 2020; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondello, G.F.; Wehbe, R.; Diamond, L.; Busch, M.; Marczewski, A.; Nacke, L.E. The Gamification User Types Hexad Scale. In Proceedings of the 2016—CHI PLAY 2016 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play, Austin, TX, USA, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 229–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hallifax, S.; Lavoué, E.; Serna, A. To tailor or not to tailor gamification? An analysis of the impact of tailored game elements on learners’ behaviours and motivation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2020, 12163, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, J.; Lester, J. Affect and Engagement in Game-BasedLearning Environments. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 5, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte Ayastuy, M.; Torres, D.; Fernández, A. Adaptive gamification in Collaborative systems, a systematic mapping study. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 39, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škuta, P.R.; Kostolányová, K. Adaptive approach to the gamification in education. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning, Transforming Learning with Meaningful Technologies, Delft, The Netherlands, 16–19 September 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; p. 367. [Google Scholar]
- Barata, G.; Gama, S.; Jorge, J.; Gonçalves, D. Gamification for smarter learning: Tales from the trenches. Smart Learn. Environ. 2015, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Knutas, A.; Van Roy, R.; Hynninen, T.; Granato, M.; Kasurinen, J.; Ikonen, J. A process for designing algorithm-based personalized gamification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 13593–13612. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.A.; Habiba, U.; Majeed, F.; Shoaib, M. Adaptive gamification in e-learning based on students’ learning styles. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2021, 29, 545–565. [Google Scholar]
- Jagušt, T.; Botički, I.; So, H.J. Examining competitive, collaborative and adaptive gamification in young learners’ math learning. Comput. Educ. 2018, 125, 444–457. [Google Scholar]
- Kickmeier-Rust, M.D. An Alien’s Guide to Multi-Adaptive Educational Computer Games; Informing Science: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, S.; Khatib, F.; Treuille, A.; Barbero, J.; Lee, J.; Beenen, M.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Baker, D.; Popović, Z. Predicting protein structures with a multiplayer online game. Nature 2010, 466, 756–760. [Google Scholar]
- Eveleigh, A.; Jennett, C.; Lynn, S.; Cox, A.L. “I want to be a captain! I want to be a captain!” gamification in the old weather citizen science project. In Proceedings of the fIrst International Conference on Gameful Design, Research, and Applications, Stratford, ON, Canada, 2–4 October 2013; pp. 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ismailović, D.; Pagano, D.; Brügge, B. Wemakewords-An adaptive and collaborative serious game for literacy acquisition. In Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference-Game and Entertainment, Rome, Italy, 20–26 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cantwell, D.; Broin, D.O.; Palmer, R.; Doyle, G. Motivating elderly people to exercise using a social collaborative exergame with adaptive difficulty. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Games Based Learning, Cork, Ireland, 4–5 October 2012; pp. 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Llanos, J.; Carro, R.M. The squares: A multi-touch adaptive game for children integration. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Computers in Education (SIIE), Setubal, Portugal, 25–27 November 2015; pp. 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tranvouez, E.; Fournier, S. A MultiAgent architecture for collaborative serious game applied to crisis management training: Improving adaptability of non player characters. EAI Endorsed Trans. Serious Games 2014, 1, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knutas, A.; van Roy, R.; Hynninen, T.; Granato, M.; Kasurinen, J.; Ikonen, J. Profile-Based Algorithm for Personalized Gamification in Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning Environments. In Proceedings of the 1st Games-Humans Interactions GHITALY@ CHItaly, Cagliari, Italy, 18 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Riedl, M.O. A sequential recommendation approach for interactive personalized story generation. In Proceedings of the AAMAS, Valencia, Spain, 4–8 June 2012; Volume 12, pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, E.J.; Guha, R.K.; Stanley, K.O. Automatic content generation in the galactic arms race video game. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2009, 1, 245–263. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.A.; Habiba, U.; Khalid, H.; Shoaib, M.; Arshad, S. An adaptive feedback system to improve student performance based on collaborative behavior. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 107171–107178. [Google Scholar]
- Feyisetan, O.; Simperl, E.; Van Kleek, M.; Shadbolt, N. Improving paid microtasks through gamification and adaptive furtherance incentives. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 333–343. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, A.; González, C.; Arnedo-Moreno, J.; Álvarez, A. Gamification of cognitive training: A crowdsourcing-inspired approach for older adults. In Proceedings of the XVII International Conference on Human Computer Interaction, Salamanca, Spain, 13–16 September 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich, K.; Neuwald, K.; Othlinghaus, J.; Ziebarth, S.; Hoppe, H.U. Training conflict management in a collaborative virtual environment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Collaboration and Technology, Raesfeld, Germany, 16–19 September 2012; Herskovic, V., Hoppe, H.U., Jansen, M., Ziegler, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 17–32. [Google Scholar]








| Player Type | Game Elements | Additional Player Types [24] |
|---|---|---|
| Disruptor | Development Tools | Free Spirit |
| Creativity Tools (Challenges) | Player, Achiever, Free Spirit | |
| Free Spirit | Unlockable | - |
| Easter Egg | Player | |
| Achiever | Badge | Player |
| Level of Progression | Player | |
| Player | Lottery | - |
| Leaderboard | - | |
| Gift Opener (Prizes) | - | |
| Points | - | |
| Socializer | Social Network | Free Spirit |
| Social Status | - | |
| Philanthropist | Share Knowledge | - |
| Gifting | - |
 |  |
| Disruptor | Free Spirit |
 |  |
| Achiever | Philanthropist |
 |  |
| Socializer | Player |
| Cases/Methods | A—Constant | B—Random | C—Our Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | Dynamic | Dynamic | |
| Accurate Answers Case: | |||
| Mean Error (SD) | 0 | 0.08024 (0.00052) | 0.0070 (0.00166) |
| Worst Scenario of C | 0 | 0.0804 | 0.0105 |
| Best Scenario of C | 0 | 0.0797 | 0.0029 |
| Inaccurate Answers Case: | |||
| Mean Error (SD) | 0.0311(0.00404) | 0.08027 (0.00040) | 0.0243 (0.00475) |
| Worst Scenario of C | 0.0367 | 0.08012 | 0.0333 |
| Best Scenario of C | 0.0233 | 0.08018 | 0.0146 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, I.; Puig, A.; Rodríguez, À. Towards Adaptive Gamification: A Method Using Dynamic Player Profile and a Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010486
Rodríguez I, Puig A, Rodríguez À. Towards Adaptive Gamification: A Method Using Dynamic Player Profile and a Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010486
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Inmaculada, Anna Puig, and Àlex Rodríguez. 2022. "Towards Adaptive Gamification: A Method Using Dynamic Player Profile and a Case Study" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010486
APA StyleRodríguez, I., Puig, A., & Rodríguez, À. (2022). Towards Adaptive Gamification: A Method Using Dynamic Player Profile and a Case Study. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010486






