Exploring the Probiotic Potential of Dairy Industrial-Relevant Lactobacilli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains
2.2. Genotyping Characterization
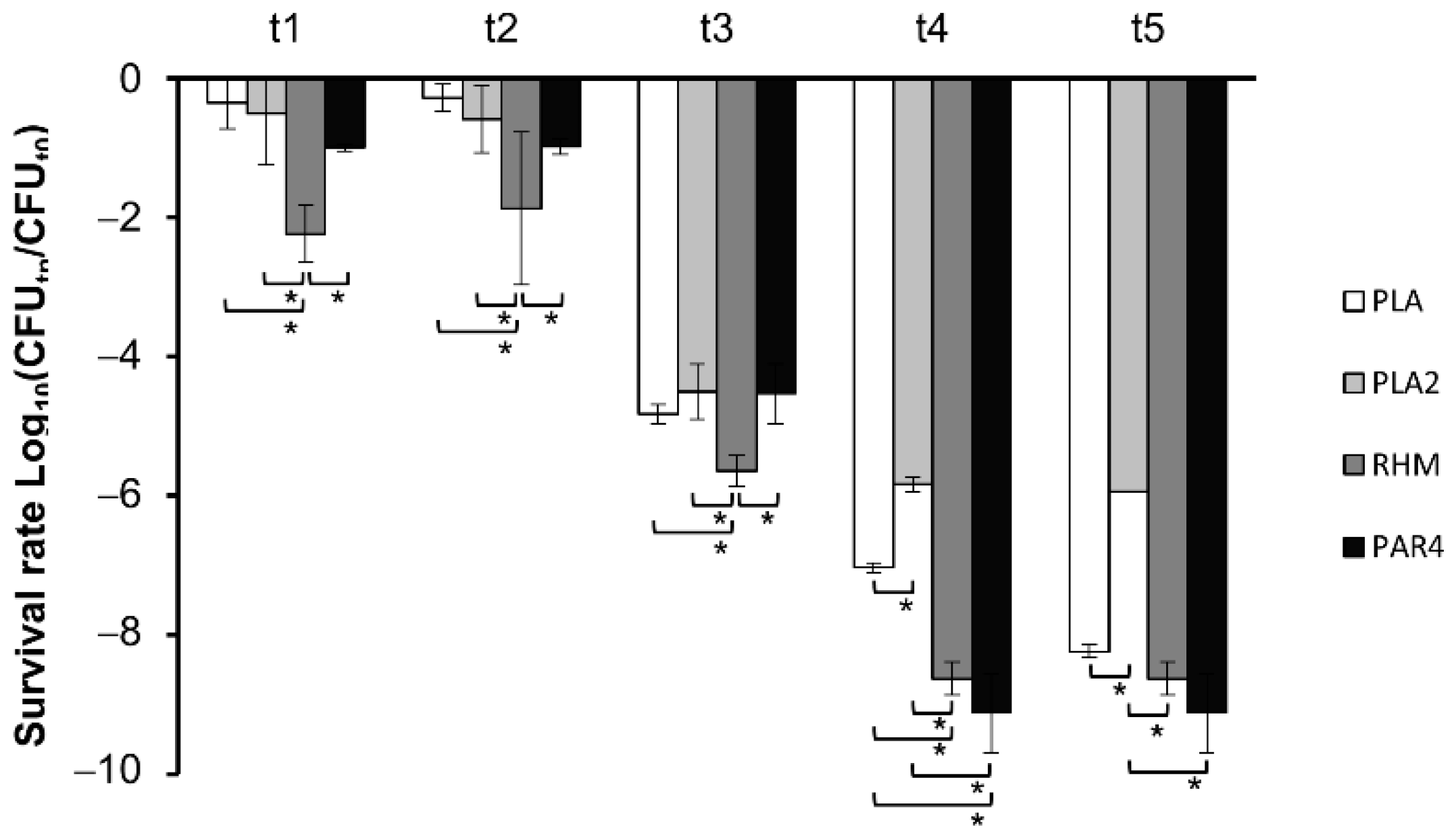
2.3. In Vitro Survival in Simulated Oro-Gastrointestinal Transit
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5. Biofilm Formation
2.6. Riboflavin Production
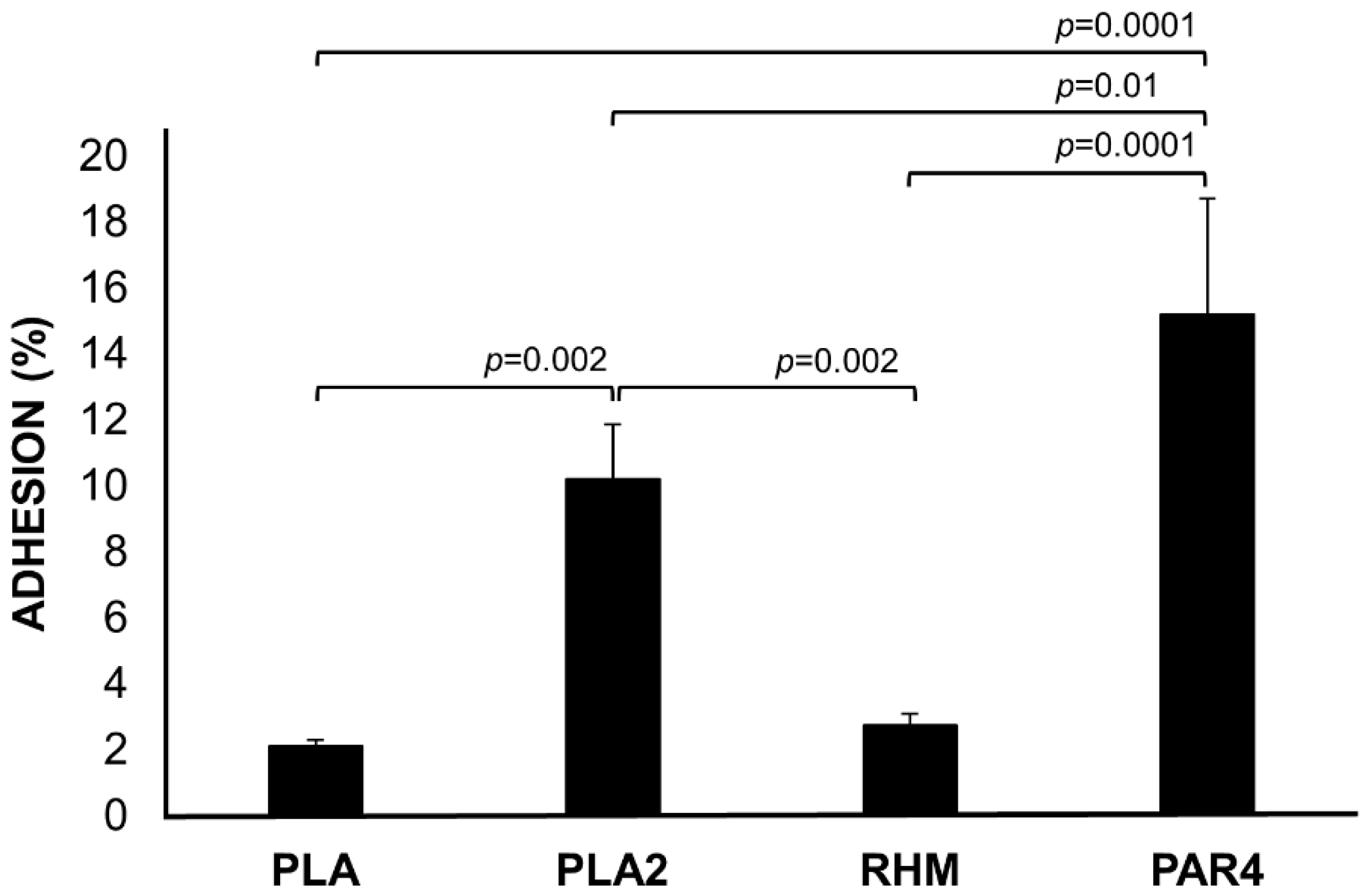
2.7. Caco-2 Adhesion Assay
2.8. Immuno-Modulation of THP-1 Macrophages
2.8.1. MTT Assay
2.8.2. Effect of LAB CFS on THP-1 Macrophages
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the Lactobacilli Strains
3.2. Survival in Simulated Oro-Gastrointestinal Stress (OGI)
3.3. Vitamin B2 Production
3.4. Antimicrobial Spectrum
3.5. Adhesion to Caco-2 Monolayer Cells
3.6. Biofilm Formation Assays
3.7. Immuno-Modulatory Effect of LAB CFS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timmis, K.; De Vos, W.M.; Ramos, J.L.; Vlaeminck, S.; Prieto, A.; Danchin, A.; Verstraete, W.; De Lorenzo, V.; Lee, S.Y.; Brüssow, H.; et al. The contribution of microbial biotechnology to sustainable development goals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzi, V.; Russo, P.; Dueñas, M.T.; López, P.; Spano, G. Lactic acid bacteria producing B-group vitamins: A great potential for functional cereals products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzi, V.; Fragasso, M.; Bimbo, F. Microbial Resources, Fermentation and Reduction of Negative Externalities in Food Systems: Patterns toward Sustainability and Resilience. Fermentation 2021, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.I.; Qadir, M.I.; Shirazi, J.H.; Khan, I.U. Beneficial effects of lactic acid bacteria on human beings. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 37, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizeikiene, D.; Jagelaviciute, J. Investigation of Antibacterial Activity and Probiotic Properties of Strains Belonging to Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Genera for Their Potential Application in Functional Food and Feed Products. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1387–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Arora, K.; Prakash, S. Microbial Medicine: Prebiotic and Probiotic Functional Foods to Target Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosola, C.; Rocchetti, M.; di Bari, I.; Acquaviva, P.M.; Maranzano, V.; Corciulo, S.; Di Ciaula, A.; Di Palo, D.M.; La Forgia, F.M.; Fontana, S.; et al. An Innovative Synbiotic Formulation Decreases Free Serum Indoxyl Sulfate, Small Intestine Permeability and Ameliorates Gastrointestinal Symptoms in a Randomized Pilot Trial in Stage IIIb-IV CKD Patients. Toxins 2021, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Cosola, C.; di Bari, I.; Magnani, S.; Galleggiante, V.; Scandiffio, L.; Dalfino, G.; Netti, G.S.; Atti, M.; Corciulo, R.; et al. Efficacy of Divinylbenzenic Resin in Removing Indoxyl Sulfate and P-cresol Sulfate in Hemodialysis Patients: Results from an in vitro Study and an in vivo Pilot Trial (xuanro4-Nature 3.2). Toxins 2020, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, S.; Singh, N.; Nadda, A.K.; Goel, G. Probiotics and Their Potential Applications: An Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 21, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Omatola, C.A.; Olaniran, A.O. Applications of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins against Food Spoilage Microorganisms and Foodborne Pathogens. Molecules 2021, 26, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, M.P.; Capozzi, V.; Russo, P.; Dridier, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Immunobiosis and probiosis: Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria with a focus on their antiviral and antifungal properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9949–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, P.; Pérez Ibarreche, M.; Blanco Massani, M.; Fontana, C.; Vignolo, G.M. Strategies for Pathogen Biocontrol Using Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Metabolites: A Focus on Meat Ecosystems and Industrial Environments. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, N.; Capozzi, V.; de Chiara, M.L.V.; Amodio, M.L.; Brahimi, S.; Colelli, G.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Russo, P. Screening of Lactic Acid Bacteria for the Bio-Control of Botrytis cinerea and the Potential of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum for Eco-Friendly Preservation of Fresh-Cut Kiwifruit. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazelas, E.; Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Esseddik, Y.; de Edelenyi, F.S.; Agaesse, C.; De Sa, A.; Lutchia, R.; Rebouillat, P.; Srour, B.; Debras, C.; et al. Exposure to food additive mixtures in 106,000 French adults from the NutriNet-Santé cohort. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornsenee, P.; Singkhamanan, K.; Sangkhathat, S.; Saengsuwan, P.; Romyasamit, C. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus Species Isolated from Fermented Palm Sap in Thailand. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheziel, C.; Russo, P.; Arena, M.P.; Spano, G.; Ouzari, H.-I.; Kheroua, O.; Saidi, D.; Fiocco, D.; Kaddouri, H.; Capozzi, V. Evaluating the Probiotic Potential of Lactobacillus plantarum Strains from Algerian Infant Feces: Towards the Design of Probiotic Starter Cultures Tailored for Developing Countries. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 11, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, S.; Fernández-Pacheco, P.; Seseña, S.; Pintado, C.; Palop, M.L. Selection of probiotic Lactobacillus strains with antimicrobial activity to be used as biocontrol agents in food industry. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 111142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Pereira, G.V.; de Oliveira Coelho, B.; Magalhães Júnior, A.I.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. How to select a probiotic? A review and update of methods and criteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 2060–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, D.; Longo, A.; Arena, M.P.; Russo, P.; Spano, G.; Capozzi, V. How probiotics face food stress: They get by with a little help. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 1552–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendeboodi, F.; Khorshidian, N.; Mortazavian, A.M.; da Cruz, A.G. Probiotic: Conceptualization from a new approach. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Man, J.C.; Rogosa, M.; Sharpe, M.E. A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1960, 23, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-U.; Park, Y.J.; Yu, H.H.; Jung, S.-C.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effect of ε-Polylysine against Salmonella Enteritidis, Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli in Tryptic Soy Broth and Chicken Juice. Foods 2021, 10, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, M.A.; Antonio, M.A.D.; Hillier, S.L. Comparison of API 50 CH Strips to Whole-Chromosomal DNA Probes for Identification of Lactobacillus Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5309–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APIWEB. Available online: https://apiweb.biomerieux.com (accessed on 13 May 2002).
- Piotrowska, A.; Gosiewski, T.; Bulanda, M.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M. Using of the 16S rDNA sequencing for identification of Lactobacillus species. Med. Dosw. Mikrobiol. 2017, 68, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, A.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Knock out of sHSP genes determines some modifications in the probiotic attitude of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 43, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, P.; Gallone, A.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; Albenzio, M.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Probiotic features of Lactobacillus plantarum mutant strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudana, S.B.; Dhanani, A.S.; Bagchi, T. Probiotic attributes of Lactobacillus strains isolated from food and of human origin. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arena, M.P.; Silvain, A.; Normanno, G.; Grieco, F.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Use of Lactobacillus plantarum Strains as a Bio-Control Strategy against Food-Borne Pathogenic Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Hadjilouka, A.; Beneduce, L.; Capozzi, V.; Paramithiotis, S.; Drosinos, E.H.; Spano, G. Effect of different conditions on Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation and removal. Czech J. Food Sci. 2018, 36, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; De Simone, N.; Capozzi, V.; Mohedano, M.L.; Ruiz-Masó, J.; del Solar, G.; López, P.; Spano, G. Selection of Riboflavin Overproducing Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Riboflavin Direct Quantification by Fluorescence. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Barile, M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; López, P.; Capozzi, V.; De Palencia, P.F.; Dueñas, M.T.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Beta-Glucans Improve Growth, Viability and Colonization of Probiotic Microorganisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6026–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garai-Ibabe, G.; Dueñas, M.T.; Irastorza, A.; Sierra-Filardi, E.; Werning, M.L.; López, P.; Corbi, A.L.; Fernández de Palencia, P. Naturally occurring 2-substituted (1,3)-β-d-glucan producing Lactobacillus suebicus and Pediococcus parvulus strains with potential util-ity in the production of functional foods. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9254–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández de Palencia, P.; López, P.; Corbí, A.L.; Peláez, C.; Requena, T. Probiotic strains: Survival under simulated gastro-intestinal conditions, in vitro adhesion to Caco-2 cells and effect on cytokine secretion. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.P.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; Rascón, A.; Felis, G.E.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Combinations of cereal β-glucans and probiotics can enhance the anti-inflammatory activity on host cells by a synergistic effect. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossman, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Bioprospecting Antimicrobials from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: Key Factors Underlying Its Probiotic Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Liu, X.; Zhi, A.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Characterization and Selection of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus paracasei for prevention of oral bacterial infections from Chinese pickle. AMB Express 2021, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, F.R.L.; dos Santos, K.M.O.; de Barcelos, S.C.; do Egito, A.S.; Ribeiro, T.S.; da Conceição, M.L.; Magnani, M.; de Oliveira, M.E.G.; do Queiroga, R.D.C.R. Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus EM1107 in simulated gastrointestinal conditions and its inhibitory effect against pathogenic bacteria in semi-hard goat cheese. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak-Różańska, L.; Berthold-Pluta, A.; Pluta, A.; Dasiewicz, K.; Garbowska, M. Effect of Simulated Gastrointestinal Tract Conditions on Survivability of Probiotic Bacteria Present in Commercial Preparations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, F.; De Bellis, P.; Lonigro, S.L.; Morelli, L.; Visconti, A.; Lavermicocca, P. In vitro and in vivo Survival and Transit Tolerance of Potentially Probiotic Strains Carried by Artichokes in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3042–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levit, R.; De Giori, G.S.; LeBlanc, A.; Leblanc, J.G. Effect of riboflavin-producing bacteria against chemically induced colitis in mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 124, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, M.P.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; López, P.; Fiocco, D.; Spano, G. Probiotic abilities of riboflavin-overproducing Lactobacillus strains: A novel promising application of probiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7569–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, J.G.; Chain, F.; Martín, R.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Courau, S.; Langella, P. Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.; Tomar, S.K.; De, S. Lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory for riboflavin production. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 9, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xie, S.; Lv, D.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Y. A reduction in the butyrate producing species Roseburia spp. and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is associated with chronic kidney disease progression. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 109, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.M.; Miguel, M.A.; Peixoto, R.S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Paschoalin, V.M.; Mayo, B.; Delgado, S. Probiotic potential of selected lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from Brazilian kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Xie, X.Q.; Ding, Y.; Cai, S.Z.; Ye, Q.H.; Chen, M.T.; Xue, L.; et al. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Probiotic Potential of Lactobacillus plantarum Isolated from Chinese Homemade Pickles. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.K.; the Korea INfectious Diseases (KIND) study group; Kim, Y.K.; Jung, S.-I.; Park, W.B.; Song, K.-H.; Park, K.-H.; Choe, P.G.; Jang, H.-C.; Lee, S.; et al. agr functionality affects clinical outcomes in patients with persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 36, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaya, J.A.; Mera, R.M.; Cassidy, A.; O’Hara, P.; Amrine-Madsen, H.; Burstin, S.; Miller, L.G. Incidence and cost of hospitalizations associated with Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft tissue infections in the United States from 2001 through 2009. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, N. The Combined Use of Tea Polyphenols and Lactobacillus plantarum ST8SH Bacteriocin in a Rabbit Model of Infection Following Femoral Fracture with Internal Fixation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, H.; Smoragiewicz, W. Role of probiotics in the prevention and treatment of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalho, L.P.; Jorge, G.P.; Noleto, D.A.; Silva, C.E.; Abreu, J.S.; Piran, M.V.; Brocchi, M.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Biopreservation and probiotic potential of a large set of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Brazilian artisanal cheeses: From screening to in product approach. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 242, 126622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Luo, X.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Quorum Sensing, Biofilm, and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier: Involvement the Role of Probiotic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 538077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Ramírez, L.M.; Hernández-Chiñas, U.; Moreno-Guerrero, S.S.; Ramírez-Pacheco, A.; Eslava, C.A. Probiotic Properties and Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Dairy Products. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, G.M.; Arechavaleta, N.N.; Siqueira, F.M.; de Souza da Motta, A. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Raw Buffalo Milk: A Screening for Novel Probiotic Candidates and Their Transcriptional Response to Acid Stress. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 13, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.P.; Caggianiello, G.; Fiocco, D.; Russo, P.; Torelli, M.; Spano, G.; Capozzi, V. Barley β-Glucans-Containing Food Enhances Probiotic Performances of Beneficial Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3025–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, H.C.; Melo, D.D.S.; Ramos, C.L.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F. Probiotic Properties of Lactobacilli and Their Ability to Inhibit the Adhesion of Enteropathogenic Bacteria to Caco-2 and HT-29 Cells. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. Characterization and transcriptomic basis of biofilm formation by Lactobacillus plantarum J26 isolated from traditional fermented dairy products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 125, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; Xia, Y.; Lai, P.F.H.; Ai, L. A Surface Protein From Lactobacillus plantarum Increases the Adhesion of Lactobacillus Strains to Human Epithelial Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.C.; Mowat, A.M. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C. The Interleukins Orchestrate Mucosal Immune Responses to Salmonella Infection in the Intestine. Cells 2021, 10, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, S.; Sichetti, M.; Muradyan, D.; Piccioni, M.; Traina, G.; Pagiotti, R.; Pietrella, D. Probiotic Cell-Free Supernatants Exhibited Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity on Human Gut Epithelial Cells and Macrophages Stimulated with LPS. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1756308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, M.P.; Strap, J.L.; Taggart, H.J.; Green-Johnson, J.M. Suppression of Intestinal Epithelial Cell Chemokine Production by Lactobacillus rhamnosus R0011 and Lactobacillus helveticus R0389 Is Mediated by Secreted Bioactive Molecules. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domoto, R.; Sekiguchi, F.; Tsubota, M.; Kawabata, A. Macrophage as a Peripheral Pain Regulator. Cells 2021, 10, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, L.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Fierer, J. Epithelial cells secrete the chemokine interleukin-8 in response to bacterial entry. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Chae, S.A.; Bang, W.Y.; Lee, M.; Ban, O.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Yang, J. Anti-inflammatory potential of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IDCC 3501 and its safety evaluation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Romero, F.; Gil, A. Lactobacillus rhamnosus and its cell-free culture supernatant differentially modulate inflammatory biomarkers in Escherichia coli-challenged human dendritic cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Strain | E. coli | S. aureus | L. monocytogenes |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. plantarum PLA | ++ (5.5 ± 1.0) | ++ (3.5 ± 0.0) | ++ (5.0 ± 1.0) |
| L. plantarum PLA2 | ++ (5.5 ± 0.5) | + (2.5 ± 0.5) | ++ (5.0 ± 1.0) |
| L. rhamnosus RHM | ++ (3.5 ± 0.0) | + (2.0 ± 0.5) | + (2.0 ± 0.5) |
| L. rhamnosus PAR4 | ++ (6.0 ± 1.5) | ++ (3.5 ± 0.5) | ++ (4.5 ± 0.5) |
| Relative Cell Viability | 15% CSF | 10% CFS | 5% CFS |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. plantarum PLA | 71.0 ± 5.3 | 91.1 ± 23.2 | 101.1 ± 22.4 |
| L. plantarum PLA2 | 67.0 ± 20.1 | 73.9 ± 28.1 | 82.3 ± 19.1 |
| L. rhamnosus RHM | 55.5 ± 14.9 | 92.5 ± 18.5 | 95.3 ± 23.3 |
| L. rhamnosus PAR4 | 109.7 ± 23.9 | 106.8 ± 19.6 | 109.0 ± 10.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocchetti, M.T.; Russo, P.; Spano, G.; De Santis, L.; Iarusso, I.; De Simone, N.; Brahimi, S.; Fiocco, D.; Capozzi, V. Exploring the Probiotic Potential of Dairy Industrial-Relevant Lactobacilli. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104989
Rocchetti MT, Russo P, Spano G, De Santis L, Iarusso I, De Simone N, Brahimi S, Fiocco D, Capozzi V. Exploring the Probiotic Potential of Dairy Industrial-Relevant Lactobacilli. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104989
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocchetti, Maria Teresa, Pasquale Russo, Giuseppe Spano, Letizia De Santis, Ilenia Iarusso, Nicola De Simone, Samira Brahimi, Daniela Fiocco, and Vittorio Capozzi. 2022. "Exploring the Probiotic Potential of Dairy Industrial-Relevant Lactobacilli" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104989
APA StyleRocchetti, M. T., Russo, P., Spano, G., De Santis, L., Iarusso, I., De Simone, N., Brahimi, S., Fiocco, D., & Capozzi, V. (2022). Exploring the Probiotic Potential of Dairy Industrial-Relevant Lactobacilli. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104989









