A Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Probability of Brain Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
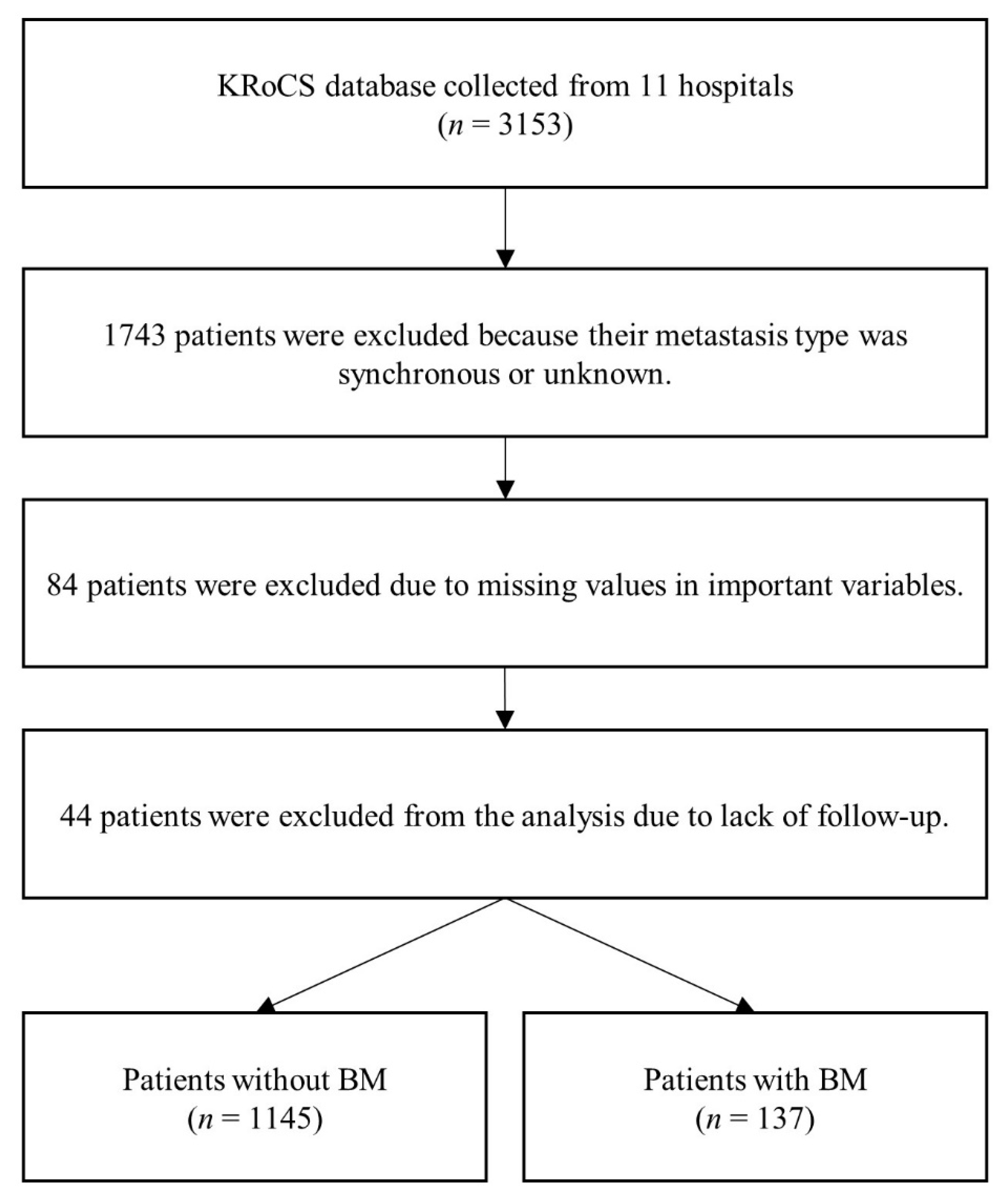
2.1. Study Population and Variable Selection
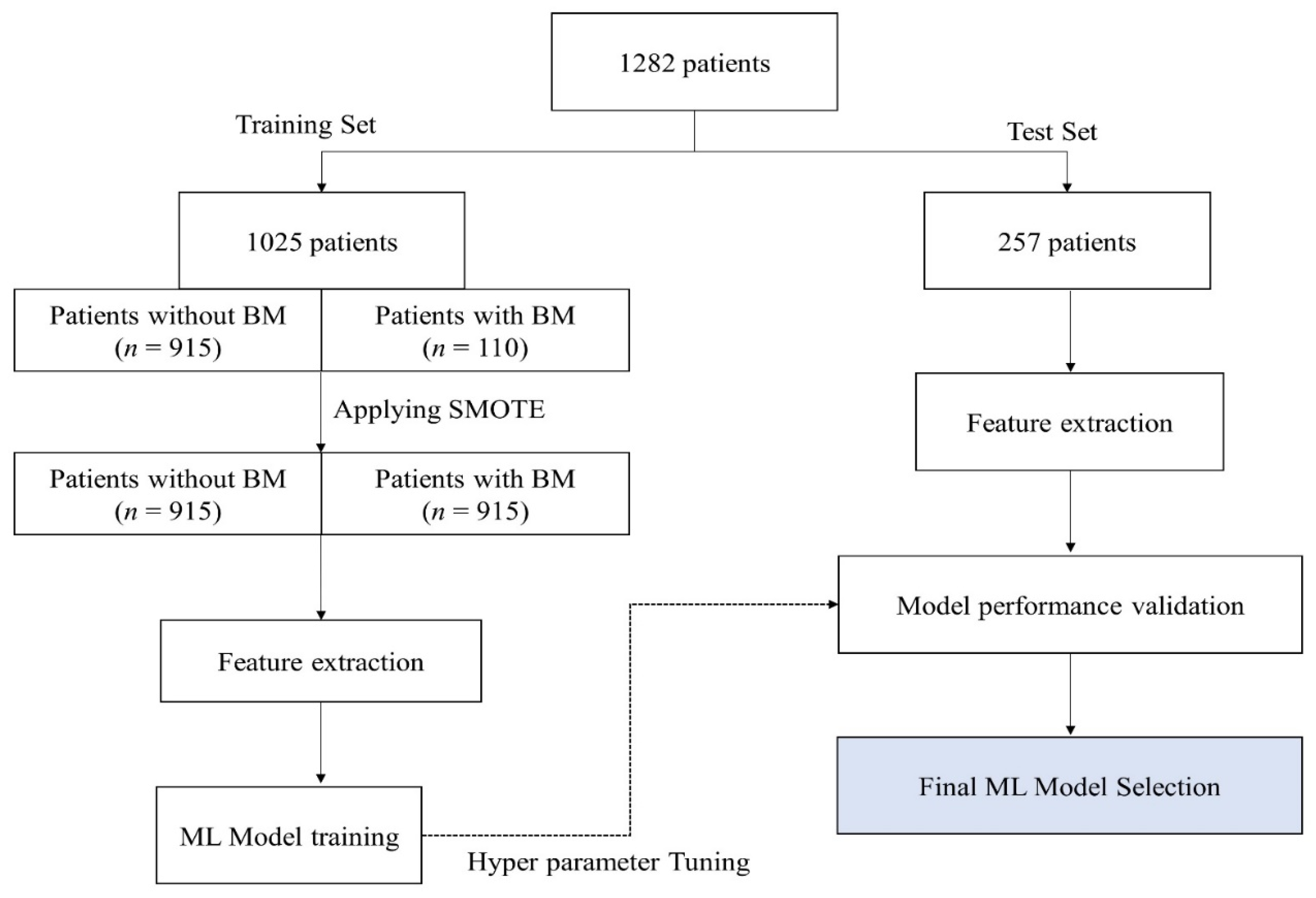
2.2. Data Split and ML Model Development
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Participants
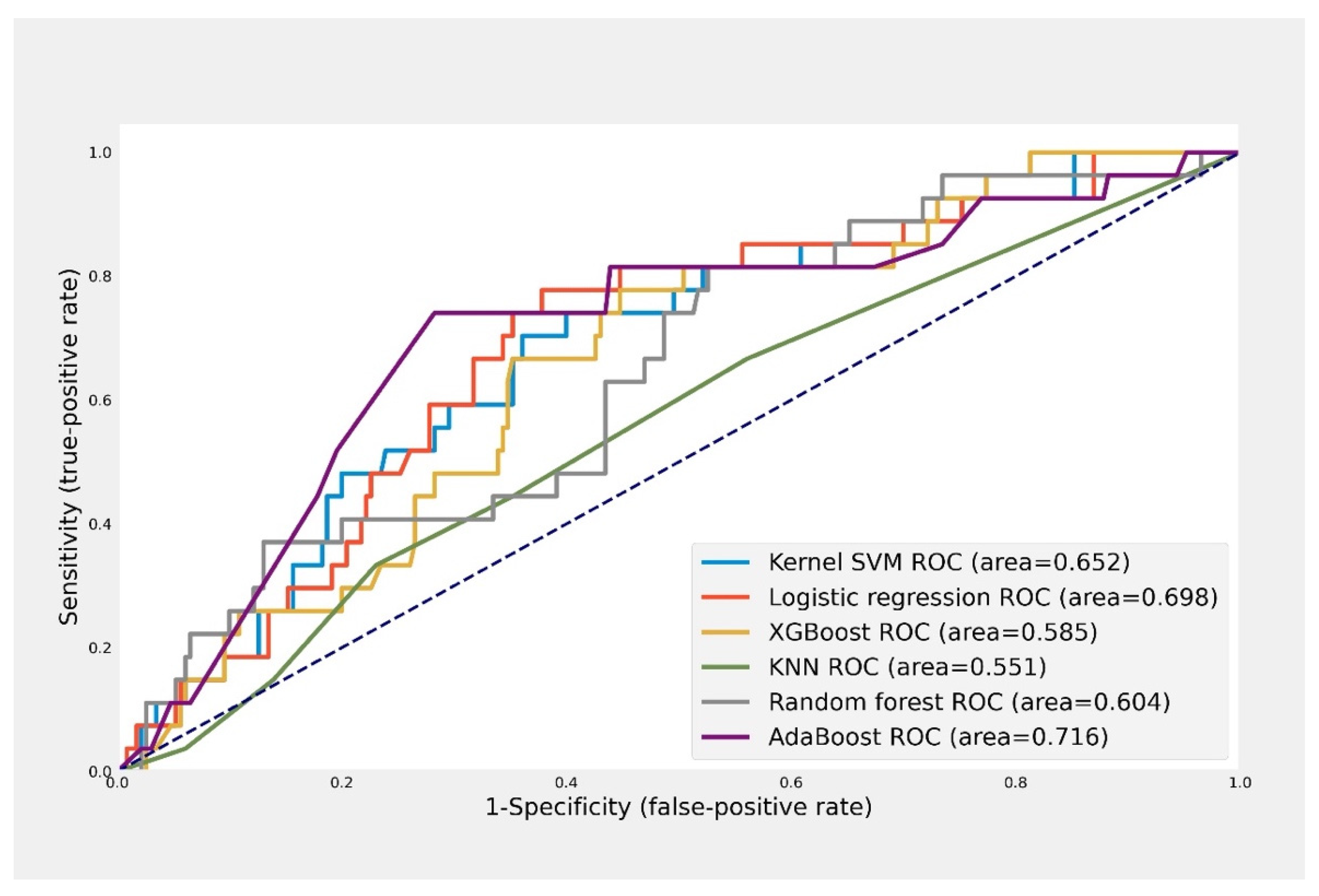
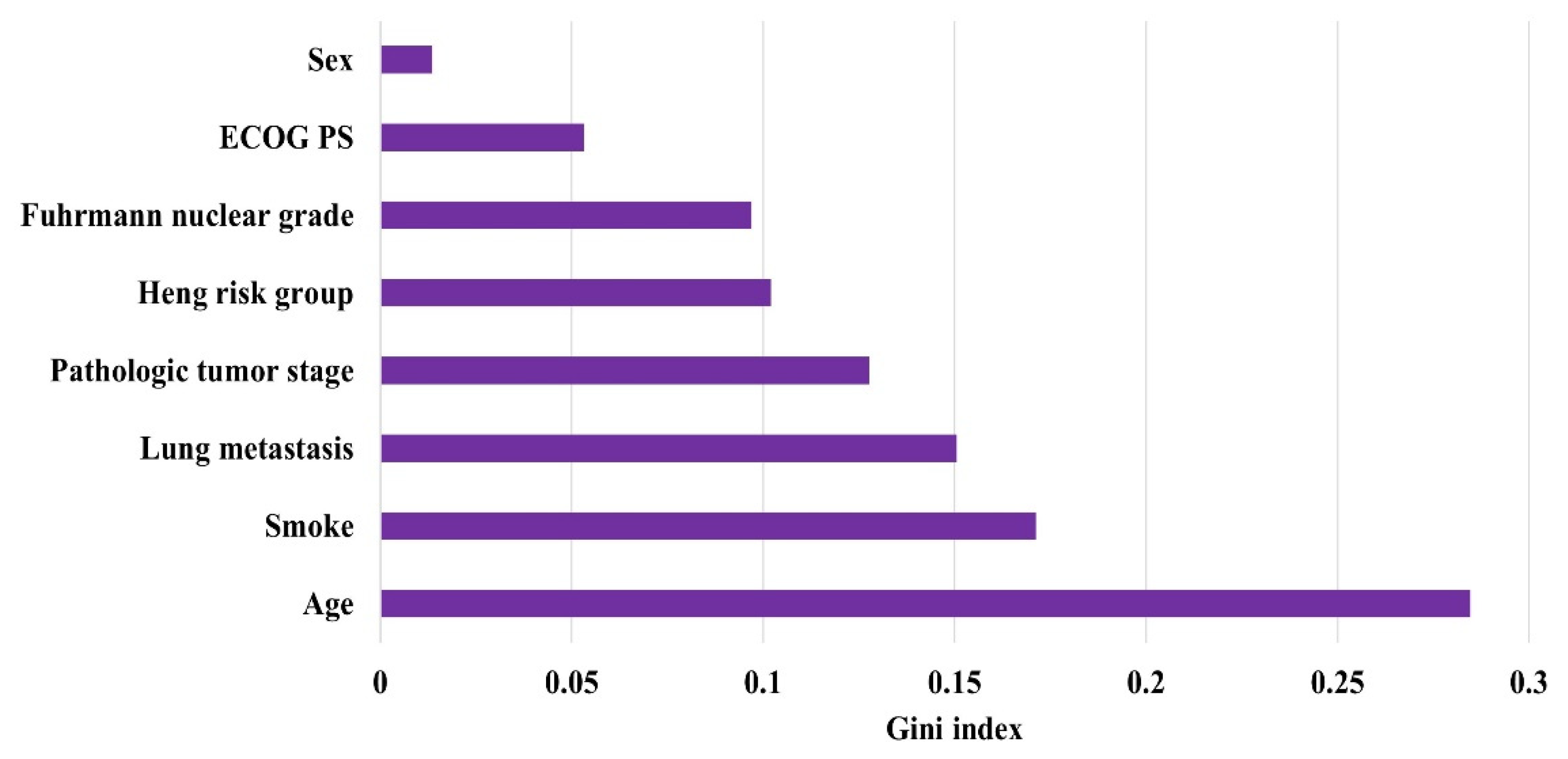
3.2. Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tabouret, E.; Chinot, O.; Metellus, P.; Tallet, A.; Viens, P.; Goncalves, A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: An overview. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Sarmiento, A.; Nguyen, K.A.; Syed, J.S.; Nolte, A.; Ghabili, K.; Cheng, M.; Liu, S.; Chiang, V.; Kluger, H.; Hurwitz, M.; et al. Brain metastasis from renal-cell carcinoma: An institutional study. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 17, e1163–e1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitoh, S.; Hasegawa, H.; Ohtsuki, H.; Obashi, J.; Fujiwara, M.; Sakurai, M. Cerebral neoplasms initially presenting with massive intracerebral hemorrhage. Surg. Neurol. 1984, 22, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrier, S.; Moriceau, G.; Attignon, V.; Haddad, V.; Pissaloux, D.; Guerin, N.; Carrie, C. Activity of Cabozantinib in radioresistant brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, M.E.; Hariharan, S.; Porta, C.; Bracarda, S.; Hawkins, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Oudard, S.; Lee, S.H.; Carteni, G.; Nieto, A.; et al. Sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with brain metastases. Cancer 2011, 117, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Klaassen, Z.; Goldberg, H.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Hamilton, R.J.; Fleshner, N.E. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Patterns and predictors of metastases—A contemporary population-based series. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 661.e7–661.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzly, M.; Abbotoy, D.; Creighton, T.; Diorio, G.; Mehedint, D.; Murekeyisoni, C.; Attwood, K.; Kauffman, E.; Fabiano, A.J.; Schwaab, T. Early identification of asymptomatic brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.P.; et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: Phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, B.; Cowan, N.C.; Hanbury, D.C.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Merseburger, A.S.; Patard, J.J.; Mulders, P.F.A.; Sinescu, I.C.E.A.U.; European Association of Urology Guideline Group. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: The 2010 update. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, S.M.; Diaz, M.; Bishoff, J.T.; Coleman, J.A.; Dahm, P.; Derweesh, I.H.; Herrell, S.D.; Hilton, S.; Jonasch, E.; Lin, D.W.; et al. Follow-up for clinically localized renal neoplasms: AUA guideline [AUA guideline]. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Haque, M.R.; Iqbal, H.; Hasan, M.M.; Hasan, M.; Kabir, M.N. Breast cancer prediction: A comparative study using machine learning techniques. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, H.; Mao, S.; Khushi, M. Predicting high-risk prostate cancer using machine learning methods. Data 2019, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, Z.B.; Chen, S.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, Y.P.; Lin, F.; Xue, X.Y.; Zheng, Q.S.; Xu, N.; Wei, Y. Risk factors for brain metastases in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6836234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogl, U.M.; Bojic, M.; Lamm, W.; Frischer, J.M.; Pichelmayer, O.; Kramer, G.; Haitel, A.; Kitz, K.; Harmankaya, K.; Zielinski, C.C.; et al. Extracerebral metastases determine the outcome of patients with brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Chung, J.; Kwak, C.; Jeong, C.W.; Seo, S., II; Kang, M.; Hong, S.H.; Song, C.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, E.C.; et al. Targeted therapy response in early versus late recurrence of renal cell carcinoma after surgical treatment: A propensity score-matched study using the Korean Renal Cancer Study Group Database. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, T.J.; Song, C.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Seo, S.; Kang, M.; Chung, J.; Hong, S.H.; Hwang, E.C.; Park, J.Y.; et al. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas: Clinical features and treatment outcome. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 123, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruste, V.; Sunyach, M.P.; Tanguy, R.; Jouanneau, E.; Schiffler, C.; Carbonnaux, M.; Moriceau, G.; Neidhardt, E.M.; Boyle, H.; Robin, S.; et al. Synchronous brain metastases as a poor prognosis factor in clear cell renal carcinoma: A strong argument for systematic brain screening. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 153, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyshnav, M.T.; Sowmya, V.; Gopalakrishnan, E.A.; Sajith Variyar, V.V.; Menon, V.K.; Soman, K.P. Deep learning based approach for multiple myeloma detection. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference Computability Communal Network Technologia ICCCNT, Kharagpur, India, 1–3 July 2020; Volume 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Cohn, A.G.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, M. Machine learning-based classification of rock discontinuity trace: SMOTE oversampling integrated with GBT ensemble learning. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Khushi, M. Smote-Enc: A novel smote-based method to generate synthetic data for nominal and continuous features. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, L.V. An imprecise extension of SVM-based machine learning models. Neurocomputing 2019, 331, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymarczyk, T.; Kozłowski, E.; Kłosowski, G.; Niderla, K. Logistic regression for machine learning in process tomography. Sensors 2019, 19, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoo, F.; Meenakshi, S.; Singh, S. Comparison and analysis of logistic regression, naïve Bayes and KNN machine learning algorithms for credit card fraud detection. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 13, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.; Baron, D.; Shahaf, S. Probabilistic random forest: A machine learning algorithm for noisy data sets. Astron. J. 2018, 157, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Jin, S.; Savi, P.; Gao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. GNSS-R soil moisture retrieval based on a XGboost machine learning aided method: Performance and validation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Shen, B.; Wang, X.; Yoo, S.J.; Strong Machine Learning, A. Classifier and decision stumps based hybrid AdaBoost classification algorithm for cognitive radios. Sensors 2019, 19, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, A.P. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Cai, K.; Xu, L.; Chen, A. Grid search parametric optimization for FT-NIR quantitative analysis of solid soluble content in strawberry samples. Vib. Spectrosc. 2018, 94, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinç, E. An empowered AdaBoost algorithm implementation: A COVID-19 dataset study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 165, 107912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabalas, A.; Gowen, E.; Poliakoff, E.; Casson, A.J. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, S.; Baratloo, A.; Elfil, M.; Negida, A. Part 5: Receiver operating curve and area under the curve. Emergency 2016, 4, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Without BM Group (n = 1145) | With BM Group (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 56.8 ± 11.2 | 53.0 ± 10.6 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.005 | ||
| Male | 902 (78.8%) | 93 (67.9%) | |
| Female | 243 (21.2%) | 44 (32.1%) | |
| Smoking | 0.392 | ||
| Non-smoker | 785 (68.6%) | 97 (70.8%) | |
| Ex-smoker | 252 (22.0%) | 24 (17.5%) | |
| Current-smoker | 108 (9.4%) | 16 (11.7%) | |
| ECOG PS | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 910 (79.5%) | 84 (61.3%) | |
| 1 | 198 (17.3%) | 44 (32.1%) | |
| >1 | 37 (3.2%) | 9 (6.6%) | |
| Pathological tumor stage | 0.063 | ||
| 1–2 | 594 (51.9%) | 59 (43.1%) | |
| 3–4 | 551 (48.1%) | 78 (56.9%) | |
| Fuhrmann nuclear grade | 0.156 | ||
| 1 | 21 (1.8%) | 4 (2.9%) | |
| 2 | 277 (24.2%) | 30 (21.9%) | |
| 3 | 492 (43.0%) | 49 (35.8%) | |
| 4 | 355 (31.0%) | 54 (39.4%) | |
| Heng risk group | 0.042 | ||
| Favorable | 526 (46.2%) | 50 (36.5%) | |
| Intermediate | 557 (48.6%) | 75 (54.7%) | |
| Poor | 59 (5.2%) | 12 (8.8%) | |
| Lung metastasis | 0.001 | ||
| No | 370 (32.3%) | 24 (17.5%) | |
| Yes | 775 (67.7%) | 113 (82.5%) |
| Model (Hyperparameters) | AUROC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kernel SVM (kernel) | ||||
| (linear) 1 | 0.652 | 0.704 | 0.600 | 0.611 |
| (rbf) | 0.557 | 0.370 | 0.743 | 0.704 |
| Logistic regression (penalty, C) | ||||
| (L1, 0.1) 1 | 0.698 | 0.778 | 0.617 | 0.624 |
| (L1, 1) | 0.663 | 0.704 | 0.622 | 0.630 |
| (L1, 100) | 0.658 | 0.704 | 0.613 | 0.623 |
| (L2, 0.1) | 0.654 | 0.704 | 0.604 | 0.615 |
| (L2, 0.5) | 0.648 | 0.667 | 0.630 | 0.634 |
| (L2, 0.01) | 0.637 | 0.704 | 0.570 | 0.584 |
| KNN (neighbors) | ||||
| (3) | 0.527 | 0.260 | 0.800 | 0.739 |
| (5) 1 | 0.551 | 0.333 | 0.770 | 0.724 |
| (10) | 0.548 | 0.370 | 0.726 | 0.689 |
| Random forest (number of trees) | ||||
| (10) | 0.538 | 0.259 | 0.817 | 0.759 |
| (50) 1 | 0.604 | 0.407 | 0.800 | 0.759 |
| (100) | 0.585 | 0.370 | 0.800 | 0.755 |
| XGBoost (number of trees) | ||||
| (10) | 0.519 | 0.519 | 0.630 | 0.619 |
| (50) 1 | 0.585 | 0.444 | 0.726 | 0.696 |
| (100) | 0.512 | 0.259 | 0.765 | 0.712 |
| AdaBoost (number of trees) | ||||
| (10) | 0.707 | 0.741 | 0.673 | 0.681 |
| (50) 1 | 0.716 | 0.741 | 0.691 | 0.696 |
| (100) | 0.684 | 0.704 | 0.665 | 0.669 |
| Model | 3-Fold Mean (Standard Deviation) | 5-Fold Mean (Standard Deviation) |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel SVM | 0.533 (0.036) | 0.504 (0.044) |
| Logistic regression | 0.640 (0.057) | 0.654 (0.076) |
| KNN | 0.525 (0.044) | 0.546 (0.024) |
| Random forest | 0.597 (0.055) | 0.599 (0.060) |
| XGBoost | 0.636 (0.045) | 0.647 (0.077) |
| AdaBoost | 0.678 (0.065) | 0.696 (0.087) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.M.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Song, C.; Kang, M.; Seo, S.I.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, H.; Chung, J.; Hwang, E.C.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Probability of Brain Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126174
Kim HM, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Song C, Kang M, Seo SI, Kim JK, Lee H, Chung J, Hwang EC, et al. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Probability of Brain Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126174
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyung Min, Chang Wook Jeong, Cheol Kwak, Cheryn Song, Minyong Kang, Seong Il Seo, Jung Kwon Kim, Hakmin Lee, Jinsoo Chung, Eu Chang Hwang, and et al. 2022. "A Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Probability of Brain Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126174
APA StyleKim, H. M., Jeong, C. W., Kwak, C., Song, C., Kang, M., Seo, S. I., Kim, J. K., Lee, H., Chung, J., Hwang, E. C., Park, J. Y., Choi, I. Y., & Hong, S.-H. (2022). A Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Probability of Brain Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126174






