Bio_Fabricated Levan Polymer from Bacillus subtilis MZ292983.1 with Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Burn Healing Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Bacterial Strain
2.2. Qualitative Screening of Levan Polymer
2.3. Molecular Identification of Bacterial Strain
2.3.1. DNA Extraction and PCR
2.3.2. DNA Sequence Analysis
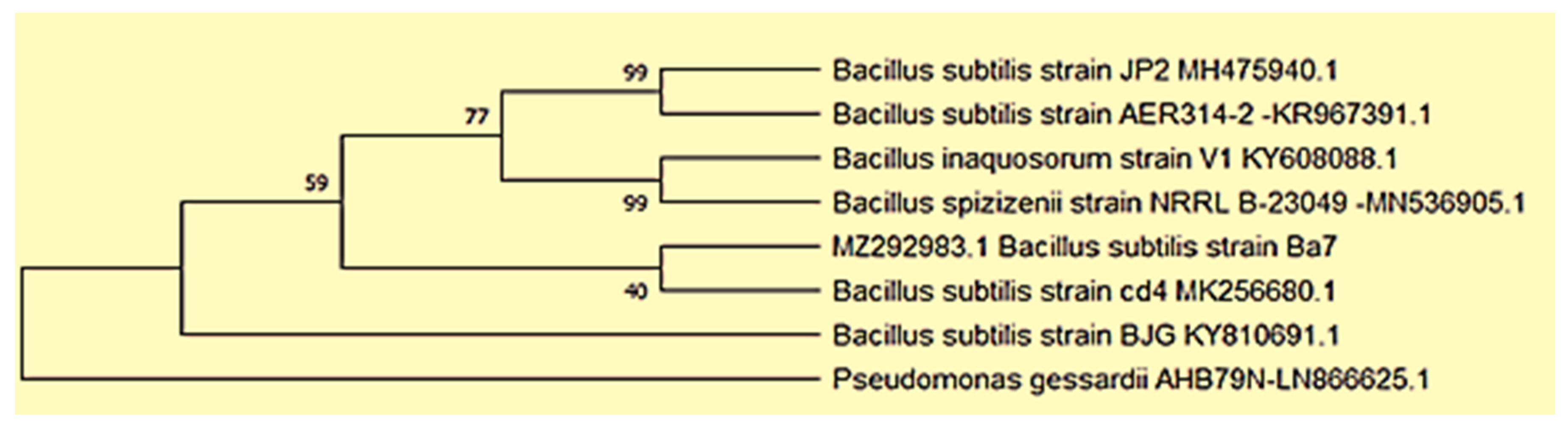
2.3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Production and Extraction of Levan Polymer
2.5. Determination of Total Soluble Carbohydrates
2.6. Detection of Reducing Sugar by Dinitrosalicylic Acid Method (DNS)
2.7. Partial Purification of Levan Polymer
2.8. Characterization of Levan Polymer
2.8.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.8.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.9. Antibacterial Activity of Levan
2.9.1. Microorganisms and Culture Conditions
2.9.2. Well Diffusion Assay
2.9.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.10. Antibiofilm Mechanism of Levan against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain MW846272 Using Crystal Violet Quantitative Assay
2.11. Burn Healing Properties of Levan
2.11.1. Animals
2.11.2. Induction of Burn Wounds
2.11.3. Histopathological Evaluation of Burn Healing Ability of Levan
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Bacterial Strain
3.2. Total Soluble Carbohydrates and Reducing Sugars
3.3. Characterization of Levan Polymer
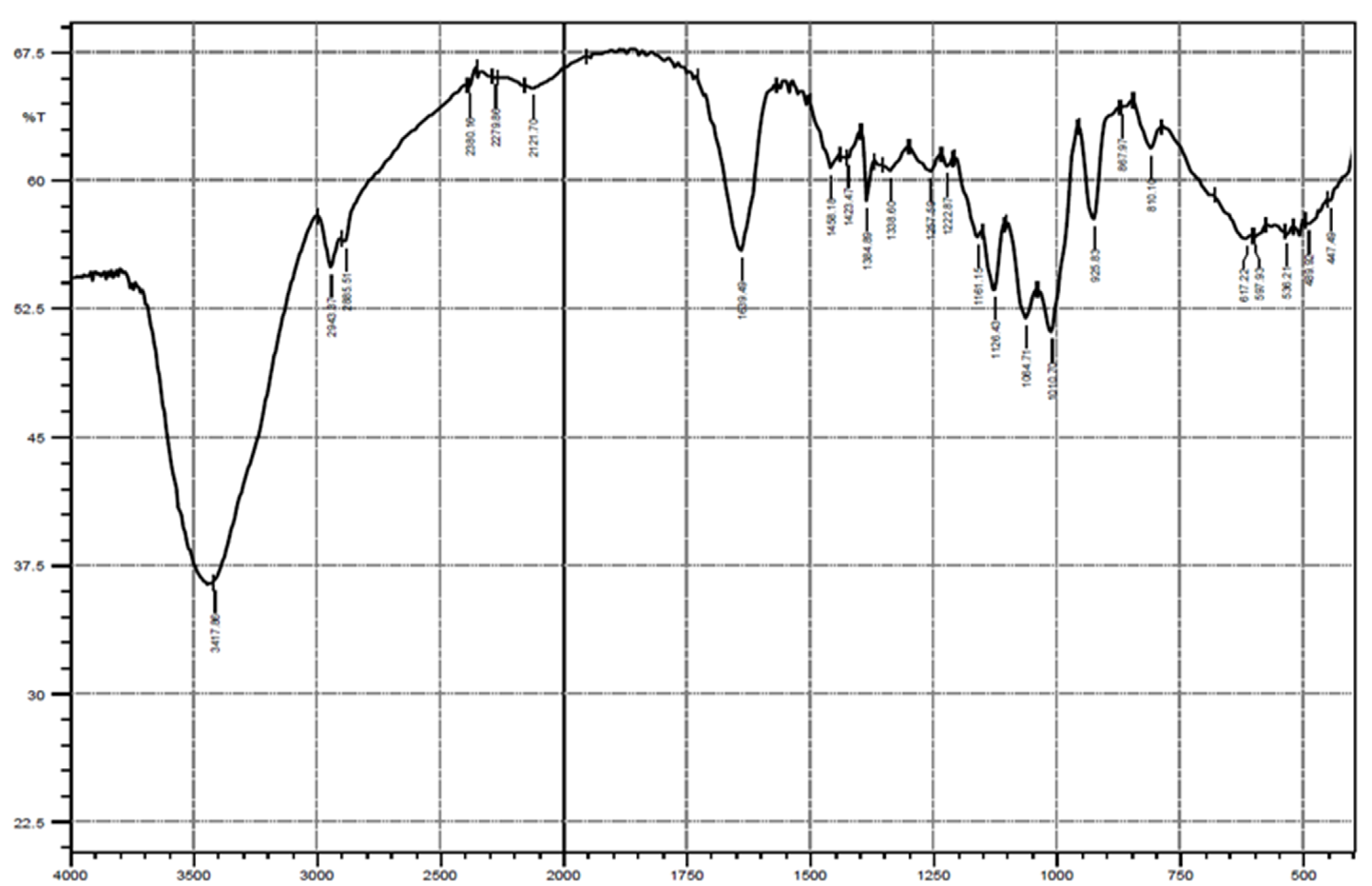
3.3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy
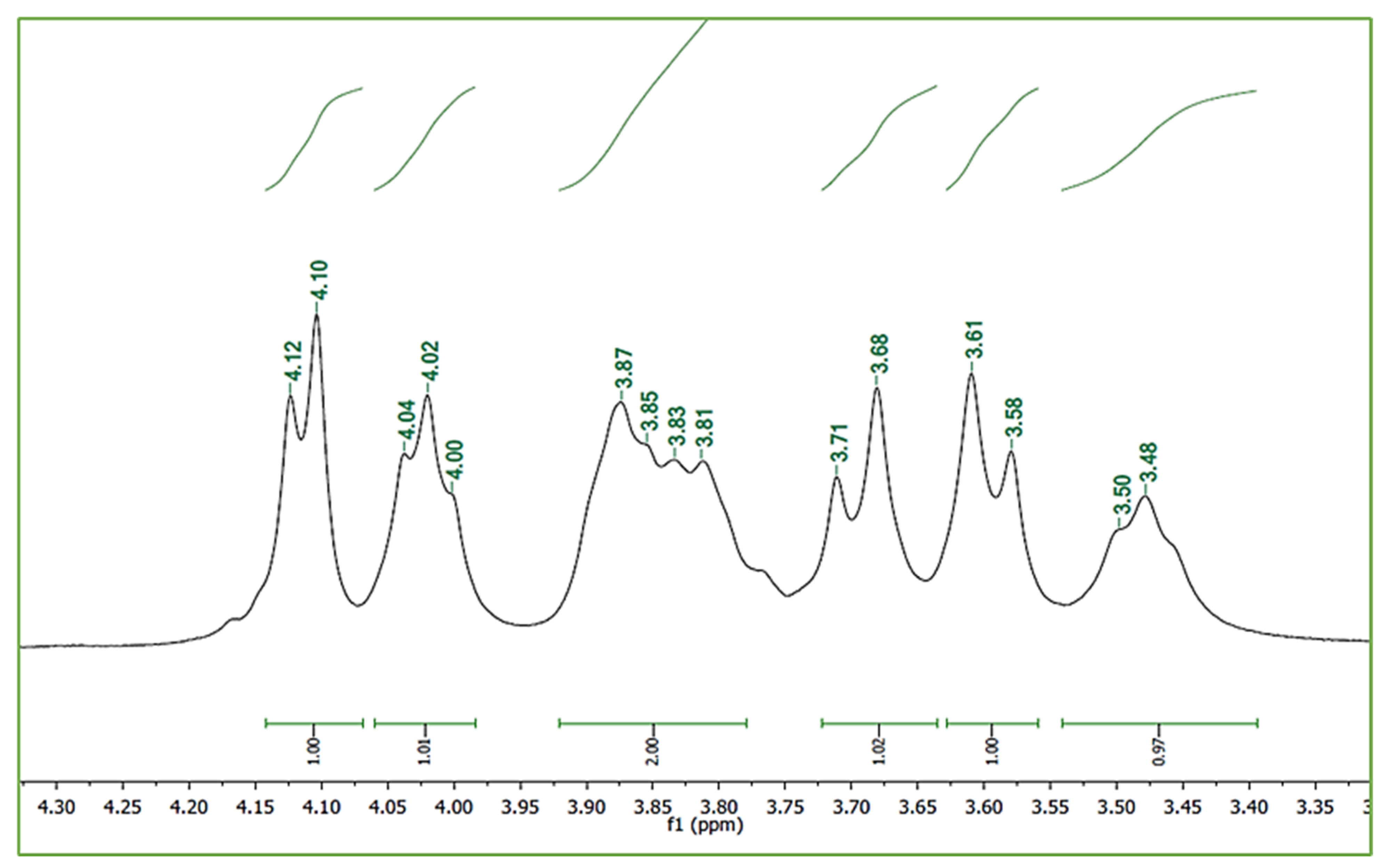
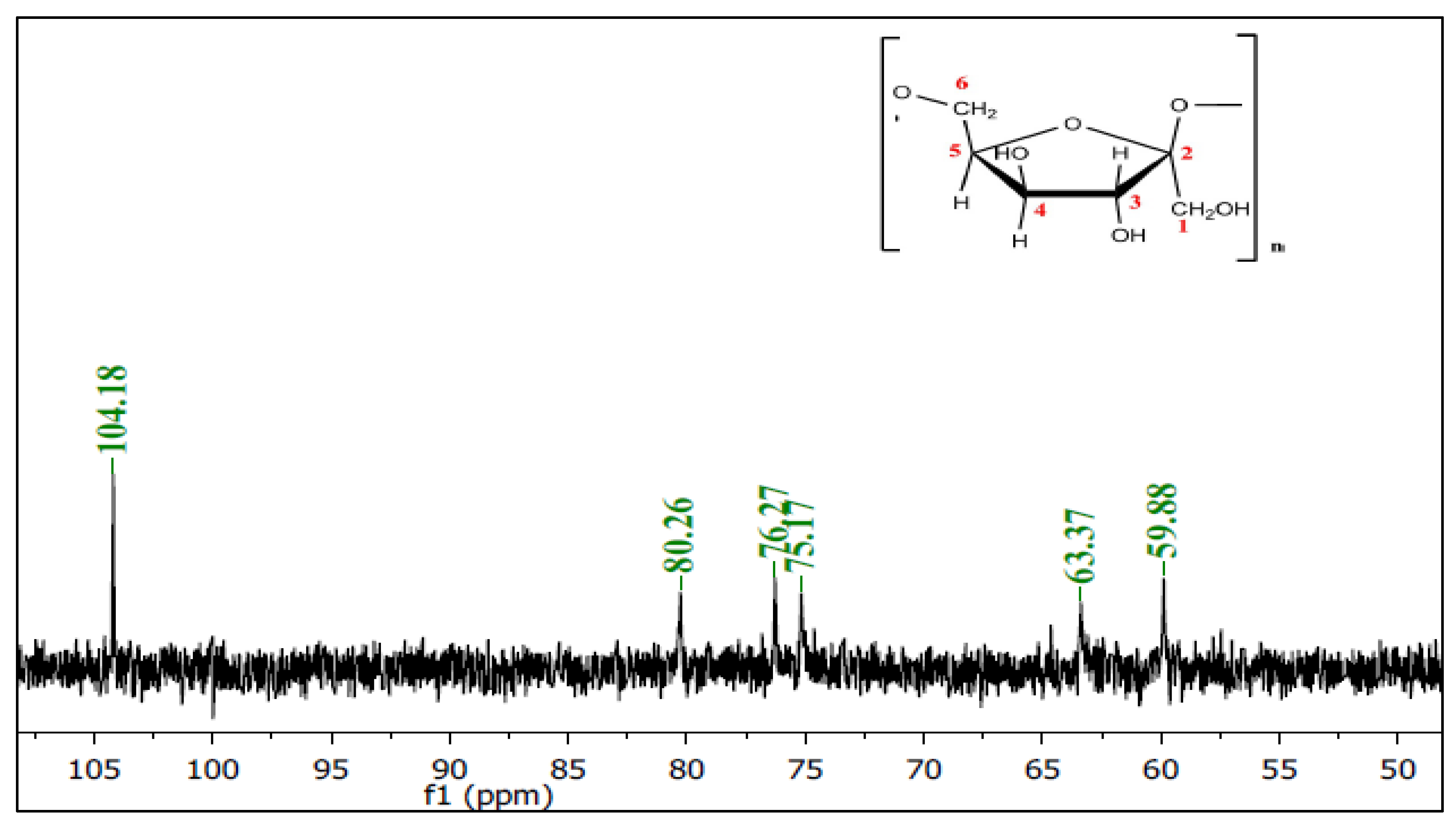
3.3.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
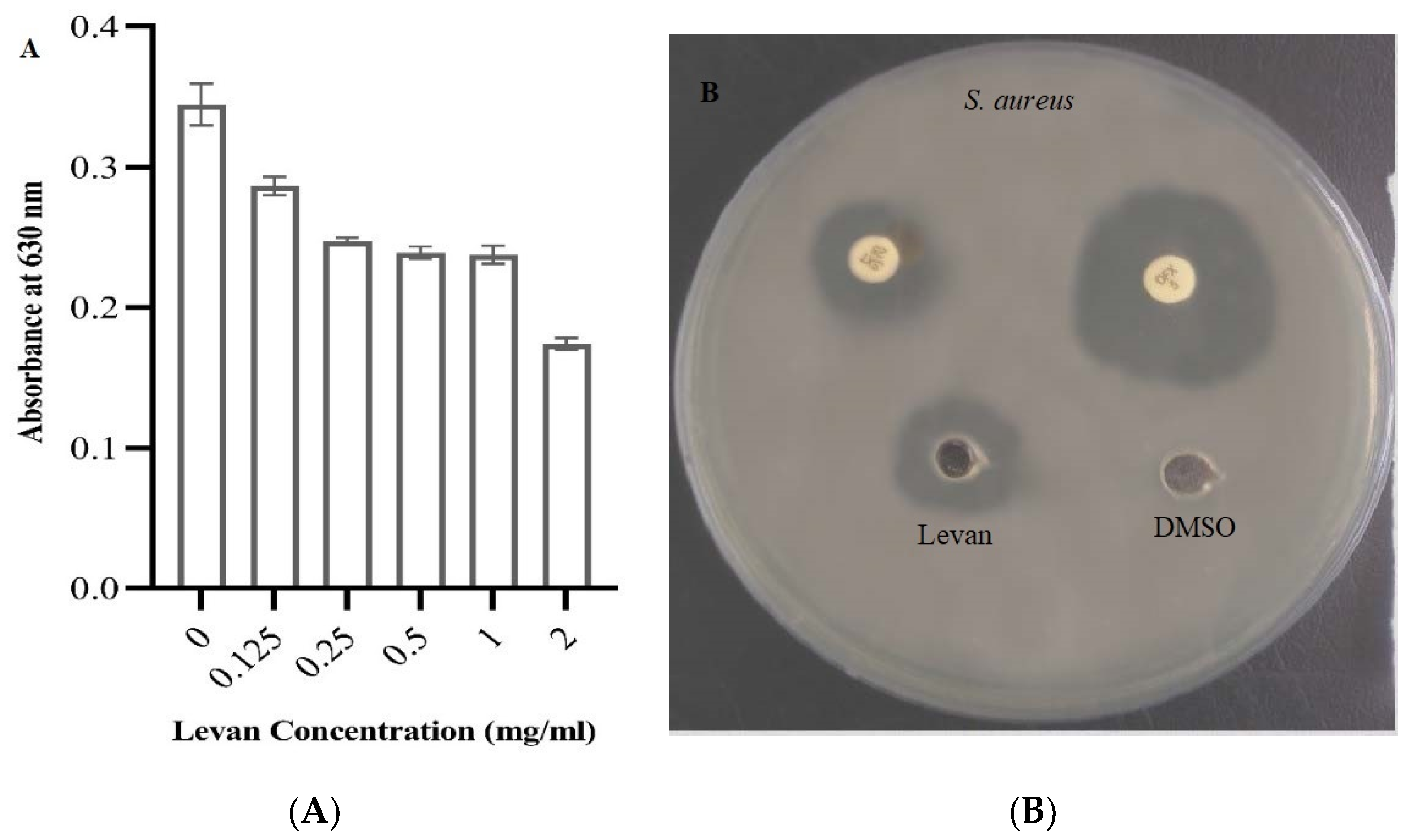
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of Levan
3.5. Antibiofilm Activity of Levan
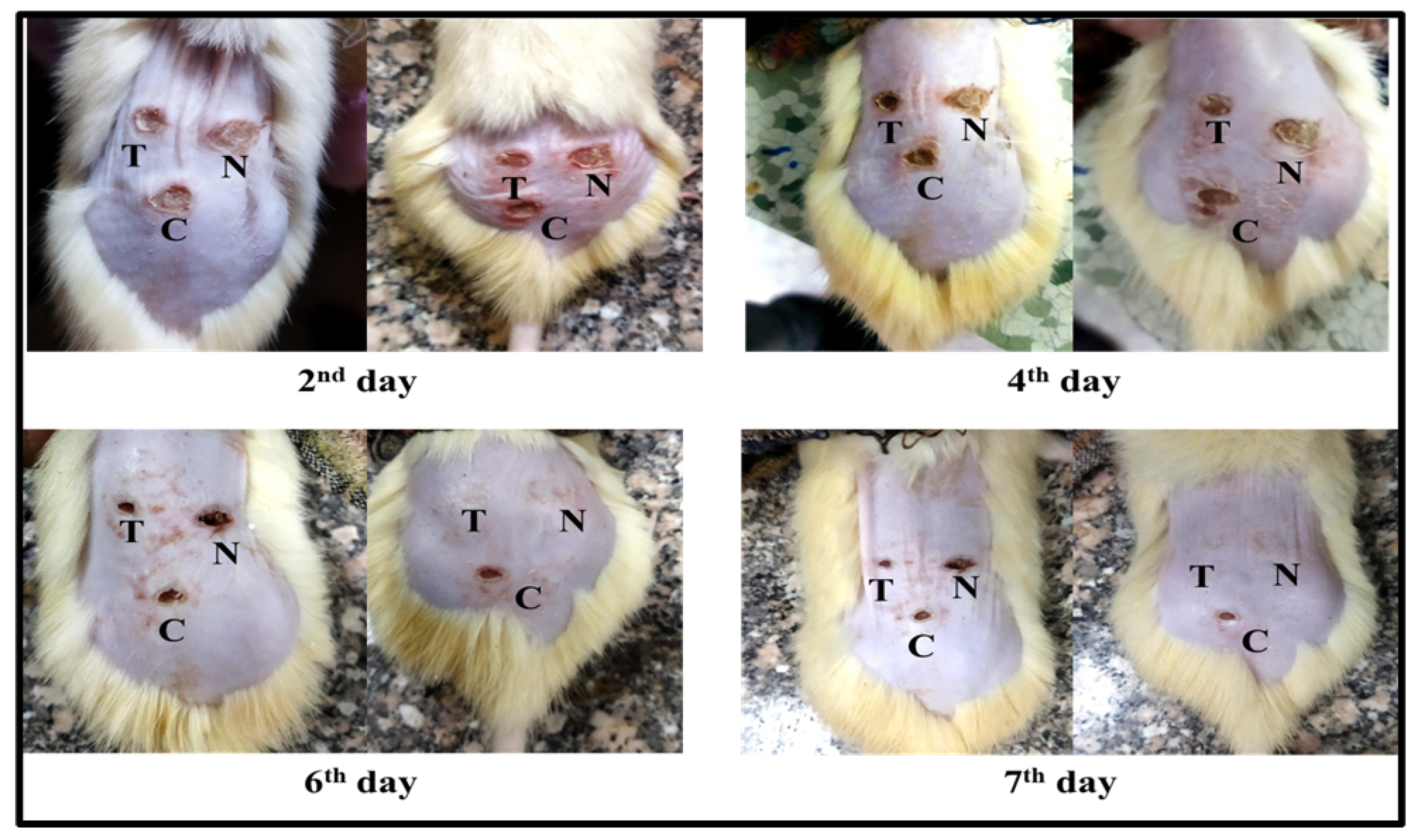
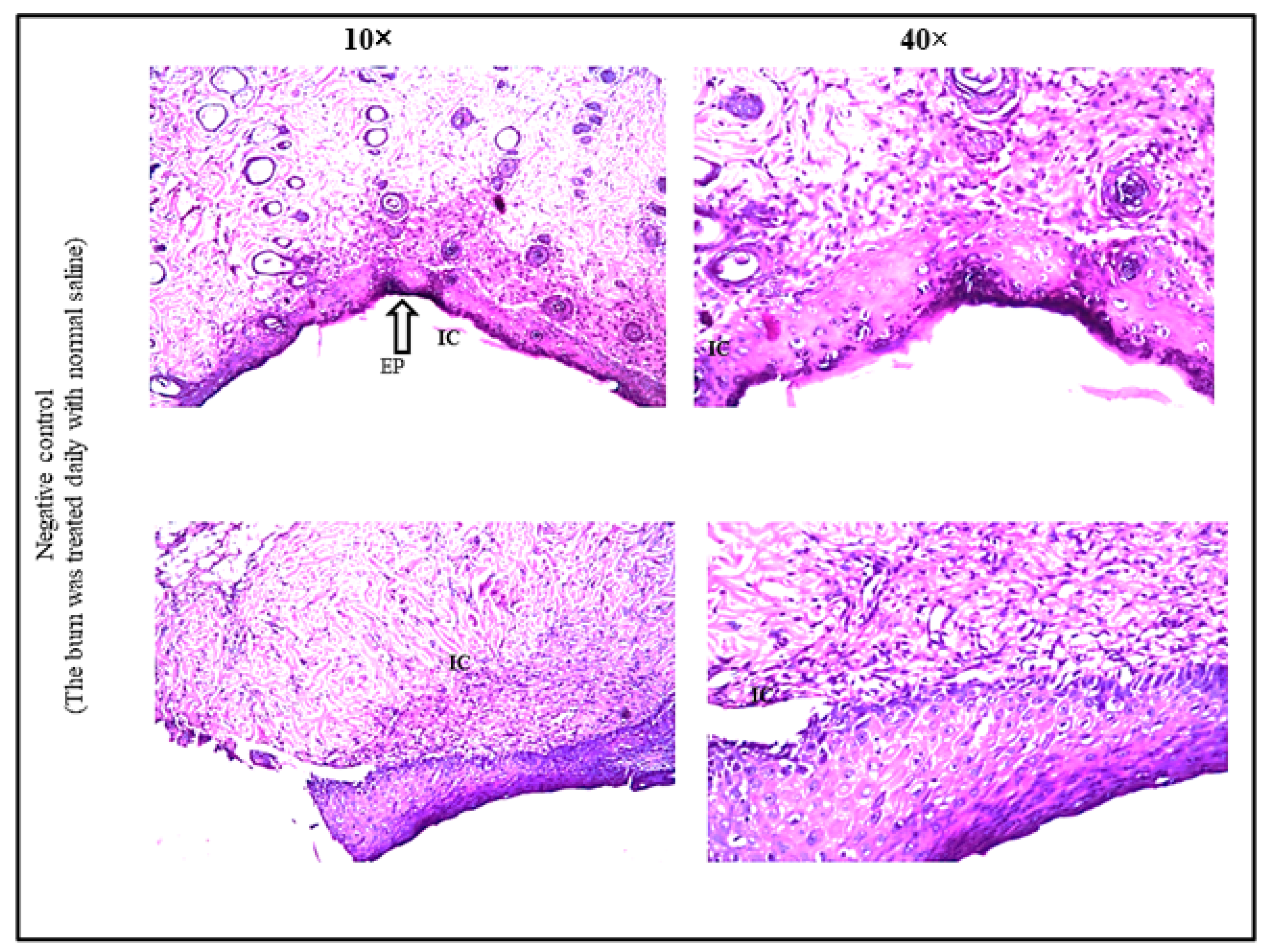
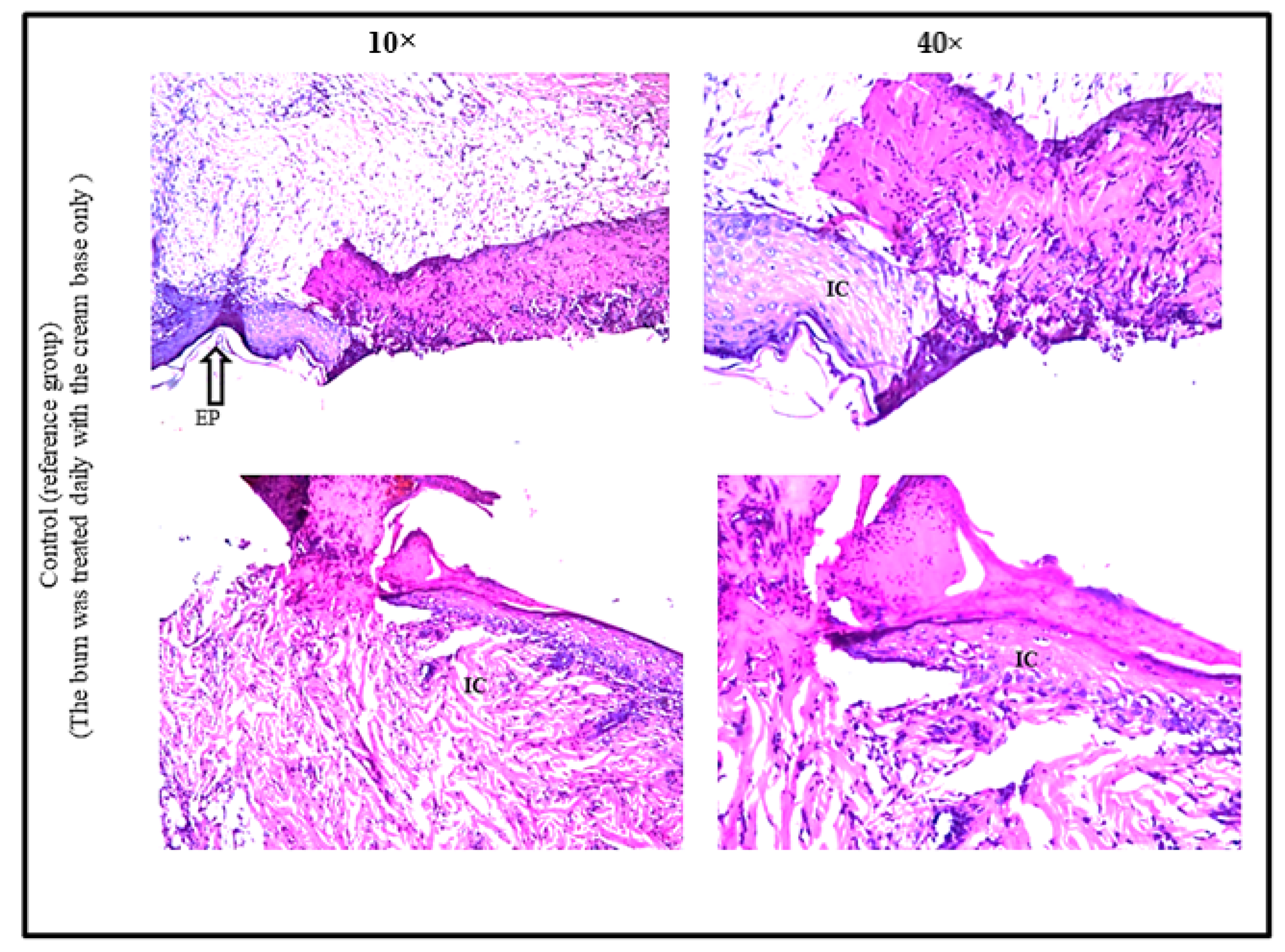
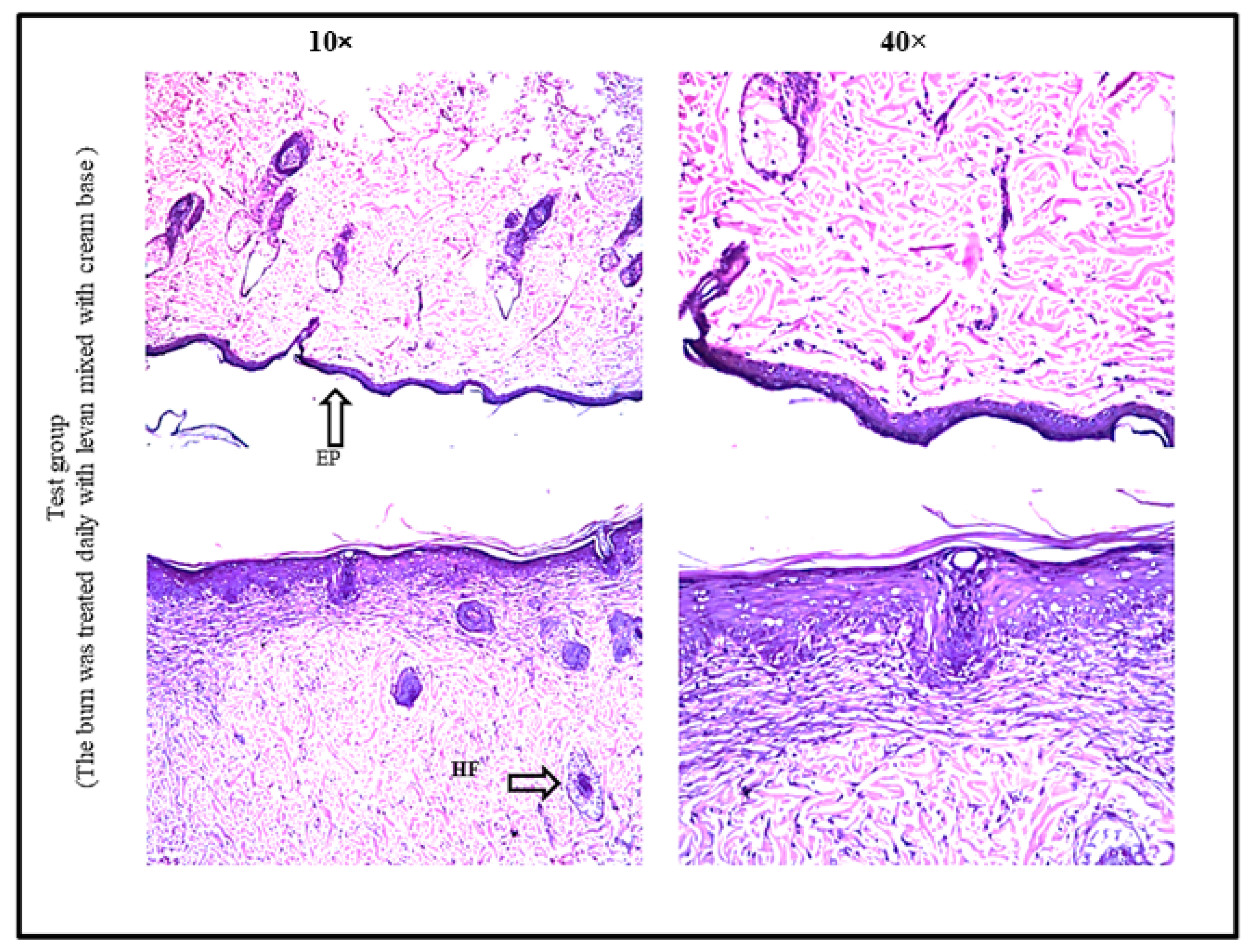
3.6. Burn Healing Properties of Levan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas, F.; Torres, C.A.V.; Araújo, D.; Farinha, I. Functional Properties and Applications of Microbial Polysaccharides. In Biopolymers for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Fata Moradali, M., Eds.; WILEY-VCH GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2021; pp. 19–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Corsaro, M.M. Exopolysaccharides FrCasillo, Angelaom Marine and Marine Extremophilic Bacteria: Structures, Properties, Ecological Roles and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouallegue, A.; Casillo, A.; Chaari, F.; La Gatta, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Corsaro, M.M.; Bachoual, R.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S. Levan from a New Isolated Bacillus subtilis AF17: Purification, Structural Analysis and Antioxidant Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.M.; Zahed, F.; Crispim, A.C.; de Souza Bento, E.; de Freitas Oliveira França, R.; Pinheiro, I.O.; Pardo, L.A.; Carvalho, B.M. Production of Levan from Bacillus subtilis Var. Natto and Apoptotic Effect on SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ağçeli, G.K.; Cihangir, N. Nano-Sized Biopolymer Levan: Its Antimicrobial, Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Cancer Effects. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 494, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, F.; Momeni-moghaddam, M. Regeneration and Repair of Skin Wounds: Various Strategies for Treatment. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2019, 18, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevgi, M.; Toklu, A.; Vecchio, D.; Hamblin, M.R. Topical Antimicrobials for Burn Infections—An Update. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiaso-daniel, J.; Gallagher, J.J.; Norbury, W.B.; Celeste, C.; Herndon, D.N.; Culnan, D.M. 11—Treatment of Infection in Burn Patients, 5th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, C.M.N.; Oliveira, R.C.; Freire, R.K.B.; Piazentin, A.C.M.; Pereira, W.A.; Gudiña, E.J.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Converti, A.; Santos, J.H.P.M.; Nunes, C.; et al. Characterization of Levan Produced by a Paenibacillus sp. Isolated from Brazilian Crude Oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korany, S.M.; El-Hendawy, H.H.; Sonbol, H.; Hamada, M.A. Partial Characterization of Levan Polymer from Pseudomonas fluorescens with Significant Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6679–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, D.Q.; Wahyuningrum, D.; Hertadi, R. Screening and Characterization of Levan Secreted by Halophilic Bacterium of Halomonas and Chromohalobacter Genuses Originated from Bledug Kuwu Mud Crater. Procedia Chem. 2015, 16, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Yagi, Y. Production of Levan by a Zymomonas sp. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1990, 70, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.A.; Krieg, N.R. Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. In American Society for Microbiology; ASM Press: Herndon, VA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-taleb, K.A.; Abdel-Monem, M.O.; Yassin, M.H.; Draz, A.A. Production, Purification and Characterization of Levan Polymer from Bacillus lentus V8 Strain. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 2015, 5, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing by a Standardized Single Disk Method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgouras, D.; Maragkoudakis, P.; Petraki, K.; Eriotou, E.; Michopoulos, S.; Kalantzopoulos, G.; Tsakalidou, E. In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Lactobacillus casei Strain Shirota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Han, F.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; No, H.K.; Ge, B. Evaluation of Diffusion and Dilution Methods to Determine the Antimicrobial Activity of Water-Soluble Chitosan Derivatives. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alqahtani, M.A.; Al Othman, M.R.; Mohammed, A.E. Bio Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Abilities Using Lichens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, L. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Peppermint Essential Oil against Staphylococcus aureus. LWT 2019, 101, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. The Specific Effect of Gallic Acid on Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation by Regulating PgaABCD Genes Expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares Pereira, D.D.S.; Lima-Ribeiro, M.H.M.; de Pontes-Filho, N.T.; Carneiro-Leão, A.M.D.A.; Correia, M.T.D.S. Development of Animal Model for Studying Deep Second-Degree Thermal Burns. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 460841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banchroft, J.D.; Stevens, A.; Turner, D.R. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 4th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.W.; Clarke, M.A. Production and Characterization of Microbial Levan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, T.I.M.; Shalaby, A.S.G.; Awdan, S.A.E.; El-Bassyouni, G.T.; Salama, B.M.; Helmy, W.A.; Esawy, M.A. Role of Levan Extracted from Bacterial Honey Isolates in Curing Peptic Ulcer: In Vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegari, A.A.; Hashemzaei, M.; Majdani, R.; Alihemmati, A.-R. Effects of Topical Treatment of Second-Degree Burn Wounds with Lactobacillus acidophilus on the Wound Healing Process in Male Rats. Pharm. Biomed. Res. 2017, 3, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopi, S.; Amalraj, A. Effective Drug Delivery System of Biopolymers Based On Nanomaterials and Hydrogels—A Review. Drug Des. Open Access 2016, 5, 2169-0138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salman, J.A.S.; Ajah, H.A.; Khudair, A.Y. Analysis and Characterization of Purified Levan from Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. cremoris and its Effects on Candida albicans Virulence Factors. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 12, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Nabot, M.; Guérin, M.; Sivakumar, D.; Remize, F.; Garcia, C. Variability of Bacterial Homopolysaccharide Production and Properties during Food Processing. Biology 2022, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathammal, R.; Sudha, N.; Guru Prasad, L.; Ganga, N.; Krishnakumar, V. Spectroscopic (FTIR, FT-Raman, UV and NMR) Investigation and NLO, HOMO-LUMO, NBO Analysis of 2-Benzylpyridine Based on Quantum Chemical Calculations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, R.; Reddy, C.H.S.S.S.; Siddartha, G.; Ramaiah, M.J.; Uppuluri, K.B. Review on Production, Characterization and Applications of Microbial Levan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 120, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.; Morgenlie, S. Classification of Grass Fructans by 13C NMR Spectroscopy. Acta Chem. Scand. 1990, 44, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hijum, S.A.F.T.; Bonting, K.; Van Der Maarel, M.J.E.C.; Dijkhuizen, L. Purification of a Novel Fructosyltransferase from Lactobacillus reuteri Strain 121 and Characterization of the Levan Produced. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 205, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Han, J.; Yan, M.; Wu, Z. Characterization of the Levan Produced by Paenibacillus bovis sp. Nov BD3526 and Its Immunological Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylan, O.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Dertli, E. Partial Characterization of a Levan Type Exopolysaccharide (EPS) Produced by Leuconostoc Mesenteroides Showing Immunostimulatory and Antioxidant Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavasis, I. Production of Microbial Polysaccharides for Use in Food. In Microbial Production of Food Ingredients, Enzymes and Nutraceuticals; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 413–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Low-Level Laser in Burn Wound Models in Rats. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2017, 6, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khedir, S.B.; Bardaa, S.; Chabchoub, N.; Moalla, D.; Sahnoun, Z.; Rebai, T. The Healing Effect of Pistacia Lentiscus Fruit Oil on Laser Burn. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Cen, Y. Burn Wound Healing Potential of a Polysaccharide from Sanguisorba officinalis L. in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, I.; Slima, S.B.; Ktari, N.; Bardaa, S.; Elkaroui, K.; Abdeslam, A.; Ben Salah, R. Purification, Composition and Biological Activities of a Novel Heteropolysaccharide Extracted from Linum usitatissimum L. Seeds on Laser Burn Wound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktari, N.; Trabelsi, I.; Bardaa, S.; Triki, M.; Bkhairia, I.; Ben Slama-Ben Salem, R.; Nasri, M.; Ben Salah, R. Antioxidant and Hemolytic Activities, and Effects in Rat Cutaneous Wound Healing of a Novel Polysaccharide from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) Seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Matejczyk, M.; Rosochacki, S. Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs), the Main Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Enzymes in Collagen Degradation, as a Target for Anticancer Drugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öner, E.T.; Hernández, L.; Combie, J. Review of Levan Polysaccharide: From a Century of Past Experiences to Future Prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturzoiu, C.; Petrescu, M.; Galateanu, B.; Anton, M.; Nica, C.; Simionca, G.I.; Dinischiotu, A.; Stoian, G. Zymomonas Mobilis Levan Is Involved in Metalloproteinases Activation in Healing of Wounded and Burned Tissues. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 44, 453–458. [Google Scholar]
- Zainulabdeen, S.M. Purification and Characterization of Levan from Lactobacillus Gasseri and Its Effect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. NVEO Nat. Volatiles Essent. Oils J. NVEO 2021, 8, 5788–5808. [Google Scholar]

| Levan of Bacterial Strain | Chemical Shift (ppm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | |
| Standard Levan of Z. mobilis [26] | 60.76 | 104.64 | 77.68 | 75.75 | 80.78 | 63.95 |
| Standard Levan of Bacillus sp. [27]. | 59.85 | 104.19 | 76.27 | 75.73 | 80.28 | 63.33 |
| Standard Levan of Pseudomonas fluorescens [10] | 59.87 | 104.17 | 76.26 | 75.17 | 80.26 | 63.36 |
| Levan of Bacillus subtilis strain MZ292983.1 | 59.88 | 104.18 | 76.27 | 75.17 | 80.26 | 63.37 |
| Rat Number | Burn Healing Percentage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Group (T) | Negative Control Group (N) | Control Group (C) | |||||||
| Day 4 | Day 6 | Day 7 | Day 4 | Day 6 | Day 7 | Day 4 | Day 6 | Day 7 | |
| 1 | 59.8 | 79.1 | 91.4 | 27.2 | 53.1 | 70.1 | 36.0 | 45.0 | 77.9 |
| 2 | 32.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 23.0 | 89.5 | 96.3 | 14.7 | 46.0 | 78.4 |
| 3 | 61.2 | 72.4 | 90.4 | 29.5 | 56.3 | 76.3 | 39.4 | 47.0 | 71.6 |
| 4 | 55.2 | 75.3 | 86.8 | 54.8 | 61.4 | 69.4 | 34.2 | 66.0 | 81.7 |
| 5 | 54.6 | 68.5 | 88.1 | 44.2 | 55.6 | 73.2 | 40.3 | 53.4 | 78.9 |
| Rat 1 | Rat 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Test Group (T) | Negative Control Group (N) | Control Group (C) | Test Group (T) | Negative Control Group (N) | Control Group (C) | |
| Histopath Alteration | |||||||
| Ulceration in epidermal layer with inflammatory reaction | - | - | ++ | - | - | +++ | |
| Non ulcerative epidermis and dermis with inflammatory reaction | - | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamada, M.A.; Hassan, R.A.; Abdou, A.M.; Elsaba, Y.M.; Aloufi, A.S.; Sonbol, H.; Korany, S.M. Bio_Fabricated Levan Polymer from Bacillus subtilis MZ292983.1 with Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Burn Healing Properties. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136413
Hamada MA, Hassan RA, Abdou AM, Elsaba YM, Aloufi AS, Sonbol H, Korany SM. Bio_Fabricated Levan Polymer from Bacillus subtilis MZ292983.1 with Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Burn Healing Properties. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136413
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamada, Marwa A., Rasha A. Hassan, Amr M. Abdou, Yasmin M. Elsaba, Abeer S. Aloufi, Hana Sonbol, and Shereen M. Korany. 2022. "Bio_Fabricated Levan Polymer from Bacillus subtilis MZ292983.1 with Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Burn Healing Properties" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136413
APA StyleHamada, M. A., Hassan, R. A., Abdou, A. M., Elsaba, Y. M., Aloufi, A. S., Sonbol, H., & Korany, S. M. (2022). Bio_Fabricated Levan Polymer from Bacillus subtilis MZ292983.1 with Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Burn Healing Properties. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136413






