Dosimetric Effect of Injection Ports in Tissue Expanders on Post-Mastectomy Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Planning for Left-Sided Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Expander
2.2. Computed Tomography Simulation
2.3. Radiation Therapy Planning
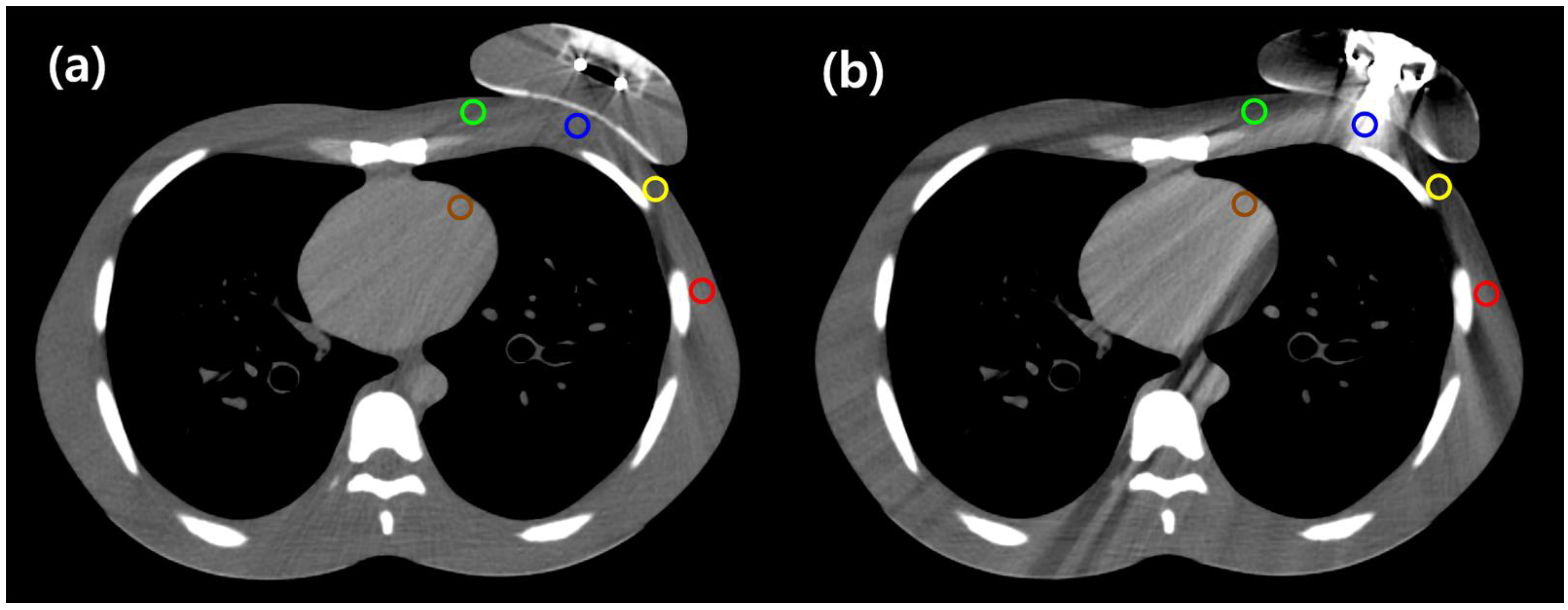
2.4. Computed Tomography Image Analysis
2.5. Assessment of Plan Quality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayorov, K.; Ali, E. Magnitude and dosimetric impact of inter-fractional positional variations of the metal port of tissue expanders in postmastectomy patients treated with radiation. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemal, Y.; Albornoz, C.R.; Disa, J.J.; McCarthy, C.M.; Mehrara, B.J.; Pusic, A.L.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Matros, E. A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: Part 2. The influence of changing mastectomy patterns on reconstructive rate and method. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 320e–326e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovan, C. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy using the temporary expander. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, E.; Pesce, M.; Santi, P.; Raposio, E. Two-stage tissue-expander breast reconstruction: A focus on the surgical technique. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1791546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albornoz, C.R.; Bach, P.B.; Mehrara, B.J.; Disa, J.J.; Pusic, A.L.; McCarthy, C.M.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Matros, E. A paradigm shift in U.S. Breast reconstruction: Increasing implant rates. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhangkhoee, H.; Matros, E.; Disa, J. Trends and concepts in post-mastectomy breast reconstruction. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Chang, J.S.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, W.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, I.J.; Yoon, W.S.; Cha, J.; et al. Post-mastectomy radiation therapy in breast reconstruction: A patterns of care study of the Korean Radiation Oncology Group. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2020, 38, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, N.; Battista, J.J.; Boyer, A.; Kappas, C. Tissue Inhomogeneity Corrections for Megavoltage Photon Beams; AAPM Report No. 85; Task Group No. 85; Task Group No. 65; Medical Physics Publishing: Madison, WI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bayasgalan, M.; Munhoz, A.M.; Shellock, F.G. Breast tissue expander with radiofrequency identification port: Assessment of MRI issues. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaidar-Person, O.; Vrou Offersen, B.; Hol, S.; Arenas, M.; Aristei, C.; Bourgier, C.; Cardoso, M.J.; Chua, B.; Coles, C.E.; Engberg Damsgaard, T.; et al. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline for target volume delineation in the setting of postmastectomy radiation therapy after implant-based immediate reconstruction for early stage breast cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Moran, J.M.; Koelling, T.; Chughtai, A.; Chan, J.L.; Freedman, L.; Hayman, J.A.; Jagsi, R.; Jolly, S.; Larouere, J.; et al. Development and validation of a heart atlas to study cardiac exposure to radiation following treatment for breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaw, E.; Kline, R.; Gillin, M.; Souhami, L.; Hirschfeld, A.; Dinapoli, R.; Martin, L. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: Radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1993, 27, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damast, S.; Beal, K.; Ballangrud, A.; Losasso, T.J.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Disa, J.J.; Hong, L.; McCormick, B.L. Do metallic ports in tissue expanders affect postmastectomy radiation delivery? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asena, A.; Kairn, T.; Crowe, S.B.; Trapp, J.V. Establishing the impact of temporary tissue expanders on electron and photon beam dose distributions. Phys. Med. 2015, 31, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darby, S.C.; Ewertz, M.; McGale, P.; Bennet, A.M.; Blom-Goldman, U.; Brønnum, D.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Gagliardi, G.; Gigante, B.; et al. Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease in Women after Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darby, S.C.; McGale, P.; Taylor, C.W.; Peto, R. Long-term mortality from heart disease and lung cancer after radiotherapy for early breast cancer: Prospective cohort study of about 300,000 women in US SEER cancer registries. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, K.E.; McGale, P.; Taylor, C.; Darby, S.C. Radiation-related mortality from heart disease and lung cancer more than 20 years after radiotherapy for breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onal, C.; Efe, E.; Guler, O.C.; Yildirim, B.A. Dosimetric comparison of sequential versus simultaneous-integrated boost in early-stage breast cancer patients treated with breast-conserving surgery. In Vivo 2019, 33, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ju, E.; Heo, E.J.; Park, C.G.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.H.; Shim, J.B.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, N.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, S. Dosimetric comparison of VitalBeam® and HalcyonTM 2.0 for hypofractionated VMAT with simultaneous integrated boost treatment of early-stage left-sided breast cancer. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommen, J.; Schorn, L.; Sproll, C.; Haussmann, J.; Kübler, N.R.; Budach, W. Reduction of CT artifacts using polyetheretherketone (PEEK), polyetherketoneketone (PEKK), polyphenylsulfone (PPSU), and polyethylene (PE) reconstruction plates in oral oncology. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
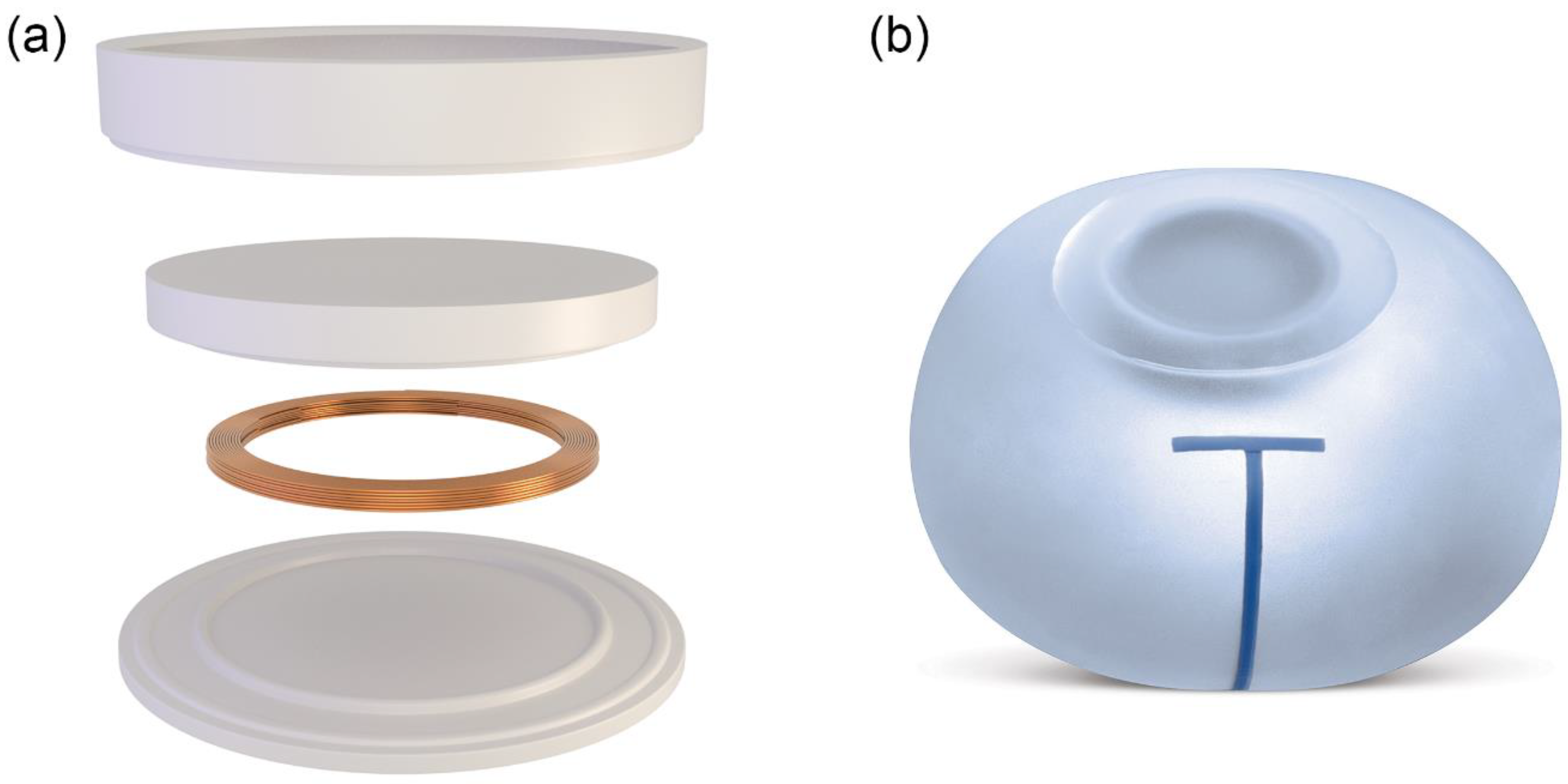

| Parameter | Traditional Expander | Motiva Flora® |
|---|---|---|
| Identification of port location | Magnet | RFID coil |
| Material | Neodymium | Copper |
| Density | 7.01 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Diameter | 13.3 mm * | Outer: 24.7 mm Inner: 20.3 ± 0.2 mm |
| Height | 4.4 mm * | 2.150 ± 0.1 mm |
| Needle guide | ||
| Material | Stainless steel | Polyetheretherketone |
| Density | 7.5~8 g/cm3 | 1.3 g/cm3 |
| Diameter | 36.5 mm * | Dome: 40.1 mm *, Needle stop: 26.8 mm * Base: 42.5 mm * |
| Height | 10.0 mm * | 12.9 mm * |
| Thickness | 2.1 mm * | 1.5 mm * |
| Points of the Reference ROIs | RFID Port | Metallic Port | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Averaged HU | Averaged HU Difference | p-Value | Averaged HU | Averaged HU Difference | p-Value | |
| A (central chest wall) | −2.73 | −18.33 | 0.043 | 118.57 | −139.63 | 0.007 |
| B (medial chest wall) | −19.36 | 8.17 | 0.028 | −34.62 | 23.43 | 0.017 |
| C (lateral chest wall) | −37.36 | 14.93 | 0.028 | −74.37 | 51.94 | 0.005 |
| D (axilla) | −0.92 | −15.14 | 0.005 | −12.32 | −3.74 | 0.169 |
| E (left anterior descending artery) | 32.41 | −2.86 | 0.059 | 44.71 | −15.16 | 0.005 |
| Parameter | RFID Port | Metallic Port | Percentage Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
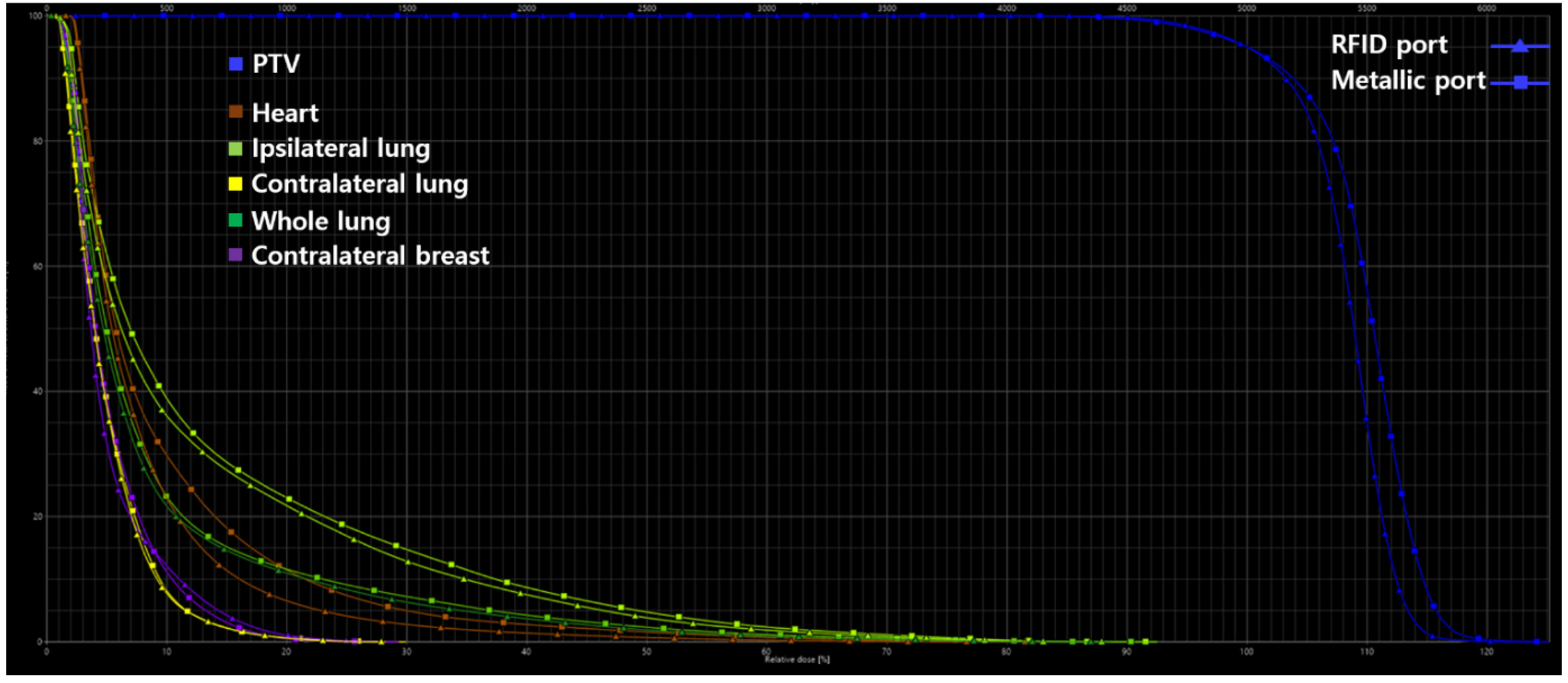
| PTV | |||
| HI | 1.31 | 1.32 | 0.76 |
| CI | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0 |
| QOC | 0.92 | 0.90 | 2.19 |
| V95, % | 98.40 | 98.10 | 0.30 |
| V107, % | 71.70 | 80.80 | 11.93 |
| Heart | |||
| V5Gy, % | 22.91 | 29.75 | 25.97 |
| V10Gy, % | 6.54 | 11.46 | 54.66 |
| V15Gy, % | 2.77 | 4.97 | 56.84 |
| V20Gy, % | 1.39 | 2.75 | 65.70 |
| V30Gy, % | 0.23 | 0.68 | 98.90 |
| Dmean, Gy | 4.08 | 4.92 | 18.66 |
| Ipsilateral lung | |||
| V5Gy, % | 36.08 | 38.86 | 7.41 |
| V15Gy, % | 12.85 | 14.73 | 13.63 |
| V20Gy, % | 7.50 | 8.67 | 14.47 |
| V30Gy, % | 1.87 | 2.36 | 23.16 |
| Dmean, Gy | 6.43 | 6.94 | 7.62 |
| Contralateral lung | |||
| Dmean, Gy | 2.44 | 2.51 | 2.82 |
| Whole lung | |||
| V20Gy, % | 3.69 | 4.25 | 14.10 |
| Dmean, Gy | 4.40 | 4.68 | 6.16 |
| Contralateral breast | |||
| Dmean, Gy | 2.58 | 2.68 | 3.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, N.-H.; Kim, M.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, S.; Hwang, J. Dosimetric Effect of Injection Ports in Tissue Expanders on Post-Mastectomy Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Planning for Left-Sided Breast Cancer. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6461. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136461
Hwang N-H, Kim M, Lee NK, Lee S, Hwang J. Dosimetric Effect of Injection Ports in Tissue Expanders on Post-Mastectomy Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Planning for Left-Sided Breast Cancer. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6461. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136461
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Na-Hyun, Myungsoo Kim, Nam Kwon Lee, Suk Lee, and Jinho Hwang. 2022. "Dosimetric Effect of Injection Ports in Tissue Expanders on Post-Mastectomy Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Planning for Left-Sided Breast Cancer" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6461. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136461
APA StyleHwang, N.-H., Kim, M., Lee, N. K., Lee, S., & Hwang, J. (2022). Dosimetric Effect of Injection Ports in Tissue Expanders on Post-Mastectomy Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Planning for Left-Sided Breast Cancer. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6461. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136461






