The Application of Blockchain in Social Media: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Blockchain
2.1. Cryptography Hash Function
2.2. Immutable Ledger
2.3. Distributed Peer-to-Peer Networks
2.4. Distributed Application
2.5. Consensus Protocol
2.6. Smart Contracts
3. Social Media Basics
3.1. The Different Types of Social Media
3.1.1. Social Networking Sites
3.1.2. Social Media for Sharing Photos, Videos, and Music
3.1.3. Professional Networks
3.1.4. Social Media Messaging
3.1.5. Forums
3.2. The Most Popular Social Media Sites Today
3.3. Existing Blockchain-Based Social Media Platforms
- Society2 is a social media architecture that is decentralized according to the client, management of information, and speech. Members have options such as exchanging information, and the platform handles their status, conversation, and contacts [40].
- Peepeth consists of Ethereum and IPFS from the database and the Peepeth frontend. Peepeth’s posting, liking, following, and other behaviors need to pay gas fees to be packaged on the blockchain. With no company controlling the data, anyone can build a frontend that reads and writes smart contracts, saving the content to the blockchain [41].
- Sapien is another platform based on Ethereum; it has the goal of using a proof of value consensus protocol to return control of the social media experience to users by creating a truly autonomous social network environment that compensates content creators and combats bogus information. It provides users with a speech structure and promotes community enthusiasm and participation [42].
- Steemit is a decentralized social media structure that promises to develop groups and improve social interactions by awarding members with cryptocurrency for their content based on the number of positive reviews they receive. The platform provides users with structured news and analysis, appropriate replies to personalized inquiries, and a stable cryptocurrency pegged to the US dollar, among other things [43].
4. Methodology
4.1. Eligibility Criteria
4.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Papers published in journals or conference proceedings, as these are much better indexed in scholarly databases and are easier to find;
- Papers written in English;
- Papers containing the following keywords: (“Blockchain” OR “Blockchain platform” OR “Blockchain application”) AND (“Social media” OR “Social network” OR “Social platform” OR “Online community” OR “media platform”);
- Papers must have proposed methods to resolve an issue in social media by applying blockchain to improve privacy and security or have proposed a model using one of the characteristics or components of blockchain.
4.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Reviews, reports, case reports, abstract-only papers, patents, magazines, and editorials, as well as books, dissertations, and theses, all of which are hard to find and infrequently available online;
- Papers for which the full text was not available online;
- Papers with a title and abstract not explicitly related to both blockchain and social media.
4.2. Information Sourcing
- Scopus
- Web of Science
- IEEE Xplore
- ACM digital library
- ScienceDirect
- Wiley Online Library
- EBSCO
- ProQuest
4.3. Search Strategy
4.4. Data Selection Process
5. Results
5.1. Selected Documents by Year
5.2. Included Studies by Country
5.3. Publication Type
5.4. Publication by Subject Area
5.5. Classification of Selected Papers
6. Discussion
6.1. Research Question Answers
6.1.1. The Different Methods and Techniques Proposed by Past Studies to Leverage Blockchain Technology in Social Media
6.1.2. The Existing Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Application in Social Media
6.1.3. Knowledge Gaps Which Future Research Can Address
6.2. Limitations of This SLR
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheung, C.M.K.; Lee, M.K.O.; Wagner, C. Introduction to Social Media and E-Business Transformation Minitrack. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abawajy, J.H.; Ninggal, M.I.H.; Herawan, T. Privacy Preserving Social Network Data Publication. Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1974–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guille, A.; Hacid, H.; Favre, C.; Zighed, D.A. Information Diffusion in Online Social Networks: A Survey. SIGMOD Rec. 2013, 42, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIT. The Social Media Summit @ MIT (SMS@MIT) 2021—MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy. 2021. Available online: https://ide.mit.edu/events/the-social-media-summit-mit-smsmit/ (accessed on 17 April 2022).
- Kayes, I.; Iamnitchi, A. Privacy and security in online social networks: A survey. Online Soc. Netw. Media 2017, 3–4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Fake News Detection on Social Media: A Data Mining Perspective. SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2017, 19, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoughi, S.; Roy, D.; Aral, S. The spread of true and false news online. Science 2018, 359, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, B.; Michienzi, A. The Decentralization of Social Media through the Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM Web Science Conference 2021, Virtual Event, 21–25 June 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Weber, I.; Staples, M. Introduction. In Architecture for Blockchain Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, C. Blockchain Social Media and Crypto Social Media. 2022. Available online: https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/blockchain-social-media-decentralized-social-media (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Haimoud, E. Blockchain-Based Social Media Will Be More Secure. 2022. Available online: https://cisomag.eccouncil.org/blockchain-based-social-media/ (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Benshahar, A. 6 Ways the Blockchain Is Revitalizing Social Networking. CryptoPotato. 2021. Available online: https://cryptopotato.com/6-ways-blockchain-revitalizing-social-networking/ (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Poongodi, T.; Sujatha, R.; Sumathi, D.; Suresh, P.; Balamurugan, B. Blockchain in Social Networking. In Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Chapter 4; pp. 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.K. How Will Blockchain Revive Social Media? 2018. Available online: https://www.blockchain-council.org/blockchain/how-will-blockchain-revive-social-media/ (accessed on 11 June 2022).
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Fernández-Caramés, T. Fake News, Disinformation, and Deepfakes: Leveraging Distributed Ledger Technologies and Blockchain to Combat Digital Deception and Counterfeit Reality. IT Prof. 2020, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kathryn, H.; Amelia, L. How Blockchain Can Help Combat Disinformation. 2021. Available online: https://hbr.org/2021/07/how-blockchain-can-help-combat-disinformation (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Chakravarty, S.R.; Sarkar, P. Introduction to Blockchain; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2020; pp. 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xie, S.; Dai, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, H. An Overview of Blockchain Technology: Architecture, Consensus, and Future Trends. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebacher, S.; Schüritz, R. Blockchain Technology as an Enabler of Service Systems: A Structured Literature Review. In Proceedings of the Exploring Services Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tama, B.A.; Kweka, B.J.; Park, Y.; Rhee, K.H. A critical review of blockchain and its current applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (ICECOS), Palembang, Indonesia, 22–23 August 2017; pp. 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Gill, S.S. Chapter 4—Applications of blockchain in automated heavy vehicles: Yesterday, today, and tomorrow. In Autonomous and Connected Heavy Vehicle Technology; Krishnamurthi, R., Kumar, A., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Intelligent Data-Centric Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenfield, J. Distributed Applications (DApps). 2021. Available online: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/distributed-applications-apps.asp (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- Kramer, M. What Are Consensus Protocols? A Super Speedy Guide. 2019. Available online: https://decrypt.co/resources/consensus-protocols-what-are-they-guide-how-to-explainer (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Kaur, S.; Chaturvedi, S.; Sharma, A.; Kar, J. A research survey on applications of consensus protocols in Blockchain. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinloye, D.P.; Teh, J.S.; Jamil, N.; Alawida, M. Blockchain Consensus: An Overview of Alternative Protocols. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.N.; Loukil, F.; Ghedira-Guegan, C.; Benkhelifa, E.; Bani-Hani, A. Blockchain Smart Contracts: Applications, challenges, and future trends. Peer-Peer Netw. Appl. 2021, 14, 2901–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobeinikov, A. 9 Most Common Smart Contract Vulnerabilities Found by Blaize. 2022. Available online: https://blaize.tech/article-type/9-most-common-smart-contract-vulnerabilities-found-by-blaize/ (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Zou, W.; Lo, D.; Kochhar, P.S.; Le, X.B.D.; Xia, X.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B. Smart Contract Development: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2021, 47, 2084–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Zhou, Z.; Miller, A.; Wang, Y. Exploring Security Practices of Smart Contract Developers. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, T. Reconfigurable Smart Contracts for Renewable Energy Exchange with Re-Use of Verification Rules. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.; Ali Babar, M.; Zhu, L. Continuous Integration, Delivery and Deployment: A Systematic Review on Approaches, Tools, Challenges and Practices. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 3909–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, T. Towards Continuous Deployment for Blockchain. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Dar, M.; Tahir, R.M.; Masood, F. Impact of social media on academic: A quantitative study. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), Sukkur, Pakistan, 3–4 March 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garima, K. Different Types of Social Media Networks 2022. Available online: https://www.digitalvidya.com/blog/types-of-social-media/ (accessed on 11 June 2022).
- Synapse. What Are the Different Types of Social Media? 2022. Available online: https://synapsereality.io/what-are-the-different-types-of-social-media/ (accessed on 11 June 2022).
- Team, I.E. 10 Types of Social Media to Promote Your Brand. 2021. Available online: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/types-of-social-media (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Bishop, A. 13 Awesome Professional Networking Alternatives to Linkedin. 2019. Available online: https://www.searchenginejournal.com/linkedin-alternatives/297409/#close (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Alfred, L. 20 Top Social Media Sites to Consider for Your Brand. Available online: https://buffer.com/library/social-media-sites/ (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- EES. Blockchain Based Social Media Platforms To Know—EES Corporation. 2022. Available online: https://www.eescorporation.com/blockchain-based-social-media/ (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- SOCIETY2. SOCIETY2—Own Your Digital Life—Decentralized Social Media. Available online: https://society2.com/ (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Peepeth. Peepeth | Peepeth. Available online: https://peepeth.com/about (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Giffin, K. Should Social Media Be More Rewarding? Sapien Thinks So—UC Berkeley Sutardja Center. 2020. Available online: https://scet.berkeley.edu/sapien-network-rewards-you-for-using-social-media/ (accessed on 23 April 2022).
- Bhattacharya, R.; White, M.; Beloff, N. An Exploration of Blockchain in Social Networking Applications. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, F.; Gao, J. CL-BC: A Secure Data Storage Model for Social Networks. Secur. Commun. Networks 2022, 2022, 5428539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Pal, S.; Srivastava, G. Blockchain-based Framework for Reducing Fake or Vicious News Spread on Social Media/Messaging Platforms. ACM Trans. Asian-Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, L.K.; Muralidharan, R.R.A.; Sampathkumar, R.; Gururajan, I.; Subbiah, P. Blockchain Based Fictitious Detection in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition (SoCPaR 2021), Online, 25–17 December 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koly, W.; Jamil, A.; Rahman, M.; Bhuiyan, H.; Bhuiyan, M.; Al Omar, A. Towards a Location-Aware Blockchain-Based Solution to Distinguish Fake News in Social Media. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 1557 CCIS, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ush Shahid, I.; Anjum, M.; Hossain Miah Shohan, M.; Tasnim, R.; Al-Amin, M. Authentic Facts: A Blockchain Based Solution for Reducing Fake News in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Blockchain Technology and Applications (ICBTA 2021), Xi’an, China, 17–19 December 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Breslin, J. Rumour prevention in social networks with layer 2 blockchains. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2021, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arquam, M.; Singh, A.; Sharma, R. A blockchain-based secured and trusted framework for information propagation on online social networks. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2021, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, A.; Patnaik, G. Fake news detection of social media news in blockchain framework. Indian J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2021, 12, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, G.; Russo, A.; Fascì, L. A Blockchain-based approach for matching desired and real privacy settings of social network users. Inf. Sci. 2021, 557, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Murugesan, R. Protecting Data Privacy and Prevent Fake News and Deepfakes in Social Media via Blockchain Technology. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 1347, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cho, D.Y. A Blockchain based Autonomous Decentralized Online Social Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering, ICCECE 2021, Guangzhou, China, 15–17 January 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang Zen, T.; Hong, C.; Mohan, P.; Balachandran, V. ABC-Verify: AI-Blockchain Integrated Framework for Tweet Misinformation Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics, SOLI 2021, Singapore, 11–12 December 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaawy, Y.; Sen, A.; Bahbouh, N.; Alkhodre, A.; Nadeem, A. Lightweight Chain For Detection Of Rumors And Fake News In Social Media. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.; Ilmananda, A.; Romano, D. Social trust-based blockchain-enabled social media news verification system. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2021, 27, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X. Construction of online social network data mining model based on blockchain. Soft Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, T.; Arthur Sandor, V.; Weng, T.H.; Liang, W.; Su, J. A novel blockchain-based privacy-preserving framework for online social networks. Connect. Sci. 2021, 33, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.; Singh, R.; Dhall, S.; Srivastava, G.; Pal, S. Tracing the source of fake news using a scalable blockchain distributed network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Smart Systems, MASS 2020, Delhi, India, 10–13 December 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rahman, M.; Guidi, B.; Baiardi, F. Blockchain-based access control management for Decentralized Online Social Networks. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 144, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroucheh, Z.; Alissa, M.; Buchanan, W.J.; Liu, X. TRUSTD: Combat Fake Content using Blockchain and Collective Signature Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 44th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Madrid, Spain, 13–17 July 2020; pp. 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakounté, F.; Amadou Calvin, K.; Ari, A.; Fotsa Mbogne, D. A smart contract logic to reduce hoax propagation across social media. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Hu, C.; Alrawais, A. An Efficient Blockchain-Based Bidirectional Friends Matching Scheme in Social Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 150902–150913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, G.; Nemeth, D.; Neville, D.; Zhelezov, D.; Yalcin, A.; Fohrmann, O.; Krishnamachari, B. WhistleBlower: Towards A Decentralized and Open Platform for Spotting Fake News. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain, Blockchain 2020, Rhodes, Greece, 2–6 November 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Nguyen, H.; Swapna, D.; Rao, K.; Kumar, D. The efficient way to detect and stall fake articles in public media using the blockchain technique: Proof of trustworthiness. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 11, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, X. BCOSN: A Blockchain-Based Decentralized Online Social Network. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2019, 6, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, S.; Gambini, M.; Belussi, A. A Blockchain-based solution to fake check-ins in location-based social networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Analytics for Local Events and News, LENS 2019, Chicago, IL, USA, 5 November 2019; Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, F.Y. A decentralized social networking architecture enhanced by blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics, SOLI 2019, Zhengzhou, China, 11–13 October 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, H.; Lv, K.; Wei, S.; Hu, C. DEPLEST: A blockchain-based privacy-preserving distributed database toward user behaviors in social networks. Inf. Sci. 2019, 501, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Joy, J.I.; Sarker, S.; Shakib, A.A.H.; Ahmed, S.; Das, A.K. Fake News Detection in Social Media using Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Smart Computing Communications (ICSCC), Miri, Malaysia, 28–30 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Kim, S.; Hwang, H.; Lee, K. Blockchain-based Notarization for Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1–13 January 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torky, M.; Nabil, E.; Said, W. Proof of credibility: A blockchain approach for detecting and blocking fake news in social networks. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Bin, S.; Jiang, M.; Cao, N.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, L. Research on public opinion propagation model in social network based on blockchain. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2019, 60, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, K.; Wang, L.; Jia, W. Autonomous Resource Request Transaction Framework Based on Blockchain in Social Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 43666–43678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, I.S.; de Mello, G.; Silva, L.A.; Gomes, A.J.P.; Fernandes, A.M.R.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. FakeChain: A Blockchain Architecture to Ensure Trust in Social Media Networks. In Proceedings of the Quality of Information and Communications Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; Ahmad, A.; Mohaisen, A. Fighting Fake News Propagation with Blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Qadir, J.; Janjua, M.; Sher, F. Using Blockchain to Rein in the New Post-Truth World and Check the Spread of Fake News. IT Prof. 2019, 21, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murimi, R. A Blockchain Enhanced Framework for Social Networking. Ledger 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinter, K.; Schmelz, D.; Lamber, R.; Strobl, S.; Grechenig, T. Towards a Multi-party, Blockchain-Based Identity Verification Solution to Implement Clear Name Laws for Online Media Platforms. In Proceedings of the Business Process Management: Blockchain and Central and Eastern Europe Forum; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Song, Z.; Mong Goh, R.S.; Li, Y. Building an Ethereum and IPFS-Based Decentralized Social Network System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 24th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Singapore, 11–13 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y. RPchain: A Blockchain-Based Academic Social Networking Service for Credible Reputation Building. In Proceedings of the Blockchain—ICBC 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–30 June 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, J.; Xu, T.; Gao, J.; An, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yu, M. Authentication with Block-Chain Algorithm and Text Encryption Protocol in Calculation of Social Network. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 24944–24951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huckle, S.; White, M. Fake News: A Technological Approach to Proving the Origins of Content, Using Blockchains. Big Data 2017, 5, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, A.; Rong, C. Ushare: User Controlled Social Media Based on Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, IMCOM 2017, Beppu, Japan, 5–7 January 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Database | Query Strings |
|---|---|
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (((“Blockchain” OR “Blockchain platform” OR “Blockchain application” ) AND (“Social media” OR “Social network” OR “Social platform” OR “Online community” OR “media platform”))) |
| Web of Science | TS = (((“Blockchain” OR “Blockchain platform” OR “Blockchain application” ) AND (“Social media” OR “Social network” OR “Social platform” OR “Online community” OR “media platform”))) |
| IEEE Xplore | (“All Metadata”: blockchain OR ”All Metadata”: blockchain platform OR “All Metadata”: blockchain application) AND (“All Metadata”: social media OR ”All Metadata”: social network OR “All Metadata”: social platform OR “All Metadata”: online community OR ”All Metadata”: media platform) |
| ACM digital library | [[All: “blockchain”] OR [All: “blockchain platform”] OR [All: “blockchain application”]] AND [[All: “social media”] OR [All: “social network”] OR [All: “social platform”] OR [All: “online community”] OR [All: “media platform”]] AND [[All: “blockchain”] OR [All: “blockchain platform”] OR [All: “blockchain application”]] AND [[All: “social media”] OR [All: “social network”] OR [All: “social platform”] OR [All: “online community”] OR [All: “media platform”]] |
| ScienceDirect | ((“blockchain” OR “blockchain platform” OR “blockchain application” ) AND (“social media” OR “social network” OR “social platform” OR “Online community” OR “media platform”)) |
| Wiley Online Library | “(blockchain OR blockchain platform OR blockchain application) AND (social media OR social network OR social platform OR online community OR media platform)” anywhere |
| EBSCO | (“blockchain” OR “blockchain platform” OR “blockchain application”) AND (“social media” OR “social network” OR “social platform” OR “online community” OR “media platform”) |
| ProQuest | ti(((“blockchain” OR “blockchain platform” OR “blockchain application” ) AND (“social media” OR “social network” OR “social platform” OR “online community” OR “media platform”))) OR ab(((“blockchain” OR “blockchain platform” OR “blockchain application” ) AND (“social media” OR “social network” OR “social platform” OR “online community” OR “media platform”))) |
| Reference | Year | Country | Type | Subject Area | Cited |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [45] | 2022 | China | Journal | Computer Science | - |
| [46] | 2022 | Denmark India Taiwan | Journal | Computer Science | 3 |
| [47] | 2022 | India | Conference | Computer Science Engineering | - |
| [48] | 2022 | Australia Bangladesh United States | Conference | Computer Science Mathematics | - |
| [49] | 2021 | Bangladesh | Conference | Computer Science | - |
| [50] | 2021 | Ireland | Journal | Computer Science Engineering Social Sciences | - |
| [51] | 2021 | Estonia India | Journal | Computer Science Engineering Social Sciences | 1 |
| [52] | 2021 | India | Journal | Computer Science Engineering | - |
| [53] | 2021 | Italy | Journal | Computer Science Decision Sciences Engineering Mathematics | 3 |
| [54] | 2021 | Malaysia | Conference | Computer Science Mathematics | 1 |
| [55] | 2021 | China | Conference | Computer Science Engineering Physics and Astronomy | 1 |
| [56] | 2021 | Singapore | Conference | Computer Science Decision Science Engineering | - |
| [57] | 2021 | Saudi Arabia Spain | Journal | Computer Science | - |
| [58] | 2021 | Indonesia United Kingdom | Journal | Computer Science Mathematics | - |
| [59] | 2021 | China | Journal | Computer Science Mathematics | - |
| [60] | 2021 | China Taiwan | Journal | Computer Science | 16 |
| [61] | 2020 | Canada Denmark India | Conference | Computer Science Decision Sciences Engineering | 4 |
| [62] | 2020 | Italy | Journal | Computer Science Mathematics | 9 |
| [63] | 2020 | United Kingdom | Conference | Computer Science Social Sciences | 3 |
| [64] | 2020 | Cameroon France | Journal | Computer Science | 3 |
| [65] | 2020 | China Saudi Arabia | Journal | Computer Science Engineering Materials Science | 2 |
| [66] | 2020 | Germany United States | Conference | Business Computer Science Decision Sciences Engineering | 2 |
| [67] | 2020 | India Viet Nam | Journal | Agricultural and Biological Sciences Business Engineering | - |
| [68] | 2019 | China | Journal | Computer Science Mathematics Social Sciences | 24 |
| [69] | 2019 | Italy | Conference | Computer Science | 1 |
| [70] | 2019 | China | Conference | Business Computer Science Decision Sciences | - |
| [71] | 2019 | China | Journal | Computer Science Decision Sciences Engineering Mathematics | 41 |
| [72] | 2019 | Bangladesh | Conference | Computer Science Engineering | 18 |
| [73] | 2019 | South Korea | Conference | Engineering | 17 |
| [74] | 2019 | Egypt Saudi Arabia | Journal | Computer Science | 5 |
| [75] | 2019 | China Ireland | Journal | Computer Science Engineering Materials Science Mathematics | 29 |
| [76] | 2019 | China Macao | Journal | Computer Science Engineering Materials Science | 7 |
| [77] | 2019 | Brazil Portugal | Conference | Computer Science Mathematics | 11 |
| [78] | 2019 | United States | Conference | Computer Science Decision Sciences Engineering | 13 |
| [79] | 2019 | Germany | Journal | Computer Science | 29 |
| [80] | 2019 | United States | Journal | Computer Science | 5 |
| [81] | 2019 | Austria | Conference | Business Computer Science Decision Sciences Engineering Mathematics | 2 |
| [82] | 2019 | China Singapore | Conference | Computer Science | 4 |
| [83] | 2018 | China | Conference | Computer Science | 8 |
| [84] | 2017 | China United States | Conference | Computer Science | 27 |
| [85] | 2017 | United Kingdom | Journal | Computer Science Decision Sciences | 29 |
| [86] | 2017 | Norway | Conference | Computer Science | 43 |
| Category | References |
|---|---|
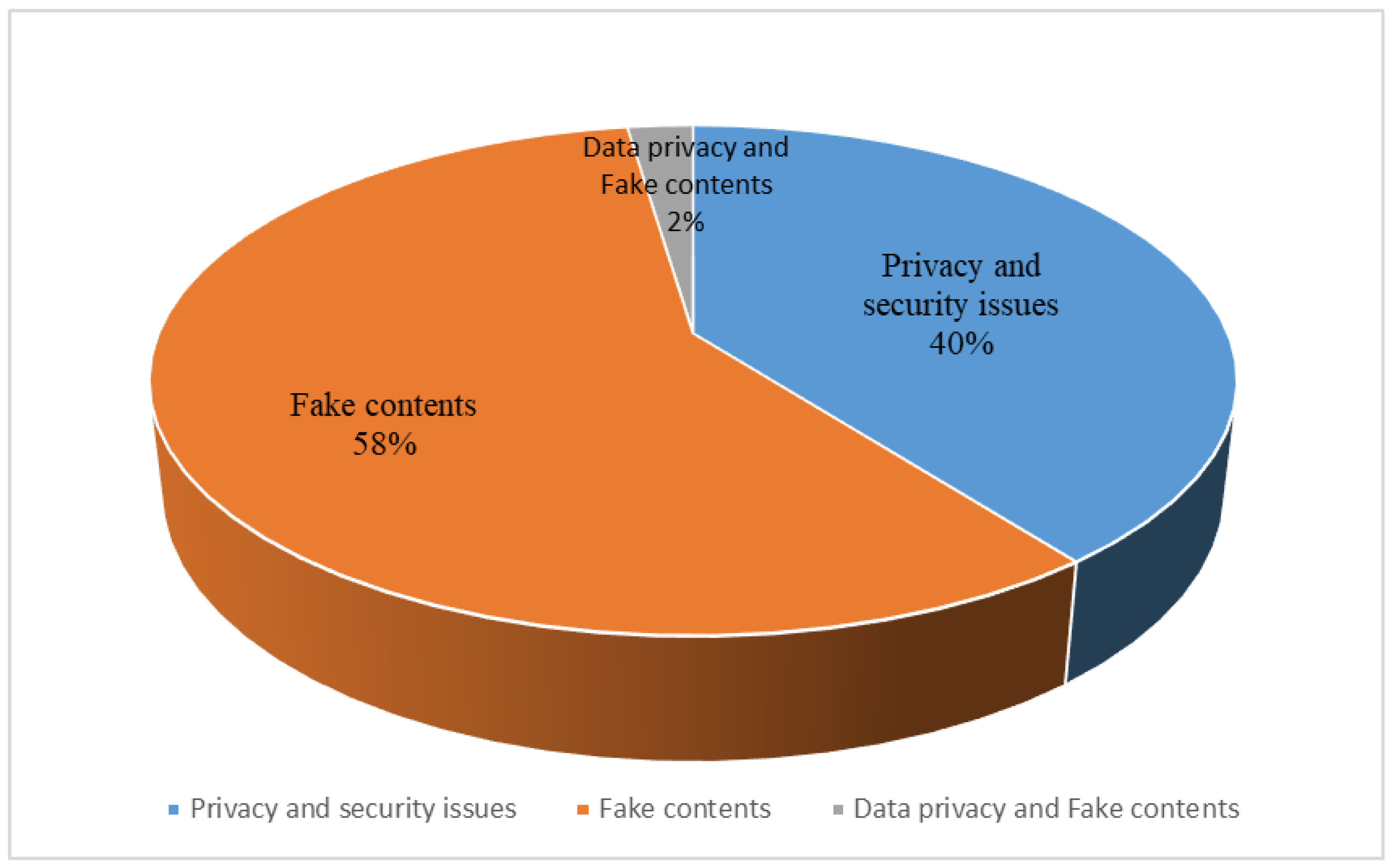
| Data privacy and security | [45,53,55,59,60,62,65,68,70,71,76,80,81,82,83,84,86] |
| Fake content | [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,56,57,58,61,63,64,66,67,69,72,73,74,75,77,78,79,85] |
| Data privacy and Fake content | [54] |
| Reference | Proposed Model |
|---|---|
| [46] | Blockchain and keyed watermarking-based framework |
| [47] | Architecture of blockchain-based fictitious detection system |
| [48] | Architecture to store validation records in the blockchain |
| [49] | Rating system to detect the authenticity of news |
| [50] | A secure and privacy-preserving method |
| [51] | A framework for safely sharing information at the peer level |
| [52] | Machine Learning-based model using Blockchain |
| [56] | AI with a Proof-of-Stake smart contract algorithm architecture |
| [57] | Blockchain with Text Mining (TM) algorithm |
| [58] | Social media news-spreading model |
| [61] | A blockchain and watermarking-based social media framework |
| [63] | TRUSTD, a blockchain and collective signature-based ecosystem |
| [64] | A smart contract-based technique to avert fake posts |
| [66] | WhistleBlower, a decentralized fake news detection platform |
| [67] | Proof of Trustworthiness (PoT) |
| [69] | Avoiding false check-ins in Location-Based Social Networks |
| [72] | Method using the concept of decentralization |
| [73] | A blockchain-based social media notarization method |
| [74] | A blockchain consensus called Proof of Credibility (PoC) |
| [75] | A public opinion communication model |
| [77] | Architecture using data mining as a consensus algorithm |
| [78] | A prototype to counter the dissemination of fake news |
| [79] | Proof of Truthfulness (PoT) for news verification |
| [85] | Provenator, a blockchain-based distributed application |
| Reference | Proposed Model |
|---|---|
| [45] | Model based on security data storage |
| [53] | Solution to managing the privacy preferences of a user |
| [55] | Autonomous decentralized online social network architecture |
| [59] | Blockchain-based data mining methodology |
| [60] | A blockchain-based privacy-preserving framework (BPP) |
| [62] | An auditable and trustworthy access control structure |
| [65] | A hierarchical blockchain-based attribute matching system |
| [68] | BCOSN, a blockchain-based Online Social Network |
| [70] | A decentralized social networking architecture |
| [71] | A blockchain-based model for data storage |
| [76] | An autonomous resource request transaction framework |
| [80] | Blockchain-enhanced version of social networking (BEV-SNSs) |
| [81] | Blockchain-based identity providers |
| [82] | A decentralized social network based on Ethereum and IPFS |
| [83] | RPchain, a blockchain based academic social networking platform |
| [84] | A protocol and authentication with a blockchain algorithm |
| [86] | Ushare: a blockchain scheme for social networks |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hisseine, M.A.; Chen, D.; Yang, X. The Application of Blockchain in Social Media: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136567
Hisseine MA, Chen D, Yang X. The Application of Blockchain in Social Media: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136567
Chicago/Turabian StyleHisseine, Mahamat Ali, Deji Chen, and Xiao Yang. 2022. "The Application of Blockchain in Social Media: A Systematic Literature Review" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136567
APA StyleHisseine, M. A., Chen, D., & Yang, X. (2022). The Application of Blockchain in Social Media: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136567






