Evaluation of the Hydrochemical and Water Quality Characteristics of an Aquifer Located in an Urbanized Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Spatial and Temporal Assessment of Groundwater Quality
2.4. Water Quality Assessment
2.4.1. Drinking Water Quality Index
2.4.2. Hydrochemical Characteristics
2.4.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of Groundwater Quality Parameters
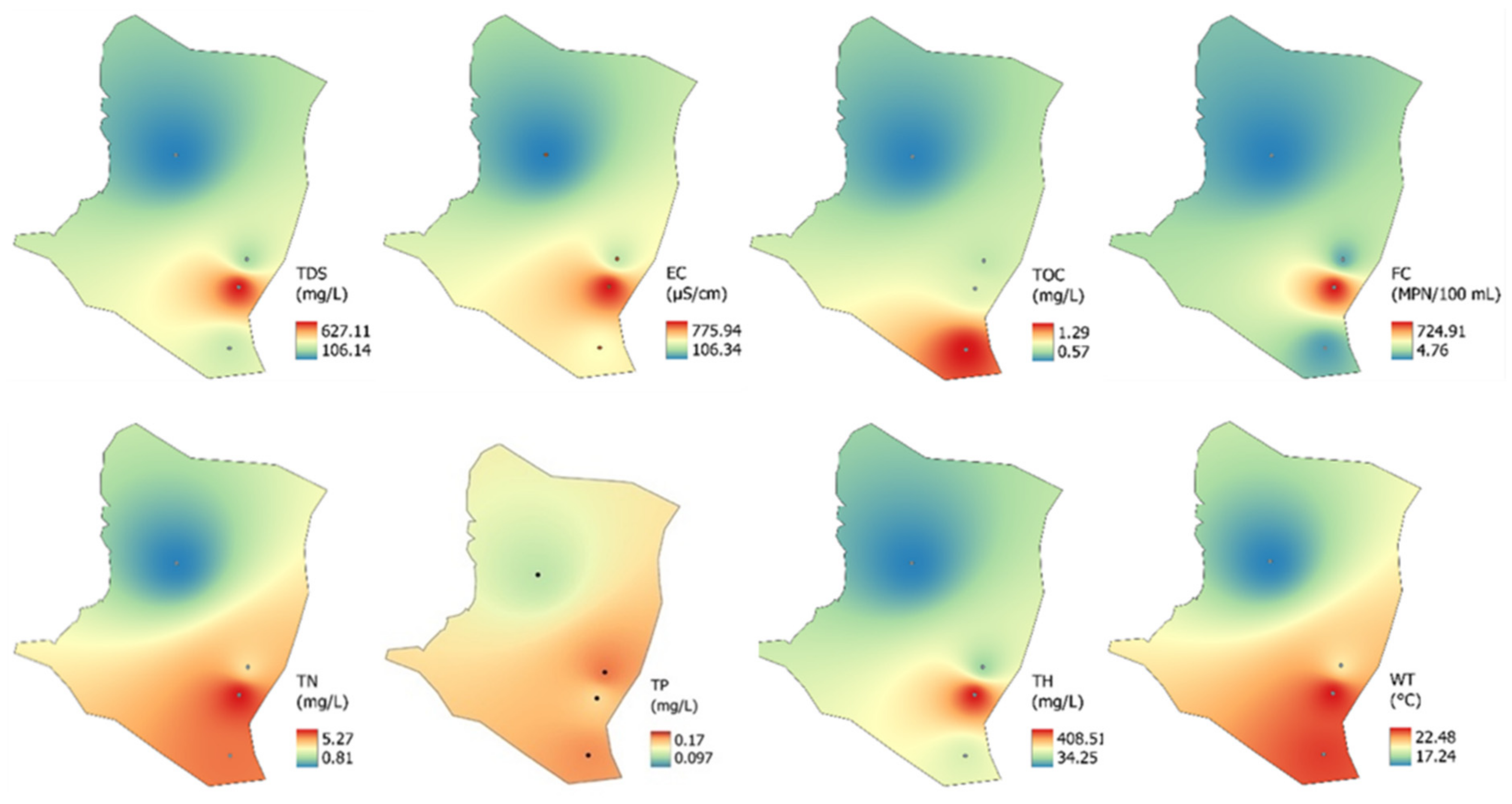
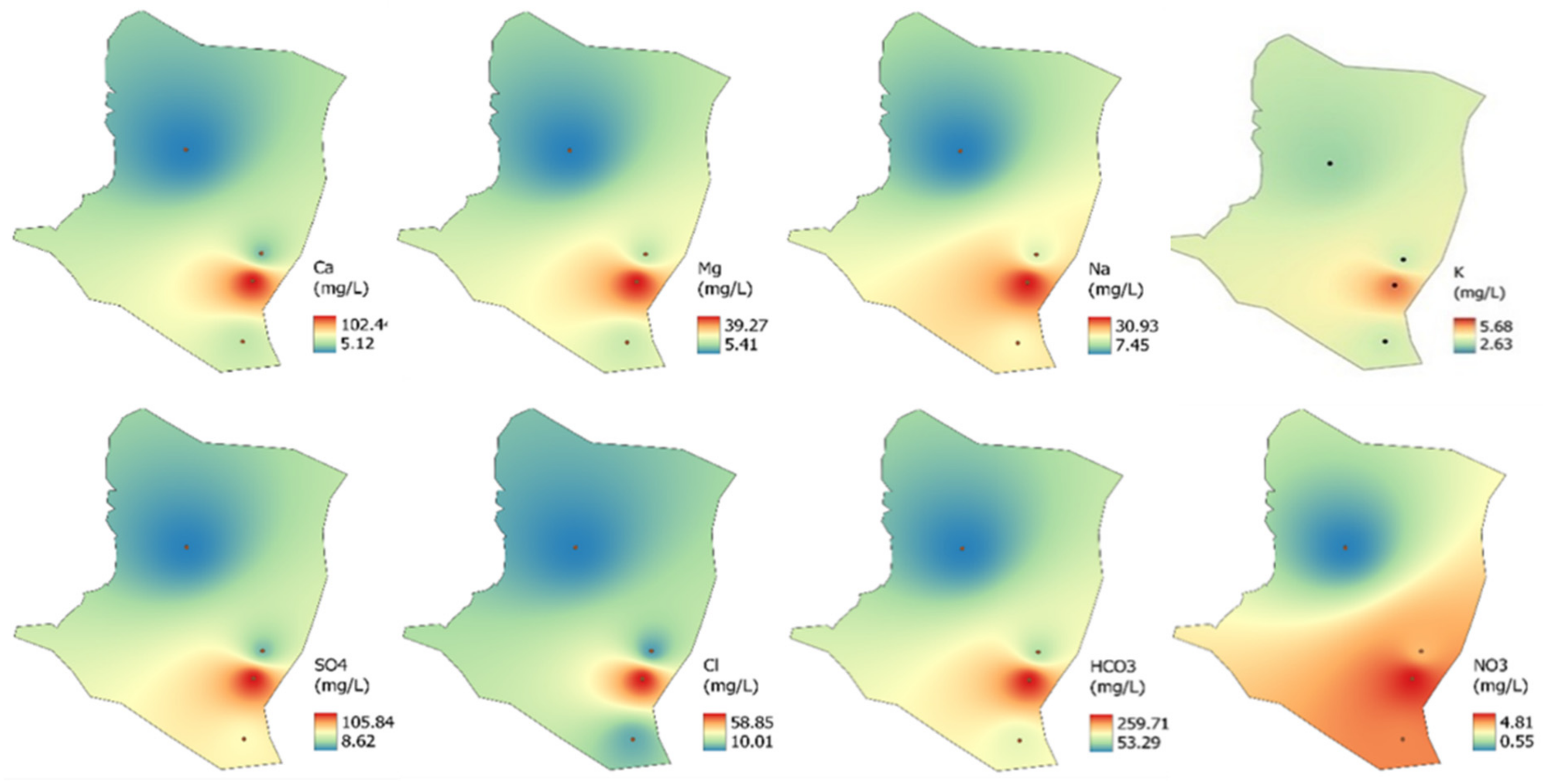
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Measuring Indicators
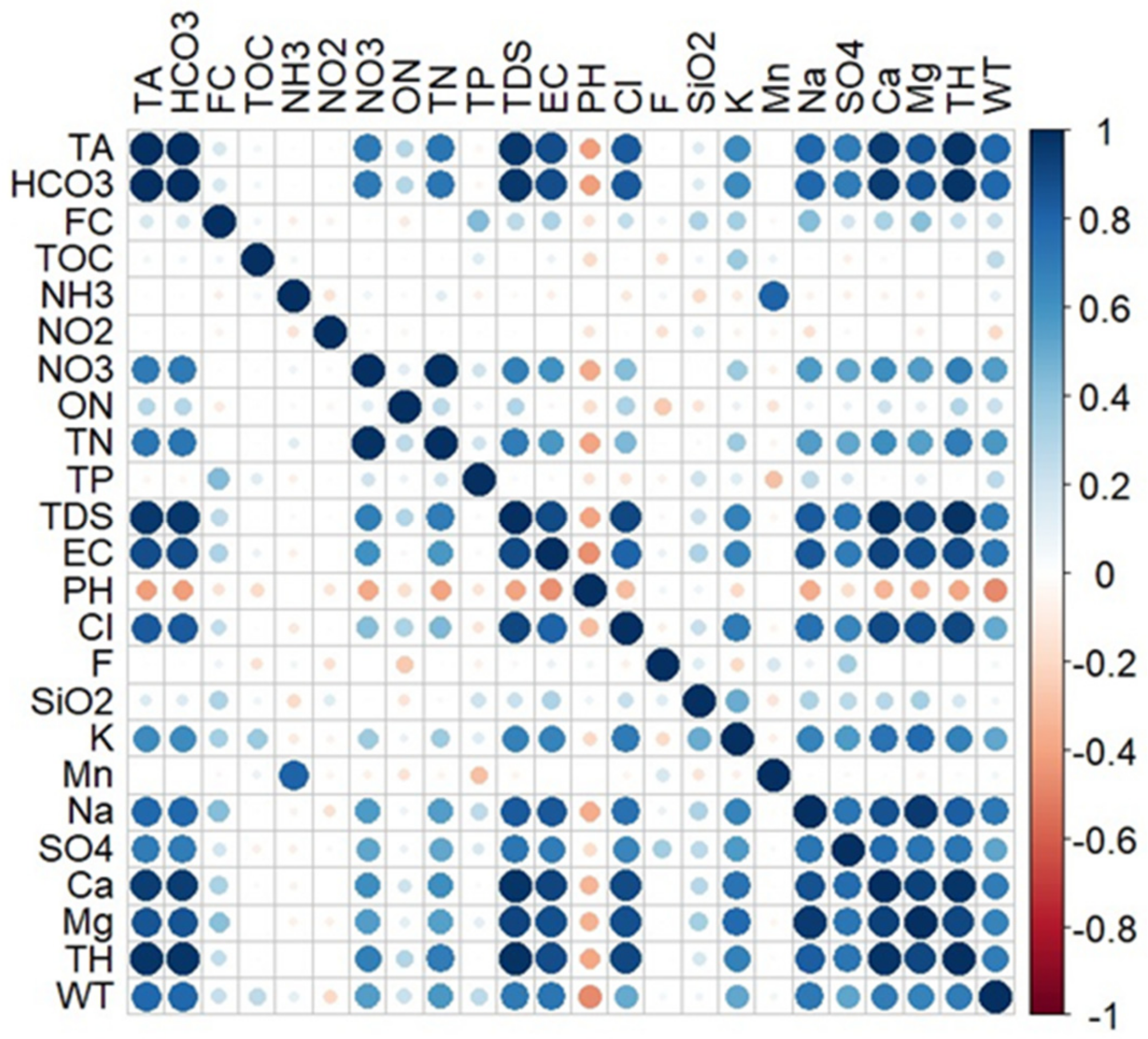
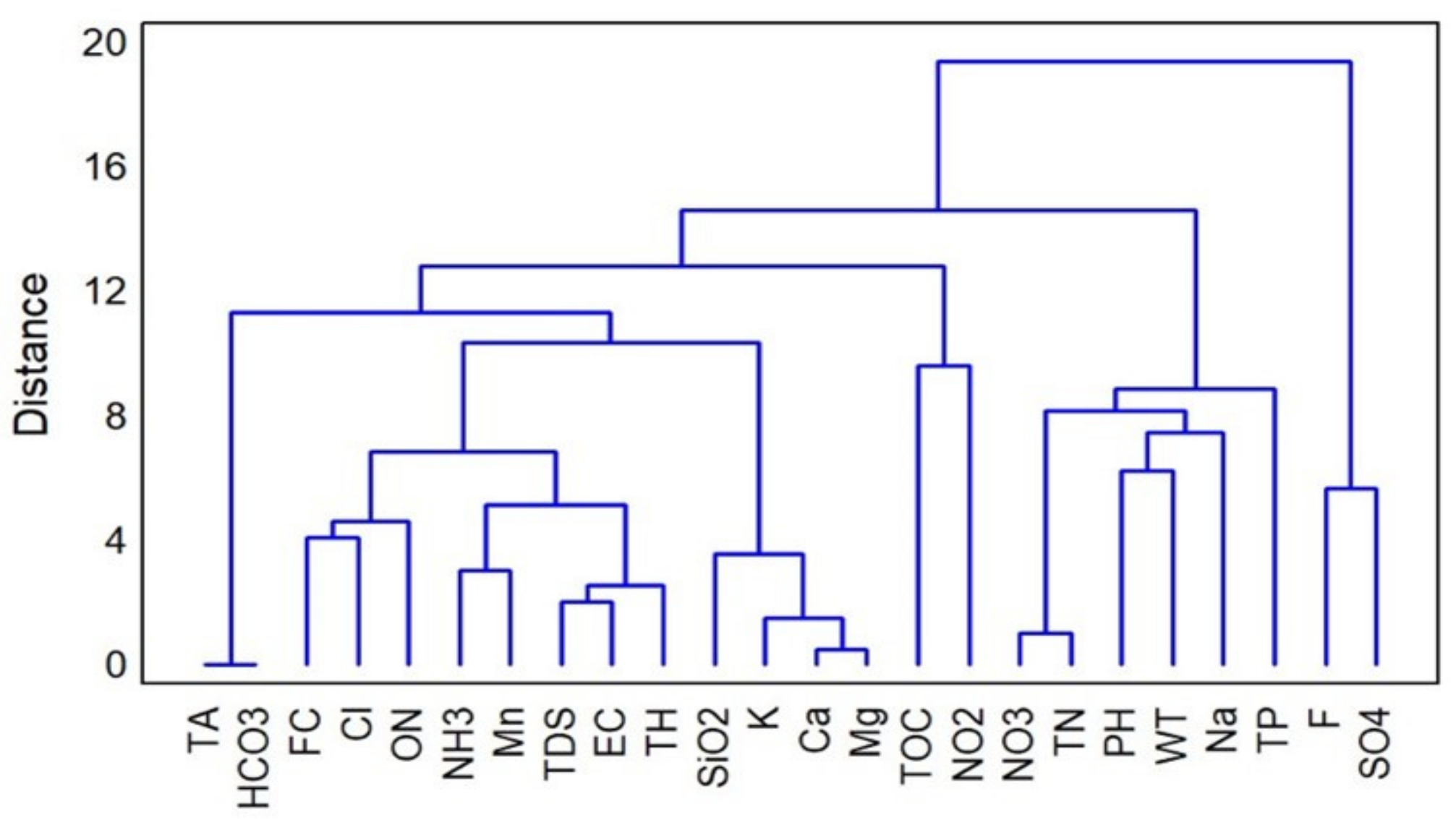
3.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
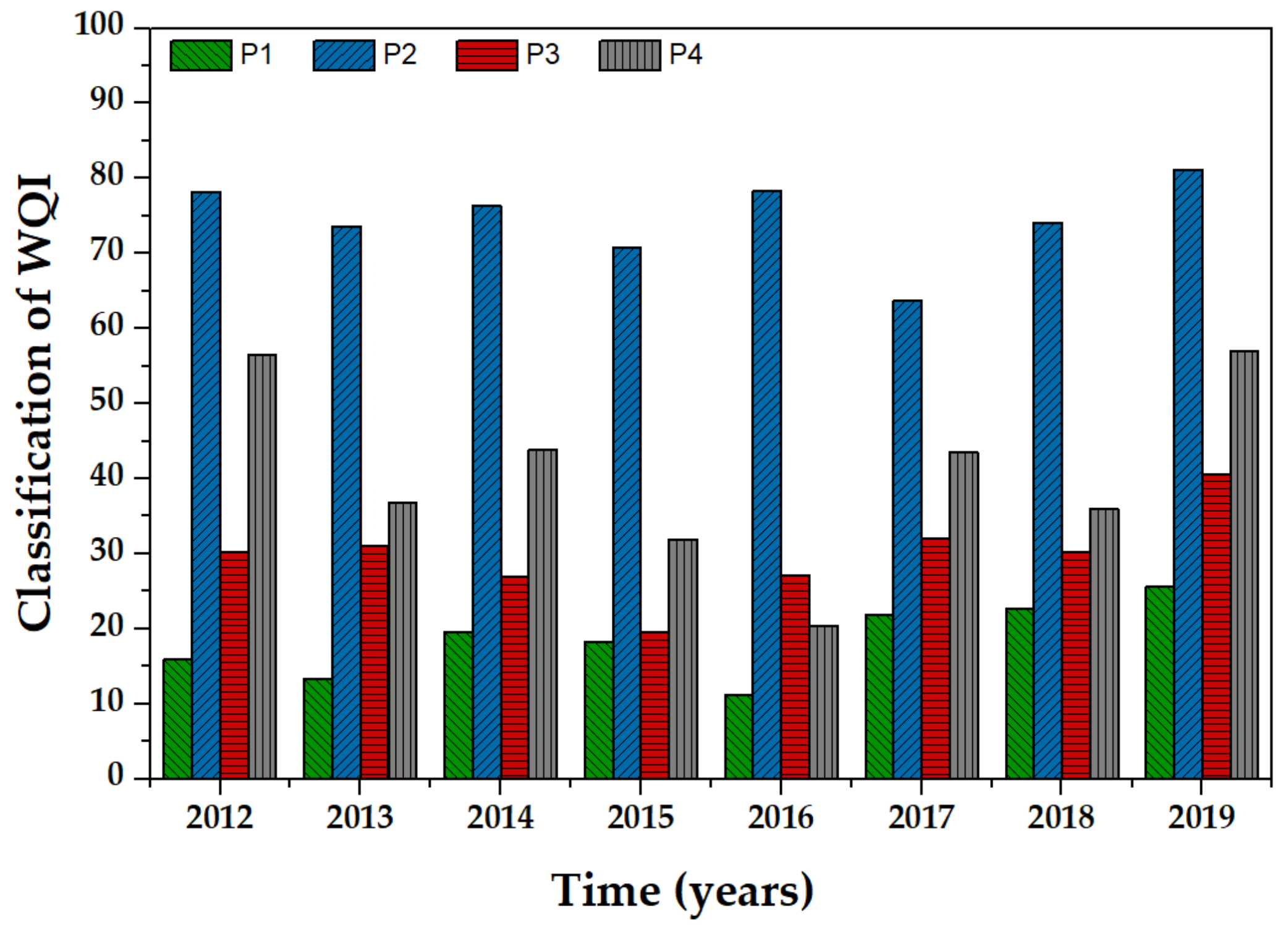
3.4. Drinking Water Quality Index
3.5. Hydrochemical Characteristics
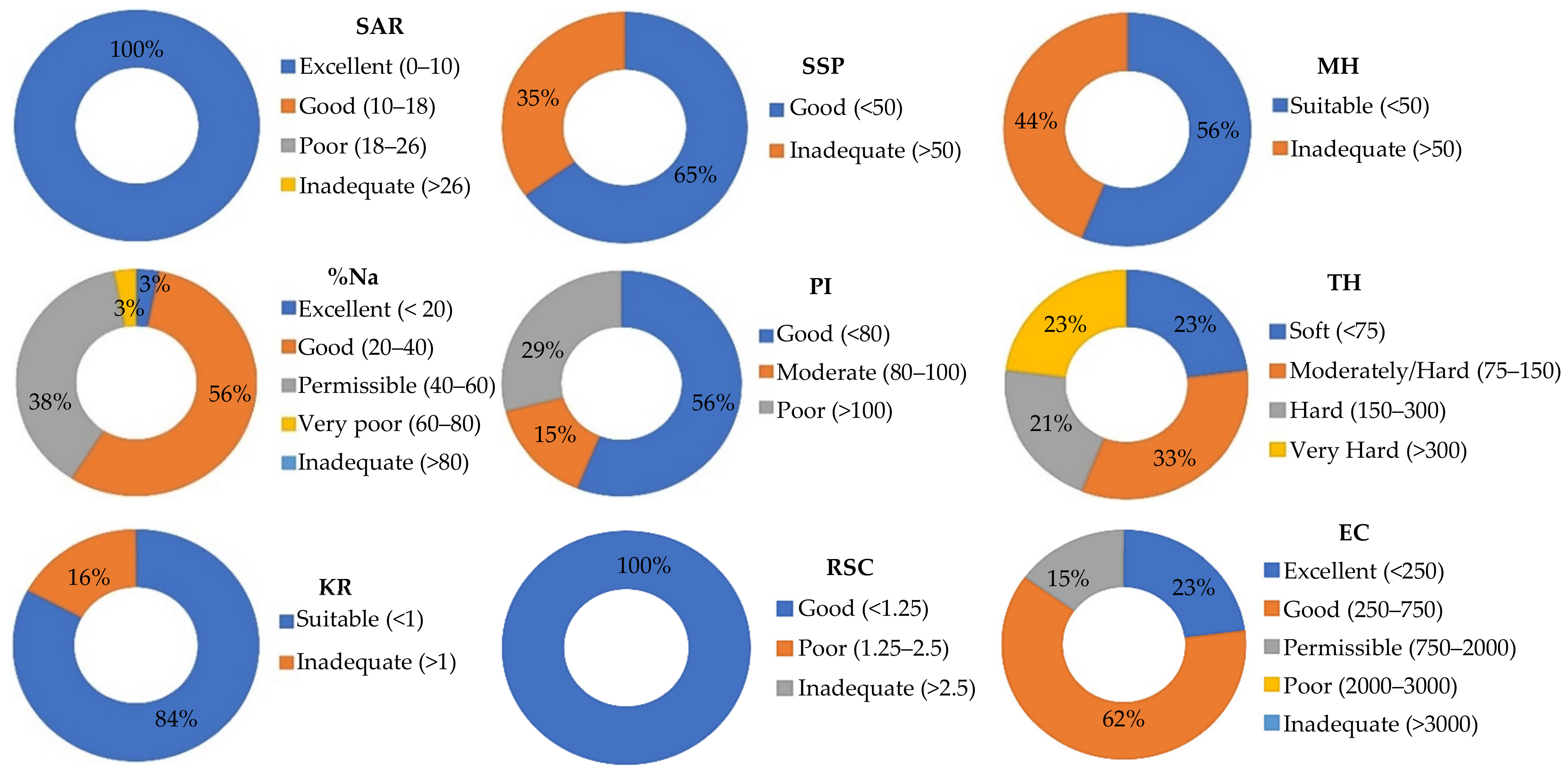
3.6. Groundwater Indices Based on Hydrochemical Features
4. Conclusions
- The hydrological and hydrochemical conditions of the Cuernavaca aquifer were evaluated through the application of water quality indices and statistical techniques. This study provides an approach to the spatial and temporal behavior of an urbanized aquifer and assesses its vulnerability due to population growth.
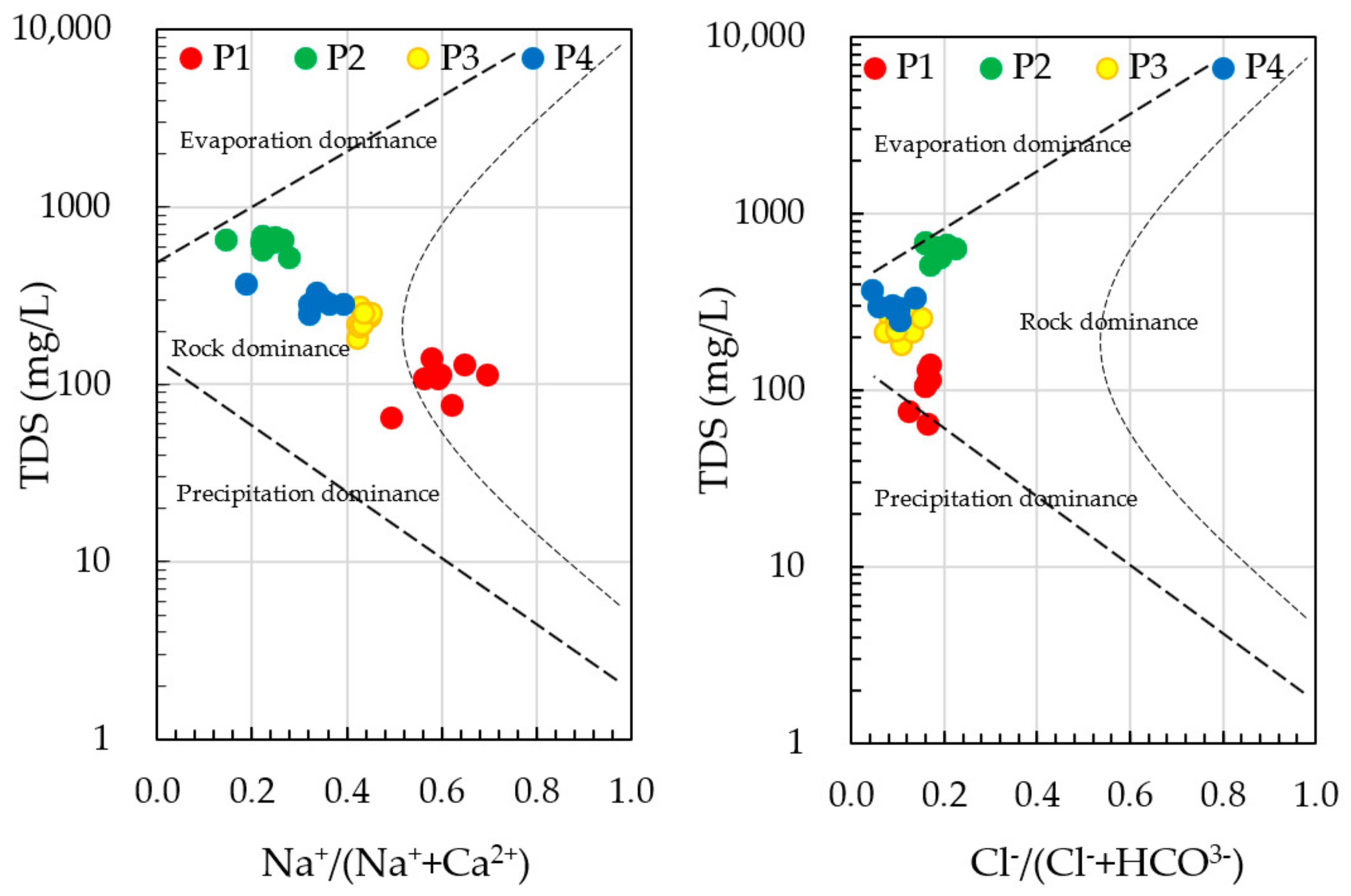
- This study identified spatial variations between the sampling sites and evidenced the influence of urbanization on groundwater chemistry and quality in the Cuernavaca aquifer. The spatial variation of the chemical elements highlights the vulnerability of the aquifer, especially at P2.
- The time series analysis demonstrated no trend, seasonal, or cyclic patterns in the groundwater quality data. The multivariate statistical analysis showed a high number of correlations between the groundwater parameters. These parameters were grouped based on hierarchical cluster analysis which revealed the main chemical processes controlling groundwater chemistry in the aquifer.
- Most of the parameters (physicochemical and ions) measured in the Cuernavaca aquifer were within the standards allowed by the WHO for irrigation purposes. This situation was confirmed by the water quality indexes since the groundwater of the aquifer was classified as good quality. However, the presence of fecal coliforms, organic matter, and the high content of ions such as Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− is an important situation that must be addressed to reduce the vulnerability of the aquifer.
- This study provides an approach to describe the behavior of the hydrochemical features and water quality of the Cuernavaca aquifer and points out the main driving factors for the deterioration of groundwater quality in an aquifer located in an urban area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Bindary, M.A.; El-Desouky, M.G.; El-Bindary, A.A. Adsorption of industrial dye from aqueous solutions onto thermally treated green adsorbent: A complete batch system evaluation. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 346, 117082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Shamir, E.; Cruz-Ayala, M.-B.; Megdal, S.B. Assessing Groundwater Withdrawal Sustainability in the Mexican Portion of the Transboundary Santa Cruz River Aquifer. Water 2022, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza, J.G.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Sanhouse-García, A.J.; Monjardín-Armenta, S.A.; Mora-Félix, Z.D.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.A. Assessment of Water Quality in A Tropical Reservoir in Mexico: Seasonal, Spatial and Multivariable Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, V.; Nethononda, V.G.; Manivannan, V.; Rajmohan, N.; Li, P.; Elango, L. Groundwater quality assessment and ap-plication of multivariate statistical analysis in Luvuvhu catchment, Limpopo, South Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 171, 103967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Moreau, C.; Bertrand, G.; Mahlknecht, J. Mapping salinization and trace element abundance (including As and other metalloids) in the groundwater of north-central Mexico using a double-clustering approach. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannenberg, M.; Ntona, M.M.; Busico, G.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Mitrakas, M.; Vargemezis, G.; Fikos, I.; Kazakis, N.; Voudouris, K. Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Regime Evaluation in Flamouria Basin in Edessa (Northern Greece). Environments 2020, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.; Lee, E.; An, H.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Kim, G.-B.; Ko, K.-S. Evaluation of Seasonal Groundwater Quality Changes Associated with Groundwater Pumping and Level Fluctuations in an Agricultural Area, Korea. Water 2020, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, M.; Chandola, V.K.; Kumar, V.; Saini, R.K.; Pant, N.; Kumari, N.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; et al. Groundwater Quality Issues and Challenges for Drinking and Irrigation Uses in Central Ganga Basin Dominated with Rice-Wheat Cropping System. Water 2021, 13, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, V.; Singh, O.; Singh, R.; Chhoden, K.; Kumar, J.; Yadav, S.; Singh, N.; Shrivastava, N.; Carvalho, L. Ecological health and water quality of village ponds in the subtropics limiting their use for water supply and groundwater recharge. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 277, 111450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuqan, N.; Haie, N.; Ahmad, M.T. Assessment of the Agricultural Water Use in Jericho Governorate Using Sefficiency. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, C.N.; Haque, M.; Jana, H.; Basu, D.; Karak, S. Socio Economic Factors Responsible for Groundwater Consumption in Purba Bardhaman District of West Bengal. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šperac, M.; Zima, J. Assessment of the Impact of Climate Extremes on the Groundwater of Eastern Croatia. Water 2022, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qi, S.; Wang, W. Groundwater Quality in Agricultural Lands Near a Rapidly Urbanized Area, South China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Y.S.A.; Akurugu, B.A.; Manu, E.; Aliou, A.S. Assessment of groundwater quality and the main controls on its hydro-chemistry in some Voltaian and basement aquifers, northern Ghana. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N.; Anornu, G.; Adomako, D.; Owusu-Nimo, F.; Gibrilla, A. Evolution of groundwater hydrogeochemistry and assessment of groundwater quality in the Anayari catchment. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 12, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisitthammasri, W.; Chotpantarat, S.; Thitimakorn, T. Multivariate statistical analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics of a volcano sedimentary aquifer in Saraburi Province, Thailand. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeenezhad, A.; Tabatabaee, H.R.; Nikbakht, H.-A.; Radfard, M.; Abbasnia, A.; Baghapour, M.A.; Alhamd, M. Estimation of the groundwater quality index and investigation of the affecting factors their changes in Shiraz drinking groundwater, Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). 2020. Available online: https://sigagis.conagua.gob.mx/gas1/Edos_Acuiferos_18/morelos/DR_1701.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). Estadísticas del Agua en México 2018. Available online: https://sina.conagua.gob.mx/publicaciones/EAM_2018.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2021).
- Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). Calidad del Agua en México. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conagua/articulos/calidad-del-agua (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, K.; Chao, L.; Liu, Z.; Du, Y.; Xu, Q. Quantifying natural recharge characteristics of shallow aquifers in groundwater overexploitation zone of North China. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartier, P.M.; Keller, C. Multivariate interpolation to incorporate thematic surface data using inverse distance weighting (IDW). Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baba, M.; Kayastha, P.; Huysmans, M.; De Smedt, F. Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine. Water 2020, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acharya, S.; Sharma, S.; Khandegar, V. Assessment of groundwater quality by water quality indices for irrigation and drinking in South West Delhi, India. Data Brief 2018, 18, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gabr, M.E.; Soussa, H.; Fattouh, E. Groundwater quality evaluation for drinking and irrigation uses in Dayrout city Upper Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 12, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikrishna, K.; Purushotham, D.; Sunitha, V.; Reddy, Y.S.; Linga, D.; Kumar, B.K. Data for the evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and regression analysis in parts of Nalgonda district, Telangana, Southern India. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, A.K.; Wassie, A.B.; Sinshaw, B.G.; Defersha, D.T.; Takele, T.A.; Atanaw, S.B.; Tesfaye, A.T.; Getu, E.; Fenta, H.M.; Atinkut, H.B.; et al. Groundwater quality evaluation of the alluvial aquifers using GIS and water quality indices in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.N.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Reza, A.S.; Khan, R.; Akbor, M.A.; Elius, I.B.; Hasan, M. Vulnerability assessment of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of southern Bangladesh: Water quality appraisals. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doza, B.; Islam, A.T.; Ahmed, F.; Das, S.; Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S. Characterization of groundwater quality using water evaluation indices, multivariate statistics and geostatistics in central Bangladesh. Water Sci. 2016, 30, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelaziz, S.; Gad, M.I.; El Tahan, A.H.M. Groundwater quality index based on PCA: Wadi El-Natrun, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 172, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, S.K.; Kadam, A.K.; Ramgir, R.R.; Kashikar, A.S.; Wagh, V.; Kandekar, A.M.; Gaikwad, S.P.; Madale, R.B.; Pawar, N.J.; Kamble, K.D. Assessment of the groundwater geochemistry from a part of west coast of India using statistical methods and water quality index. HydroResearch 2020, 3, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Yousefi, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Radfard, M.; Yousefi, M.; Alimohammadi, M. Evaluation of ground-water quality using water quality index and its suitability for assessing water for drinking and irrigation purposes: Case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Patra, P.K.; Begum, S.N.; Rahaman, C.H. Spatial and sensitivity analysis of integrated groundwater quality index towards irrigational suitability investigation. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaa, H.; El Achheb, A.; Namr, K.I. Spatial variation of groundwater quality and assessment of water table fluctuations in Plio-Quaternary aquifer formations in Doukkala Plain, Morocco. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigui, M.R.; Trabelsi, R.; Zouari, K.; Agoun, A. Implication of hydrogeological and hydrodynamic setting on water quality of the Complex Terminal Aquifer in Kebili (southern Tunisia): The use of geochemical indicators and modelling. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 176, 104121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, R.; Lv, Z. Chemical characteristics of groundwater and source identification in a coastal city. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Khurshid, S.; Madan, R.; Abu Amarah, B.A.; Naushad, M. Water quality assessment of shallow aquifer based on Canadian Council of Ministers of the environment index and its impact on irrigation of Mathura District, Uttar Pradesh. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.M.; Behera, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Biswal, T.K. Recharge and Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater in Fractured Basement Aquifers (NW India): Insights from Environmental Isotopes (δ18O, δ2H, and 3H) and Hydrogeochemical Studies. Water 2022, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjderem, B.; Torres-Martínez, J.; Mahlknecht, J. Intensive long-term pumping in the Principal-Lagunera Region aquifer (Mexico) causing heavy impact on groundwater quality. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, G.O.; Akinyemi, O.D.; Gbadebo, A.M.; Oyedepo, J.A. Hydrochemical analysis of groundwater quality along the coastal aquifers in part of Ogun Waterside, Ogun State, southwestern Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragon, K. Identification of groundwater conditions in the recharge zone of regionally extended aquifer system with use of water chemistry and isotopes (Lwowek region, Poland). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 34, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotalib, A.Z.; Heggy, E.; El Bastawesy, M.; Ismail, E.; Gad, A.; Attwa, M. Groundwater mounding: A diagnostic feature for mapping aquifer connectivity in hyper-arid deserts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Li, P. Entropy water quality index and probabilistic health risk assessment from geochemistry of groundwaters in hard rock terrain of Nanganur County, South India. Geochemistry 2019, 80, 125544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Moghanm, F.; Almarshadi, M.; Alshammari, A.; Khedher, K.; Eid, E.; Hussein, H. Combining Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling to Assess Surface Water Quality in the Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeshani, W.; Dissanayake, H.; Gunatilake, S.; Chandrajith, R. Assessment of groundwater quality using water quality index (WQI): A case study of a hard rock terrain in Sri Lanka. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutmez, B.; Hatipoglu, Z.; Kaymak, U. Modelling electrical conductivity of groundwater using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lü, X.; Han, Z.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J. Influence of Urbanization on Groundwater Chemistry at Lanzhou Valley Basin in China. Minerals 2022, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

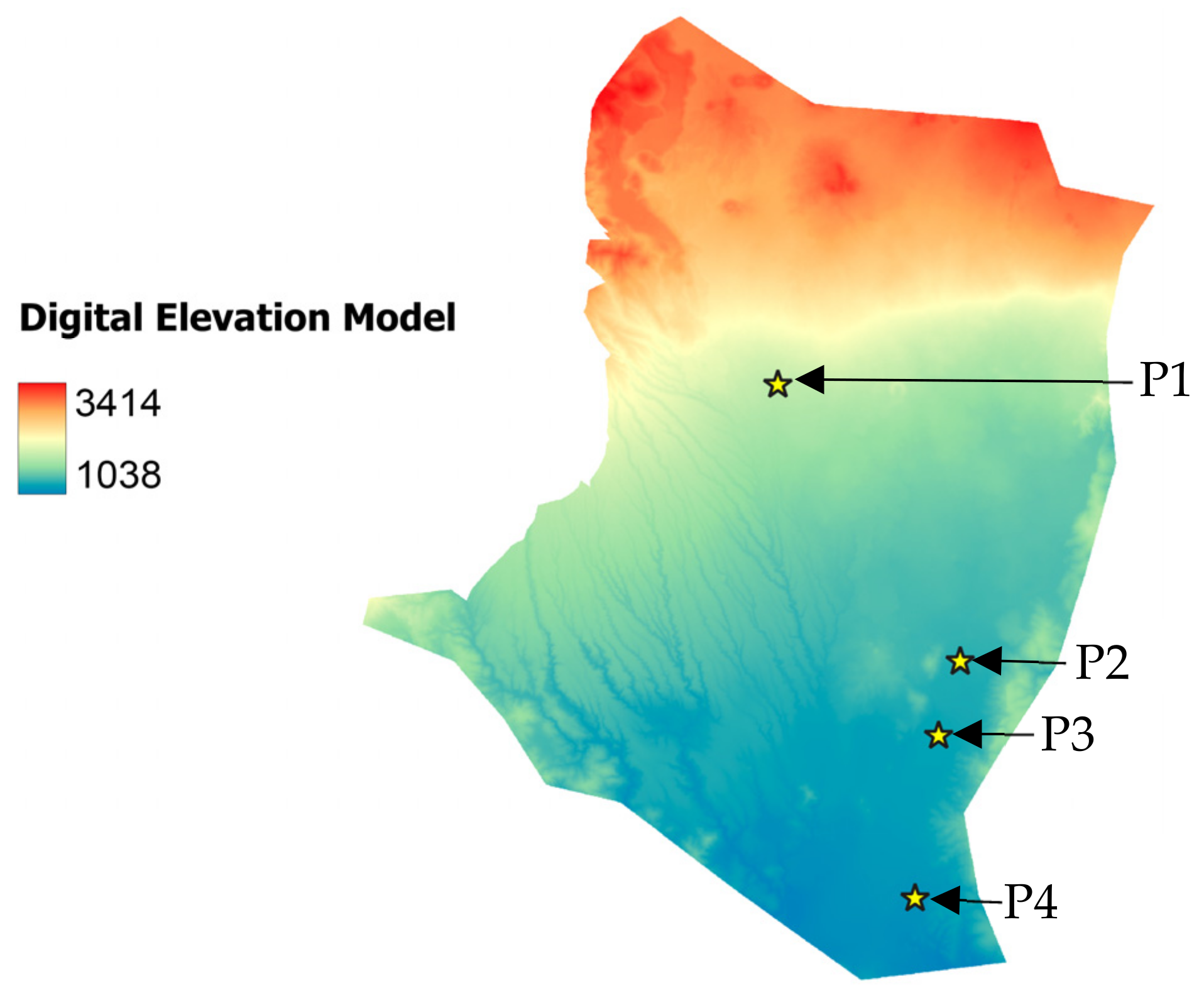

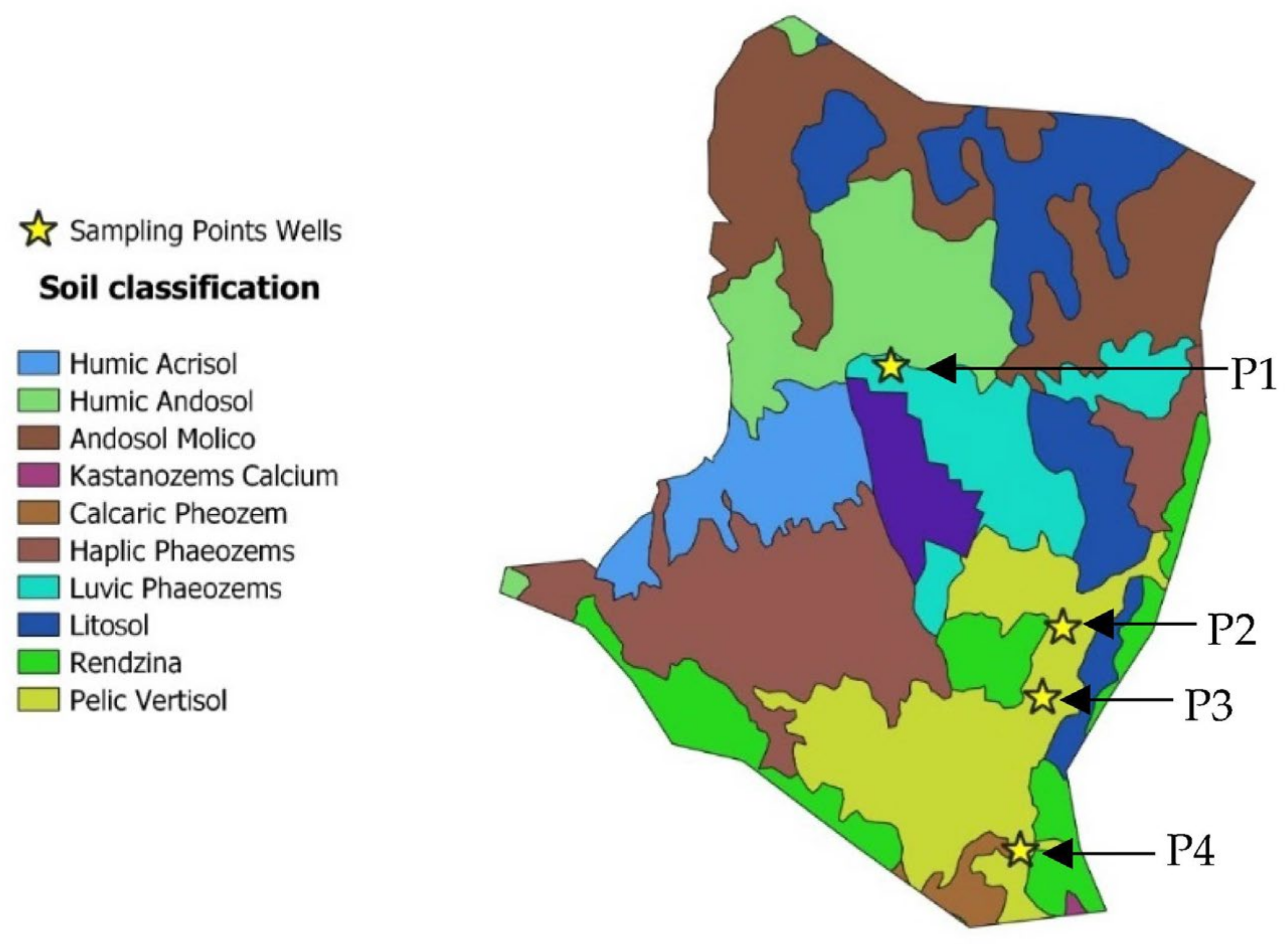
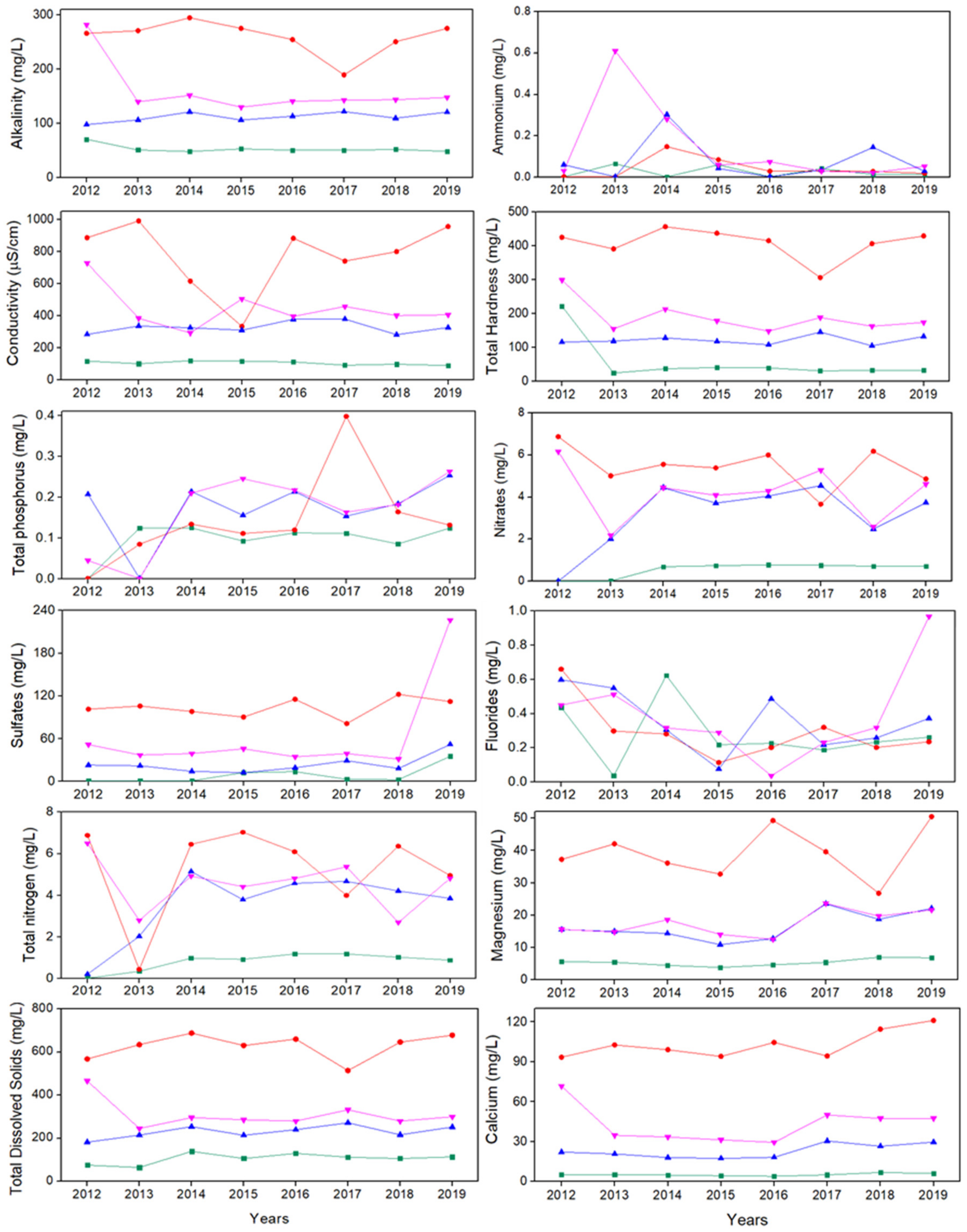
 ), P2 (
), P2 ( ), P3 (
), P3 ( ) y P4 (
) y P4 ( ).
).
 ), P2 (
), P2 ( ), P3 (
), P3 ( ) y P4 (
) y P4 ( ).
).
| Indices | Acronym | Equation | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium adsorption ratio | SAR | Abdelaziz et al. [34] | |
| Soluble sodium percentage | SSP | Tefera et al. [31] | |
| Sodium percentage | %Na | Abbasnia et al. [36] | |
| Residual Sodium Carbonate | RSC | Zakaria et al. [16] | |
| Magnesium Hazard | MH | Hossain et al. [37] | |
| Permeability index | PI | Kumar et al. [8] | |
| Kelly Ratio | KR | Acharia et al. [27] | |
| Total Hardness | TH | TH = (Ca + Mg) ∗ 50 | Tefera et al. [31] |
| Parameters | Abbreviation | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicarbonates (mg/L) | HCO3− | 48.40 | 294.90 | 145.12 | 79.75 |
| Fecal coliforms (MPN/100 mL) | FC | 1.00 | 2909.00 | 276.62 | 719.15 |
| Total organic carbon (mg/L) | TOC | 0.08 | 2.87 | 0.92 | 0.72 |
| Ammonium (mg/L) | NH3 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| Nitrites (mg/L) | NO2− | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Nitrates (mg/L) | NO3− | 0.00 | 6.87 | 3.24 | 2.13 |
| Organic Nitrogen (mg/L) | ON | 0.00 | 1.55 | 0.24 | 0.29 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | TN | 0.01 | 7.03 | 3.56 | 2.20 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | TP | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| Total dissolved solids (mg/L) | TDS | 64.64 | 688.00 | 316.01 | 195.16 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) | EC | 90.00 | 991.00 | 409.79 | 266.25 |
| pH | PH | 6.20 | 8.40 | 7.29 | 0.45 |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | Cl− | 8.44 | 78.25 | 23.89 | 20.62 |
| Fluorides (mg/L) | F | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.32 | 0.19 |
| Silicon oxides (mg/L) | SiO2 | 30.42 | 91.29 | 67.10 | 13.56 |
| Potassium (mg/L) | K+ | 1.32 | 7.72 | 3.68 | 1.60 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | Mn | 0.00 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.08 |
| Sodium (mg/L) | Na+ | 1.92 | 40.01 | 18.59 | 9.43 |
| Sulfates (mg/L) | SO42− | 0.82 | 226.38 | 48.41 | 49.98 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | Ca2+ | 3.87 | 121.10 | 41.93 | 37.57 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | Mg2+ | 3.82 | 50.47 | 19.25 | 13.07 |
| Total hardness (mg/L) | TH | 24.60 | 456.80 | 184.46 | 141.14 |
| Water temperature (°C) | WT | 17.25 | 22.49 | 20.24 | 21.68 |
| Parameter | Site (Spatial) | Year (Temporal) |
|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | |
| Bicarbonates (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.7058 |
| Fecal coliforms NMP/100 mL | 0.2229 | 0.8342 |
| Total organic carbon (mg/L) | 0.3044 | 0.1937 |
| Ammonium (mg/L) | 0.3219 | 0.4469 |
| Nitrites (mg/L) | 0.7001 | 0.4622 |
| Nitrates (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.0911 |
| Organic Nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.1192 | 0.1272 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.1061 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 0.2540 | 0.0283 |
| Total dissolved solids (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.5686 |
| Electrical conductivity µS/cm | 0.0000 * | 0.4360 |
| pH | 0.0002 * | 0.0034 |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.4176 |
| Fluorides (mg/L) | 0.3992 | 0.0844 |
| Silicon oxides (mg/L) | 0.0315 * | 0.0001 * |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 0.0001 * | 0.2912 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | 0.5720 | 0.8024 |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.0143 * |
| Sulfates (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.0134 * |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.2466 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.0058 * |
| Total hardness (mg/L) | 0.0000 * | 0.3337 |
| Water temperature °C | 0.0000 * | 0.8973 |
| DWQI | Classification of Water | Samples | % of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| <50 | Excellent water | 24 | 70.5 |
| 50–100 | Good water | 10 | 29.5 |
| 100–200 | Poor water | 0 | 0 |
| 200–300 | Very poor water | 0 | 0 |
| >300 | Unsuitable for drinking | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loaiza, J.G.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Monjardín-Armenta, S.A.; Quevedo-Castro, A.; Estrada-Vazquez, R.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G. Evaluation of the Hydrochemical and Water Quality Characteristics of an Aquifer Located in an Urbanized Area. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12146879
Loaiza JG, Bustos-Terrones Y, Bustos-Terrones V, Monjardín-Armenta SA, Quevedo-Castro A, Estrada-Vazquez R, Rangel-Peraza JG. Evaluation of the Hydrochemical and Water Quality Characteristics of an Aquifer Located in an Urbanized Area. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(14):6879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12146879
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoaiza, Juan G., Yaneth Bustos-Terrones, Victoria Bustos-Terrones, Sergio Alberto Monjardín-Armenta, Alberto Quevedo-Castro, Rogelio Estrada-Vazquez, and Jesús Gabriel Rangel-Peraza. 2022. "Evaluation of the Hydrochemical and Water Quality Characteristics of an Aquifer Located in an Urbanized Area" Applied Sciences 12, no. 14: 6879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12146879
APA StyleLoaiza, J. G., Bustos-Terrones, Y., Bustos-Terrones, V., Monjardín-Armenta, S. A., Quevedo-Castro, A., Estrada-Vazquez, R., & Rangel-Peraza, J. G. (2022). Evaluation of the Hydrochemical and Water Quality Characteristics of an Aquifer Located in an Urbanized Area. Applied Sciences, 12(14), 6879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12146879









