Protozoa as the “Underdogs” for Microbiological Quality Evaluation of Fresh Vegetables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
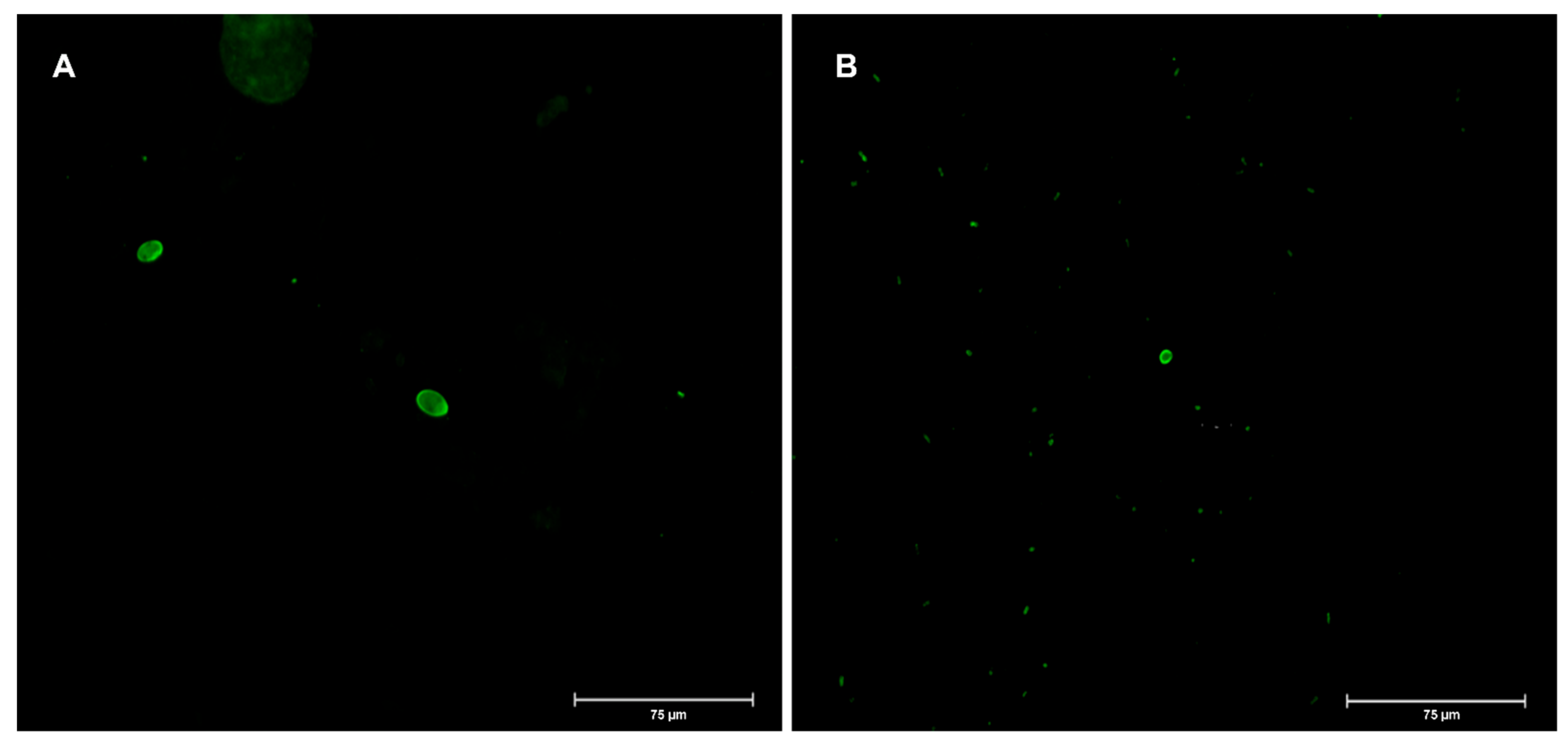
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Fact Sheet N_237, Food Safety and Foodborne Illness. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Wolf, J.; Corvalán, C.; Neville, T.; Bos, R.; Neira, M. Diseases due to unhealthy environments: An updated estimate of the global burden of disease attributable to environmental determinants of health. J. Public Health 2016, 39, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losio, M.; Pavoni, E.; Bilei, S.; Bertasi, B.; Bove, D.; Capuano, F.; Farneti, S.; Blasi, G.; Comin, D.; Cardamone, C.; et al. Microbiological survey of raw and ready-to-eat leafy green vegetables marketed in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 210, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macieira, A.; Barbosa, J.; Teixeira, P. Food Safety in Local Farming of Fruits and Vegetables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B. Transmission dynamics of foodborne parasites on fresh produce. In Foodborne Parasites in the Food Supply Web, Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Gajadhar, A.A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2015; Chapter 13; pp. 317–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKerr, C.; Adak, G.K.; Nichols, G.; Gorton, R.; Chalmers, R.M.; Kafatos, G.; Cosford, P.; Charlett, A.; Reacher, M.; Pollock, K.G.; et al. An Outbreak of Cryptosporidium parvum across England & Scotland Associated with Consumption of Fresh Pre-Cut Salad Leaves, May 2012. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, L.A.; Nogareda, F.; Weill, F.-X.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Loukiadis, E.; Gault, G.; Jourdan-DaSilva, N.; Bingen, E.; Macé, M.; Thevenot, D.; et al. Outbreak of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 Associated With Organic Fenugreek Sprouts, France, June 2011. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willis, C.; McLauchlin, J.; Aird, H.; Amar, C.; Barker, C.; Dallman, T.; Elviss, N.; Lai, S.; Sadler-Reeves, L. Occurrence of Listeria and Escherichia coli in frozen fruit and vegetables collected from retail and catering premises in England 2018–2019. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 334, 108849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.; Hijjawi, N.; Xiao, L. Foodborne cryptosporidiosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto-Ferreira, F.; Caldart, E.T.; Pasquali, A.K.S.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Freire, R.L.; Navarro, I.T. Patterns of Transmission and Sources of Infection in Outbreaks of Human Toxoplasmosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlinder, J.; Svedberg, A.-L.; Nystedt, A.; Dryselius, R.; Jacobsson, K.; Hägglund, M.; Brindefalk, B.; Forsman, M.; Ottoson, J.; Troell, K. Use of metagenomic microbial source tracking to investigate the source of a foodborne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2021, 26, e00142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjilouka, A.; Tsaltas, D. Cyclospora Cayetanensis—Major Outbreaks from Ready to Eat Fresh Fruits and Vegetables. Foods 2020, 9, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reh, L.; Muadica, A.S.; Köster, P.C.; Balasegaram, S.; Verlander, N.Q.; Chércoles, E.R.; Carmena, D. Substantial prevalence of enteroparasites Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis and Blastocystis sp. in asymptomatic schoolchildren in Madrid, Spain, November 2017 to June 2018. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, L.J.; Lalle, M.; Paulsen, P. Why we need a European focus on foodborne parasites. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 214, 107900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ). Compendium of Microbiological Criteria for Food. Available online: https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/publications/Documents/Compedium%20of%20Microbiological%20Criteria/Compendium_revised-jan-2018.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- NSW Food Authority. Microbiological Quality of Fresh Cut Vegetables—A Survey to Determine the Safety of Fresh Cut Leafy Salad Vegetables Sold in NSW. Available online: https://www.foodauthority.nsw.gov.au/sites/default/files/_Documents/scienceandtechnical/microbiological_quality_fresh_cut_vegetables.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No. 1441/2007 of 5 December 2007 Amending Regulation (EC) No. 2073/2005 on Micro-Biological Criteria for Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32007R1441&from=EN (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDPC). The European Union One Health 2019 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorny, P.; Praet, N.; Deckers, N.; Gabriel, S. Emerging food-borne parasites. Veter. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Macpherson, C.N. The socioeconomic burden of parasitic zoonoses: Global trends. Veter. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slifko, T.R.; Smith, H.V.; Rose, J.B. Emerging parasite zoonoses associated with water and food. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Outbreaks of clinical toxoplasmosis in humans: Five decades of personal experience, perspectives and lessons learned. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Zoonotic Potential and Molecular Epidemiology of Giardia Species and Giardiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 110–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, B.R. Giardia duodenalis in humans and animals—Transmission and disease. Res. Veter. Sci. 2020, 135, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.; Kintz, E.; Hunter, P. Risk factors for Cryptosporidium infection in low and middle income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Villena, I. Congenital toxoplasmosis in humans: An update of worldwide rate of congenital infections. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, L.S.; Gajadhar, A.A. Cyclospora cayetanensis, a food- and waterborne coccidian parasite. Veter. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathison, B.A.; Pritt, B.S. Cyclosporiasis—Updates on Clinical Presentation, Pathology, Clinical Diagnosis, and Treatment. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, D. Foodborne protozoan parasites. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 103, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, A.; La Carbona, S.; Dumètre, A.; Robertson, L.J.; Gargala, G.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Favennec, L.; Villena, I.; Gérard, C.; Aubert, D. Assessing viability and infectivity of foodborne and waterborne stages (cysts/oocysts) of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and Toxoplasma gondii: A review of methods. Parasite 2018, 25, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirza Alizadeh, A.; Jazaeri, S.; Shemshadi, B.; Hashempour-Baltork, F.; Sarlak, Z.; Pilevar, Z.; Hosseini, H. A review on inactivation methods of Toxoplasma gondii in foods. Pathog. Glob. Health 2018, 112, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumètre, A.; Le Bras, C.; Baffet, M.; Meneceur, P.; Dubey, J.; Derouin, F.; Duguet, J.-P.; Joyeux, M.; Moulin, L. Effects of ozone and ultraviolet radiation treatments on the infectivity of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Veter. Parasitol. 2008, 153, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, M.F.; Sancho, A.N.; Mendoza, L.M.; Mota, C.R.; Verbyla, M.E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of time-temperature pathogen inactivation. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 230, 113595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, F.E.; Singh, G.; Reddy, P.; Bux, F.; Stenström, T.A. Efficiency of chlorine and UV in the inactivation of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in wastewater. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.C.; Ortega, Y.R. Inactivation of Protozoan Parasites in Food, Water, and Environmental Systems. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2786–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajadhar, A.; Scandrett, W.B.; Forbes, L.B. Overview of food- and water-borne zoonotic parasites at the farm level. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2006, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, T.; Tysnes, K.R.; Utaaker, K.S.; Robertson, L.J. Parasite contamination of berries: Risk, occurrence, and approaches for mitigation. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2018, 10, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, C.N.; Sodha, S.V.; Shaw, R.K.; Griffin, P.M.; Pink, D.; Hand, P.; Frankel, G. Fresh fruit and vegetables as vehicles for the transmission of human pathogens. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Moreira, B.; Richards, K.; Brennan, F.; Abram, F.; Burgess, C.M. Microbial Contamination of Fresh Produce: What, Where, and How? Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1727–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, C.; Sousa, S.; Castro, A.; Da Costa, J.M.C. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in fresh vegetables and berry fruits. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 180–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 1623.1: Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Water by Filtra-Tion/IMS/FA. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P100J7G4.PDF?Dockey=P100J7G4.PDF (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Almeida, A.; Moreira, M.J.; Soares, S.; Delgado, M.D.L.; Figueiredo, J.; Silva, E.; Castro, A.; Da Cosa, J.M.C. Presence of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in Drinking Water Samples in the North of Portugal. Korean J. Parasitol. 2010, 48, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, S.; Almeida, A.; Delgado, L.; Conceição, A.; Marques, C.; Da Costa, J.M.C.; Castro, A. rTgOWP1-f, a specific biomarker for Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Moreira, M.J.; Soares, S.; Delgado, M.D.L.; Figueiredo, J.; Magalhães, E.S.; Castro, A.; Da Costa, A.V.; Da Costa, J.M.C. Biological and Genetic Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis Isolates from Five Hydrographical Basins in Northern Portugal. Korean J. Parasitol. 2010, 48, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendonça, C.; Almeida, A.; Castro, A.; Delgado, M.D.L.; Soares, S.; da Costa, J.M.C.; Canada, N. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium and Giardia isolates from cattle from Portugal. Veter. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.A.; Delgado, M.L.; Soares, S.C.; Castro, A.O.; Moreira, M.J.; Mendonça, C.M.; Canada, N.B.; Da Costa, J.M.C. Genotype Analysis of Giardia Isolated from Asymptomatic Children in Northern Portugal. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, S177–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.A.; Delgado, M.L.; Soares, S.C.; Castro, A.O.; Moreira, M.J.; Mendonça, C.M.; Canada, N.B.; Da Costa, J.M.C.; Coelho, H.G. Genetic Characterization of Cryptosporidium Isolates from Humans in Northern Portugal. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, S26–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Singh, A.; Limor, J.; Graczyk, T.K.; Gradus, S.; Lal, A. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium Oocysts in Samples of Raw Surface Water and Wastewater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cacciò, S.M.; De Giacomo, M.; Pozio, E. Sequence analysis of the β-giardin gene and development of a polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism assay to genotype Giardiaduodenalis cysts from human faecal samples. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4833; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 16140-2:2016; Microbiology of the food chain—Method validation—Part 2: Protocol for the validation of alternative (proprietary) methods against a reference method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 21528-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain-Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 16649-2; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Beta-Glucuronidase-Positive Escherichia coli—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique at 44 °C Using 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl beta-D-glucuronide. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- ISO 11290-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria Monocytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 2: Enumeration Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 21527-1; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Moulds—Part 1: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Greater Than 0.95. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 11290-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria Monocytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 6579-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Berrouch, S.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Harrak, R.; Huguenin, A.; Flori, P.; Favennec, L.; Villena, I.; Hafid, J.; Salma, B.; Sandie, E.-B.; et al. Detection methods and prevalence of transmission stages of Toxoplasma gondii, Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in fresh vegetables: A review. Parasitology 2020, 147, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, C.; Torgerson, P.R.; Robertson, L.J. Foodborne Parasites in Europe: Present Status and Future Trends. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caradonna, T.; Marangi, M.; Del Chierico, F.; Ferrari, N.; Reddel, S.; Bracaglia, G.; Normanno, G.; Putignani, L.; Giangaspero, A. Detection and prevalence of protozoan parasites in ready-to-eat packaged salads on sale in Italy. Food Microbiol. 2017, 67, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaaker, K.S.; Skjerve, E.; Robertson, L.J. Keeping it cool: Survival of Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts on lettuce leaves. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 255, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhu, M. Practical in-storage interventions to control foodborne pathogens on fresh produce. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4584–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Lopes, F.; Costa, R.; Komora, N.; Ferreira, V.; Fernandes, V.C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Teixeira, P. Microbiological and Chemical Quality of Portuguese Lettuce—Results of a Case Study. Foods 2020, 9, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, J.D.A.F.F.; Maffei, D.F.; Dias, M.; Mendes, M.A.; Pinto, U.M. Microbiological quality and safety of minimally processed parsley (Petroselinum crispum) sold in food markets, southeastern Brazil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 131, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yamamoto, E.; Murphy, J.; Locas, A. Microbiological safety of ready-to-eat fresh-cut fruits and vegetables sold on the Canadian retail market. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 335, 108855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food Safety Authority of Ireland. Guidelines for the Interpretation of Results of Microbiological Testing of Ready-to-Eat Foods Placed on the Market (Revision 4); FSAI: Dublin, Ireland, 2020; p. 50. ISBN 0-9539183-5-1. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, M.; Correia, C.B.; Cunha, I.C.; Maia, C.; Bonito, C.C.; Furtado, R.; Calhau, M.A. Interpretação dos resultados de ensaios microbiológicos em alimentos prontos para consumo e em superfícies do ambiente de produção e distribuição alimentar: Valores-guia. Repositório Científico do Instituto Nacional de Saúde Dr. Ricardo Jorge 2019. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.18/5610 (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Morrison, C.M.; Hogard, S.; Pearce, R.; Gerrity, D.; von Gunten, U.; Wert, E.C. Ozone disinfection of waterborne pathogens and their surrogates: A critical review. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Number | Product | Origin | Collection Date | Product Presentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Watercress | Portugal | 27 September 2018 | bulk |
| 2 | Coriander | Portugal | 27 September 2018 | bulk |
| 3 | Parsley | Portugal | 27 September 2018 | bulk |
| 4 | Watercress | Portugal | 2 October 2018 | RTE |
| 5 | Mixed salad | Portugal | 2 October 2018 | RTE |
| 6 | Coriander | Portugal | 2 October 2018 | packaged |
| 7 | Parsley | Portugal | 2 October 2018 | packaged |
| 8 | Watercress | Portugal | 12 October 2018 | RTE |
| 9 | Mixed salad | Portugal | 12 October 2018 | RTE |
| 10 | Coriander | Portugal | 12 October 2018 | packaged |
| 11 | Parsley | Portugal | 12 October 2018 | packaged |
| 12 | Mixed salad | Portugal | 4 February 2019 | RTE |
| 13 | Mixed salad | Spain | 17 June 2019 | RTE |
| 14 | Mixed salad | Spain | 17 June 2019 | RTE |
| 15 | Arugula | Spain | 17 June 2019 | RTE |
| 16 | Lettuce | Portugal | 18 June 2019 | bulk |
| Sample | Product | Product Presentation | No. Cysts Giardia | PCR Giardia | No. (oo)cysts Cryptosporidium | PCR Cryptosporidium | Genotyping (Assemblage) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Coriander | bulk | 2 | Negative | 0 | n.a. | n.a. | ||
| 8 | Watercress | RTE | 1 | Positive | 0 | n.a. | A | ||
| 9 | Mixed salad | RTE | 1 | Positive | 0 | n.a. | A | ||
| 12 | Mixed salad | RTE | 4 | Positive | 8 | Negative | A | ||
| 13 | Mixed salad | RTE | 0 | n.a. | 1 | Negative | n.a. | ||
| 15 | Arugula | RTE | 0 | n.a. | 1 | Negative | n.a. | LMO | LMO, detection |
| 16 | Lettuce | bulk | 0 | n.a. | 2 | Negative | n.a. | Present < 4.0 × 101 | Positive in 25 g |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, C.S.; Sousa, S.; Castro, A.; Ferreira, V.; Teixeira, P.; da Costa, J.M.C. Protozoa as the “Underdogs” for Microbiological Quality Evaluation of Fresh Vegetables. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147145
Marques CS, Sousa S, Castro A, Ferreira V, Teixeira P, da Costa JMC. Protozoa as the “Underdogs” for Microbiological Quality Evaluation of Fresh Vegetables. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(14):7145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147145
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Cláudia S., Susana Sousa, António Castro, Vânia Ferreira, Paula Teixeira, and José M. Correia da Costa. 2022. "Protozoa as the “Underdogs” for Microbiological Quality Evaluation of Fresh Vegetables" Applied Sciences 12, no. 14: 7145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147145
APA StyleMarques, C. S., Sousa, S., Castro, A., Ferreira, V., Teixeira, P., & da Costa, J. M. C. (2022). Protozoa as the “Underdogs” for Microbiological Quality Evaluation of Fresh Vegetables. Applied Sciences, 12(14), 7145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147145






