Equivalent Dynamic Analysis of a Cable-Driven Snake Arm Maintainer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
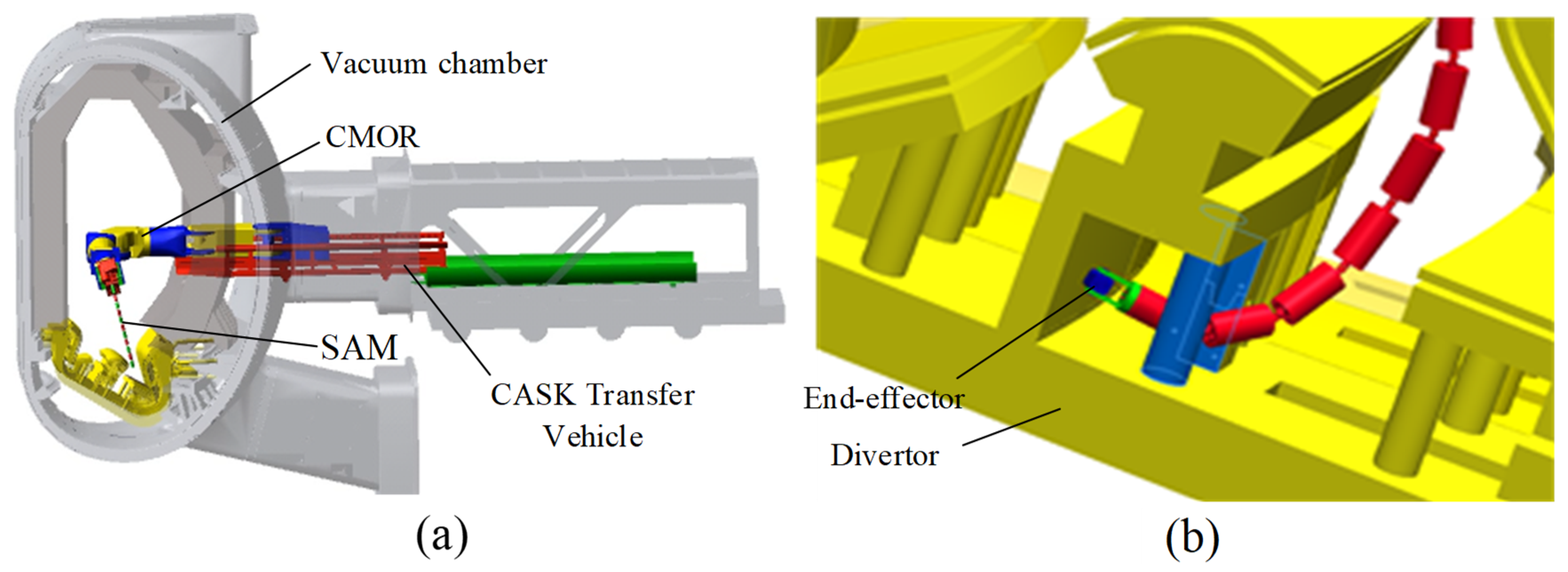
2.1. Underactuated SAM Platform
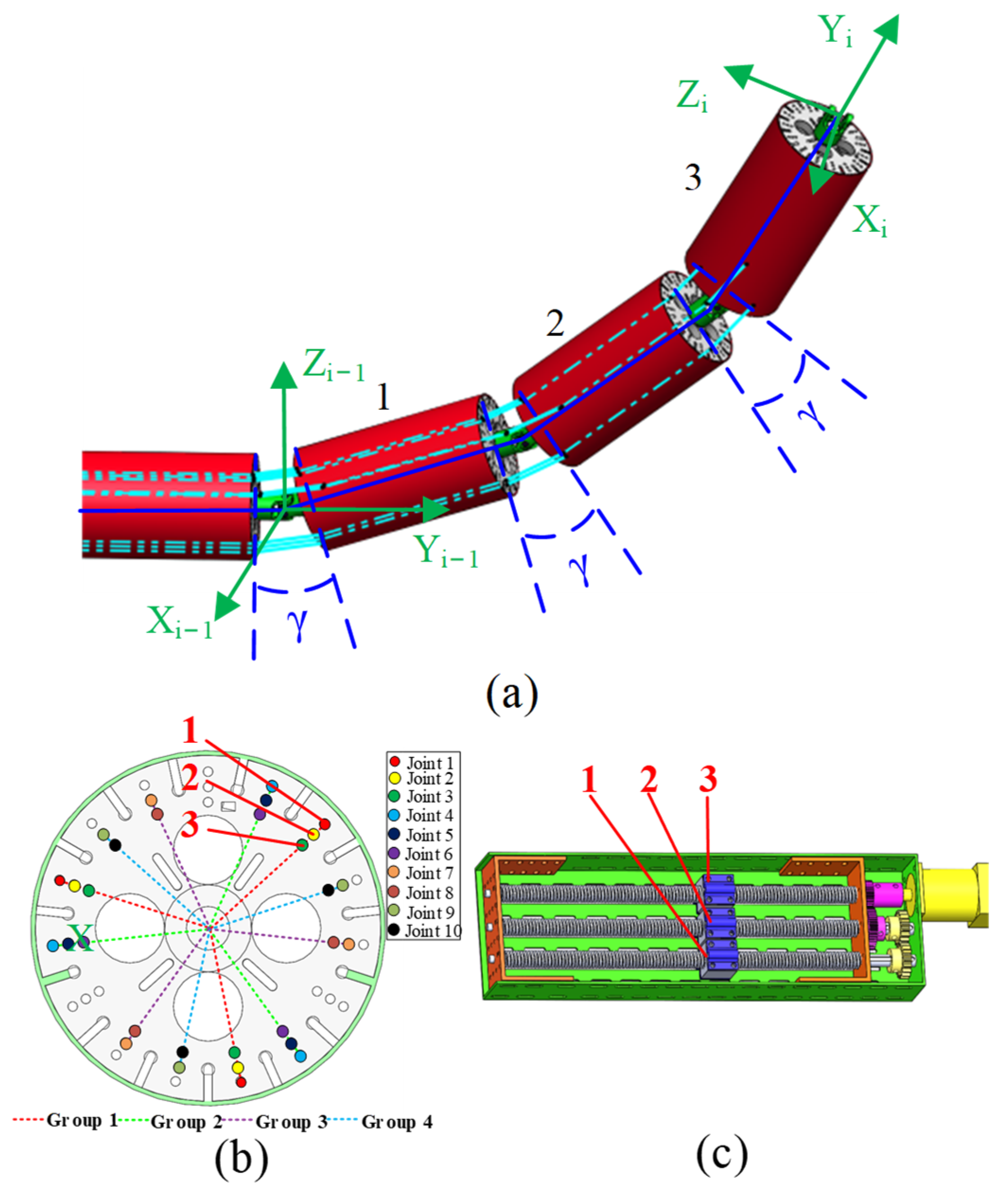
2.2. SAM Kinematics Analysis
3. Methods
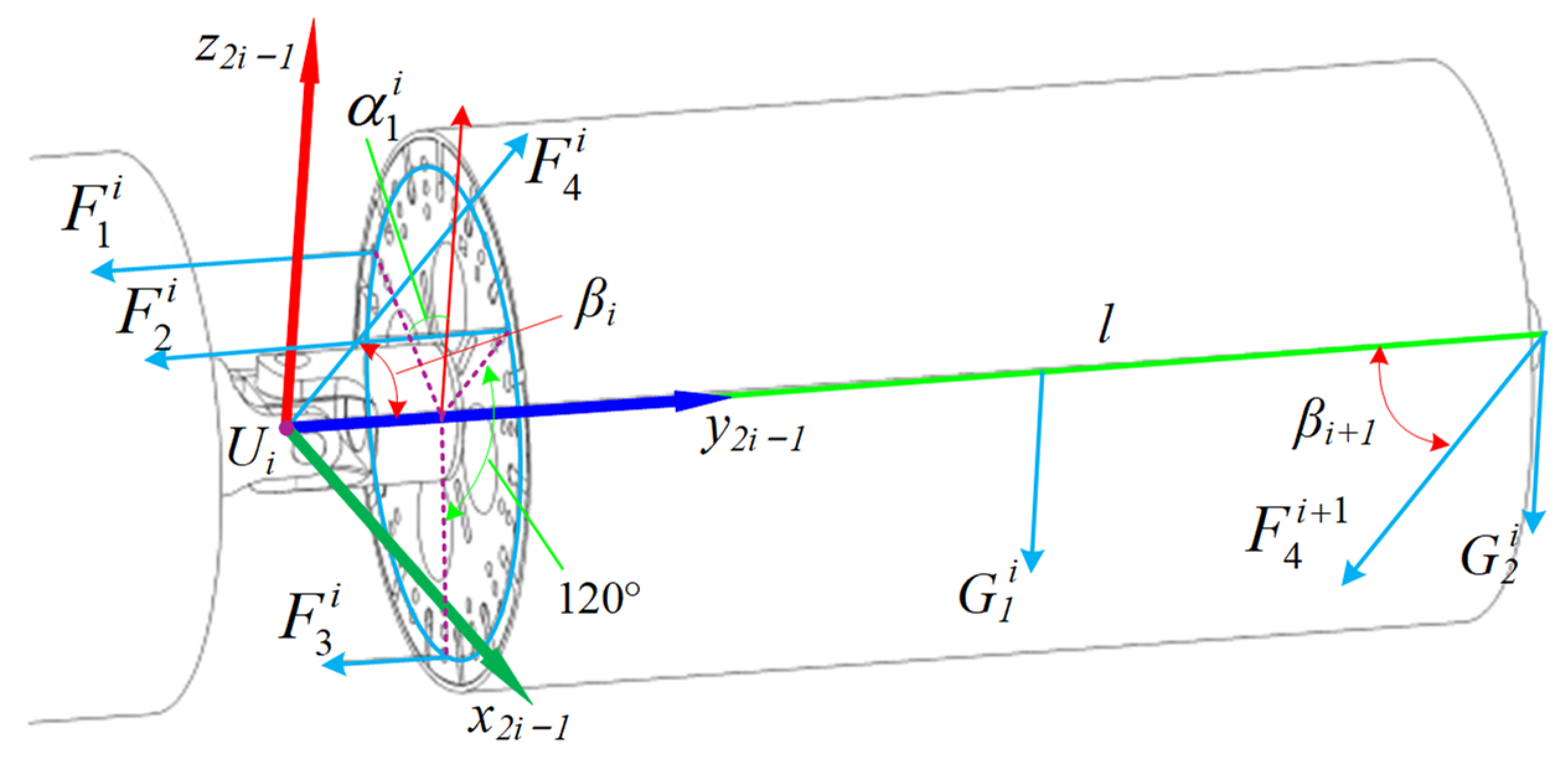
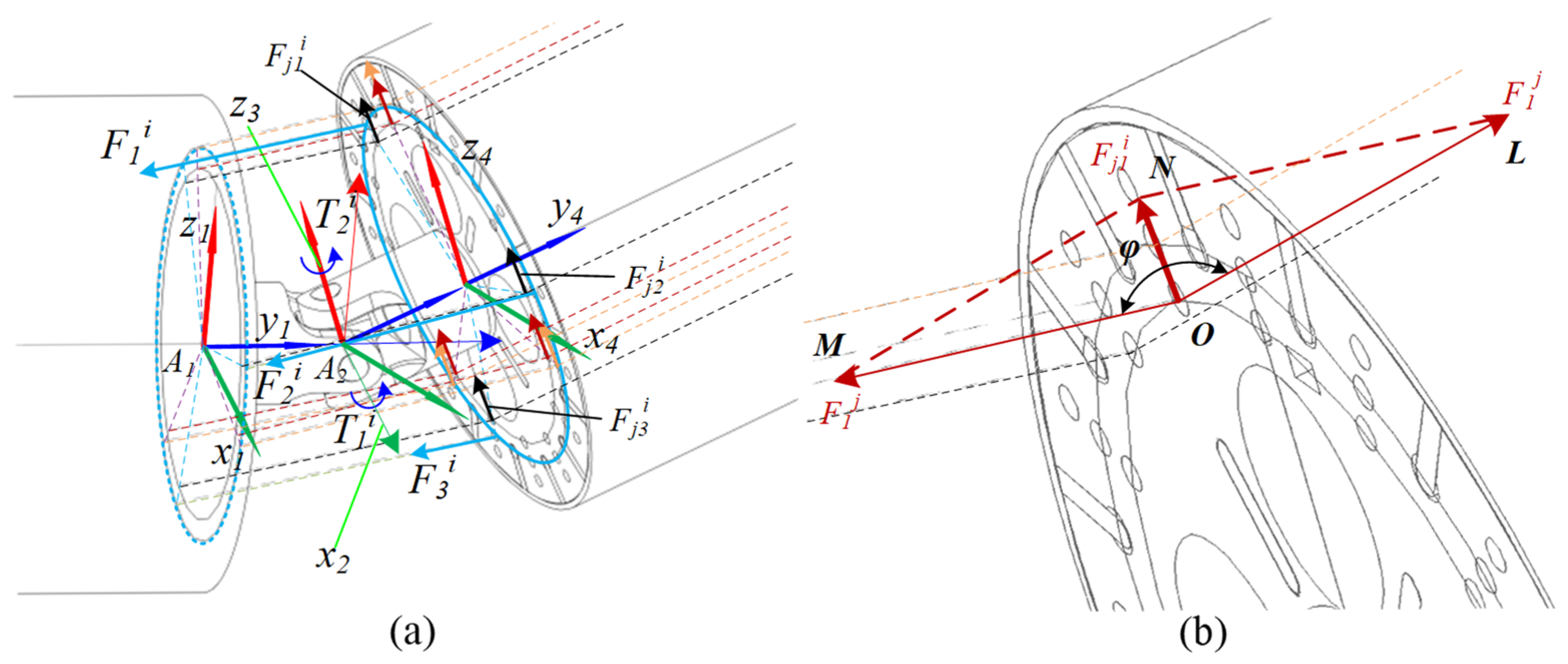
3.1. Static Cable Force
3.2. Equivalent Joint Dynamics
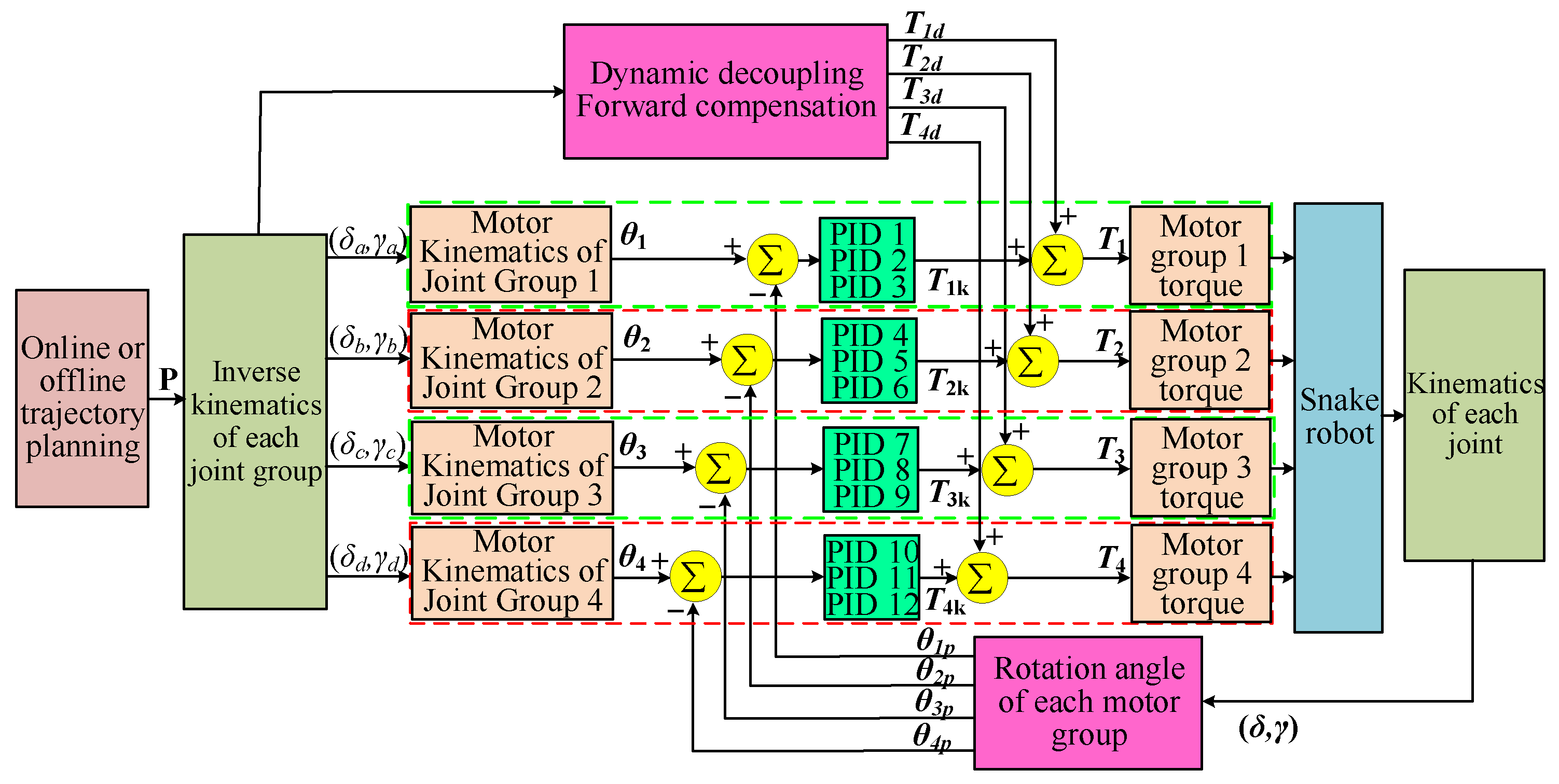
4. Model-Based Control
5. Simulation and Experiments
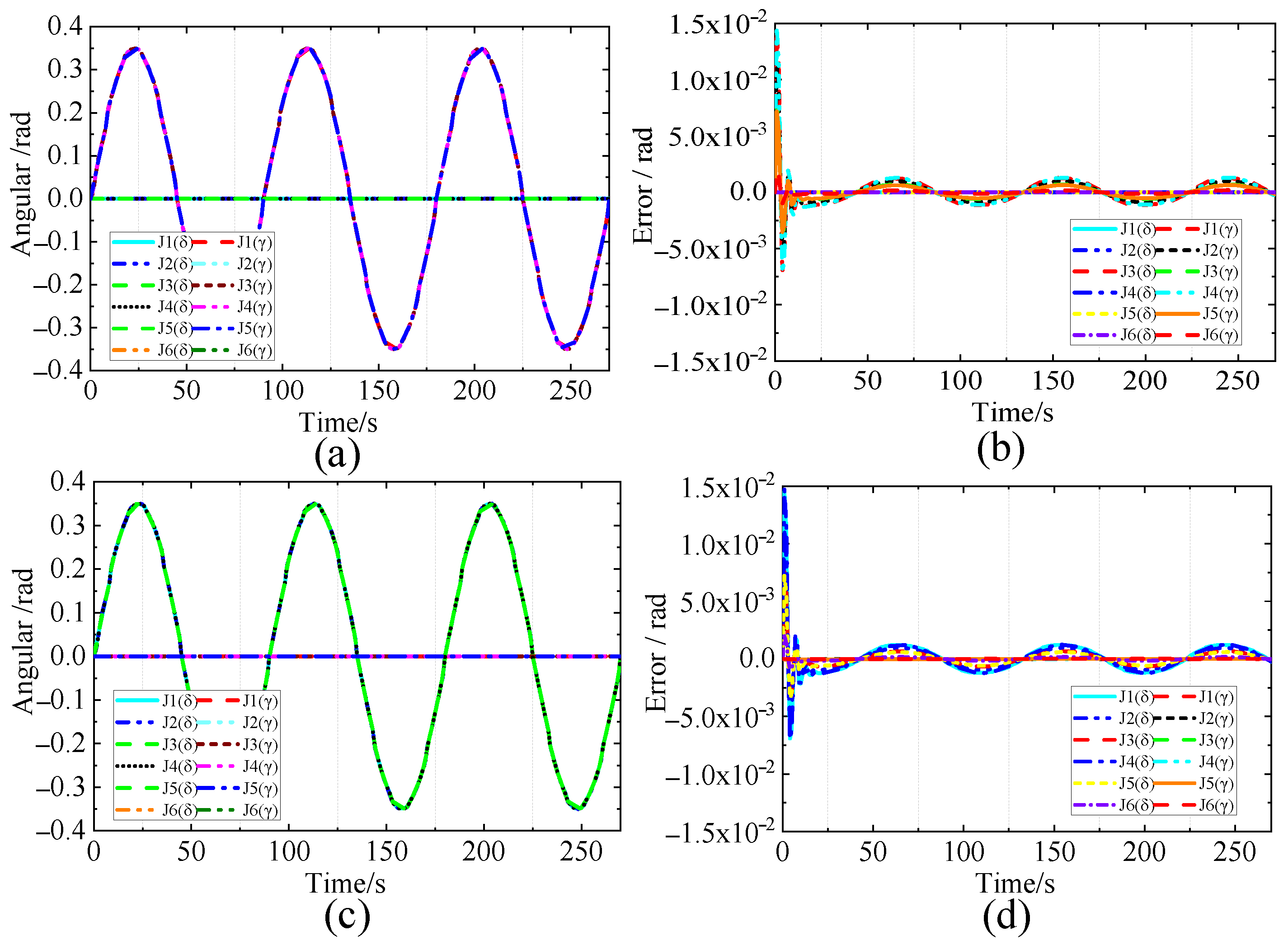
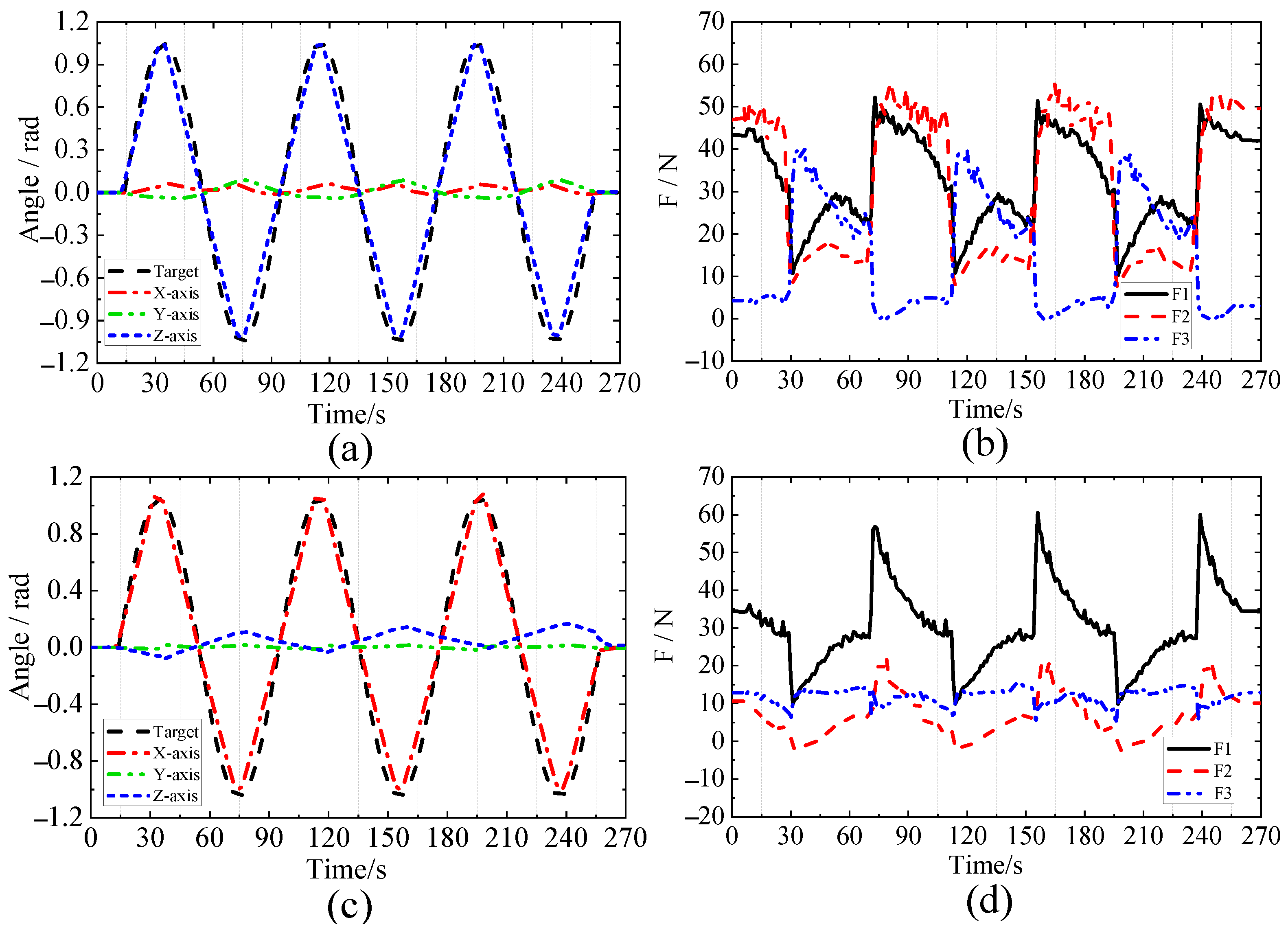
5.1. Simulation Tests
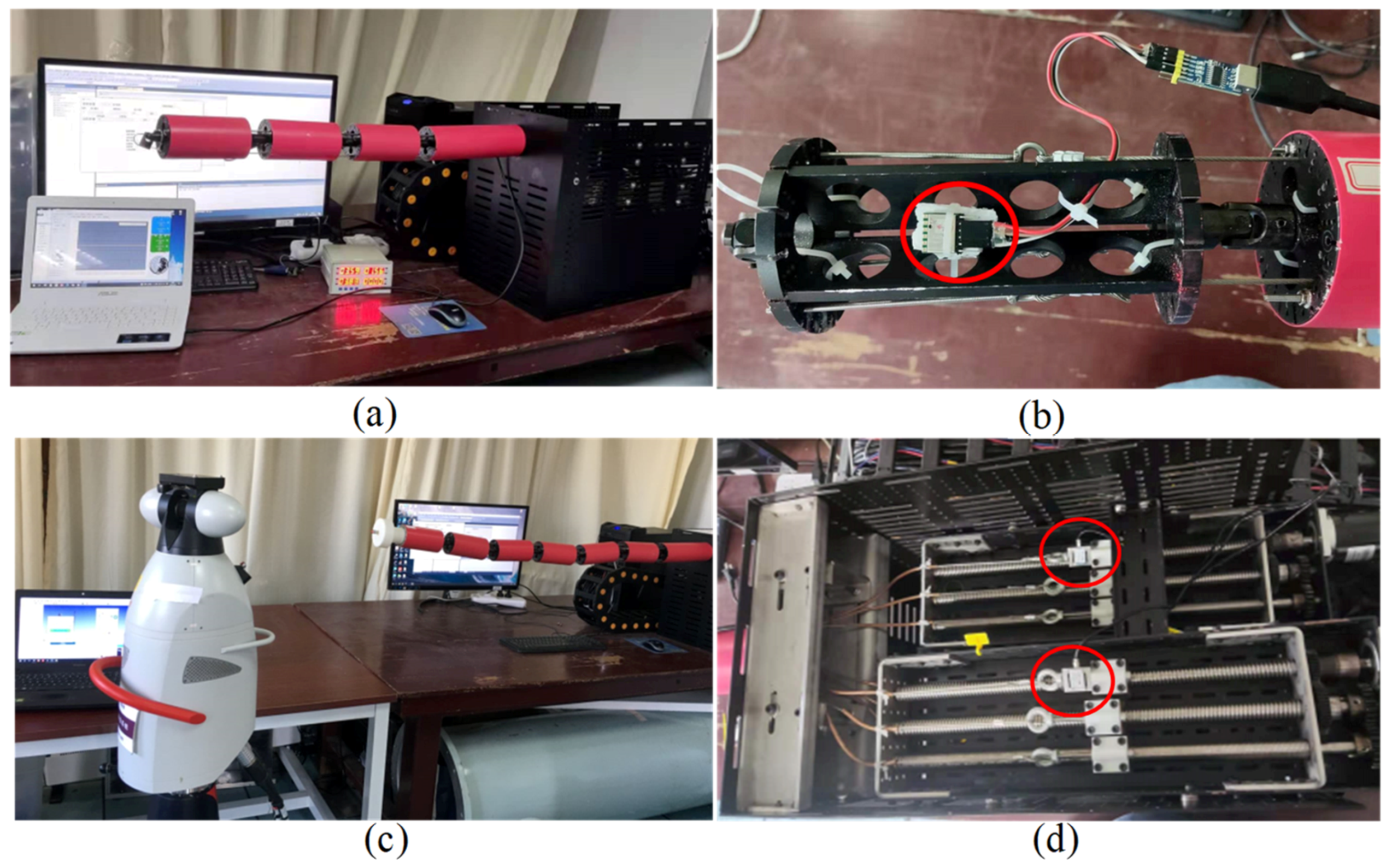
5.2. Traction Force Experiments
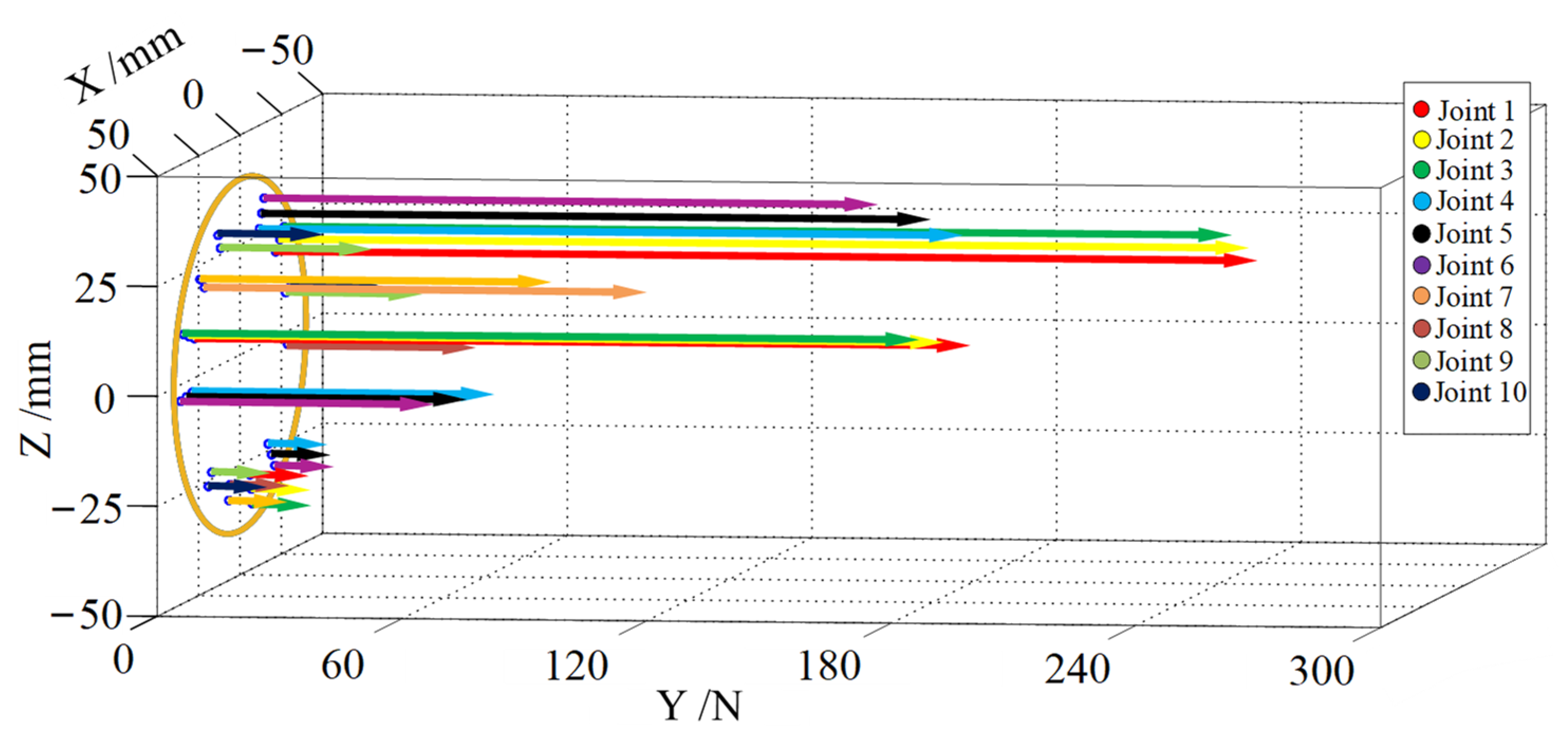
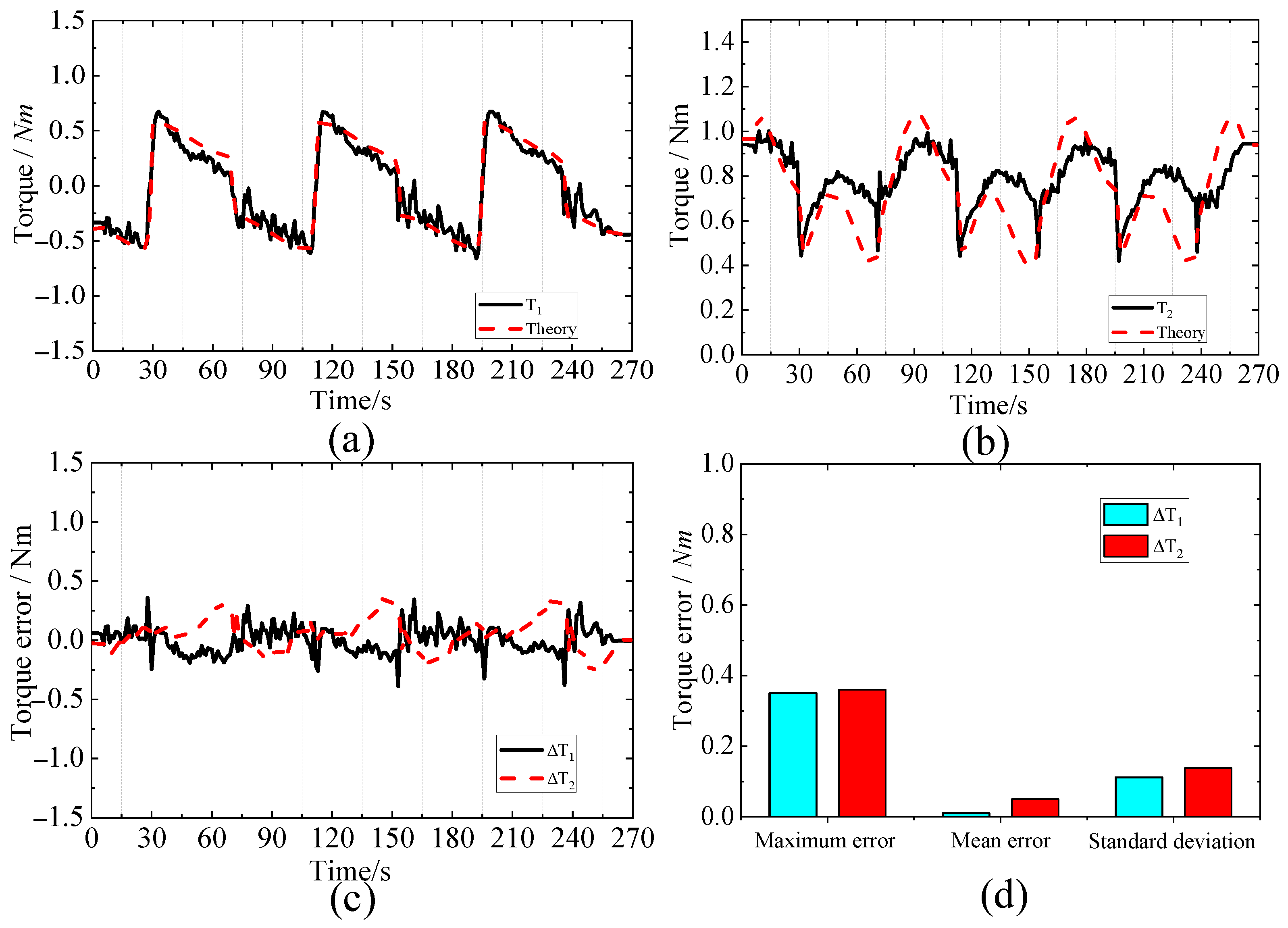
5.3. Equivalent Joint Dynamic Analysis
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckingham, R.; Graham, A. Nuclear snake-arm robots. Ind. Robot. 2012, 39, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, C.; Pistone, A.; Ludovico, D.; Guardiani, P.; Gagliardi, R.; De Mari Casareto Dal Verme, L.; Sofia, G.; Caldwell, D.G. Design of a Novel Long-Reach Cable-Driven Hyper-Redundant Snake-like Manipulator for Inspection and Maintenance. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Huang, C.H.; Hung, Y.; Chang, C.Y. Sensing pipes of a nuclear power mechanism using low-cost snake robot. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1687814018781286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.B.; Ye, M.Y.; Song, Y.T.; Mao, X.; Chen, P.M.; Qian, X.Y. Engineering conceptual design of CFETR divertor. Fusion Eng. Des. 2015, 99, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Jiang, J.J.; Hou, Y.W.; Duan, W.X.; Ni, M.Y.; Xing, C. Preliminary Cost Assessment and Compare of China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor. J. Fusion. Energ. 2015, 34, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, R.O.; Graham, A.C. Dexterous Manipulators for Nuclear Inspection and Maintenance-Case Study. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Applied Robotics for the Power Industry, Montreal, QC, Canada 5–7 October 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.G.; Xu, W.F.; Liang, B. Avoidance of multiple moving obstacles during active debris removal using a redundant space manipulator. Int. J. Control. Autom. 2017, 15, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.W.; Walker, I.D. Kinematics and the implementation of an elephant’s trunk manipulator and other continuum style robots. J. Robot. Syst. 2003, 20, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Du, J.L.; Bao, H. The Control Strategy of Tendon-Driven Continuum/Soft Robot. Robot 2020, 42, 116–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Tang, J.; Nie, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qin, L. Visual Tracking Control of Cable-Driven Hyper-Redundant Snake-Like Manipulator. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, R. Snake arm robots. Ind. Robot 2002, 29, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.B.; Dai, J.S.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Althoefer, K. A Novel Continuum Manipulator Design Using Serially Connected Double-Layer Planar Springs. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Racioppo, P.; Ben-Tzvi, P. Design and Control of a Cable Driven Articulated Modular Snake Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, K.W.; Tosi, K.H.; Vitiello, V.; Clark, J.; Chow, G.C.T.; Luk, W.; Yang, G.Z. Dimensionality Reduction in Controlling Articulated Snake Robot for Endoscopy Under Dynamic Active Constraints. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Wang, J.G.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Zhu, X.Y. Design of a cable-driven hyper-redundant robot with experimental validation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417734458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ni, F.L.; Liu, H. A Head Control Strategy of the Snake Robot Based on Segmented Kinematics. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, Y.L. Recursive Newton–Euler formulation for flexible dynamic manufacturing analysis of open-loop robotic systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 29, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.D.; Ji, A.H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, W.L.; Pan, H.T.; Cheng, Y.; Song, Y.T. Analyzing trajectory tracking accuracy of a flexible multi-purpose deployer. Fusion. Eng. Des. 2019, 151, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Walker, I. Kinematics for multisection continuum robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, X.; Nabil, S. Analytic Formulation for Kinematics, Statics, and Shape Restoration of Multi backbone Continuum Robots Via Elliptic Integrals. J. Mech. Robot. 2010, 2, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Du, R.X. Design and Analysis of a Bio-Inspired Wire-Driven Multi-Section Flexible Robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.; Jones, B. Design and kinematic modeling of constant curvature continuum robots: A review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuruthel, T.; Falotico, E.; Renda, F.; Laschi, C. Learning dynamic models for open loop predictive control of soft robotic manipulators. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 066003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, F.; Lebastard, V.; Candelier, F.; Renda, F. Dynamics of Continuum and Soft Robots: A Strain Parameterization Based Approach. IEEE. Trans. Robot. 2020, 37, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenhahn, V.; Mahl, T.; Hildebrandt, A.; Neumann, R. Dynamic Modeling of Bellows-Actuated Continuum Robots Using the Euler–Lagrange Formalism. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurezu-Gherghe, L.; Dumitru, N.; Geonea, I.; Copilui, C. Dynamic and Modal Analysis of a Snake Like Robot. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2020, 896, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossoughi, G.; Pendar, H.; Heidari, Z.; Mohammadi, S. Assisted passive snake-like robots: Conception and dynamic modeling using Gibbs–Appell method. Robotica 2008, 26, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.Q.; Xu, W.F.; Yang, T.W.; Hu, Z.H.; Liang, B. Dynamic modeling and trajectory tracking control method of segmented linkage cable-driven hyper-redundant robot. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 101, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.F.; Liu, T.L.; Li, Y.M. Kinematics, Dynamics, and Control of a Cable-Driven Hyper-Redundant Manipulator. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mech. 2018, 23, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Chen, M.Z.; Han, X.H.; Zhang, X.C.; Zheng, F.Y.; Zhuang, W.H. Research on the vibration model and vibration performance of cold orbital forging machines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 236, 828–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Huang, F.H.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Zhu, S. Teleoperation Control Design with Virtual Force Feedback for the Cable-Driven Hyper-Redundant Continuum Manipulator. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.G.; Liang, B.; Wang, T.S. Dynamic analysis of a hyper-redundant space manipulator with a complex rope network. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.D.; Ji, A.H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, W.L.; Pan, H.T.; Shi, S.S.; Song, Y.T. A Snake-Inspired Layer-driven Continuum Robot. Soft Robot. 2021, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.J. SIASUN Special Robotics Snake Arm Robot; SIASUN Robot & Automation Co., Ltd.: Shenyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Spong, M.W.; Hutchinson, S.; Vidyasagar, M. Robot Modeling and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 163–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kurfess, T.R. Lagrangian dynamics. In Robotics and Automation Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.G.; Zhao, Y.J.; Jin, L.; Zhang, P.; Chen, C.W. Dynamic feedforward control in decoupling space for a four-degree-of-freedom parallel robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16, 1729881418820451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Z.G.; Liu, T.L.; Xu, W.F.; Lou, Y.J.; Liang, B. Dynamic feedforward control of spatial cable-driven hyper-redundant manipulators for on-orbit servicing. Robotica 2019, 37, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | OC Robotics | SIASUN | SAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total arm length | >2000 mm | 2269 mm | 2300 mm |
| Diameter | 140 mm | 125 mm | 80 mm |
| Number of joints | 12 | 12 | 10 |
| Number of motors | 36 + 1 | 36 + 1 | 12 + 1 |
| Degrees of freedom | 24 + 1 | 24 + 1 | 8 + 1 |
| Self-weight | >1000 kg | 1400 kg | <200 kg |
| Single bending angle | 27.5° | 22° | 25° |
| Maximum bending angle | 225° | 180° | 250° |
| Load | 10 kg | 5 kg | >5 kg |
| Length, width, and height | / | 3800 × 800 × 1550 | 2900 × 400 × 500 |
| Repeatable positioning accuracy | ±1 mm | ±1 mm | ±5 mm |
| i | Angle (°) | Range (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0, 90°, 0) | (0, 300, 0) | −25°~+25° | |
| 2 | (0, −90°, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | −25°~+25° | |
| ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ |
| 19 | (0, 90°, 0) | (0, 200, 0) | −25°~+25° | |
| 20 | (0, −90°, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | −25°~+25° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, G.; Wu, H.; Ji, A. Equivalent Dynamic Analysis of a Cable-Driven Snake Arm Maintainer. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157494
Qin G, Wu H, Ji A. Equivalent Dynamic Analysis of a Cable-Driven Snake Arm Maintainer. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157494
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Guodong, Huapeng Wu, and Aihong Ji. 2022. "Equivalent Dynamic Analysis of a Cable-Driven Snake Arm Maintainer" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157494
APA StyleQin, G., Wu, H., & Ji, A. (2022). Equivalent Dynamic Analysis of a Cable-Driven Snake Arm Maintainer. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157494







