H&E Multi-Laboratory Staining Variance Exploration with Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Characterization
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Preprocessing, Feature Extraction, and Engineering (Unsupervised Learning)
2.3.1. Cropping Regions of Interest
2.3.2. Background Thresholding
2.3.3. Image Intensity Normalization
2.3.4. Histogram Feature Vectors
2.3.5. Descriptive Analysis—PCA
2.3.6. Data Clustering and Validation
2.3.7. Model Selection and Figure of Merit
2.3.8. Clustering Comparison—Rand Index
2.4. Preprocessing, Feature Extraction, and Engineering (Supervised Learning)
2.4.1. ROI Image Tiling
2.4.2. Feature Extraction
2.4.3. Classification Algorithm
2.4.4. Random Classifier Baseline
2.4.5. Feature Selection
2.4.6. Validation Approach
3. Results
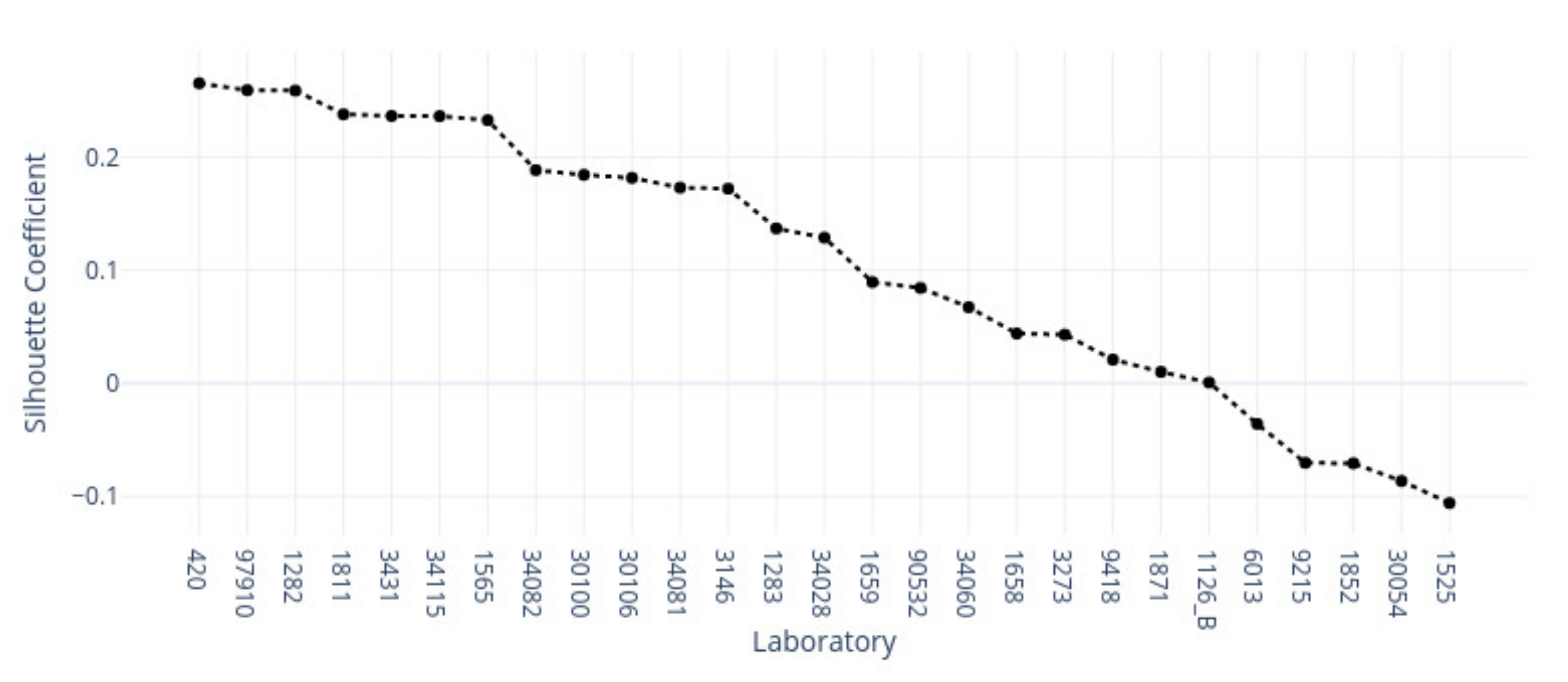
3.1. k-Means Silhouette Scores
3.2. H&E Clusters and Visualization
3.2.1. Kidney Sample Clusters
3.2.2. Skin Sample Clusters
3.2.3. Colon Sample Clusters
3.2.4. Rand Index Results
3.3. Classification Results (Supervised Learning)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A










References
- Glatz-Krieger, K.; Spornitz, U.; Spatz, A.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Glatz, D. Factors to keep in mind when introducing virtual microscopy. Virchows Arch. 2006, 448, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macenko, M.; Niethammer, M.; Marron, J.S.; Borland, D. A method for normalizing histology slides for quantitative analysis. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, ISBI 2009, Boston, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 1107–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Ljungberg, A.; Johansson, O. Methodological aspects on immunohistochemistry in dermatology with special reference to neuronal markers. Histochem. J. 1993, 25, 735–745. [Google Scholar]
- Anghel, A.; Stanisavljevic, M.; Andani, S.; Papandreou, N.; Rüschoff, J.H.; Wild, P.; Gabrani, M.; Pozidis, H. A high-performance system for robust stain normalization of whole-slide images in histopathology. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissueand cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 3, pdb.prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciompi, F.; Geessink, O.; Bejnordi, B.E.; De Souza, G.S.; Baidoshvili, A.; Litjens, G.; Van Ginneken, B.; Nagtegaal, I.; Van Der Laak, J. The importance of stain normalization in colorectal tissue classification with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), Melbourne, Australia, 18–21 April 2017; pp. 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, S.M.; Colclough, A.B.; Dinnen, J.S.; Eakins, D.; Evans, D.M.; Gradwell, E.; O’Sullivan, J.P.; Summerell, J.M.; Newcombe, R.G. Observer variation in histopathological diagnosis and grading of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. BMJ 1989, 298, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tellez, D.; Litjens, G.; Bándi, P.; Bulten, W.; Bokhorst, J.-M.; Ciompi, F.; van der Laak, J. Quantifying the effects of data augmentation and stain color normalization in convolutional neural networks for computational pathology. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tosta, T.A.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Neves, L.A.; Nascimento, M.Z.d. Computational normalization of H&E-stained histological images: Progress, challenges and future potential. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 95, 118–132. [Google Scholar]
- Piórkowski, A.; Gertych, A. Color normalization approach to adjust nuclei segmentation in images of hematoxylin and eosin stained tissue. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 762, pp. 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard, E.; Adhikhmin, M.; Gooch, B.; Shirley, P. Color transfer between images. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2001, 21, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosta, T.A.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Neves, L.A.; Nascimento, M.Z.D. Color normalization of faded H&E-stained histological images using spectral matching. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vijh, S.; Saraswat, M.; Kumar, S. A new complete color normalization method for H&E stained histopatholgical images. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 7735–7748. [Google Scholar]
- Zarella, M.D.; Yeoh, C.; Breen, D.E.; Garcia, F.U. An alternative reference space for H&E color normalization. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174489. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, P.; Chalechale, A. Pix2pix-based stain-to-stain translation: A solution for robust stain normalization in histopathology images analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), Qom, Iran, 18–20 February 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.M.; Rajpoot, N.; Treanor, D.; Magee, D. A Nonlinear Mapping Approach to Stain Normalization in Digital Histopathology Images Using Image-Specific Color Deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Jain, A.K.; Lal, S.; Kini, J. A study about color normalization methods for histopathology images. Micron 2018, 114, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahadane, A.; Peng, T.; Sethi, A.; Albarqouni, S.; Wang, L.; Baust, M.; Steiger, K.; Schlitter, A.M.; Esposito, I.; Navab, N. Structure-Preserving Color Normalization and Sparse Stain Separation for Histological Images. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2016, 35, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, E.L.; Treanor, D. Colour in digital pathology: A review. Histopathology 2017, 70, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschman, J.; Farahani, H.; Darbandsari, A.; Ahmadvand, P.; Van Spankeren, A.; Farnell, D.; Levine, A.B.; Naso, J.R.; Churg, A.; Jones, S.J.; et al. The utility of color normalization for AI -based diagnosis of hematoxylin and eosin-stained pathology images. J. Pathol. 2022, 256, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianconi, F.; Kather, J.N.; Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C. Experimental Assessment of Color Deconvolution and Color Normalization for Automated Classification of Histology Images Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin. Cancers 2020, 12, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadermayr, M.; Cooper, S.S.; Klinkhammer, B.; Boor, P.; Merhof, D. A quantitative assessment of image normalization for classifying histopathological tissue of the kidney. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Basel, Switzerland, 13–15 September 2017; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Yu, J. Otsu method and K-means. In Proceedings of the 2009 9th International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems, HIS 2009, Shenyang, China, 12–14 August 2009; Volume 1, pp. 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Macqueen, J. On convergence of the k-means and partitions with minimum average variance. Ann. Math. Stat. 1965, 36, 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. K-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, LO, USA, 7–9 January 2007; pp. 1027–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starczewski, A.; Krzyzak, A. Performance evaluation of the silhouette index. In Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence (Subseries of Lecture Notes in Computer Science); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9120, pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Franco-Penya, H.H.; Kelleher, J.D.; Pugh, J.; Ross, R. An analysis of the application of simplified silhouette to the evaluation of k-means clustering validity. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10358, pp. 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Larose, D.T. Data Mining and Predictive Analytics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, W.M. Objective Criteria for the Evaluation of Clustering Methods. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1971, 66, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezja, F. Developing and Testing Sub-Band Spectral Features in Music Genre and Music Mood Machine Learning. Master’s Thesis, University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dudani, S.A. The Distance-Weighted k-Nearest-Neighbor Rule. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1976, SMC–6, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, O. K-nearest neighbors. In Dimensionality Reduction with Unsupervised Nearest Neighbors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in {P}ython. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreer, J. A question of terminology. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 1957, 3, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On Information and Sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Volume 2, pp. 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
















|
| Silhouette Value Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Good evidence for cluster existence in the data. | |
| Some evidence for cluster existence in the data, domain-specific knowledge, can be brought to bear to support the presence of the clusters. | |
| Scant evidence of cluster reality. |
| Kidney Sample Scores | Cluster 1 (C1) | Cluster 2 (C2) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Median Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Minimum Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Kidney Sample Scores | Cluster 1 (C1) | Cluster 2 (C2) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Median Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Minimum Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Kidney Sample Scores | Cluster 1 (C1) | Cluster 2 (C2) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Median Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Minimum Silhouette Score |  |  |
| Tissue Type Pair | Rand Index Score |
|---|---|
| Kidney–Colon | |
| Skin–Colon | |
| Kidney–Skin |
| Tissue Type | KNN | KNN (Feature Selected) | Random Classifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney | 0.395 (0.010) | 0.706 (0.009) | 0.014 (0.001) |
| Skin | 0.553 (0.007) | 0.617 (0.009) | 0.014 (0.003) |
| Colon | (0.007) | 0.513 (0.006) | 0.009 (0.002) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prezja, F.; Pölönen, I.; Äyrämö, S.; Ruusuvuori, P.; Kuopio, T. H&E Multi-Laboratory Staining Variance Exploration with Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7511. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157511
Prezja F, Pölönen I, Äyrämö S, Ruusuvuori P, Kuopio T. H&E Multi-Laboratory Staining Variance Exploration with Machine Learning. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7511. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157511
Chicago/Turabian StylePrezja, Fabi, Ilkka Pölönen, Sami Äyrämö, Pekka Ruusuvuori, and Teijo Kuopio. 2022. "H&E Multi-Laboratory Staining Variance Exploration with Machine Learning" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7511. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157511
APA StylePrezja, F., Pölönen, I., Äyrämö, S., Ruusuvuori, P., & Kuopio, T. (2022). H&E Multi-Laboratory Staining Variance Exploration with Machine Learning. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7511. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157511






