A pH Monitoring Algorithm for Orifice Plate Culture Medium
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
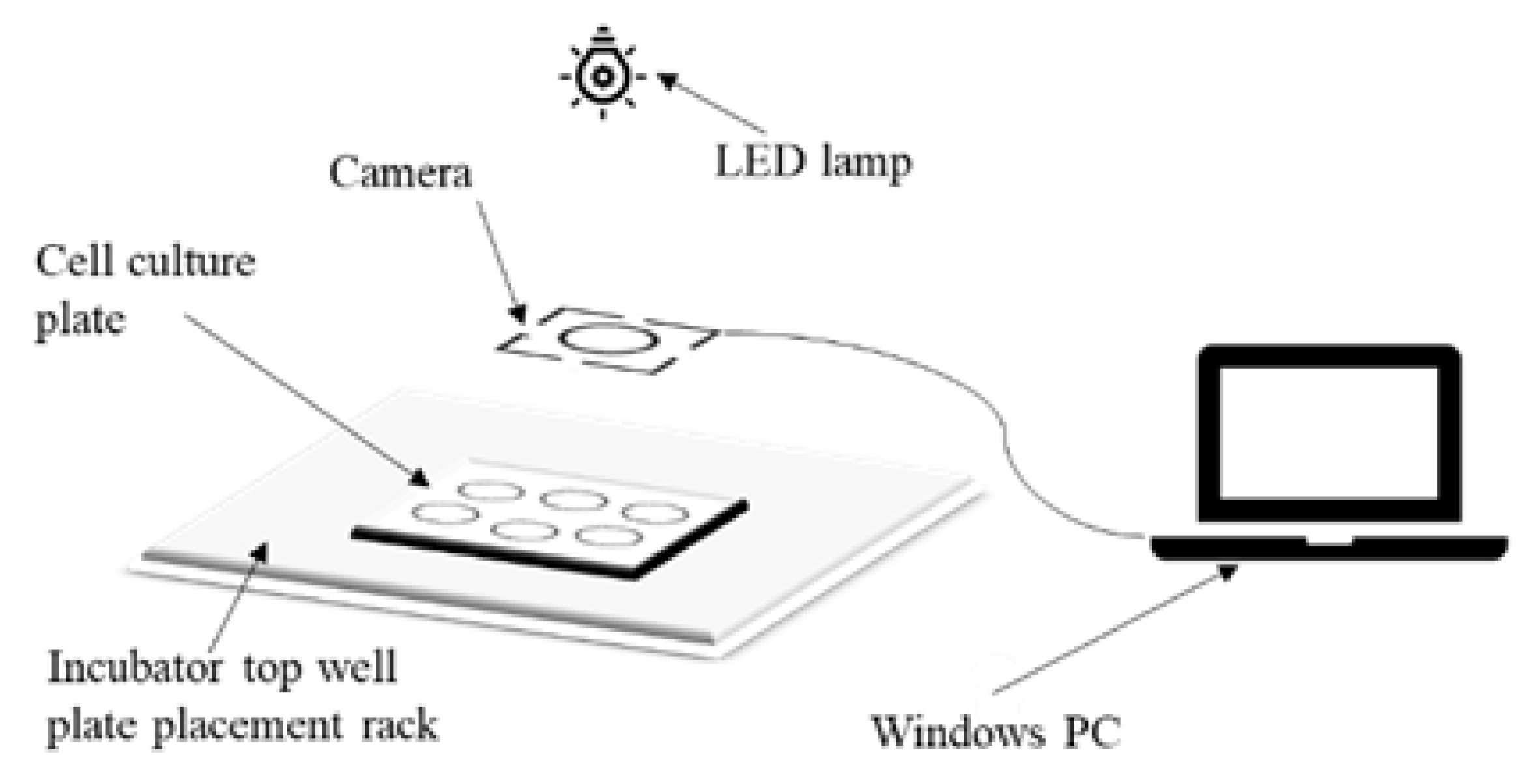
2.1. Image Acquisition
2.2. Image Processing Scheme
2.3. Scheme for pH Measurement
2.4. Regression Model Analysis of pH and HSV Curve
3. Algorithm Principle and Result Analysis
3.1. Algorithm Principle
3.1.1. Target Image and Background Segmentation
3.1.2. Removal of Orifice Edge Profile
3.1.3. Image after Cutting the Liquid in The Hole
3.1.4. Color Moments in HSV Color Space
- (1)
- Convert the image from RGB to HSV (hexconemodel) [28] format to obtain the HSV component of the image; calculate the number of image pixels;
- (2)
- Then, the average, variance, and skewness of HSV are obtained;
- (3)
- Coexist the obtained value with the measured pH value. For example, in the table file, the table is arranged according to the value of pH;
- (4)
- Find out the color characteristics that meet the linear relationship, establish a functional model, and analyze the functional relationship between HSV and pH.
3.2. Analysis of HSV and pH Function Model
3.2.1. HSV Characteristic Quantification Value Selection
3.2.2. Curve-Fitting Analysis between the Average of Hue and pH
3.3. Verification of Functional Model
3.3.1. Function Model Range Setting
3.3.2. Error Analysis of Function Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doulgkeroglou, M.-N.; Di Nubila, A.; Niessing, B.; König, N.; Schmitt, R.H.; Damen, J.; Szilvassy, S.J.; Chang, W.; Csontos, L.; Louis, S.; et al. Automation, Monitoring, and Standardization of Cell Product Manufacturing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, A.; Ariza-Jiménez, L.; Uribe, D.; Arroyave, J.C.; Galeano, J.; Cortés-Mancera, F.M. Bio-EdIP: An automatic approach for in vitro cell confluence images quantificatio. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 145, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refresh cell culture. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 5, 783–784. [CrossRef]
- Trebinska-Stryjewska, A.; Swiech, O.; Opuchlik, L.J.; Grzybowska, E.A.; Bilewicz, R. Impact of Medium pH on DOX Toxicity toward HeLa and A498 Cell Lines. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7979–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiech, O.; Majdecki, M.; Opuchlik, L.J.; Bilewicz, R. Impact of pH and cell medium on the interaction of doxorubicin with lipoic acid cyclodextrin conjugate as the drug carrier. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020, 97, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoncello, I. Optimizing the Cell Culture Microenvironment. In Mouse Cell Culture; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1940, pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.T.; Zhao, P. Effect of different pH values on the growth of human embryonic lung diploid fibroblasts MRC-5. J. Shanxi Med. Univ. 2014, 45, 347–349. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, P.S.; Zhu, D.F.; Chen, F.H.; Hu, B.; Zhuang, J.S.; Lin, X.M.; Hu, L.Y.; He, L.N. Effect of pH on the prolif eration of LAK cells and the combination with rIL-2 against malignant tumors. Chin. J. Microcirc. 2002, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.L.; Luo, N.; Yang, H.; Shen, X.F.; Ju, G. Effect of pH on the survival of adult rat olfactory sheath cells cultured in vitro. Chin. J. Neuroanat. 2006, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.S.; Li, Y.M.; Hua, Y.F.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.W.; Jin, S.X. Effect of pH on vitro matura tion of porcine oocytes in culture. J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2005, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinska, A.; Wnuk, M.; Slota, E.; Bartosz, G. Total anti-oxidant capacity of cell culture media. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Computers and biology. Commun. ACM 2001, 44, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürig, M.D.; Donoughe, S.; Svensson, E.I.; Porto, A.; Tsuboi, M. Computer Vision, Machine Learning, and the Promise of Phenomics in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 642774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.W.; Liu, W. Fully automated cell culture based on FPGA. Digit. User 2019, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Guangzhou Institute of Biomedicine and Health; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Development of fully automated stem cell induction culture equipment. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2018, 33, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Korzynska, A.; Iwanowski, M.; Neuman, U.; Dobrowolska, E.; Hoser, P. Comparison of the methods of microscopic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 11th International Congress of the IUPESM/World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Edlund, C.; Jackson, T.R.; Khalid, N.; Bevan, N.; Dale, T.; Dengel, A.; Ahmed, S.; Trygg, J.; Sjögren, R. LIVECell—A large-scale dataset for label-free live cell segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loesdau, M.; Chabrier, S.; Gabillon, A. Hue and Saturation in the RGB Color Space. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image and Signal Processing (ICISP), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 12–15 May 2014; Volume 8509, pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Deng, P.; Dan, B. Image segmentation of argon blowing based on improved Otsu algorithm. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems (ICoIAS), Wuhan, China, 14–16 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.Y.; Basah, S.N.; Yazid, H.; Safar, M.J.A. Performance analysis of Otsu thresholding for sign language segmentation. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 21499–21520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Ren, K.; Gu, G.; Zhang, X.; Qian, W.; Chen, Q.; Yu, S. Infrared Small Moving Target Detection via Saliency Histogram and Geometrical Invariability. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Feng, K.; Yu, J.; Gu, H. River Extraction of Color Remote Sensing Image Based on HSV and Shape Detection. In Proceedings of the 7th Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications, Kunming, China, 5–7 November 2020; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liby, J.J.; Jaya, T. HSV model based data hiding in video for watermark applications. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandotiya, Y.; Atre, A. Image Retrieval using Edge Detection, RLBP, Color Moment Method for YCbCr and HSV Color Space. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference of Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 20–22 April 2017; Volume 2, pp. 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Shrivastava, S.; Gupta, M. Optimization of Image Retrieval by using HSV Color Space, Zernike Moment &DWT Technique. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC), Tamilnadu, India, 10–12 December 2015; pp. 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Hamuda, E.; Mc Ginley, B.; Glavin, M.; Jones, E. Automatic crop detection under field conditions using the HSV colour space and morphological operations. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 133, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, M.A.; Orengo, M. Similarity of Color Images. In Storage and Retrieval for Image and Video Databases III; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1970; Volume 2420, pp. 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Shi, Y.Q.; Xuan, G. Identifying Computer Graphics using HSV Color Model and Statistical Moments of Characteristic Functions. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Beijing, China, 2–5 July 2007; pp. 1123–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Krycer, J.R.; Lor, M.; Fitzsimmons, R.L.; Hudson, J.E. A cell culture platform for quantifying metabolic substrate oxidation in bicarbonate-buffered medium. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 298, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Hole Number | pH |
|---|---|
| Hole 1 | 7.03 |
| Hole 2 | 7.17 |
| Hole 3 | 7.36 |
| Hole 4 | 7.46 |
| Hole 5 | 7.42 |
| Hole 6 | 7.50 |
| H-Mean | H-Standard Deviation | H-Skewness | S-Mean | S-Standard Deviation | S-Skewness | V-Mean | V-Standard Deviation | V-Skewness | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.079131 | 0.004208 | 0.003359 | 0.250748 | 0.029091 | 0.033622 | 0.590624 | 0.030555 | 0.032838 | 7.03 |
| 0.069579 | 0.004518 | 0.002654 | 0.229366 | 0.017402 | 0.009339 | 0.547119 | 0.029626 | 0.020605 | 7.17 |
| 0.038364 | 0.003331 | 0.002590 | 0.254440 | 0.029068 | 0.026202 | 0.507212 | 0.030528 | 0.019104 | 7.36 |
| 0.023946 | 0.002124 | 0.002119 | 0.260534 | 0.024595 | 0.024652 | 0.644441 | 0.057229 | 0.034309 | 7.42 |
| 0.014058 | 0.006678 | 0.031144 | 0.277370 | 0.020455 | 0.020543 | 0.668518 | 0.050389 | 0.047473 | 7.46 |
| 0.008604 | 0.017224 | 0.065762 | 0.302191 | 0.029799 | 0.020806 | 0.648446 | 0.072580 | 0.031329 | 7.50 |
| Number | pH | Hmean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 3 | Position 4 | Position 5 | ||
| 1 | 7.03 | 0.079131 | 0.079114 | 0.079093 | 0.077901 | 0.078625 |
| 2 | 7.17 | 0.069579 | 0.067355 | 0.067878 | 0.068542 | 0.066463 |
| 3 | 7.36 | 0.038364 | 0.030121 | 0.038853 | 0.035652 | 0.039785 |
| 4 | 7.42 | 0.023946 | 0.020722 | 0.025150 | 0.023590 | 0.026532 |
| 5 | 7.46 | 0.014058 | 0.011945 | 0.015283 | 0.013090 | 0.013878 |
| 6 | 7.50 | 0.008604 | 0.006950 | 0.010457 | 0.009035 | 0.010730 |
| Number | Hmean | pH |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.013427 | 7.36 |
| 3 | 0.010624 | 7.42 |
| 5 | 0.965239 | 7.60 |
| Number | Hmean | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.013427 | 0.013818 | 0.013914 | 0.016804 | 0.012618 | 0.01268 | 7.36 |
| 3 | 0.010624 | 0.006117 | 0.008446 | 0.00916 | 0.00712 | 0.002938 | 7.42 |
| 5 | 0.965239 | 0.968422 | 0.974566 | 0.974045 | 0.969344 | 0.961255 | 7.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Huang, A.; Zhang, T.; Wen, L.; Shi, Z.; Shi, L. A pH Monitoring Algorithm for Orifice Plate Culture Medium. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157560
Li Y, Huang A, Zhang T, Wen L, Shi Z, Shi L. A pH Monitoring Algorithm for Orifice Plate Culture Medium. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157560
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuqi, Anyi Huang, Tao Zhang, Luhong Wen, Zhenzhi Shi, and Lulu Shi. 2022. "A pH Monitoring Algorithm for Orifice Plate Culture Medium" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157560
APA StyleLi, Y., Huang, A., Zhang, T., Wen, L., Shi, Z., & Shi, L. (2022). A pH Monitoring Algorithm for Orifice Plate Culture Medium. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157560





