Cervical Cell Segmentation Method Based on Global Dependency and Local Attention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A module based on global dependency and local attention for contextual information modeling and feature refinement is proposed, based on a comprehensive consideration of feature differences and information dependency, which can be used as a basic component of the network to effectively enhance feature representation and improve the network’s ability to extract and utilize features.
- Considering information dependency, as well as the closure and uniqueness of the nuclei, the global context is modeled using long-range dependency.
- A hybrid attention module is constructed to provide adaptive input information and enhance key information representation to suppress useless information. Among them, the spatial attention module extracts spatial detail information sufficiently and effectively to better refine the target boundaries.
- An improved U-Net network, which implements an end-to-end network training model, is evaluated on the Herlev dataset to show that the segmentation performance can be steadily improved.
2. Related Work
2.1. Segmentation of Cervical Cells
2.2. Global Dependency
2.3. Local Attention
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Global Dependency Module
3.2. Channel Attention Module
3.3. Spatial Attention Module
4. Experiment
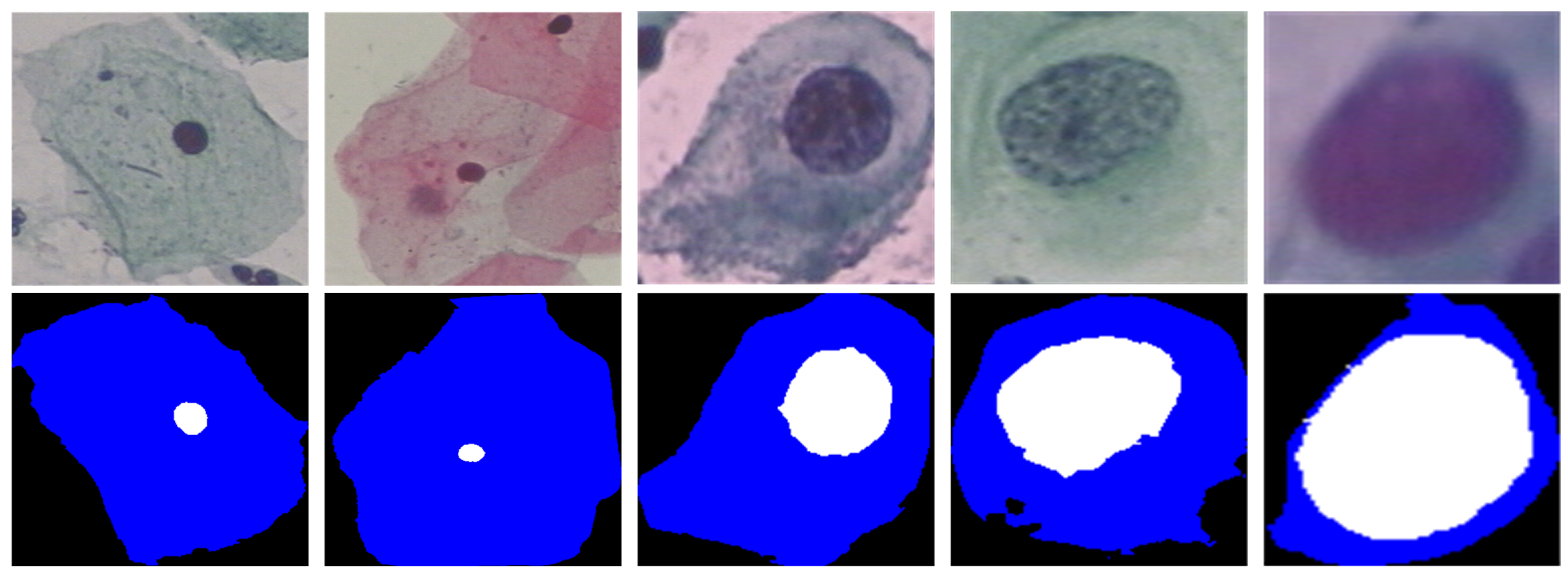
4.1. Dataset and Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Comparison Experiments
4.4. Ablation Experiments
4.5. Subjective Effect Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDLA | Global Dependency and Local Attention |
| MRF | Markov random field |
| ZSI | Zijdenbos similarity index |
| SA | Spatial Attention |
| CA | Channel Attention |
| GD | Global Dependency |
References
- Cohen, P.A.; Jhingran, A.; Oaknin, A.; Denny, L. Cervical cancer. Lancet 2019, 393, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, K.; Wang, M.; Yin, J.; Zhu, E.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Zhu, C. Automatic cytoplasm and nuclei segmentation for color cervical smear image using an efficient gap-search MRF. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 71, 46–56. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kong, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Sonka, M. Graph-based segmentation of abnormal nuclei in cervical cytology. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2017, 56, 38–48. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Tan, E.L.; Jiang, X.; Cheng, J.-Z.; Ni, D.; Chen, S.; Lei, B.; Wang, T. Accurate Cervical Cell Segmentation from Overlapping Clumps in Pap Smear Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, B. Segmentation of Overlapping Cervical Cells with Mask Region Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 3890988. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Ni, D.; Lei, B.; Wang, T. Accurate Segmentation of Cervical Cytoplasm and Nuclei Based on Multiscale Convolutional Network and Graph Partitioning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. Automated Segmentation of Cervical Nuclei in Pap Smear Images Using Deformable Multi-Path Ensemble Model. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 1514–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Yu, F.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L. PGU-net+: Progressive Growing of U-net+ for Automated Cervical Nuclei Segmentation. In Multiscale Multimodal Medical Imaging; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Johansen, D.; de Lange, T.; Johansen, H.D.; Halvorsen, P.; Riegler, M.A. A Comprehensive Study on Colorectal Polyp Segmentation With ResUNet++, Conditional Random Field and Test-Time Augmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2021, 25, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, D.; Taylor, Z.; Carneiro, G.; Syeda-Mahmood, T.; Martel, A.; Maier-Hein, L.; Tavares, J.M.R.; Bradley, A.; Papa, J.P.; Belagiannis, V.; et al. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop (DLMIA 2018) and 8th International Workshop (ML-CDS 2018), Granada, Spain, 18–20 September 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Lee, H.; Kim, D. UACANet: Uncertainty Augmented Context Attention for Polyp Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 2167–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Jha, D.; Chanda, S.; Pal, U.; Johansen, H.D.; Johansen, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Ali, S.; Halvorsen, P. Msrf-net: A multi-scale residual fusion network for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.07451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Sindagi, V.A.; Hacihaliloglu, I.; Patel, V.M. KiU-Net: Overcomplete Convolutional Architectures for Biomedical Image and Volumetric Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. DoubleU-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MN, USA, 28–30 July 2020; pp. 558–564. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.-Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. nnFormer: Interleaved Transformer for Volumetric Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.03201. [Google Scholar]
- Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Patel, V.M. UNeXt: MLP-based Rapid Medical Image Segmentation Network. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.04967. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6230–6239. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.G.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C. Concurrent Spatial and Channel ‘Squeeze & Excitation’ in Fully Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; pp. 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.03545. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Yao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Qi, S. A Survey for Cervical Cytopathology Image Analysis Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 61687–61710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lu, Z.; Liu, W.; Yin, J. Cytoplasm and nuclei segmentation in cervical smear images using Radiating GVF Snake. Pattern Recogn. 2012, 5, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gençtav, A.; Aksoy, S.; Önder, S. Unsupervised segmentation and classification of cervical cell images. Pattern Recogn. 2012, 45, 4151–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chankong, T.; Theera-Umpon, N.; Auephanwiriyakul, S. Automatic cervical cell segmentation and classification in Pap smears. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 539–560. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Mangat, K.K. An improved nucleus segmentation for cervical cell images using FCM clustering and BPNN. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Jaipur, India, 21–24 September 2016; pp. 1924–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, S.; Bhavsar, A.; Sao, A.K.; Harinarayan, K.K. CNN based segmentation of nuclei in PAP-smear images with selective pre-processing. In Medical Imaging 2018: Digital Pathology; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Houston, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Allehaibi, K.H.S.; Nugroho, L.E.; Lazuardi, L.; Prabuwono, A.S.; Mantoro, T. Segmentation and classification of cervical cells using deep learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 16925–116941. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Song, Q.; Li, A.; Zhang, P.; Gui, Z. Automatic segmentation of cervical nuclei based on deep learning and a conditional random field. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 53709–53721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, N.F.; Miller, G.; Moen, E.; Kong, A.; Kagel, A.; Dougherty, T.; Fullaway, C.C.; McIntosh, B.J.; Leow, K.X.; Schwartz, M.S.; et al. Whole-cell segmentation of tissue images with human-level performance using large-scale data annotation and deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 555–565. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Huang, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Fu, C. TCTrack: Temporal Contexts for Aerial Tracking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01885. [Google Scholar]
- Konwer, A.; Xu, X.; Bae, J.; Chen, C.; Prasanna, P. Temporal Context Matters: Enhancing Single Image Prediction with Disease Progression Representations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01933. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, G.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. DenseCLIP: Language-Guided Dense Prediction with Context-Aware Prompting. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.01518. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, S.; Wei, F.; Hu, H. GCNet: Non-Local Networks Meet Squeeze-Excitation Networks and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1971–1980. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.-H.; Xu, T.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Liu, Z.-N.; Jiang, P.-T.; Mu, T.-J.; Zhang, S.-H.; Martin, R.R.; Cheng, M.-M.; Hu, S.-M. Attention Mechanisms in Computer Vision: A Survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.07624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Wu, B.G.; Zhu, P.F.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11531–11539. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q.B. Rotate to attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3138–3147. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, A.M.; Marques, R.C.; Medeiros, F.N.; Neto, J.F.R.; Bianchi, A.G.; Carneiro, C.M.; Ushizima, D.M. Hierarchical median narrow band for level set segmentation of cervical cell nuclei. Measurement 2021, 176, 109232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Methods | Nuclei | Cytoplasm | #Params | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSI | Precision | Recall | ZSI | Precision | Recall | ||
| UNet (baseline) | 0.875 ± 0.12 | 0.865 ± 0.13 | 0.890 ± 0.13 | 0.764 ± 0.14 | 0.748 ± 0.12 | 0.780 ± 0.15 | 13.40 M |
| UNet + GC [38] | 0.894 ± 0.11 | 0.877 ± 0.13 | 0.912 ± 0.12 | 0.781 ± 0.13 | 0.767 ± 0.13 | 0.786 ± 0.12 | 13.74 M |
| UNet + SE [41] | 0.887 ± 0.10 | 0.873 ± 0.10 | 0.908 ± 0.12 | 0.775 ± 0.12 | 0.751 ± 0.12 | 0.800 ± 0.13 | 13.44 M |
| UNet + CBAM [42] | 0.892 ± 0.10 | 0.862 ± 0.09 | 0.924 ± 0.12 | 0.786 ± 0.13 | 0.782 ± 0.15 | 0.790 ± 0.15 | 13.48 M |
| UNet + GDLA (ours) | 0.913 ± 0.09 | 0.888 ± 0.11 | 0.936 ± 0.13 | 0.796 ± 0.11 | 0.805 ± 0.08 | 0.787 ± 0.11 | 14.09 M |
| Methods | ZSI | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGVF algorithm [26] | 0.87 ± 0.19 | 0.83 ± 0.20 | 0.96 ± 0.13 |
| Unsupervised [27] | 0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.88 ± 0.15 | 0.93 ± 0.15 |
| FCM [29] | 0.80 ± 0.24 | 0.85 ± 0.21 | 0.83 ± 0.25 |
| SP-CNN [30] | 0.90 ± N/A | 0.89 ± N/A | 0.91 ± N/A |
| Gap-search MRF [2] | 0.91 ± 0.07 | N/A | N/A |
| Mask-RCNN [32] | 0.95 ± 0.10 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 0.96 ± 0.11 |
| D-MEM [7] | 0.933 ± 0.14 | 0.946 ± 0.06 | 0.984 ± 0.00 |
| PUG-Net [8] | 0.911 ± 0.10 | 0.890 ± 0.12 | 0.950 ± 0.11 |
| HMLS [45] | 0.90 ± 0.12 | 0.91 ± 0.13 | 0.93 ± 0.13 |
| Proposed | 0.913 ± 0.09 | 0.888 ± 0.11 | 0.936 ± 0.13 |
| Methods | Nuclei | Cytoplasm | #Params | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSI | Precision | Recall | ZSI | Precision | Recall | ||
| baseline | 0.875 ± 0.12 | 0.865 ± 0.13 | 0.890 ± 0.13 | 0.764 ± 0.14 | 0.748 ± 0.12 | 0.780 ± 0.15 | 13.40 M |
| + s1 | 0.893 ± 0.11 | 0.862 ± 0.12 | 0.927 ± 0.14 | 0.778 ± 0.11 | 0.786 ± 0.12 | 0.775 ± 0.12 | 13.43 M |
| + s1 + s2 | 0.902 ± 0.11 | 0.873 ± 0.11 | 0.934 ± 0.12 | 0.785 ± 0.10 | 0.792 ± 0.12 | 0.777 ± 0.12 | 13.56 M |
| + s1 + s2 + s3 | 0.913 ± 0.09 | 0.888 ± 0.11 | 0.936 ± 0.13 | 0.796 ± 0.11 | 0.805 ± 0.08 | 0.787 ± 0.11 | 14.09 M |
| SA | CA | GD | Nuclei | Cytoplasm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.875 ± 0.12 | 0.764 ± 0.14 | |||
| ✓ | 0.872 ± 0.08 | 0.763 ± 0.10 | ||
| ✓ | 0.887 ± 0.10 | 0.774 ± 0.10 | ||
| ✓ | 0.894 ± 0.07 | 0.781 ± 0.08 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.885 ± 0.12 | 0.770 ± 0.11 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.904 ± 0.10 | 0.786 ± 0.15 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.907 ± 0.12 | 0.787 ± 0.13 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.913 ± 0.09 | 0.796 ± 0.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Sun, C.; Xu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K. Cervical Cell Segmentation Method Based on Global Dependency and Local Attention. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157742
Li G, Sun C, Xu C, Zheng Y, Wang K. Cervical Cell Segmentation Method Based on Global Dependency and Local Attention. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157742
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gang, Chengjie Sun, Chuanyun Xu, Yu Zheng, and Keya Wang. 2022. "Cervical Cell Segmentation Method Based on Global Dependency and Local Attention" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157742
APA StyleLi, G., Sun, C., Xu, C., Zheng, Y., & Wang, K. (2022). Cervical Cell Segmentation Method Based on Global Dependency and Local Attention. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157742





