Investigation of Sonosensitizers Based on Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
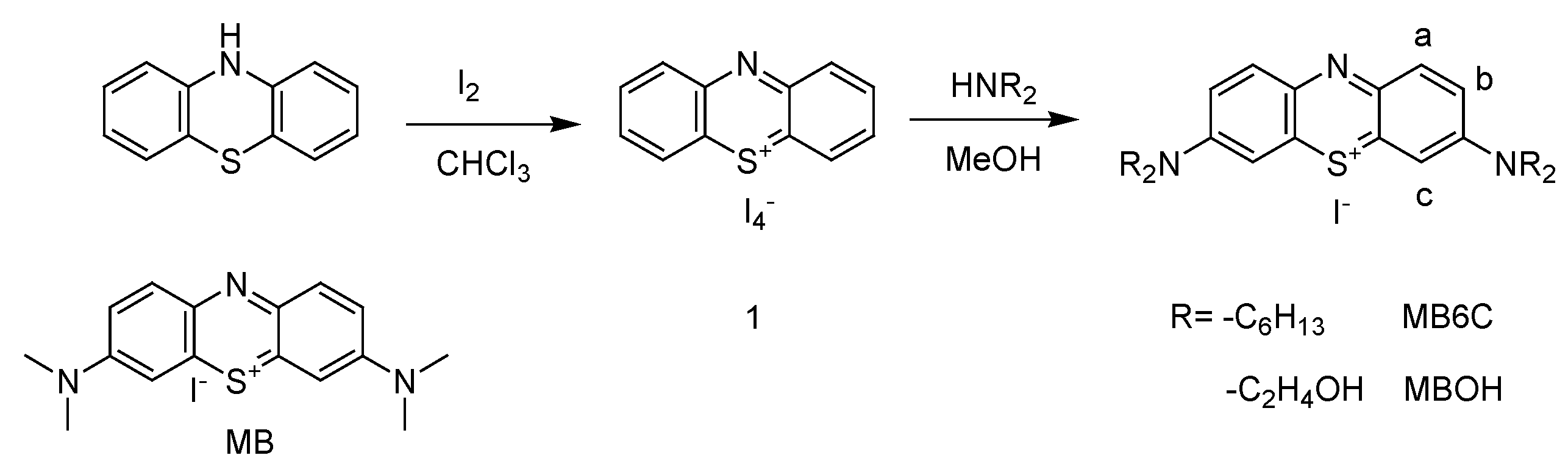
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. MTT Assay
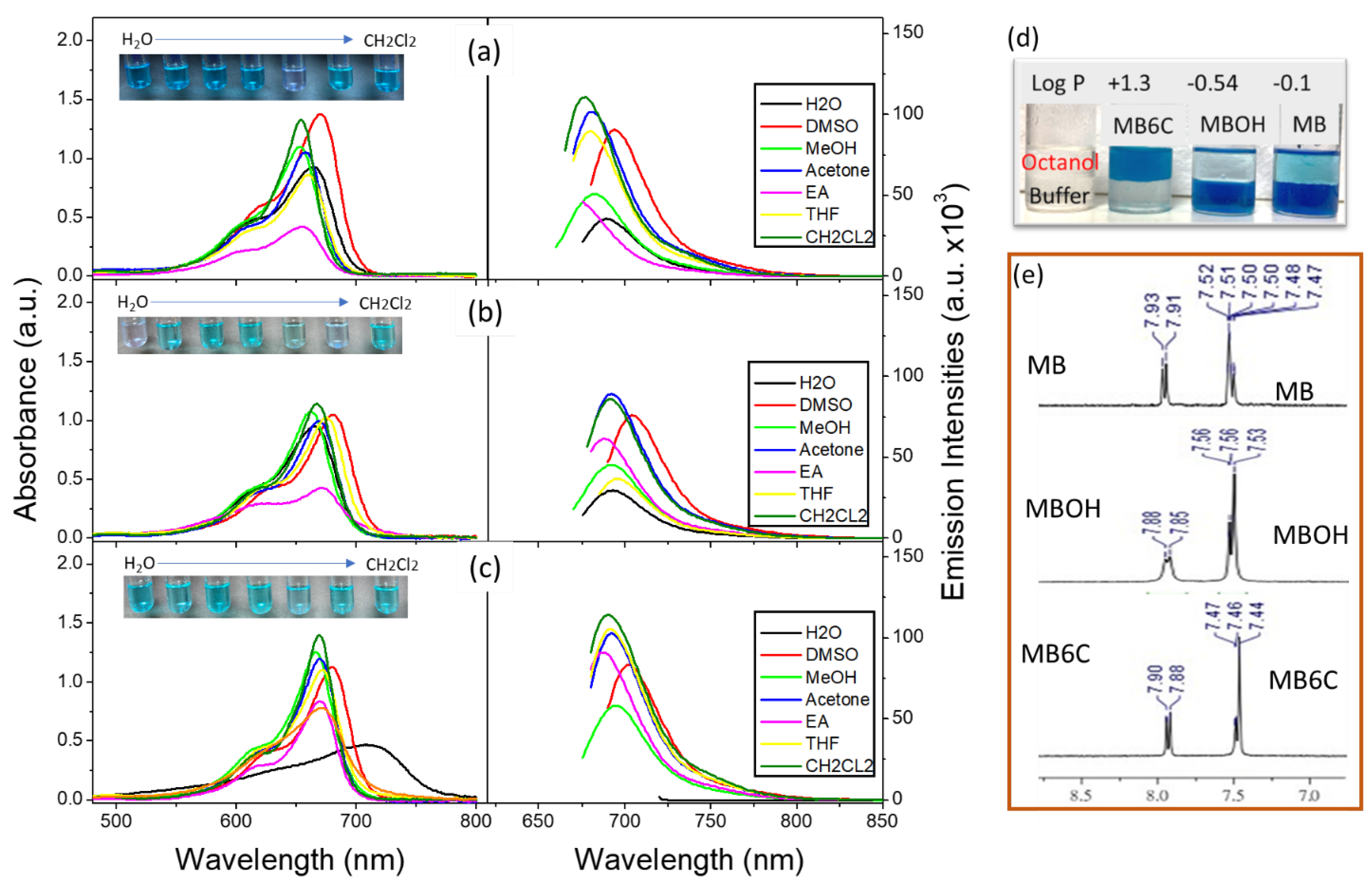
2.5. Hydrophilic–Lipophilic Balance (LogP)
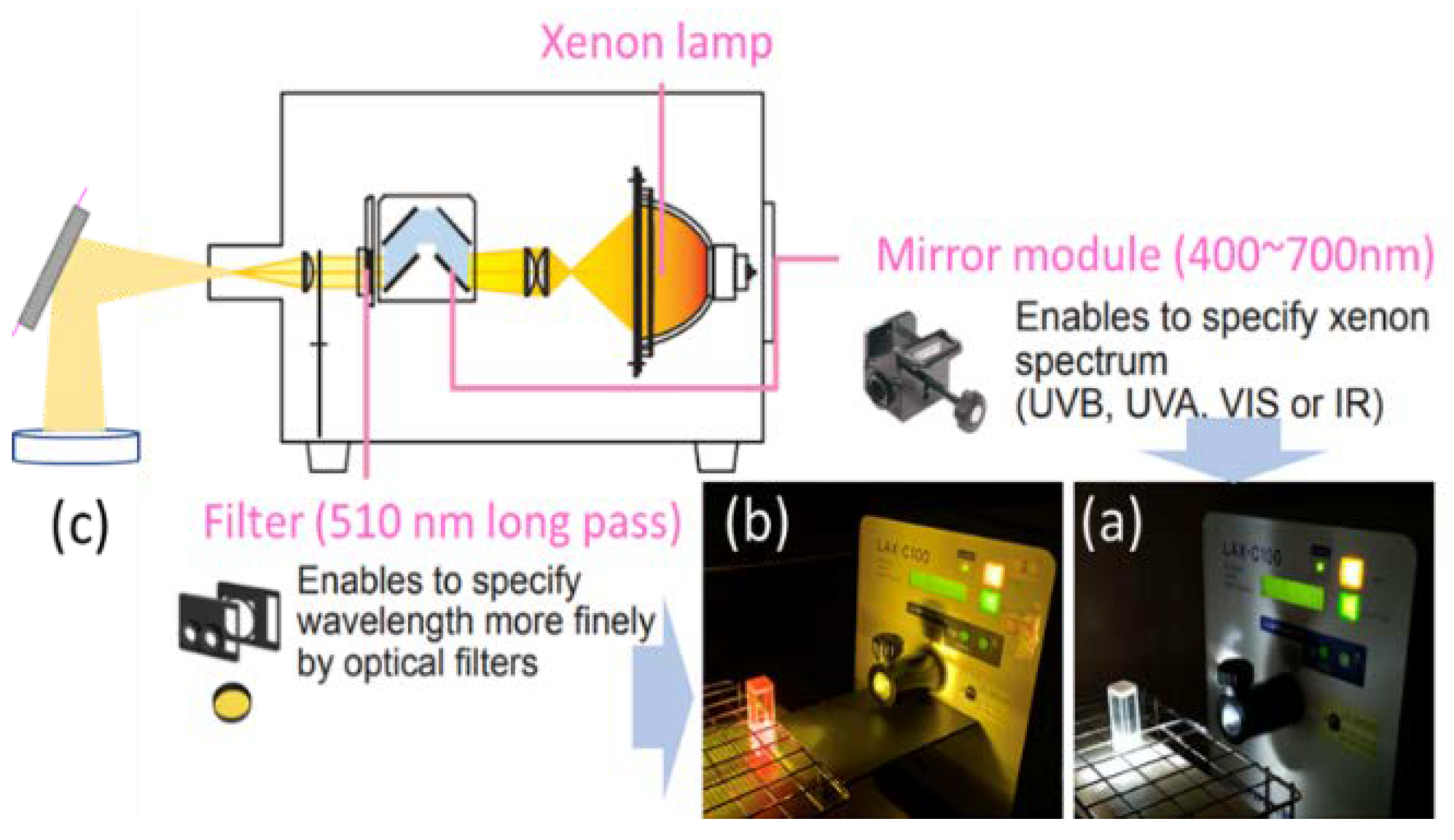
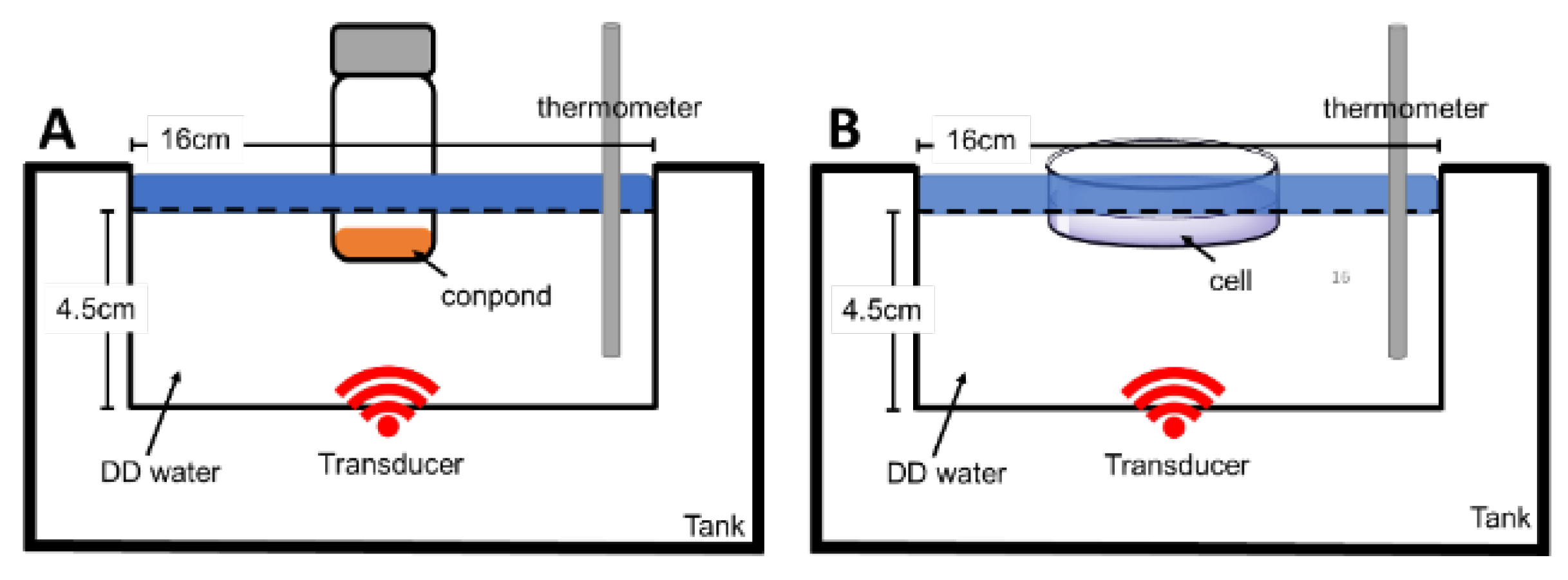
2.6. Design of PDT and SDT Apparatus Setting
2.6.1. Measurement of Photoinduced ROS and Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6.2. Measurement of Sono-Induced ROS and Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7. Sinlet Oxygen (1O2) Detection Using a Chemical Probe
2.8. Double Stain Apoptosis Detection (Hoechst 33342/PI)
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Basic Spectroscopic Properties
3.2. Generation and Stability of Singlet Oxygen
3.3. Cellular Toxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Han, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, C.; et al. Light-Triggered In Situ Gelation to Enable Robust Photodynamic-Immunotherapy by Repeated Stimulations. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1900927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Kuang, J.; Li, C.-X.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, D.; Zeng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.-Z. Enhanced Immunotherapy Based on Photodynamic Therapy for Both Primary and Lung Metastasis Tumor Eradication. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1978–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Sheng, Z.; Gao, G.; Siu, F.; Liu, C.; Wan, Q.; Gong, P.; Zheng, H.; Ma, Y.; Cai, L. Activatable albumin-photosensitizer nanoassemblies for triple-modal imaging and thermal-modulated photodynamic therapy of cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 93, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y. Micro/Nanoparticle-Augmented Sonodynamic Therapy (SDT): Breaking the Depth Shallow of Photoactivation. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8097–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolekile, N.; Nelana, S.; Oluwafemi, O.S. Porphyrin as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agent. Molecules 2019, 24, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebedeva, N.S.; Gubarev, Y.A.; Koifman, M.O.; Koifman, O.I. The Application of Porphyrins and Their Analogues for Inactivation of Viruses. Molecules 2020, 25, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatesti, N.; Munitic, I.; Jurak, I. Porphyrin-based cationic amphiphilic photosensitisers as potential anticancer, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive agents. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yumita, N.; Nishigaki, R.; Umemura, K.; Umemura, S.-I. Hematoporphyrin as a Sensitizer of Cell-damaging Effect of Ultrasound. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1989, 80, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; He, G.; Yin, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Lan, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, B. Titania-coated 2D gold nanoplates as nanoagents for synergistic photothermal/sonodynamic therapy in the second near-infrared window. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Based Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepagan, V.G.; You, D.G.; Um, W.; Ko, H.; Kwon, S.; Choi, K.Y.; Yi, G.-R.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, K.; et al. Long-Circulating Au-TiO2 Nanocomposite as a Sonosensitizer for ROS-Mediated Eradication of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6257–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Bai, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, X.; Liu, H. Metal-Organic-Framework-Derived Carbon Nanostructure Augmented Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1800180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, N.; Igarashi, T.; Riesz, P. Evidence against singlet oxygen formation by sonolysis of aqueous oxygen-saturated solutions of Hematoporphyrin and Rose Bengal: The mechanism of sonodynamic therapy. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2000, 7, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumita, N.; Iwase, Y.; Nishi, K.; Komatsu, H.; Takeda, K.; Onodera, K.; Fukai, T.; Ikeda, T.; Umemura, S.-I.; Okudaira, K.; et al. Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species in Sonodynamically Induced Apoptosis Using a Novel Porphyrin Derivative. Theranostics 2012, 2, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumita, N.; Okuyama, N.; Sasaki, K.; Umemura, S.-I. Sonodynamic therapy on chemically induced mammary tumor: Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and sonodynamically induced antitumor effect of gallium–porphyrin complex ATX-70. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 60, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, B.; Tang, F.; Huang, J. Recent progress in development of new sonosensitizers for sonodynamic cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, W.; Honda, H.; Feril, L.B.; Kudo, N.; Kondo, T. Comparison between sonodynamic effect and photodynamic effect with photosensitizers on free radical formation and cell killing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2006, 13, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, P.; Hu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Sonodynamic antitumor effect of a novel sonosensitizer on S180 solid tumor. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, C.; Owen, J.; Stride, E.; Fowley, C.; Nesbitt, H.; Cochrane, D.; Coussios, C.; Borden, M.; Nomikou, N.; McHale, A.P.; et al. Oxygen carrying microbubbles for enhanced sonodynamic therapy of hypoxic tumours. J. Control. Release 2015, 203, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costley, D.; Nesbitt, H.; Ternan, N.; Dooley, J.; Huang, Y.; Hamblin, M.R.; McHale, A.P.; Callan, J.F. Sonodynamic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria using a Rose Bengal–antimicrobial peptide conjugate. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, W.; Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Nan, F.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Lee, C.-S.; Wang, P. Biodegradable Natural Product-Based Nanoparticles for Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging-Guided Sonodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18178–18185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, P. Comparison of hypocrellin B-mediated sonodynamic responsiveness between sensitive and multidrug-resistant human gastric cancer cell lines. J. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 46, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Luo, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Oxygen-Self-Produced Nanoplatform for Relieving Hypoxia and Breaking Resistance to Sonodynamic Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12849–12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Song, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, K.; Tan, B.; Wang, D.; Yang, N.; Wang, Z.-G.; Li, X. Mitochondria-Targeted and Ultrasound-Activated Nanodroplets for Enhanced Deep-Penetration Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9355–9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.-W.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N. Recent advances of sonodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomikou, N.; Sterrett, C.; Arthur, C.; McCaughan, B.; Callan, J.F.; McHale, A.P. The Effects of Ultrasound and Light on Indocyanine-Green-Treated Tumour Cells and Tissues. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Sun, X.; Zhu, X.; Lv, F.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Guo, W.; Cao, W.; Yang, L.; Tian, Y. Apoptosis of THP-1 Derived Macrophages Induced by Sonodynamic Therapy Using a New Sonosensitizer Hydroxyl Acetylated Curcumin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ip, M.; Leung, A.W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, B.-T.; Ip, S.-P.; Xu, C. Sonodynamic action of curcumin on foodborne bacteria Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli. Ultrasonics 2015, 62, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Cheng, J.; Sun, X.; Guo, S.; Cao, W.; Chen, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy on macrophages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, H.; Yao, J.; et al. Inhibition of VDAC1 prevents Ca2+-mediated oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by 5-aminolevulinic acid mediated sonodynamic therapy in THP-1 macrophages. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teranishi, R.; Matsuda, T.; Yuba, E.; Kono, K.; Harada, A. Sonodynamic Therapeutic Effects of Sonosensitizers with Different Intracellular Distribution Delivered by Hollow Nanocapsules Exhibiting Cytosol Specific Release. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, e1800365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Deng, X.; Xu, G.; Xiao, X.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Ma, P.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J. A Novel Pt–TiO2 Heterostructure with Oxygen-Deficient Layer as Bilaterally Enhanced Sonosensitizer for Synergistic Chemo-Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghahosseini, F.; Arbabi-Kalati, F.; Fashtami, L.A.; Djavid, G.E.; Fateh, M.; Beitollahi, J.M. Methylene blue-mediated photodynamic therapy: A possible alternative treatment for oral lichen planus. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, K.; Beck, G.; Genze, F.; Rück, A. Methylene blue mediated photodynamic therapy in experimental colorectal tumors in mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 57, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, M.; Crossley, K. Methylene Blue—A Therapeutic Dye for All Seasons? J. Chemother. 2002, 14, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, R.H.; Coulibaly, B.; Stich, A.; Scheiwein, M.; Merkle, H.; Eubel, J.; Becker, K.; Becher, H.; Müller, O.; Zich, T.; et al. Methylene blue as an antimalarial agent. Redox Rep. 2003, 8, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komori, C.; Okada, K.; Kawamura, K.; Chida, S.; Suzuki, T. The sonodynamic antitumor effect of methylene blue on sarcoma180 cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2411–2415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Xia, X.; Jiang, Y.; Leung, A.W.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Yu, H.; Bai, D.; Xu, C. Apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells induced by methylene blue-mediated sonodynamic action. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Leung, A.W.; Xu, C. Effect of Ultrasound Sonication on Clonogenic Survival and Mitochondria of Ovarian Cancer Cells in the Presence of Methylene Blue. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, A.; Harvey, B.H.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Methylene Blue Analogues with Marginal Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Retain Antidepressant-like Activity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2917–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellish, K.J.; Cox, R.D.; Vernon, D.I.; Griffiths, J.; Brown, S.B. In Vitro Photodynamic Activity of a Series of Methylene Blue Analogues. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 75, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Crozals, G.; Farre, C.; Sigaud, M.; Fortgang, P.; Sanglar, C.; Chaix, C. Methylene blue phosphoramidite for DNA labelling. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4458–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollnick, K.; Griesbeck, A. Singlet oxygen photooxygenation of furans: Isolation and reactions of (4 + 2)-cycloaddition products. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, C.; Qi, W.; Meng, X.; Tian, R.; Qi, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, J. Synthesis, cytotoxicity and antitumour mechanism investigations of polyoxometalate doped silica nanospheres on breast cancer MCF-7 cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.; Koch, B. In vitro Anticancer Activities of Ethanolic Extracts of Dendrobium crepidatum and Dendrobium chrysanthum against T-cell lymphoma. J. Cytol. Histol. 2016, 7, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Su, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-C. Special Reactive Oxygen Species Generation by a Highly Photostable BODIPY-Based Photosensitizer for Selective Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12935–12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
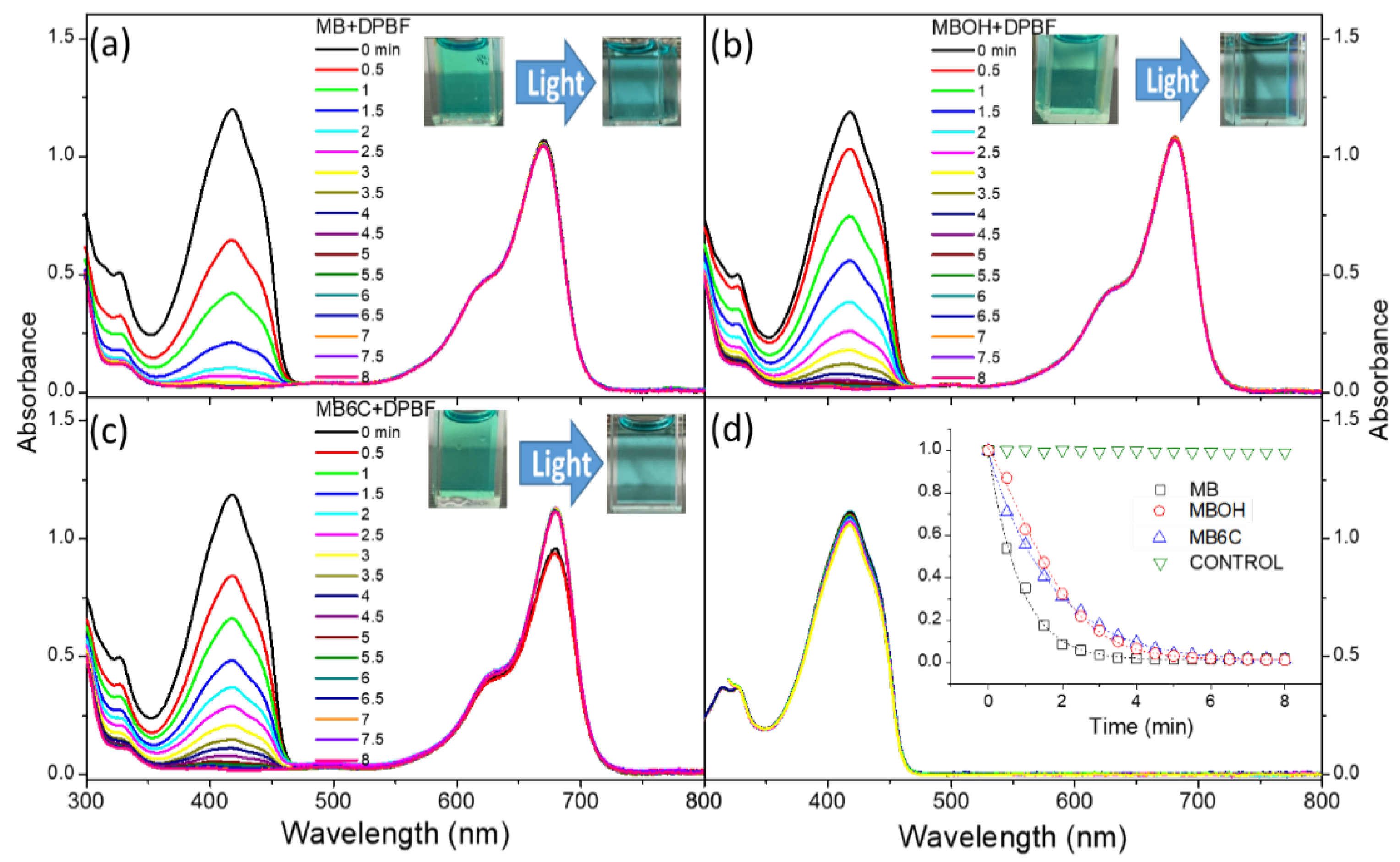
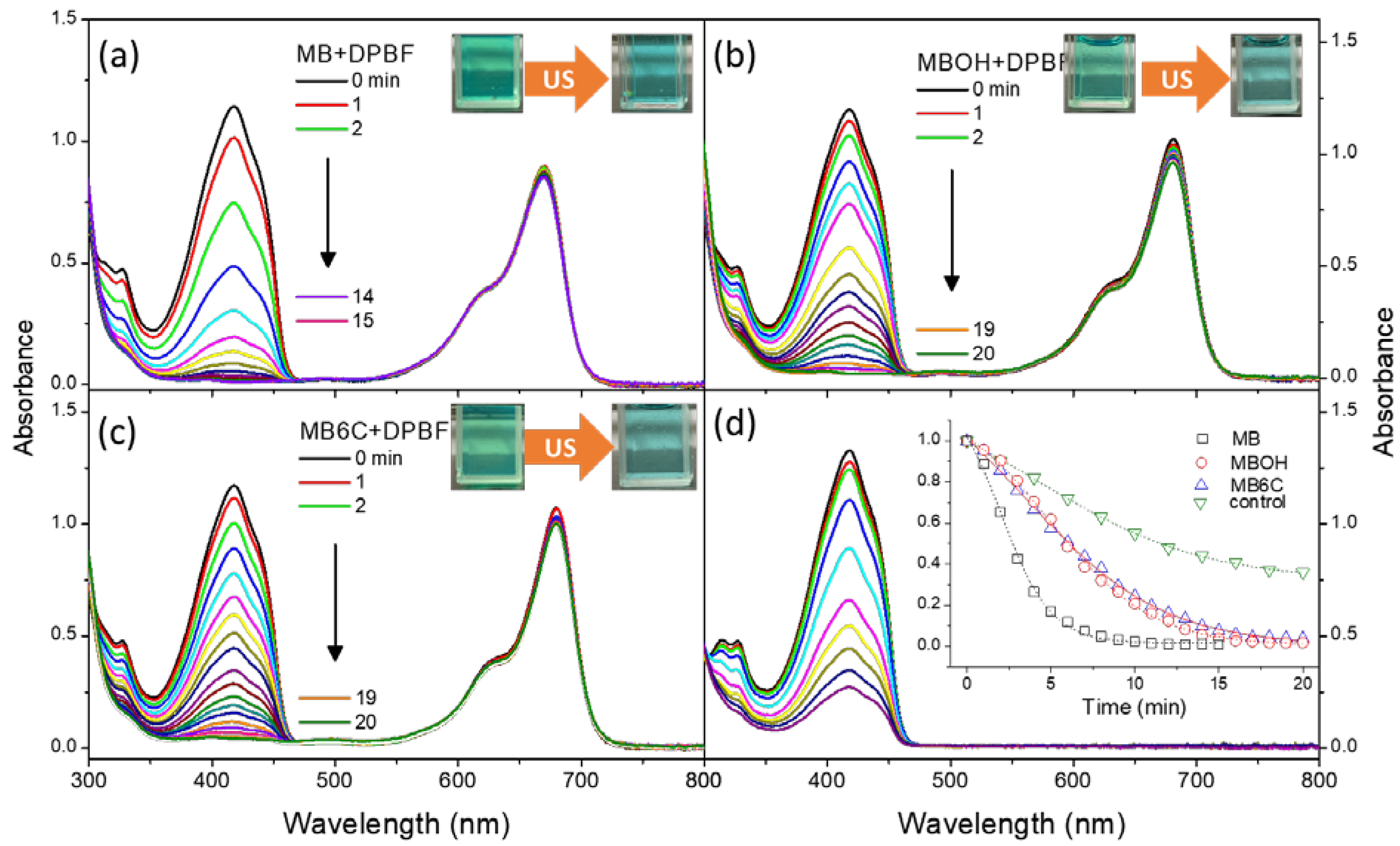
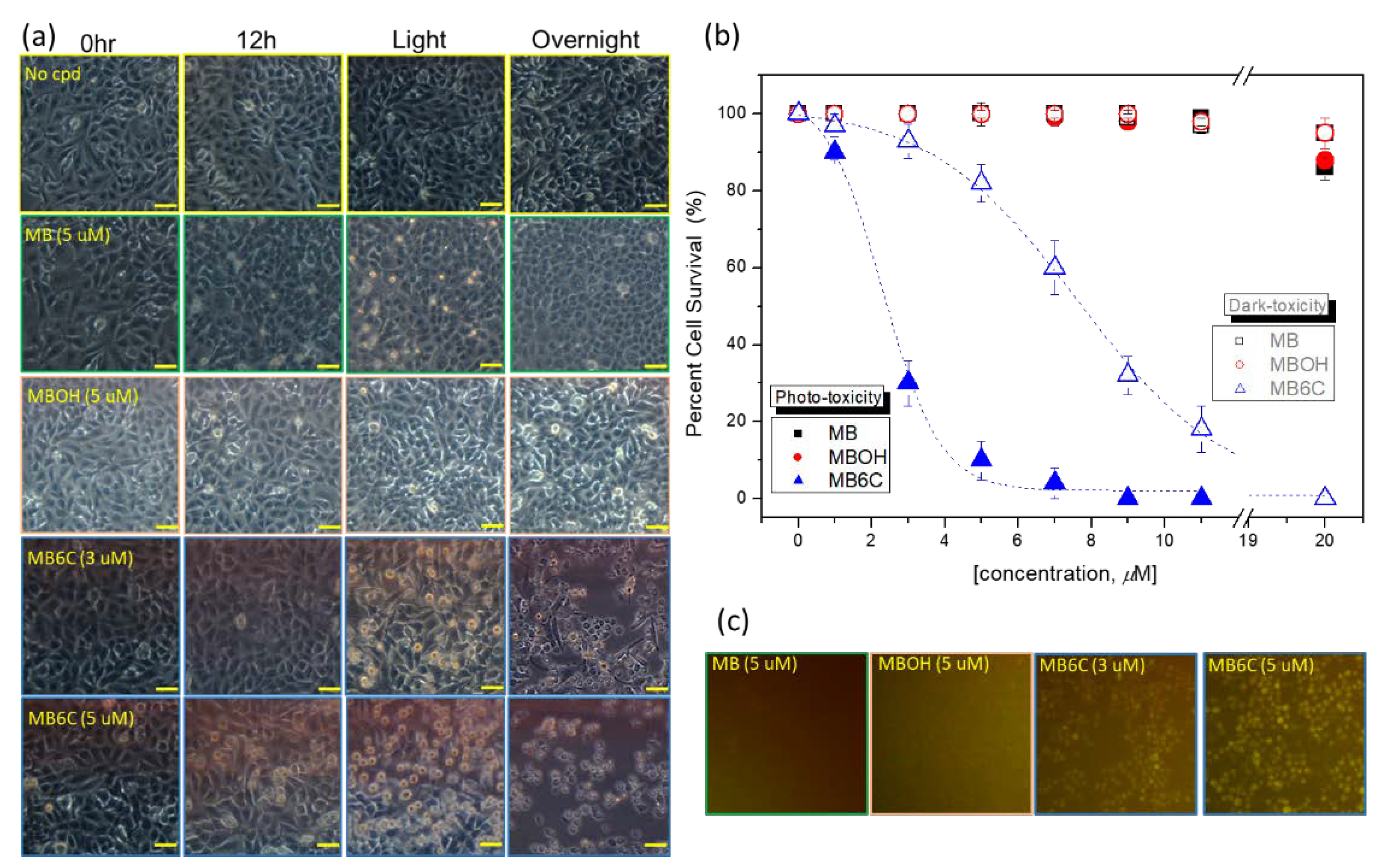

| LogP | Toxicity (IC50, μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark- | Photo- | Sono- * | ||
| MB | −0.1 | >20 | >20 | >20 |
| MBOH | −0.54 | >20 | >20 | >20 |
| MB6C | +1.3 | ~7 | ~2.5 | 5 (×1), 1.5 (×2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-C.; Hsieh, C.-F.; Wu, H.-J.; Ameen, M.; Hung, T.-P. Investigation of Sonosensitizers Based on Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7819. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157819
Chang C-C, Hsieh C-F, Wu H-J, Ameen M, Hung T-P. Investigation of Sonosensitizers Based on Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7819. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157819
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Cheng-Chung, Chia-Feng Hsieh, Hsing-Ju Wu, Mohamed Ameen, and Tun-Pin Hung. 2022. "Investigation of Sonosensitizers Based on Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7819. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157819
APA StyleChang, C.-C., Hsieh, C.-F., Wu, H.-J., Ameen, M., & Hung, T.-P. (2022). Investigation of Sonosensitizers Based on Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7819. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157819






