A Scoping Literature Review of Relative Fundamental Frequency (RFF) in Individuals with and without Voice Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
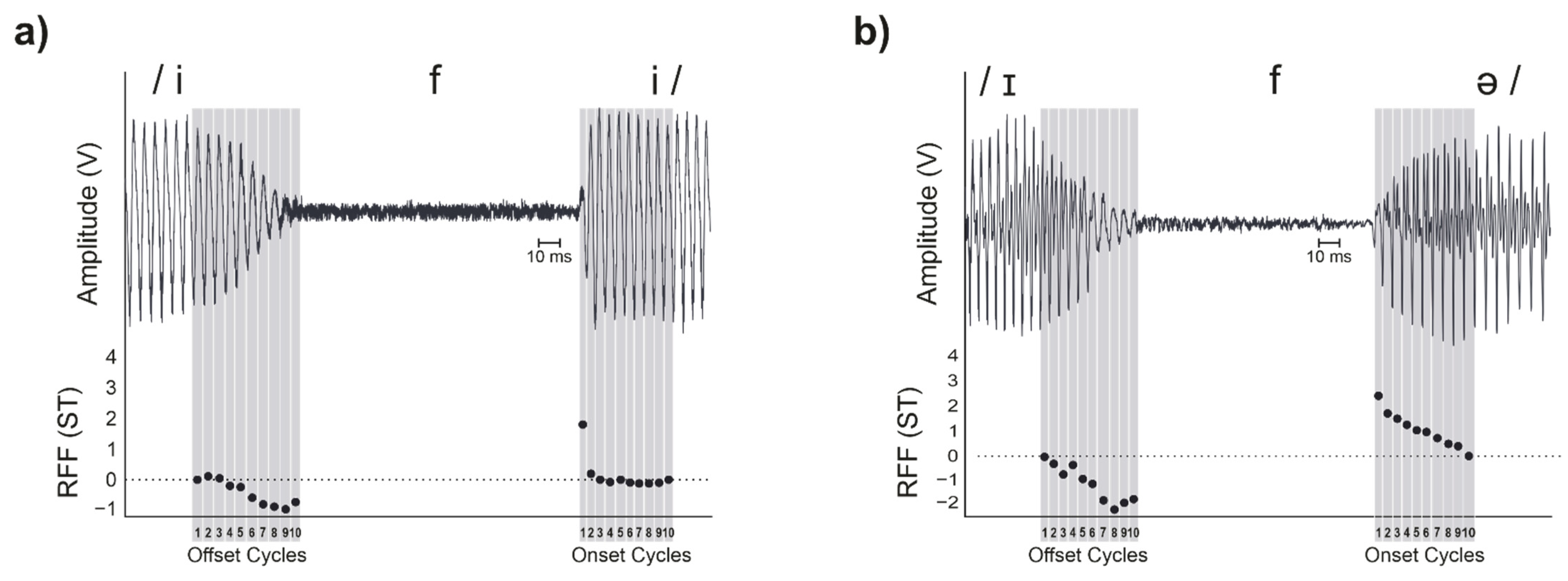
1.1. Stimuli and Calculation
1.2. Physiological Basis
1.3. Clinical Challenges
1.4. Purpose
2. Materials and Methods
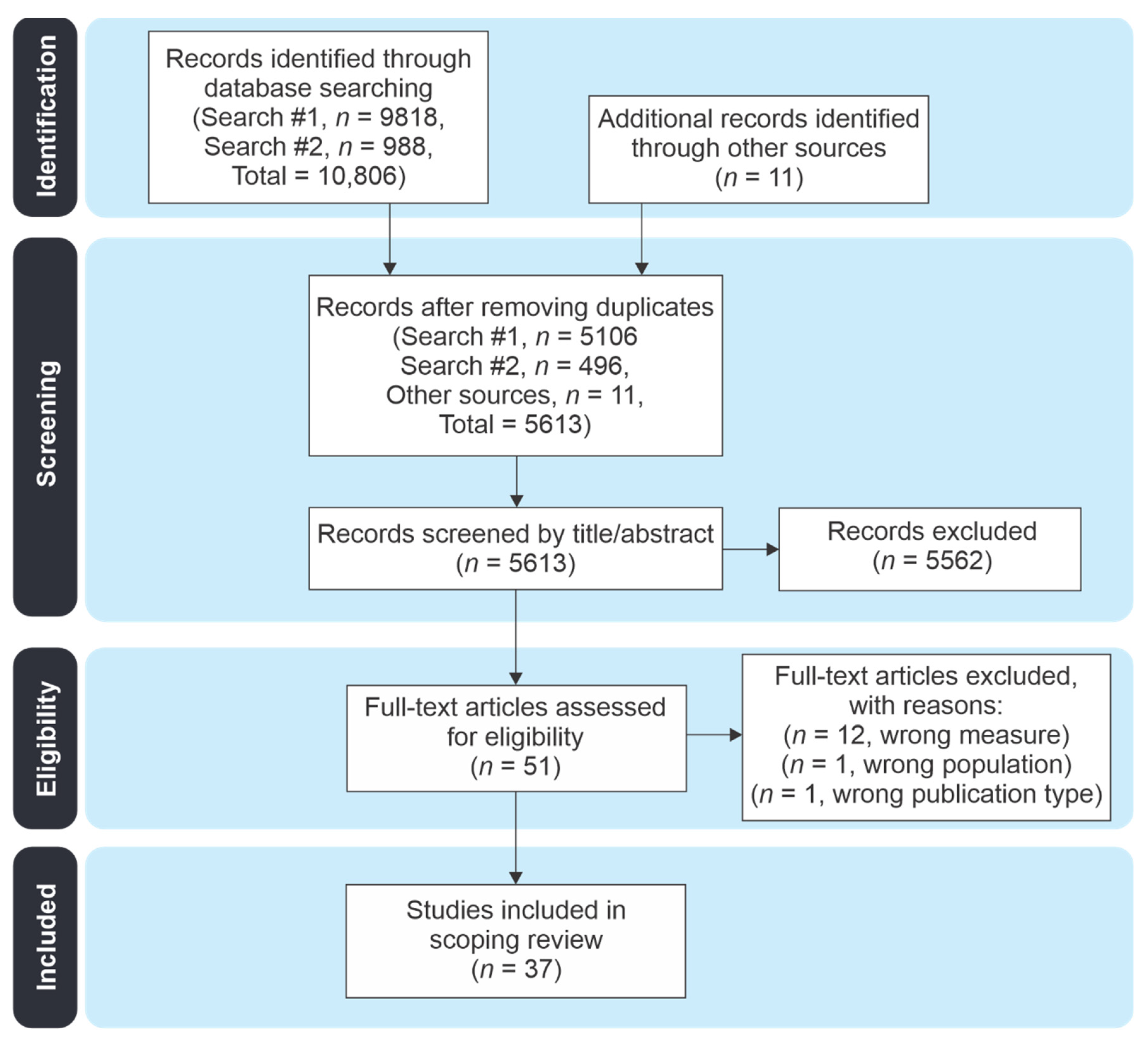
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Review Procedures
2.2.1. Study Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.2. Article Review and Data Extraction
- Study Information: author(s), year published, journal
- Subject Information: number of subjects, ages, sex/gender, diagnoses
- RFF Extraction Methods: speech stimuli, processing methods
- RFF Values for Offset Cycle 10 and Onset Cycle 1: for each population and/or study condition. Values that were reported in graphical form were not included or estimated.
- Statistical Results and Interpretations.
3. Results
3.1. Study Summary Information
3.2. RFF Acquisition and Processing
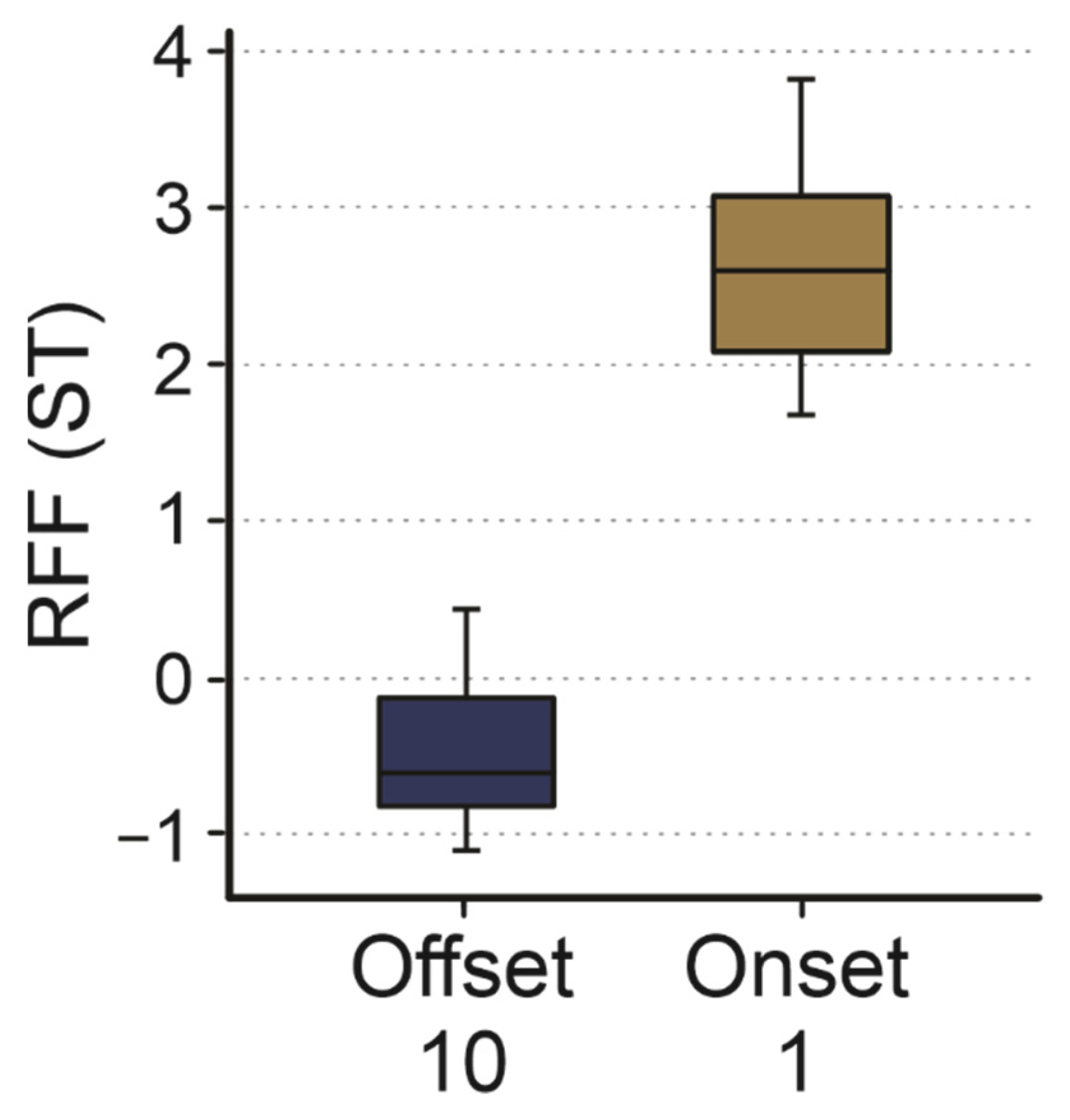
3.3. Onset Cycle 1 and Offset Cycle 10
3.4. Between- and Within-Subject Analyses
3.5. Perceptual Measures: Effort, Strain, and Dysphonia
4. Discussion
4.1. Method of RFF Computation
4.2. Interpreting RFF in Clinical Practice
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Example Search String: Embase
References
- McKenna, V.S.; Heller Murray, E.S.; Lien, Y.-A.S.; Stepp, C.E. The Relationship Between Relative Fundamental Frequency and a Kinematic Estimate of Laryngeal Stiffness in Healthy Adults. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2016, 59, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, D.P.; Cadiz, M.D.; Eadie, T.L.; Stepp, C.E. Acoustic Model of Perceived Overall Severity of Dysphonia in Adductor-Type Laryngeal Dystonia. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramig, L.O.; Verdolini, K. Treatment Efficacy: Voice Disorders. J. Speech Lang Hear. Res. 1998, 41, S101–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eadie, T.L.; Stepp, C.E. Acoustic Correlate of Vocal Effort in Spasmodic Dysphonia. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2013, 122, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goberman, A.M.; Blomgren, M. Fundamental Frequency Change During Offset and Onset of Voicing in Individuals with Parkinson Disease. J. Voice 2008, 22, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller Murray, E.S.; Lien, Y.-A.S.; Van Stan, J.H.; Mehta, D.D.; Hillman, R.E.; Noordzij, J.P.; Stepp, C.E. Relative Fundamental Frequency Distinguishes Between Phonotraumatic and Non-Phonotraumatic Vocal Hyperfunction. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.-A.S.; Michener, C.M.; Eadie, T.L.; Stepp, C.E. Individual Monitoring of Vocal Effort with Relative Fundamental Frequency: Relationships with Aerodynamics and Listener Perception. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2015, 58, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, V.S.; Stepp, C.E. The relationship between acoustical and perceptual measures of vocal effort. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Cádiz, M.D.; Nagle, K.F.; Stepp, C.E. Perceptual and Acoustic Assessment of Strain Using Synthetically Modified Voice Samples. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 3897–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Stepp, C.E. The Effects of Stress Type, Vowel Identity, Baseline f0, and Loudness on the Relative Fundamental Frequency of Individuals with Healthy Voices. J. Voice 2019, 33, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, G. Voice and Articulation Drillbook, 2nd ed.; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, B.C. Fundamental frequency during phonetically governed devoicing in normal young and aged speakers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 3642–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, C.E.; Hillman, R.E.; Heaton, J.T. The Impact of Vocal Hyperfunction on Relative Fundamental Frequency During Voicing Offset and Onset. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2010, 53, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, M.; Stevens, K. A note on Laryngeal Features; Quartely Prog. Rep. 101; Research Laboratory of Electronics MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg, M.; Mahshie, J.J. Monitoring Vocal Fold Abduction through Vocal Fold Contact Area. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1988, 31, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfqvist, A.; Baer, T.; McGarr, N.S.; Story, R.S. The cricothyroid muscle in voicing control. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M. Morphological Structure of the Vocal Cord as a Vibrator and its Variations. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 1974, 26, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, R.D.; Moll, K.L. Vocal-Tract Characteristics of the Stop Cognates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1969, 46, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, A.S.; Fairbanks, G. The Influence of Consonant Environment upon the Secondary Acoustical Characteristics of Vowels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1953, 25, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfqvist, A.; Koenig, L.L.; Mcgowan, R.S. Vocal tract aerodynamics in /aCa/ utterances: Measurements. Speech Commun. 1995, 16, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Ohala, J.; Vennard, W. The Function of Laryngeal Muscles in Regulating Fundamental Frequency and Intensity of Phonation. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1969, 12, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohde, R.N. Fundamental frequency as an acoustic correlate of stop consonant voicing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1984, 75, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohde, R.N. Fundamental frequency correlates of stop consonant voicing and vowel quality in the speech of preadoles-cent children. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, C.E.; Merchant, G.R.; Heaton, J.T.; Hillman, R.E. Effects of Voice Therapy on Relative Fundamental Frequency During Voicing Offset and Onset in Patients with Vocal Hyperfunction. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2011, 54, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, R.E.; Holmberg, E.B.; Perkell, J.S.; Walsh, M.; Vaughan, C. Objective assessment of vocal hyperfunction: An experi-mental framework and initial results. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1989, 32, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.R.; Awan, S.N.; Barkmeier-Kraemer, J.; Courey, M.; Deliyski, D.; Eadie, T.; Paul, D.; Švec, J.G.; Hillman, R. Recommended Protocols for Instrumental Assessment of Voice: American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Expert Panel to Develop a Protocol for Instrumental Assessment of Vocal Function. AJSLP 2018, 27, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, C.E.; Sawin, D.E.; Eadie, T.L. The Relationship Between Perception of Vocal Effort and Relative Fundamental Frequency During Voicing Offset and Onset. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Straus, S.E.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, R.M.; Zebrowski, P.M.; Moon, J.B. Phonetically governed voicing onset and offset in preschool children who stutter. J. Fluen. Disord. 2012, 37, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.L.; Stepp, C.E. Changes in Relative Fundamental Frequency Under Increased Cognitive Load in Individuals with Healthy Voices. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, R.B.; Chapleau, A.; Sundarrajan, A.; McKenna, V.; Sivasankar, M.P. The Interaction of Surface Hydration and Vocal Loading on Voice Measures. J. Voice 2017, 31, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, M.D.; Vojtech, J.M.; Hablani, S.; Mehta, D.D.; Buckley, D.P.; Noordzij, J.P.; Stepp, C.E. Automated Relative Fundamental Frequency Algorithms for Use with Neck-Surface Accelerometer Signals. J Voice 2022, 36, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller Murray, E.S.; Hands, G.L.; Calabrese, C.R.; Stepp, C.E. Effects of Adventitious Acute Vocal Trauma: Relative Fun-damental Frequency and Listener Perception. J. Voice 2016, 30, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller Murray, E.S.; Segina, R.K.; Woodnorth, G.H.; Stepp, C.E. Relative Fundamental Frequency in Children with and without Vocal Fold Nodules. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, L.S.; Heaton, J.T. The Effectiveness of Low-Level Light Therapy in Attenuating Vocal Fatigue. J. Voice 2017, 31, 384.e15–384.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.-A.S.; Calabrese, C.R.; Michener, C.M.; Heller Murray, E.; Van Stan, J.H.; Mehta, D.D.; Hillman, R.E.; Noordzij, J.P.; Stepp, C.E. Voice Relative Fundamental Frequency Via Neck-Skin Acceleration in Individuals with Voice Disorders. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2015, 58, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.-A.S.; Gattuccio, C.I.; Stepp, C.E. Effects of Phonetic Context on Relative Fundamental Frequency. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2014, 57, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.-A.S.; Heller Murray, E.S.; Calabrese, C.R.; Michener, C.M.; Van Stan, J.H.; Mehta, D.D.; Hillman, R.E.; Noordzij, J.P.; Stepp, C.E. Validation of an Algorithm for Semi-automated Estimation of Voice Relative Fundamental Frequency. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2017, 126, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.-A.S.; Stepp, C.E. Automated estimation of relative fundamental frequency 2013. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2136–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Lien, Y.-A.S.; Stepp, C.E. Comparison of voice relative fundamental frequency estimates derived from an accelerometer signal and low-pass filtered and unprocessed microphone signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 2977–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, V.S.; Kendall, C.L.; Patel, T.H.; Howell, R.J.; Gustin, R.L. Impact of Face Masks on Speech Acoustics and Vocal Effort in Healthcare Professionals. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, V.S.; Patel, T.H.; Kendall, C.L.; Howell, R.J.; Gustin, R.L. Voice Acoustics and Vocal Effort in Mask-Wearing Healthcare Professionals: A Comparison Pre- and Post-Workday. J. Voice 2021, S089219972100151X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Wang, F.; Díaz-Cádiz, M.; Vojtech, J.M.; Groll, M.D.; Stepp, C.E. Vocal fold kinematics and relative fundamental frequency as a function of obstruent type and speaker age. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Stepp, C.E. Test–Retest Reliability of Relative Fundamental Frequency and Conventional Acoustic, Aerodynamic, and Perceptual Measures in Individuals with Healthy Voices. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2019, 62, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, M.P.; Smith, A.B. Fundamental frequency onset and offset behavior: A comparative study of children and adults. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2002, 45, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Fetrow, R.A.; Merrill, R.M.; Dromey, C. Exploring the Clinical Utility of Relative Fundamental Frequency as an Objective Measure of Vocal Hyperfunction. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2016, 59, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Robb, M.P. Factors underlying short-term fundamental frequency variation during vocal onset and offset. Speech Lang. Hear. 2013, 16, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, C.E. Relative fundamental frequency during vocal onset and offset in older speakers with and without Parkinson’s disease. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mersbergen, M.; Lanza, E. Modulation of Relative Fundamental Frequency During Transient Emotional States. J. Voice 2019, 33, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtech, J.M.; Segina, R.K.; Buckley, D.; Kolin, K.R.; Tardif, M.C.; Noordzij, J.P.; Stepp, C.E. Refining algorithmic estimation of relative fundamental frequency: Accounting for sample characteristics and fundamental frequency estimation method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3184–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtech, J.; Cilento, D.; Luong, A.; Noordzij, J.; Diaz-Cadiz, M.; Groll, M.; Buckley, D.; McKenna, V.; Noordzij, J.; Stepp, C. Acoustic Identification of the Voicing Boundary during Intervocalic Offsets and Onsets Based on Vocal Fold Vibratory Measures. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerathunge, H.R.; Segina, R.K.; Tracy, L.; Stepp, C.E. Accuracy of Acoustic Measures of Voice via Telepractice Videocon-ferencing Platforms. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 2586–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, P. Praat, a system for doing phonetics by computer. Glot. Int. 2001, 5, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Kopf, L.M.; Jackson-Menaldi, C.; Rubin, A.D.; Skeffington, J.; Hunter, E.J.; Skowronski, M.D.; Shrivastav, R. Pitch Strength as an Outcome Measure for Treatment of Dysphonia. J. Voice 2017, 31, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, R.; Eddins, D.A.; Anand, S. Pitch strength of normal and dysphonic voices. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, C.E. RFF. BU STEPP Lab Sensorimotor Rehabil Eng n.d. Available online: https://sites.bu.edu/stepplab/research/rff/ (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Cheyne, H.A.; Hanson, H.M.; Genereux, R.P.; Stevens, K.N.; Hillman, R.E. Development and Testing of a Portable Vocal Ac-cumulator. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2003, 46, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, R.E.; Heaton, J.T.; Masaki, A.; Zeitels, S.M.; Cheyne, H.A. Ambulatory Monitoring of Disordered Voices. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2006, 115, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.D.; Van Stan, J.H.; Zañartu, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Guttag, J.V.; Espinoza, V.M.; Cortés, J.P.; Cheyne, H.A.I.; Hillman, R.E. Using Ambulatory Voice Monitoring to Investigate Common Voice Disorders: Research Update. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stan, J.H.; Mehta, D.D.; Zeitels, S.M.; Burns, J.A.; Barbu, A.M.; Hillman, R.E. Average Ambulatory Measures of Sound Pressure Level, Fundamental Frequency, and Vocal Dose Do Not Differ Between Adult Females with Phonotraumatic Lesions and Matched Control Subjects. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stan, J.H.; Ortiz, A.J.; Sternad, D.; Mehta, D.D.; Huo, C.; Hillman, R.E. Ambulatory Voice Biofeedback: Acquisition and Retention of Modified Daily Voice Use in Patients with Phonotraumatic Vocal Hyperfunction. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2022, 31, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsner-Smith, M.R.; Díaz-Cádiz, M.E.; Vojtech, J.M.; Buckley, D.P.; Mehta, D.D.; Hillman, R.E.; Tracy, L.F.; Noordzij, J.P.; Eadle, T.L.; Stepp, C.E. Clinical Cutoff Scores for Acoustic Indices of Vocal Hyperfunction That Combine Relative Fundamental Frequency and Cepstral Peak Prominence. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2022, 65, 1349–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenny, S.; Varacallo, M. Evidence Based Medicine; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kempster, G.B.; Gerratt, B.; Abbott, K.V.; Barkmeier-Kraemer, J.; Hillman, R.E. Consensus Auditory-Perceptual Evaluation of Voice: Development of a Standardized Clinical Protocol. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2009, 18, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Bottalico, P.; Gray, C. Vocal Fatigue in Prospective Vocal Professionals. J. Voice 2019, 35, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowell, S.Y.; Kelley, R.T.; Awan, S.N.; Colton, R.H.; Chan, N.H. Spectral- and Cepstral-Based Acoustic Features of Dysphonic, Strained Voice Quality. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2012, 121, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.L.; Lowell, S.Y.; Colton, R.H. Aerodynamic and Acoustic Features of Vocal Effort. J. Voice 2014, 28, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serry, M.A.; Stepp, C.E.; Peterson, S.D. Physics of phonation offset: Towards understanding relative fundamental frequency observations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.P.; Vojtech, J.M.; Stepp, C.E. Relative Fundamental Frequency in Individuals with Globus Syndrome and Muscle Tension Dysphagia. J. Voice 2021, S0892199721003477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.L.; François, F.A.; Buckley, D.P.; Stepp, C.E. Voice and Speech Changes in Transmasculine Individuals Following Circumlaryngeal Massage and Laryngeal Reposturing. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2022, 31, 1368–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, V.S.; Gustin, R.L.; Howell, R.J.; Patel, T.H.; Emery, M.B.; Kendall, C.L.; Kelliher, N.J. Developing Educational Health Modules to Improve Vocal Wellness in Mask-Wearing Occupational Voice Users. J. Voice 2021, S0892199721003921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtech, J.M.; Stepp, C.E. Effects of Age and Parkinson’s Disease on the Relationship between Vocal Fold Abductory Kinematics and Relative Fundamental Frequency. J. Voice 2022, S0892199722000704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McKenna, V.S.; Vojtech, J.M.; Previtera, M.; Kendall, C.L.; Carraro, K.E. A Scoping Literature Review of Relative Fundamental Frequency (RFF) in Individuals with and without Voice Disorders. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168121
McKenna VS, Vojtech JM, Previtera M, Kendall CL, Carraro KE. A Scoping Literature Review of Relative Fundamental Frequency (RFF) in Individuals with and without Voice Disorders. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(16):8121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168121
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcKenna, Victoria S., Jennifer M. Vojtech, Melissa Previtera, Courtney L. Kendall, and Kelly E. Carraro. 2022. "A Scoping Literature Review of Relative Fundamental Frequency (RFF) in Individuals with and without Voice Disorders" Applied Sciences 12, no. 16: 8121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168121
APA StyleMcKenna, V. S., Vojtech, J. M., Previtera, M., Kendall, C. L., & Carraro, K. E. (2022). A Scoping Literature Review of Relative Fundamental Frequency (RFF) in Individuals with and without Voice Disorders. Applied Sciences, 12(16), 8121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168121







