Abstract
Attention has been paid to bioflocculants production because of their effectiveness, innocuousness and environmental friendliness. This study aimed to characterise a bioflocculant from Bacillus megaterium BMBF and apply it in wastewater treatment. The proteins, carbohydrates and uronic acid were calculated using the Bradford, phenol–sulphuric acid and carbazole assays, respectively. An energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) and infrared spectrometry were employed for the identification of the elemental composition and effective units, respectively. Cytotoxicity was carried out against Vero (African green monkey kidney) and bovine dermis cells using a colorimetric cytotoxicity assay. The reduction in chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biological oxygen demand (BOD) in domestic and coal mine wastewater was studied using the Jar test. The flocculant was composed of 12% protein, 27% carbohydrates and 61% uronic acid. Infrared spectrometry indicated hydroxyl, carboxyl and amino groups. EDX indicated C (61%) and O (17.5%) as the main elements. The bioflocculant revealed the mean inhibition concentration of 59 ug/mL against bovine dermis and 240 µg/mL on Vero cells. Maximum COD and BOD removal percentages of 97% and 99.3% were recorded on coal mine wastewater treatment and about 99.2% (COD) and 93% (BOD) on domestic wastewater. In conclusion, the bioflocculant from B. megaterium has potential industrial utility.
1. Introduction
The constant development of industries and increase in population have led to the steady increase in the volumes of wastewater discharged into water bodies [1]. Annually, approximately 109 m3 of wastewater is globally produced. About 30% of the generated wastewater is from municipal wastewater, whereas over 60% comes from industries, such as coal mines [2]. The disposal of wastewater remains the main challenge, especially in third-world countries where roughly 8% of wastewater is treated prior to being discharged [3]. Water pollution imposes a threat to environment and human and animal health [4]. More than 70% of disease cases in third-world countries are associated with the consumption or drinking of polluted water [5]. Thus, recently, much attention has been given to the treatment of wastewater [4].
Flocculation is one of the methods which is widely employed to combat the challenge of wastewater [6]. During flocculation, colloids are eliminated or reduced from solution using flocculants. It is mainly used due to its efficiency, convenience and financial feasibility [7]. Flocculants are classified into: organic synthetic flocculants (i.e., acrylamide derivatives), inorganic flocculants (i.e., aluminium and ferric salts) and biological flocculants, which include microbial flocculants [8]. Inorganic flocculants are widely preferred and operational due to their economic advantages [9]. Nonetheless, they have moderate solubility and are highly sensitive to pH changes [10]. Thus, the shortcomings of the inorganic flocculants have led to the use of organic synthetic flocculants as alternatives [11]. Organic synthetic flocculants are effective at low concentrations and are inert to pH variations [12]. Nevertheless, the toxicity and nondegradation nature of their monomers have been major hindrances, as they impose a threat to humans, aquatic life and the environment [13]. Owing to ever-increasing environmental and health concerns, biological flocculants have been recently viewed as promising substitutes.
Microbial flocculants are biomolecules secreted by fungi, actinomycetes and bacteria during their growth and environmental interactions. They are in the form of lipids, proteins, polysaccharides and glycoproteins [13]. Microbial flocculants have gained attention due to their biodegradability, nontoxic nature and effectiveness [14]. The genus Bacillus of the family Bacillaceae consists of diverse bacterial strains known to secrete effective biofloccuants in larger quantities [15]. For instance, the bioflocculants from Bacillus salmalaya 139SI-7 have been used in the reduction of wastewater pollutants [16], whereas the bioflocculants from Bacillus licheniformis NJ3 were utilised to reduce turbidity in water [17]. Moreover, the bioflocculants from Bacillus megaterium PL8 and Bacillus megaterium SP1 were efficient in remediating dye and pollutants in wastewater [18,19]. Therefore, in our previous study, we isolated Bacillus megaterium BMBF from the intestines of the marine fish from Mthunzine Beach, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, and its culture parameters were optimised for effective bioflocculant production (unpublished).
This study aimed to characterise the bioflocculant from Bacillus megaterium BMBF and apply it in the remediation of domestic and coal mine wastewater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Media
The chemical substances and media were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The chemicals included: KBr salt, HCl, NaOH, LiCl, CaCl, KCl, NaCl, BaCl2, MnCl2, MgCl2, FeCl3, bovine serum albumin, glucose, Bradford reagent, Carbazole reagent, MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide), DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), 5-fluorouracil, FBS (fetal bovine serum) and streptomycin. The media included: MEM (minimum essential medium) and the production medium for the bioflocculant, which consisted of NaCl (0.1 g), starch (20.0 g), KH2PO4 (2.0 g), MgSO4 (0.2 g), casein (1.2 g) and K2HPO4 (5.0 g) in a litre of sterilised filtered sea water.
2.2. Bacterium, Extraction and Purification
B. megaterium BMBF was obtained from the −80 °C fridge in the microbiology laboratory at the University of Limpopo. It was then resuscitated in the medium at 37 °C, 220 rpm for 24 h. The precipitation technique was used to obtain the bioflocculant from the broth culture. B. megaterium BMBF (2% inoculum size) was inoculated into a litre of the bioflocculant production medium and cultured at a shaking speed of 220 rpm and a temperature of 30 °C and pH 7 for 60 h. Afterwards, the broth was centrifuged (10,000 rpm for 15 min) and a volume of sterilised distilled water was poured into the supernatant, slowly agitated gently and centrifuged. Thereafter, 2 volumes of 99% ethanol were transferred into the free-cell supernatant, stirred and placed at 4 °C for 720 min. The formed precipitate was dried and the flocculant was dissolved in 100 mL of the autoclaved distilled water. Subsequently, the bioflocculant was purified by adding a solution of chloroform and butanol (2:5: v/v), prior to being left to stand for 720 min. Afterwards, the whitish precipitate was centrifuged and dried. The weight of the obtained flocculant was expressed as g/L [20].
2.3. Chemical Compounds
The phenol–sulphuric acid method was utilised for the evaluation of the carbohydrate content using glucose as the standard. The biopolymer (0.2 g) was dissolved in the autoclaved distilled water (100 mL). Thereafter, phenol (0.2 mL) and 1 mL of sulphuric acid were also added. The solution was incubated for 12 min at room temperature. The mixture of 2 mL of the autoclaved distilled water, 10 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid and 2 mL of 5% phenol was used as a blank. The readings of the absorbance were then recorded at 496 nm [21]. The Bradford assay was employed to determine the total protein content. Briefly, the protein standard was prepared using bovine serum albumin (BSA). BSA standard solution (40 µL) and the bioflocculant treated with BSA (40 uL) were both transferred to 96-microwell plates. Then, Bradford reagent (185 µL) was loaded and the solutions were then incubated at room temperature for 2 min. For the blank, sterilised distilled water and Bradford reagent were used. The solutions were recorded at the wavelength of 590 nm. The standard curve was plotted and the total protein content was derived from the curve [22]. The carbazole–sulphuric acid assay was utilised to evaluate the amount of uronic acid using glucuronic acid as the standard. To the bioflocculant solution (0.5 mg in 0.2 mL), 20 µL of 4 mol/L sulfamic acid–potassium sulfamate was pipetted followed by the addition of 1.2 mL of the concentrated H2SO4. After the mixture cooled to room temperature, 50 µL of the carbazole reagent (0.15% w/v of carbazole in 99% ethanol) was added. Thereafter, the mixture was boiled in a water bath for 20 min, followed by cooling in an ice-water bath until it reached room temperature. The absorbance of the mixture was recorded at 525 nm [23].
2.4. Characterisation of the Bioflocculant
The physical morphologies of the samples (flocculated kaolin, flocculant and kaolin) were assessed by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The samples were sputter-coated with silicon and inserted into the scan electron microscope (SIGMA VP-03-67, ZEISS Microscopy, Cambridge, UK), and their surface images were captured in a low-vacuum mode at 20 kV [24]. The elemental analyser (X-Max EDS system, Oxford Instruments Inc, Oxford, UK) was utilised to identify different elements within the bioflocculant. Briefly, 5.0 mg of the biopolymer was fixed onto the silicon-coated slides and then inserted into the instrument for evaluation [25]. The effective components were studied by Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. The biopolymer was first pulverised with KBr. Then, an FTIR spectroscope (PerkinElmer UATR TWO, 2000, PerkinElmer LAS, Rodgau, Germany) was run at 500–4000 cm−1 [26]. The pyrolysis of the biopolymer was explored by thermogravimetric mass spectrometry. The sample was inserted into the instrument (Model: DTG-60, Shimadzu Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and heated at a rate of 15 °C per minute. The nitrogen (N) gas was supplied at a constant flow of 20 mL/minute [27].
2.5. Impact of Dosage Size and Metal Ions
The Jar test was used to ascertain the impact of dosage on flocculation. Two millilitres of different concentrations of the bioflocculant (0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 mg/mL) were pipetted separately into 95 mL of kaolin clay suspension (4 g/L), followed by the addition of 3 mL of 1% CaCl2. The mixtures were shaken at 180 rpm for 2 min. Thereafter, they were gently agitated at 50 rpm for 5 min and left to sediment. After 5 min, the top supernatant was drawn and the flocculating efficiency was evaluated by recording its absorbance at the wavelength of 550 nm. For control, the supernatant was replaced with the sterilised medium (see Section 2.1). Thereafter, the percentage flocculating efficiency (%FE) was recorded as:
where Aa and Bb represent the absorbance at 552 nm of the control and treated samples [28]. The influence of cations on flocculation was assessed. CaCl2 solution, which was utilised in the standard method (see Section 2.9), was substituted with dissimilar metal ions. The mixture of the bioflocculant and kaolin clay in the absence of the metal ions served as the control. The flocculation rate was then calculated as defined above [29].
(%FE) = Aa − Bb/Aa × 100
2.6. pH and Thermal Stabilities of the Bioflocculant
The pH stability of the biopolymer was estimated by following the protocol described by He et al. [30]. The kaolin’s (4 g/L) pH was altered within pH 3 to 12. The biopolymer and CaCl2 were pipetted into the kaolin clay solution. The flocculating action was assessed as stipulated previously. The thermal effect on the biopolymer was investigated using the Jar test. Ten millilitres of the biopolymer was exposed to different temperatures (50 to 100 °C) for 30 min. Thereafter, the heated bioflocculant (2 mL) and 3 mL of CaCl2 (1% v/w) were both poured into kaolin clay solution (95 mL, 4 g/mL). Afterwards, the flocculation was determined following the previously described protocol [31].
2.7. Cytotoxicity
The cytotoxicity of the biopolymer was evaluated on Vero and bovine dermis using the MTT technique. Both cells were cultured on MEM, which was supplemented with streptomycin (100 µg/mL) and 10% of FBS. The MTT assay was performed using 96-microwell plates, which contained 1.5 × 103 cells/well in 100 µL MEM. Prior to inoculation, the cells were grown at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 24 h. Afterwards, different bioflocculant concentrations (50–300 µg/mL) were pipetted into the wells and reincubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 48 h, followed by the MTT assay. The 5-fluorouracil was used as the standard, whereas 0.2% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) replaced the flocculant as the negative control. The used medium was substituted with the fresh medium, which was supplemented with 10% MTT reagent and reincubated for 4 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2. Thereafter, the formazan particles were solubilised in DMSO. The absorbance was recorded at 576 nm. The median inhibitory concentration of the bioflocculant (IC50) was calculated from the GraphPad Prism version 6, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) using the linear regression technique [32].
2.8. Reduction of Pollutants in Wastewater
The domestic wastewater was aseptically obtained from East Rand Treatment Plant in Johannesburg, South Africa, and the coal mine wastewater was sampled at the local mine wastewater plant. The BOD and COD of the samples were measured using the test kits, following the manufacturers’ instructions. The wastewater samples were adjusted to pH 7 prior to treatment. Thereafter, 3 mL of CaCl2 and 2 mL of the obtained optimum bioflocculant concentration were pipetted into 95 mL of the water samples. The solutions were stirred for 2 min at 180 rpm; the agitation was lowered for 5 min to 50 rpm and then left to sediment for 5 min. For comparison, aluminium chloride and ferric chloride were applied as positive controls, in the same concentrations as the bioflocculant. The percentage reduction efficiencies (%RE) of the flocculants were measured using the formula:
where Aa and Bb are the readings of the samples before and after treatment, respectively [20].
%RE = Aa − Bb/Aa × 100
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The obtained data were articulated as the mean ± standard deviation. The tests were performed in triplicates. The obtained results were analysed using ANOVA (one-way analysis of variance) to find the differences, using Graph Pad Prism™ 6.1. The obtained readings were regarded as different when p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. B. megaterium BMBF’s Bioflocculant Yield
The recovered yield of the bioflocculant from Bacillus megaterium BMBF was 3.013 g/L. The findings matched the yields of other Bacillus strains such as Bacillus velezensis 40B [33] and Bacillus subtilis UPMB13 [34], which gave the yields of 3.2 and of 3.02 g/L, respectively. The yield was slightly higher than that of Bacillus licheniformis (2.94 g/L) [35]. However, it was lower than the yields of 10 and 16.55 g/L obtained from Bacillus firmus and Bacillus licheniformis, respectively [36]. Nevertheless, in summary, the up-scaling of the bioflocculant production by B. megaterium BMBF using appropriate settings is essential for its application.
3.2. Chemical Components
A quantitative study of the components of the biopolymer was performed using different standard methods. The bioflocculant was composed mainly of uronic acid (61%) and the protein content was the least (12%) (Table 1). The high quantity of uronic acid was indicative of the high number of acidic polysaccharides within the bioflocculant. Similar results were recorded in the literature, where the bioflocculant synthesised by Bacillus firmus was composed mainly of acidic polysaccharides [37]. The high quantity of carbohydrates (neutral sugar and acidic carbohydrates) implied that the carbohydrates were the predominant active constituents during the flocculation process [38]. Moreover, the presence of carbohydrates and proteins also confirmed the bioflocculant to be a glycoprotein biopolymer [39].

Table 1.
Constituents of the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF.
3.3. Characterisation of the Bioflocculant
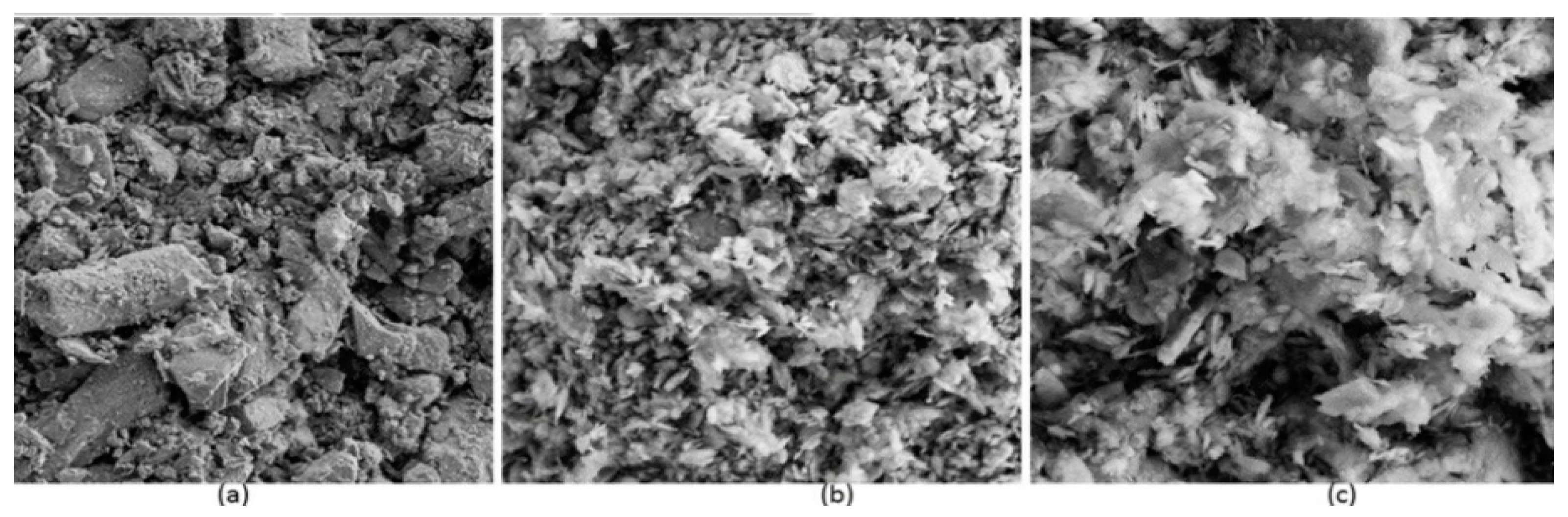
Figure 1 displays the structural images of the (a) flocculant, (b) kaolin clay and (c) flocculated kaolin clay. The biopolymer (bioflocculant) revealed a longitudinal structure. The kaolin clay particles showed amorphous shape and were uniformly scattered. The kaolin particles that were flocculated by the bioflocculant appeared clustered together, indicative of the formed flocs. The bioflocculant’s configuration might be responsible for its flocculating efficacy. Tsilo et al. [40] observed similar findings where the flocculated kaolin particles appeared clustered together.
Figure 1.
Structures of (a) flocculant, (b) kaolin particles and (c) flocculated kaolin clay particles.
The elemental analyser revealed the bioflocculant to have different elements, mainly C (61%), followed by O (17.5%) and P (8.1%). K was the least constituent (0.5% w/w) (Table 2). The concentrations of C and O were high because of the fact that these elements are the building blocks of the bioflocculant’s backbone structure [41]. Moreover, the high percentage composition of C further confirmed the presence of carbohydrates while the least presence of nitrogen (1.1%, w/w) affirmed the low content of proteins. Moreover, the presence of C and N generally confirmed the bioflocculant to be a glycoprotein molecule [34]. Similarly, the bioflocculant from Bacillus megaterium MW386824 was mainly composed of C and O [42].

Table 2.
The elemental composition of the bioflocculant as illustrated by EDX analysis.
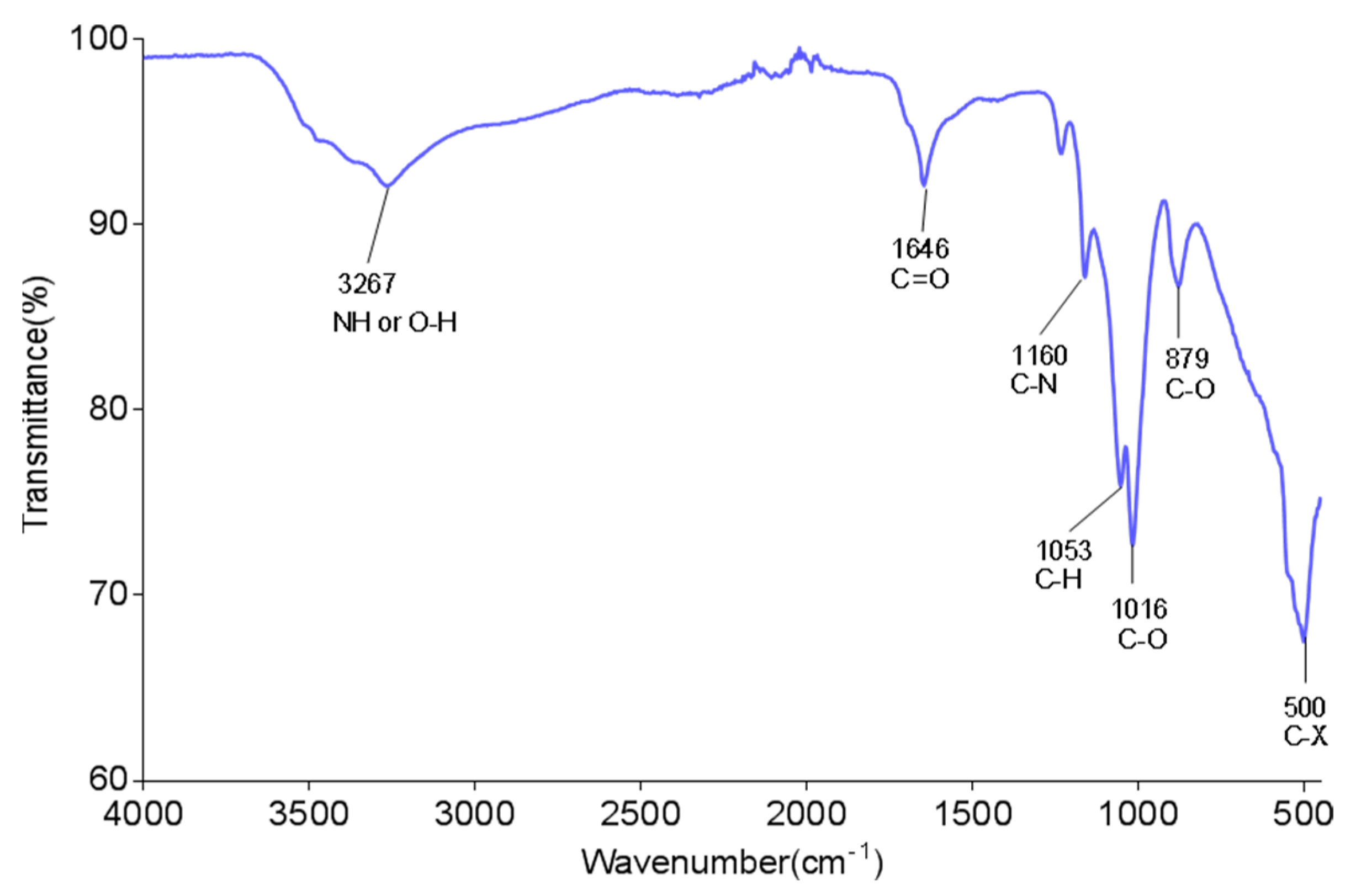
The functional structures of the bioflocculant were analysed by using FTIR equipment. The absorptive frequency, 3267 cm−1, corresponded to the vibration of OH or NH (Figure 2). The frequency 1646 cm−1 was distinctive of the symmetrical or antisymmetrical vibration of the carboxylate group [43]. The frequencies at 1053 and 1160 cm−1 revealed the stretches of C-N and C-H, respectively. These functional components served as the binding areas of kaolin [33]. Moreover, the FTIR spectrum further suggested the bioflocculant to be a glycoprotein biomolecule. The findings were comparable to those noted in other studies where the hydroxyl, amine and carboxyl groups were the effective structures [44,45].
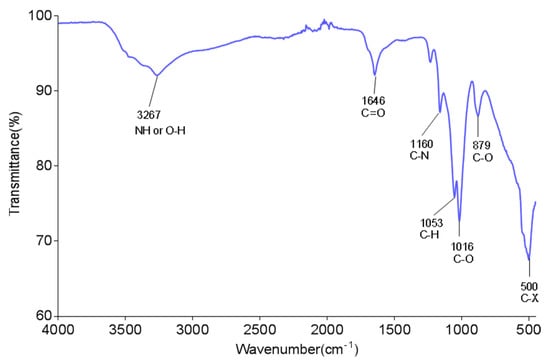
Figure 2.
FTIR spectrum of the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF.
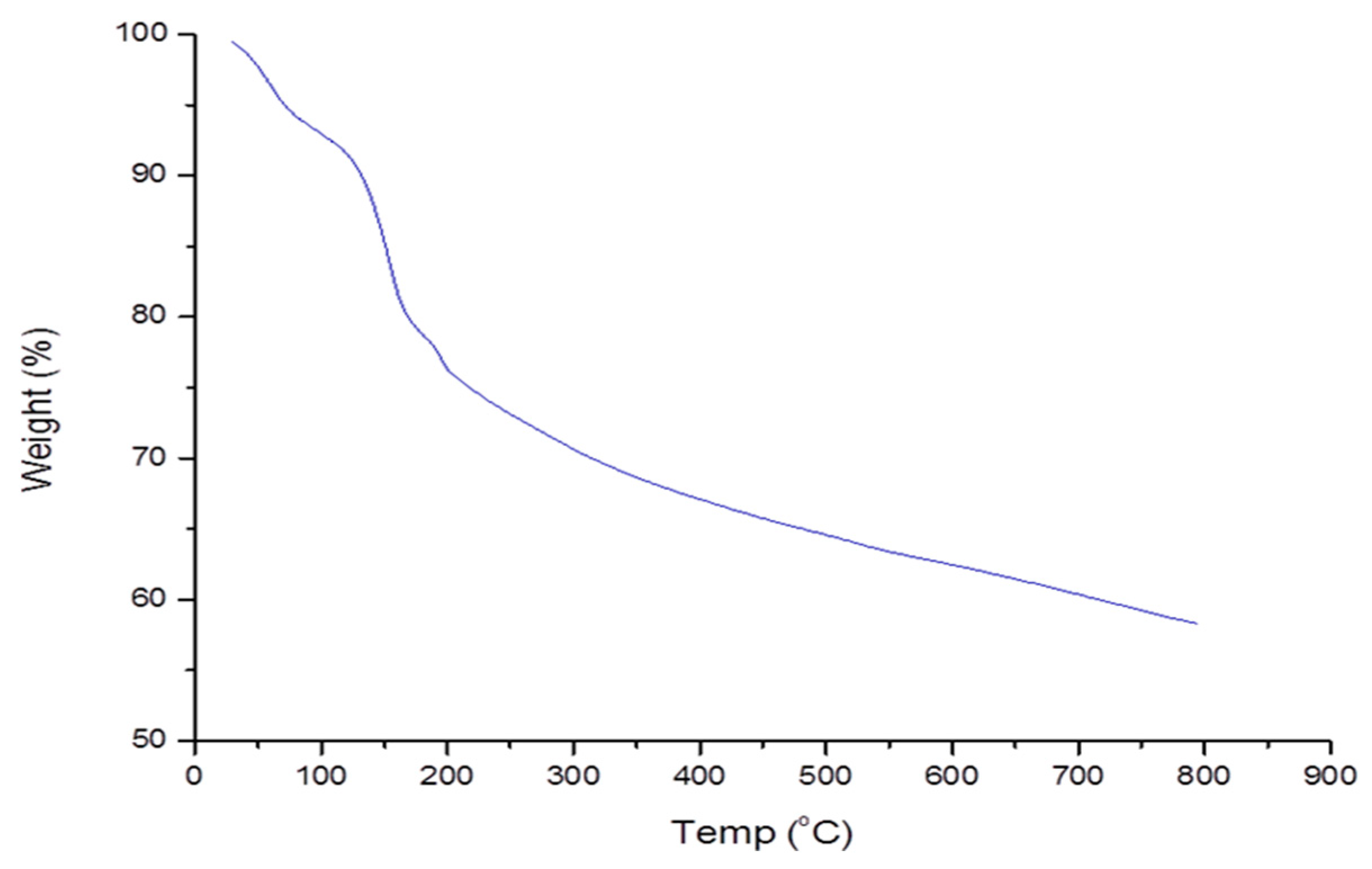
The thermogravimetric assay was used to investigate the pyrolysis chracteristics of the biopolymer. The first loss of weight (8%) was noted at 50 to 130 °C (Figure 3). The reduction in weight was attributed to the loss of the water content. The water content was derived from the functional components such as the carboxyl and hydroxyl [46]. Further weight loss was observed at 200 to 800 °C. The loss was credited to the dissociation of bioflocculant structure due to high temperatures. At 800 °C, about 58% of the bioflocculant residue was obtained. The obtained results affirmed the thermal stability of the biopolymer.
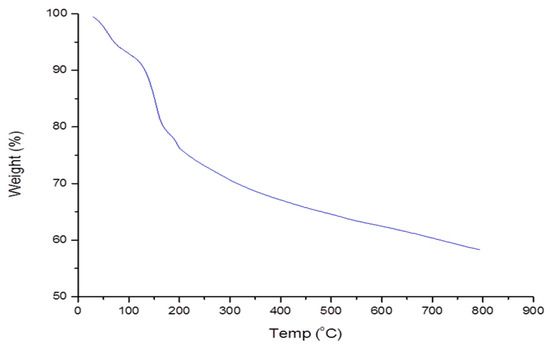
Figure 3.
Pyrolysis profile of the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF.
3.4. Impact of Dosage and Metal Ions
The dosage effect of the extracted biopolymer on flocculation was evaluated. The biopolymer displayed the peak flocculation (95%) at the least dosage and revealed the lowest activity (92%) at 0.8 mg/mL. However, there were no differences (p > 0.05) in the activities shown by all used concentrations (Table 3). The decline in the flocculating capability with the increase in the dosage was owed to the formation of the high viscosity, which hindered the interaction between the effective structures of the biopolymer and kaolin [47,48]. The profound activity at the low dosage size of the bioflocculant implied its economic advantage. Our observations contrasted those reported by Makapela et al. [49], where the flocculating activity of the bioflocculant produced by Bacillus pumilus was maximum (96.5%) at the low dosage of 0.1 mg/L. However, they were in conformity with those observed by Cosa and Okoh [50], where the dosage size of 0.2 mg/mL revealed the maimum flocculation.

Table 3.
Impact of dosage, metal ions, pH and temperature on the flocculation.
The influence of metal ions on flocculation was assessed. The subsequent addition of Li+, Ca2+ and Ba2+ into the bioflocculant solution led to an improvement in the flocculating rate, while the addition of Na+ led to the decrease in the flocculating performance. Ca2+ gave the peak flocculating efficiency of 96%; however, the activity was statistically equal to those obtained when Li+ and Ba2+ were utilised (Table 3). This implied that, of Li+, Ca2+ and Ba2+, any of the three metal ions could be used during the application of this bioflocculant, as they effectively neutralised and stabilised the charges of the functional structures of the kaolin and the biopolymer, consequently leading to an improved flocculation process. Our observations aligned with the discoveries by Agunbiade et al. [51], in which Ca2+ effectively stimulated the rate of flocculation.
3.5. pH and Thermal Stabilities of the Bioflocculant
Table 3 illustrates the pH stability of the flocculant. The biopolymer was active within an extensive pH range (3–12), giving flocculating efficiencies above or equal to 89% (Table 3). The pH of solutions tends to alter the charge status of biopolymers and the structural profiles of colloids, consequently affecting flocculation rate [52]. Therefore, the profound efficacy of the bioflocculant within the wide pH range further affirms its economic friendliness, as it could cut costs of adjusting pH during its application. He et al. [53] also recorded that the bioflocculant from Halomonas sp. V3a attained maximum activity at pH 7. The characteristics of the bioflocculant under heat treatment are illustrated in Table 3. More than 85% residual flocculation was retained after exposure to heat at varied temperatures. It should be noted that there were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in flocculation at all tested temperatures. Therefore, the bioflocculant was as classified as being heat-stable. The thermal stability was credited to the high content of polysaccharides. Generally, bioflocculants rich in polysaccharides are known to be more heat-stable in comparison to the protein-rich ones. The results were in agreement with those of the bioflocculant from Arcuadendron sp., which showed thermal stability under exposure at different temperatures [54].
3.6. Cytotoxicity
The MTT technique was utilised to estimate the bioflocculant’s cytotoxicity. The negative control (0.1% DMSO) had 100% cell viability. The bioflocculant revealed a higher level of cytotoxicity against bovine dermis cells (IC50 of 59 µg/mL) compared to Vero cells, which displayed IC50 of 240 µg/mL. The standard drug (5-fluorouracil) demonstrated the most cytotoxic in comparison to the bioflocculant on both cell lines (Table 4). Microbial bioflocculants are considered to be cytotoxic when they display IC50 < 30 µg/mL [55]. Therefore, the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF is safe for use, as it revealed insignificant cytotoxic effects on both cells. It was therefore concluded that the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF can be utilised without posing any health risk. Our findings confirmed those obtained in other studies where the bioflocculants were found to be nontoxic [45,56].

Table 4.
IC50 (µg/mL) of the flocculant on two cells (bovine dermis and Vero cells).
3.7. Reduction of Pollutants in Wastewater
Table 5 presents the reduction efficiencies of the tested flocculants (bioflocculant, aluminium chloride and ferric chloride) on the pollutants from coal mine wastewater from the local coal mine wastewater treatment plant and domestic wastewater from East Rand Wastewater Treatment Plant. Prior to the treatment, the BOD and COD of the wastewater from the local coal mine were 6.4 and 1557 mg/L, whereas Erwat wastewater had 85 (BOD) and 1240 (COD) mg/L, respectively. There was 99.3% BOD and 97% COD reduction noted when the bioflocculant was used to treat the coal mine wastewater. Moreover, the reduction efficiencies of 99.2% (COD) and 93% (BOD) by the bioflocculant were observed on the domestic wastewater. The removal efficiencies of the bioflocculant were corporately similar (p > 0.05) to those observed when the conventional flocculants (aluminium chloride and ferric chloride) were used. The profound reduction ability of the bioflocculant on the tested pollutants was accredited to the occurrence of the revealed functional components of the bioflocculant. Our findings were consistent with the results obtained where the bioflocculants effectively reduced pollutants in solutions [38,56].

Table 5.
%RE of the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF in comparison to other flocculants.
4. Conclusions
The goal of the present study was to produce, characterise and apply the bioflocculant from B. megaterium BMBF. B. megaterium BMBF yielded the maximum bioflocculant of 3.02 g/L. The results affirmed the bioflocculant as a glycoprotein biopolymer, with uronic acid as the dominant component. It revealed three predominant functional groups. The bioflocculant also demonstrated a broad pH stability, with the maximum flocculation being observed at pH 7. The bioflocculant is safe to use, as it revealed no cytotoxic effect on the tested cell lines. After treating the domestic and coal mine wastewater, the bioflocculant demonstrated significant flocculating abilities with COD and BOD reduction efficiencies above 90%. The observed characteristics and flocculating capabilities of the biofloccuant indicate its potential application in wastewater treatment. For future studies, the use of cost-effective substrates, the evaluation of genes responsible for bioflocculant production, scaling up and other industrial applications are important.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, T.N.S., K.M. and P.M.; formal analysis, T.S.M.; supervision, T.N.S.; investigation, T.S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S.M.; writing—review and editing, R.A.; project administration, P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the staff in the Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Biotechnology and the Department of Water and Sanitation at the University of Limpopo for the ultimate support they demonstrated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, O.; Lu, C.; Liu, A.; Zhu, L.; Wang, P.-M.; Qian, C.-D.; Jiang, X.-H.; Wu, X.-C. Optimization and characterization of polysaccharide-based bioflocculant produced by Paenibacillus elgii B69 and its application in wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Guest, J.S.; Peters, C.A.; Zhu, X.; Rau, G.H.; Ren, Z.J. Wastewater treatment for carbon capture and utilization. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Qadir, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Endo, T.; Zahoor, A. Global, regional, and country level need for data on wastewater generation, treatment, and use. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 130, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, K.; Liao, D.X.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.B.; Liu, X.; Zeng, G.M.; Li, X. A novel bioflocculant produced by Klebsiella sp. and its application to sludge dewatering. Water Environ. J. 2012, 26, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetu, W.M.; Karanja, A.M. Waterborne disease risk factors and intervention practices: A review. Open Access Libr. J. 2021, 8, e7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, V.H.; Cameron, N.R.; Saito, K. Synthesis, properties and performance of organic polymers employed in flocculation applications. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Shu, X.; Jia, P.; Li, Q. High-performance flocculants for purification: Solving the problem of waste incineration bottom ash and unpurified water. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13259–13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, D.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Recent advances and perspectives in efforts to reduce the production and application cost of microbial flocculants. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Du, C.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, C. Preparation, performances, and mechanisms of microbial flocculants for wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćczak, P.; Kaczmarek, H.; Ziegler-Borowska, M. Recent achievements in polymer bio-based flocculants for water treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabinya, L.V.; Cosa, S.; Mkwetshana, N.; Okoh, A.I. Halomonas sp. OKOH—A marine bacterium isolated from the bottom sediment of Algoa Bay—Produces a polysaccharide bioflocculant: Partial characterization and biochemical analysis of its properties. Molecules 2011, 16, 4358–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brostow, W.; Lobland, H.H.; Pal, S.; Singh, R.P. Polymeric flocculants for wastewater and industrial effluent treatment. J. Mater. Educ. 2009, 31, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ajao, V.; Fokkink, R.; Leermakers, F.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.; Temmink, H. Bioflocculants from wastewater: Insights into adsorption affinity, flocculation mechanisms and mixed particle flocculation based on biopolymer size-fractionation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajao, V.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.; Temmink, H. Natural flocculants from fresh and saline wastewater: Comparative properties and flocculation performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbenyen, A.M.; Simonis, J.J.; Basson, A.K. Screening for bioflocculant-producing bacteria from the marine environment of Sodwana Bay, South Africa. Ann. Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Tawila, Z.M.; Ismail, S.; Dadrasnia, A.; Usman, M.M. Production and characterization of a bioflocculant produced by Bacillus salmalaya 139SI-7 and its applications in wastewater treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Rathod, M.; Vyas, D.; Kumar, R.; Mody, K. Multiple pollutants removal from industrial wastewaters using a novel bioflocculant produced by Bacillus licheniformis NJ3. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, S306–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Zeng, Y.-J.; Xu, P.; Li, F.-Z.; Zong, M.-H.; Yang, J.-G.; Lou, W.-Y. Using a novel polysaccharide BM2 produced by Bacillus megaterium strain PL8 as an efficient bioflocculant for wastewater treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X.; Du, X.; Wang, C.A.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q. Isolation, identification, and optimization of culture conditions of a bioflocculant-producing bacterium Bacillus megaterium SP1 and its application in aquaculture wastewater treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2758168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaiyeto, K.; Nwodo, U.U.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoli, A.S.; Okoh, A.I. Evaluation of flocculating performance of a thermostable bioflocculant produced by marine Bacillus sp. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kisara, K.; Danielsson, S.; Lindström, M.E.; Gellerstedt, G. An improved methodology for the quantification of uronic acid units in xylans and other polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Li, J. Aspergillus oryzae, a novel eco-friendly fungal bioflocculant for turbid drinking water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasulov, B.A.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Mohamad, O.A.; Xiao, M.; Ma, J.-B.; Li, W.-J. Production, characterization and structural modification of exopolysaccharide-based bioflocculant by Rhizobium radiobacter SZ4S7S14 and media optimization. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo-Tayo, B.C.; Adebami, G.E. Production, characterization and effect of cultural condition on bioflocculant produced by Alcaligenes aquatilis AP4. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2017, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, N.G.; Basson, A.K.; Pullabhotla, V. Biosynthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using a bioflocculant extracted from Alcaligenis faecalis HCB2. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2019, 11, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makapela, B.; Okaiyeto, K.; Ntozonke, N.; Nwodo, U.U.; Green, E.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I. Assessment of Bacillus pumilus isolated from fresh water milieu for bioflocculant production. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuku, S.K. Synthesis and Application of a Grafted Flocculant Produced from a Chemical Combination of a Bioflocculant TKT and Acrylamide (AM). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zululand, Richards Bay, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Geng, L.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, C. Fermentation optimization, characterization and bioactivity of exopolysaccharides from Funalia trogii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntozonke, N.; Okaiyeto, K.; Okoli, A.S.; Olaniran, A.O.; Nwodo, U.U.; Okoh, A.I. A marine bacterium, Bacillus sp. isolated from the sediment samples of Algoa Bay in South Africa produces a polysaccharide-bioflocculant. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.A.; Elkady, M.F.; Farag, S.; Abd-El-Haleem, D. Characterization and flocculation properties of a carbohydrate bioflocculant from a newly isolated Bacillus velezensis 40B. J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 34, 51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zulkeflee, Z.; Shamsuddin, Z.H.; Aris, A.Z.; Yusoff, M.K.; Komilis, D.; Sánchez, A. Glutamic acid independent production of bioflocculants by Bacillus subtilis UPMB13. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; He, N. Production and characterization of a novel bioflocculant from Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2778–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K. Production and characterization of bioflocculants for mineral processing applications. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 137, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.-F.; Jiang, P.-J. Composition and characterization of microbiological flocculant SC06. Environ. Chem. 2002, 21, 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Tsilo, P.H.; Basson, A.K.; Ntombela, Z.G.; Maliehe, T.S.; Pullabhotla, V.R. Production and characterization of a bioflocculant from Pichia kudriavzevii MH545928. 1 and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliehe, T.; Simonis, J.; Basson, A.; Reve, M.; Ngema, S.; Xaba, P. Production, characterisation and flocculation mechanism of bioflocculant TMT-1 from marine Bacillus pumilus JX860616. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 2352–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Tsilo, P.H.; Basson, A.K.; Ntombela, Z.G.; Maliehe, T.S.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Isolation and optimization of culture conditions of a bioflocculant-producing fungi from Kombucha tea SCOBY. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, N.G.; Basson, A.K.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Wastewater treatment by a polymeric bioflocculant and iron nanoparticles synthesized from a bioflocculant. Polymers 2020, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, J.; Hasan, H.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R. Properties of bioflocculant-producing bacteria for high flocculating activity efficiency. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Fu, L.; Cao, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. Microbial flocculant produced by a novel Paenibacillus sp., strain A9, using food processing wastewater to replace fermentation medium and its application for the removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, F.; Qu, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, A.; Guo, J.; Yu, B. Characterization of a compound bioflocculant produced by mixed culture of Rhizobium radiobacter F2 and Bacillus sphaeicus F6. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliehe, T.; Basson, A.; Singh, M. Wastewater treatment by a novel bioflocculant from a consortium of Bacillus pumilus JX860616 and Bacillus Subtilis CSM5. Biosci. Res. 2020, 17, 1610–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Maliehe, T.S.; Basson, A.K.; Dlamini, N.G. Removal of pollutants in mine wastewater by a non-cytotoxic polymeric bioflocculant from Alcaligenes faecalis HCB2. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawila, Z.M.A.; Ismail, S.; Amr, S.S.A.; Abou Elkhair, E.K. A novel efficient bioflocculant QZ-7 for the removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27825–27834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuboori, A.H.R.; Uemura, Y.; Osman, N.B.; Yusup, S. Production of a bioflocculant from Aspergillus niger using palm oil mill effluent as carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makapela, B. Evaluation of Bioflocculant-Producing Potential of Bacillus pumilus Strain Isolated from Tyume River in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Master’s Thesis, University of Fort Hare, East London, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cosa, S.; Okoh, A. Bioflocculant production by a consortium of two bacterial species and its potential application in industrial wastewater and river water treatment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Agunbiade, M.O.; Van Heerden, E.; Pohl, C.H.; Ashafa, A.T. Flocculating performance of a bioflocculant produced by Arthrobacter humicola in sewage waste water treatment. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Yang, Q.; Huang, K.; Zeng, G.-M.; Liao, D.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Long, W.-F. Screening and characterization of a bioflocculant produced by Aeromonas sp. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2007, 20, 274. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zou, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. Characteristics and flocculating mechanism of a novel bioflocculant HBF-3 produced by deep-sea bacterium mutant Halomonas sp. V3a’. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Yeomans, W.G.; Allen, A.L.; Deng, F.; Gross, R.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Biosynthesis of novel exopolymers by Aureobasidium pullulans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5265–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.; Devi, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Sarma, H.; Subudhi, S.; Lal, B. Production of a non-cytotoxic bioflocculant by a bacterium utilizing a petroleum hydrocarbon source and its application in heavy metal removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 66037–66046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.-X.; Wang, S.-G.; Sun, X.-F.; Liu, X.-W.; Yue, Q.-Y.; Gao, B.-Y. Bioflocculant production by culture of Serratia ficaria and its application in wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4668–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).