Abstract
Background: To assess the changes in the inclination of the premolar and molar during a maxillary expansion with a micro-implant-assisted skeletal expander (MSE). Materials and Methods: A total of 21 patients (16 females, 5 males) with a mean age of 18.6 ± 4.5 (range 11.3–26.3 years) with a transverse maxillary deficiency were included in this study. They all received an MSE appliance for the maxillary skeletal expansion. The activation protocol consisted of about 0.5 mm expansion a day until a diastema was observed and continued with about 0.25 mm a day until the desired transverse relationship between the maxilla and mandible was achieved. OnDemand3D software was used for the measurements of the inclination change in the maxillary premolars and molars, pre- and post-expansion. Graphpad was used to compare the mean change in each tooth with the zero value (no change), and the p values of these changes with every tooth were calculated. Moreover, the changes and the mean values of all the teeth on the left and right sides were calculated separately. Results: A total of sixteen measurements were conducted for each patient. The first premolars tipped palatally after the expansion, while the second premolars and molars tipped buccally. The changes were significant for the molars and the left second premolar. Conclusions: The MSE induced some changes in the tooth inclination. The first premolars moved palatally, most likely due to perioral musculature and mastication force, while the first and second molars moved buccally. The second molar buccal movement is most likely due to the craniofacial rotation caused by the MSE as they were not subject to the expansion force.
1. Background
A maxillary transverse deficiency is a commonly encountered problem in orthodontic practice [1] and is generally treated with the tooth-borne rapid maxillary expansion technique (RME) [2]. However, two factors are associated with the limitations of such an approach: the treatment timing and the dental or periodontal side effects.
In growing patients, RME is a highly predictable approach with a significant orthopedic effect. In mature patients, it is more difficult to achieve skeletal effects during the expansion [3] because of the complex interdigitation/interlocking of the craniofacial sutures [4] which produces higher levels of resistance against the expansion. Furthermore, detrimental side effects such as dental tipping, alveolar bone loss or periodontal dehiscence have been associated with this procedure [5,6]. These unwanted changes have been observed even in growing patients and are significantly more severe in skeletally mature patients.
In order to overcome these limitations and to avoid complex surgical options [7], especially for skeletally mature patients, an alternative treatment has been proposed: the micro-implant-assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) [8]. A number of designs of MARPE appliances with various treatment outcomes have been reported [9,10,11]. The Midfacial Skeletal Expander (MSE) [12] is one MARPE with unique features, designed to produce a favorable posterior and superior force vectors during the expansion by the posterior positioning of the appliance between the zygomatic buttress bones [13].
Although the orthopedic effect of the MSE [14,15,16] and other types of MARPE appliances is being continuously documented, their effect on dental inclination changes needs further investigation. Some studies have reported changes in dental tipping following MARPE especially on the maxillary first molar [17,18,19,20,21,22], and only a few of them have addressed the tipping of the maxillary premolars [23,24,25,26]. The inclination changes with the anchor teeth are understandable; however, the reason for the changes observed with non-anchor teeth must be explored further.
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of the bone-borne MSE expander on the inclination of the maxillary teeth and the cause of the changes.
2. Materials and Methods
A total of 21 patients (16 females, 5 males) with a mean age of 18.64 ± 4.5 (range 11–26.25 years) were included in this retrospective study approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of California, Los Angeles. The inclusion criteria were: (1) patients with transverse maxillary deficiency treated with MSE, (2) the availability of two CBCT images: pretreatment and within 3 weeks after the completion of MSE expansion and (3) no previous orthodontic treatment. All patients were treated at the orthodontic clinic, UCLA School of Dentistry, Institutional Review Board approval (IRB number 17-000567). For diagnosing the maxillary deficiency, the transverse analysis method described in the previous studies was used [13,15].
2.1. MSE Design and Activation Protocol
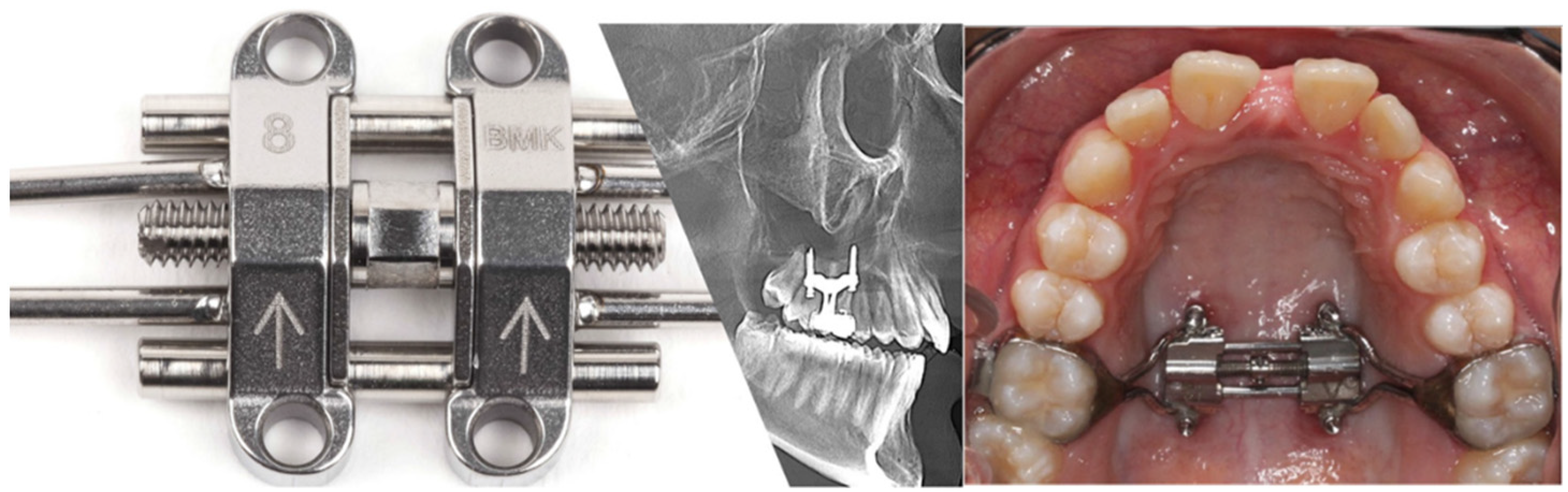
The MSE appliance was fixed at the palatal bone between the two zygomatic buttresses by means of four micro-implants (1.8 mm in diameter and 11 or 13 mm in length) with bicortical engagement. The appliance has a central jackscrew, four parallel holes for micro-implants insertion and two arms on each side to help stabilize the jackscrew during expansion (Figure 1).
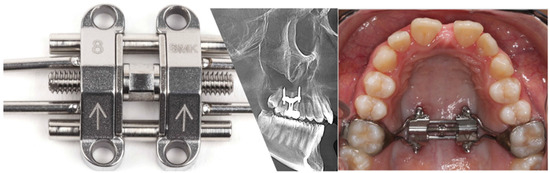
Figure 1.
Maxillary Skeletal Expander device together with an X-ray showing the bicortical engagement and a photo demonstration of its intraoral application.
The arms are made with a soft alloyed metal in order to minimize the transmission of the expansion force to the anchor teeth when the micro-implants tip or move laterally, cutting through the palatal bone, during the expansion. The soft arms bend, absorbing the lateral force, reducing the load on molars and preventing unwanted tooth movements; however, it provides the necessary stability of the jackscrew position during the activation period. The activation protocol started with about 0.5 mm expansion a day until a diastema was observed and continued with about 0.25 mm activations a day until the desired transverse relationship between maxilla and mandible was achieved. Once the active expansion was completed, the MSE was kept in place for six months as skeletal retention while bone filled the widened suture.
2.2. Evaluation Method
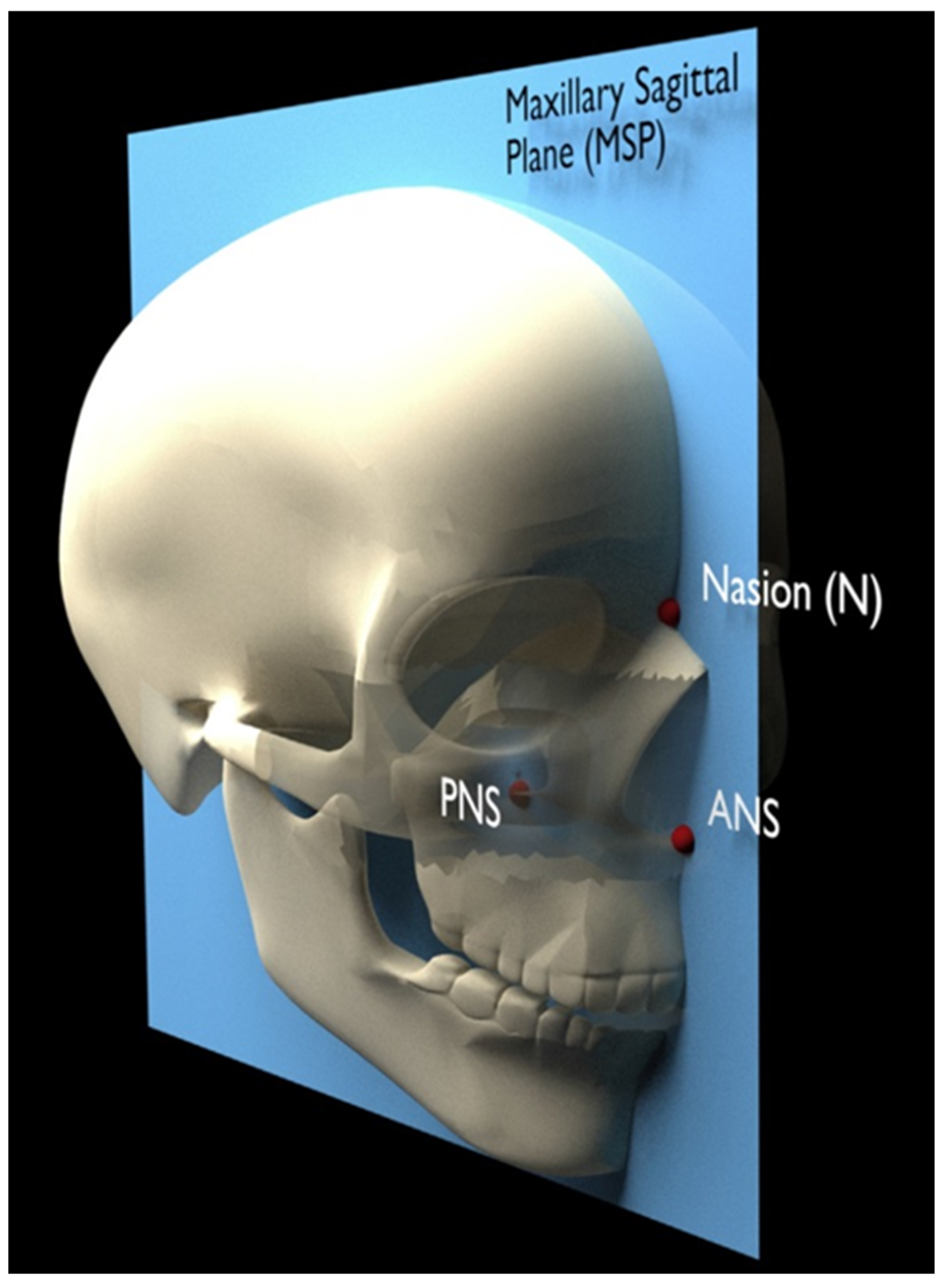
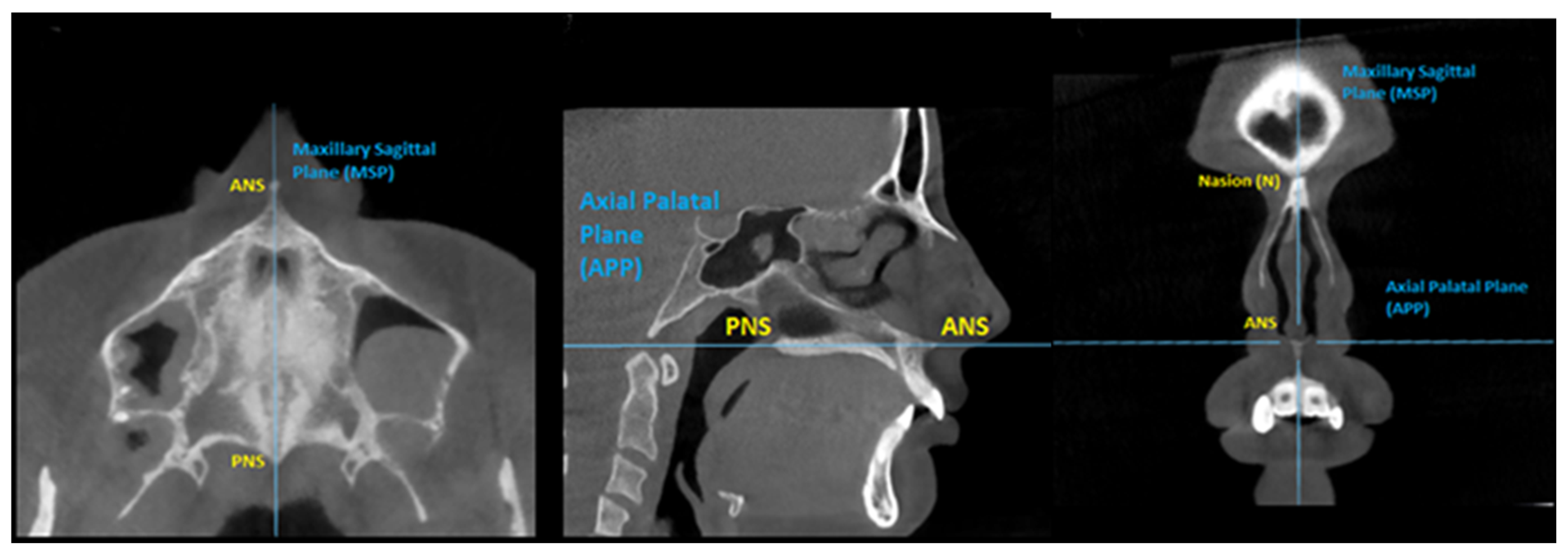
The same scanner (5G; NewTom, Verona, Italy) with an 18 × 16 cm field of view was used for all patients to obtain the pre- and post-expansion CBCT images. The step-by-step procedure for the three-dimensional analysis was: First, the superimposition of the pre- and post-expansion CBCT images was performed with the automated voxel-based registration function of OnDemand3D software (Cybermed, Daejeon, Korea). The accuracy of such superimposition was previously validated [27]. Following the superimposition, the orientation of the images was established by identifying the maxillary sagittal plane (MSP) on the primary CBCT, passing through three reference points: anterior nasal spine (ANS), posterior nasal spine (PNS) and Nasion (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
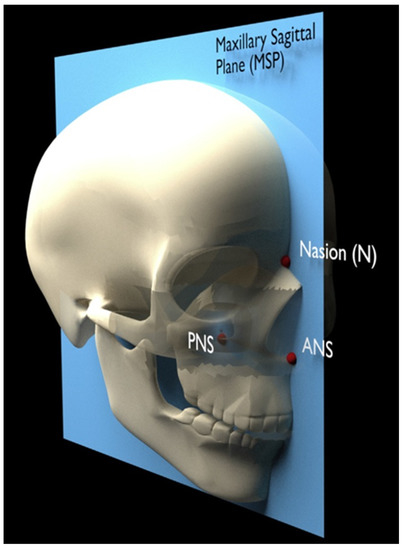
Figure 2.
Three-dimensional visualization of the midsagittal plane passing through ANS, PNS and Nasion.
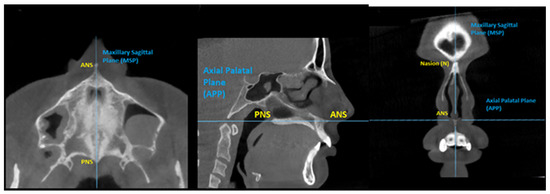
Figure 3.
Identification of the reference points for the midsagittal plane at the axial, sagittal and coronal sections.
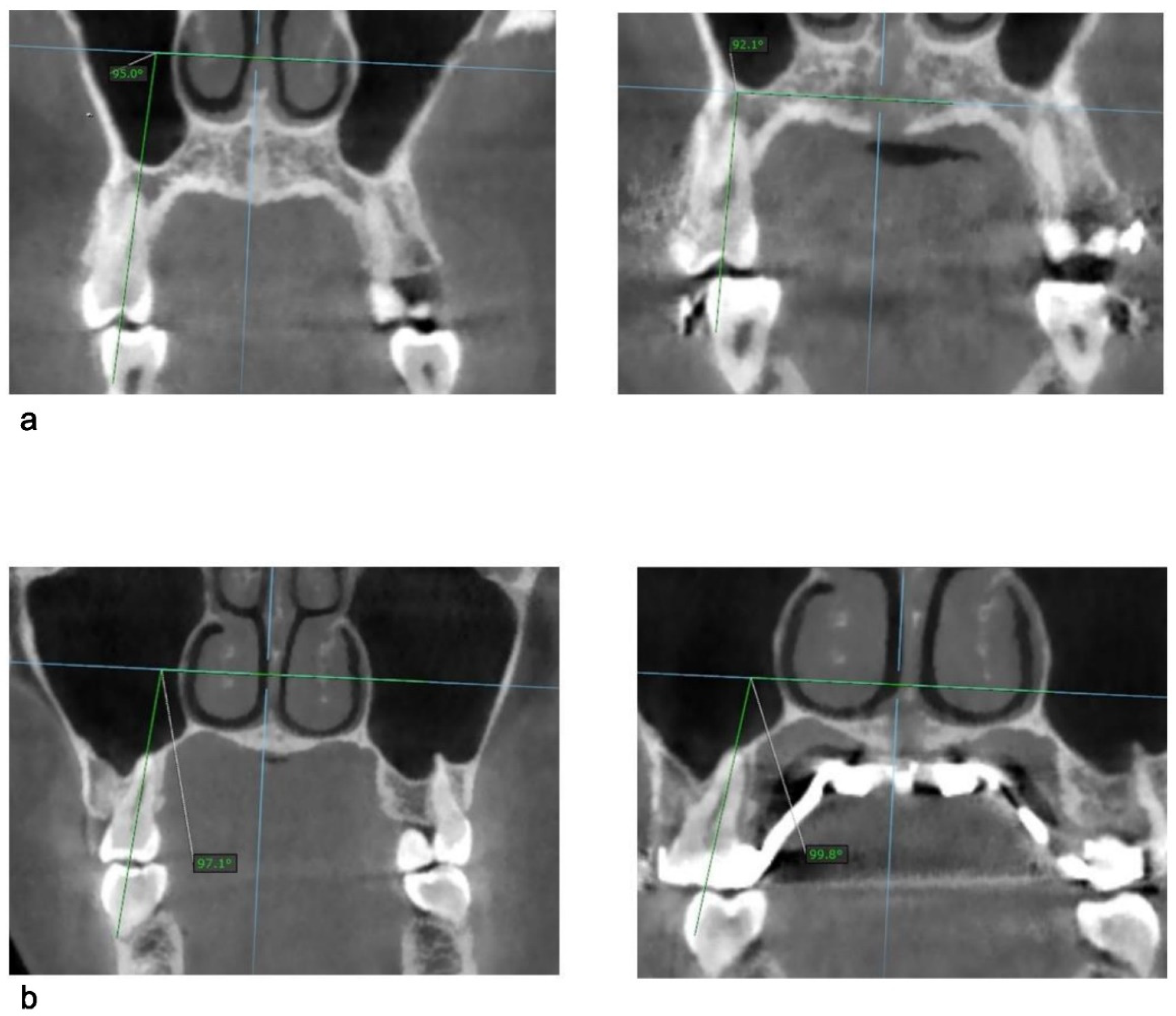
Eight maxillary teeth were examined for each patient: first and second premolars and first and second molars, bilaterally. All measurements were taken from the coronal view of the primary CBCT, followed by the same set of measurements from the secondary CBCT. Tooth inclination was determined by the angle between the long axis of the tooth and the horizontal reference line. The long axis of a tooth was defined as the line passing through the occlusal fossa of the crown and the apical point of the palatal root for molars and first premolar, and the apical point of the root of second premolar. The horizontal reference line is the representation of the axial palatal plane in the coronal view. As described by Cantarella et al. [13], the axial palatal plane is perpendicular to the maxilla sagittal plane and passess through ANS and PNS. Once the inclination of a specific tooth was measured at the primary CBCT, the secondary CBCT was selected without changing the orientation of the horizontal reference line (Figure 4).
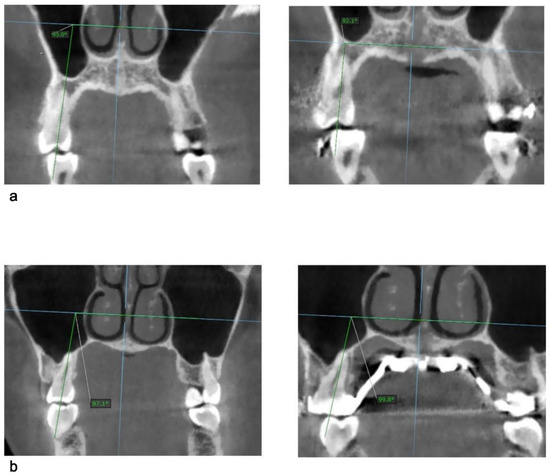
Figure 4.
Illustration of measurement of tooth inclination as an angle between tooth axis and the horizontal line for: (a) first premolar before expansion (left) and after expansion (right); (b) first molar before expansion (left) and after expansion (right).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
For each patient, the pre-expansion tooth inclination value was extracted from the post-expansion value of every tooth to calculate the change. The mean change in each tooth for all patients was then calculated. Graphpad 5.0 software was used to compare the mean change in each tooth with the zero value (no change) using paired t-test, and p values were calculated. Moreover, the changes and the mean values of all teeth on left and right sides were calculated separately.
2.4. Three-Dimensional Visualization
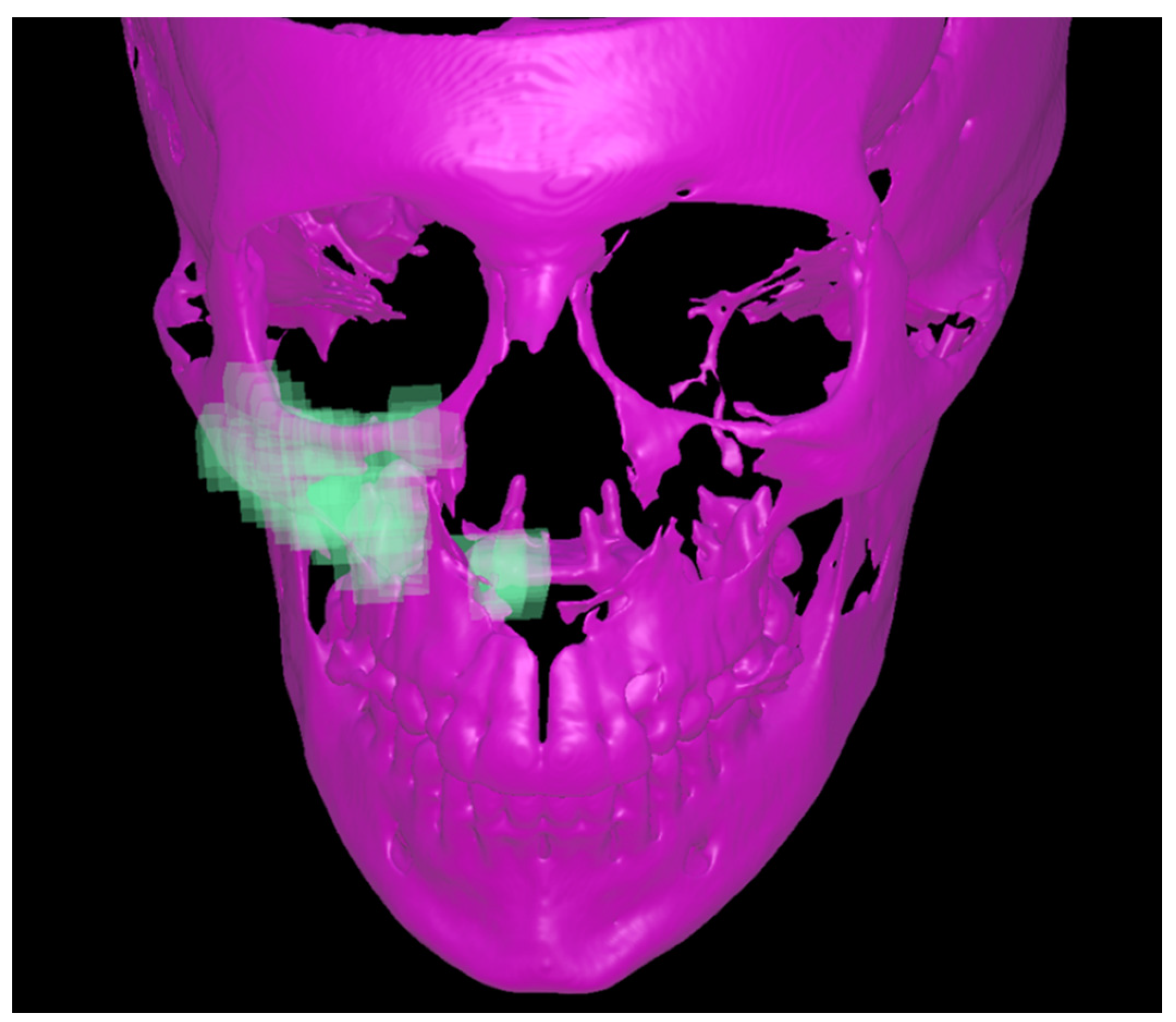
Three-dimensional volumetric registration was performed to isolate the tooth movement relative to the maxilla. The registration was performed to superimpose the initial CBCT and the post-expansion CBCT at the zygomatic buttress and the palate for the right and left sides separately (Figure 5).
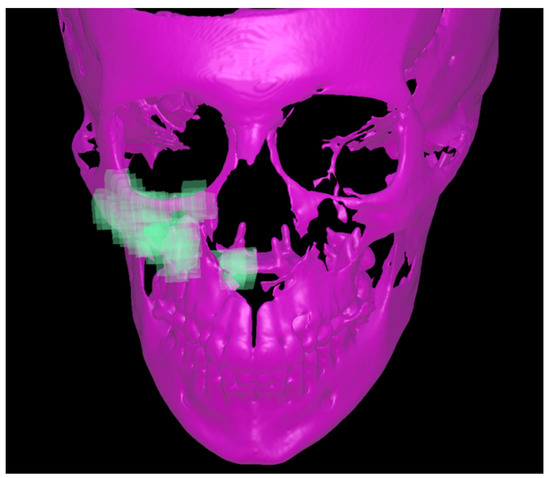
Figure 5.
The registration of the pre- and post-expansion CBCT by using the zygomatic and palatal bone of each side as region of interest for superimposition (the green part).
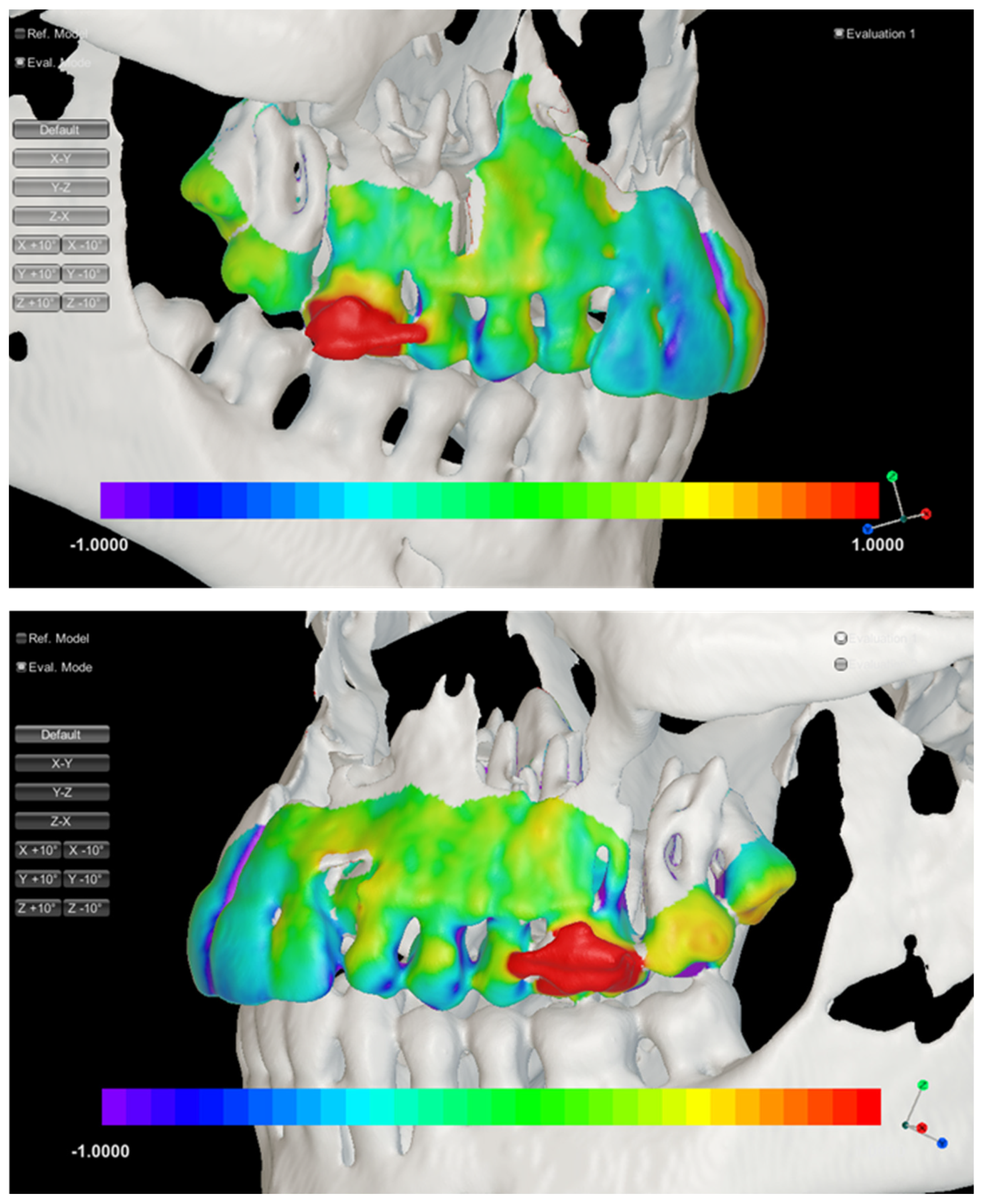
After this registration, bone and tooth surfaces were constructed using the marching cubes algorithm. To visualize the direction of the tooth movement with respect to maxilla, a color contour map was generated in order to differentiate the direction of the movements from the surface of initial CBCT to the surface of the post-expansion (Figure 6).
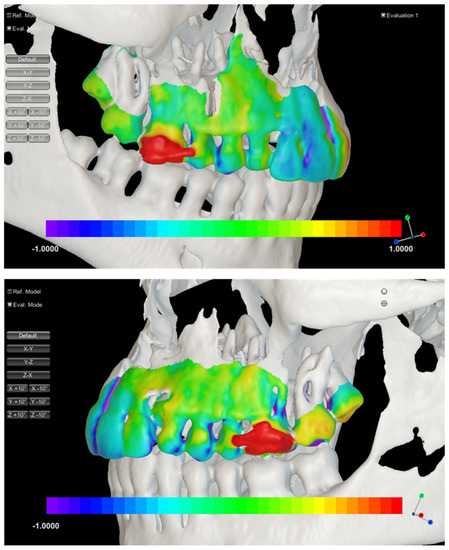
Figure 6.
Three-dimensional visualization and color mapping of tooth movement after expansion in the left and right side. The blue color indicates palatal tipping and the red color buccal tipping.
3. Results
A total of sixteen measurements were conducted for each patient. The mean pre- and post-expansion tooth inclinations, the mean change and the p-value of the comparison with the zero change are reported in Table 1. The first premolars tipped palatally after the expansion, while the second premolars and molars tipped buccally. The changes were significant for the molars and left second premolar. The comparison between the left and right mean inclination changes for each tooth is reported in Table 2. No significant difference was found.

Table 1.
Mean and SD of pre- and post-expansion tooth inclination and inclination change (in degrees). A positive Mean change indicates a buccal inclination, a negative mean change indicates a palatal inclination. The p-values of the comparison with the zero change are tabulated. The asterisk indicates statistical significance.

Table 2.
Mean change, SD and p-value of the difference between left and right sides.
4. Discussion
In the present study, the inclination changes in the maxillary premolars and the molars following the MSE treatments is reported. The MSE is a specific MARPE appliance which is designed to produce posterior and superior force vectors by inserting the micro-implants posteriorly between the two zygomatic buttresses and superiorly engaging both the palatal and nasal cortical bones [13]. These posterior and superior expansion forces are proven to be effective against the posterior and superior resistances. The bicortical engagement of micro-implants produces a more parallel pattern of expansion [12,13].
Regarding the maxillary molar inclination changes, the mean buccal tipping values of the first and second molars were 3.1° ± 2.3 degrees and 2.1° ± 2.5, respectively. Because the second molars were not anchor teeth, this buccal inclination change cannot be from the dental tipping. Cantarella et al. described the MSE expansion as a skeletal rotation of the hemifacial structure with the fulcrum near the frontozygomatic suture [14]. This type of skeletal rotation would change the buccal inclination of the molars because the landmarks further away from the fulcrum would move more. This concept was first described by Paredes et al. [15]. However, the first molar could have tipped buccally when the micro-implants tipped or moved laterally within the palatal bone during the expansion, because the molars were the anchor teeth. Based on the fact that the second molar inclination changed by 2.1° without any expansion force on it, we can conclude that the skeletal rotation caused by the MSE was the reason for this change. Assuming the 2.1° change with the second molar was from the skeletal rotation, the first molar tipping may be about 1° [3.1°–2.1°]. When analyzing the dental tipping in the coronal plane, the changes occurred from a rotation of the entire craniofacial structure and maxillary basal bone. The dental tipping has to be analyzed within the alveolar bony housing.
While the existing studies show similar results for the molar inclination changes with the MARPE treatments, the studies for the premolar inclination changes are few and contradictory [19,23,24,25,26]. The MARPE devices used in these studies were of different designs, either with two or four micro-implants inserted posteriorly or laterally in the palate, with various numbers of teeth banded. Two studies reported a significant buccal tipping of the first premolars [19,25]. Ngan et al. [19] treated a total of eight cases with an MSE device and reported a mean buccal tipping of 5.86 ± 5.71 for the first premolars. However, they used bands on the first premolars to stabilize the MSE and positioned the MSE device in various palatal locations. Akin et al. [25] reported a mean premolar buccal tipping of 3.06° ± 1.41. They treated a total of nine patients with a hybrid MARPE with two micro-implants and palatal resin pads which produced a v-shaped expansion, with a greater expansion anteriorly. Other studies reported either no changes [18,23] or a palatal tipping of the premolars [9,24,25]. All of them used a MARPE device with four micro-implants inserted laterally or posteriorly in the palate, except for Toklu et al. [26] who used a MARPE with two anterior mini-screws. However, the mean age of the patients included in the study was 13.8 ± 2.2, younger than the other studies. The appliance design can greatly influence the pattern of the maxillary expansion and dentoalveolar changes, and it is not possible to generalize the changes in all MARPE. Each appliance should be studied separately, and the changes must be analyzed based on the appliance design and its impact on craniofacial structures.
The mean palatal tipping values of 0.6° ± 2.7 and 0.4° ± 1.8 for the first right and left premolars were observed in the current study with the MSE, whereas almost no changes for the second premolars were observed. The skeletal rotation caused by the MSE produced 2.1° of the second molar inclination change, and similar changes in the buccal direction can be expected from the premolars. However, the premolar movements were not significant, with the first premolars moving in the palatal direction. One possible explanation for the palatal movement of the first premolars and the relative palatal movement of the second premolars might be the resistance force of the perioral muscles during the expansion. The skeletal rotation by the MSE may have changed their inclination in the buccal direction initially, but the external force by the perioral muscles tipped them in the palatal direction, reversing and reducing the buccal inclinations of the first and second premolars, respectively. This impact appears to be more prominent in the anterior region and the influence seems to decrease posteriorly (Table 1). If this is the case, the differences in the inclination changes between the first and second molars may have been caused by the buccal perioral muscles. Because the first molars were attached to the MSE and no movement was allowed, but the second molars were subject to the perioral influence, the discrepancy may be the result of the second molars moving palatally. Another contributing factor might be the occlusion forces that may have uprighted the buccally inclining posterior teeth during the mastication. The occlusal contacts of the second molars in younger patients are lighter than the premolars, and the uprighting of the second molars by the occlusal force may have been less than that of the premolars. This may be the reason why the inclination changes in the buccal direction were observed more with the second molars than both the first and second premolars. Because the first molars could not be influenced by the occlusal interference, the inclination changes were greatest, although it was a minimal difference between the first and second molars. A study by Paredes et al. illustrated the MSE treatment resulted in 96% skeletal rotation with insignificant dentoalveolar changes [15], and the majority of the 3.1° first molar inclination change may be due to the skeletal rotation. It is conceivable that the entire buccal segment rotated as much as the first molars with the MSE, and the perioral musculature and occlusal function may have uprighted the buccally inclining premolars and second molars with more prominent movement in the anterior region. This means the dental tipping within the alveolar housing may be negligible, even with the first molars. Although the MSE expansion caused skeletal rotation with negligible dental movement, the changes with buccal bone have not been evaluated. A further study evaluating the changes in the buccal bone thickness in correlation with the current study would be important in understanding the risk involved with skeletal expansion.
Lastly, no significant difference in the inclination change was observed between the left and right sides for both the premolars and molars. Because the expansion force is reciprocal and the human skull is generally not symmetric, an asymmetric expansion is expected. However, the magnitude of asymmetry did not yield significant differences in the buccal inclination changes between the two sides.
5. Conclusions
The tooth inclinations of the second molars changed in the buccal direction during the MSE treatment, even though they were not subjected to the expansion force, indicating that the changes were due to the craniofacial rotation caused by the MSE. The premolar inclination changes were less than that of the second molars, and the first premolars moved in the palatal direction, indicating an uprighting of the teeth, most likely due to the perioral musculature and mastication force. These changes were more prominent in the anterior region. The first molar had slightly more buccal inclination because it was stabilized by the MSE, not allowing the uprighting.
Author Contributions
L.K., D.C. and N.A.P., design of the study, data collection and article writing. W.M., conceptualization, study design and data interpretation. R.H., study design, 3D evaluation and visualization. M.D.F., statistical analysis, interpretation of data and evaluation of the statistical results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The present study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of California, Los Angeles. All patients gave their written consent for their participation in the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data of the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- McNamara, J.A. Maxillary transverse deficiency. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 2000, 117, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, A.J. The treatment of maxillary deficiency by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1965, 35, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Cameron, C.G.; McNamara, J.A. Treatment Timing for Rapid Maxillary Expansion. Angle Orthod. 2001, 71, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Melsen, B. Palatal growth studied on human autopsy material. A histologic microradiographic study. Am. J. Orthod. 1975, 68, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, A.; Uysal, T.; Veli, I.; Ozer, T.; Karadede, I.; Hekimoglu, S. Evaluation of alveolar bone loss following rapid maxillary expansion using cone-beam computed tomography. Korean J. Orthod. 2013, 43, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, N.; Kiki, A.; Oktay, H. A comparison of dentoalveolar inclination treated by two palatal expanders. Eur. J. Orthod. 2008, 30, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byloff, F.K.; Mossaz, C.F. Skeletal and dental changes following surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Eur. J. Orthod. 2004, 26, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Park, Y.C.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, W.S. Miniscrew-assisted nonsurgical palatal expansion before orthognathic surgery for a patient with severe mandibular prognathism. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, M.I.; Kaddah, M.A.; Abd Elsayed, F.A.; Elsayed, H.S. Comparison of transverse changes during maxillary expansion with 4-point bone-borne and tooth-borne maxillary expanders. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 148, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassar, J.W.; Karydis, A.; Trojan, T.; Fisher, J. Dentoskeletal effects of a temporary skeletal anchorage device-supported rapid maxillary expansion appliance [TSADRME]: A pilot study. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmes, B.; Nienkemper, M.; Drescher, D. Application and effectiveness of a mini-implant- and tooth-borne rapid palatal expansion device: The hybrid hyrax. World J. Orthod. 2010, 11, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlson, C.; Sung, J.; McComb, R.W.; MacHado, A.W.; Moon, W. Microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion appliance to orthopedically correct transverse maxillary deficiency in an adult. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarella, D.; Dominguez-Mompell, R.; Mallya, S.M.; Moschik, C.; Pan, H.C.; Miller, J.; Moon, W. Changes in the midpalatal and pterygopalatine sutures induced by micro-implant-supported skeletal expander, analyzed with a novel 3D method based on, CBCT imaging. Prog. Orthod. 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarella, D.; Dominguez-Mompell, R.; Moschik, C.; Sfogliano, L.; Elkenawy, I.; Pan, H.C.; Mallya, S.M.; Moon, W. Zygomaticomaxillary modifications in the horizontal plane induced by micro-implant-supported skeletal expander, analyzed with CBCT images. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, N.; Colak, O.; Sfogliano, L.; Elkenawy, I.; Fijany, L.; Fraser, A.; Zhang, B.; Moon, W. Differential assessment of skeletal, alveolar, and dental components induced by microimplant-supported midfacial skeletal expander [MSE], utilizing novel angular measurements from the fulcrum. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colak, O.; Paredes, N.A.; Elkenawy, I.; Torres, M.; Bui, J.; Jahangiri, S.; Moon, W. Tomographic assessment of palatal suture opening pattern and pterygopalatine suture disarticulation in the axial plane after midfacial skeletal expansion. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Dong, W.; Martin, D.; Guo, J. Skeletal effects of monocortical and bicortical mini-implant anchorage on maxillary expansion using cone-beam computed tomography in young adults. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 157, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Ahn, H.W.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Nelson, G. Tooth-borne vs. bone-borne rapid maxillary expanders in late adolescence. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, P.; Nguyen, U.K.; Nguyen, T.; Tremont, T.; Martin, C. Skeletal, Dentoalveolar, and Periodontal Changes of Skeletally Matured Patients with Maxillary Deficiency Treated with Microimplant-assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion Appliances: A Pilot Study. APOS Trends Orthod. 2018, 8, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Park, J.; Lagravere-Vich, M.O. Comparison of traditional RPE with two types of micro-implant assisted RPE: CBCT study. Semin. Orthod. 2019, 25, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, V.; Macherone, C.; Zursiedel, M.I.; Valenzuela, J.G. Rapid maxilary expansion in young adults: Comparison of tooth-borne and bone-borne appliances, a cohort study. J. Oral Res. 2019, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Tang, B.; Hua, F.; He, H.; Ngan, P. Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes in the transverse dimension using microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion [MARPE] appliances. Semin. Orthod. 2019, 25, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celenk-Koca, T.; Erdinc, A.E.; Hazar, S.; Harris, L.; English, J.D.; Akyalcin, S. Evaluation of miniscrew-supported rapid maxillary expansion in adolescents: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calil, R.C.; Marin Ramirez, C.M.; Otazu, A.; Torres, D.M.; Gurgel, J.d.A.; Oliveira, R.C.; de Oliveira, R.C.G.; Valarelli, F.P.; Freitas, K.M.S. Maxillary dental and skeletal effects after treatment with self-ligating appliance and miniscrew-assisted rapid maxillary expansion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, e93–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.; Akgul, Y.E.; Ileri, Z.; Basciftci, F.A. Three-dimensional evaluation of hybrid expander appliances: A pilot study. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunyuz Toklu, M.; Germec-Cakan, D.; Tozlu, M. Periodontal, dentoalveolar, and skeletal effects of tooth-borne and tooth-bone-borne expansion appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 148, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, L.H.S.; Bailey, L.J.; Tucker, G.R.; Styner, M.A.; Mol, A.; Phillips, C.L.; Proffit, W.R.; Turvey, T. Superimposition of 3D cone-beam, C.T.; Models of orthognathic surgery patients. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2005, 34, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).