Mechanistic Exploration of Visible Light-Activated Carbon/TiO2 Hybrid Dots Damaging Bacterial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
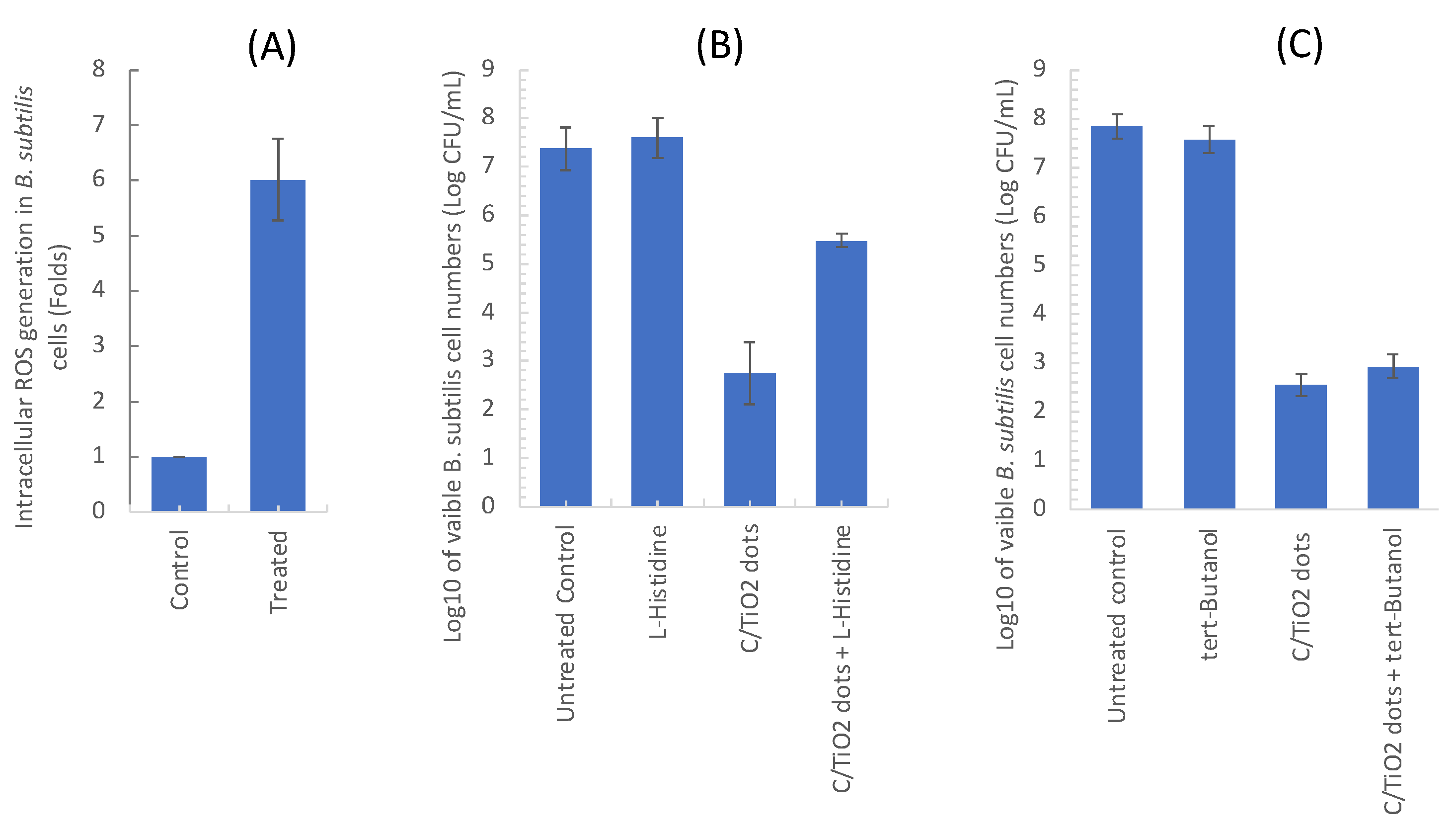
2.1. Intracellular ROS Measurement
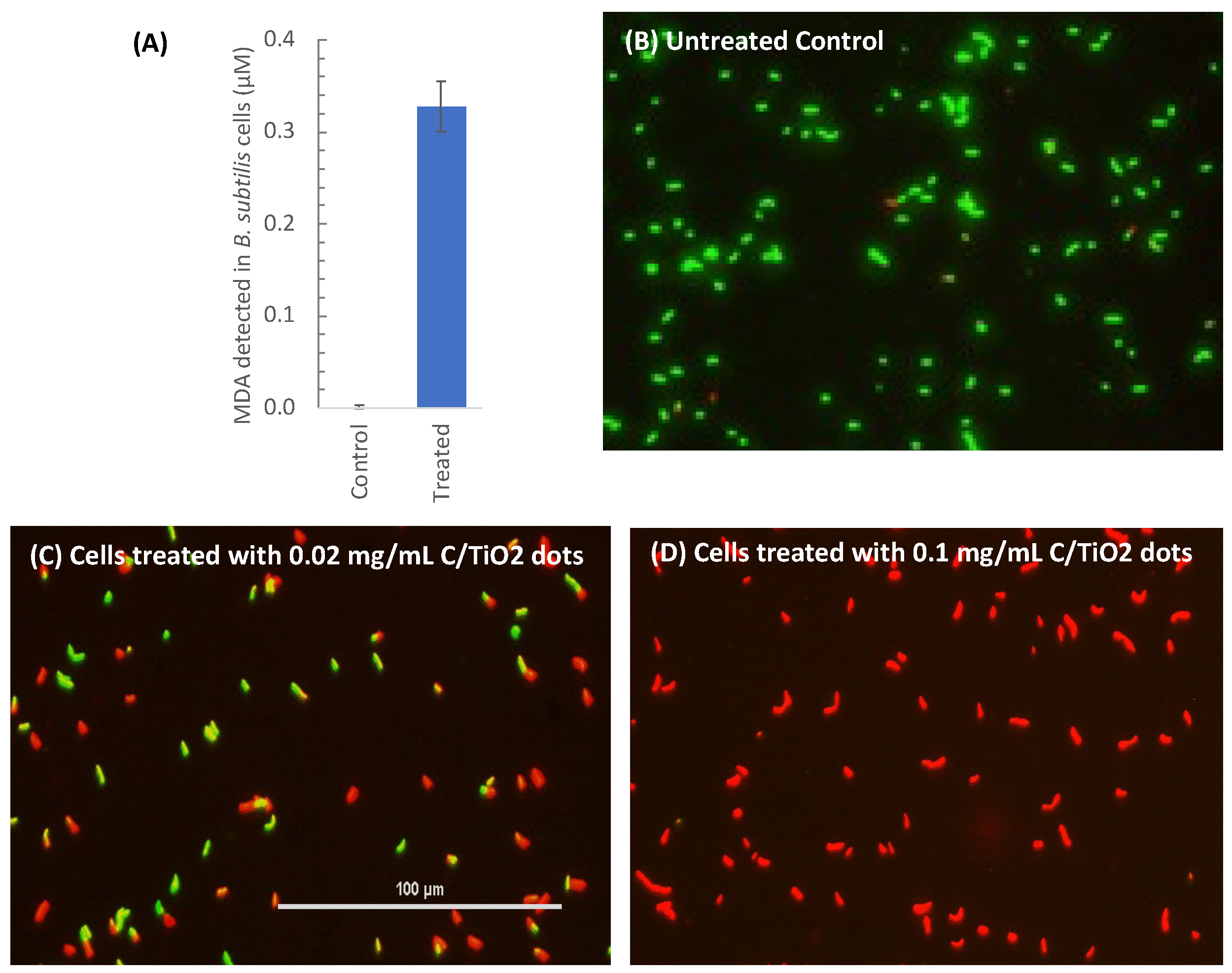
2.2. Membrane Damage—Live/Dead Bacterial Staining
2.3. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation
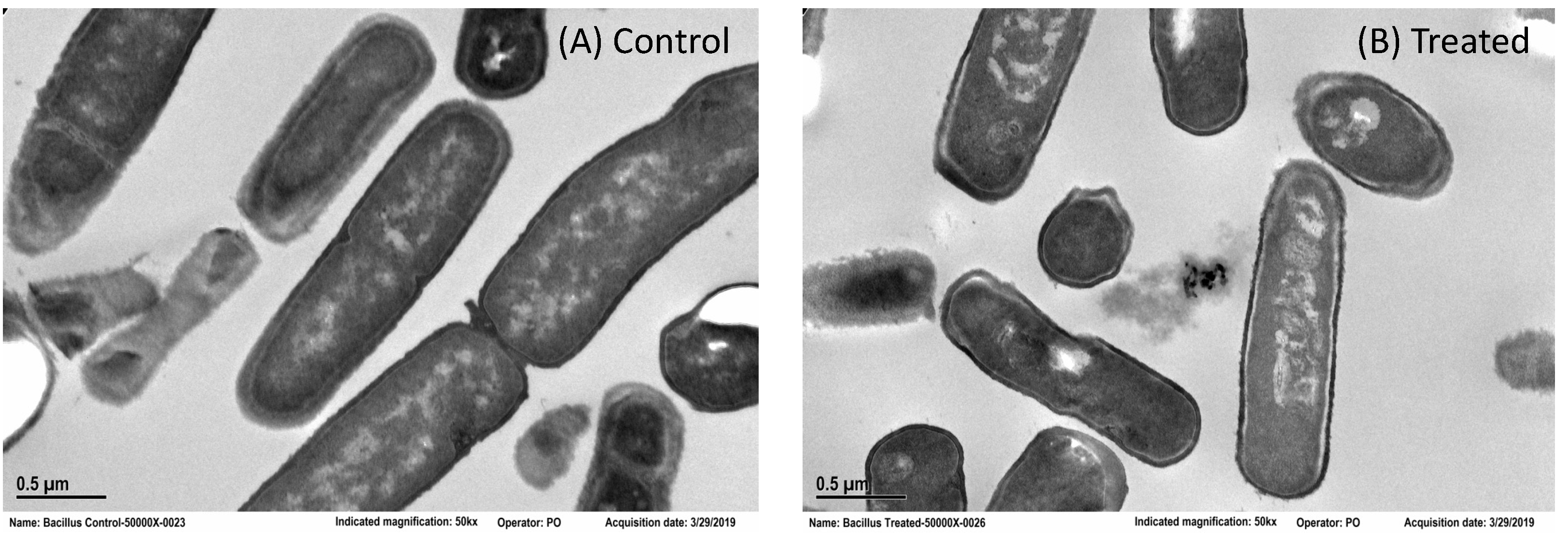
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Imaging
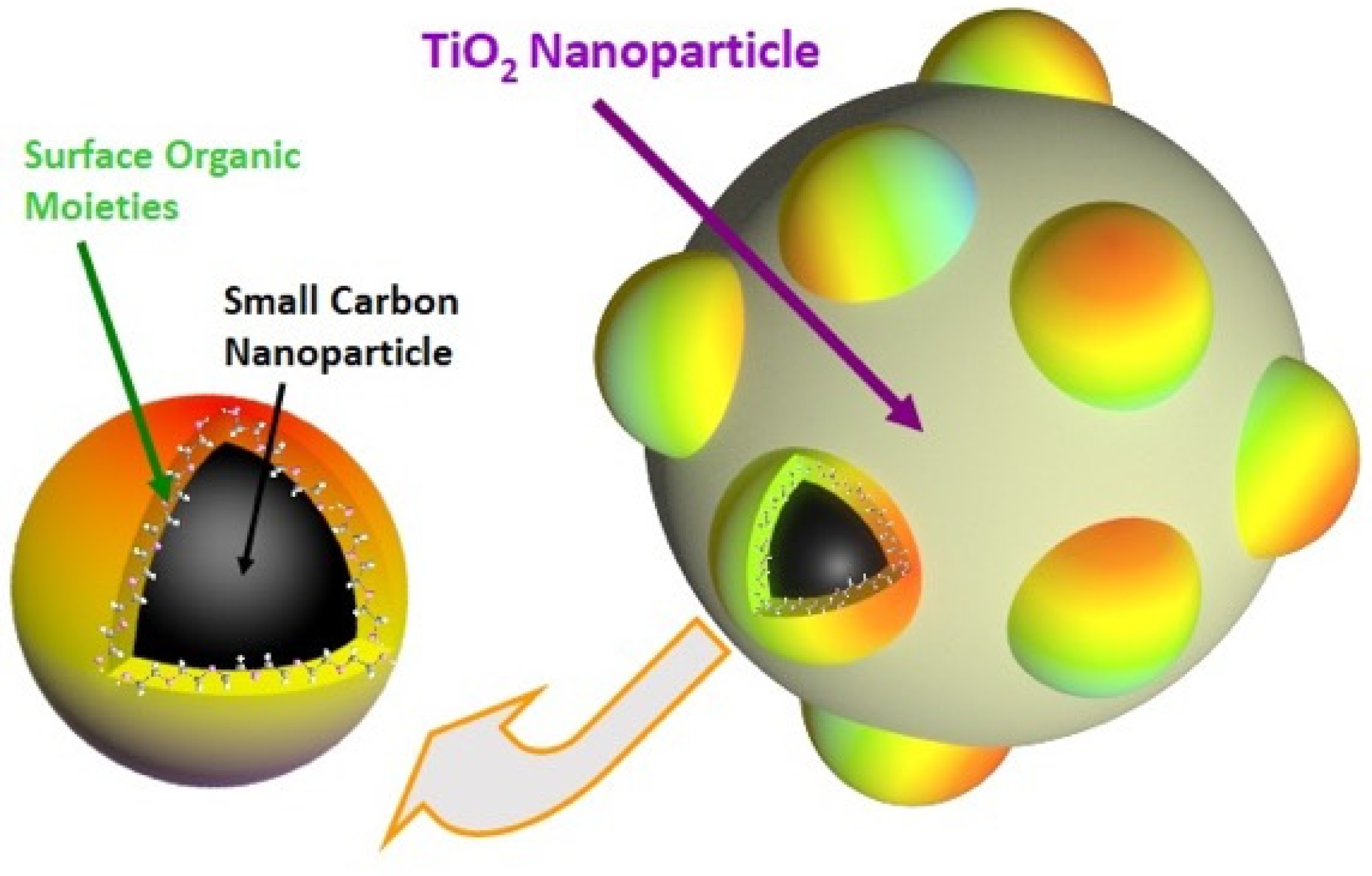
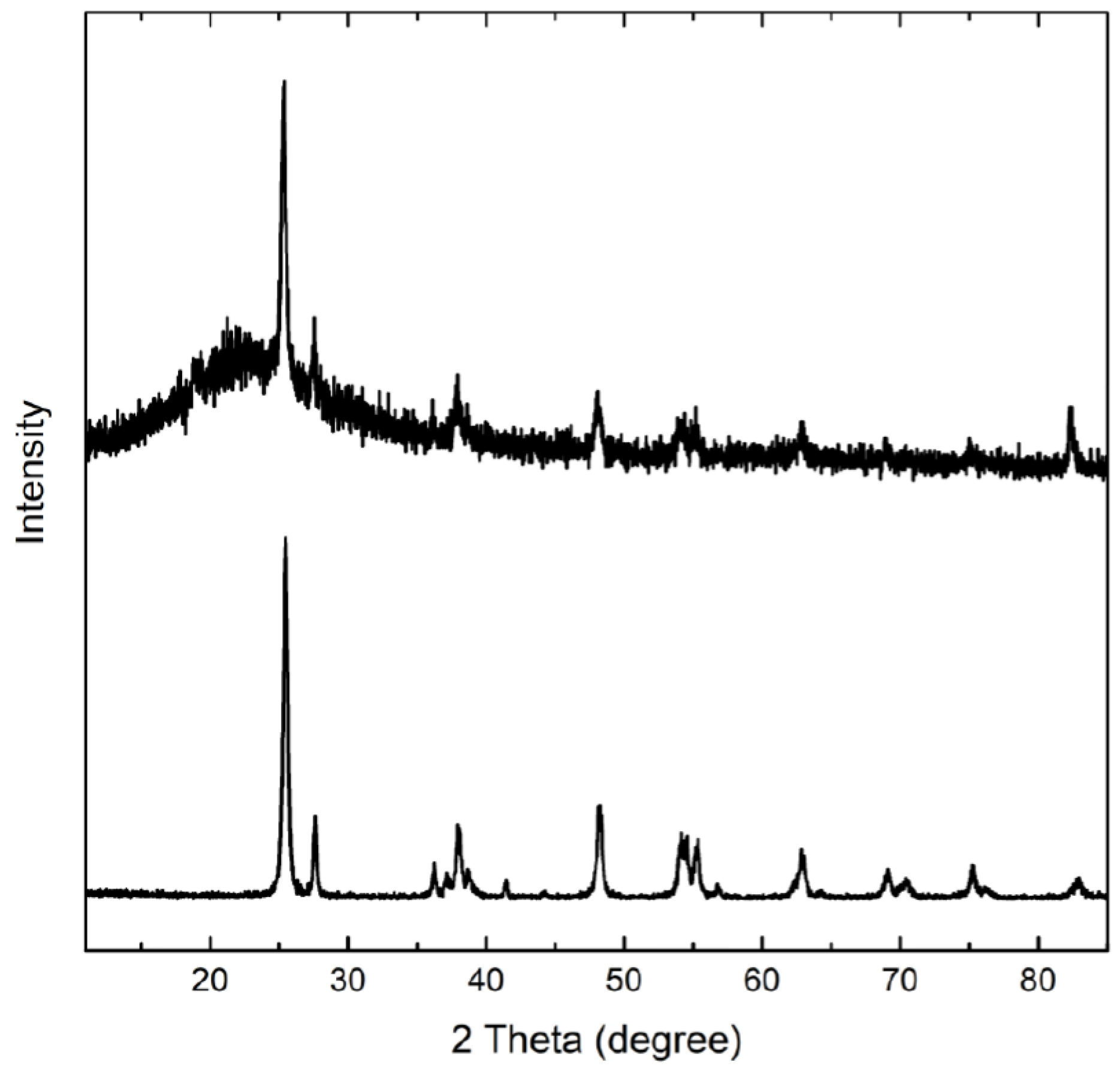
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Particles for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-P. Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent 7,829,772 B2, 9 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots—Exploring Carbon at Zero-Dimension; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.G.; Sahu, S.; Yang, S.-T.; Sonkar, S.K.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; LeCroy, G.E.; Cao, L.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon “Quantum” Dots for Optical Bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2116–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhu, A.; Tian, Y. Functional Surface Engineering of C-Dots for Fluorescent Biosensing and in Vivo Bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.G.; Yang, F.; Yang, S.-T.; Sonkar, S.K.; Yang, L.; Broglie, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon-Based Quantum Dots for Fluorescence Imaging of Cells and Tissues. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 10791–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, K.A.S.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Lewis, W.K.; Guliants, E.A.; Jafariyan, A.; Wang, P.; Bunker, C.E.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Quantum Dots and Applications in Photocatalytic Energy Conversion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8363–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCroy, G.E.; Yang, S.-T.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Bunker, C.E.; Hu, Y.; Luo, P.G.; Sun, Y.-P. Functionalized Carbon Nanoparticles: Syntheses and Applications in Optical Bioimaging and Energy Conversion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 320, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Han, X.; Li, S.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Carbon Dots: Biomacromolecule Interaction, Bioimaging and Nanomedicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 343, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, G.A.M.; Martindale, B.C.M.; Reisner, E. Carbon Dots as Photosensitisers for Solar-Driven Catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6111–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Pramanik, P. Carbon Quantum Dots from Natural Resource: A Review. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Liang, W.; Seilkop, A.; Veca, L.M.; Sun, Y.-P.; Bunker, C.E. Carbon Dots for Energy Conversion Applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 220903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lin, Q.; Chang, H.-T. Recent Advances and Sensing Applications of Carbon Dots. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liang, W.; Meziani, M.J.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Carbon Dots as Potent Antimicrobial Agents. Theranostics 2020, 10, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indriyati; Primadona, I.; Permatasari, F.A.A.; Irham, M.A.; Nasir, D.E.M.; Iskandar, F. Recent Advances and Rational Design Strategies of Carbon Dots towards Highly Efficient Solar Evaporation. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 7523–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziani, M.J.; Dong, X.; Zhu, L.; Jones, L.P.; LeCroy, G.E.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Visible-Light-Activated Bactericidal Functions of Carbon “Quantum” Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10761–10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, N.; Okonjo, P.A.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Optical and Photodynamic Properties of Carbon/TiO2 Hybrid Dots in Different Nanoscale Configurations. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 763, 137208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Rabe, D.I.; Mohammed, O.O.; Dong, X.; Patel, A.K.; Overton, C.M.; Tang, Y.; Kathariou, S.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Carbon Dots for Highly Effective Photodynamic Inactivation of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Edmondson, R.; Yang, F.; Tang, Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Carbon Dots for Effective Photodynamic Inactivation of Virus. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 33944–33954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Overton, C.M.; Tang, Y.; Darby, J.P.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Visible Light-Activated Carbon Dots for Inhibiting Biofilm Formation and Inactivating Biofilm-Associated Bacterial Cells. Front. Bioeng. 2021, 9, 786077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mayyahi, A.; Everhart, B.M.; Shrestha, T.B.; Back, T.C.; Amama, P.B. Enhanced Charge Separation in TiO2/Nanocarbon Hybrid Photocatalysts through Coupling with Short Carbon Nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11702–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, N.T.; Thomas, N.; Louis, J.; Mathew, D.T.; Ganguly, P.; John, H.; Pillai, S.C. Graphene Coupled TiO2 Photocatalysts for Environmental Applications: A Review. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.; Hauptmann, J.R.; Nygard, J.; Sadowski, J.; Lindelöf, P.E. Hybrid Devices from Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes Epitaxially Grown into a Semiconductor Heterostructure. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qian, H.; Wang, P.; LeCroy, G.E.; Bunker, C.E.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Yang, L.; Reibold, M.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon-TiO2 Hybrid Dots in Different Configurations—Optical Properties, Redox Characteristics, and Mechanistic Implications. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10798–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Sahu, S.; Anilkumar, P.; Bunker, C.E.; Xu, J.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Wang, P.; Guliants, E.A.; Tackett, K.N., II; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Nanoparticles as Visible-Light Photocatalysts for Efficient CO2 Conversion and Beyond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4754–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Sahu, S.; Cao, L.; Bunker, C.E.; Peng, G.; Liu, Y.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Wang, P.; Guliants, E.A.; Meziani, M.J.; et al. Efficient Fluorescence Quenching in Carbon Dots by Surface-Doped Metals--Disruption of Excited State Redox Processes and Mechanistic Implications. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16141–16147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anilkumar, P.; Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Sahu, S.; Liu, J.-H.; Wang, P.; Korch, K.; Tackett, K.N., II; Parenzan, A.; Sun, Y.-P. Toward Quantitatively Fluorescent Carbon-Based “Quantum” Dots. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.W.; Chang, H.H. Bactericidal Effects and Mechanisms of Visible Light-Responsive Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysts on Pathogenic Bacteria. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2012, 60, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Kuang, W.; Shi, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q.; Tan, S. Carbon Quantum Dot-Decorated TiO2 for Fast and Sustainable Antibacterial Properties under Visible-Light. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Moreira, J.; Gomaa, H.; Ray, A.K. Visible-Solar-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenol with Dye-Sensitized TiO2: Parametric and Kinetic Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 4523–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xu, S. Facile Preparation of Squarylium Dye Sensitized TiO2 Nanoparticles and Their Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 564, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, J.-L.; Hao, H.; Lang, X. Visible Light-Induced Selective Oxidation of Alcohols with Air by Dye-Sensitized TiO2 Photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 232, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Madonia, A.; Gazzetto, M.; Sciortino, L.; Rohwer, E.J.; Feurer, T.; Gelardi, F.M.; Cannas, M.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. The Interaction of Photoexcited Carbon Nanodots with Metal Ions Disclosed Down to the Femtosecond Scale. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11902–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciortino, A.; Gazzetto, M.; Soriano, M.L.; Cannas, M.; Cardenas, S.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. Ultrafast Spectroscopic Investigation on Fluorescent Carbon Nanodots: The Role of Passivation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 16459–16467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Bunker, C.E.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots: Zero-Dimensional Carbon Allotrope with Unique Photoinduced Redox Characteristics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Ge, L.; Abu Rabe, D.I.; Mohammed, O.O.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y.; Kathariou, S.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.-P. Photoexcited State Properties and Antibacterial Activities of Carbon Dots Relevant to Mechanistic Features and Implications. Carbon 2020, 170, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxser, S.E.; Sawada, G.; Raub, T.J. Analytical and Numerical Techniques for Evaluation of Free Radical Damage in Cultured Cells Using Imaging Cytometry and Fluorescent Indicators. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 300, 256–275. [Google Scholar]
- Petrat, F.; Pindiur, S.; Kirsch, M.; de Groot, H. NAD(P)H, A Primary Target of 1O2 in Mitochondria of Intact Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCroy, G.E.; Messina, F.; Sciortino, A.; Bunker, C.E.; Wang, P.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Sun, Y.-P. Characteristic Excitation Wavelength Dependence of Fluorescence Emissions in Carbon “Quantum” Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 28180–28186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal Nanoparticles: Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Antibacterial Activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, H.; Yu, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; He, L. Morphology-Dependent Bactericidal Activities of Ag/CeO2 Catalysts Against Escherichia Coli. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 135, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, J.; German, J.B.; Kinsella, J.E. Initiation of Lipid Peroxidation in Biological Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1987, 25, 317–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, A.W. Lipid Hydroperoxide Generation, Turnover, and Effector Action in Biological Systems. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Porter, N.A. Free Radical Lipid Peroxidation: Mechanisms and Analysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5944–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, Y.H.; Ng, A.M.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Wong, M.T.; Chan, C.M.; Guo, M.Y.; Ng, Y.H.; Djurišić, A.B.; et al. Mechanisms of Antibacterial Activity of MgO: Non-ROS Mediated Toxicity of MgO Nanoparticles towards Escherichia Coli. Small 2013, 10, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, J.P.; Cornejo, J.A.; Sumner, J.J.; Schuler, A.J.; Atanassov, P.; Ista, L.K. Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles as a Tool for Probing the Bacterial Cell Envelope: The Case of Shewanella Oneidensis MR-1. Biointerphases 2016, 11, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carre, G.; Hamon, E.; Ennahar, S.; Estner, M.; Lett, M.C.; Horvatovich, P.; Gies, J.P.; Keller, V.; Keller, N.; Andre, P. TiO2 Photocatalysis Damages Lipids and Proteins in Escherichia Coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 65, 4094–4098. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Wang, P.; Darby, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Overton, C.M.; Kathariou, S.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Photoactivated Carbon Dots for Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens Listeria and Salmonella. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H.; Cheeseman, K.H. Determination of Aldehydic Lipid Peroxidation Products: Malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, W.A. On the Detection of Lipid Hydroperoxides in Biological Samples. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1989, 7, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adcock, A.F.; Liang, W.; Okonjo, P.A.; Dong, X.; Sheriff, K.; Wang, P.; Ferguson, I.S.; Hwu, S.-J.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yang, L. Mechanistic Exploration of Visible Light-Activated Carbon/TiO2 Hybrid Dots Damaging Bacterial Cells. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199633
Adcock AF, Liang W, Okonjo PA, Dong X, Sheriff K, Wang P, Ferguson IS, Hwu S-J, Sun Y-P, Yang L. Mechanistic Exploration of Visible Light-Activated Carbon/TiO2 Hybrid Dots Damaging Bacterial Cells. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199633
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdcock, Audrey F., Weixiong Liang, Peter A. Okonjo, Xiuli Dong, Kirkland Sheriff, Ping Wang, Isaiah S. Ferguson, Shiou-Jyh Hwu, Ya-Ping Sun, and Liju Yang. 2022. "Mechanistic Exploration of Visible Light-Activated Carbon/TiO2 Hybrid Dots Damaging Bacterial Cells" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199633
APA StyleAdcock, A. F., Liang, W., Okonjo, P. A., Dong, X., Sheriff, K., Wang, P., Ferguson, I. S., Hwu, S.-J., Sun, Y.-P., & Yang, L. (2022). Mechanistic Exploration of Visible Light-Activated Carbon/TiO2 Hybrid Dots Damaging Bacterial Cells. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199633






