Comparison of Canopy Cover and Leaf Area Index Estimation from Airborne LiDAR and Digital Aerial Photogrammetry in Tropical Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
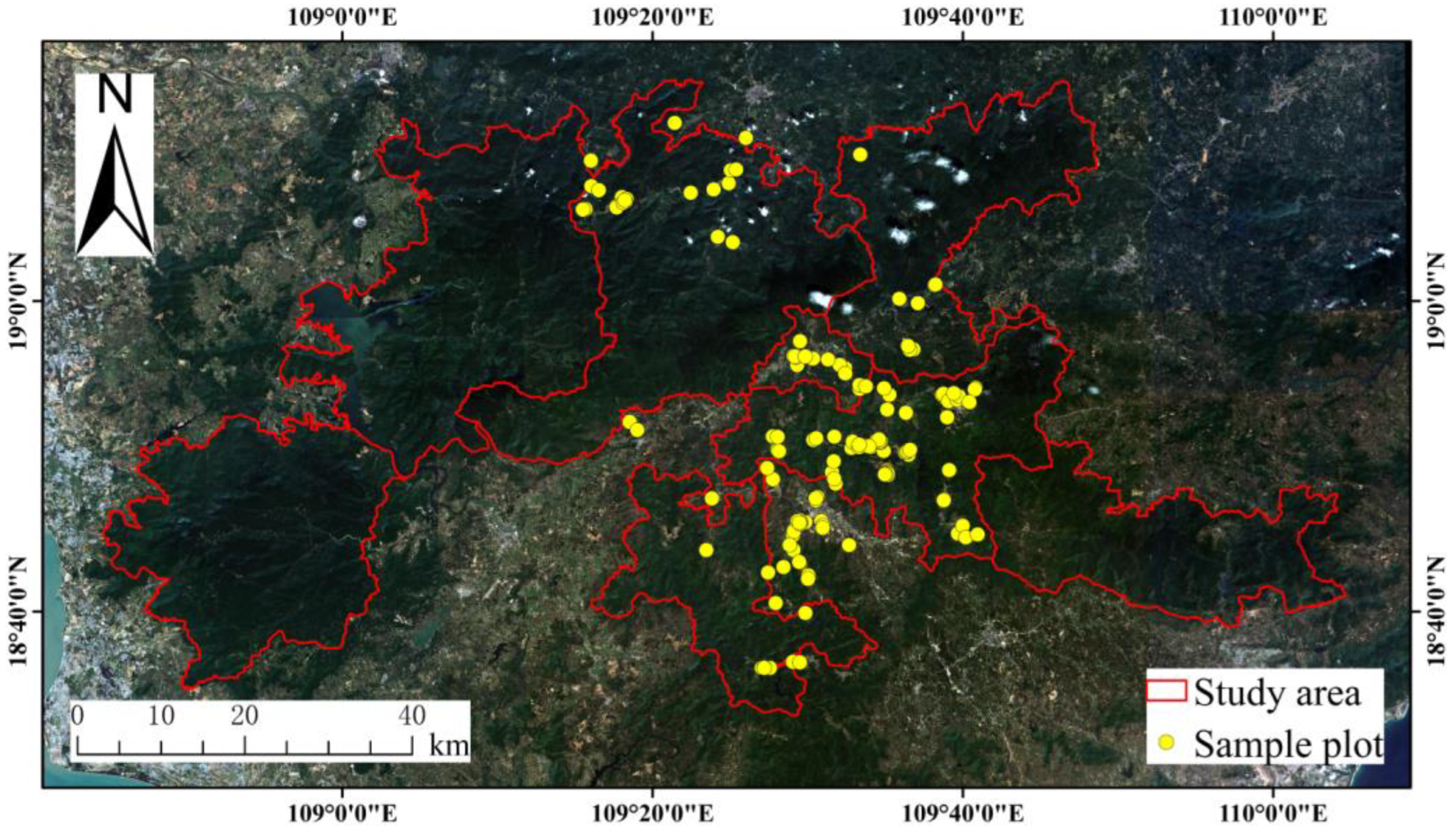
2.1. Study Area and Field Inventory of Plots
2.2. Airborne LiDAR Data and Preprocess
2.3. Airborne Digital Imagery and Preprocess
3. Methods
3.1. Canopy Cover Estimation
3.1.1. Estimating Canopy Cover from Airborne LiDAR
3.1.2. Estimating Canopy Cover from Digital Aerial Photogrammetry
3.2. Leaf Area Index (LAI) Estimation
3.3. Sentinel-2-Based LAI Estimation
4. Results
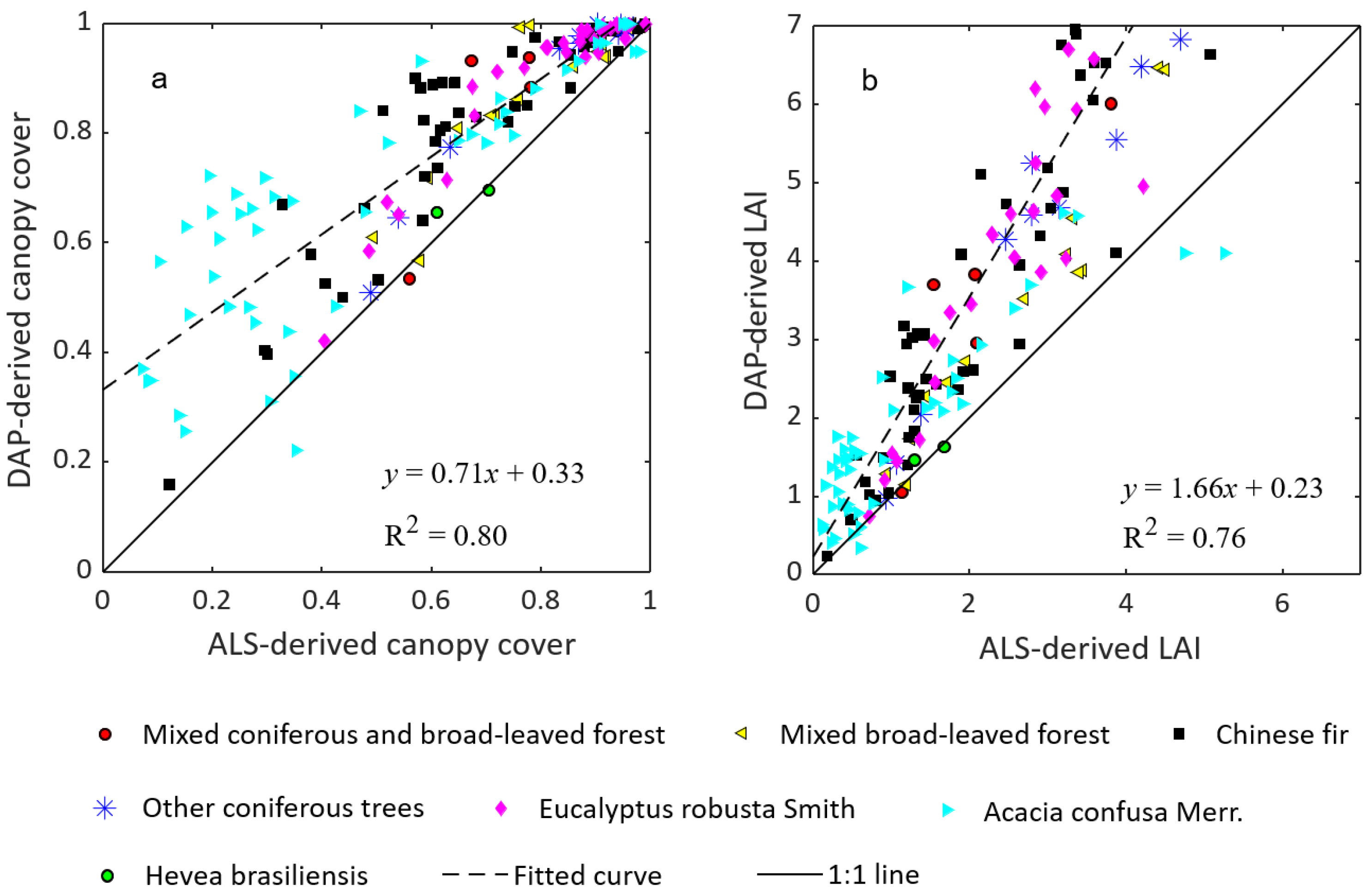
4.1. Comparison of Canopy Cover and LAI Estimates
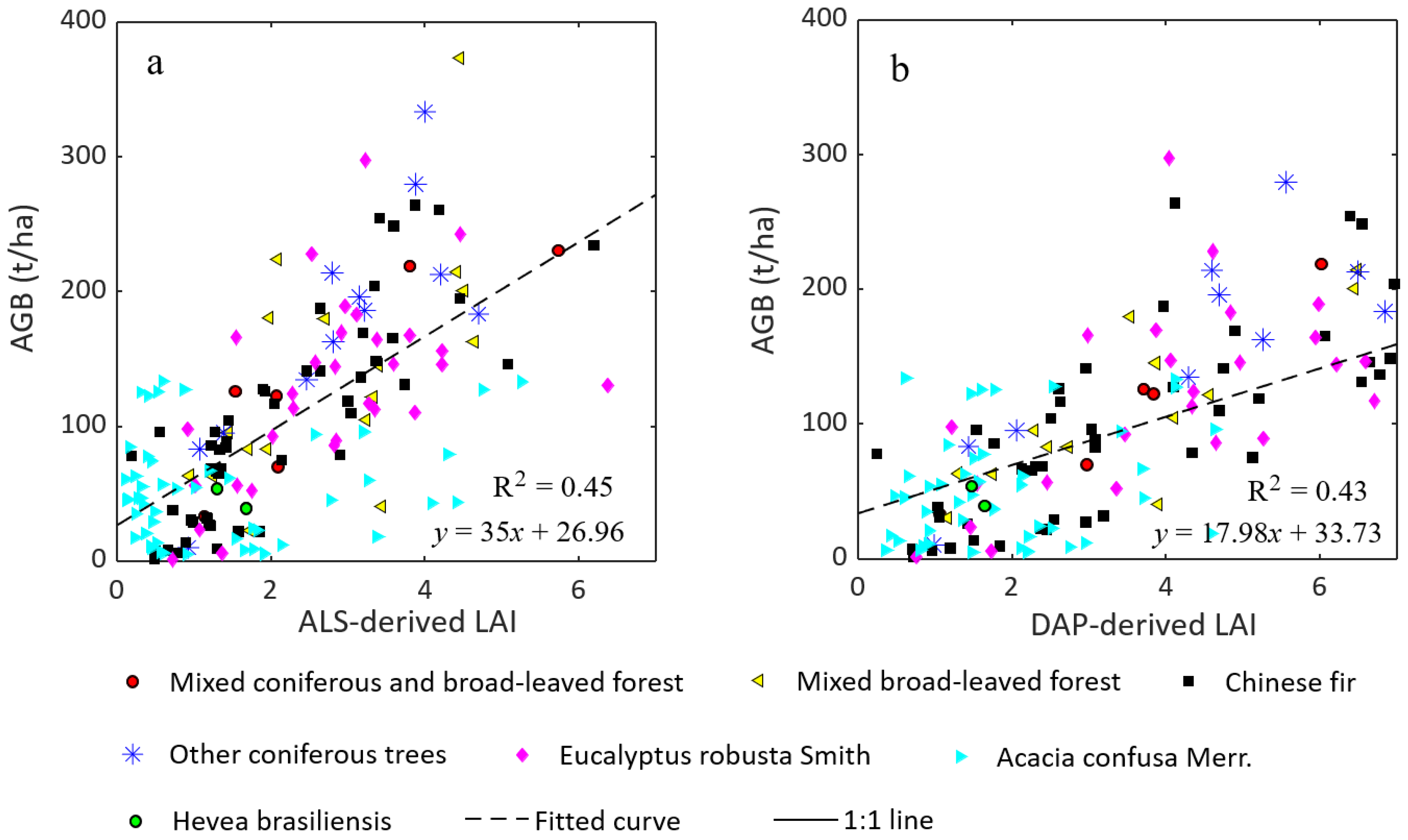
4.2. Relationship between LAI and Aboveground Biomass
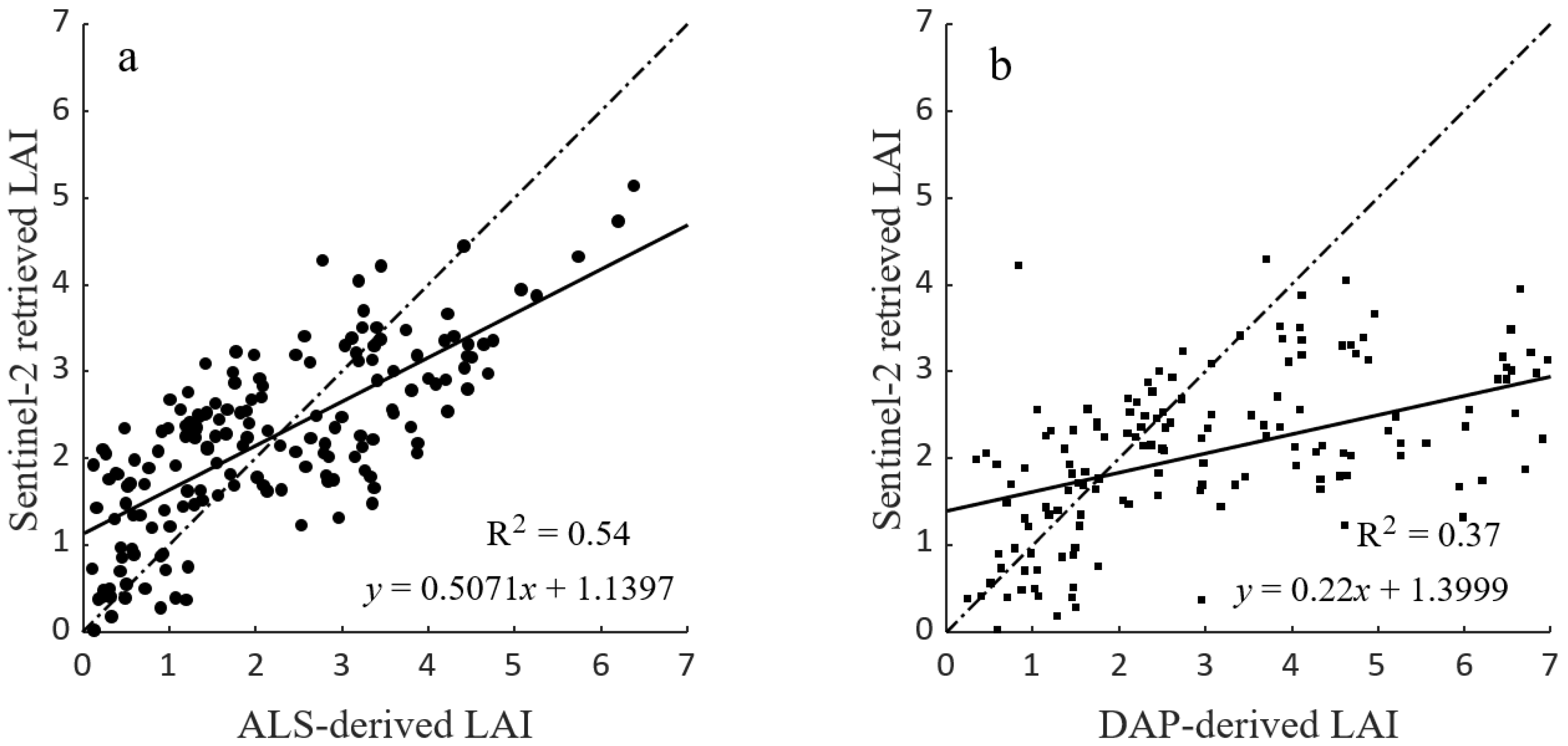
4.3. Comparison between Airborne and Sentinel-2 LAI Estimates
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Smith, G.J.; Jonckheere, I.; Coppin, P. Review of methods for in situ leaf area index (LAI) determination: Part II. Estimation of LAI, errors and sampling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 121, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, L.; Korpela, I.; Heiskanen, J.; Maltamo, M. Airborne discrete-return LIDAR data in the estimation of vertical canopy cover, angular canopy closure and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Mu, X.; Li, W.; Yan, G.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W. Quantifying Understory and Overstory Vegetation Cover Using UAV-Based RGB Imagery in Forest Plantation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.B.; Brown, N.D.; Sheil, D. Assessing forest canopies and understorey illumination: Canopy closure, canopy cover and other measures. Forestry 1999, 72, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Hu, R.; Luo, J.; Weiss, M.; Jiang, H.; Mu, X.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W. Review of indirect optical measurements of leaf area index: Recent advances, challenges, and perspectives. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.-L.; Anderson, J.; Fladeland, M. Forest canopy structural properties. In Field Measurements for Forest Carbon Monitoring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 179–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bonan, G.B. Importance of leaf area index and forest type when estimating photosynthesis in boreal forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 43, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholcyzk, P.; Smets, B. GEOV1: LAI and FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.J. Comparative physiological studies on the growth of field crops: I. Variation in net assimilation rate and leaf area between species and varieties, and within and between years. Ann. Bot. 1947, 11, 41–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.B.; Ramakrishna, R.; Nemani, R.; Running, S.W. Estimation of global leaf area index and absorbed PAR using radiative transfer models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1380–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, P.C.; Strever, A.; Poblete-Echeverría, C. Comparison of vegetation indices for leaf area index estimation in vertical shoot positioned vine canopies with and without grenbiule hail-protection netting. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT + SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Nelson, R.F.; Næsset, E.; Ørka, H.O.; Coops, N.C.; Hilker, T.; Bater, C.W.; Gobakken, T. Lidar sampling for large-area forest characterization: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armston, J.; Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; Scarth, P.; Phinn, S.; Lucas, R.; Bunting, P.; Goodwin, N. Direct retrieval of canopy gap probability using airborne waveform lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Tompalski, P.; Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A. Comparison of airborne laser scanning and digital stereo imagery for characterizing forest canopy gaps in coastal temperate rainforests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Armston, J.; Goodwin, N.; Scarth, P. Modelling canopy gap probability, foliage projective cover and crown projective cover from airborne lidar metrics in Australian forests and woodlands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandois, J.P.; Ellis, E.C. High spatial resolution three-dimensional mapping of vegetation spectral dynamics using computer vision. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsdorf, F.; Kötz, B.; Meier, E.; Itten, K.I.; Allgöwer, B. Estimation of LAI and fractional cover from small footprint airborne laser scanning data based on gap fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. Voxel-based 3-D modeling of individual trees for estimating leaf area density using high-resolution portable scanning lidar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, H. Estimation of LAI with the LiDAR technology: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Hill, R.; Rosette, J.; Suárez, J. Comparing discrete echoes counts and intensity sums from ALS for estimating forest LAI and gap fraction. In Proceedings of the SilviLaser, Edinburgh, UK, 17–19 September 2008; pp. 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.M.; Rich, P.M.; Gower, S.T.; Norman, J.M.; Plummer, S. Leaf area index of boreal forests: Theory, techniques, and measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 29429–29443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, C.; Chasmer, L. Testing LiDAR models of fractional cover across multiple forest ecozones. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; Bookhagen, B.; McFadden, J.P.; Sun, A.; Roberts, D.A. Mapping urban forest leaf area index with airborne lidar using penetration metrics and allometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gu, X.; Pang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, L. Estimation of forest aboveground biomass and leaf area index based on digital aerial photograph data in northeast China. Forests 2018, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, L.; Bollandsås, O.M.; Ørka, H.O.; Næsset, E.; Gobakken, T. Comparing the accuracies of forest attributes predicted from airborne laser scanning and digital aerial photogrammetry in operational forest inventories. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglhaut, J.; Cabo, C.; Puliti, S.; Piermattei, L.; O’Connor, J.; Rosette, J. Structure from Motion Photogrammetry in Forestry: A Review. Curr. For. Rep. 2019, 5, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Clemente, R.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; Romero Ramírez, F.J.; Hornero, A.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. A novel methodology to estimate single-tree biophysical parameters from 3D digital imagery compared to aerial laser scanner data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11627–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mu, X.; Chianucci, F.; Qi, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Yan, G.; Liu, S. Ultrahigh-resolution boreal forest canopy mapping: Combining UAV imagery and photogrammetric point clouds in a deep-learning-based approach. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastaranta, M.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Pekkarinen, A.; Tuominen, S.; Ginzler, C.; Kankare, V.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H. Airborne laser scanning and digital stereo imagery measures of forest structure: Comparative results and implications to forest mapping and inventory update. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 39, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Wen, K.; Qi, J.; Huang, H. Crown Structure Metrics to Generalize Aboveground Biomass Estimation Model Using Airborne Laser Scanning Data in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, W.; Jin, S.; Shao, J.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Yan, G. Improving the estimation of canopy cover from UAV-LiDAR data using a pit-free CHM-based method. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Qi, J.; Cook, B.D.; Morton, D.C.; Wei, S.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P. Modeling Small-Footprint Airborne Lidar-Derived Estimates of Gap Probability and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Kuusk, A.; Mõttus, M.; Rautiainen, M.; Nilson, T. Canopy gap fraction estimation from digital hemispherical images using sky radiance models and a linear conversion method. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilson, T. A theoretical analysis of the frequency of gaps in plant stands. Agric. Meteorol. 1971, 8, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.R.G.; Xiang, Y. Estimation of leaf area index from transmission of direct sunlight in discontinuous canopies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1986, 37, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.C.; Skakun, S.V.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlerf, M.; Atzberger, C. Inversion of a forest reflectance model to estimate structural canopy variables from hyperspectral remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Popescu, S. Lidar-based mapping of leaf area index and its use for validating GLOBCARBON satellite LAI product in a temperate forest of the southern USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1628–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumäe, T.; Lang, M. Estimation of canopy cover in dense mixed-species forests using airborne lidar data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 51, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Brunner, A.; Hanssen, K.H.; Lange, H.; Næsset, E.; Rautiainen, M.; Stenberg, P. Mapping LAI in a Norway spruce forest using airborne laser scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Yan, G.; Nerry, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Mu, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, D. Using Airborne Laser Scanner and Path Length Distribution Model to Quantify Clumping Effect and Estimate Leaf Area Index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3196–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Verrelst, J.; Calvo, L.; Suárez-Seoane, S. Hybrid inversion of radiative transfer models based on high spatial resolution satellite reflectance data improves fractional vegetation cover retrieval in heterogeneous ecological systems after fire. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Mu, X.; Qi, J.; Pisek, J.; Roosjen, P.; Yan, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Baret, F. Characterizing reflectance anisotropy of background soil in open-canopy plantations using UAV-based multiangular images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 177, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tree Species and Forest Types | Allometry Equation of Individual Tree | AGB of Plot (t/ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 124.6106.4 | |
| Broad-leaved mixed forest | 113.5 260.2 | |
| Other coniferous trees | 185.0 174.6 | |
| Chinese fir | 46.8 7.3 | |
| Eucalyptus robusta Smith | 89.2 175.3 | |
| Acacia confusa Merr. | 127.6170.0 | |
| Hevea brasiliensis | 46.5 87.7 |
| Coefficients of Determination | Canopy Cover | LAI |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest | 0.64 | 0.87 |
| Mixed broad-leaved forest | 0.79 | 0.54 |
| Other coniferous trees | 0.94 | 0.66 |
| Eucalyptus robusta Smith | 0.81 | 0.84 |
| Acacia confusa Merr. | 0.89 | 0.82 |
| Hevea brasiliensis | 0.71 | 0.67 |
| All | 0.80 | 0.76 |
| Coefficients of Determination | LAIALS–AGB | LAIDAP–AGB |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest | 0.77 | 0.96 |
| Mixed broad-leaved forest | 0.39 | 0.65 |
| Other coniferous trees | 0.67 | 0.55 |
| Eucalyptus robusta Smith | 0.67 | 0.63 |
| Acacia confusa Merr. | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| Hevea brasiliensis | 0.03 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Li, L.; Jiang, J. Comparison of Canopy Cover and Leaf Area Index Estimation from Airborne LiDAR and Digital Aerial Photogrammetry in Tropical Forests. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199882
Li C, Zheng Y, Zhang X, Wu F, Li L, Jiang J. Comparison of Canopy Cover and Leaf Area Index Estimation from Airborne LiDAR and Digital Aerial Photogrammetry in Tropical Forests. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199882
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chenyun, Yanfeng Zheng, Xinjie Zhang, Fayun Wu, Linyuan Li, and Jingyi Jiang. 2022. "Comparison of Canopy Cover and Leaf Area Index Estimation from Airborne LiDAR and Digital Aerial Photogrammetry in Tropical Forests" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199882
APA StyleLi, C., Zheng, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, F., Li, L., & Jiang, J. (2022). Comparison of Canopy Cover and Leaf Area Index Estimation from Airborne LiDAR and Digital Aerial Photogrammetry in Tropical Forests. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199882






