Abstract
Postoperative delirium after spinal surgery in elderly patients has been a recent concern. However, there has not been a study of delirium after spinal surgery based on electroencephalography (EEG) signals from a compact wearable device. We aimed to analyze differences in EEG signals from a wearable device in patients with and without delirium after spinal surgery. Thirty-seven patients who underwent cervical or lumbar decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative spinal disease were included. EEG waves were collected from a compact wearable device, and percentage changes from baseline to within 1 week and 3 months after surgery were compared between patients with and without delirium. In patients with delirium, the anxiety- and stress-related EEG waves—including the H-beta (19.3%; p = 0.003) and gamma (18.8%; p = 0.006) waves—and the tension index (7.8%; p = 0.011) increased, and the relaxation-related theta waves (−23.2%; p = 0.016) decreased within 1 week after surgery compared to the non-delirium group. These results will contribute to understanding of the EEG patterns of postoperative delirium and can be applied for the early detection and prompt treatment of postoperative delirium after spinal surgery.
1. Introduction
Delirium is a clinical syndrome with core symptoms of inattention and acute cognitive dysfunction that often fluctuate []. The incidence of postoperative delirium after spinal surgery is reported to be 4.5–24.3% [,,,] and has been found to be associated with prolonged hospital stays and increased costs of care, postoperative functional deterioration, and increased mortality [,]. Up to USD 82.4 billion is spent annually on medical costs associated with delirium in the United States alone []. Well-known risk factors include older age, duration of surgery, and blood loss during surgery []. As global life expectancy is continuously increasing [], and considering the characteristics of spinal surgery [,,]—including a long surgical duration and increased risk of blood loss—the individual, societal, and financial burdens of postoperative delirium after spinal surgery are expected to increase [].
Early diagnosis and treatment of delirium can reduce length of stay, in-hospital morbidity, and healthcare costs []. A diagnosis of delirium is primarily made by trained psychiatrists based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5). For other medical personnel to detect and evaluate delirium easily, an assessment tool called the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) has been developed [], and for the case of intensive care unit (ICU) patients, the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) has been developed and validated. Although several biomarkers have been studied for an objective diagnostic test for delirium, further research is required to apply them in clinical practice [,].
Electroencephalography (EEG) has attracted attention as an objective diagnostic tool for delirium []. EEG waves are known to correspond to certain mental functions and states. Delta waves are associated with deep sleep stages []. Theta waves reflect relaxation, drowsiness, and meditation. Alpha waves reflect relaxation and reduced anxiety []. Sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) waves reflect active, busy, or anxious thinking. M-beta waves indicate anxiety and performance []. H-beta waves are associated with significant stress, anxiety, and arousal []. Gamma waves reflect stress and conscious perception [,]. However, the inconvenience of testing methods using EEG recording devices remains a limitation. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been a study of delirium after spinal surgery based on EEG signals from a compact wearable device. In this study, we aimed to analyze EEG signals from such a device in patients with and without delirium both before and after spinal surgery.
2. Materials and Methods
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the corresponding author’s hospital (Yonsei University IRB and Ethics Committee: 4-2018-0709). All methods were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Yonsei University’s institutional guidelines. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardians.
From April 2019 to April 2020, 37 patients at least 60 years of age who underwent cervical or lumbar spinal surgery were prospectively enrolled. The enrolled patients were limited to elective surgery for degenerative cervical or lumbar spine disease, excluding trauma or tumor cases. The main diagnoses included cervical spondylotic radiculomyelopathy (6 patients), adjacent segment disease (4 patients), degenerative spondylolisthesis (7 patients), lumbar spinal stenosis (16 patients), and degenerative scoliosis (4 patients). All included patients underwent spinal decompression and instrumented spinal fusion, and all procedures were performed by a single surgeon (B.H.L.).
The patients were divided into two groups: with and without delirium (the delirium and non-delirium groups, respectively). The patients who presented with delirious behavior and were diagnosed with delirium by a psychiatrist within 1 week after surgery were classified as the delirium group. The detection of delirium symptoms was carried out by ward nurses, residents, and caregivers jointly observing the patient 24 h per day. The Confusion Assessment Method (CAM), which is the most common assessment tool, was used, and the following four factors were assessed: (1) acute onset, (2) inattention, (3) disorganized thinking, and (4) altered levels of consciousness. The evaluation of delirium was performed every 1–2 h while checking the patient’s condition. After the detection of delirium symptoms, the patient’s delirium status was accurately diagnosed and treated through emergency consultation with a psychiatrist or psychiatric residents in the hospital. All patients in the delirium group had fluctuating symptoms during the hospitalization period and recovered their normal mental status by the time of discharge. For all patients in the two groups, immediate postoperative pain was controlled with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) containing 1 mg of fentanyl for 2–3 days. Oral analgesics, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pregabalin, and gabapentin, were administered at the recommended dose or less, regardless of the groups. The doses of pregabalin and gabapentin were increased to 75 mg BID and 100 mg TID, respectively, as needed. The average length of stay ranged from 7 to 10 days depending on the general condition and recovery of delirium.
2.1. Evaluation of EEG Signals from a Wearable Device
A wearable device for acquiring EEG signals (model: Amp GS5001; SOSO H&C [], Kyungpook University, Daegu, Korea) was used for this study. This device was used in three previous published studies on surgeons’ and nurses’ mental stress [,,]. The device consists of a headband, a main board, two dry electrodes as EEG sensors, and a reference electrode. Two electrodes were positioned at the prefrontal 1 and 2 (Fp1 and Fp2) sites according to the International 10–20 EEG system []. The reference electrode was placed on the right earlobe (Figure 1).
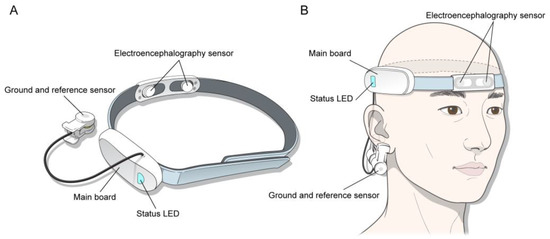
Figure 1.
(A) Profile of the wearable device. (B) The device shown on the patient’s head.
The cortical activity of the frontal lobe was measured with the patient in a resting state with eyes open and closed for 3 min each. To reject artifacts caused by eyeball movement, a neurologist specializing in EEG performed a visual inspection. EEG data were reanalyzed using MATLAB R2012b (MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA) software, and a bandpass filter of 1–50 Hz was applied to the fast Fourier transform. Data analysis using the software was performed by SOSO H&C after anonymization, and the company was blinded to the study. The frequency power was calculated as the square of the amplitudes for delta (0.5–3.5 Hz), theta (4–7 Hz), alpha (8–12 Hz), SMR (12–15 Hz), mid-range beta (M-beta, 15–20 Hz), high-range beta (H-beta, 20–30 Hz), and gamma waves (30–50 Hz) []. Relative frequency power was calculated as the ratio of the corresponding frequency powers to the whole frequency (Figure 2). In addition, we calculated the tension index using the following formula from SOSO H&C based on references for tension [,]:
Tension = {[Log(H-Beta/Alpha) + 1.0843]/2.058993} × 99 + 1
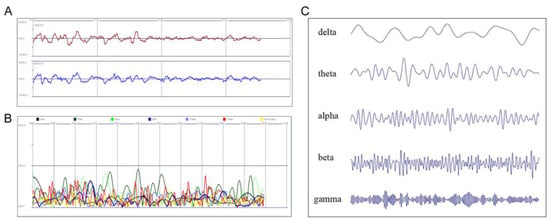
Figure 2.
(A) Raw and (B) reanalyzed EEG signals, according to the frequency bands displayed in the MATLAB software. (C) EEG waveforms, according to the frequency bands. EEG: electroencephalography.
All patients were assessed three times: preoperatively (baseline), within 1 week postoperatively, and 3 months postoperatively. All data measurements were performed in the same manner. The patients waited 1 min while wearing the device in a resting state, and the EEG data were collected with the eyes open and closed for 3 min each. The patients were seated, in a distraction-free environment, and a research nurse who was familiar with the measurement methods measured the EEG data using the device. For the baseline and 3 months after surgery, the measurements were performed in an empty outpatient clinic room, while the measurement within 1 week after surgery was performed in a ward room. Baseline EEG data were obtained one day before surgery for admitted patients. Data were then gathered 1–7 days after surgery when the patients were diagnosed with delirium by psychiatrists. The average presentation time of delirium symptoms was 2 days after surgery. Through consultation with psychiatrists and prompt communication with ward nurses, research nurses, and residents, EEG signals in patients with delirium were measured immediately after the presentation of delirium symptoms with the consent of the patients’ guardians. If the measurement was impossible because the patient was excessively hyperactive and unable to cooperate, the measurement was performed after waiting until the agitation subsided. After discharge, data were gathered at the three-month outpatient follow-up visit. Percentage changes in data from baseline to within 1 week after surgery and from baseline to 3 months after surgery were compared between the delirium and non-delirium groups.
2.2. Statistical Analyses
The study population characteristics are presented as means ± standard deviations for continuous variables and frequencies (percentages) for categorical variables. For comparisons between the delirium and non-delirium groups, the independent two sample t-test was used for continuous variables, while Fisher’s exact test was used for categorical variables. We applied a linear mixed model (LMM) to assess the interaction according to the time and group of EEG signals measured over three times. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS (version 9.4; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) and R version 4.1.3 (http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 23 September 2022). The statistical significance of the interaction p-value was set to p < 0.15, and other than that the significance threshold was p < 0.05.
3. Results
All enrolled patients were sent to the general ward after surgery; no serious postoperative complications except for delirium were observed. Postoperative delirium developed in 6 of 37 patients (16.2%): 4 females (67%) and 2 males (33%). The mean age of these patients was 72.7 ± 3.0 years. Affected patients presented symptoms of hyperactive delirium, including rambling, restlessness, hallucinations, and aggressiveness. The demographics and surgical characteristics of the delirium and non-delirium groups are shown in Table 1. The Mental component Summary (MCS) of the 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) was marginally lower in the delirium group than in the non-delirium group (p = 0.061). There were no significant differences in age, gender, American Society of Anesthesiologists class, history of dementia, physical component summary of the SF-36, surgical site, surgical duration, volume of intraoperative blood loss, or total units of transfused packed red blood cells.

Table 1.
Demographics and surgical characteristics of the enrolled patients.
According to the results of the LMM, the interactions between group and time were significant in the theta waves (p = 0.083), H-beta waves (p = 0.014), gamma waves (p = 0.023), and tension index (p = 0.105), while the other variables were not significant. The results of performing a group post hoc analysis of these variables are shown in Table 2. In patients with delirium, H-beta and gamma waves and the tension index increased, while theta waves decreased, within 1 week after surgery. Patients in the delirium group showed significantly more changes in H-beta (19.3%; p = 0.003), gamma (18.8%; p = 0.006), and theta waves (−23.2%; p = 0.016), as well as the tension index (7.8%; p = 0.011), within 1 week after surgery from baseline compared to patients in the non-delirium group. In the graph of H-beta, gamma, and theta waves and tension index, patterns of peaks and troughs 1 week after surgery followed by recovery to baseline levels by 3 months after surgery were noted in the delirium group, whereas a somewhat flat pattern was noted in the non-delirium group (Figure 3).

Table 2.
Percentage changes in EEG signals from baseline to within 1 week and to 3 months after surgery in the delirium and non-delirium groups.
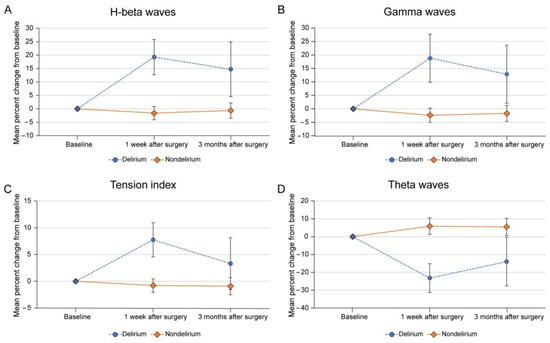
Figure 3.
Mean percentage changes in (A) H-beta waves, (B) gamma waves, (C) tension index, and (D) theta waves within 1 week and 3 months after surgery compared to baseline in patients with and without delirium. The error bars shown are standard errors of the mean.
4. Discussion
Postoperative delirium after spinal surgery in elderly patients has been a recent concern, and several attempts to achieve effective and objective diagnoses of delirium have been reported. However, to the best of our knowledge, there has not been a study of delirium after spinal surgery based on EEG signals from a compact wearable device. Using EEG signals from such a device, we found greater changes in H-beta, gamma, and theta waves and tension index within 1 week after surgery from baseline in the delirium group compared to the non-delirium group. Based on these results, EEG analysis using a wearable device appears to be an effective diagnostic tool and may be applicable during the early diagnosis of delirium after spinal surgery.
While postoperative delirium has been an increasing concern for spinal surgeons recently, it remains an elusive concept and difficult to diagnose []. A diagnosis of delirium is based on the patient’s clinical history, behavioral observations, and cognitive assessments []. It is not easy for spinal surgeons and nurses to recognize delirium, and even psychiatrists may overlook or misdiagnose this disorder. Although there are clinical assessment tools for delirium, novel diagnostic methods—such as biomarkers and wearable accelerometer devices—are being actively studied [,,,].
The association between EEG changes and delirium has been studied, but there are few published reports. EEG has been mainly used to differentiate delirium from non-convulsive status epilepticus or other psychiatric conditions [,]. Bispectral index monitoring and adjustments of the depth of anesthesia appear to correlate with reduced postoperative delirium [,]. Since Koponen et al. first reported reduced alpha waves and increased theta and delta waves in patients with delirium [], other studies have followed. In a study of 28 patients with delirium who underwent cardiothoracic surgery, an increase in delta waves from the frontal and parietal lobes was the only difference between patients with and without delirium []. Urdanibia-Centelles et al. reported high mean global field power—mainly driven by delta wave activity—in septic patients with delirium and proposed continuous EEG monitoring for its diagnosis []. However, Oh et al. pointed out that the routine use of EEG monitoring for delirium screening is time-consuming and inefficient [].
In the present study, we found differences in specific EEG waves between patients with and without delirium after spinal surgery. H-beta and gamma waves, which are known to be related to stress [], increased in patients with delirium. Moreover, the tension index—which consists of alpha and H-beta waves—increased, whereas theta waves decreased, in patients with delirium. These results are somewhat different from those of published studies. Most studies of delirium were performed in ICUs [,,]; however, our patients did not require ventilators or ICU care. We believe that patients in the ICU are more likely to show subdued and hypoactive features than those in the general ward, possibly due to the severity of their illness []. Therefore, slow waves such as delta and theta waves are more likely to be predominant in ICU patients. On the other hand, restless and agitated states, which are commonly seen in hyperactive delirium, correlate well with features of H-beta and gamma waves [,]. Confused, anxious, and irritable behaviors are commonly seen in patients with delirium in the general ward and are a concern for most spinal surgeons and nurses. We believe that our results accurately reflect these aspects of patients with delirium.
In the analysis of demographic and surgical risk factors, we found marginally significant differences only in the MCS of the SF-36 between the two groups. Considering the preliminary nature and small sample size of this study, we believe that this is a potentially important finding. The MCS reflects emotional problems, vitality, mental health, and social functioning. MCS scores can vary from 0 to 100, with higher MCS scores indicating better mental health []. Patients with delirium in our study had lower MCS scores, which could be related to the mental vulnerability identified in the changing EEG wave patterns.
This study has a number of major strengths. By measuring EEG signals immediately after the onset of delirium, not only the medical staff but also the patients’ guardians were able to accurately recognize the patients’ condition. Second, this study highlights a novel EEG wave pattern in patients with delirium after spinal surgery. The major features of anxiety and stress in patients with delirium were identified, which will likely lead to a deeper understanding of the mental health of patients undergoing spinal surgery. Third, to the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to investigate delirium after spinal surgery using a compact wearable device. Numerous applications of this device can be used in the future, such as monitoring the mental status of patients who undergo spinal surgery, including those in the hospital or even after discharge to home, which would never be possible with traditional EEG monitoring. In addition, further analyses of mental health according to the type of spinal disease and surgery needed could be performed more easily.
Our study has several limitations. Due to the preliminary nature of this study and the low incidence rate of postoperative delirium, the number of enrolled patients with and without delirium was relatively small. Further large-scale studies are needed to confirm our results. Furthermore, we did not evaluate the effects of baseline cognitive function, medication use, and severity of illness on the outcome measures. Because EEG changes can be affected by many other factors, further analyses of additional factors should be conducted. Finally, the correlation between EEG and the type and duration of delirium was not analyzed in this study and needs to be investigated in the future.
5. Conclusions
In the delirium group, H-beta and gamma waves and the tension index increased, while theta waves decreased, compared to the non-delirium group 1 week after surgery. Our data show that EEG signals from a wearable device have the potential to be used to screen patients for delirium, which may lead to earlier diagnoses and treatments for delirium after spinal surgery. Future large-scale studies are needed to investigate the effects of factors related to delirium, such as baseline cognitive function, medication use, and severity of illness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-B.L. and B.H.L.; methodology, J.-W.K.; software, S.S.; validation, S.-H.M.; formal analysis, S.-B.L.; investigation, B.H.L.; resources, J.-W.K.; data curation, S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-B.L.; writing—review and editing, S.-B.L.; visualization, S.-B.L.; supervision, B.H.L.; project administration, B.H.L.; funding acquisition, B.H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Yonsei University (protocol code 4-2018-07-09, 6 September 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank SOSO H&C for analyzing the data, Dong Su Jang for providing illustrations, and Hye Sun Lee and Juyeon Yang, for statistically analyzing the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fong, T.G.; Tulebaev, S.R.; Inouye, S.K. Delirium in elderly adults: Diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.J.; Ko, J.H.; Kwon, T.Y.; Choi, B.W. Etiology and related factors of postoperative delirium in orthopedic surgery. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 11, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.S.; Park, S.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Chung, C.; Kim, Y.B. Risk factors for delirium after spine surgery in elderly patients. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2014, 56, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Park, Y.S. Delirium after spinal surgery in korean population. Spine 2010, 35, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Kanamori, M.; Ishihara, H.; Abe, Y.; Nobukiyo, M.; Sigeta, T.; Hori, T.; Kimura, T. Postoperative delirium in spine surgery. Spine J. 2006, 6, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazemi, A.K.; Gowd, A.K.; Carmouche, J.J.; Kates, S.L.; Albert, T.J.; Behrend, C.J. Prevention and management of postoperative delirium in elderly patients following elective spinal surgery. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, L.J.; Schmitt, E.M.; Kosar, C.M.; Tabloski, P.; Saczynski, J.S.; Robinson, T.; Cooper, Z.; Rogers, S.O., Jr.; Jones, R.N.; Marcantonio, E.R.; et al. Effect of delirium and other major complications on outcomes after elective surgery in older adults. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchin, I.; Mitchell, E.; Agar, M.; Trepel, D. The economic cost of delirium: A systematic review and quality assessment. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Suh, S.W. Incidence & risk factors of postoperative delirium after spinal surgery in older patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9232. [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2019 Demographics Collaborators. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (hale), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: A comprehensive demographic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1160–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.G.; Patel, J.Y.; Asati, S.; Mewara, N. “Spine surgery checklist”: A step towards perfection through protocols. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Mizutamari, M.; Hatake, K. Surgical invasiveness of single-segment posterior lumbar interbody fusion: Comparing perioperative blood loss in posterior lumbar interbody fusion with traditional pedicle screws, cortical bone trajectory screws, and percutaneous pedicle screws. Asian Spine J. 2021, 15, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Ushirozako, H.; Yamato, Y.; Yoshida, G.; Yasuda, T.; Banno, T.; Arima, H.; Oe, S.; Yamada, T.; Ide, K.; et al. Impact of spinal correction surgeries with osteotomy and pelvic fixation in patients with kyphosis due to osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Asian Spine J. 2021, 15, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morino, T.; Hino, M.; Yamaoka, S.; Misaki, H.; Ogata, T.; Imai, H.; Miura, H. Risk factors for delirium after spine surgery: An age-matched analysis. Asian Spine J. 2018, 12, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, S.K.; van Dyck, C.H.; Alessi, C.A.; Balkin, S.; Siegal, A.P.; Horwitz, R.I. Clarifying confusion: The confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 113, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.N.; Raeburn, C.D.; Angles, E.M.; Moss, M. Low tryptophan levels are associated with postoperative delirium in the elderly. Am. J. Surg. 2008, 196, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.T.; Park, J.Y. Postoperative delirium. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 72, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kooi, A.W.; Zaal, I.J.; Klijn, F.A.; Koek, H.L.; Meijer, R.C.; Leijten, F.S.; Slooter, A.J. Delirium detection using eeg: What and how to measure. Chest 2015, 147, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatum, W.O.t.; Husain, A.M.; Benbadis, S.R.; Kaplan, P.W. Normal adult eeg and patterns of uncertain significance. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 23, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, B.R.; Polich, J. Meditation states and traits: Eeg, erp, and neuroimaging studies. Psychol. Bull. 2006, 132, 180–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmizi-Alsan, E.; Bayraktaroglu, Z.; Gurvit, H.; Keskin, Y.H.; Emre, M.; Demiralp, T. Comparative analysis of event-related potentials during go/nogo and cpt: Decomposition of electrophysiological markers of response inhibition and sustained attention. Brain Res. 2006, 1104, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Lopes da Silva, F.H. Event-related eeg/meg synchronization and desynchronization: Basic principles. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.S.; Demiralp, T. Human eeg gamma oscillations in neuropsychiatric disorders. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2719–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillon, J.; Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Pelayo, F. Stress assessment by prefrontal relative gamma. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SOSO H&C. Available online: http://www.soso-g.co.kr/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Kwon, J.W.; Lee, S.B.; Sung, S.; Park, Y.; Ha, J.W.; Kim, G.; Suk, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.M.; Moon, S.H.; et al. Which factors affect the stress of intraoperative orthopedic surgeons by using electroencephalography signals and heart rate variability? Sensors 2021, 21, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.W.; Sung, S.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, H.M.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, B.H. Intraoperative real-time stress in degenerative lumbar spine surgery: Simultaneous analysis of electroencephalography signals and heart rate variability: A pilot study. Spine J. 2020, 20, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, S.; Kwon, J.-W.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Lee, S.-K.; Moon, S.-H.; Lee, B.H. Real-time stress analysis affecting nurse during elective spinal surgery using a wearable device. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klem, G.H.; Luders, H.O.; Jasper, H.H.; Elger, C. The ten-twenty electrode system of the international federation. The international federation of clinical neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 1999, 52, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abhang, P.A.; Gawali, B.W.; Mehrotra, S.C. Technical aspects of brain rhythms and speech parameters. In Introduction to Eeg and Speech-Based Emotion Recognition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 51–79. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, C.; He, F.; Zhao, X.; Qi, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, L.; Ming, D. How physical activities affect mental fatigue based on eeg energy, connectivity, and complexity. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deksnyte, A.; Aranauskas, R.; Budrys, V.; Kasiulevicius, V.; Sapoka, V. Delirium: Its historical evolution and current interpretation. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, A.; Manini, T.M.; Bihorac, A.; Rashidi, P. Role of wearable accelerometer devices in delirium studies: A systematic review. Crit. Care Explor. 2019, 1, e0027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerejeira, J.; Batista, P.; Nogueira, V.; Vaz-Serra, A.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B. The stress response to surgery and postoperative delirium: Evidence of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hyperresponsiveness and decreased suppression of the gh/igf-1 axis. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2013, 26, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osse, R.J.; Tulen, J.H.; Hengeveld, M.W.; Bogers, A.J. Screening methods for delirium: Early diagnosis by means of objective quantification of motor activity patterns using wrist-actigraphy. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 8, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oh, E.S.; Fong, T.G.; Hshieh, T.T.; Inouye, S.K. Delirium in older persons: Advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA 2017, 318, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.M.; Loh, N.K.; Tan, N.C. Clinical risk factors for non-convulsive status epilepticus during emergent electroencephalogram. Seizure 2013, 22, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Whitlock, E.L.; Torres, B.A.; Lin, N.; Helsten, D.L.; Nadelson, M.R.; Mashour, G.A.; Avidan, M.S. Postoperative delirium in a substudy of cardiothoracic surgical patients in the bag-recall clinical trial. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 118, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.T.; Cheng, B.C.; Lee, T.M.; Gin, T.; Group, C.T. Bis-guided anesthesia decreases postoperative delirium and cognitive decline. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2013, 25, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, H.; Partanen, J.; Paakkonen, A.; Mattila, E.; Riekkinen, P.J. Eeg spectral analysis in delirium. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1989, 52, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdanibia-Centelles, O.; Nielsen, R.M.; Rostrup, E.; Vedel-Larsen, E.; Thomsen, K.; Nikolic, M.; Johnsen, B.; Moller, K.; Lauritzen, M.; Benedek, K. Automatic continuous eeg signal analysis for diagnosis of delirium in patients with sepsis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, A.; Crouch, B.; Webster, N.; Platt, B. Delirium screening in the intensive care unit using emerging qeeg techniques: A pilot study. AIMS Neurosci. 2020, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Cour, K.N.; Andersen-Ranberg, N.C.; Weihe, S.; Poulsen, L.M.; Mortensen, C.B.; Kjer, C.K.W.; Collet, M.O.; Estrup, S.; Mathiesen, O. Distribution of delirium motor subtypes in the intensive care unit: A systematic scoping review. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Okamoto, E.; Nishimura, H.; Mizuno-Matsumoto, Y.; Ishii, R.; Ukai, S. Beta activities in eeg associated with emotional stress. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Med. Sci. Image Process. 2009, 3, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.H.; Cid, F.M.; Otárola, J.; Rojas, R.; Alarcón, O.; Cañete, L. Eeg beta band frequency domain evaluation for assessing stress and anxiety in resting, eyes closed, basal conditions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 162, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, R.D.; Morales, L.S. The rand-36 measure of health-related quality of life. Ann. Med. 2001, 33, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).