Remote Practice Methods of Survey Education for HBIM in the Post-Pandemic Era: Case Study of Kuiwen Pavilion in the Temple of Confucius (Qufu, China)
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Structure of the Article
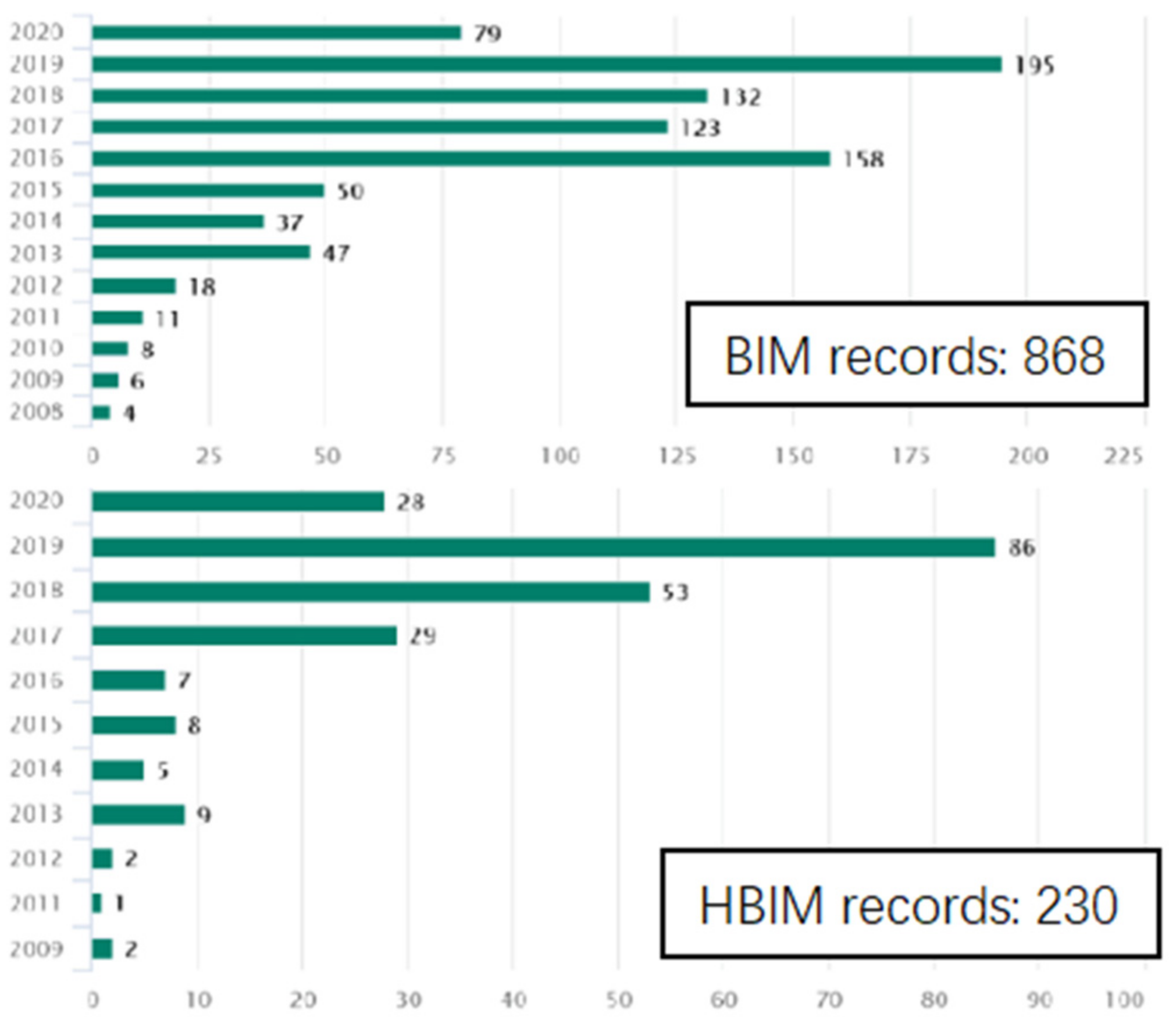
1.2. Review of Related Works
1.3. Background Information of Kuiwen Pavilion
1.4. Overview of Survey Education
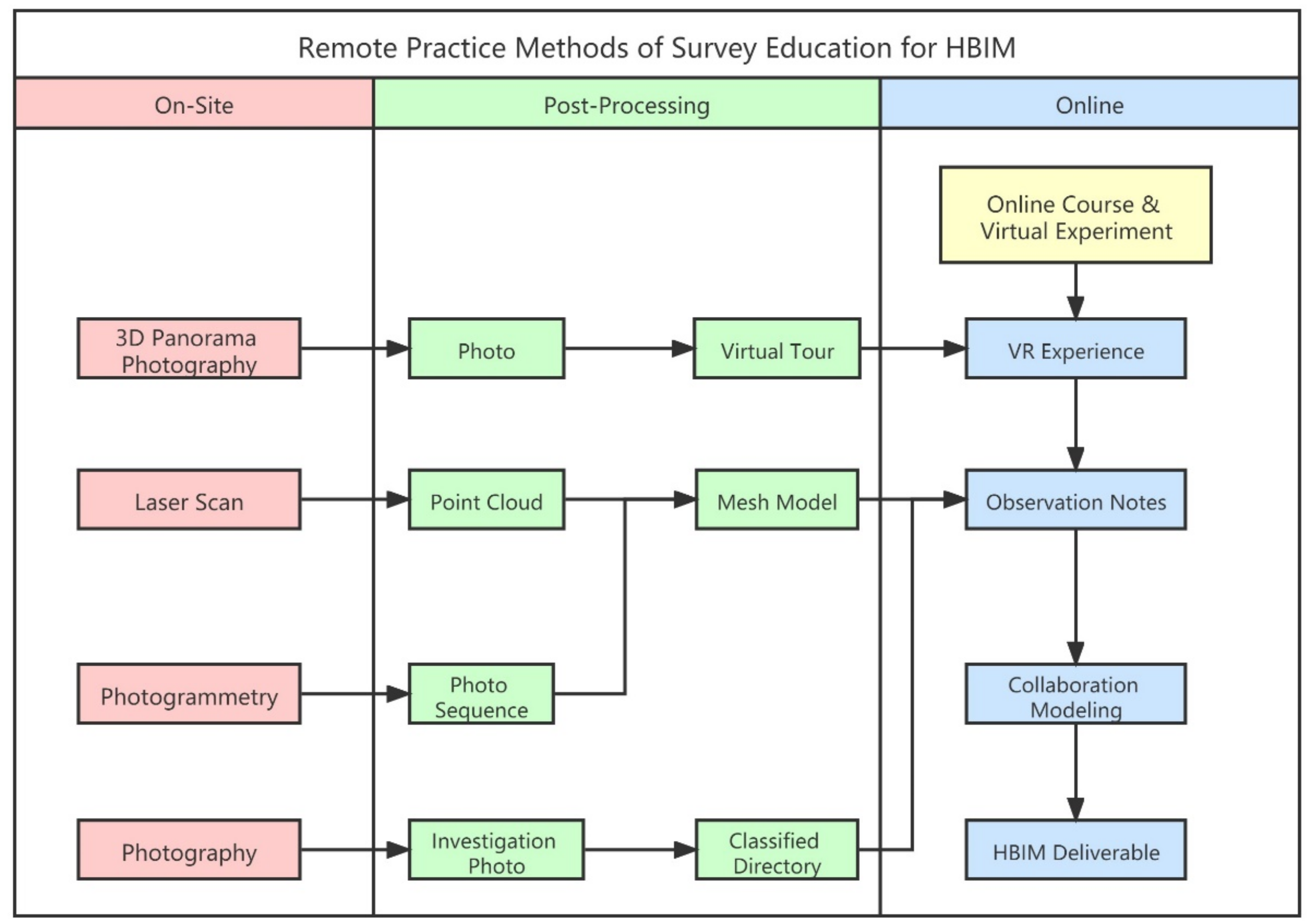
2. Preparations: Materials and Methods
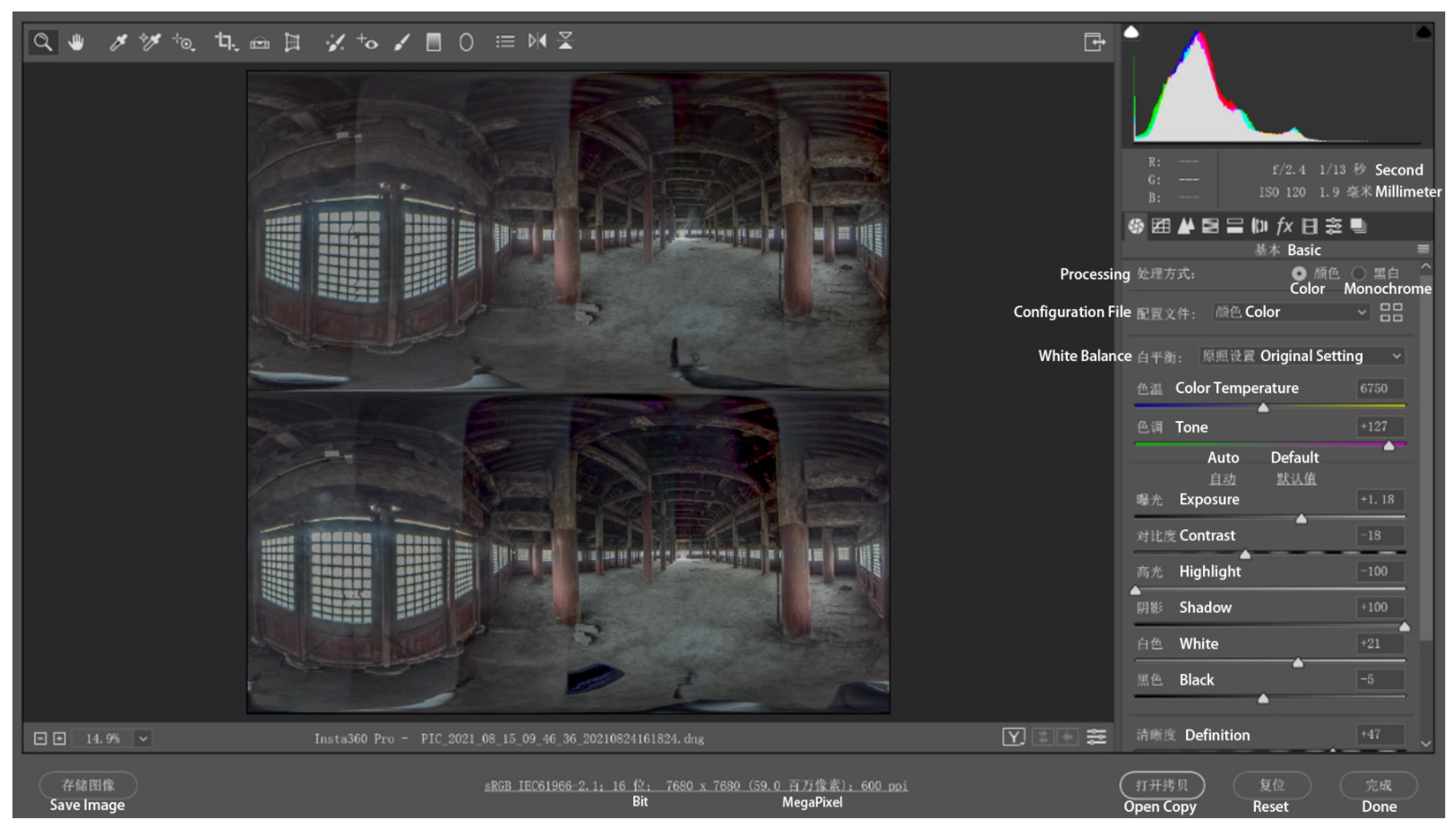
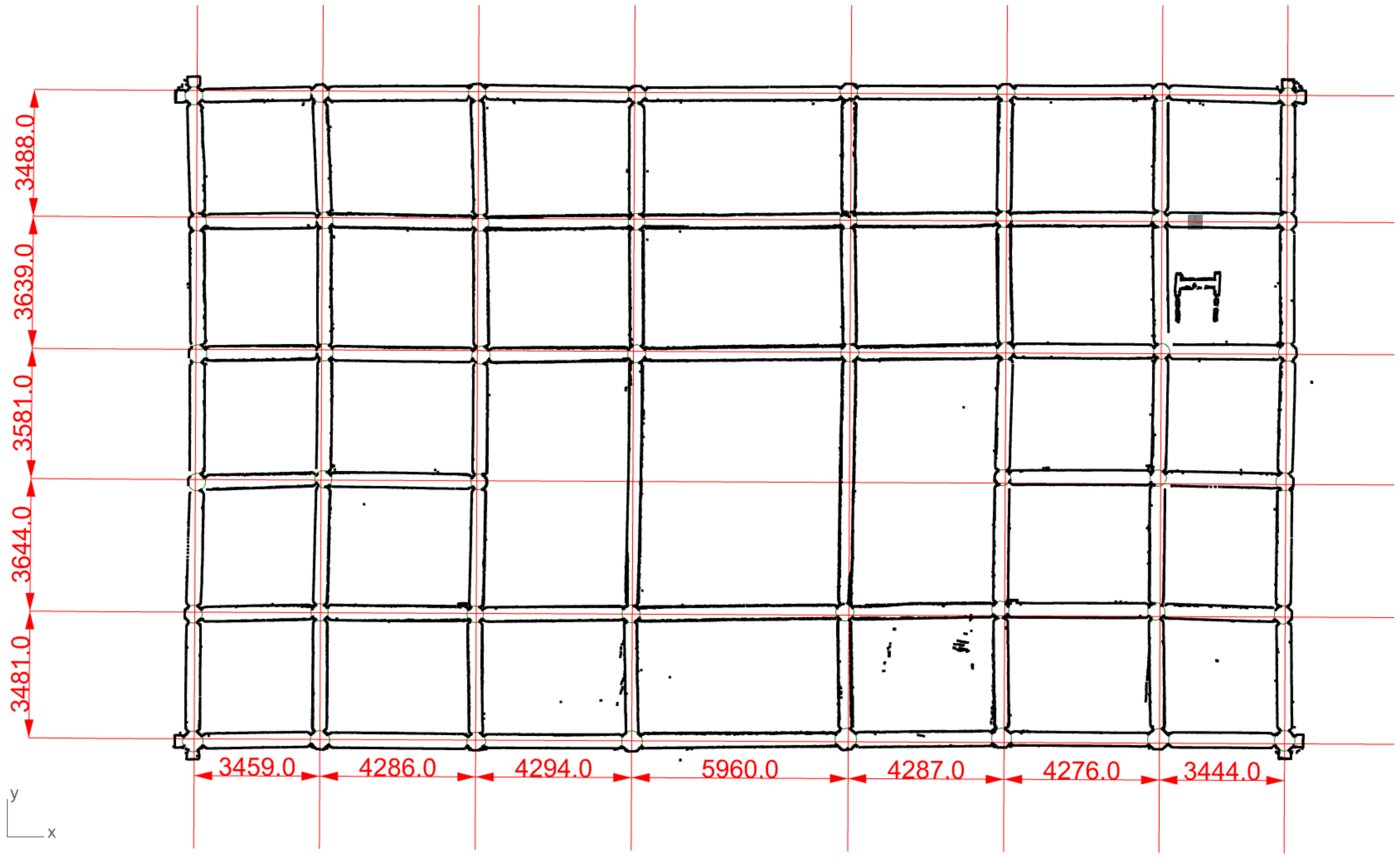
2.1. On-Site Data Acquisition
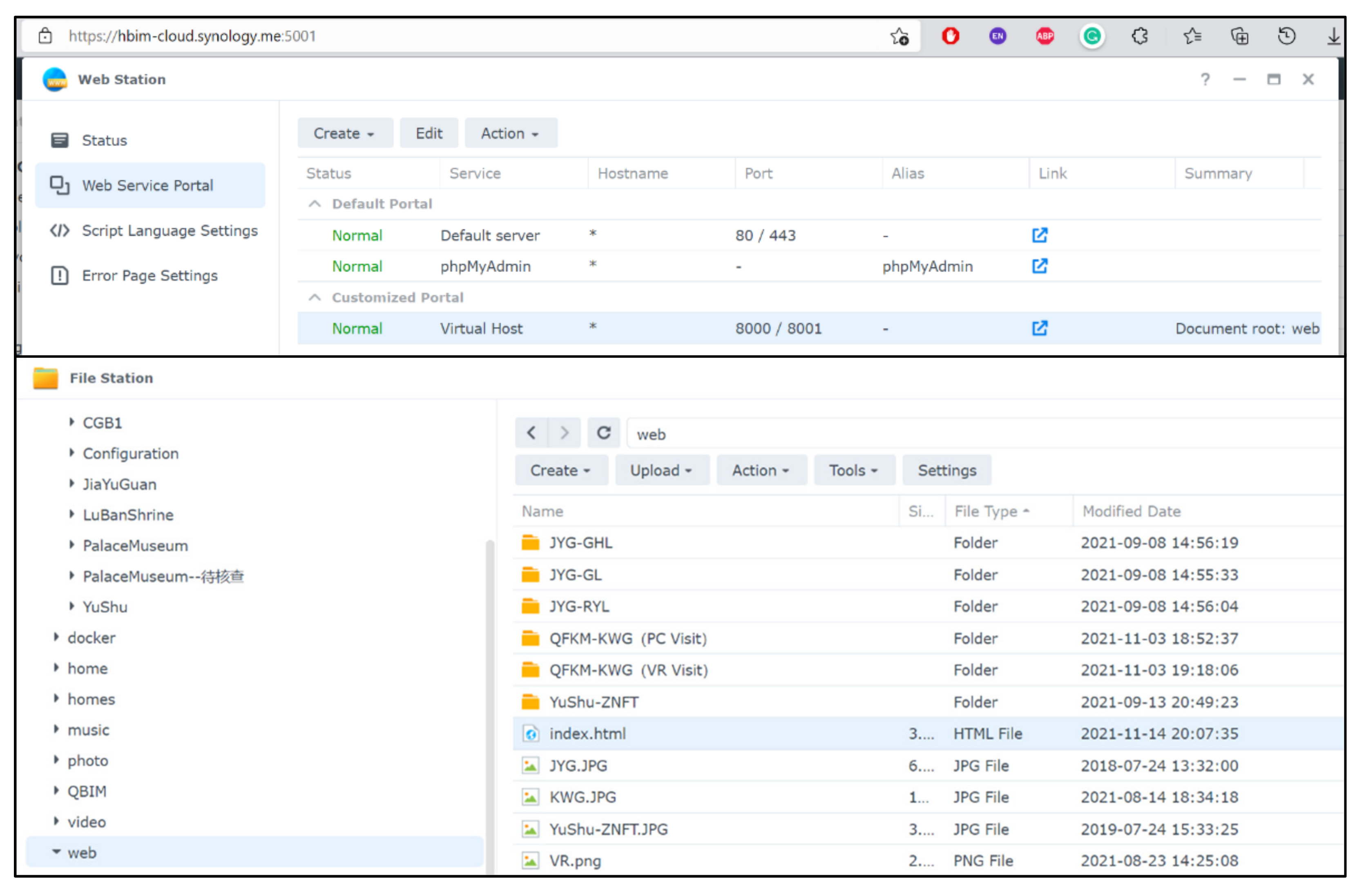
2.2. Standardized Classification with Cloud Storage
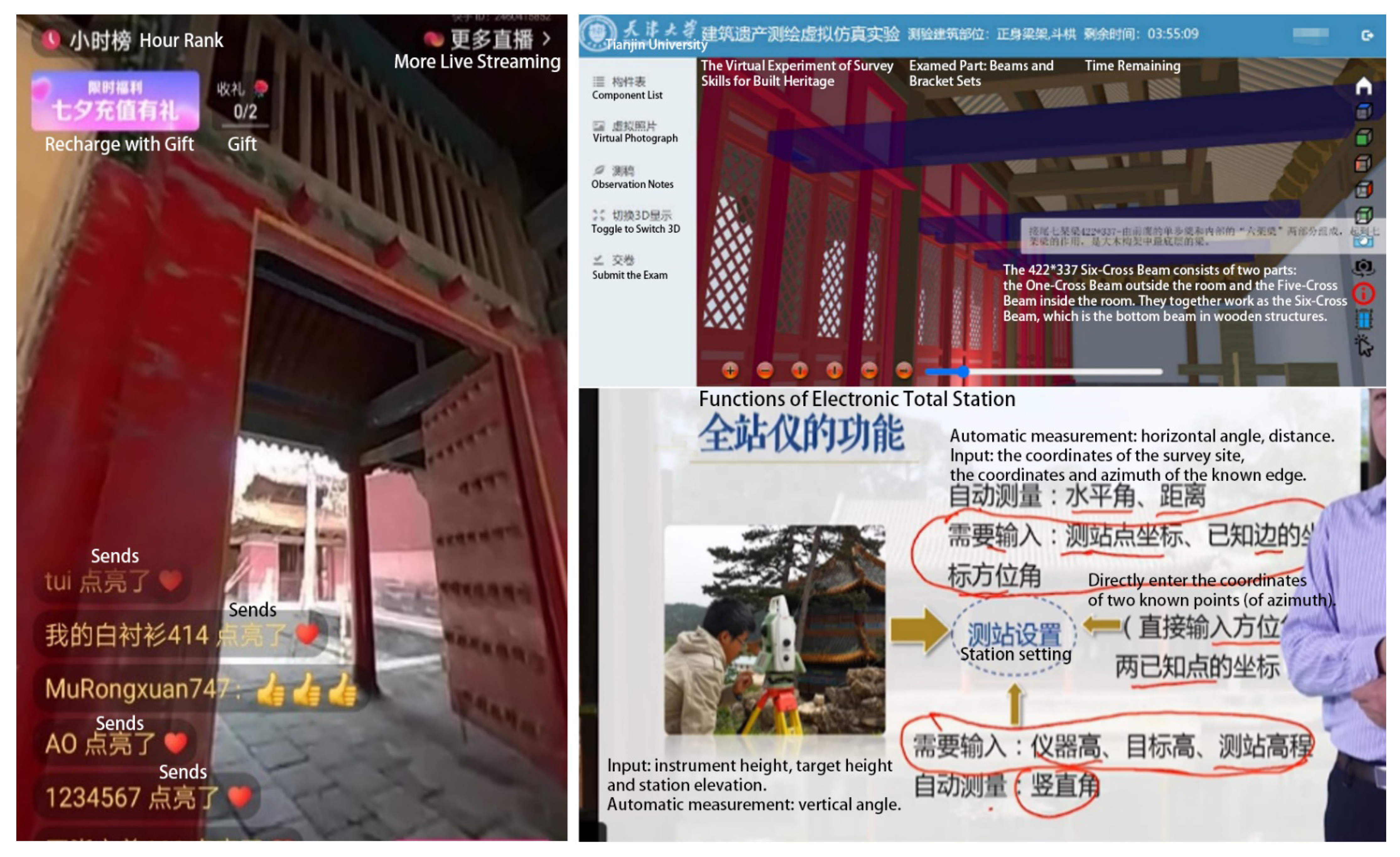
2.3. Online Education
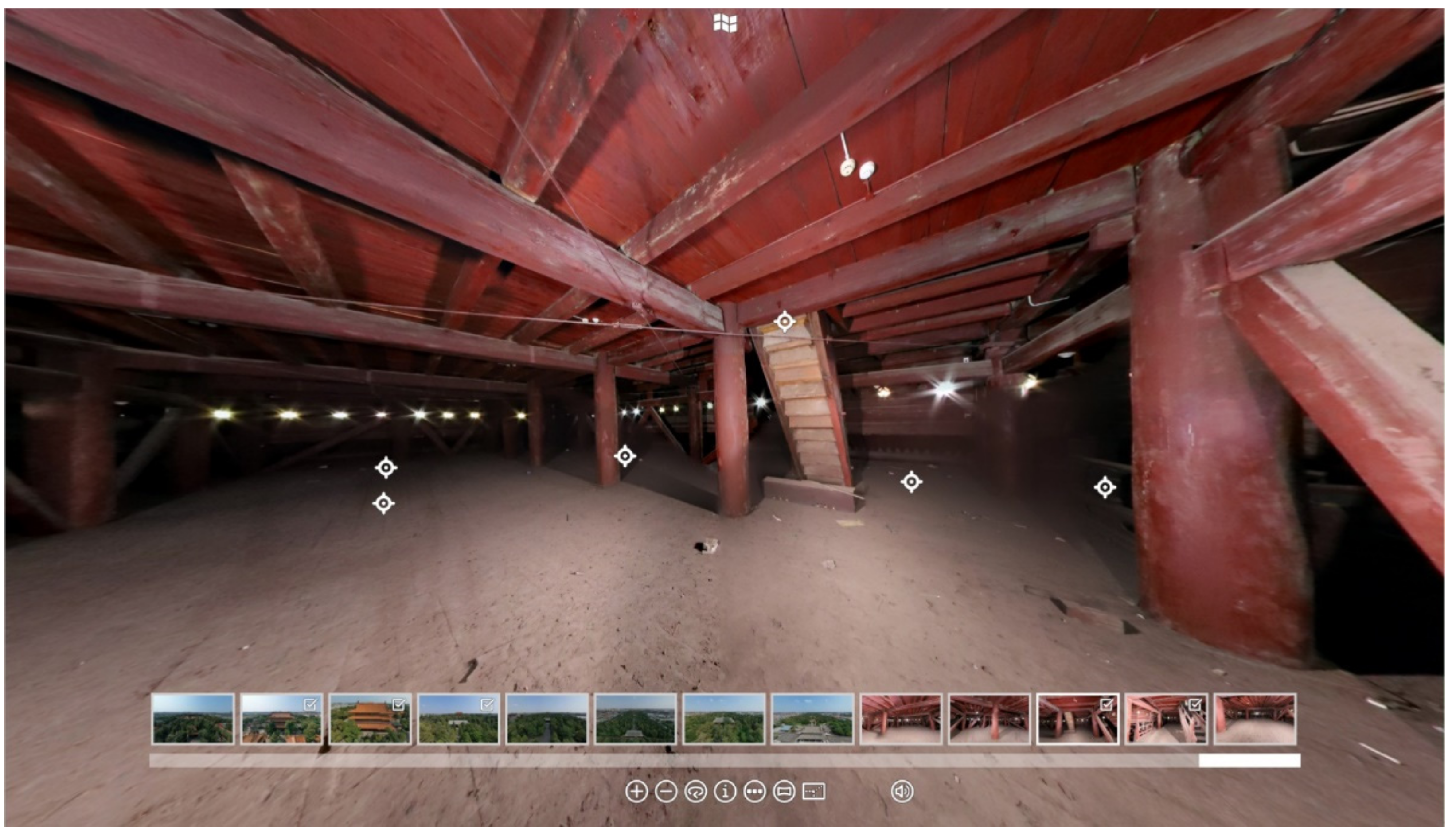
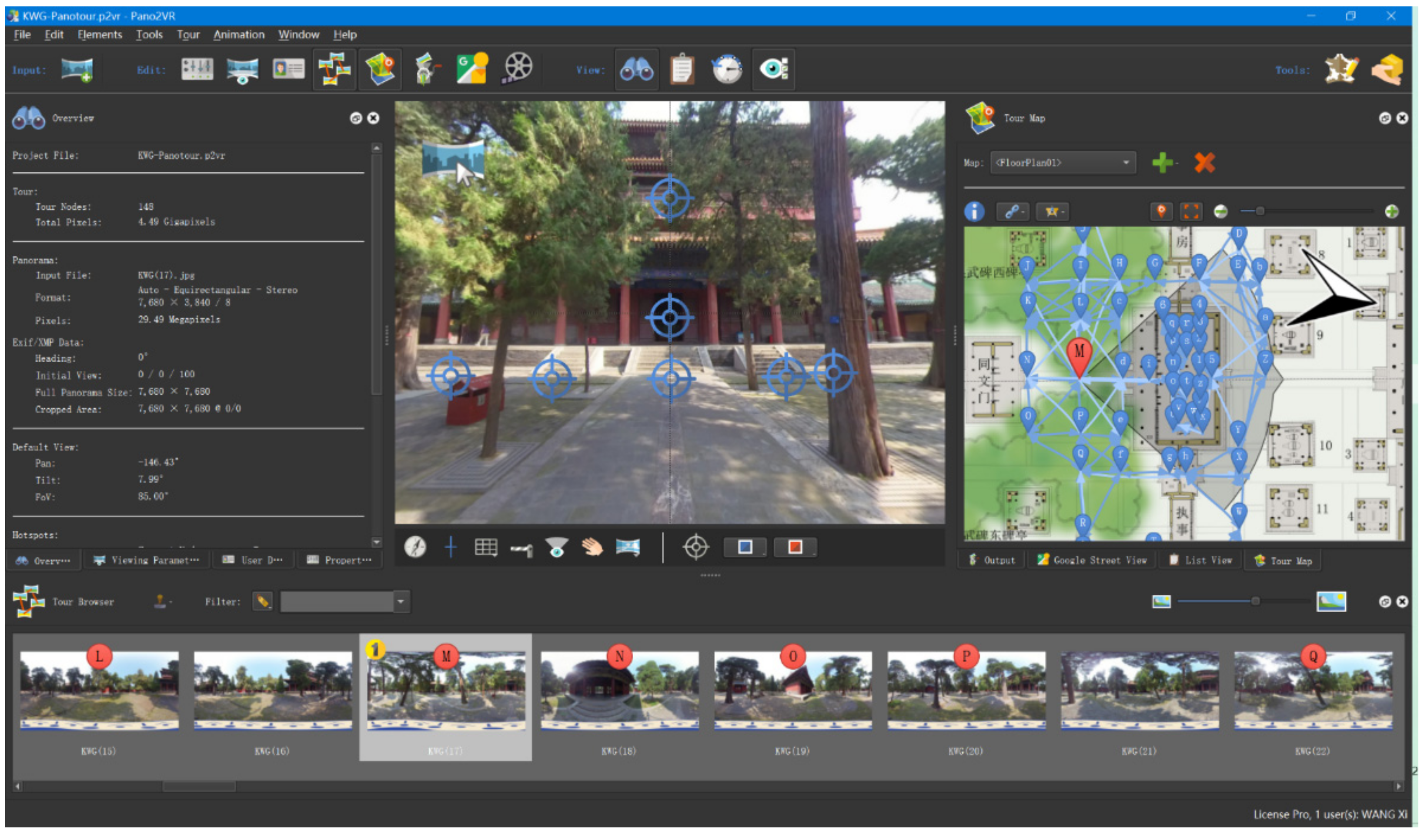
2.4. Virtual Tour Generation
2.5. Platform of Cloud Service
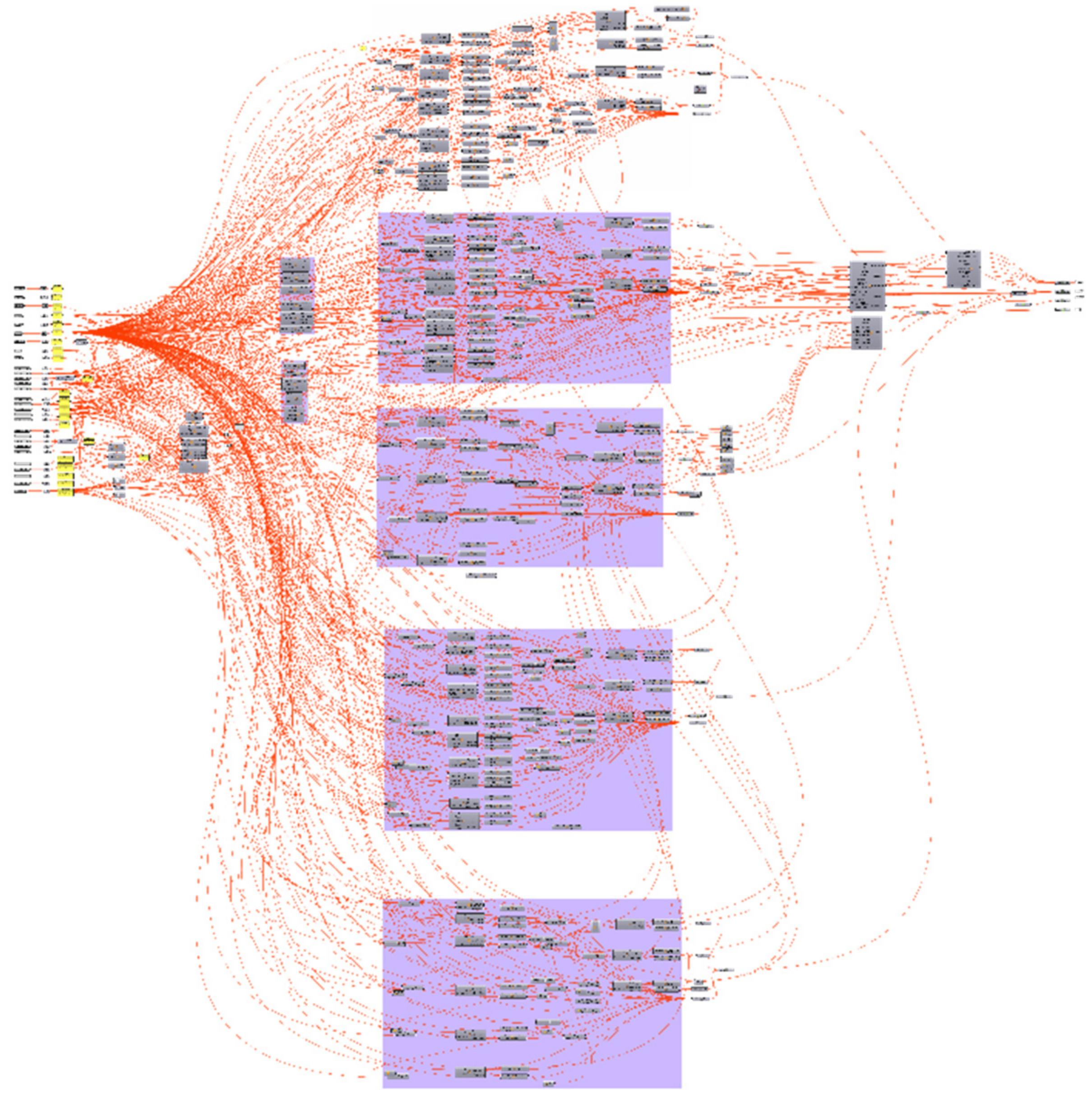
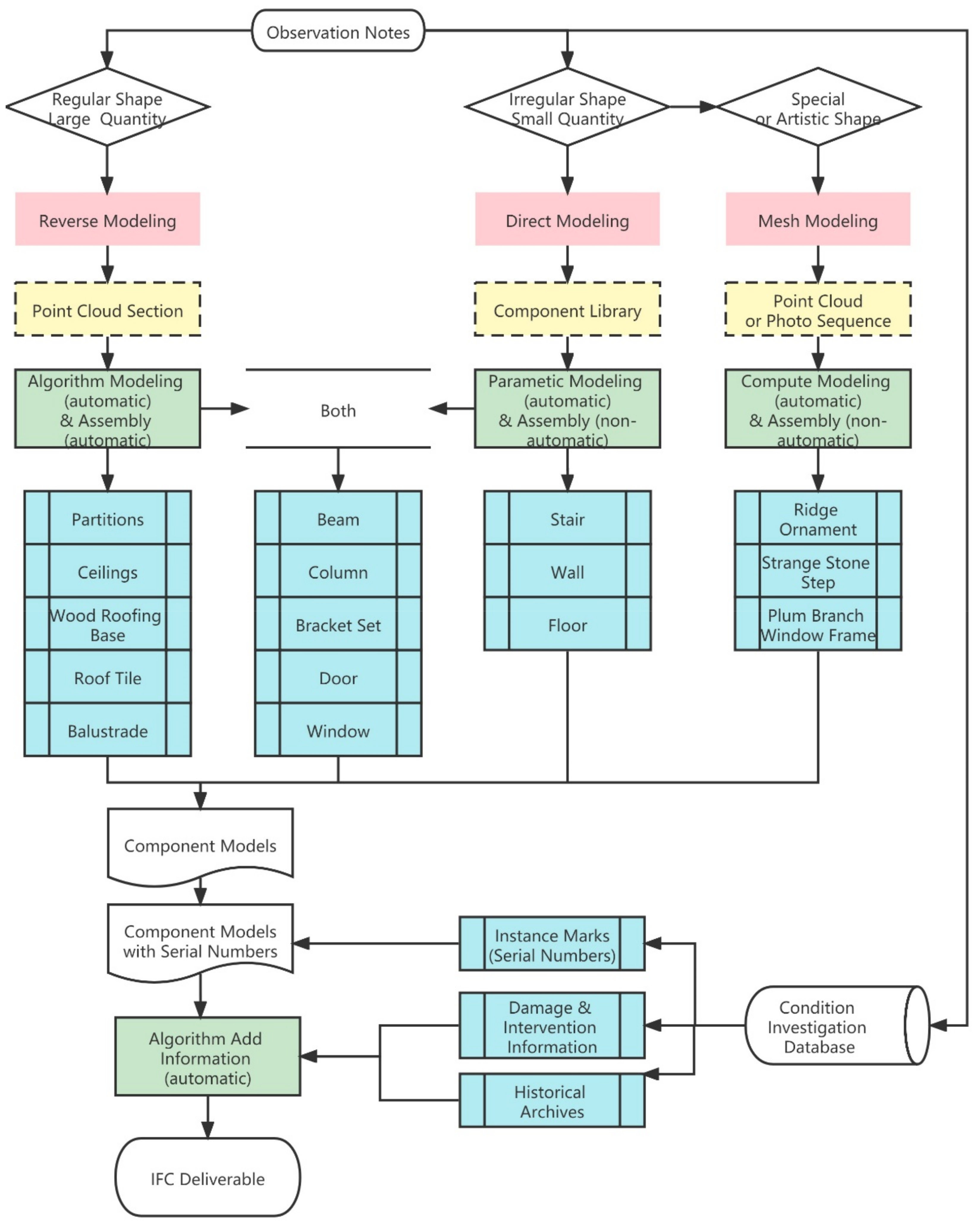
2.6. The Schema of the HBIM Component Library and Suggested Workflow
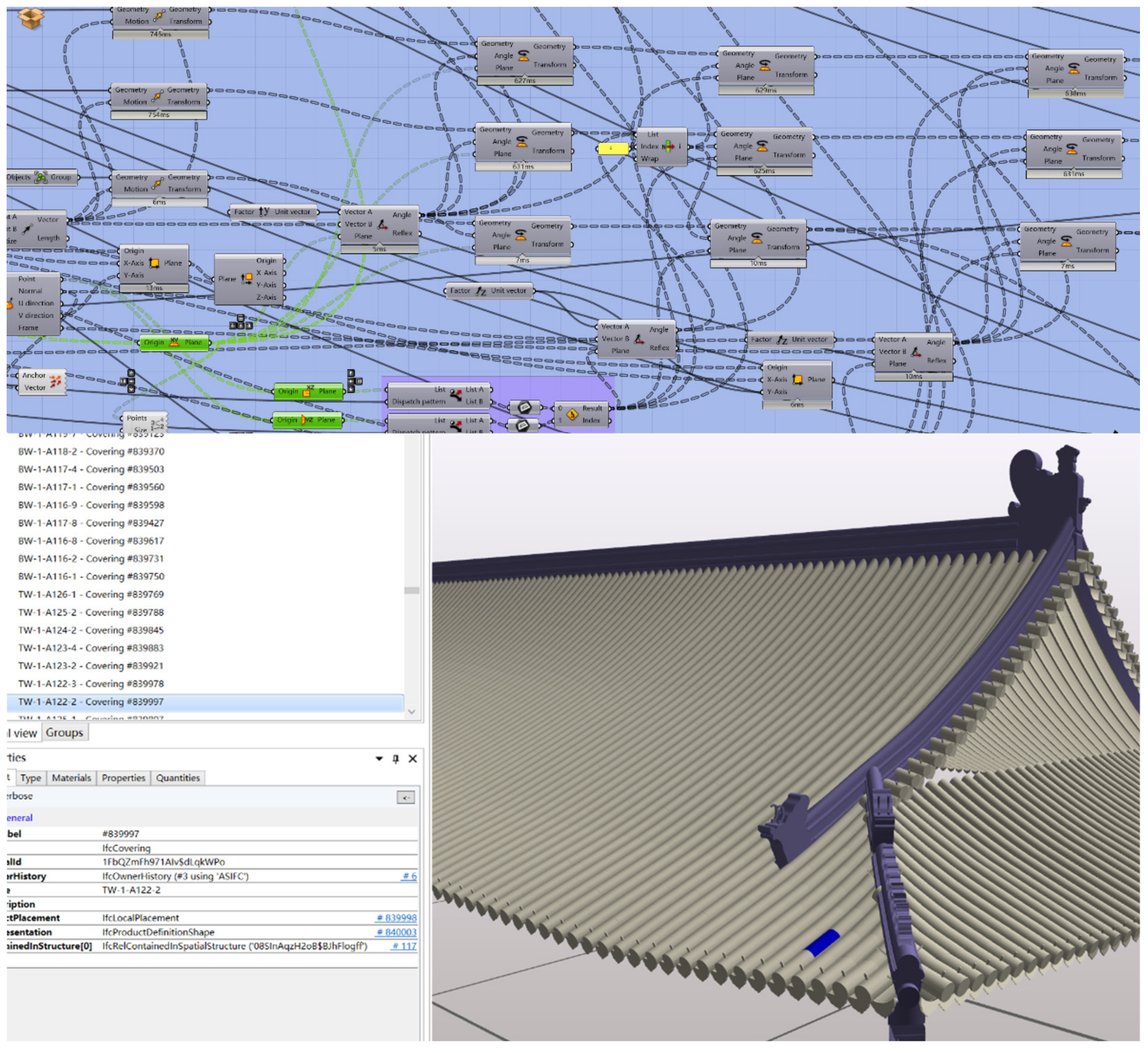
- (1)
- Automatic generative modeling and automatic assembly. For components with better regularity and large quantities, such as roof tiles (also including roof-like components such as a canopy made of polished, transparent seashell tiles), wood roofing base, floor tiles, wall tiles, ceilings, indoor wood partitions. Stored as GH and 3DM files.
- (2)
- Direct modeling then manual assembly. Components with little difference from modern buildings, such as stairs, steps, doors, and windows, can be modeled and assembled directly with the basic functions of BIM software. Alternatively, special-shaped components, or “artistic components”, which lack regularity, such as ridge ornaments, strange stone steps, plum branch window frame, etc., need to be automatically generated as mesh surface models according to laser scanning or photogrammetry, then assembled manually. Stored as 3DM, DGN, and RFA files.
2.7. Event Log
3. Results: Remote Practice on Kuiwen Pavilion
3.1. Virtual Tour Experience
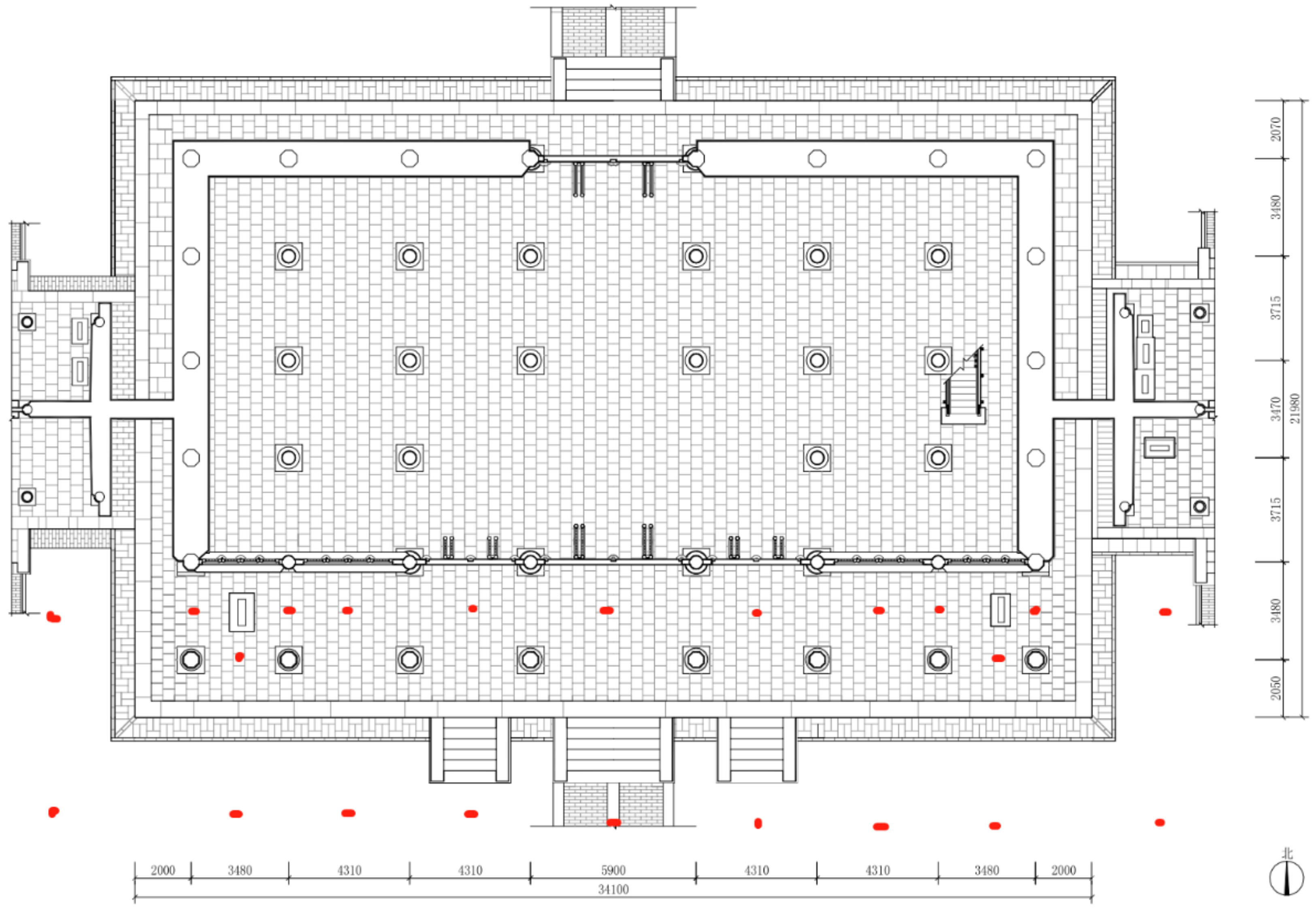
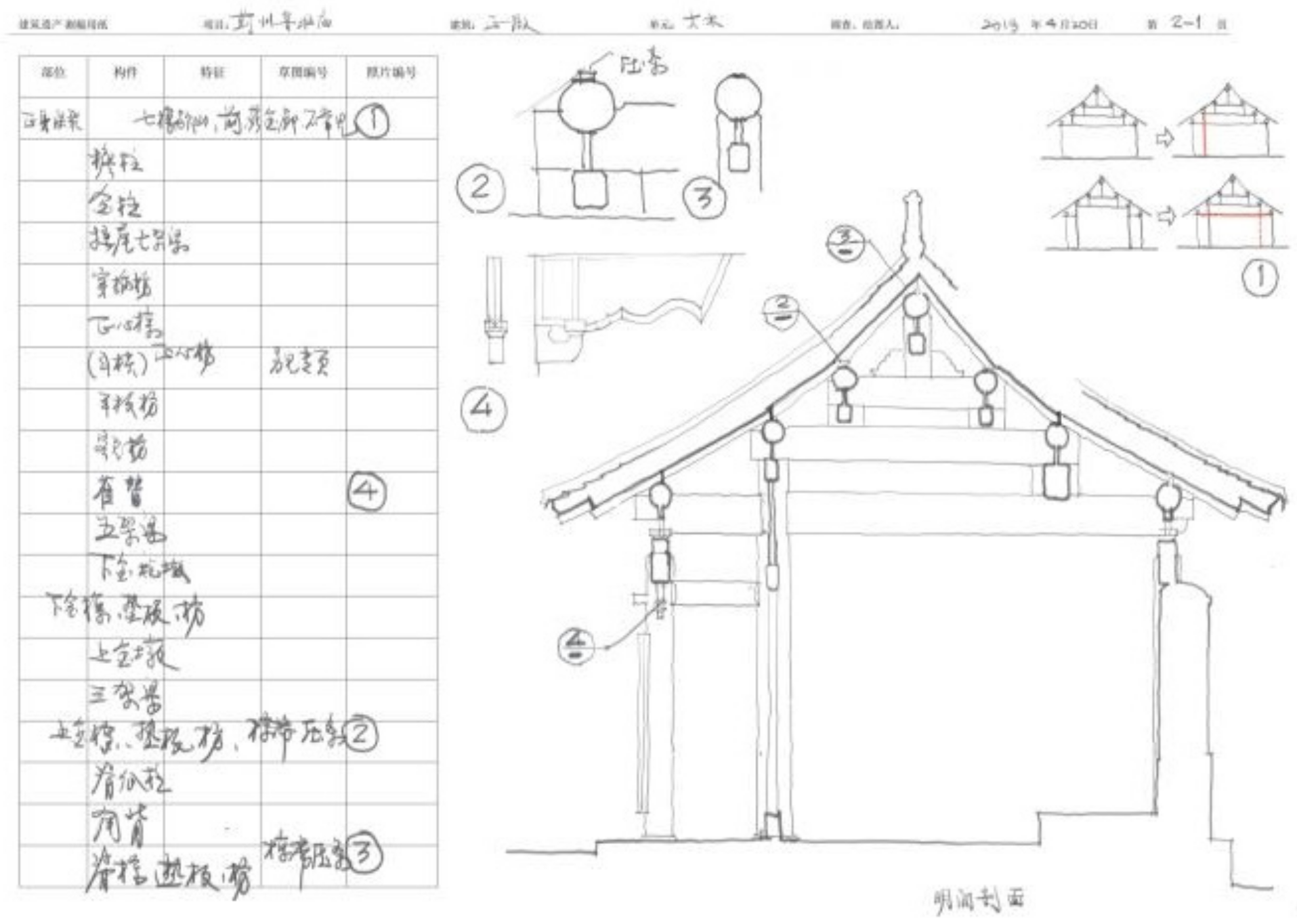
3.2. Observation Notes
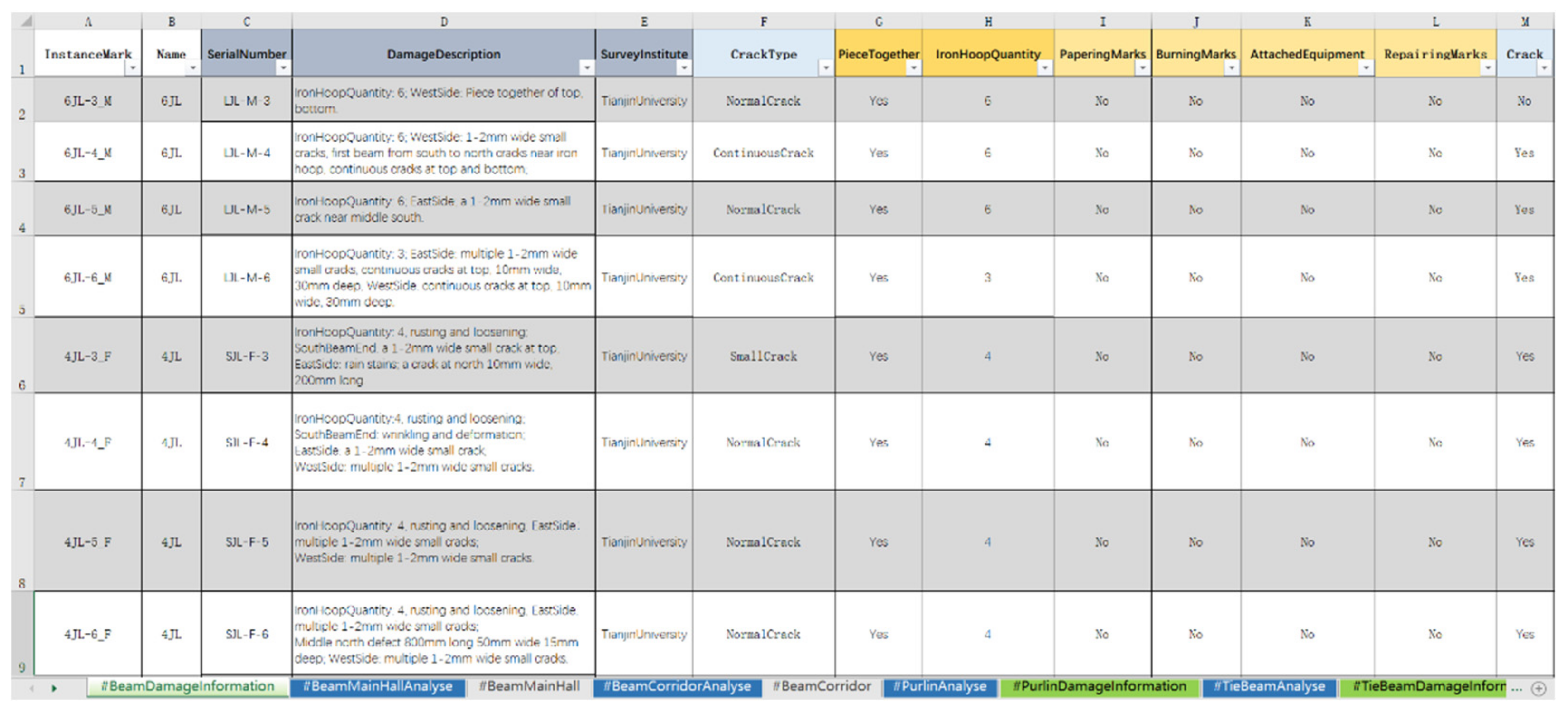
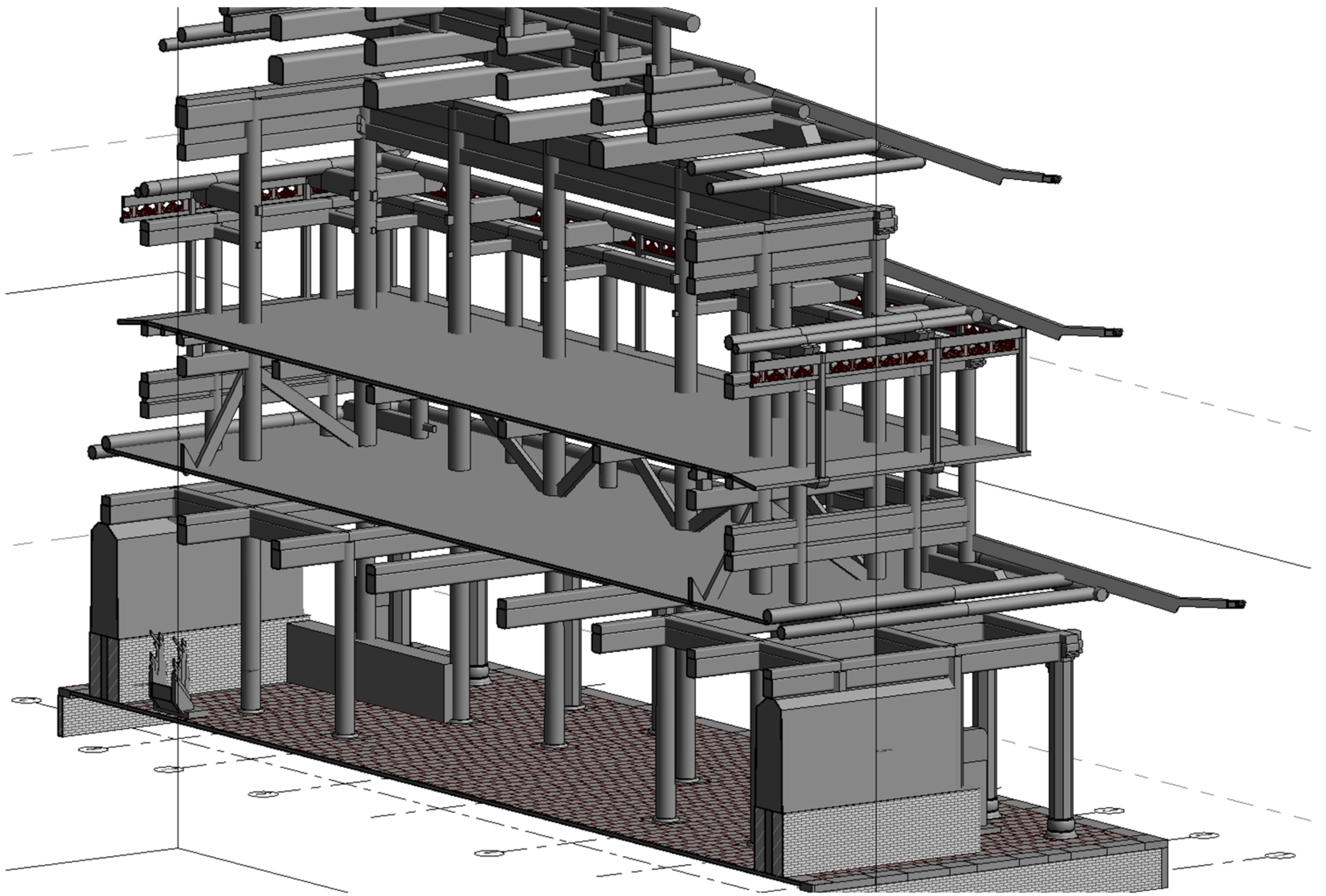
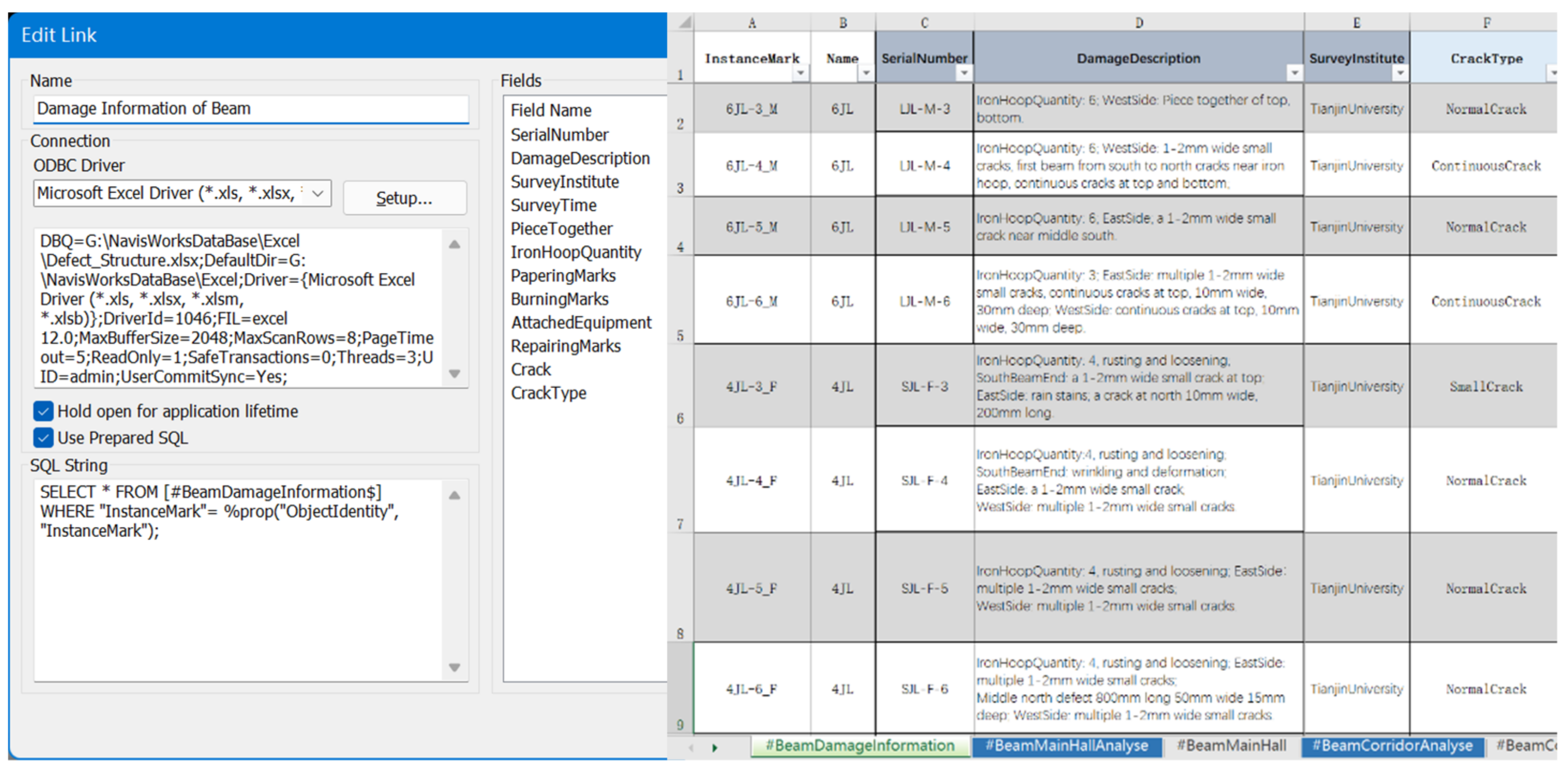
3.3. HBIM Modeling and Information Association
3.4. IFC Delivery of Mass-Produced Components
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, M.; McGovern, E.; Pavía, S. Parametric Vector Modelling of Laser and Image Surveys of 17th Century Classical Architecture in Dublin. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Cultural Heritage VAST, Brighton, UK, 26–30 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, M.; McGovern, E.; Pavia, S. Historic building information modelling (HBIM). Struct. Surv. 2009, 27, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Li, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. From digitization to informatization: The application of information technology in the field of Architectural Heritage. China Cult. Herit. 2016, 2, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, X.; Bai, C.; Wu, C. Discussion on the Problem of Regularized Reconstruction in HBIM. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W15, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.F.; Du, J. Digital Presentation and Communication of Cultural Heritage in the Post-Pandemic Era. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, VIII-M-1-2021, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collao, J.; Lozano-Galant, F.; Lozano-Galant, J.A.; Turmo, J. BIM Visual Programming Tools Applications in Infrastructure Projects: A State-of-the-Art Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besné, A.; Pérez, M.Á.; Necchi, S.; Peña, E.; Fonseca, D.; Navarro, I.; Redondo, E. A Systematic Review of Current Strategies and Methods for BIM Implementation in the Academic Field. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Que, R.; Bai, C. Algorithm Modeling of Ancient Architecture for Heritage Documentation. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 1209, XLII-2-W15, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagnolo, V.; Argiolas, R.; Cuccu, A. Digital Survey and Algorithmic Modeling in Hbim. Towards a Library of Complex Construction Elements. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-4/W12, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepe, M.; Costantino, D.; Garofalo, A.R. An Efficient Pipeline to Obtain 3D Model for HBIM and Structural Analysis Purposes from 3D Point Clouds. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, F.J.; Lerones, P.M.; Llamas, J.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Zalama, E. A Review of Heritage Building Information Modeling (H-BIM). Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruno, S.; Musicco, A.; Fatiguso, F.; Dell’Osso, G. The Role of 4D Historic Building Information Modelling and Management in the Analysis of Constructive Evolution and Decay Condition within the Refurbishment Process. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2019, 15, 1250–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achille, C.; Fassi, F.; Mandelli, A.; Perfetti, L.; Rechichi, F.; Teruggi, S. From a Traditional to a Digital Site: 2008–2019. The History of Milan Cathedral Surveys; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Que, R. Regularized Rebuild Workflow of HBIM for Built Heritage Documentation. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, VIII-M-1-2021, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Rizzi, G.; Achille, C. Learning through Virtual Tools: Visit a Place in the Pandemic Era. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, XLVI-M-1-2021, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achille, C.; Fassi, F.; Mandelli, A.; Del Pero, C.; Leonforte, F.; Aste, N. Designing Remote Places in the Post-War and Pandemic Scenarios. Smart Surveying of the Gahayr Campus in Mogadishu. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, XLVI-M-1-2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, F.; Mandelli, A. Interactive Virtual Objects (IVOs) for Next Generation of Virtual Museums: From Static Textured Photogrammetric and HBIM Models to XR Objects for VR-AR Enabled Gaming Experiences. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, XLVI-M-1-2021, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupry, C.; Noblecourt, S.; Richard, P.; Baudry, D.; Bigaud, D. BIM-Based Digital Twin and XR Devices to Improve Maintenance Procedures in Smart Buildings: A Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustín, L.; Quintilla, M. Virtual Reconstruction in BIM Technology and Digital Inventories of Heritage. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W15, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rechichi, F.; Achille, C.; Roncella, R.; Fassi, F. Integration of Historical GIS data in a HBIM System. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B4-2020, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. ARK-BIM: Open-Source Cloud-Based HBIM Platform for Archaeology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelli, A.; Achille, C.; Tommasi, C.; Fassi, F. Integration of 3D Models and Diagnostic Analyses through a Conservation-Oriented Information System. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W5, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, M.; Chenaux, A.; Keenaghan, G.; Gibson, V.; Butler, J.; Pybusr, C. Armagh Observatory—Historic Building Information Modelling for Virtual Learning in Building Conservation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W5, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napolitano, R.K.; Scherer, G.; Glisic, B. Virtual tours and informational modeling for conservation of cultural heritage sites. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 29, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, F.; Brumana, R.; Aljishi, A.; Al Sayeh, N.; Quintero, M.S.; Cuca, B.; Oreni, D.; Midali, C. Generative Modeling, Virtual Reality and HBIM Interaction: Immersive Environment for Built Heritage: Case Study of Shaikh Isa Bin Ali House, Bahrain. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference of Geomatics and Restoration (GEORES), Milan, Italy, 8–10 May 2019; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Ahn, J.; Woo, W. Context-aware risk management for architectural heritage using historic building information modeling and virtual reality. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 38, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Pavia, S.; Cahill, J.; Lenihan, S.; Corns, A. An Initial Design Framework for Virtual Historic Dublin. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference of Geomatics and Restoration (GEORES), Milan, Italy, 8–10 May 2019; pp. 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Cantatore, E.; Lasorella, M.; Fatiguso, F. Virtual Reality to Support Technical Knowledge in Cultural Heritage. The Case Study of Cryptoporticus in the Archaeological Site of Egnatia (Italy). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIV-M-1-2020, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. Cloud Data Sharing and Exchange of HBIM Projects for Archaeology: Possible Solutions and Proposals. In Proceedings of the Joint International Event 9th ARQUEOLÓGICA 2.0 & 3rd GEORES, Valencia, Spain, 26–28 April 2021; pp. 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. What the Master Would Not Discuss. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/What_the_Master_Would_Not_Discuss (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- UNESCO. Temple and Cemetery of Confucius and the Kong Family Mansion in Qufu. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. Available online: http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/704 (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- GB/T51301-2018; Standard for Design Delivery of Building Information Modeling. MOHURD: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Bai, C. Regularized Reconstruction of Grid System for Traditional Chinese Timber Structure Building in HBIM. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W15, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






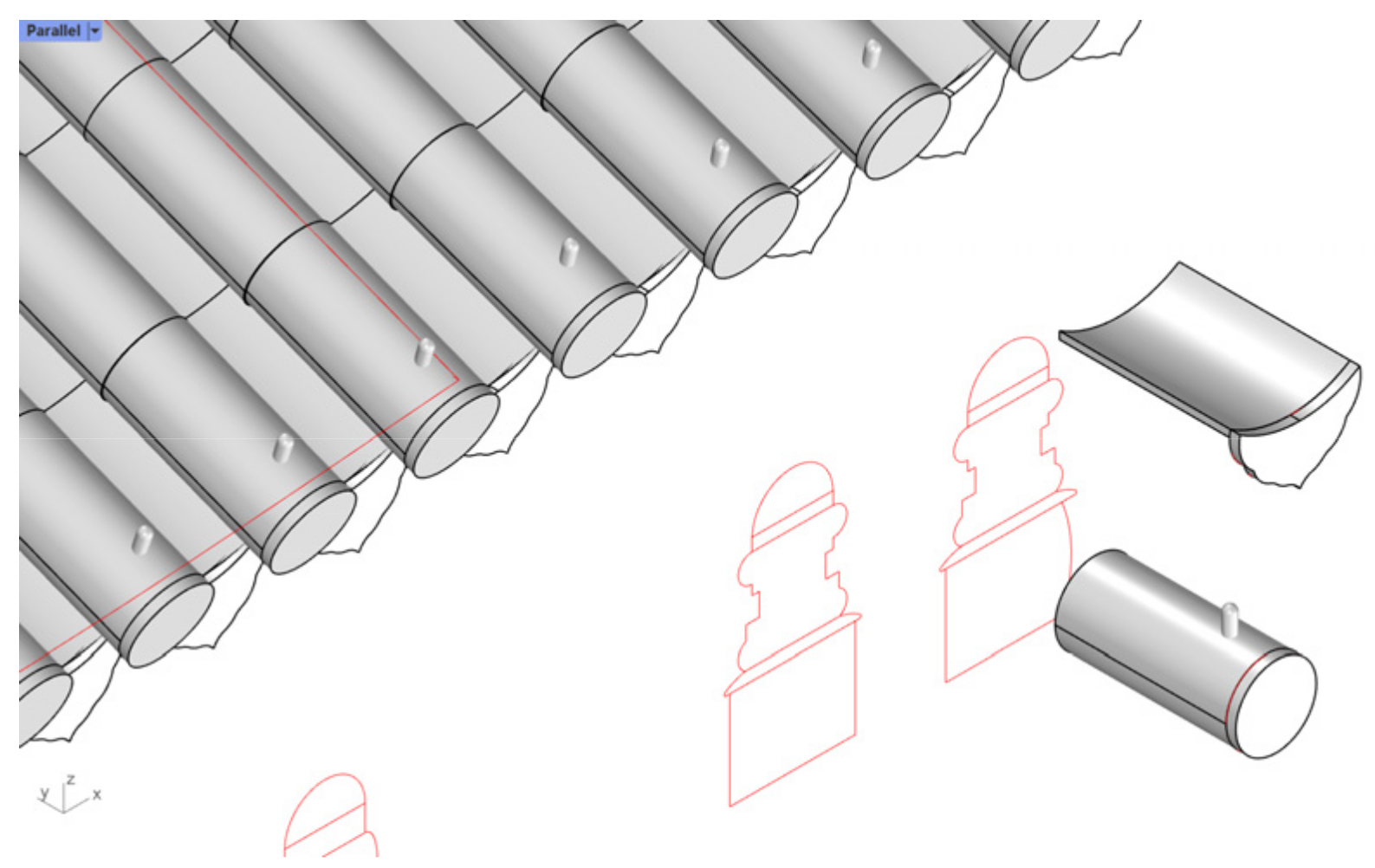


| Roof Tiles | Roof Tile Rows | A Flat Tile | The Top Surface | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | LOD1.0/G1/N1 | LOD2.0/G1/N2 | LOD3.0/G1/N3 | LOD4.0/G1/N4 |
| Solid | LOD1.0/G2/N1 | LOD2.0/G2/N2 | LOD3.0/G2/N3 | LOD4.0/G2/N4 |
| True shape | LOD1.0/G3/N1 | LOD2.0/G3/N2 | LOD3.0/G3/N3 | LOD4.0/G3/N4 |
| True shape with patterns | LOD1.0/G4/N1 | LOD2.0/G4/N2 | LOD3.0/G4/N3 | LOD4.0/G4/N4 |
| Event | Data | Session | Software | Hardware |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser scan | Point cloud | On-site | FARO Focus S350 | |
| Laser scan | Point cloud | Post-processing | Cyclone | Workstation |
| Laser scan | Mesh model | Post-processing | Geomagic Wrap | Workstation |
| Photogrammetry | Photo | On-site | Canon M2 | |
| Photogrammetry | Mesh model | Post-processing | Context Capture | Workstation |
| Photography | Photo | On-site | Sony RX100 | |
| Photography | Photo database | Post-processing | Synology Manager | Synology NAS |
| Virtual tour | 3D Panorama photo | On-site | DJI Mavic 2 Pro | |
| Virtual tour | 3D Panorama photo | On-site | Insta360 Pro | |
| Virtual tour | 3D Panorama photo | On-site | Canon 6D | |
| Virtual tour | 3D Panorama photo | Post-processing | Camera Raw | Workstation |
| Virtual tour | 3D panorama tour | Post-processing | Pano2VR | Workstation |
| Virtual tour | Website page | Post-processing | Visual Studio | Workstation |
| Virtual tour | VR experience | Online | Firefox reality | HTC Vive Focus 3 |
| Cloud Service | Website database | Online | Synology Manager | Synology NAS |
| Observation | Notes | Online | Firefox explorer | PC |
| Collaboration | HBIM model | Online | Revit | PC |
| Optimization | Algorithm | Post-processing | Rhino, Grasshopper, VisualARQ | Workstation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, W.; Cong, W. Remote Practice Methods of Survey Education for HBIM in the Post-Pandemic Era: Case Study of Kuiwen Pavilion in the Temple of Confucius (Qufu, China). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020708
Xi W, Cong W. Remote Practice Methods of Survey Education for HBIM in the Post-Pandemic Era: Case Study of Kuiwen Pavilion in the Temple of Confucius (Qufu, China). Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(2):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020708
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Wang, and Wu Cong. 2022. "Remote Practice Methods of Survey Education for HBIM in the Post-Pandemic Era: Case Study of Kuiwen Pavilion in the Temple of Confucius (Qufu, China)" Applied Sciences 12, no. 2: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020708
APA StyleXi, W., & Cong, W. (2022). Remote Practice Methods of Survey Education for HBIM in the Post-Pandemic Era: Case Study of Kuiwen Pavilion in the Temple of Confucius (Qufu, China). Applied Sciences, 12(2), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020708







