Featured Application
The proposed method in this paper has the potential to solve the task-AGV allocation problem in a complex assembly environment where both multiple-AGV cooperative handling tasks and single-AGV handling tasks exist.
Abstract
An AGV system can be used to transport different-size materials in an assembly line. The hybrid task allocation problem is involved in the assembly line, where both single-AGV tasks and multi-AGV tasks exist. However, there is little research on this problem. The goal of solving this problem is to obtain a task allocation scheme with minimum idle time and maximum system throughput. Since all necessary materials must be delivered to the assembly station before the operation can start, the delivery tasks are not independent of each other in a task group serving the operation. To solve the problem above, a hybrid task allocation method based on a task binding strategy and an improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) is proposed. Firstly, a mathematical model considering the punctuality of material delivery and the cooperative relationship between tasks is established. Secondly, a task binding strategy and four heuristic rules are devised to improve the quality of randomly- and heuristic-generated individuals in the initial population for model optimization. Thirdly, an IPSO is developed to help the optimization algorithm jump out of local optimums. Finally, a simulation is performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed methods. The simulation results show that a better scheme can be obtained by our hybrid task allocation method, compared to conventional Genetic Algorithms and PSO algorithms.
1. Introduction
An automatic guided vehicle (AGV) system is a logistic robot system for material transportation. It has been applied in many fields, especially manufacturing shops [1,2], port transportation [3,4] and warehousing distribution [5,6]. Research on AGV systems mainly focuses on task allocation [7], traffic control [8], guide-path network design [9,10] and path planning [11,12]. Among them, task allocation is always a hot research direction. The key to the task allocation problem is to determine the assignment relationship between tasks and AGVs, and the order in which AGVs execute tasks.
In a large equipment assembly shop, such as bus chassis assembly line (BCAL), a fleet of homogeneous AGVs with limited transport capacity is responsible to deliver assembly materials to assembly stations. The materials include regular-size parts and large-size components. For a regular-size part, its size and weight are both within the capacity of an AGV, a single AGV transports it individually, and the corresponding material handling task is a single-AGV task. While, for a large-size component, several AGVs are combined as a multi-AGV group to carry it, and the corresponding material handling task is a multi-AGV task. In the above assembly shop, the hybrid task allocation problem is involved. It is important for these assembly shops to solve the hybrid task allocation problem because an efficient task allocation can increase productivity. However, there are few studies on hybrid task allocation problems.
An assembly operation at a station needs to consume several materials. When a station sends a signal to the control system to request materials for the next operation, several tasks transporting materials for the operation, are generated simultaneously. Moreover, these tasks are packaged as a task group. An operation can begin only when all tasks in the corresponding task group have been completed. So, for an operation, the tasks in a task group are not independent of each other. We call this non-independence a cooperative relationship. Each task has the best delivery time interval with two time attributes: the start time and the end time. The start time is set for the limited storage space in the storage area beside the station, and there is no space available for unloading when materials are delivered earlier than the start time. The operating delay occurs when materials are delivered later than the end time. So, for each task, the AGV or the multi-AGV group must deliver the material on its best delivery time interval. As described above, the completeness of materials and the punctuality of material delivery are two important points that must be considered when solving the task allocation problem.
Although many studies have been carried out on the task allocation problem, there is no research on the hybrid task allocation problem with consideration of the cooperative relationship between tasks. Our study aims to fill this research gap by proposing new algorithms for the problem. Therefore, in this paper, an effective hybrid task allocation method is proposed for the considered hybrid task allocation problem, and the proposed method takes the cooperative relationship between tasks and the best delivery time interval of tasks into account. Our highlights and main contributions are four-fold: (1) A mathematical model is established in view of the completeness of materials and the punctuality of material delivery; (2) a task binding strategy is proposed to reduce coding effort and to improve the quality of random solutions in initial population; (3) several heuristic rules are proposed to generate promising heuristic solutions for initial population; (4) an improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) algorithm is developed with a mutation operation to help the algorithm jumping out of local optimums.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. The next section summarizes related work. The problem definition is dedicated in Section 3. Section 4 provides the details of the task binding strategy, heuristic rules and IPSO. After that, the simulation model and results are given in Section 5. Finally, the conclusions are presented in Section 6.
2. Related Work
According to the number of AGVs required by a task, tasks can be divided into single-AGV tasks and multi-AGV tasks. At present, the research mainly focuses on the task allocation problem of single-AGV tasks. When solving the task allocation problem involving multi-AGV tasks, the completeness of materials and the punctuality of material delivery should be considered. In this section, we review literature closely related to the problem under consideration.
For the task allocation problem of single-AGV tasks, many methods have been proposed. Some methods aimed at decreasing the makespan, such as a method integrated with several evolutionary algorithms [13,14] and Giffler and Thompson algorithms with different priority dispatching rules [15]. Some methods aimed at avoiding deadlock [16,17], minimizing the total tardiness of tasks [18], or minimizing the overall energy consumption [19], etc.
The task allocation of multi-AGV tasks is a multi-object task assignment problem. As for the multi-object task assignment problem, studies are mainly distributed in the field of ship dispatching and robot scheduling. To ship dispatching, Chen et al. [20] proposed a genetic ant colony hybrid algorithm to improve task allocation efficiency. For robot scheduling, García et al. [21] studied the dynamic task assignment strategy for heterogeneous multi-robot teams. Liu et al. [22,23] proposed a subpopulation-based Genetic Algorithm (GA) and a novel memetic algorithm. Bischoff et al. [24] proposed a local improvement heuristic based on a neighborhood operator. Maoudj et al. [25] presented a new approach based on negotiation and priority rules.
Regarding the completeness of materials, [26,27,28] considered that all materials for an operation could be packaged into one task. Zhang et al. [29] considered that each station involved material-handling tasks and tool-handling tasks. Zhang et al. [30] divided materials required by each station into one or multiple tasks, according to AGV capacity. However, the research above regards material handling tasks of one operation as one or more independent tasks, without considering the cooperative relationship between tasks. When multiple tasks in a task group are late, the operating delay time calculated by the literature above is bigger than the practical value.
Concerning the punctuality of material delivery, there have been many studies. Yang et al. [31] proposed a dynamic time estimation based on the AGV dispatching algorithm. Zhang et al. [32] introduced the design of the handshake. Jens et al. [33] optimized the combination of rules based on the trained network. However, the studies above only required tasks to be delivered before the end time, without considering the problem that the material cannot be unloaded earlier than the start time of the corresponding task.
Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is one of the most prevalent intelligence algorithms. Due to its fewer parameters, ease of implementation and strong competitiveness compared with other swarm intelligence algorithms, many researchers have employed PSO to solve task allocation problems. To mention a few, Mousavi et al. [34] presented A fuzzy hybrid GA-PSO algorithm for multi-objective AGV scheduling in a flexible manufacturing system (FMS). Zhang et al. [35] used a hybrid PSO to settle the AGV scheduling problems at container terminals. A hybrid GA-PSO was applied for AGV scheduling problems in FMS in [14]. In terms of the excellent achievements of these papers, we hope to exploit a PSO variant for the problem under consideration.
From the above brief review, we can see that task allocation is a very active research field. Moreover, the existing research has a strong reference value for us to solve the hybrid task allocation problem considered in this paper. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to account for the cooperative relationship between tasks in the hybrid task allocation problem.
3. Problem Definition
In a BCAL, the assembly operations involve a variety of materials with significant differences in size, shape and weight; the task allocation problem is a typical hybrid task allocation problem. Therefore, we take the task allocation problem in the BCAL as the research object.
A BCAL with an AGV system is simplified, the schematic layout is shown in Figure 1. The BCAL simplified consists of processing line 1 and processing line 2, and it contains 16 stations. Each station is equipped with a storage area for accessories. A bus under manufacturing enters the BCAL from station 1, passes through each station of processing line 1 in sequence, and the corresponding operation is completed at the same time, and then enters the buffer area, after that, it enters processing line 2 and passes through each station in sequence; after all the operations in processing line 2 are completed, it leaves the BCAL from station 16. Each operation needs to consume some materials, which are stored in a parts warehouse before being sent to stations by AGVs. Some materials, such as bus chassis frames and front axle assemblies, need to be transported by a multi-AGV group because they are too large or heavy for an AGV. Some materials, such as tires, can be transported by an AGV individually. It should be noted that an AGV can transport several sets of accessories concurrently for a station, for small-sized and lightweight accessories. When an AGV handles a task, it first departs from its current location, then arrives at the parts warehouse and waits for loading until other AGVs handling the same task arrive at the parts warehouse; then it reaches the target station and unloads the materials after the start time and finally stays at the target station until it handles the next task. We should notice that when the AGVs assigned to handle a task are not from the same multi-AGV group, there will be a disassembly time to disassemble old multi-AGV groups and an adjustment time to combine these AGVs into a new multi-AGV group.

Figure 1.
Schematic layout of a bus chassis assembly line with an AGV system.
As shown in Figure 1, a task group, consisting of a two-AGV task T1 and a four-AGV task T2, serves the next operation at station 1. There is a cooperative relationship between the two multi-AGV tasks. When anyone of them is late, the operation cannot begin and the station will be idle.
3.1. Assumptions
The assumptions considered are as follows:
- There will be no malfunction, AGV collision or other accidents;
- When a multi-AGV group completes the current task and there are no other tasks allocated to any AGV of it, and it keeps the combined state at the unloading station;
- When AGVs stay at a station or the parts warehouse, it will not affect the unloading, loading and passage of other AGVs here;
- An AGV or a multi-AGV group can only handle a task at a time;
- The speed of an AGV does not change whether the AGV is independent or combined;
- The assembly operation time of each station is the same;
- The loading and unloading time of materials and the transport time of semi-finished products between stations are not considered.
3.2. Notations
The notations used in the study are described in Table 1.

Table 1.
The notations used in the study.
3.3. Decision Variables
if AGV is assigned to handle task and 0 otherwise.
, the sequence in which AGV handles tasks allocated to it in the current task allocation, where indicates the total number of tasks that AGV need to handle.
3.4. Objective Function
The punctuality of material delivery and the completeness of materials are two points that must be considered when solving the problem studied in this paper. The former is reflected in the delay time of operations, while the latter highlights that an operation cannot begin until all tasks transporting materials for it reach the target station, i.e., the delay time of an operation is only related to the tardiness time of the latest delivered task in the corresponding task group. So, we take the tardiness time of the latest delivered task in each task group as the indicator of the two points. In the practical assembly line, the delay time of an operation is reflected in the idle time of the corresponding station. Therefore, in our model, objective (1) is to minimize the average idle time of stations.
where indicates the tardiness time of the latest delivered task in task group.
The tardiness time of task can be expressed as:
3.5. Constraints
Constraints (3) and (6) impose restrictions on the decision variable. Constraint (3) requires that each task should be allocated to as many AGVs as the task required. Constraint (5) suggests that an AGV must handle tasks in sequence. Constraint (6) guarantees that an AGV cannot handle the tasks to be assigned to it in the current task allocation before the task allocation is made. Constraint (7) requires that materials of a task can be loaded to AGVs just when all AGVs handling the task are already located in the parts warehouse. Constraint (8) requires that materials of a task can be unloaded when responsible AGVs are already located at the unloading station. Constraint (9) ensures that the unloading time of a task cannot be earlier than the start time of the task. Constraints (10) and (11) guarantee that all tasks in a task group are serving the same operation and tasks in different task groups are serving different operations. As mentioned in the introduction, there is a cooperative relationship between tasks in a task group. The cooperative relationship is embodied in the fact that these tasks have the same best delivery time interval and unloading station.
4. Hybrid Task Allocation Method Based on Task Binding Strategy and IPSO
The process of the hybrid task allocation method based on task binding strategy and IPSO is shown in Figure 2. First, the task binding strategy is used to layer task groups and bind tasks. Then, an initial population composed of random and heuristic individuals is generated; the heuristic individuals are generated based on the proposed heuristic rules. After that, an IPSO algorithm developed with a mutation operation is adopted to solve the problem considered. Finally, we get a task allocation scheme.
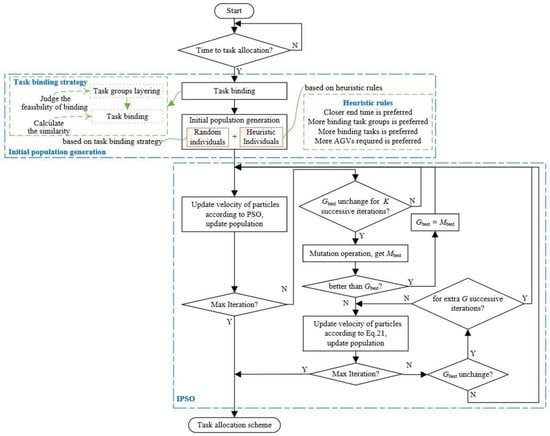
Figure 2.
The flow chart of the hybrid task allocation method based on task binding strategy and IPSO.
4.1. Period of Task Allocation and Task Generation Rules
4.1.1. Period of Task Allocation
Every station needs time ξ to complete the current operation and then prepare for the next one. Thus, every time ξ, each station generates a new task group, which contains all the material handling tasks serving the station’s next operation. Therefore, we take ξ as the period of task allocation.
4.1.2. Task Generation Rules
For materials except for accessories, there is no storage area beside the stations to store them temporarily. Thus, the best delivery time of materials for the next operation is the moment when the current operation is completed. Considering the travel time, material handling tasks are generated time ξ earlier than the best delivery time of materials. Because the best delivery time is a time point, which is not convenient for task allocation, the fault-tolerant time is proposed. The best delivery time interval of material handling task can be expressed as:
where is the start time of the current operation at the station; is the estimated completion time of the current operation.
For accessories, a material handling task is generated when the stock level of accessories stored in the storage area drops to a given limit value. Considering lean production, the limit value is set as 1. The best delivery time interval of material handling task can be expressed as:
where is the generation time of .
4.2. Coding and Decoding
Matrix coding is adopted, which consists of task coding and AGV coding. The first column of the coding matrix is task execution sequence coding, followed by AGV coding, as shown in Figure 3.
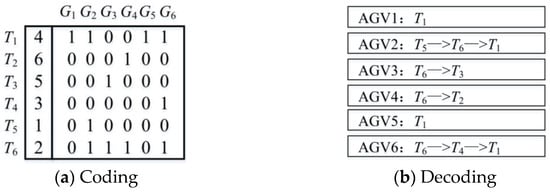
Figure 3.
An example of coding and decoding.
4.3. Initial Population Generation
Firstly, the task binding strategy is proposed to bind tasks, and random individuals are generated based on the tasks after binding; after that, several heuristic individuals are generated based on the proposed heuristic rules; finally, the initial population is composed of random individuals and heuristic individuals is formed.
4.3.1. Task Binding Strategy
To reduce the number of rows in the coding matrix and improve the quality of random individuals in the initial population, a task binding strategy is proposed. The task binding strategy contains the task group layering strategy and task binding method and involves the feasibility of binding and similarity between task groups. First, the task group layering strategy is used to divide task groups into different layers; then, the similarity between task groups in adjacent layers is calculated; after that, the task binding method is used to bind the tasks of two task groups with non-zero similarity in adjacent layers; finally, the task after binding is obtained.
A. Feasibility of binding between task groups
It is assumed that tasks and belong to task group and , respectively, and they require the same number of AGVs to handle. If an AGV or a multi-AGV group can deliver at after delivering, it is considered that binding to is feasible. The conditions under which can be bound to can be expressed as:
If an AGV or a multi-AGV group delivers task at and then handle, the delivery time of is still earlier than , is called the forward task group of. The conditions under which is the forward task group of can be expressed as:
B. Similarity between task groups
It is assumed that task group can be bound to the task group. The task arrays of and are [a b b c] and [b b c d], respectively, the number of elements in a task array is equal to the number of tasks in the task group, and the element is the number of AGVs required by each task in the task group. A similar array of and is [b b c]. The formula for calculating the similarity between task groups is as follows:
If cannot be bound to and cannot be bound to , the similarity between them is zero.
C. Task binding based on task group layering strategy
The task group layering strategy is used to divide task groups one by one and gradually forms multiple layers storing task groups. Task groups with binding feasibility are placed in adjacent layers. The main steps of the task group layering strategy are given in Algorithm 1.
Every time a layer is formed, the task binding method is used to bind task groups with non-zero similarity in adjacent layers, and then to bind tasks of the task groups bound. The task group binding follows the principle that task groups with bigger similarities are preferred. Moreover, task binding acquires that tasks require the same number of AGVs to handle. One task group or task can bind or be bound only once. For example, task groups is bound to, and the task arrays of and are [b b c d] and [a b b c], respectively, so the binding scheme between and is to , to and to , while and are free. The main steps of the task binding method are given in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 1. Task group layering strategy pseudo algorithm |
| input: the set of task groups () output: task group architecture sort () by the end time of Best delivery time interval |
| the current layer number of task group architecture x = 1 the sequence number of task group in s = 2 put the fisrt task group into the current layer while do for all task groups in the xth layer if can be bound to one of these task groups Go task binding method x= x + 1 break end if one of these task groups is the forward task group of go task binding method x= x + 1 break end next put into the xth layer |
| end while |
| Algorithm 2. Task binding method pseudo algorithm |
| input: task groups in the current layer and the upper layer output: task binding scheme the number of task groups in the current layer is the number of task groups in the upper layer is |
| calculate the similarity between the task groups in the current layer and the task groups in the upper layer copy input and the calculated similarity while do find the two task groups with the biggest similarity (>0) from the copy, assumed that they are in the upper layer and in the current layer bind to bind tasks in to tasks in delete and from the copy end while |
| go task group layering strategy |
4.3.2. Heuristic Rules
In order to improve the quality of the initial population, four heuristic rules are proposed. Based on each heuristic rule, a heuristic individual is generated.
The four heuristic rules are as follows:
(a) Task group with a closer end time is preferred
where denotes the end time of the best delivery time interval of task group , denotes ascending sort.
(b) Task group with more task groups bound is preferred
where denotes the number of task groups bound to task group , denotes descending sort. It should be noted that contains the number if is bound to .
(c) Task group with more tasks bound is preferred
where denotes the number of tasks bound to task . It should be noted that contains the number if is bound to .
(d) Task group requiring more AGVs is preferred
According to the priority of task groups generated, tasks in task groups are allocated to AGVs in sequence. The allocation follows that the AGVs chosen can handle the task earlier than other AGVs. Every time a task is allocated, the delivery time of the task needs to be calculated, and the available time of the AGVs chosen needs to be updated.
4.4. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization
Since the average idle time of stations is only related to the latest delivery task of each task group, it will not change, even if the delivery time of any other task is advanced in the iterative evolution. When the delivery time of the latest delivery tasks is not advanced for several generations, the algorithm adopted mistakenly gets the conclusion, reaching the optimal solution. Then the algorithm falls into a local optimum. Therefore, the feasible domain of the problem considered has many local optimum traps, which are difficult to escape from.
Compared with the traditional task allocation problem, the problem considered involves more complex coding and it is more difficult to solve. Therefore, PSO is adopted to solve the problem considering its strong abilities of convergence and escaping from local optimal traps.
To further improve the ability of PSO to escape from local optimum traps, improved PSO (Algorithm 3) is proposed, which combines PSO with a mutation operation and uses the mutation solution to guide evolution. The improved points are as follows:
When the global optimal solution does not change for K successive iterations, copy and mutate the copy, then mutate the mutation solution until obtaining M mutation solutions, and pick the best solution from the M mutation solutions. If is greater than , use to guide the subsequent evolution instead of , if not, the formula to update the velocity of each particle at the next G iterations is changed as follows:
where denotes the th particle in the th generation; denotes the optimal solution found by the th particle; is the inertia factor; , and are acceleration coefficients; , and are independent random numbers uniformly distributed in the range of [0, 1].
| Algorithm 3. Improved particle swarm optimization pseudo algorithm |
| initialize population while do update velocity of each particle according to PSO update population if no change end while do = while do mutate to get end while set as the best solution of {, , …, } if is better than = else while do update velocity of each particle according to Equation (20) update population if changes break end end while end end while |
| end while |
4.5. Algorithm Time Complexity Analysis
As shown in Figure 2, the proposed algorithm in this paper includes three methods: (1) task binding strategy; (2) IPSO; (3) heuristic rules. Moreover, the computational load of the proposed algorithm is mainly focused on the first two methods.
4.5.1. Time Complexity of Task Binding Strategy,
The computational load of the task binding strategy is mainly focused on the task group layering strategy and task binding method.
The time complexity of the task group layer strategy is.
The time complexity of the task binding method is , where, and are the time complexity of sorting task groups by similarity, binding task groups in adjacent layers and binding tasks of two task groups, respectively. denotes the number of task groups in the upper layer, denotes the number of task groups in the current layer, and denotes the number of tasks in the task group with the most tasks.
Therefore, . Since and are both less than , and are both less than , is not higher than even in the worst case.
4.5.2. Time Complexity of IPSO,
The computational load of IPSO is mainly focused on calculating fitness and mutation operation.
The time complexity of calculating fitness is, where and are the time complexity of decoding and the Floyd algorithm, respectively. denotes the number of rows in the coding matrix, and denotes the number of nodes in the path network.
When performing mutation operations, calculating the fitness of mutation solutions and finding the best mutation solution from M mutation solutions are required. The time complexity of the mutation operation is .
Assuming that the population size and number of iterations are and, respectively, .
The time complexity of the proposed hybrid task allocation method is.
5. Simulation and Discussion
Extensive simulation tests were conducted to verify the performance of the proposed hybrid task allocation method, which contained the task binding strategy, heuristic rules and IPSO. In this section, first, the simulation settings were given. Then, we carried out a simulation to prove the ability of the proposed task binding strategy to generate high-quality random individuals for the initial population. Next, a simulation was conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed heuristic rules, which generated heuristic individuals for the initial population. After that, a simulation was performed to illustrate the ability of the proposed IPSO to escape from the local optimal traps. Finally, 48-h simulations at different numbers of AGVs were conducted to test the actual scheduling performance of the proposed methods in an assembly line.
The software Tecnomatix Plant Simulation 15.0 was used in the simulation, and all methods are coded in SimTalk language. The used software is a simulation and optimization software for factories, production lines and logistics systems. It has been used by many researchers to validate their schemes in the field of task allocation.
5.1. Simulation Settings
The simulation interface of the AGV system for transporting materials in a BCAL is shown in Figure 4. The settings of the stations are shown in Table 2, the other simulation settings are shown in Table 3.
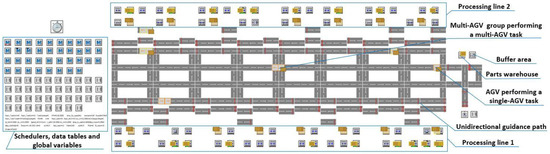
Figure 4.
The simulation interface of AGV system for transporting materials in a BCAL.

Table 2.
The settings of stations.

Table 3.
The other simulation settings besides stations.
We randomly selected six moments when the simulation system would perform the task allocation. Then we collected six sets of material handling tasks to be allocated corresponding to these six moments, respectively. Moreover, we took the six sets of tasks collected as test samples to test the performance of strategies and algorithms.
5.2. Simulation of the Proposed Task Binding Strategy
To test the performance of the proposed task binding strategy, two initial populations were generated. An initial population was randomly generated based on original tasks, noted as IP0. Another one was randomly generated based on tasks after binding, noted as IP1. GA using IP0 (GA-IP0), PSO using IP0 (PSO-IP0), GA using IP1 (GA-IP1) and PSO using IP1 (PSO-IP1) were employed to solve the problem considered based on the six sets of tasks, respectively. When the number of AGVs in the simulation system was 10, the graph of 100 iterations of the employed methods was shown in Figure 5.
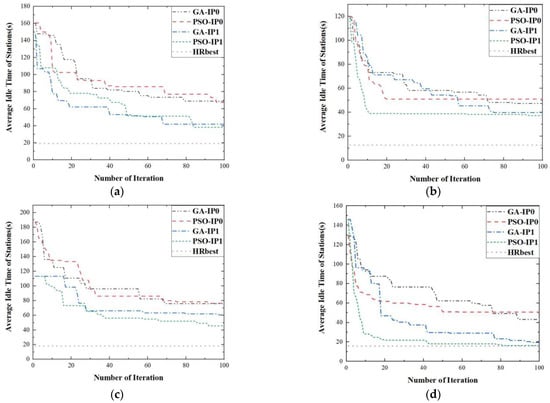

Figure 5.
The graph of 100 iterations of GA-IP0, PSO-IP0, GA-IP1, PSO-IP1. (a) The test samples is the first set of test samples. (b) The test samples is the second set of test samples. (c) The test samples is the third set of test samples. (d) The test samples is the fourth set of test samples. (e) The test samples is the fifth set of test samples. (f) The test samples is the sixth set of test samples.
As shown in Figure 5, the initial individuals of GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1 were superior to those of GA-IP0 and PSO-IP0 except in Figure 5d. This was because some tasks required the same number of AGVs to be bound by task binding strategy. It made the initial individuals more likely to have less adjustment time and disassembly time. Furthermore, the final solutions of GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1 were better than those of GA-IP0 and PSO-IP0 in all six sets of tasks. It proved that the quality of IP1 is better than that of IP0 and verified the ability of the proposed task binding strategy to generate high-quality random individuals for the initial population.
5.3. Simulation of the Proposed Heuristic Rules
The simulation in this section was conducted to verify the advancement of the proposed heuristic rules and the effective guidance of heuristic individuals on population evolution.
On the one hand, we noted the best of the four heuristic individuals generated based on heuristic rules as HRbest and compared HRbest to IP1. As shown in Figure 5a, the indicator value of HRbest was 19.28, and it was lower than that of the best individual in IP1, 147.29. For Figure 5b–f, we also observed a similar feature. It proved the advancement of the proposed heuristic rules.
On the other hand, a new initial population, noted as IP2 was generated. IP2 was composed of the four heuristic individuals and random individuals generated based on the task after binding. Then, GA using IP2 (GA-IP2) and PSO using IP2 (PSO-IP2) were employed to solve the task allocation problems based on the six sets of tasks, respectively. When the number of AGVs in the simulation system was 10, the results of 100 iterations of GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 were compared to those of GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1. The comparison was shown in Figure 6. We could see that the final solutions obtained by GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 were superior to those obtained by GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1 in all six sets of tasks. Furthermore, the current optimal solutions of GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 were always superior to those of GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1 at any number of iterations. This proved that heuristic individuals improved the quality of the initial population and could guide the algorithm to converge to a better solution.
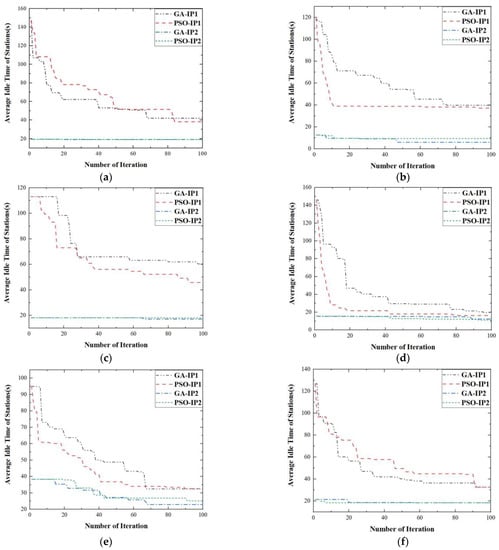
Figure 6.
The graph of 100 iterations of GA-IP1, PSO-IP1, GA-IP2, PSO-IP2. (a) The test samples is the first set of test samples. (b) The test samples is the second set of test samples. (c) The test samples is the third set of test samples. (d) The test samples is the fourth set of test samples. (e) The test samples is the fifth set of test samples. (f) The test samples is the sixth set of test samples.
It could be seen from Figure 5 and Figure 6 that GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 could converge to a relatively ideal solution, compared to GA-IP0, PSO-IP0, GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1. However, it could also be seen from Figure 5a–c,e that GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 still converged to a local optimum. It showed the difficulty of escaping from the local optimum traps when solving the problem considered.
5.4. Simulation of the Proposed IPSO
To verify the ability of the proposed IPSO to escape from the local optimal traps, IPSO using IP2 (IPSO-IP2) was employed to solve the problems considered based on the six sets of tasks, respectively. When the number of AGVs in the simulation system was 10, the results of 100 iterations of IPSO-IP2 were compared to those of GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2. The comparison was shown in Figure 7.
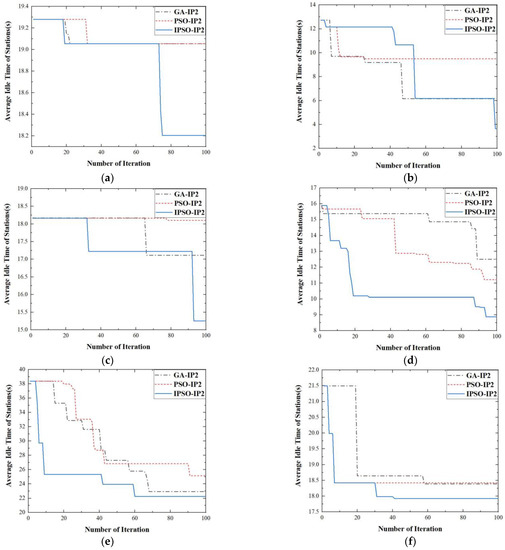
Figure 7.
The graph of 100 iterations of GA-IP2, PSO-IP2 and IPSO-IP2. (a) The test samples is the first set of test samples. (b) The test samples is the second set of test samples. (c) The test samples is the third set of test samples. (d) The test samples is the fourth set of test samples. (e) The test samples is the fifth set of test samples. (f) The test samples is the sixth set of test samples.
It could be seen that the final solutions of IPSO-IP2 were all superior to those of GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2. As shown in Figure 7a, at 20 to 35 iterations, IPSO-IP2, GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 fell into a local optimal trap with the fitness value of 19.05 in succession. In the early stage of iteration, both GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 had a strong ability to escape from the local optimum theoretically. However, both of them converged here, which indicated that it was difficult to escape from the local optimum here. However, it was noticed that the fitness of IPSO-IP2 changed to 18.20 at iteration 75.
From the above, it could be proved that IPSO could obtain better solutions, compared with conventional GA and PSO algorithms. It was because the mutation operation strengthened the ability of the IPSO to jump out of the local optimum.
5.5. 48-h Simulation
The previous simulations verified the effectiveness of the proposed methods in single task allocation. In order to further verify the actual scheduling performance of the proposed methods in an assembly line with the continuous production state, we conducted a 48-h simulation in this section. Under different numbers of AGVs, the simulation was run for 48 h under GA-IP0, PSO-IP0, GA-IP1, PSO-IP1, HRbest, GA-IP2, PSO-IP2 and IPSO-IP2, respectively. In the first 24 h, the assembly line was in the preheating state, and the material demand of each station was not stable. In 24 to 48 h, the assembly line went into steady production, which could better simulate the actual production scene. So, we took the throughput of 24–48 h as the performance indicator. The simulation results of each method were compared, shown in Figure 8.
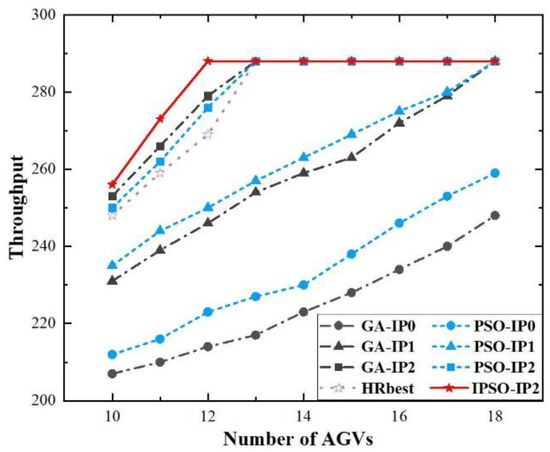
Figure 8.
The 48-h simulations under different number of AGVs and different methods.
As shown in Figure 8, when the number of AGVs was below 12, the throughput of all methods failed to reach the maximum system throughput. It was caused by the inadequate handling capacity of the AGV system. As the number of AGVs increased, the throughputs of all methods improved. When the number of AGVs was 12, the throughput of IPSO-IP2 proposed in this paper first reached the maximum system throughput. Moreover, it could be seen that IPSO-IP2 always had the highest throughput under different numbers of AGVs. It proved the effectiveness of IPSO-IP2 to solve the problem considered. Furthermore, before the number of AGVs reached 18, the throughputs of IPSO-IP2, GA-IP2 and PSO-IP2 were always higher than those of GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1. It showed that heuristic individuals were beneficial for the algorithm to find the optimal solution. Finally, the throughputs of GA-IP1 and PSO-IP1 were always higher than those of GA-IP0, and PSO-IP0, which proved the validity of the task binding strategy.
It can be found that when IP0 or IP1 was used as the initial population, the throughput of PSO was better than that of GA. It shows the strong global exploration ability of PSO. However, when IP2 was used as the initial population, the throughput of PSO is worse than that of GA. It was because most heuristic solutions in IP2 were probably local optimum traps. In this case, algorithms were easy to fall into local optimum in the early stage. The mutation operation could make GA try to search for a better solution from the neighborhood of the local optimum, while PSO without mutation operation was more likely to converge here.
6. Conclusions
Task allocation is an important research area of the AGV system. At present, research on task allocation problems mainly focuses on single-AGV tasks and less research on hybrid task allocation problems. Besides, the cooperative relationship between tasks is often simplified or ignored.
In this paper, we have studied the hybrid task allocation problem with the aim of minimizing the average idle time of stations. First, a mathematical model is established in view of the completeness of materials and the punctuality of material delivery. Then, the task binding strategy is proposed to reduce coding effort and improve the quality of random individuals in the initial population. Specifically, the task binding strategy contains a task group layering strategy and task binding method; the task group layering strategy is used to divide task groups into different layers, and the task binding method is used to bind the tasks of two task groups with non-zero similarity in adjacent layers. Next, in order to further improve the quality of the initial population, four heuristic rules are designed to generate promising individuals. After that, an IPSO algorithm is developed with a mutation operation to help the algorithm jump out of local optimums. Finally, the strategies and algorithms proposed in this paper are verified by simulations. The simulation results show that the proposed task binding strategy can generate high-quality random individuals. Moreover, the quality of the initial population can be improved significantly by the heuristic individuals generated based on heuristic rules. Besides, the IPSO could obtain better solutions compared with conventional GA and PSO algorithms, and it is suitable to solve the problem considered. Furthermore, compared with other methods, the hybrid task allocation method proposed in this paper can achieve the minimum idle time and the maximum system throughput.
Considering the great influence of the initial population on the problem studied in this paper, the task binding will be further studied by combining intelligent algorithms in the future. About the local optimal traps, a new method with a stronger ability to escape from local optimal traps will be researched.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H. and J.Z.; methodology, Y.H., X.W. and P.L.; software, Y.H.; validation, Y.H. and J.Z.; formal analysis, Y.H. and X.W.; investigation, X.Q. and P.L.; resources, X.W., X.Q. and P.L.; data curation, Y.H. and H.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.H.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. and X.W.; visualization, Y.H.; supervision, P.L.; project administration, X.W., X.Q. and P.L.; funding acquisition, X.W., X.Q. and P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61973154, No. 52005427) and was funded by the Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. 19KJB510013).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Goli, A.; Tirkolaee, E.B.; Aydin, N.S. Fuzzy Integrated Cell Formation and Production Scheduling Considering Automated Guided Vehicles and Human Factors. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 29, 3686–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demesure, G.; Defoort, M.; Bekrar, A.; Trentesaux, D.; Djemai, M.B. Decentralized Motion Planning and Scheduling of AGVs in an FMS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhou, C.; Stephen, A. Simulation model and performance evaluation of battery-powered AGV systems in automated container terminals. Simul. Model Pract Theory 2020, 106, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Qi, L.; Luan, W.J.; Guo, X.W.; Ma, H.J. Load-In-Load-Out AGV Route Planning in Automatic Container Terminal. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 157081–157088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.T.; Cheng, X.Y.; Jiang, W.G.; Chen, S.W. Research on Equipment Configuration Optimization of AGV Unmanned Warehouse. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 47946–47959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, S.; Su, Z.; Guo, D. Multi-objective AGV scheduling in an automatic sorting system of an unmanned (intelligent) warehouse by using two adaptive genetic algorithms and a multi-adaptive genetic algorithm. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Far, M.H.; Haleh, H.; Saghaei, A. A fuzzy bi-objective flexible cell scheduling optimization model under green and energy-efficient strategy using Pareto-based algorithms: SATPSPGA, SANRGA, and NSGA-II. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 3853–3879. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharia, P.T.; Xidias, E.K. AGV routing and motion planning in a flexible manufacturing system using a fuzzy-based genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, R.; Ota, J.; Arai, T. Integrated design for routing and network in AGV systems using co-evolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Intelligent Systems and Signal Processing, Changsha, China, 8–13 October 2003; Volume 1, pp. 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Rubaszewski, J.; Yalaoui, A.; Amodeo, L.; Fuchs, S. Extensions of the unidirectional flow path design problem solved by efficient metaheuristics. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragapane, G.; de Koster, R.; Sgarbossa, F.; Strandhagen, J.O. Planning and control of autonomous mobile robots for intralogistics: Literature review and research agenda. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 294, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlollahtabar, H.; Hassanli, S. Hybrid cost and time path planning for multiple autonomous guided vehicles. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Guo, S.S. A Multi-Objective and Multi-Dimensional Optimization Scheduling Method Using a Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithms with a Sectional Encoding Mode. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.; Yap, H.J.; Musa, S.N.; Tahriri, F.; Md Dawal, S.Z. Multi-objective AGV scheduling in an FMS using a hybrid of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udhayakumar, P.; Kumanan, S. Integrated scheduling of flexible manufacturing system using evolutionary algorithms. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.P.; Dai, X.Z. Deadlock-free multi-attribute dispatching method for AGV systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 45, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhai, J.; Lou, P.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, H. Deadlock-free Task Scheduling with Task Traveling Time for a Multi load AGV System. China Mech. Eng. 2021, 32, 2840–2849. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, H.F.; Janardhanan, M.N.; Nielsen, P. An integrated approach for line balancing and AGV scheduling towards smart assembly systems. Assem. Autom. 2020, 40, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jin, C.; Li, Z. Bilevel programming model of low energy consumption AGV scheduling problem at automated container terminal. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Manufacturing, Industrial & Logistics Engineering (SMILE), Hangzhou, China, 20–21 April 2019; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xiang, S.; Chen, F. Research on a Task Planning Method for Multi-Ship Cooperative Driving. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2019, 24, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, P.; Caamaño, P.; Duro, R.J.; Bellas, F. Scalable task assignment for heterogeneous multi-robot teams. Int. J. Adv. Robot Syst. 2013, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kroll, A. Performance impact of mutation operators of a subpopulation-based genetic algorithm for multi-robot task allocation problems. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Kroll, A. Memetic algorithms for optimal task allocation in multi-robot systems for inspection problems with cooperative tasks. Soft Comput. 2015, 19, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, E.; Meyer, F.; Inga, J.; Hohmann, S. Multi-Robot Task Allocation and Scheduling Considering Cooperative Tasks and Precedence Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–14 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoudj, A.; Bouzouia, B.; Hentout, A.; Toumi, R. Multi-agent approach for task allocation and scheduling in cooperative heterogeneous multi-robot team: Simulation results. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Cambridge, UK, 22–24 July 2015; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xia, B.; Zhou, B.; Xi, L. A reinforcement learning based approach for a multiple-load carrier scheduling problem. J. Intell. Manuf. 2015, 26, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Pan, Q.K.; Meng, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.L. An effective discrete artificial bee colony algorithm for multi-AGVs dispatching problem in a matrix manufacturing workshop. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Inoue, K. Local and random searches for dispatch and conflict-free routing problem of capacitated AGV systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ren, W. A dynamic scheduling method for self-organized AGVs in production logistics systems. Procedia CIRP 2021, 104, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Y. Research on hybrid-load AGV dispatching problem for mixed-model automobile assembly line. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M.; Li, C.H.; Zhao, Q.C. Dynamic Time Estimation Based AGV Dispatching Algorithm in Automated Container Terminal. In Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; pp. 7868–7873. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, W.; Duan, J.; Qin, J. Cooperative Scheduling of AGV and ASC in Automation Container Terminal Relay Operation Mode. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5764012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jens, H.; Thomas, V. Reducing mean tardiness in a flexible job shop containing AGVs with optimized combinations of sequencing and routing rules. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, H.J.; Musa, N.S.; Dawal, S.Z.M. A fuzzy hybrid GA-PSO algorithm of multi-objective AGV scheduling in FMS. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2017, 16, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Qi, L.; Luan, W.J.; Ma, H.J. Double-cycling AGV scheduling considering uncertain crane operational time at container terminals. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









