Liquid Nanofilms’ Condensation Inside a Heat Exchanger by Mixed Convection
Abstract
1. Introduction
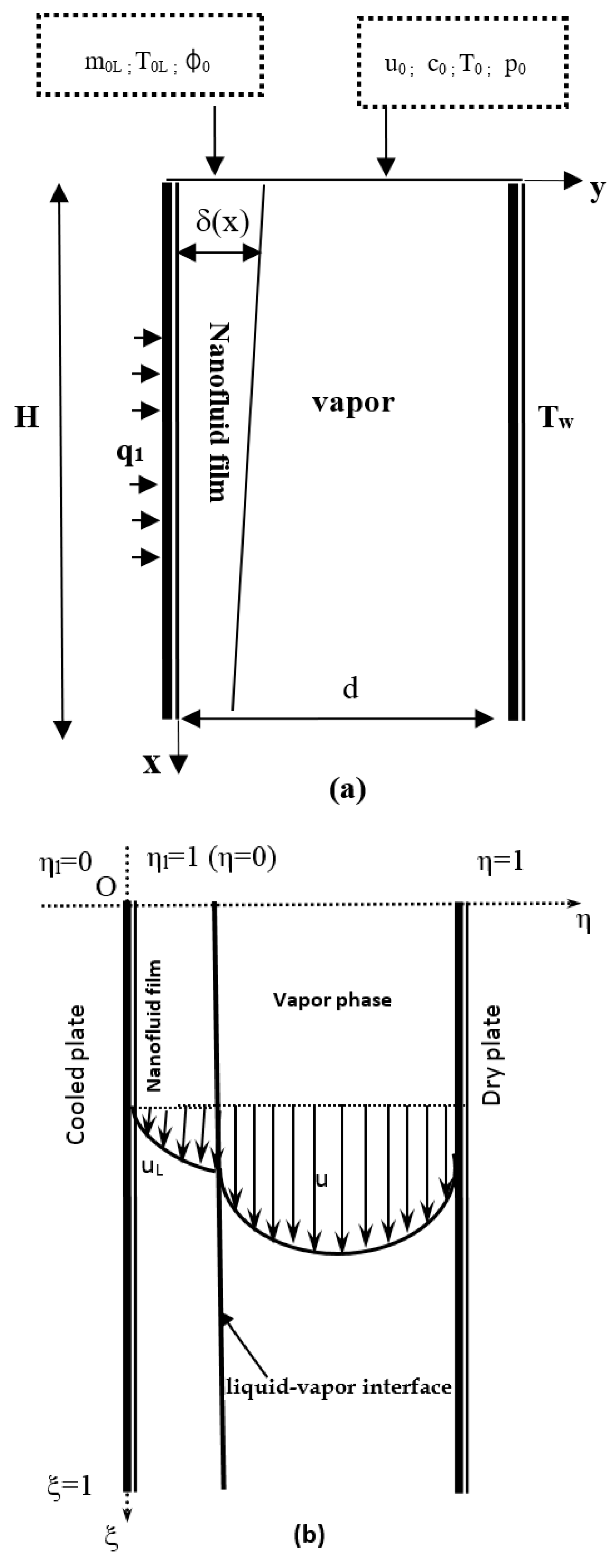
2. Numerical Modelling
2.1. Basic Equations
2.1.1. For the Liquid Phase
2.1.2. For the Gaseous Phase
2.1.3. Boundary Conditions
- For the inlet conditions (at x = 0):
- For the dry plate (at y = d):
- For the wet plate (at yL = 0):
- For the gas–liquid interface (at yL = δ and y = 0):
2.2. The Dimensionless Governing Equations
2.2.1. For the Liquid Phase
2.2.2. For the Gaseous Phase
2.2.3. Boundary Conditions
- For the inlet conditions (at ):
- For the dry plate (at η = 1):
- For the wet plate (at ηL = 0):
- For the gas–liquid interface (at η = 0 and ηL = 1):where .
- -
- The latent heat flux is given by:
- -
- The sensible heat flux is given by:
- -
- The local condensation rate is:
- -
- The cumulated condensation rate is:
3. Solution Method
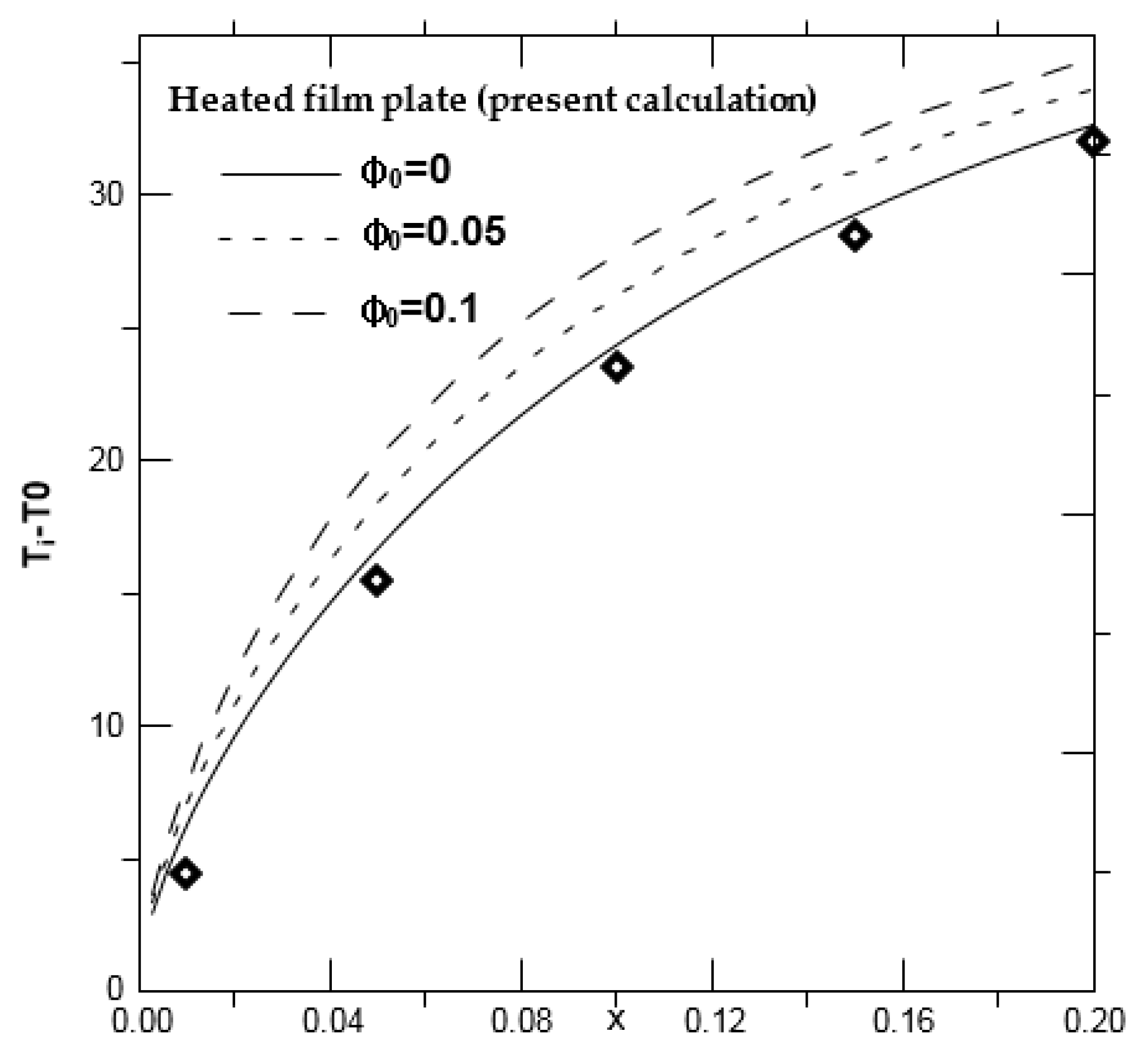
4. Results and Discussion
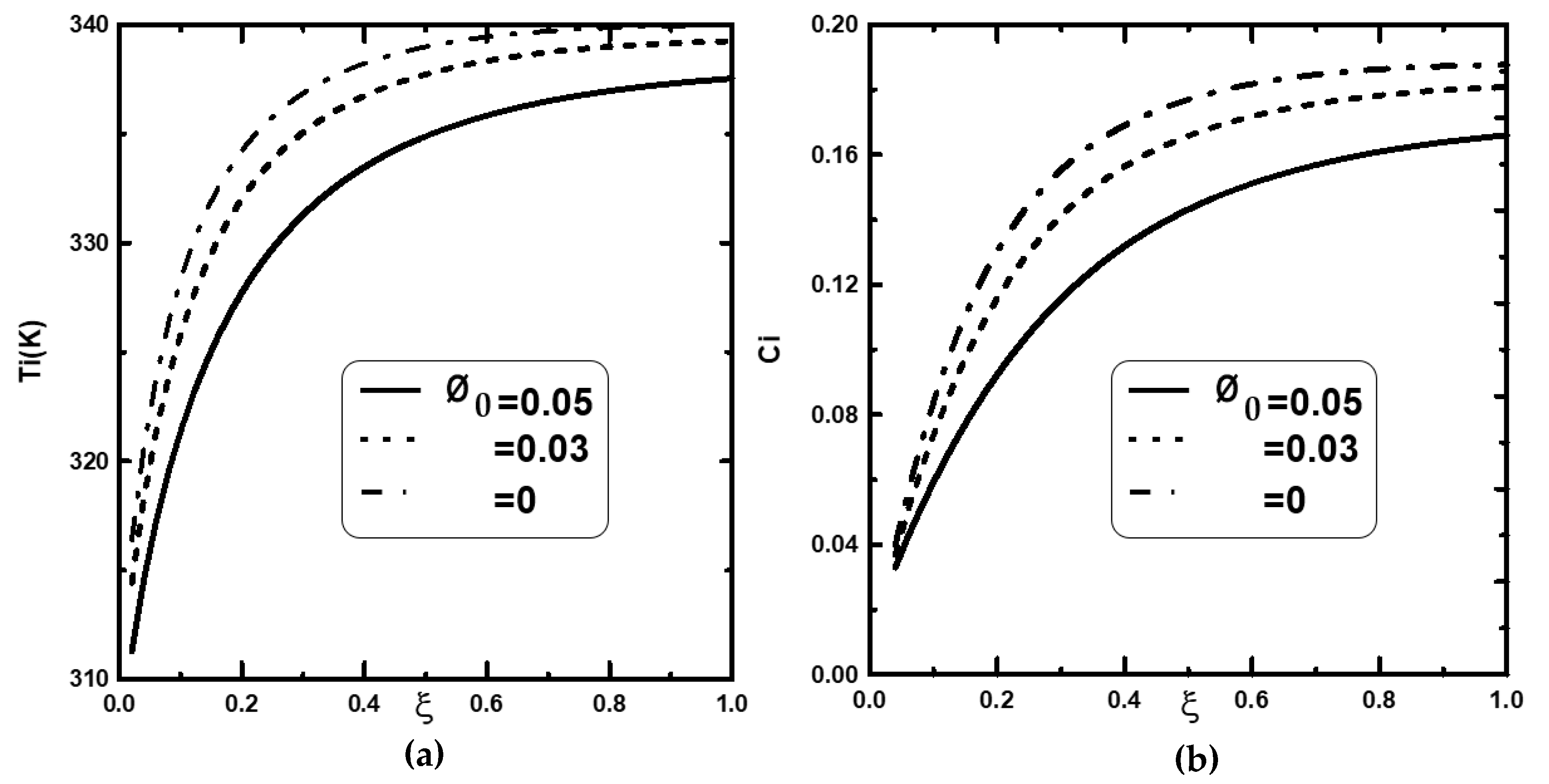
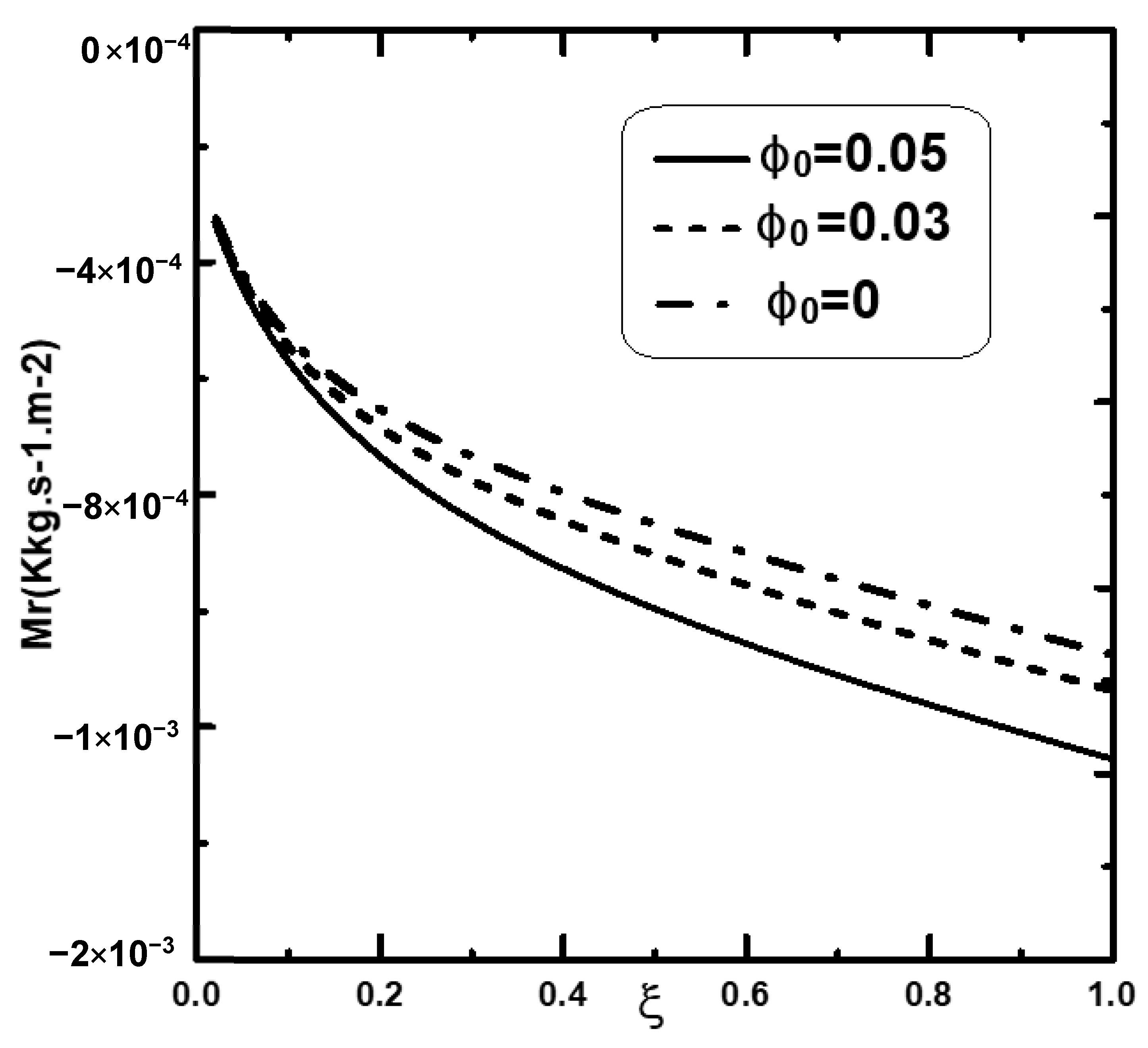
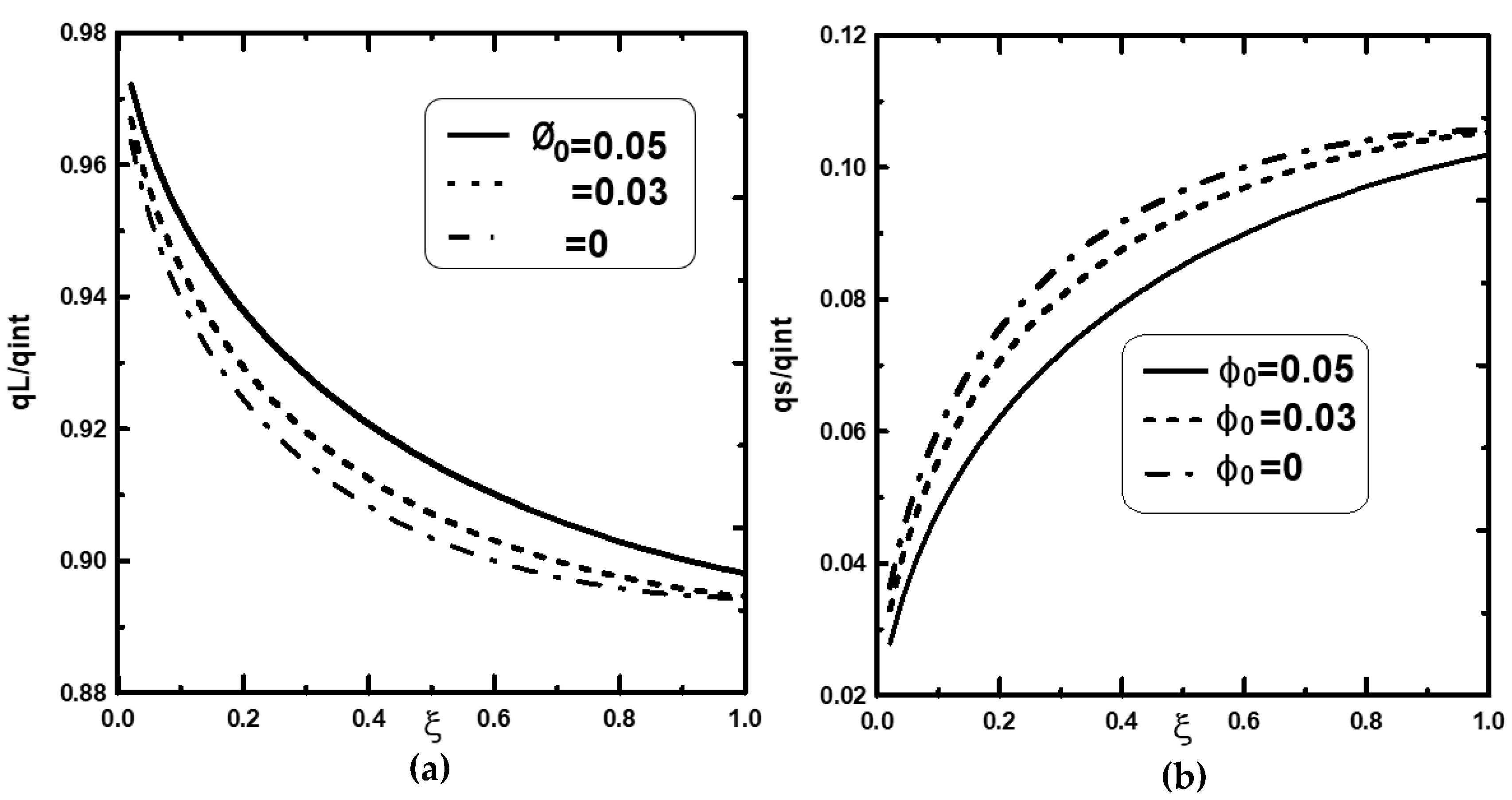
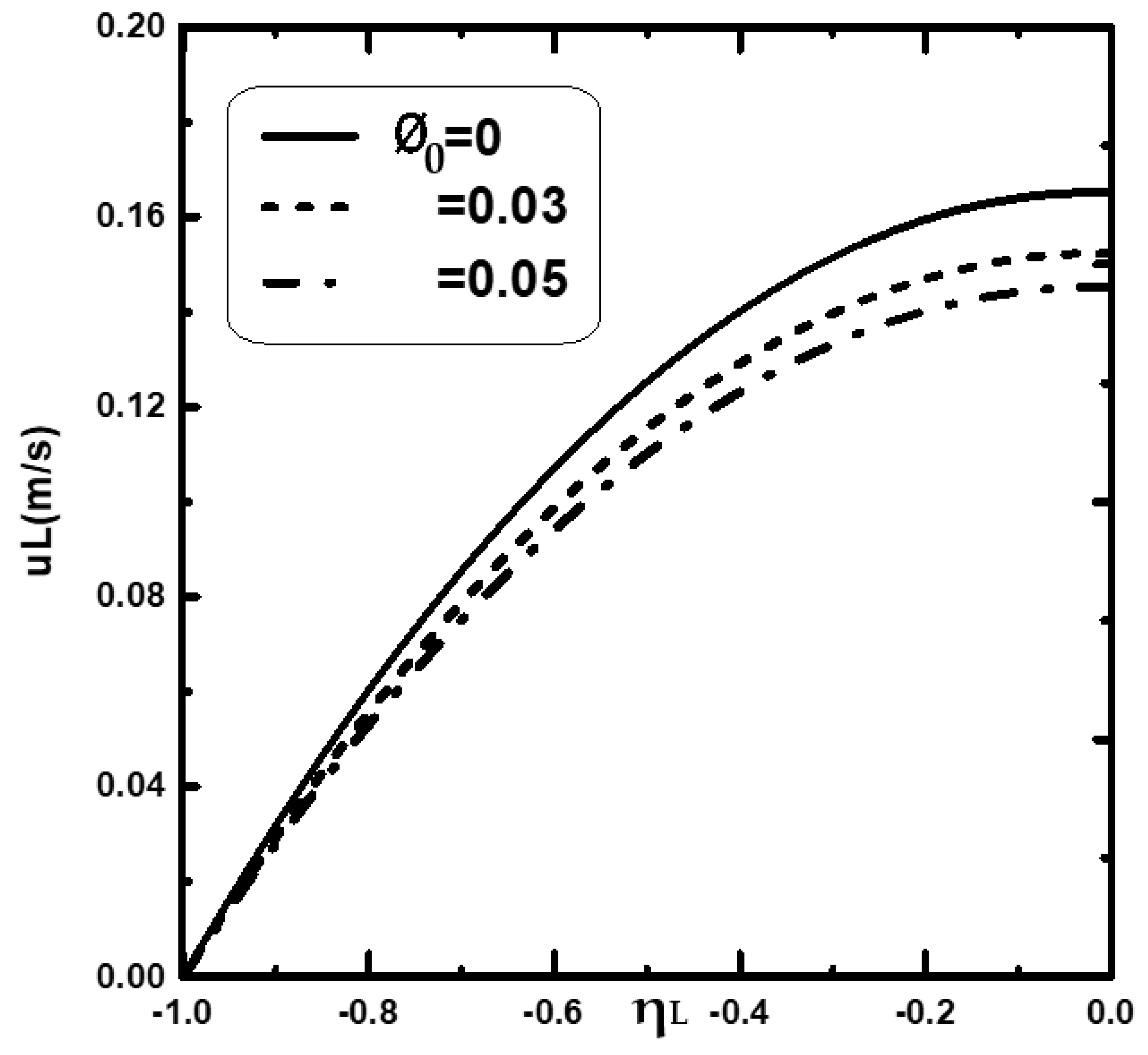
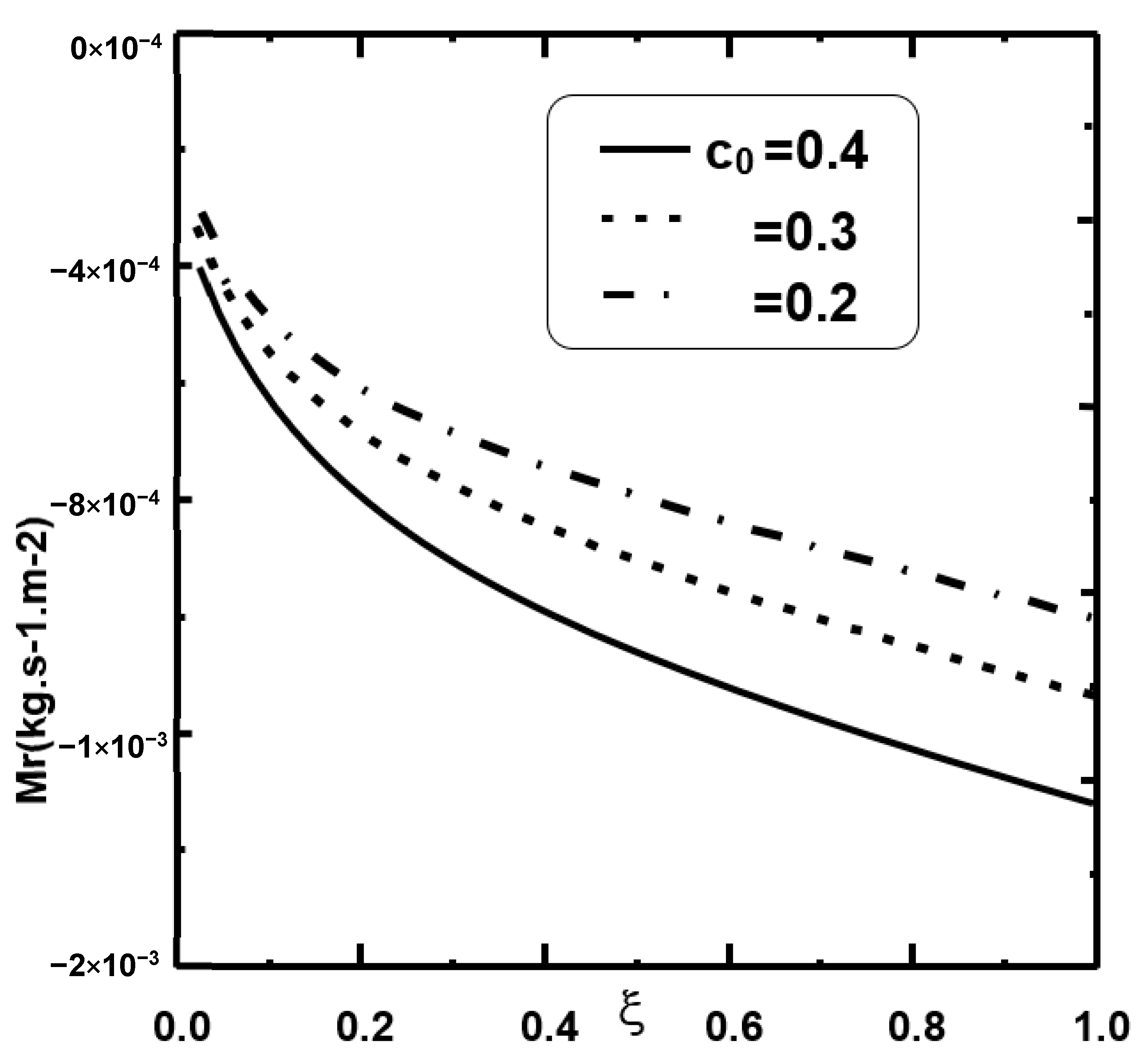
4.1. Effect of the Inlet Volume Fraction of Nanoparticles
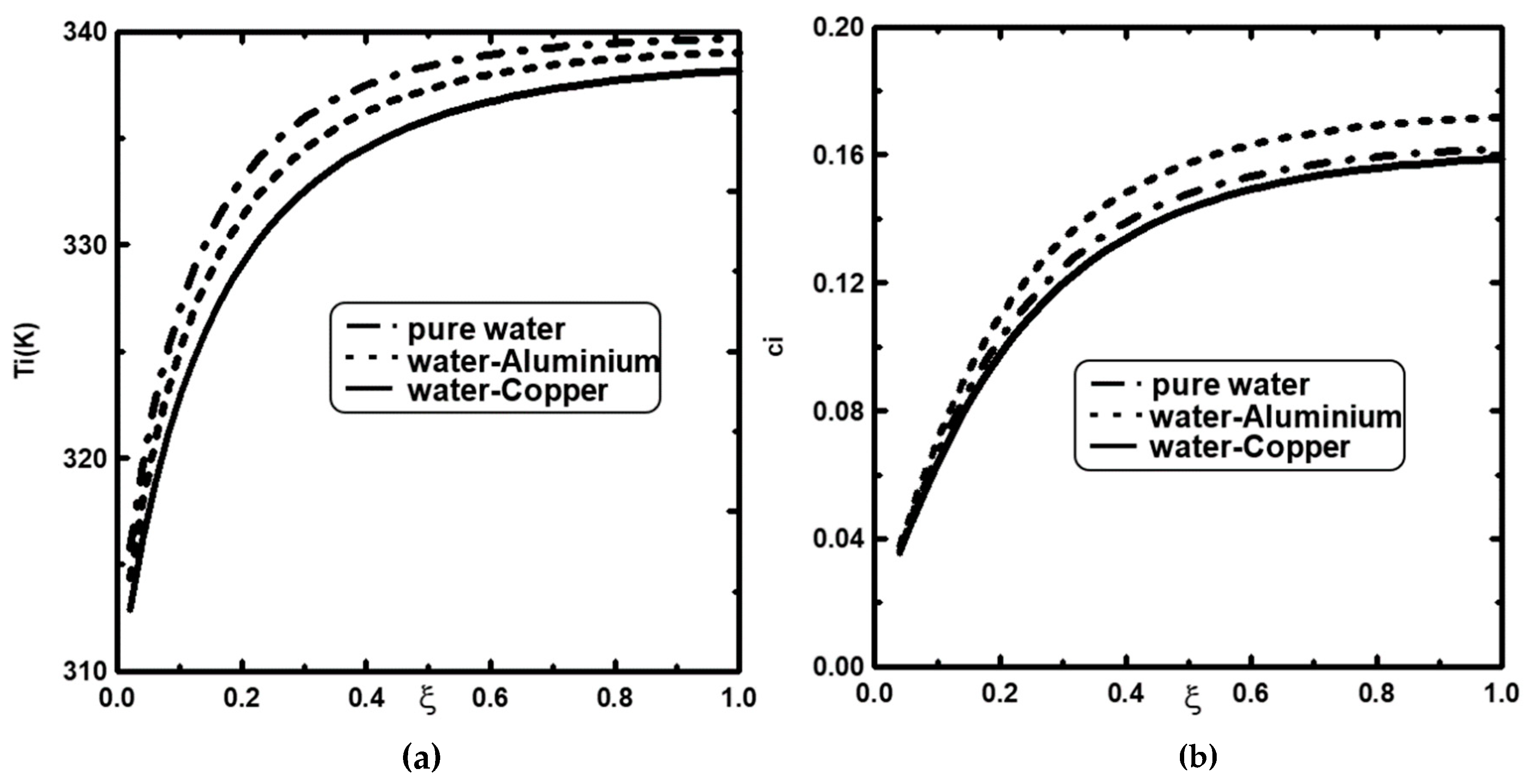
4.2. Effect of Nanoparticle Types
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The dispersion of the nanoparticles improved the mass and heat exchange during film condensation.
- (2)
- The dispersion of the nanoparticles improved the film condensation.
- (3)
- The mass and heat exchange were improved by using the Cu–water nanofluid compared to the Al–water nanofluid.
- (4)
- Compared to the Al nanoparticles and pure water, the liquid film condensation was considerably improved in the case of Cu nanoparticles.
- (5)
- It was observed that an increase in the inlet gas mass fraction improved the water film condensation.
- (6)
- An increase in the thermal flux cooling improved the water film condensation.
- (7)
- An increase in the inlet gas velocity worsened the water film condensation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| c | mass fraction for water vapour |
| cpv | heat capacity of water vapour [J kg−1 K−1] |
| cpa | heat capacity of water dry air [J kg−1 K−1] |
| D | mass diffusivity [m2 s−1] |
| DB | Brownian coefficient |
| DT | Thermal diffusion coefficient |
| Lv | latent heat of water evaporation [J kg−1] |
| P | pressure [N m−2] |
| T | temperature [K] |
| g | gravitational acceleration (m s−2) |
| u | axial velocity [m s−1] |
| v | transverse velocity [m s−1] |
| x | coordinate in the axial direction [m] |
| y | coordinate in the transverse direction [m] |
| kb | Boltzmann′s constant |
| Greek symbols | |
| dp | nanoparticles diameter |
| φ | volume fraction of nanoparticles |
| λ | thermal conductivity [W m−1 K−1] |
| μ | dynamic viscosity [kg m−1 s−1] |
| δ | thickness of liquid film (m) |
| ρ | density [kg m−3] |
| (ρcP) | heat capacity [J K−1] |
| η | dimensionless coordinate in the transverse direction |
| ηL | dimensionless transverse coordinate in the liquid (ηL = y/δ) |
| ζ | dimensionless coordinate in the flow direction |
| β | [K−1] |
| β* | |
| Subscripts | |
| n | nanoparticle |
| nf | nanofluid |
| 0 | inlet condition |
| L | liquid |
References
- Asirvatham, L.G.; Vishal, N.; Gangatharan, S.K.; Lal, D.M. Experimental Study Forced Convective Heat Transfer with Low Volume Fraction of CuO/Water Nanofluid. Energies 2009, 2, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefiane, K.; Bennacer, R. Nanofluids droplets evaporation kinetics and wetting dynamics on rough heated substrates. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheremet, M.; Cimpean, D.; Pop, I. Free convection in a partially heated wavy porous cavity filled with a nanofluid under the effects of Brownian diffusion and thermophoresis. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 113, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjaei, A.R.; Soltani, M.; Bahiraei, M.; Kashkooli, F.M. CFD simulation of nanofluid forced convection inside a three-dimensional annulus by two-phase mixture approach: Heat transfer and entropy generation analyses. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 146, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namburu, P.K.; Das, D.K.; Tanguturi, K.H.; Vajiha, R.S. Numerical study of turbulent flow and heat characteristic of nanofluids consididering variable properties. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2009, 48, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-H.; Phuoc, T.X.; Martello, D. Effects of nanoparticles on nanofluid droplet evaporation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvandi, A.; Heysiattalab, S.; Ganji, D. Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on heat transfer enhancement at film boiling of nanofluids over a vertical cylinder. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orejon, D.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Evaporation of nanofluid droplets with applied DC potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqa, S.; Begum, N.; Hossain, M.; Gorla, R.S.R.; Al-Rashed, A.A. Two-phase natural convection dusty nanofluid flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 118, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orejon, D.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Stick–Slip of Evaporating Droplets: Substrate Hydrophobicity and Nanoparticle Concentration. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12834–12843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, L.; Pajor-Swierzy, A.; Magdassi, S.; Kamyshny, A.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Evaporation of Nanosuspensions on Substrates with Different Hydrophobicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, P. Experimental study of falling film evaporation in large scale rectangular channel. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 76, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.M. Effects of film evaporation on laminar mixed heat and mass transfer in a vertical channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1992, 12, 3419–3429. [Google Scholar]
- Askounis, A.; Sefiane, K.; Koutsos, V.; Shanahan, M.E.R. The effect of evaporation kinetics on nanoparticle structuring within contact line deposits of volatile drops. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 441, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Mousa, A.A.A.; Nazir, U.; Althobaiti, S.; Althobaiti, A.; Shah, N.A.; Chung, J.D. Finite element analysis for ternary hybrid nanoparticles on thermal enhancement in pseudo-plastic liquid through porous stretching sheet. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nazir, U.; Sohail, M.; Singh, A.; Muhsen, S.; Galal, A.M.; Tag El Din, E.S.M.; Hussain, S.M. Finite element analysis for thermal enhancement in power law hybrid nanofluid. Front. Phys. 2022, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, U.; Saleem, S.; Al-Zubaidi, A.; Shahzadi, I.; Feroz, N. Thermal and mass species transportation in tri-hybridized Sisko martial with heat source over vertical heated cylinder. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 134, 106003. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, A.; Alzahrani, A.A. Liquid Nanofilms’ Evaporation Inside a Heat Exchanger by Mixed Convection. Coatings 2022, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenhain, W. The Properties of Some Copper Alloys; (Classic Reprint) Paperback-October 27; Forgotten Books: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]



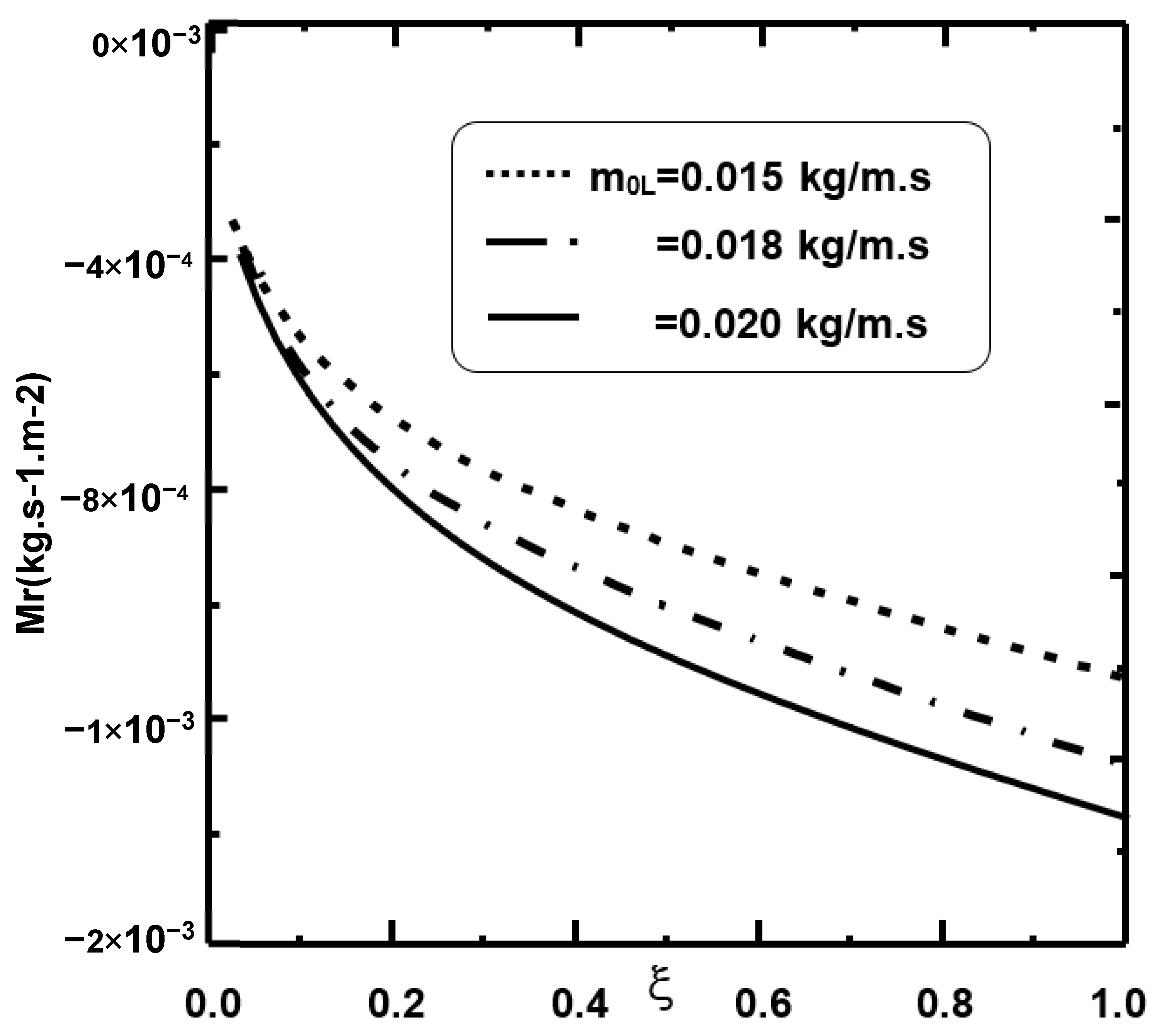
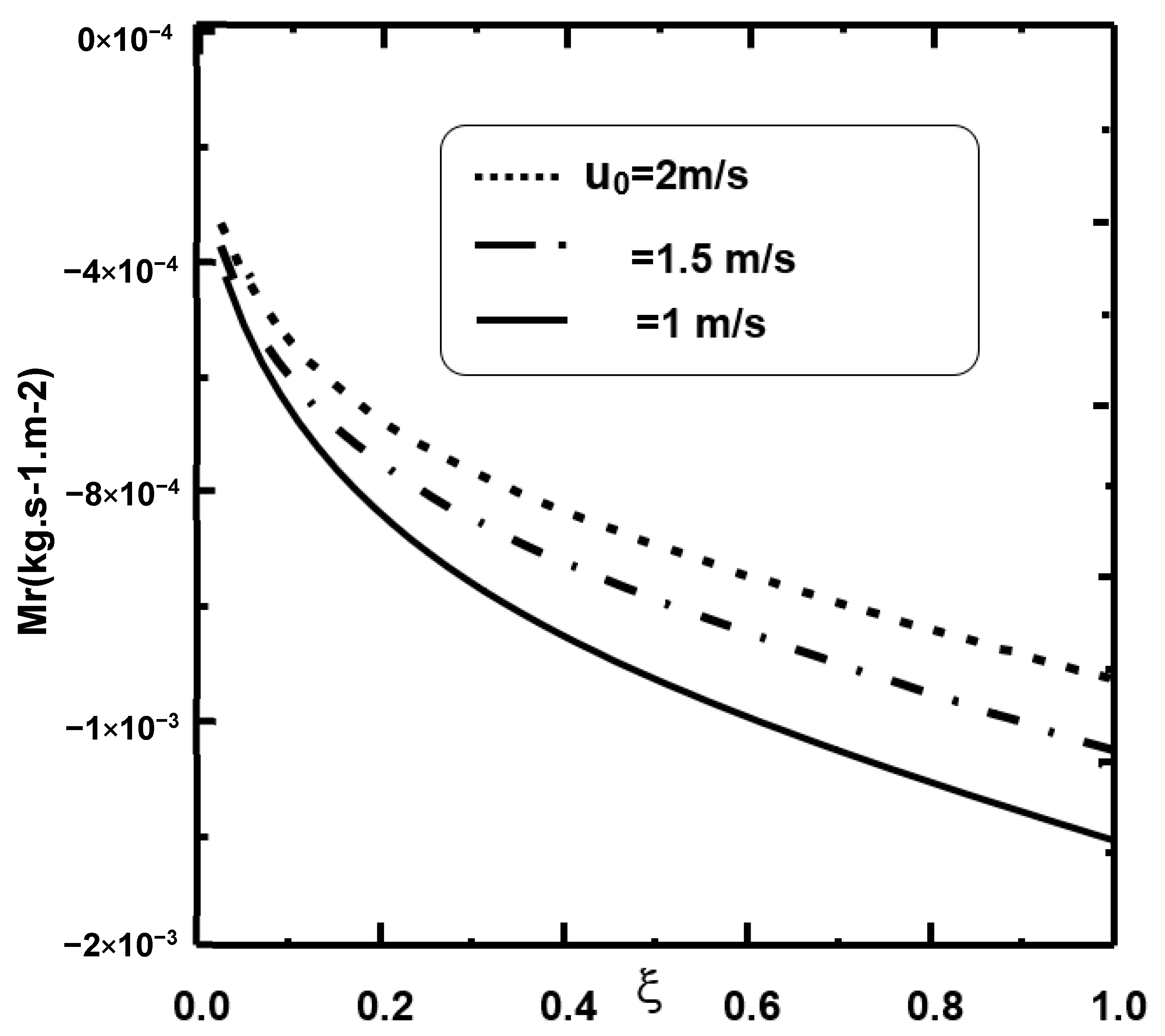
| I × (J + K) Grid Point | 101 × (101 + 41) | 101 × (71 + 41) | 71 × (51 + 41) | 51 × (51 + 21) | 51 × (21 + 31) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ξ = 0.25 | 3.960 | 3.900 | 3.973 | 3.959 | 3.936 |
| ξ = 0.50 | 6.651 | 6.530 | 6.572 | 6.593 | 6.567 |
| ξ = 0.75 | 9.140 | 9.200 | 8.984 | 8.986 | 8.959 |
| ξ = 1.00 | 11.473 | 11.400 | 11.442 | 11.425 | 11.495 |
| Thermo-Physical Properties | Aluminium | COPPER (Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg.m−3) | 2700 | 8933 |
| Cp (J.kg−1.K−1) | 900 | 385 |
| λ (W.m−2.K−1) | 240 | 401 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasr, A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.S. Liquid Nanofilms’ Condensation Inside a Heat Exchanger by Mixed Convection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122111190
Nasr A, Al-Ghamdi AS. Liquid Nanofilms’ Condensation Inside a Heat Exchanger by Mixed Convection. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(21):11190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122111190
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasr, Abdelaziz, and Abdulmajeed S. Al-Ghamdi. 2022. "Liquid Nanofilms’ Condensation Inside a Heat Exchanger by Mixed Convection" Applied Sciences 12, no. 21: 11190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122111190
APA StyleNasr, A., & Al-Ghamdi, A. S. (2022). Liquid Nanofilms’ Condensation Inside a Heat Exchanger by Mixed Convection. Applied Sciences, 12(21), 11190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122111190






