Abstract
The current study sought to assess the antitumor, anticancer, and antioxidant efficacy of Ulva lactuca-mediated selenium nanoparticles by using an in vitro model of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG-2 cells) and HAV HM175 strain of hepatitis A virus, with the evaluation of antioxidant activity conducted using DPPH assay. The study showed promising cytotoxicity at the highest concentrations of 250 and 500 µg/mL, with viability rates of 19.43 and 8.75% for cancer cells, and the lowest toxicity with the highest viability rates of 59.41 and 30.64% for normal cells, respectively. These concentrations also exhibited the highest inhibition rates (51.28 and 76.31%, respectively) against the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) enzyme and provide an explanation of the mechanism of such cytotoxicity, as this enzyme is responsible for the degradation of EGFR. Additionally, U. lactuca-mediated selenium nanoparticles (USeNPs) showed promising antiviral activity (+++) (50–<75%) with EC50 = 57.41 μg/mL and 74.13% antiviral rates against HAV HM175 at 100 µg/mL maximum noncytotoxic conc (MNCC). Using MTT assay, its selectivity index was 5.78 ≥ 2, which indicates that USeNPs exhibited antiviral activity that outweighed its toxicity. Therefore, USeNPs is an active antiviral agent and warrants further study. Furthermore, the DPPH scavenging activity of such nanoparticles was moderate as the highest sample concentration (100 µg/mL) recorded 31.64 ± 0.03% DPPH scavenging activity (with IC50 = 158.02 ± 0.07 μg/mL), a percentage which does not exceed that of standard ascorbic acid.
1. Introduction
Nanoparticles (NPs), the building blocks of nanotechnology, are described as particles at the nanoscale measure 100 nm or below [1]. Due to their beneficial and unique physical, chemical, and mechanical qualities, NPs are widely used in a range of applications, including cosmetics, medications, energy, electronics, catalysis, wastewater treatment, food production, heavy metal adsorption, and agriculture [2]. Traditional physical and chemical technologies used to create NPs include labor-intensive, expensive, and destructive environmental processes [3]. To resolve these issues, a production technique called “green synthesis” has been developed, which differs from physical and chemical methods by being more environmentally friendly, economically viable, and instantly scalable for batch production. It also provides controlled growth, crystal growth, increased influence, increased stability, and uniform size [4,5,6,7]. Many organisms, including Ulva lactuca, are recognized to have potential biological roles and activities, and facilitate such green nanotechnology [8,9]. Algal biomass (either living or dried) has grown in popularity as a “bio-nano-factory” because of its rapid development, enhanced ability for metal and metal oxide accumulation and reduction, elevated biomass yield, growth without the need of fertilizers, and capacity to be harvested regularly [10,11]. The green macroalgae, U. lactuca, which is common along Egypt’s north coast, is a member of the class Ulvophyceae and the family Ulvaceae. U. lactuca’s aqueous extract is rich in bioactive molecules, including ulvan polysaccharides, amides, pigments, proteins, amines, terpenes, phenols, and alkaloids, all of which have a significant role in the stabilization and reduction of metal [12]. U. lactuca extract has been used to create a wide variety of NPs with effective anticancer activity against the HCT-116 cell line. Acharya et al. [13] synthesized novel biogenic U-AgNPs, using U. lactuca extract, which could serve as a potential novel therapeutic agent for cancer. For humans, selenium elements with anticancer and immunomodulatory properties are crucial and required. Ahmad Rezashahverdi’s team showed that selenium NPs could greatly increase the 4T1 breast cancer tumor immune response in mice, and Gao’s team discovered that selenium NPs (SeNPs) might limit prostate carcinoma cell growth partly through apoptosis caused by cystepsin [14]. It is noteworthy that the present study is the first to synthesize and test U. lactuca-mediated selenium NPs (USeNPs) for their anticancer activity against HepG2 carcinoma cells through the suppression effect on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) since abnormal expression of EGFR is one of the therapeutic aims of cancer treatment. Vikneshan et al. [15] synthesized selenium particles but only tested them for their antibacterial activity. Extensive research on the EGFR signaling pathway has been motivated by the confirmation that the EGFR is strongly associated with tumor growth, progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis among patients [16,17]. A surge in research focused on the design and synthesis of EGFR inhibitors has been sparked by mounting evidence that EGFR inhibitors offer significant promise in the therapy of malignancies, particularly non-small-cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer [18,19,20,21,22]. The design and synthesis of 14 compounds with EGFR inhibitory activity by Li et al. [23], along with computational exploration of the action mechanism, offered important clues for developing anticancer medicines based on EGFR inhibitors. SeNPs provide anticancer, immunomodulatory, and drug delivery effects. NPs with EGFR-targeted components have been shown to be more effective at inhibiting tumor cell growth, survival, metastasis, and angiogenesis [23]. Cancer poses a grave danger to human health and has significant social and economic repercussions. Therefore, the creation of novel anticancer medications is crucial, and the ability of biological NPs to combat specific viruses aids in the creation of new antiviral drugs. This study also investigated antioxidant activity using the DPPH assay and the antiviral activity against the HAV HM175 strain of the hepatitis A virus as a novel use for such biosynthesized NPs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Macroalgal Sampling, Processing and Aqueous Extract Preparation
Macroalga (green algae) U. lactuca was chosen based on the traditional understanding of its biological functions and its year-round availability. The algae were sampled from the Egyptian coast of the Gulf of Suez. Dr. Fekry Ashour Mourad, a researcher at NIOF Egypt, identified the algae. All samples were identified as described previously and according to the methods of Aleem [24], Aleem [25], and Lipkin, and Silva [26] and were confirmed using the Algae Base website [27]. After collection, salts were rinsed under running water and then many times with seawater to remove clinging detritus, related biota, and sand. The U. lactuca was air dried in the shade and then oven dried (Memmert GmbH + Co. KG, Schwabach, Germany) for 3 h at 60 °C. Following fine grinding of the dried samples using a coffee grinder (Brown mill) and storage in plastic bags at room temperature, 10 g of algal powder was combined with 100 mL of deionized water and heated for 30 min while stirring. The supernatant from the boiling extract was utilized as a reducing agent for Na2SeO4 after being collected using a 10,000 rpm centrifuge [28].
2.2. Preparation of Se NPs
Following Kashyap et al. [29], the extract of U. lactuca was combined with a solution of 1 mM Na2SeO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, Inc., St. Louis, MO, USA) to determine the optimal conditions (1:9). After stirring for 72 h in darkness at 25 °C, and when the sodium selenite solution changed color to red, photosynthesized USeNPs were detected using UV spectroscopy (Thermo Scientific Evolution TM 300, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The absorbance was measured at between 200 and 800 nm [30]. Centrifugation of the mixture was conducted at 10,000 rpm for 30 min. After cleaning the NPs with double-distilled water, they were treated with pure ethanol [31]. The final product was baked at 50 °C, stored in an airtight container, and utilized for any characterization study or other objectives that followed [32].
2.3. Characterization of Phycosynthesized SeNPs
2.3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR analysis was conducted using KBr pellets as a test substance at 4 cm−1 resolution and 400–4000 cm−1 range, to show all possible functional groups associated with the produced NPs. The generated peaks were plotted using the X axis as transmittance (percentage) and the Y axis as the wave number (cm−1).
2.3.2. XRD
The phycosynthesized selenium NPs were dried and then subjected to XRD analysis to confirm their crystalline nature and phase composition. This analysis was performed using an XRD-6000 detector (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan), and was performed at 30 kV and 10 mA with 2.2 KW Cu anode radiation, where k = 1.54184. Scherrer’s equation (D = λk/βcosθ) was used to determine the average size of the NPs (D). Here, k was a constant nearly equal 0.9, X-ray wavelength (λ) was 1.54060, the width in radians of the peak caused by the size effect was referred to as β; θ, which was determined by the formula = (θ1 − θ2)π/180, was the diffraction angle of Bragg. In particular, the line width of the (013) reflection in XRD was used to confirm the particle size of the material.
2.3.3. TEM
The size and morphology of the synthesized USeNPs were examined by TEM (JEM-2100, JEOL, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. Deionized water was used in order to dilute the reaction mixture and was sonicated (Branson-Sonifier 250, Branson Ultrasonics Corp., Danbury, CT, USA) for 10 min [33]. The sonicated sample was then placed onto copper grids coated with carbon, which was then vacuum dried for 30 min before electron micrographs were taken of the sample [34].
2.3.4. SEM & EDX
The NP size and form were evaluated using a scanning electron microscope (JSM 6490 LV, JEOL, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Samples were put onto double-sided carbon tape, allowed to air dry, and then photographed at various magnifications. The sizes were measured using various magnifications between 15,000 and 35,000 nm, as well as voltages between 20 and 30 kV for scanning. The same instrument was used to conduct an Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) study of elemental SeNPs between 0 and 12 keV [35].
2.3.5. Zeta Potential (ζ)
A zeta analyzer was used to assess the SeNPs’ effective surface charges at various variables (ZetaPlus, Brookhaven Instruments, Holtsville, NY, USA). To prepare the sample, 25 µg of SeNP samples were diluted ten times in water. The sample was then placed in a sonicator at 20 Hz for 15 min. The mixture was run through a 0.22 µm filter before being used to measure the zeta potential. In order to prevent aggregation, SeNPs were diluted. Measurements were made between −200 and +200 mV [30].
2.4. Cytotoxicity of USeNPs against HepG2
2.4.1. Mammalian Cell Line Propagation and Chemical Use
HepG2 cells, a strain of human liver carcinoma cells, were donated by the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Rockville, MD, USA). Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) supplied fetal bovine serum, MTT, trypan blue dye, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). HEPES buffer solution, RPMI-1640, L-glutamine, 0.25% trypsin-edta, and gentamicin, were obtained from Lonza Group AG (Bornem, Belgium). The cell line was grown in RPMI-1640 media with 10% inactivated fetal calf serum and 50% gentamicin. Incubation was conducted at 37 °C in a humid atmosphere with 5% CO2 and were subcultured 2–3 times weekly.
2.4.2. Anticancer Activity Using the Viability Assay
First, the tumor cell lines were suspended in the medium at 5 × 104 cells/well concentration using Corning 96-well tissue culture plates for anticancer testing. These were incubated for 24 h. Next, USeNPs were placed onto 96-well plates to create 10 concentrations of each chemical (three duplicates). Six wells of controls with media or 0.5% DMSO were conducted as a control for each 96-well plate. After 24 h of incubation, the MTT test was utilized to determine how many viable cells were present. Briefly, 100 fresh culture media for 96-well plates were substituted for the RPMI 1640 medium in the absence of phenol red, and 10 of 12-mM MTT (5 mg of MTT in 1 mL of PBS) as a stock solution were placed in each well, including the controls (untreated). Next, the 96-well plates were incubated for a further 4 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2, then 50 µL of DMSO was added to each well, mixed carefully with a pipette, then after an 85 µL aliquot of the media had been taken out of each well, the plate was incubated at 37 °C for 10 min. The number of viable cells was then calculated using the formula [(ODt/ODc)] × 100%. ODt was the mean of wells treated with USeNPs’ optical density, and ODc was the mean of untreated cells’ optical density. This was done by measuring the optical density at 590 nm with a microplate reader (SunRise, Tecan Group Ltd., Männedorf, Switzerland). The correlation between surviving cells and drug concentration estimated the tumor cell line’s survival curve of each type after treatment with USeNPs. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) was computed using Graphpad Prism software (San Diego, CA, USA) using a dose-response curve for each amount graphic plot [36].
2.4.3. Microscopic Observation of HepG2 Cell Line Treated with the USeNPs
This experiment was carried out in accordance with the cytotoxic activity protocol. Following the completion of the treatment at the tested concentrations, the plates were inverted to remove the medium. The wells were then washed three times with 300 µL of phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.2), and using 10% formalin, the cells were fixed to the plate for 15 min at room temperature. Following fixation, these cells were stained for 20 min using 100 µL 0.25% crystal violet, and then the excess stain was removed from the plates with deionized water and the plates were dried. An Olympus CKX41 (Olympus Corp., Tokyo, Japan) inverted microscope equipped with a digital microscopy camera was used to image the changes in comparison to control cells at a magnification of 200×.
2.4.4. Evaluation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Enzyme Activity
USeNPs concentrations and controls were tested twice. This began by thawing 5× Kinase Buffer 1, ATP, and PTK substrate Poly (Glu:Tyr 4:1) (10 mg/mL), then the following was added to each well: 25 µL master mixture (6 µL 5× Kinase Buffer 1 + 1 µL ATP (500 M) + 1 µL PTK substrate Poly (Glu:Tyr 4:1) (10 mg/mL) + 17 µL water), 5 µL of USeNPs solution (as an inhibiting factor), and 5 µL of the same solution without USeNPs for the “Positive Control” and “Blank” wells. A mix of 600 µL of 5× Kinase Buffer 1 with 2400 µL of water was used to make 3 mL of 1× Kinase Buffer 1. 20 µL of 1× Kinase Buffer 1 should be added to the “Blank” wells to fill them. The thawing of the EGFR enzyme should be conducted on ice, and then the tube spun to recover its entire contents. The reaction began when 20 µL of diluted EGFR enzyme was added to the “Positive Control” and “USeNPs Control” wells. Kinase-Glo Max reagent was thawed at 30 °C for 40 min. Following the 40 min reaction, each well received 50 µL of Kinase-Glo Max reagent. Aluminum foil was used to cover the plate, and it was left at room temperature for 15 min before luminescence was measured with a microplate reader [37].
2.5. Antiviral Activity Test of USeNPs
2.5.1. Cytotoxicity Evaluation against Vero Cell Line
These cells were obtained from African green monkey kidneys from the ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). Vero cells were grown in DMEM, including 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% L-glutamine, HEPES buffer, and 50 µg/mL gentamicin. All cells were subcultured twice a week and kept at 37 °C in humidified media with 5% CO2 [38]. For the cytotoxicity experiment, the tested cells were placed in 96-well plates at a cell density of 2 × 105 cells per ml in 100 L of growth medium. After 24 h, a new medium containing different amounts of USeNPs was introduced. Confluent cell monolayers were distributed to 96-well microtiter plates with a flat bottom (Falcon, Jersey, NJ, USA) in serial two-fold dilutions of USeNPs starting at 3000 µg/mL and decreasing to 2 µg/mL using a multichannel pipette. Then, incubation for the microtiter plates was conducted for 48 h at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. For USeNPs’ concentrations, three wells were used. Control cells were grown with and without DMSO or USeNPs. The experiment was found to be unaffected by the minimal aliquot of DMSO (≤0.1%) contained in each well. Following the completion of the incubation period, the viable cell yield was determined using an MTT colorimetric [36,39]. The survival curve of the Vero cell line in the treatment with the specified drug was obtained by plotting the relationship between surviving cells and the tested compound concentration. Using the Graphpad Prism software, the dose-response curve for each concentration was plotted to obtain the 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50), which is the dosage needed to produce lethal effects in 50% of intact cells. Each compound’s maximum non-toxic concentration was also determined for future biological analyses.
2.5.2. Virus Propagation and Antiviral Activity Evaluation
The cytopathogenic strain of hepatitis A virus (HAV HM175) was propagated and tested using Vero cells as a control [40]. The Spearman–Karber method was used to calculate the tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) using eight wells for each concentration and 20 µL of inoculum in each well to numerate the infectious viruses [41]. A cytopathic effect inhibition assay was conducted for antiviral screening at the Regional Center for Mycology and Biotechnology (RCMB, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt). The MTT technique demonstrated the precise suppression of a biological process, specifically the cytopathic effect in sensitive mammalian cells [42,43]. Briefly, 96-well microtiter plates with monolayers of Vero cells (2 × 105 cells/mL) attached to the bottom of the wells were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. After being rinsed with fresh DMEM and inoculated with doses of the virus equal to 104 µL, the cultures treated with the USeNPs were concentrated on fresh maintenance medium and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C. Infection controls and an untreated Vero cell control were generated without USeNPs. Six wells were used for each concentration of the substance under investigation. Antiviral activity was estimated by comparing the inhibition of the virus effect with the control, and the level of USeNPs protection provided to the cells was also estimated. Each of the three independent experiments that were evaluated included four replicates of each treatment. Amantadine was used as a reference drug. Following the incubation period, MTT assay was used to estimate the viability of the cells as was previously discussed in the cytotoxicity section [36]. The rate of the viral inhibition was estimated as follows: [(A − B)/(C − B)] Ã 100%, where A, B, and C indicate the absorbance of the USeNPs with virus-infected cells, the virus control absorbance, and the cell control absorbance, respectively.
2.6. Determination DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
With some modifications, the USeNPs activity for free radical scavenging was estimated using the DPPH assay [44]. A 0.2 Mm 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picryl hydrazyl solution was prepared in methanol with a concentration of 0.0078 g/100 mL as a radical solution, then 1 mL of this was added to 1 mL of various concentrations of USeNPs solution with a ratio of 1:1 V/V. After 30 min of incubation at room temperature in darkness, the absorbance at 517 nm was measured using a spectrophotometer. To create a standard curve, ascorbic acid solutions ranging from 5 to 200 µg/mL were used as standards. DPPH radical scavenging activity (DPPHrsa) was expressed as mg ascorbic acid equivalents (AAE)/g-dried sample and was estimated using this equation:
DPPHrsa (% inhibition) = ((〖Abs〗_Control − 〖Abs〗_Sample))/〖Abs〗_Control × 100
The control, containing all reagents except USeNPs, and all determinations were conducted in triplicate and the average values were tabulated.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FT Characterization of Algal Extracts
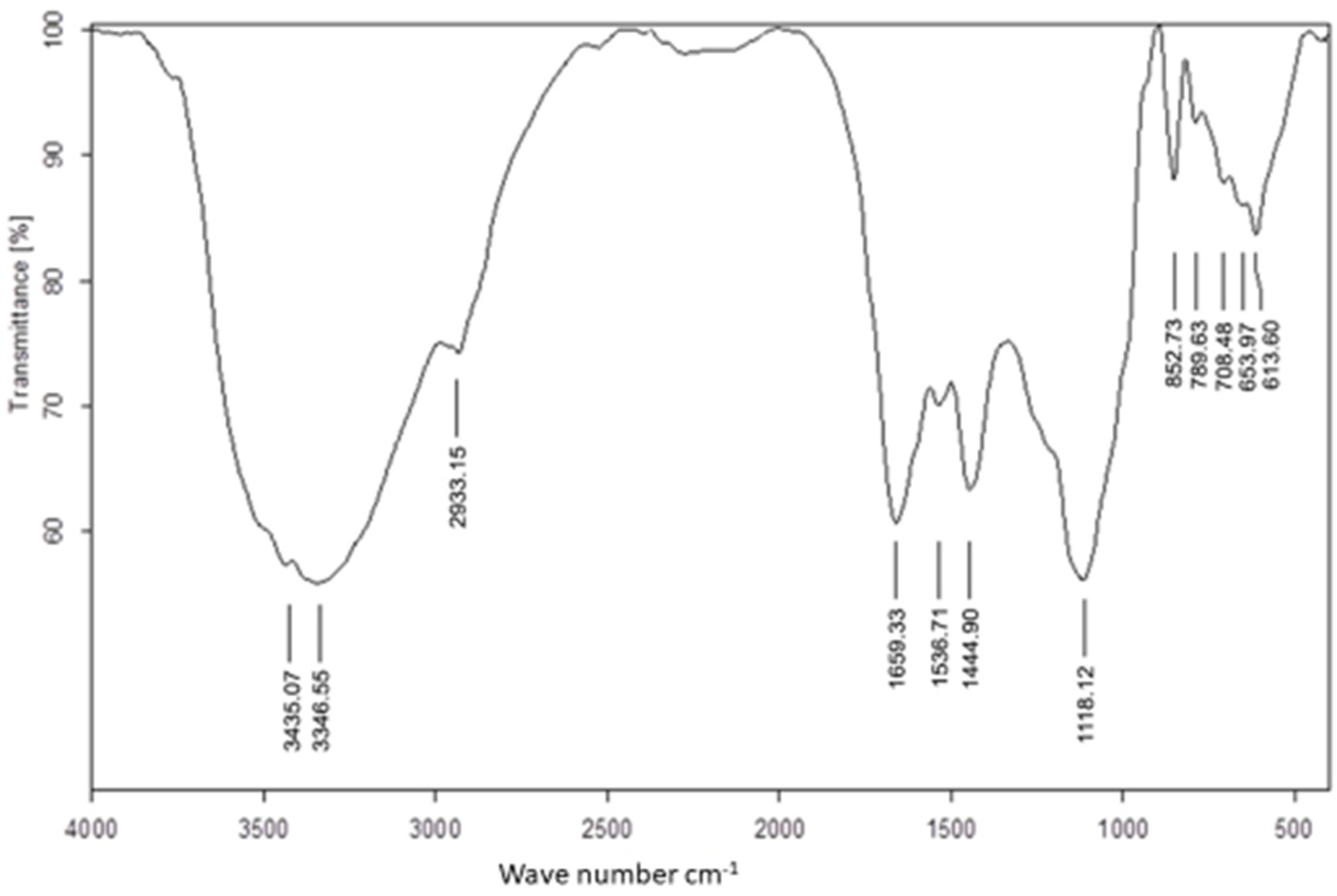
The FTIR spectrum (Figure 1) determined the active components’ functional groups according to the values of the infrared absorption bands. The absorption peaks at 3346.5464 cm−1 and 3435.0658 cm−1 resulted from -OH stretching of the aromatic rings, and the presence of alcohol and phenol groups [45]. A peak at 2933.1506 cm−1 represented the stretching vibration of C-H of alkenes and ether-me (isothiocyanate) [46]. There were amide I bands at 1659.3297 cm−1 (C=O stretch of the ester group), amide II bands at 1536.7124 cm−1 (N-H bending), 1444.9020 cm−1 (C-H asymmetric bending in CH2 and CH3 groups), and bands at 1118.1212 cm−1 and 852.7263 cm−1 resulting from aliphatic amines and carboxylic acids, respectively, in the lower wavelength range [47]. The absorption bands at 613.5960–789.6294 cm−1 (Phaeophyta and Chlorophyta) showed stretching of C=S, indicating the presence of sulfides in the tested algae [48]. Based on these findings, U. lactuca was discovered to contain a wide range of phytochemicals, including phenol, alcohol, lipid, proteins, fatty acids, and other anticancer and antiviral compounds. Furthermore, these phytochemicals may aid in the conversion of sodium selenite to SeNPs [15,49].
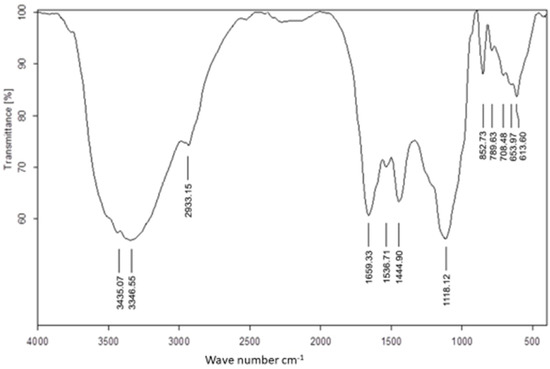
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of Ulva lactuca aqueous extract.
3.2. Nanoparticle Characterization
The USeNPs results were validated using seven different characterization techniques, including UV-Vis spectra, FTIR, XRD, TEM scanning, SEM scanning, EDX, and zeta potential.
3.2.1. UseNPs’ FTIR Analysis
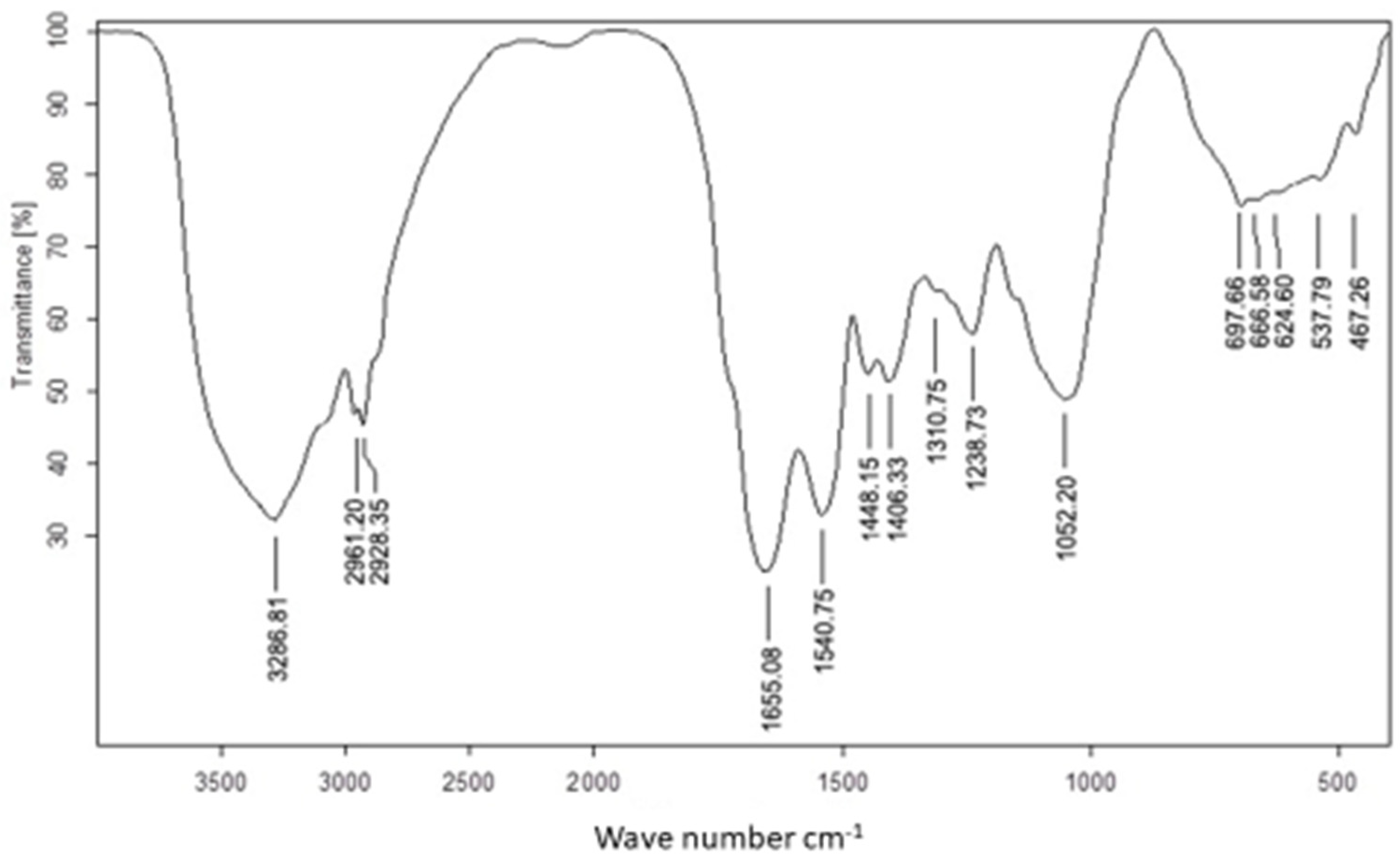
The use of FTIR for UseNPs can help identify potential active components which are responsible for the reduction of selenium ions and NP formation or those involved in stabilizing the NPs produced. The FTIR spectrum was recorded in the wavelength region from 613.5960 to 3435.0658 cm−1 (Figure 2), showing an absorption band at approximately 3435.0658 cm−1, which represented the hydroxyl group stretching vibration and indicated the presence of a hydroxyl functional group [50]. The highest absorption rate observed was at the 3346.5464 band. The shift in the spectral profile of U. lactuca extract to 3286.8142 cm−1 could be attributed to interactions between functional groups responsible for this band and USeNPs [51]. Similarly, the shift in the broad hydroxyl band could be explained by interactions between hydroxyl groups of polyphenols or sugars in the U. lactuca extract and the resulting USeNPs [50]. The occurrence of a unique peak at 2933.1506 cm−1, which represented the C-H alkenes stretching vibration, could indicate the involvement of hydrocarbon chains in the stabilization of USeNPs. These peaks also demonstrated the presence of a biopolymer, which was likely derived from algal cell walls and was linked to the SeNPs [52]. The bands at 1659.3297 cm−1 and 1536.7124 cm−1 represented the stretching vibration of the (NH) C=O group (Amide band II) for the N-H bending of the amines 1ry and 2ry, respectively, may suggest the involvement of amide groups (which could be from amino acids, peptides, or proteins). The band at 1444.9020 cm−1 was marked by N-H stretching vibrations found in protein amide linkages. Previous studies have indicated that these functional groups play a role in the stability/capping of SeNPs [53,54]. According to the literature, another absorption band at 1118.1212 cm−1 shows the superposition of in-plane C-H bending and C-N stretching vibrations of aliphatic amines, as well as the distinctive Se-O stretching vibration [55]. Some bending vibrations of the Se-O bond are highlighted from 852.7263 to 613.5960 cm−1.
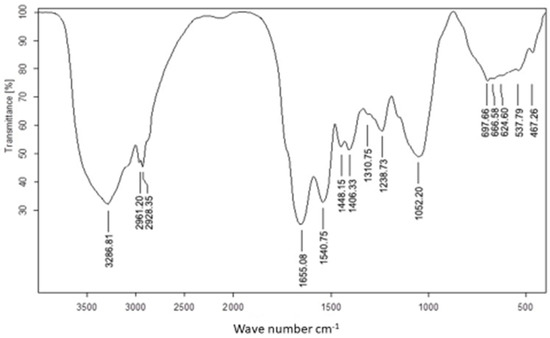
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of Ulva lactuca mediated selenium nanoparticles.
3.2.2. SPR Characteristic
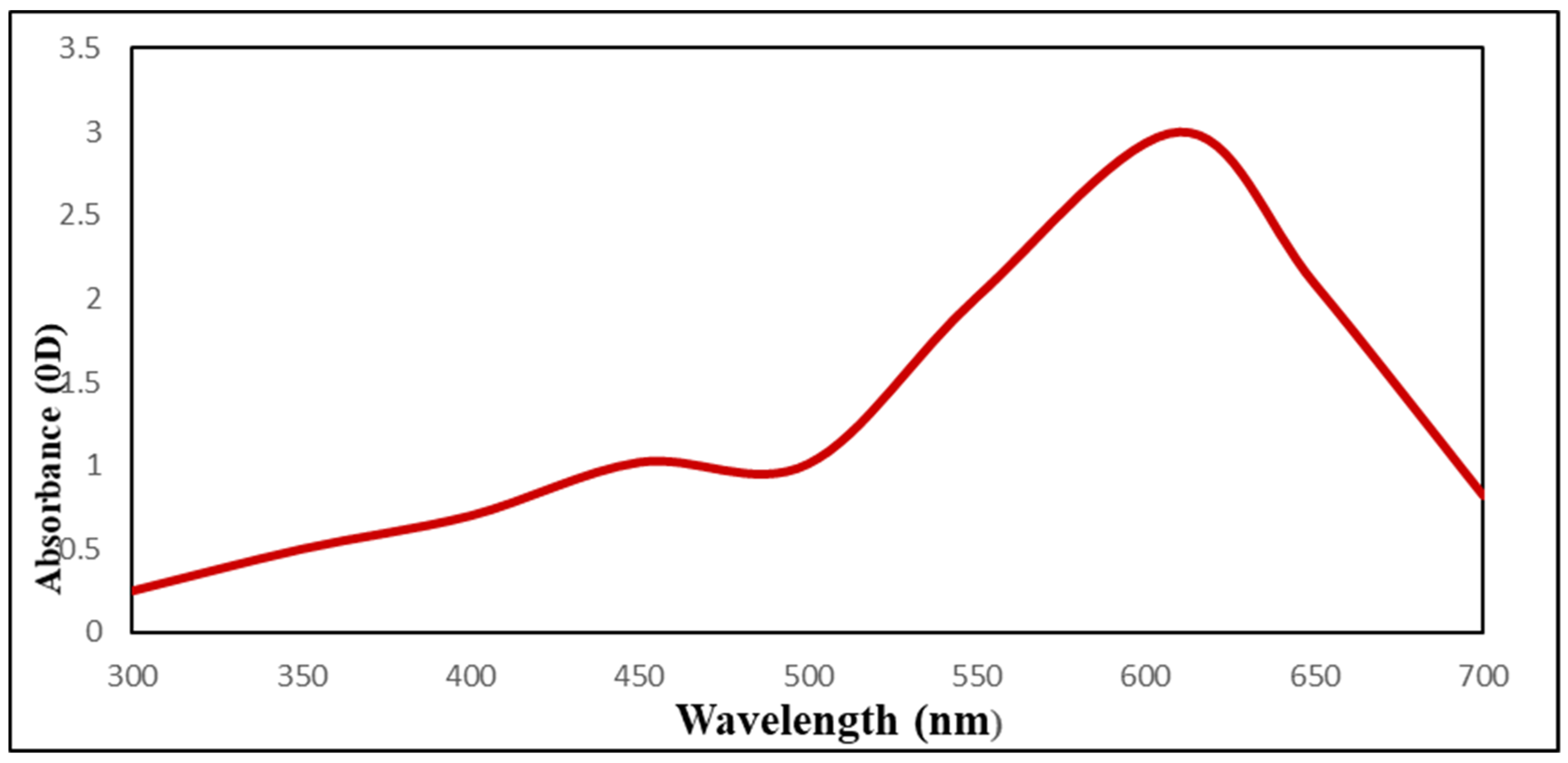
UV–Vis spectra studies confirmed that sodium selenite color changed from colorless to red (SeNPs) and that this color change was caused by SeNPs biosynthesis (Figure 3). As USeNPs increased, absorbance increased steadily from 2.6 to 3. The largest peak, however, occurred at 610 nm.
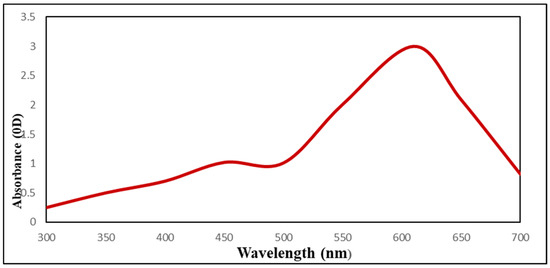
Figure 3.
The UV-Visible spectrum of Ulva lactuca mediated selenium nanoparticles.
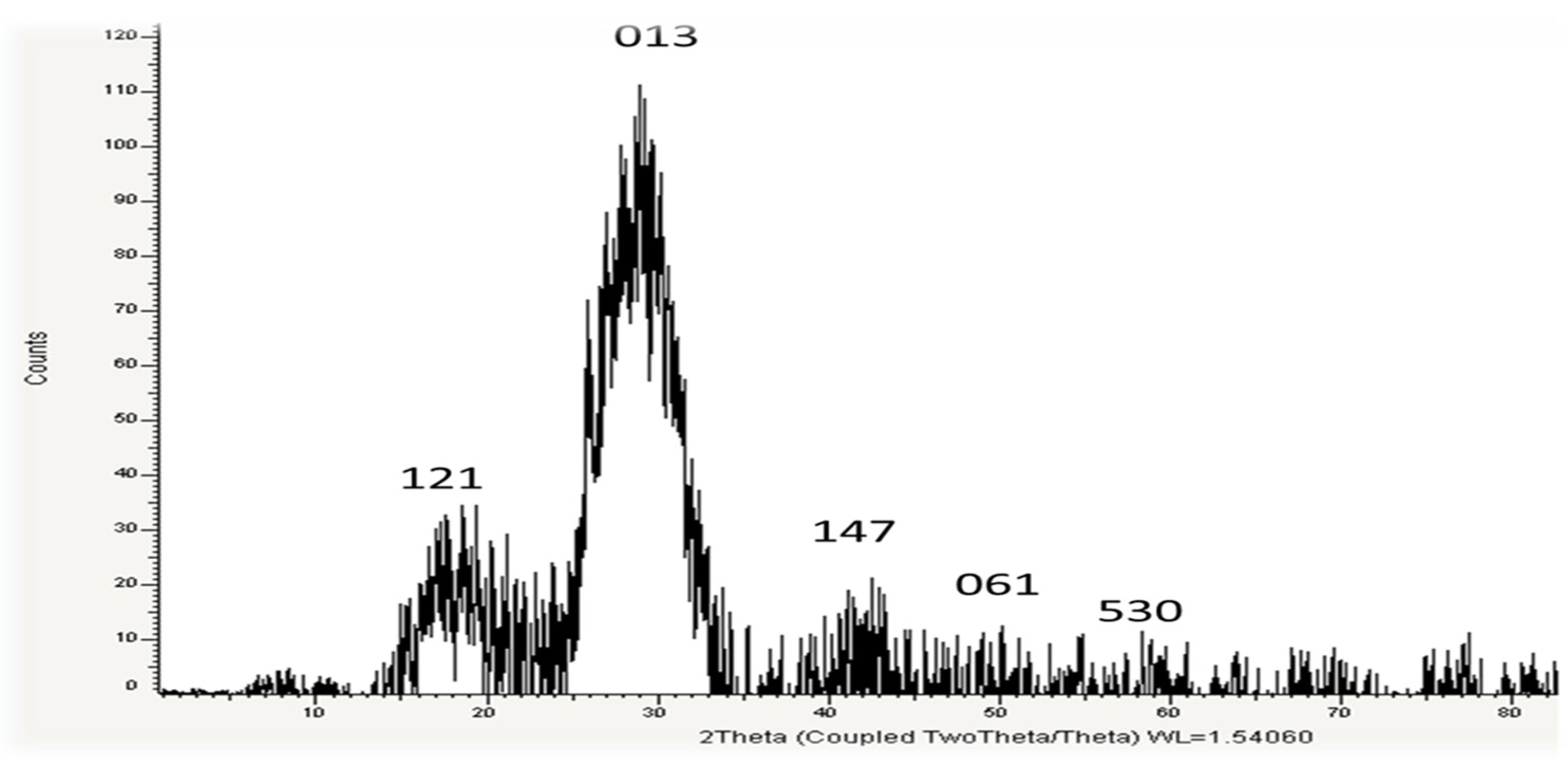
3.2.3. XRD
USeNPs phase composition and crystal structure were identified using the XRD techniques depicted in Figure 4. The sample’s XRD pattern indicates that it is nanocrystalline and closely resembles typical selenium powder, implying that selenium particles were formed. The formed NPs are selenium because at the 2θ angle in the range of 14–52.4° there is a specific diffraction peak, which is essentially consistent with the diffraction peak of JCPDS card number 65-1290. The pattern’s diffraction peak is very narrow, which is an indication that the phycosynthesized USeNPs are very small, crystalline, and have a poor amorphous character. The obtained XRD patterns showed the main peaks characteristic of crystalline SeNPs at the values of 19.01°, 30.8°, 43.5°, 28.5°, 30°, 39.42°, 50.069°, and 58.923° (Figure 4), respectively, corresponding to the crystal planes (121), (013), (147), (061), and (530). Scherrer’s equation calculated the average crystalline size of biogenic selenium nanostructures to be approximately 13.26 nm. Background noise was produced by the biological approach of SeNPs, which could result from the presence of additional bioactive compounds within the U. lactuca extract (Figure 4). The XRD pattern of the powder shows that post-annealing is not required to achieve the desired crystalline phase [30].
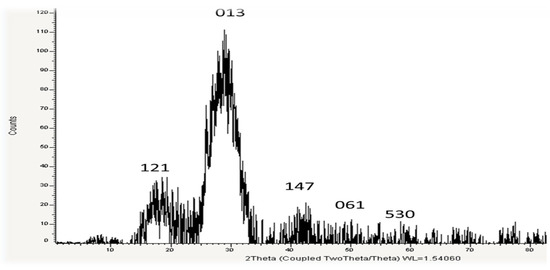
Figure 4.
XRD spectrum of UseNPs.
3.2.4. TEM Imaging
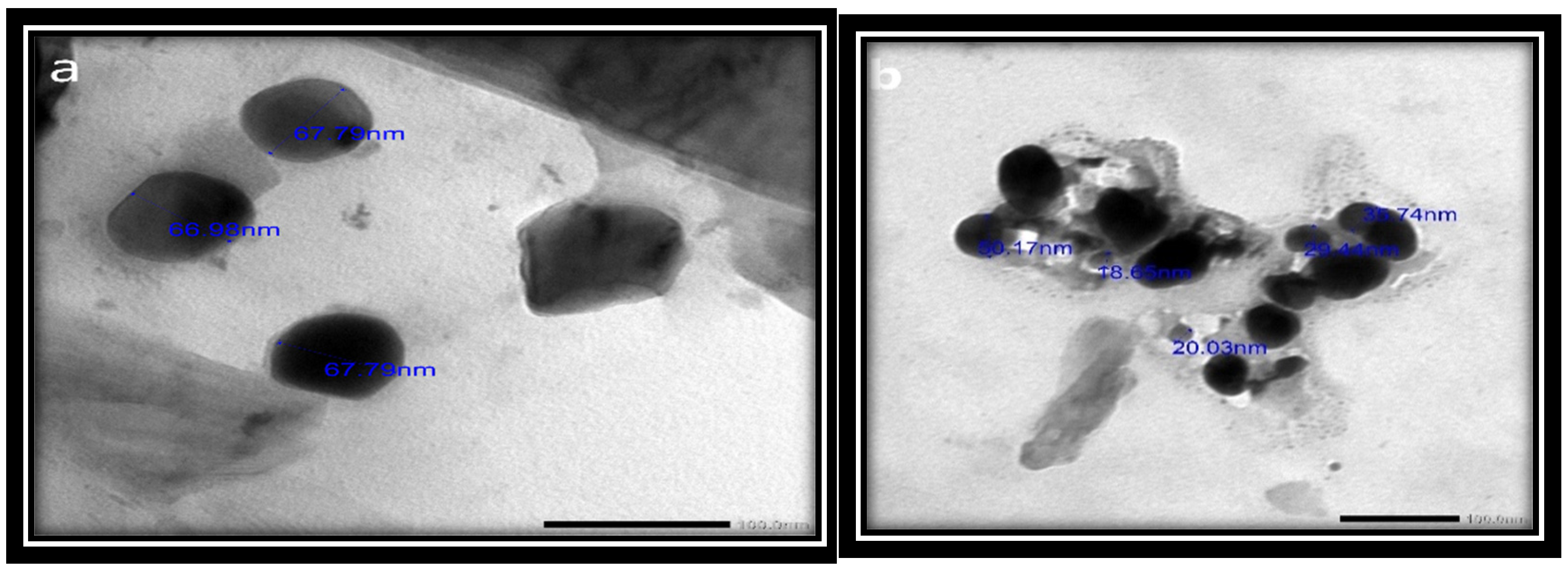
The physical and chemical properties of the synthesized SeNPs, such as their crystalline structure, shape, size dispersion, and surface condition, have been established to determine their suitability [56]. The results revealed that the synthesized SeNPs ranged in size from 18.65 to 67.79 nm and had smooth spherical and semispherical shapes (Figure 5a,b). These results agree with those of Vikneshan et al. [15] and Basant [30], who synthesized SeNPs from U. lactuca and Spirulina platensis extracts, respectively. Using TEM, they discovered that the morphology of SeNPs was smooth, spherical or ball-shaped, and uniformly distributed.
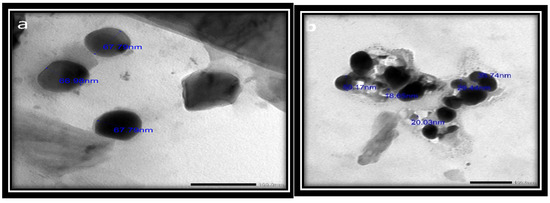
Figure 5.
(a,b) TEM photographs of USeNPS (100 nm).
3.2.5. SEM Imaging
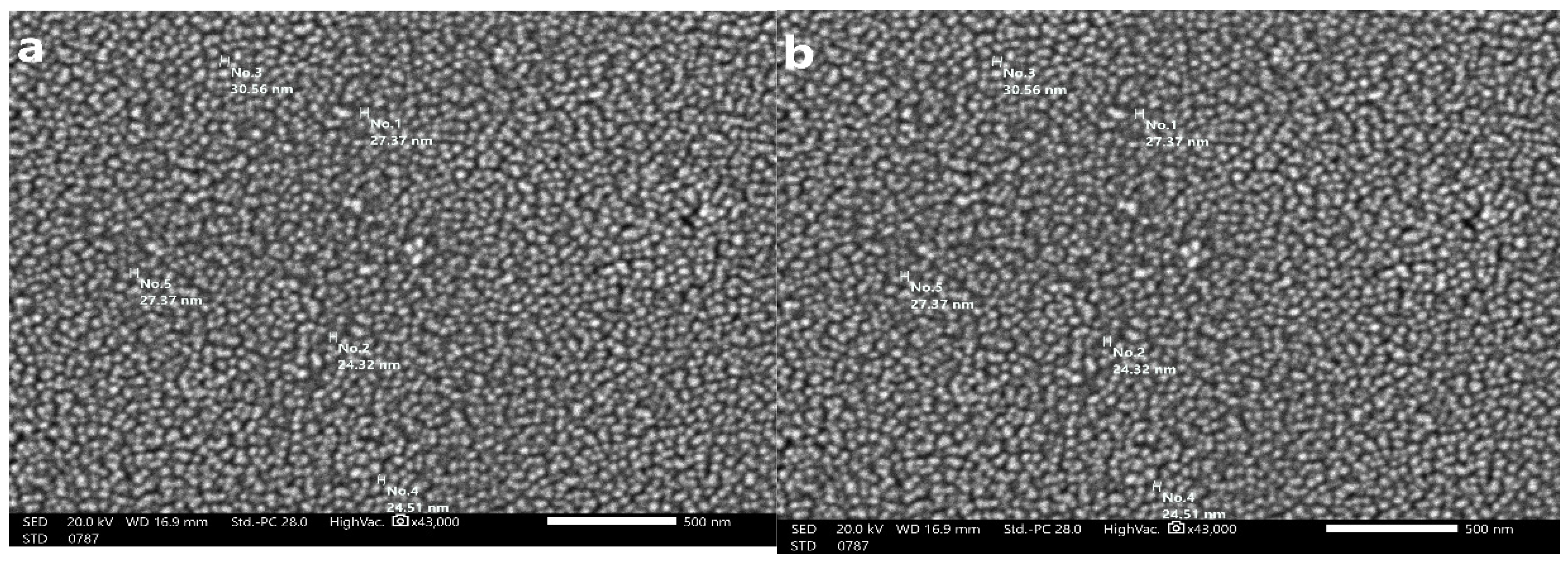
The size of the SeNPs produced by U. lactuca is depicted in Figure 6. The SEM images of the SeNPs illustrated that they had a smooth surface, were oval to spherical in shape, and ranged in size from 24.32 to 30.56 nm. The size-distribution analysis was conducted using the dynamic light scattering approach, which correlates with SEM analysis.
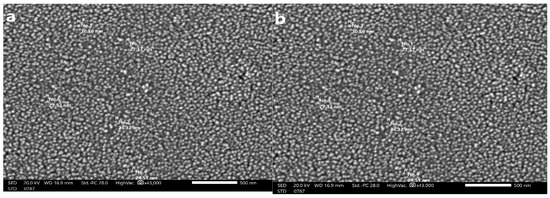
Figure 6.
SEM photographs of USeNPS (500 nm) (a,b) showing different particle sizes.
3.2.6. EDX
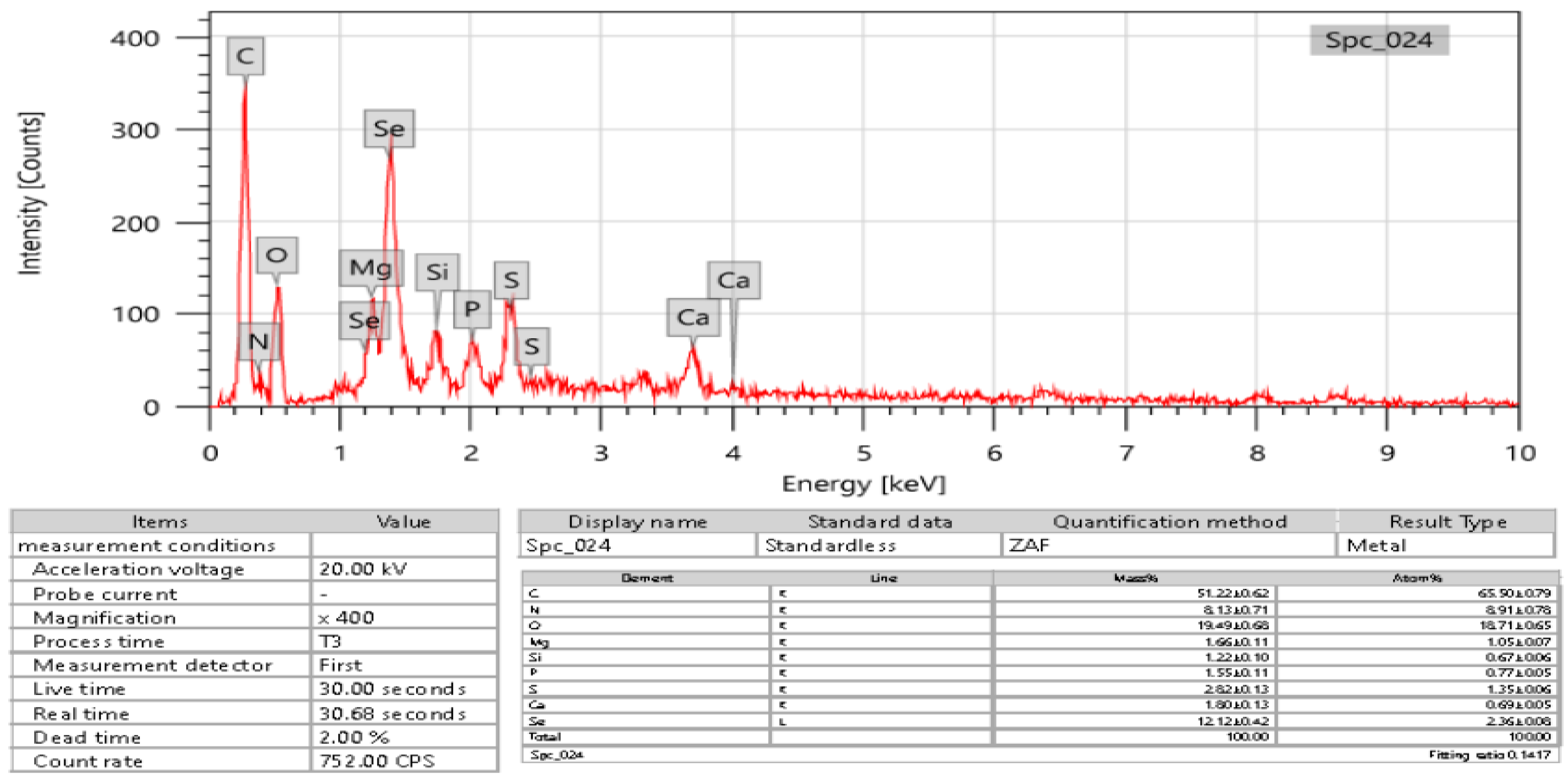
EDX was used to detect selenium in the elemental composition analysis. According to the results, the formed SeNPs had 2.36 ± 0.8 atomic percent and 12.12 ± 0.42 mass percent (Figure 7). This study discovered the presence of selenium-containing nanostructures alongside other EDX peaks, including C, N, P, S, Si, Mg, Ca, and O, with 51.22 ± 0.62, 8.13 ± 0.71, 1.55 ± 0.11, 2.82 ± 0.13, 1.22 ± 0.10, 1.66 ± 0.11, 1.80 ± 0.13, and 19.49 ± 0.68 mass percent, respectively, and 65.50 ± 0.79, 8.91 ± 0.78, 0.77 ± 0.05, 1.35 ± 0.06, 1.05 ± 0.07, 0.69 ± 0.05, and 18.71 ± 0.65 through XRD analysis, confirming the production of SeNPs.
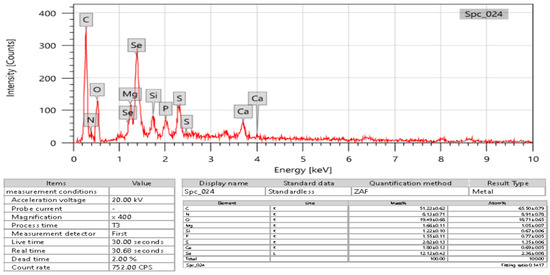
Figure 7.
EDX analysis of USeNPs.
3.2.7. Zeta Potential (ζ)
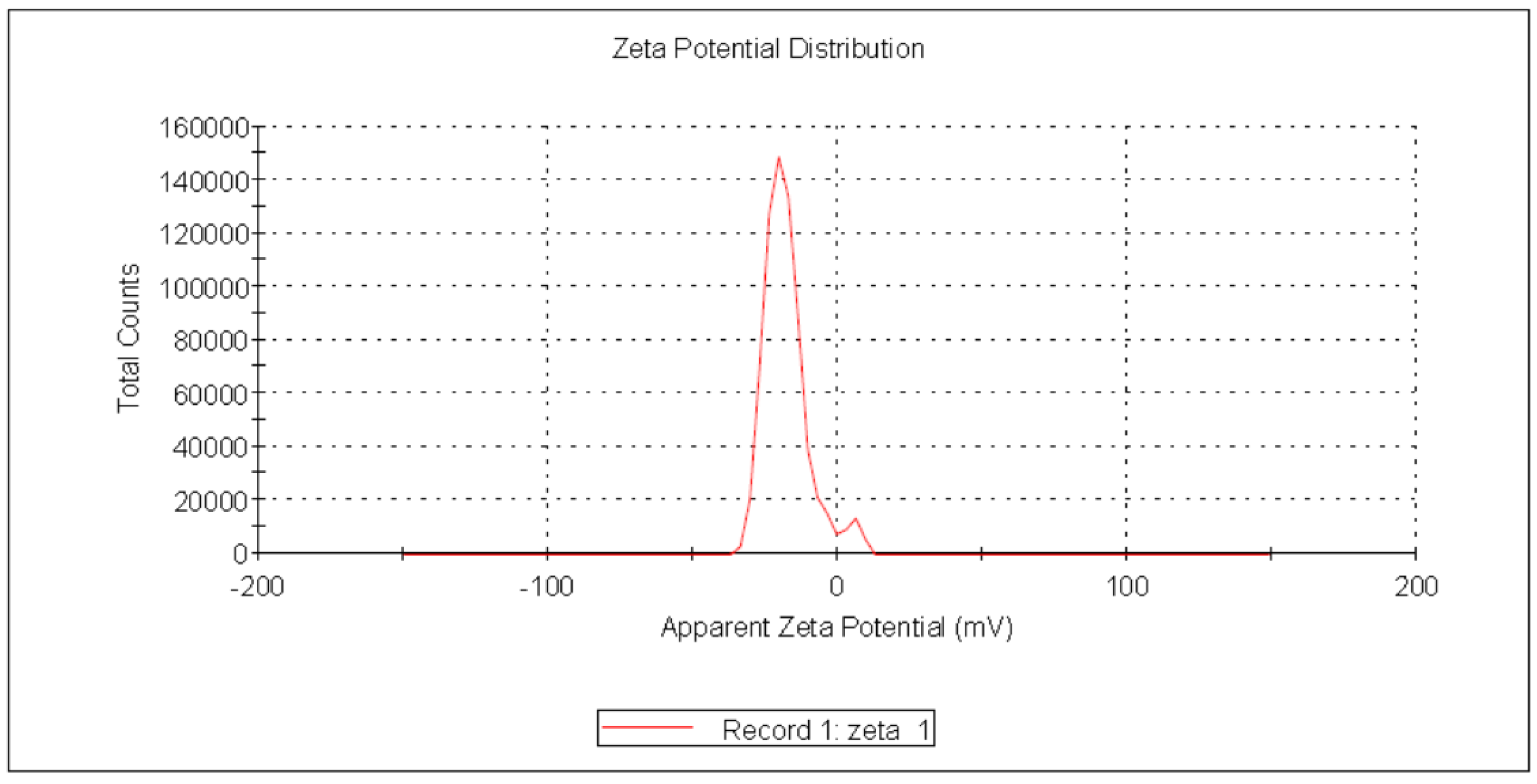
Zeta potential (ζ) reflects an estimate of the electric double layer formed in the solution by the surrounding ions rather than the actual charge on each molecule. Due to inter-particle electrostatic repulsion, NPs with values ranging from +30 mV to −30 mV exhibit high degrees of stability [57]. The negative charge of the produced USeNPs was validated, indicating that the SeNPs were more stable without aggregation. In the current study, Figure 8 shows that the zeta potential was charged with −19.0 ± 6.17 mV, the peak contained 94.9% of the area, and the zeta deviation was 4.38 ± 3.29 mV, with 0.0229 mS/cm conductivity.
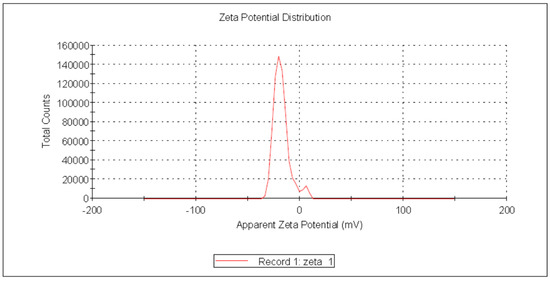
Figure 8.
Zeta potential of the USeNPs.
3.3. USeNPs Cytotoxicity
3.3.1. USeNPs Cytotoxic Activities against Normal and Cancer Cell Lines
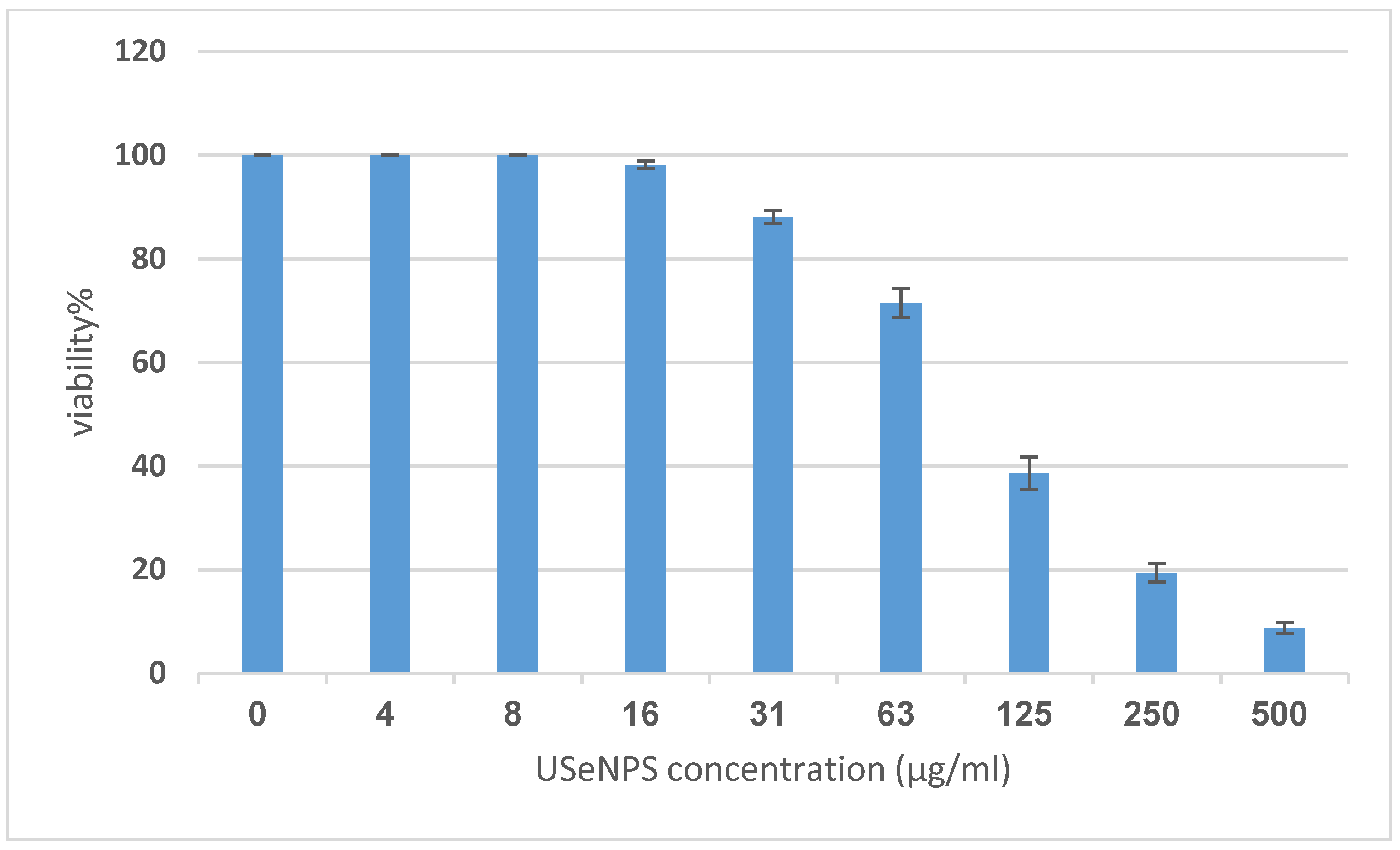
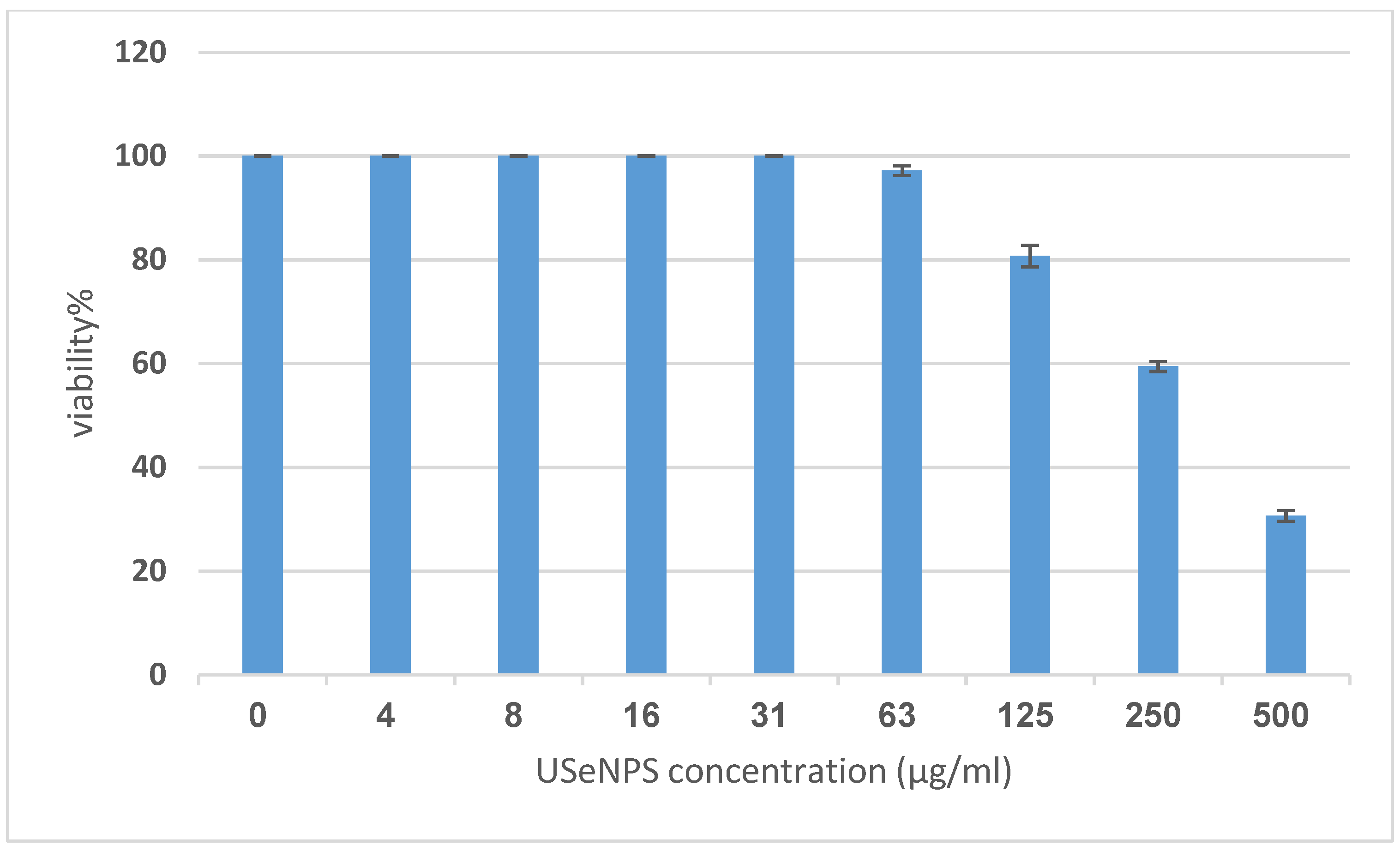
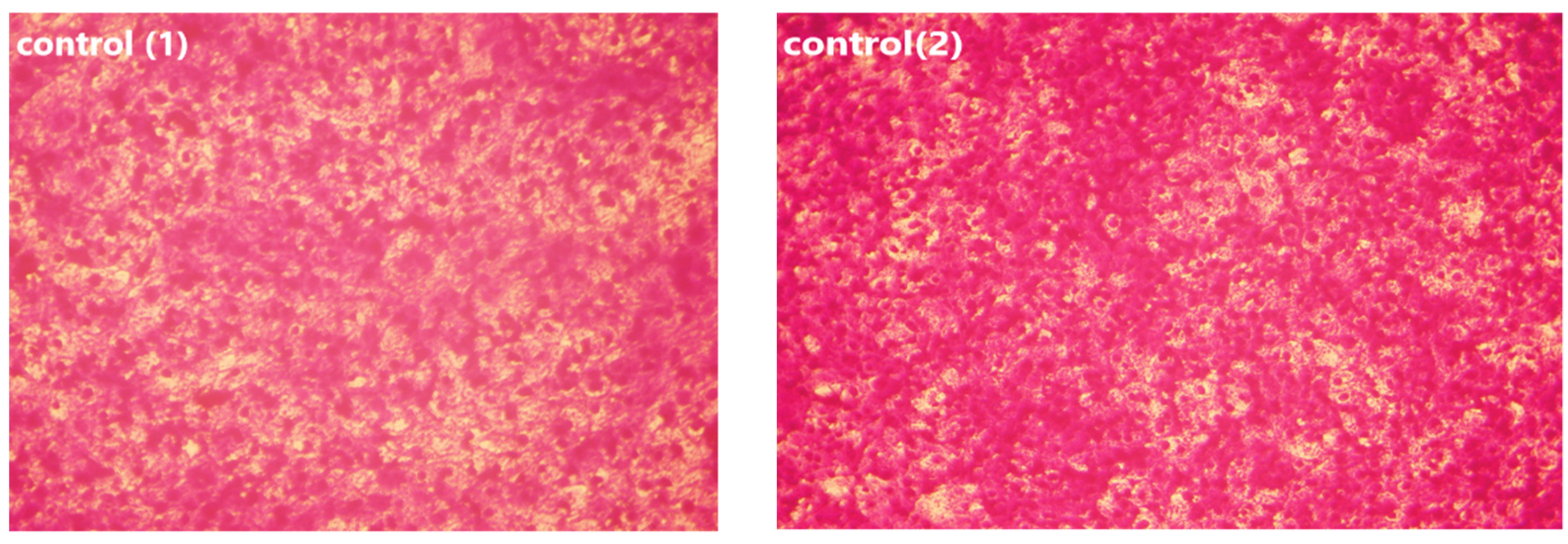
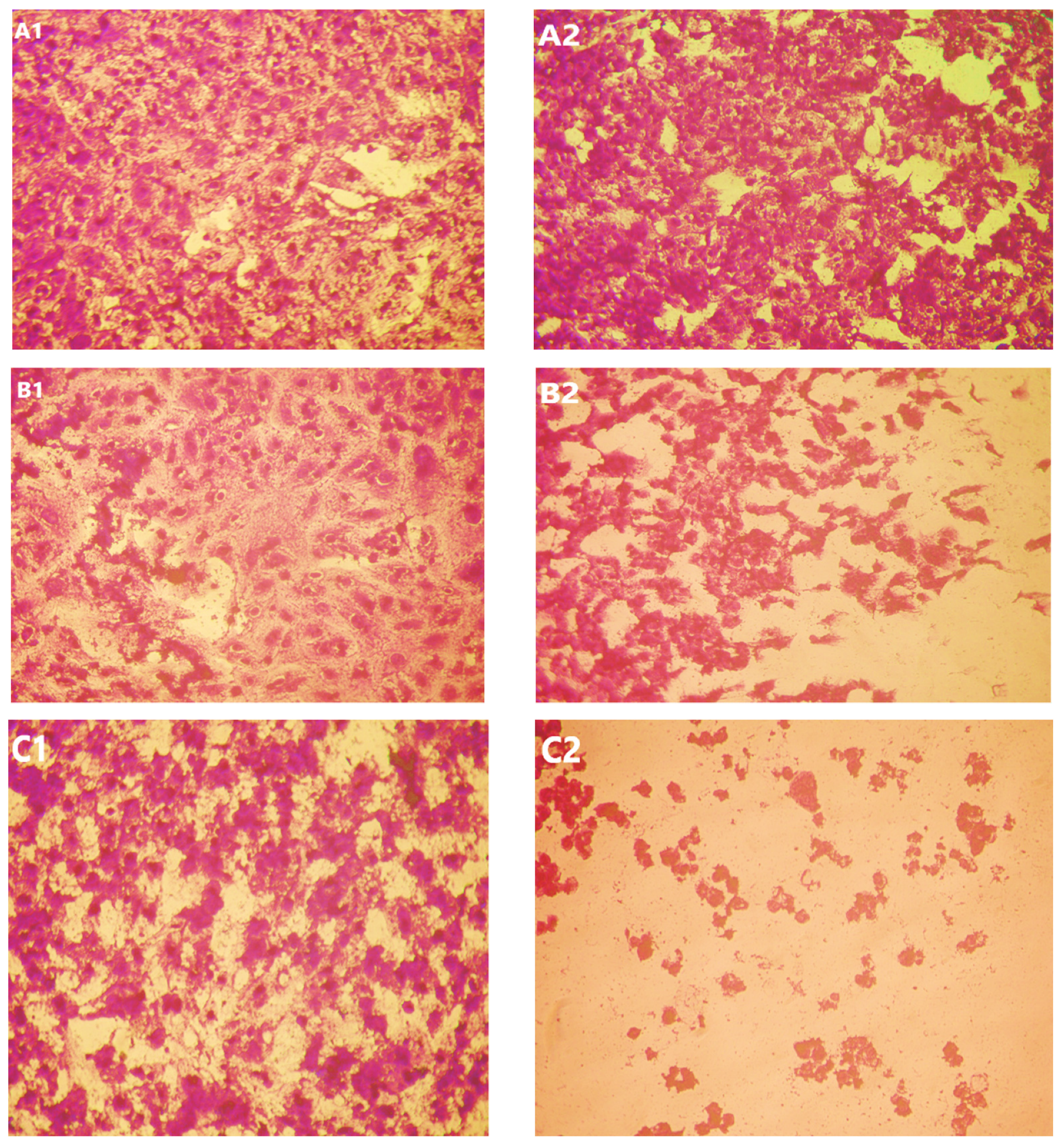
Vero and HepG2 cell lines were treated with varying doses of USeNPs (3.9–500 µg/mL), and the cytotoxicity (illustrated in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11: control1,2, A1,2, B1,2 and C1,2) occurred in a concentration-dependent manner, with CC50 = 331.76 ± 4.79 µg/mL, and IC50 = 103.36 ± 2.93 µg/mL, respectively. Preliminary clinical trial findings indicated that for its anticancer efficacy, dosage and selenium forms are essential factors [14]. All examined concentrations exhibited cytotoxic activity, except for 3.9 and 7.8 µg/mL, which exhibited 100% cell viability and 0% inhibition in both cell lines. At concentrations of 15.6 and 31.25 µg/mL, an inhibitory effect on cancer cells was observed, with inhibition rates of 1.85% and 11.96% seen, respectively. Yet they do not have any toxic effects on normal cells, which confirms the safety of such photosynthesized NPs. This is because along with the results from the remainder of the tested concentrations, which confirm the safety of these NPs, the viability percentages were 97.18 ± 0.94, 80.72 ± 2.06, 59.41 ± 3.67, and 30.64 ± 2.82% for the Vero cell line, and 71.49 ± 2.75, 38.62 ± 3.14, 19.43 ± 1.79, and 8.75 ± 1.03% for the HepG2 cell line, at concentrations of 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 µg/mL, respectively, showing improved cytotoxicity of USeNPs against HepG2 cells. These findings agreed with Abdulsalam et al. [58] who found that selenium NPs induced significant cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells at concentrations ranging from 10 to 50 µg/mL.
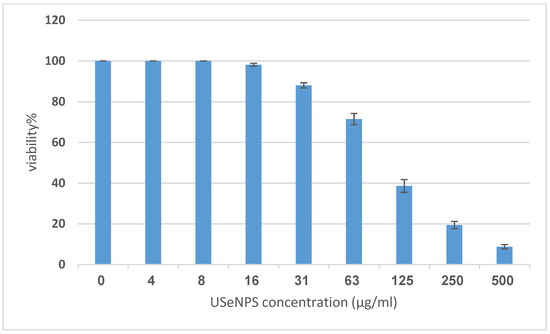
Figure 9.
The cytotoxicity of USeNPS against HepG2 with 50% cell cytotoxic concentration IC50 = 103.36 ± 2.93 µg/mL.
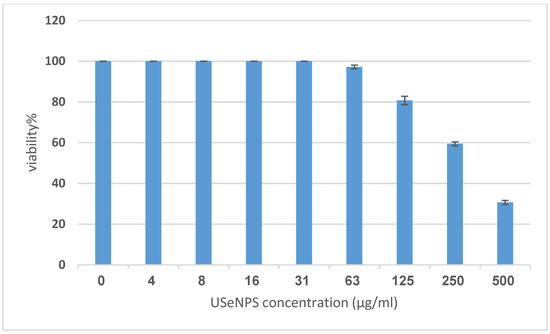
Figure 10.
The cytotoxicity of USeNPS against mammalian cells from African green monkey kidney (Vero) with 50% cell cytotoxic concentration (CC50) = 331.76 ± 4.79 µg/mL.
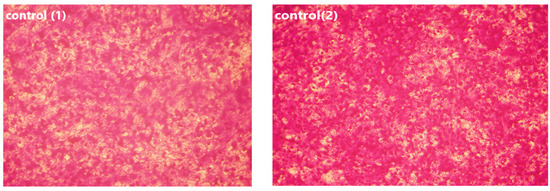
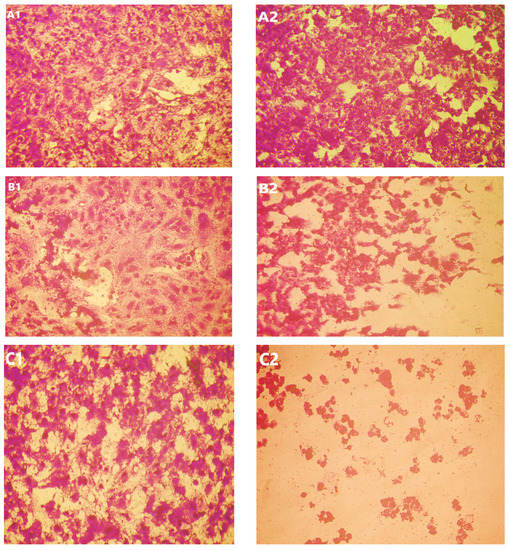
Figure 11.
Effect of USeNPS on normal Vero cell line (control1,A1,B1,C1) and HepG2 cell line (control2,A2,B2,C2). (A1,A2) at concentration 125 µg/mL, (B1,B2) at concentration 250 µg/mL and (C1,C2) at concentration 500 µg/mL.
3.3.2. Mechanism of USeNPs Cytotoxicity by EGFR Inhibition Evaluation
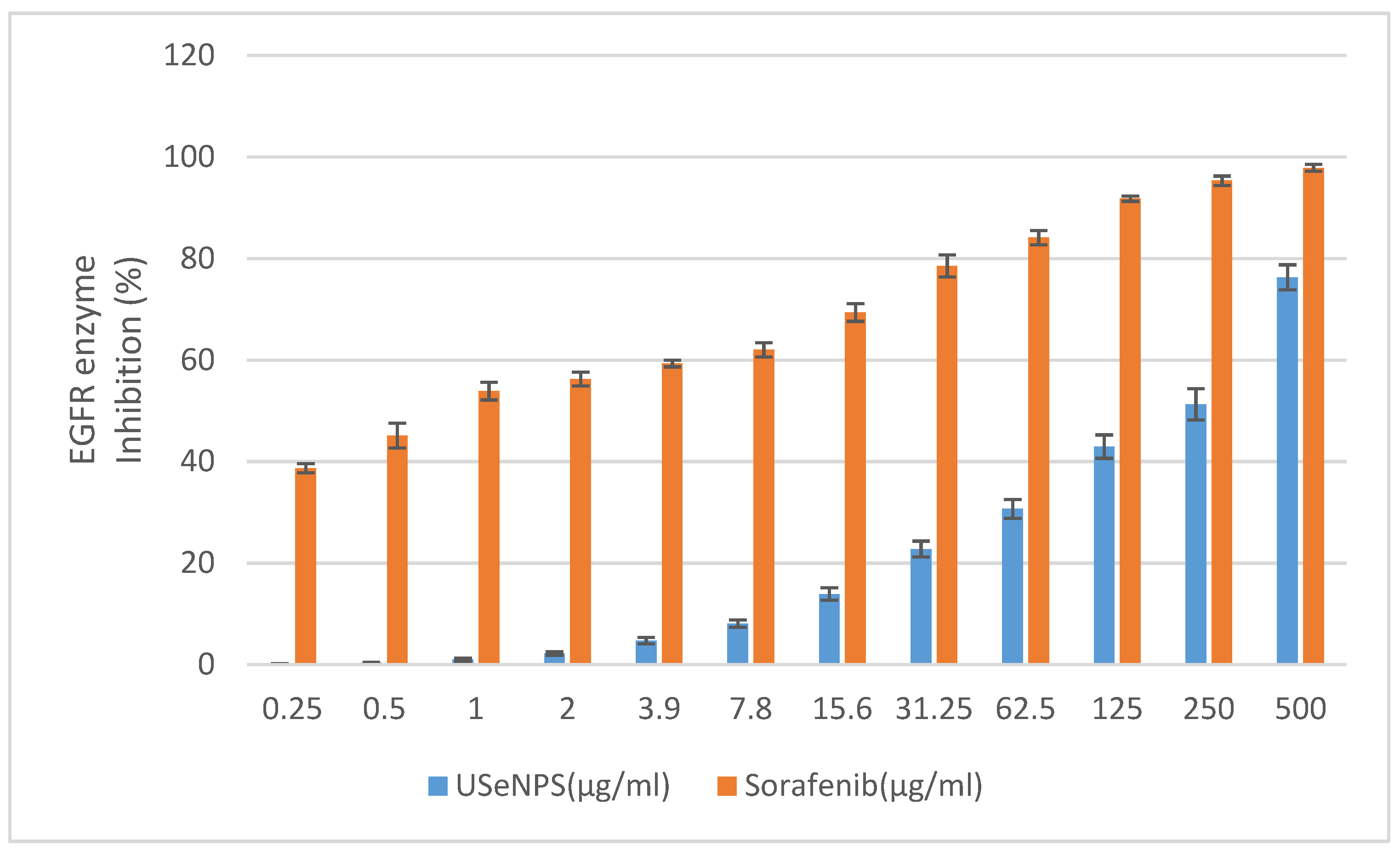
EGFR is an epidermal growth factor family member cell surface receptor, and was the first receptor tyrosine kinase identified, and the first one linked to cancer [59]. Several human cancers are associated with hyperexpression and/or hyperactivation of EGFR kinase, so searching for anticancer therapeutics targeting EGFR has become very important [37]. Investigation of USeNPs inhibitory effects on EGFR kinase enzyme was the aim of this study and used Sorafenib as a reference drug. Here, these nanoparticles were found to have inhibited HepG2 by inducing the degradation of EGFR through the inhibition of the EGFR kinase enzyme. These findings agree with those of Kim et al. [60] who found promising results for the cytotoxicity of Saccharina japonica extract against stemness of glioma stem cells by degrading EGFR variant III. Figure 12 illustrates that USeNPs has an EGFR enzyme inhibitory effect at all the tested concentrations (0.25–500 µg/mL) in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50 = 230.79 ± 3.47 µg/mL, and IC50 = 0.76 ± 0.18 µg/mL for USeNPs and Sorafenib, respectively, but does not exceed the reference drug at any concentration. Concentrations of 250 and 500 µg/mL have a strong inhibitory effect on the EGFR kinase enzyme with enzyme activity inhibition percentages of at least 50% (51.28 ± 3.06 and 76.31 ± 2.47, respectively), and their effects were near that of the reference drug. This inhibitory effect may be due to USeNPs’ hydrogen bond formation with the EGFR, providing stronger binding affinity and ensuring a promising enzyme inhibitory activity [23,61,62].
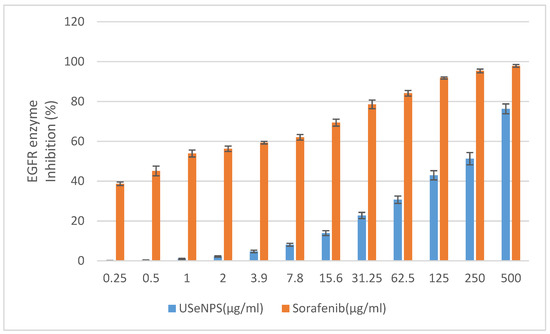
Figure 12.
Effect of USeNPS on epidermal growth factor receptors enzyme (EGFR enzyme) activity with IC50 = 230.79 ± 3.47 µg/mL. and IC50 = 0.76 ± 0.18 µg/mL. For USeNPS and Sorafenib (ref. drug).
3.4. Antiviral Activity of the SeNPs
To detect the antiviral activity of USeNPs against HAV HM175, MTT assay was utilized (Table 1) along with Vero cells (Figure 10). Figure 10 shows the cytotoxic activity of USeNPs with Vero cells with CC50 = 331.76 ± 4.79 µg/mL in order to evaluate the risk of these nanoparticles. Xia et al. [63] found that SeNPs inhibit Madin–Darby canine kidney cells with H1N1 by preventing chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation. Table 1 shows the antiviral effects of the tested compounds on the hepatitis A virus (HAV-10) when tested at maximum noncytotoxic concentration of 100 µg/mL. USeNPs have good antiviral activity (+++) against the tested virus with 74.13 ± 3.79% inhibition, and EC50 = 57.41 ± 2.37. The ratio of CC50 to EC50 was used to calculate the selectivity index ((SI) = 5.78)) to indicate whether USeNPs had sufficient antiviral activity which exceeded its toxicity [43]. This index is referred to as a therapeutic index, and it illustrated that USeNPs is an active antiviral agent which warrants further study since compounds with SI ≥ 2 are described as active43. The antiviral activity of SeNPs against various other types of viruses is likely due to the SeNPs’ direct binding to viral envelope glycoproteins which prevents viral entry into host cells, even though the mechanism of action has not been well-studied [64,65].

Table 1.
The antiviral effects of the USeNPS against hepatitis A virus (HAV-10) when tested at maximum noncytotoxic conc (MNCC).
3.5. Determination of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
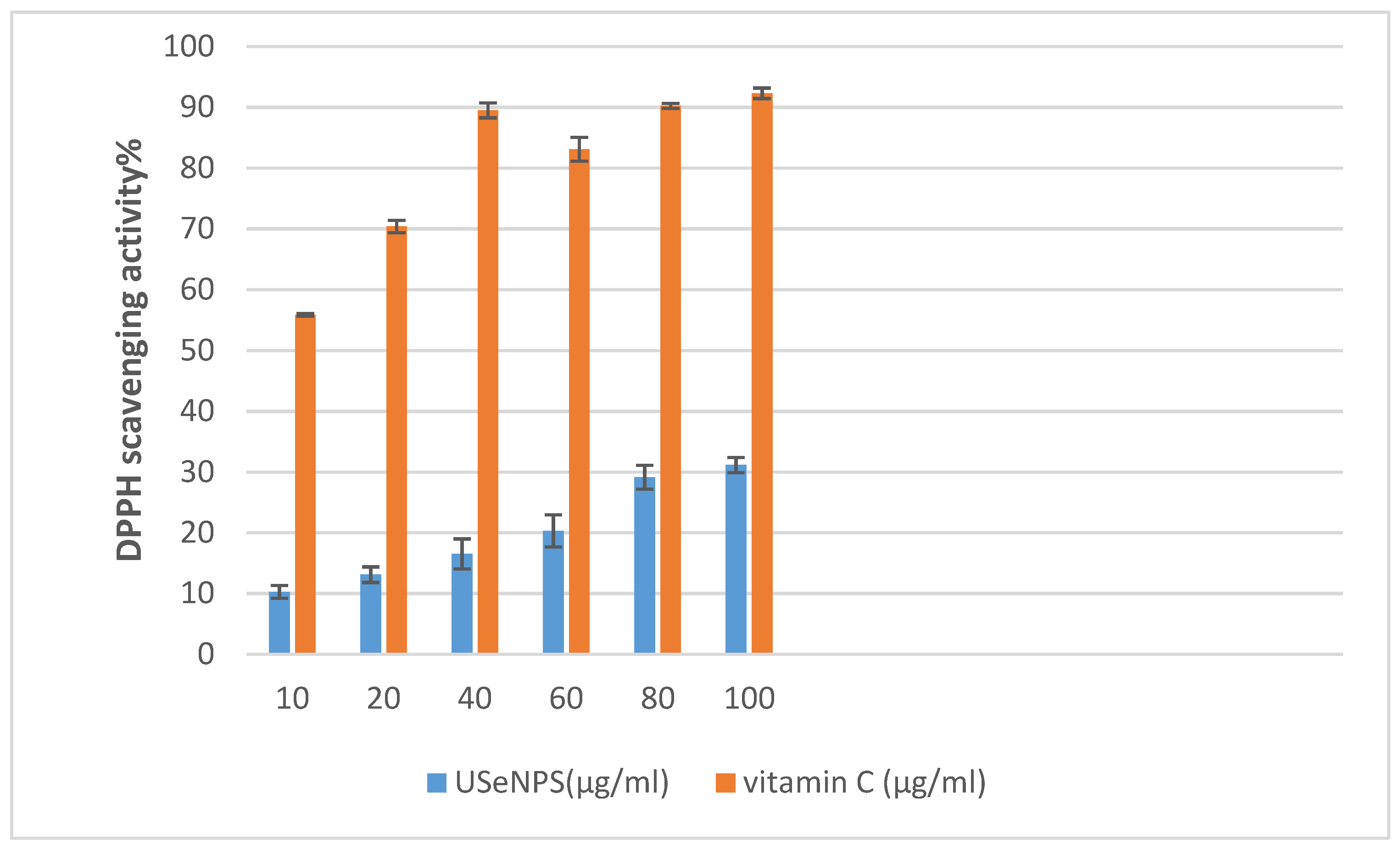
According to Figure 13, USeNPs could be considered a moderate antioxidant. Wang et al. [66] studied the DPPH scavenging activity of SeNPs capped with Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides and found that these NPs showed the lowest DPPH free radical scavenging ability. This extract’s DPPH scavenging activity and its inhibition (%) were found to change in a concentration-dependent manner, and that concurred with Nilesh et al. [67], who found that DPPH scavenging activity increased linearly with increasing concentrations of SeNPs because of the accessibility of more interaction sites on SeNPs. Despite this, its efficacy did not exceed vitamin C (reference drug) in its antioxidant properties. Duh [68] proved that reductions are generally responsible for reducing properties, and El-Shafay et al. [69], Ismail et al. [70], Farghl et al. [71], and El-Sheekh et al. [72] found that the antioxidants of some seaweed components may occur by donating electrons and reacting with free radicals to convert them into more stable products and by ending the free radical chain reaction. These strong antioxidant activities boost the seaweeds’ overall anticancer activity [73].
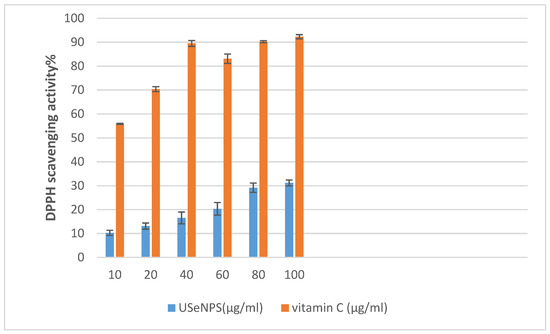
Figure 13.
The effect of different concentrations of USeNPS on DPPH radical scavenging activity with (IC50) 158.02 ± 0.07 and 4.48 ± 0.01 for USeNPS and vit. C (reference drug), respectively.
4. Conclusions
The metabolites from the aqueous extract of U. lactuca can mediate USeNPs biosynthesis. FTIR indicated the function of algal aqueous extract metabolites in stabilizing and capping freshly generated NPs. TEM and XRD results showed that spherical NPs with a size ranging from 18.65 to 67.79 nm and a crystalline character had formed. The SEM-EDX chart confirms the presence of selenium and other components in the sample. The activity of these NPs has been shown through their significant anticancer, antiviral, and antioxidant activity. All tested activities were dosage-dependent and showed promising results, with the highest tested USeNPs concentration (500 µg/mL) causing cytotoxicity for HepG2 with 91.25% inhibition through the inhibition of the EGFR enzyme that is responsible for EGFR degradation, while the same concentration caused 69.36% inhibition for normal Vero cells, which demonstrates the relative safety of such NPs. Additionally, the NPs considered as active antiviral agents against HAV-10 had good antiviral activity (+++), and USeNPs showed moderate DPPH radical scavenging activity. Therefore, we are proud to recommend the use of our discovery to potentially control HAV-10 viral activity. Additionally, these findings provide valuable clues for discovering antitumor compounds based on the EGFR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.E.-S. methodology, M.E.M.M.; software, T.M.A.-S.; validation, F.M.A. and M.E.M.M.; formal analysis, and investigation, M.E.M.M.; data curation, M.E.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.E.-S.; writing—review and editing; M.M.E.-S.; supervision, F.M.A. and T.M.A.-S.; funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are included in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support from Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2022R15), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alam, M. Photocatalytic activity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles: In vitro antimicrobial, biocompatibility, and molecular docking studies. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saied, E.; Eid, A.M.; Hassan, S.E.; Salem, S.S.; Radwan, A.A.; Halawa, M.; Saleh, F.M.; Saad, H.A.; Saied, E.M.; Fouda, A. The Catalytic Activity of Biosynthesized Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles (MgO-NPs) for Inhibiting the Growth of Pathogenic Microbes, Tanning Effluent Treatment, and Chromium Ion Removal. Catalysts 2021, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badineni, V.; Maseed, H.; Arla, S.K.; Yerramala, S.; Naidu, V.K.B.; Kaviyarasu, K. Effect of PVA/PVP protective agent on the formation of silver nanoparticles and its photo catalytic and antimicrobial activity. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsalam, S.; Agastian, P.; Esmail, G.A.; Ghilan, A.-K.M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Musa acuminata colla flower and its pharmaceutical activity against bacteria and anticancer efficacy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 201, 111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, G.T.; Nithiyavathi, R.; Ramesh, R.; John Sundaram, S.; Kaviyarasu, K. Structural and optical properties of nickel oxide nanoparticles: Investigation of antimicrobial applications. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 18, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.; Alwaleed, E.A.; Kassem, W.M.A.; Saber, H. Antialgal and anticancer activities of the algal silver nanoparticles against the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa and human tumor colon cell line. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100352. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sheekh, M.; Hassan, L.H.; Morsi, H.H. Assessment of the in vitro anticancer activities of cyanobacteria mediated silver oxide and gold nanoparticles in human colon CaCo-2 and cervical HeLa cells. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçer, A.T.; Özçimen, D. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles from macroalgae: Optimization, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A. Toxicity of Ulva lactuca and green fabricated silver nanoparticles against mosquito vectors and their impact on the genomic DNA of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 16, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair, B.; Liaqat, A.; Iqbal, H.; Menaa, B.; Razzaq, A.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Rana, N.F.; Menaa, F. Green and Cost-Effective Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles by Algae: Safe Methods for Translational Medicine. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.M.; Ravindran, R.; Narayanan, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, G. Microalgae: A prospective low cost green alternative for nanoparticle synthesis. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 20, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Raja, D.P.; Rathi, J.; Sahayaraj, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ulva fasciata (Delile) ethyl acetate extract and its activity against Xanthomonas campestris pv. malvacearum. J. Biopest. 2012, 5, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, D.; Satapathy, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Somu, P.; Mishra, G. Systemic Evaluation of Mechanism of Cytotoxicity in Human Colon Cancer HCT-116 Cells of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Marine Algae Ulva lactuca Extract. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2022, 32, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Bi, X.; Gao, X. The suppression of prostate LNCaP cancer cells growth by Selenium nanoparticles through Akt/Mdm2/AR controlled apoptosis. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6515–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikneshan, M.; Saravanakumar, R.; Mangaiyarkarasi, R.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Samuel, S.R.; Suganya, M.; Baskar, G. Algal biomass as a source for novel oral nano-antimicrobial agent. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, H.A.; Aly, E.E.; Farouk, A.K.; El Kerdawy, A.M.; Rashwan, E.; Abbass, S.E. Design and Synthesis of Some New 2,4,6-trisubstituted Quinazoline EGFR Inhibitors as Targeted Anticancer Agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; He, D.; Zhang, Y. Genetic Variant Rs7820258 Regulates the Expression of Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 in Brain Regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24035–24036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghwary, A.E.-S.; Gedawy, E.M.; Kamal, A.M.; Abuel-Maaty, S.M. Novel Thienopyrimidine Derivatives as Dual EGFR and VEGFR-2 Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Anticancer Activity and Effect on Cell Cycle Profile. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, B.; Altıntop, M.D.; Radwan, M.O.; Özdemir, A.; Otsuka, M.; Fujita, M.; Ciftci, H. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a New Series of Thiazolyl-Pyrazolines as Dual EGFR and HER2 Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-X.; Han, H.-W.; Yang, M.-K.; Wen, Z.-L.; Wang, Y.-S.; Fu, J.-Y. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzoylacrylic Acid Shikonin Ester Derivatives as Irreversible Dual Inhibitors of Tubulin and EGFR. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 115153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wei, B.; Yang, P.; He, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of Chalcone Derivatives: Inducing Apoptosis of HepG2 Cells via Regulating Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondrial Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Fu, T.; Hong, J.; Li, F.; Yao, X.; Xue, W.; Zhu, F. The Binding Mode of Vilazodone in the Human Serotonin Transporter Elucidated by Ligand Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 5132–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xue, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Cao, D.; Zhang, K.; et al. Discovery of Potent EGFR Inhibitors With 6- Arylureido-4- anilinoquinazoline Derivatives. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 647591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, A.A. Contribution to the study of the marine algae of the red sea. I-The algae in the neighborhood of al-Ghardaqa, Egypt (Cyanophyceae, Chlorophyceae and Phaeophyceae). Bull. Faculty Sci. King Abdulaziz Univ. Jeddah 1978, 2, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Aleem, A.A. Marine algae in Alexandria, Egypt; Alexandria Privately Published: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1993; pp. 1–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin, Y.; Silva, P. Marine algae and seagrasses of the Dahlak Archipelago, southern Red Sea. Nova Hedwig. 2002, 75, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, G.M. Algae Base; World-Wide Electronic Publication; National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2020; Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Ishwarya, R.; Vaseeharan, B.; Kalyani, S.; Banumathi, B.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Al-anbr, M.N.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ulva lactuca seaweed extract and evaluation of their photocatalytic, antibiofilm and insecticidal activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, B.; Solanki, M.; Pandey, A.; Prabha, S.; Kumar, P.; Kumari, B. Bacillus as Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): A Promising Green Agriculture Technology. In Plant Health Under Biotic Stress: Volume 2: Microbial Interactions; Ansari, R.A., Mahmood, I., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- Basant, E.F.; Amany, M.D.; Ahmed, A.T.; Mousa, A.A.; Moussa, S. Potent antibacterial action of phycosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using Spirulina platensis extract. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Murugaboopathy, V.; Saravankumar, R.; Mangaiyarkarasi, R.; Kengadaran, S.; Samuel, S.R.; Rajeshkumar, S. Efficacy of marine algal extracts against oral pathogens—A systematic review. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2021, 32, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Namvar, F.; Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.; Mohamad, R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using brown marine macroalga, Sargassum muticum aqueous extract. Materials 2013, 6, 5942–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Javadpour, F.; Sahimi, M. Three-Dimensional Stochastic Characterization of Shale SEM Images. Transp. Porous Media 2015, 110, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.L. Particle encapsulation with polymers via in situ polymerization in supercritical CO2. Powder Technol. 2004, 146, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, K.; Mvs, S.; Koganti, S.; Burgula, S. Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Pseudomonas stutzeri (MH191156) Show Antiproliferative and Anti-angiogenic Activity Against Cervical Cancer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 23, 4523–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.L. Nanoparticles (ASeNPs) and its catalysts activity for 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) reduction. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 11, 463–472. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, P.; Raghu, C.; Ashok, G.; Dhanaraj, S.A.; Suresh, B. Antiviral activity of medicinal plants of Nilgiris. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 120, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gomha, S.M.; Riyadh, S.M.; Mahmmoud, E.A.; Elaasser, M.M. Synthesis and Anticancer Activities of Thiazoles, 1,3-Thiazines, and Thiazolidine Using Chitosan-Grafted-Poly(vinylpyridine) as Basic Catalyst. Heterocycles 2015, 91, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo, W.; Piqueras, J.; Rodrıguez-Diaz, J.; Aznar, R.; Sanchez, G. Improving efficiency of viability-qPCR for selective detection of infectious HAV in food and water samples. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 124, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.M.; Diez, J.M.; Bosch, A. Use of the colonic carcinoma cell line CaCo-2 for in vivo amplification and detection of enteric viruses. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 44, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.M.; Hsiung, G.D. Evaluation of new antiviral agents I: In vitro prospective. Antivir. Res. 1989, 11, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salahi, R.; Alswaidan, I.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Ezzeldin, E.; Elaasser MMMarzouk, M. Docking and Antiherpetic Activity of 2-Aminobenzo[de]-isoquinoline-1,3-diones. Molecules 2015, 20, 5099–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehab, M.M.; Eman, M.F.; Rabea, A.S.; Dina, M.A.; Rawheya, A.S.; Hesham, M.A. Green biosynthesis, structural characterization and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles from the brown alga Cystoseira myrica. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 341–358. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Rasco, B.A. Determination of antioxidant content and antioxidant activity in foods using infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 853–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhika, D.; Ameer, M. Fourier transform infrared analysis of Ulva lactuca and Gracilaria corticata and their effect on antibacterial activity. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 8, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Younger, P. The Merck Index, 15th ed.; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: London, UK, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jiale, H.; Qingbiao, L.; Daohua, S.; Yinghua, L.; Yuanbo, S.; Xin, Y.; Huixuan, W.; Yuanpeng, W.; Wenyao, S.; Ning, H. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, N.S.; El Semary, N.A.; Mohamed, M.E. Silver nanoparticles green synthesis via cyanobacterium Phormidium sp.: Characterization, wound healing, antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 3083–3096. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.K.; Cai, P.F.; Cao, X.Q.; Ma, H.L.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, N.Z.; Zhao, Y.Z. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using 4-acetamido-TEMPO-oxidized curdlan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luminita, F.; Vasile, L.; Cavalu, S.; Costea, T.; Vicaş, S. Green biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using parsley (Petroselinum crispum) leaves extract. Stud. Univ. Vasile Goldis Arad Ser. Stiintele Vietii 2017, 27, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Niraimathi, K.L.; Sudha, V.; Lavanya, R.; Brindha, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alternanthera sessilis (Linn.) extract and their antimicrobial, antioxidant activities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 1, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Gnanaprakasam, P.; Emmanuel, R.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Saravanan, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mimusops elengi, Linn. for enhanced antibacterial activity against multi drug resistant clinical isolates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 1, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Mohanraj, K.; Prabhu, K.; Barathan, S.; Sivakumar, G. Synthesis of selenium nanorods with assistance of biomolecule. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2014, 37, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.H.; Elshehabi, T.A.; Bilgesu, H.I. Impact of Nanomaterials on the Rheological and Filtration Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluids. In Proceedings of the SPE Eastern Regional Meeting, Canton, OH, USA, 13–15 September 2016; Volume 978, pp. 510–515. [Google Scholar]
- Jummes, B.; Sganzerla, W.G.; da Rosa, C.G.; Noronha, C.M.; Nunes, M.R.; Bertoldi, F.C. Antioxidant and antimicrobial poly-ε-caprolactone nanoparticles loaded with Cymbopogon martinii essential oil. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, A.; Wahab, R.; Siddiqui, M.; Ahmad, J. Selenium Nanoparticles Induce Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer (MCF-7) and Liver (HepG2) Cell Lines. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2020, 12, 324–330. [Google Scholar]
- Saadaoui, I.; Rasheed, R.; Abdulrahman, N.; Bounnit, T.; Cherif, M.; Al Jabri, H.; Mraiche, F. Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds with Anti-Lung Cancer Potential. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; Chi, S.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, M.J. Saccharina japonica Extract Suppresses Stemness of Glioma Stem Cells by Degrading Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Duan, Y.; Gou, W.; Cui, J.; Ning, H.; Li, D.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 4-Anilinoquinazoline Derivatives as Hypoxia-Selective EGFR and VEGFR-2 Dual Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 181, 111552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y.; Gan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Zou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, G.; Yan, L. Design, Synthesis and In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Quinazolinone Derivatives as EGFR Inhibitors for Antitumor Treatment. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Danyang, C.; Jingyao, S.; Ruilin, Z.; Zhihui, N.; Mingqi, Z.; Bing, Z.; Yinghua, L. Selenium nanoparticles inhibited H1N1 influenza virus-induced apoptosis by ROS-mediated signaling pathways. R. Soci. Chem. 2022, 12, 3862–3870. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Sun, R.W.; Chen, R.; Hui, C.K.; Ho, C.M.; Luk, J.M.; Lau, G.K.; Che, C.M. Silver nanoparticles inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.M.; Ao, Z.; Girilal, M.; Chen, L.; Xiao, X.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Yao, X. Inactivation of microbial infectiousness by silver nanoparticles-coated condom: A new approach to inhibit HIV- and HSV-transmitted infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5007–5018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, H.; Bi, Y.; Fan, X. Preparation and antioxidant activity of selenium nanoparticles decorated by polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilesh, S.D.; Mausumi, M. Antioxidant properties of aqueous selenium nanoparticles (ASeNPs) and its catalysts activity for 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) reduction. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1205, 127637. [Google Scholar]
- Duh, P.D. Antioxidant activity of burdock (Arctium lappa Linné): Its scavenging effect on free-radical and active oxygen. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafay, S.; EI-Sheekh, M.M.; Bases, E.; El-Shenoudy, R. Antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory and anticancer potential of some seaweed extracts. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, e20521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, G.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Gheda, S.; Samy, R. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and antiviral activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles by phycobiliproteins crude extract of the cyanobacteria Spirulina platensis and Nostoc linckia. Bionanoscience 2021, 11, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghl, A.; Al-Hasawi, Z.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Assessment of Antioxidant Capacity and Phytochemical Composition of Brown and Red Seaweeds Collected from Red Sea Coast. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El Shafey El-Shenody, R.; Bases, E. Comparative assessment of antioxidant activity and biochemical composition of four seaweeds, Rocky Bay of Abu Qir in Alexandria, Egypt. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Nassef, M.; Bases, E.; El shafay, S.; Elshenoudy, R. Antitumor Immunity and Therapeutic Properties of Marine Seaweeds-derived Extracts in The Treatment of Cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).