Clinical Evaluation of Deep Learning and Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring for Head and Neck Radiation Therapy
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Imaging Data
2.2. Manual Contouring
2.3. Atlas-Based and DL Auto-Contouring
2.4. Geometric Accuracy and Contouring Time Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
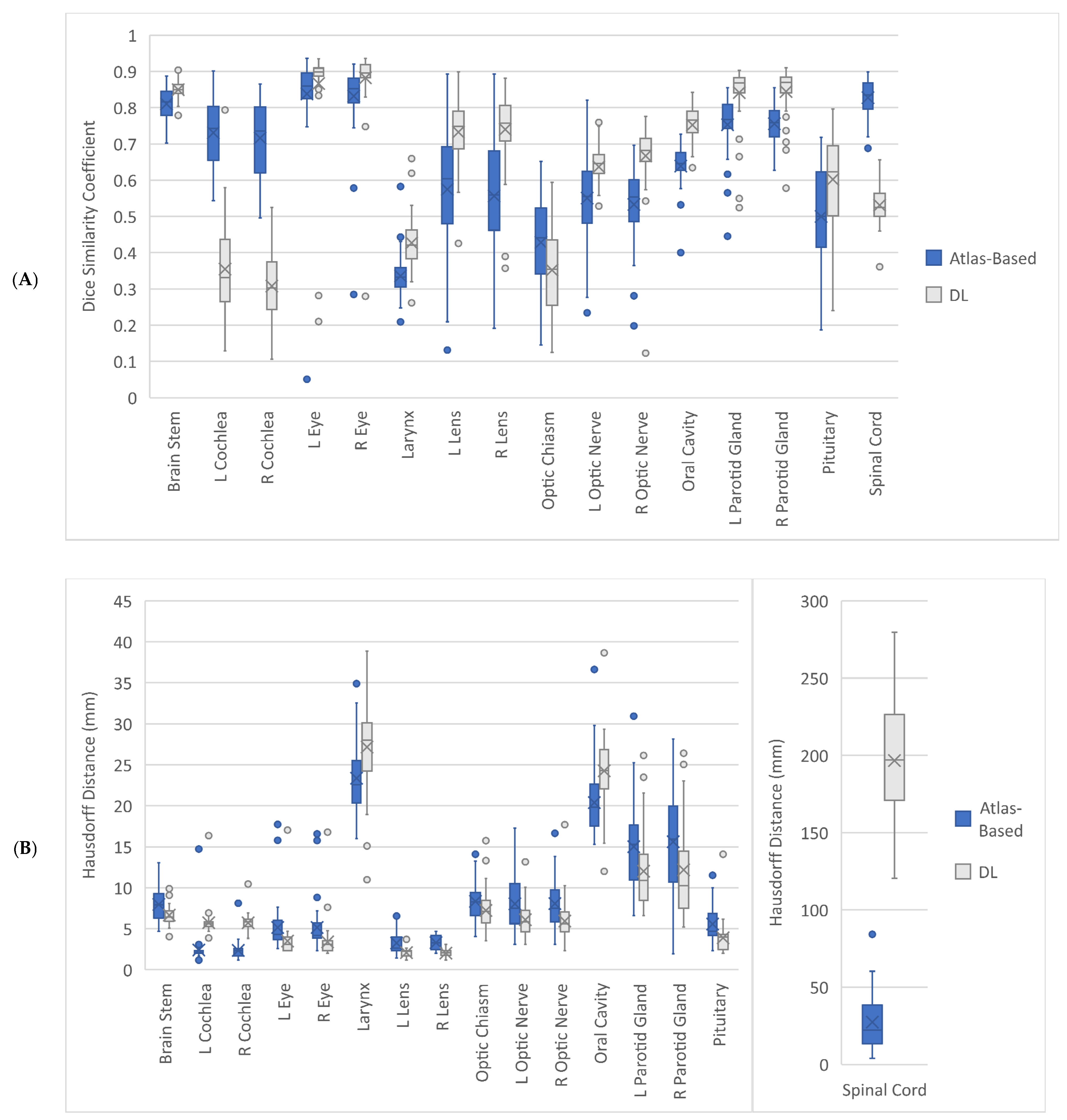
3.1. Geometric Accuracy
3.2. Contouring Time Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oktay, O.; Nanavati, J.; Schwaighofer, A.; Carter, D.; Bristow, M.; Tanno, R.; Jena, R.; Barnett, G.; Noble, D.; Rimmer, Y.; et al. Evaluation of deep learning to augment image-guided radiotherapy for head and neck and prostate cancers. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2027426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, C.E.; Beadle, B.M.; Garden, A.S.; Skinner, H.D.; Yang, J.; Rhee, D.J.; McCarroll, R.E.; Netherton, T.J.; Gay, S.S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Generating high-quality lymph node clinical target volumes for head and neck cancer radiation therapy using a fully automated deep learning-based approach. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmin, M.; Ledsam, J.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Mendes, R.; Moinuddin, S.; de Souza, D.; Gunn, L.; Kelly, C.; Hughes, C.O.; Karthikesalingam, A.; et al. Rapid advances in auto-segmentation of organs at risk and target volumes in head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 135, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.; Lee, H.; Chun, J.; Shin, J.I.; Chang, J.S.; Kim, J.S. Clinical evaluation of commercial atlas-based auto-segmentation in the head and neck region. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C.; Qu, B.; Ma, L.; Fan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, S. Evaluation exploration of atlas-based and deep learning-based automatic contouring for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 833816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Rao, S.; Chen, W.; Azghadi, S.F.; Nguyen, K.N.B.; Moran, A.; Usera, B.M.; Dyer, B.A.; Shang, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. Evaluating automatic segmentation for swallowing-related organs for head and neck cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunenberg, E.J.L.; Steinseifer, I.K.; van den Bosch, S.; Kaanders, J.H.A.M.; Brouwer, C.L.; Gooding, M.J.; van Elmpt, W.; Monshouwer, R. External validation of deep learning-based contouring of head and neck organs at risk. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, E.; Nourzadeh, H.; Choi, W.; Leandro Alves, V.G.; Siebers, J.V. An automated workflow to improve efficiency in radiation therapy treatment planning by prioritizing organs at risk. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyalusamy, A.; Vellaiyan, S.; Subramanian, S.; Ilamurugu, A.; Satpathy, S.; Nauman, M.; Katta, G.; Madineni, A. Auto-segmentation of head and neck organs at risk in radiotherapy and its dependence on anatomic similarity. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2019, 37, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Dyer, B.A.; Feng, X.; Rao, S.; Benedict, S.H.; Chen, Q.; Rong, Y. Deep learning vs. atlas-based models for fast auto-segmentation of the masticatory muscles on head and neck CT images. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Munoz, A.; Moreau, D.; Mazurier, J.; Sidorski, G.; Gasnier, A.; Beldjoudi, G.; Grégoire, V.; Deutsch, E.; Meyer, P.; et al. Clinical implementation of deep-learning based auto-contouring tools-Experience of three French radiotherapy centers. Cancer Radiother. 2021, 25, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, E.; Koreas, P.; Strouthos, I.; Leczynski, A.; Grimm, M.; Zamboglou, N.; Ferentinos, K. Evaluation of an atlas-based auto-segmentation tool of target volumes and organs at risk in head and neck radiation therapy. J. Oncol. Res. Ther. 2021, 6, 10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C. Artificial intelligence (enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial network) for calcium deblooming in coronary computed tomography angiography: A feasibility study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.C. Artificial intelligence for radiation dose optimization in pediatric radiology: A systematic review. Children 2022, 9, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C. Finetuned super-resolution generative adversarial network (artificial intelligence) model for calcium deblooming in coronary computed tomography angiography. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, W. A preliminary experience of implementing deep-learning based auto-segmentation in head and neck cancer: A study on real-world clinical cases. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 638197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, S.; Blackwell, S.; Zverovitch, A.; Mendes, R.; Livne, M.; De Fauw, J.; Patel, Y.; Meyer, C.; Askham, H.; Romera-Paredes, B.; et al. Clinically applicable segmentation of head and neck anatomy for radiotherapy: Deep learning algorithm development and validation study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e26151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Chun, J.; Chang, J.S.; Lee, C.G.; Keum, K.C.; Kim, J.S. Feasibility of continual deep learning-based segmentation for personalized adaptive radiation therapy in head and neck area. Cancers 2021, 13, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ge, Y. A deep learning based automatic segmentation approach for anatomical structures in intensity modulation radiotherapy. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 7506–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Thor, M.; Onochie, I.; Hesse, J.; Zakeri, K.; LoCastro, E.; Jiang, J.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Elguindi, S.; Lee, N.Y.; et al. Prospectively-validated deep learning model for segmenting swallowing and chewing structures in CT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilimagga, R.S.; Anchineyan, P.; Nmugam, M.S.; Thalluri, S.; Goud, P.S. Autodelineation of organ at risk in head and neck cancer radiotherapy using artificial intelligence. J. Can. Res. Ther. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.S.; Tomé, W.A.; Harari, P.M. Heterogeneity in head and neck IMRT target design and clinical practice. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 103, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segedin, B.; Petric, P. Uncertainties in target volume delineation in radiotherapy—Are they relevant and what can we do about them? Radiol. Oncol. 2016, 50, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Multi-Institutional Target Delineation in Oncology Group. Human-computer interaction in radiotherapy target volume delineation: A prospective, multi-institutional comparison of user input devices. J. Digit. Imaging 2011, 24, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kieselmann, J.P.; Kamerling, C.P.; Burgos, N.; Menten, M.J.; Fuller, C.D.; Nill, S.; Cardoso, M.J.; Oelfke, U. Geometric and dosimetric evaluations of atlas-based segmentation methods of MR images in the head and neck region. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 145007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, D.; Stride, E.; Vallis, K.; Gooding, M.J. Applications and limitations of machine learning in radiation oncology. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, L.V.; Van den Bosch, L.; Aljabar, P.; Peressutti, D.; Both, S.; Steenbakkers, R.J.H.M.; Langendijk, J.A.; Gooding, M.J.; Brouwer, C.L. Improving automatic delineation for head and neck organs at risk by deep learning contouring. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, C.L.; Steenbakkers, R.J.H.M.; Bourhis, J.; Budach, W.; Grau, C.; Grégoire, V.; van Herk, M.; Lee, A.; Maingon, P.; Nuttingt, C.; et al. CT-based delineation of organs at risk in the head and neck region: DAHANCA, EORTC, GORTEC, HKNPCSG, NCIC CTG, NCRI, NRG Oncology and TROG consensus guidelines. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 117, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machine Learning–Deep-Learning Segmentation in RayStation. Available online: https://www.raysearchlabs.com/495a00/siteassets/media/publications/white-papers/wp-pdfs/wp_ml_deeplearning_2020.03.25.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Delpon, G.; Escande, A.; Ruef, T.; Darréon, J.; Fontaine, J.; Noblet, C.; Supiot, S.; Lacornerie, T.; Pasquier, D. Comparison of automated atlas-based segmentation software for postoperative prostate cancer radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kariyawasam, L.N.; Ng, C.K.C.; Sun, Z.; Kealley, C.S. Use of three-dimensional printing in modelling an anatomical structure with a high computed tomography attenuation value: A feasibility study. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2021, 11, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Gender (n = 45) | |
| Male | 35 (78%) |
| Female | 10 (22%) |
| Age (n = 45) | |
| 18–65 years | 29 (64%) |
| >65 years | 16 (36%) |
| Tumor site | |
| Nasopharynx | 45 (100%) |
| Tumour classification | |
| T1 | 13 (29%) |
| T2 | 3 (6%) |
| T3 | 17 (38%) |
| T4 | 12 (27%) |
| Node classification | |
| N0 | 13 (29%) |
| N1 | 13 (29%) |
| N2 | 9 (20%) |
| N3 | 10 (22%) |
| Systemic treatment | |
| Yes | 37 (82%) |
| No | 8 (18%) |
| Treatment technique | |
| Volumetric arc therapy | 45 (100%) |
| Neck irradiation | |
| Bilateral | 45 (100%) |
| Organ at Risk | Geometric Accuracy Parameter | Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring (Mean (CI)) | Deep Learning Auto-Contouring (Mean (CI)) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brainstem | DSC | 0.81 (0.80, 0.82) | 0.85 (0.84, 0.86) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 7.96 (7.37, 8.55) | 6.66 (6.30, 7.05) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 4.84 (4.42, 5.22) | 3.85 (3.59, 4.11) | <0.001 | |
| Left Cochlea | DSC | 0.73 (0.71, 0.75) | 0.35 (0.32, 0.39) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 2.40 (2.02, 3.00) | 5.73 (5.34, 6.28) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 1.82 (1.52, 2.34) | 3.92 (3.59, 4.44) | <0.001 | |
| Right Cochlea | DSC | 0.72 (0.69, 0.75) | 0.31 (0.28, 0.34) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 2.36 (2.10, 2.67) | 5.72 (5.45, 6.00) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 1.69 (1.48, 1.97) | 4.04 (3.81, 4.32) | <0.001 | |
| Left Eye | DSC | 0.84 (0.80, 0.87) | 0.87 (0.82, 0.90) | 0.339 |
| HD (mm) | 5.15 (4.43, 6.03) | 3.49 (3.03, 4.17) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 3.58 (3.03, 4.27) | 2.40 (2.06, 2.95) | <0.001 | |
| Right Eye | DSC | 0.83 (0.80, 0.86) | 0.88 (0.85, 0.90) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 5.14 (4.46, 6.09) | 3.39 (2.89, 4.06) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 3.54 (3.04, 4.18) | 2.32 (1.98, 2.81) | <0.001 | |
| Larynx | DSC | 0.34 (0.32, 0.35) | 0.43 (0.41, 0.45) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 23.37 (22.29, 24.49) | 27.17 (25.61, 28.65) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 14.55 (13.88, 15.24) | 15.55 (14.75, 16.35) | 0.021 | |
| Left Lens | DSC | 0.57 (0.52, 0.63) | 0.73 (0.71, 0.76) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 3.26 (2.92, 3.67) | 2.08 (1.94, 2.23) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 2.40 (2.15, 2.67) | 1.41 (1.33, 1.49) | <0.001 | |
| Right Lens | DSC | 0.56 (0.51, 0.60) | 0.74 (0.71, 0.77) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 3.30 (3.05, 3.58) | 2.02 (1.88, 2.14) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 2.55 (2.35, 2.78) | 1.35 (1.28, 1.43) | <0.001 | |
| Optic Chiasm | DSC | 0.43 (0.39, 0.46) | 0.35 (0.32, 0.38) | 0.005 |
| HD (mm) | 8.34 (7.68, 9.05) | 7.23 (6.59, 7.91) | 0.013 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 4.53 (4.12, 4.99) | 4.13 (3.73, 4.60) | 0.131 | |
| Left Optic Nerve | DSC | 0.55 (0.52, 0.58) | 0.64 (0.62, 0.66) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 8.03 (7.04, 8.95) | 6.10 (5.51, 6.76) | 0.007 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 4.55 (3.68, 5.58) | 3.70 (2.92, 4.87) | 0.005 | |
| Right Optic Nerve | DSC | 0.53 (0.50, 0.56) | 0.67 (0.64, 0.69) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 8.07 (7.16, 8.92) | 5.92 (5.28, 6.71) | 0.002 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 4.21 (3.80, 4.65) | 3.05 (2.69, 3.55) | <0.001 | |
| Oral Cavity | DSC | 0.64 (0.62, 0.65) | 0.75 (0.73, 0.77) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 20.39 (19.24, 21.52) | 24.26 (23.03, 25.40) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 12.32 (11.72, 12.97) | 13.78 (13.01, 14.64) | <0.001 | |
| Left Parotid Gland | DSC | 0.75 (0.73, 0.78) | 0.84 (0.82, 0.86) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 15.01 (13.58, 16.47) | 12.02 (10.64, 13.63) | 0.006 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 7.08 (6.49, 7.60) | 4.62 (3.99, 5.31) | <0.001 | |
| Right Parotid Gland | DSC | 0.76 (0.74, 0.77) | 0.84 (0.83, 0.86) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 15.61 (13.86, 17.30) | 12.18 (10.45, 14.05) | 0.009 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 7.00 (6.46, 7.57) | 4.74 (4.11, 5.42) | <0.001 | |
| Pituitary | DSC | 0.50 (0.46, 0.54) | 0.60 (0.56, 0.64) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 5.57 (4.99, 6.17) | 3.89 (3.40, 4.53) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 4.02 (3.55, 4.51) | 2.76 (2.44, 3.19) | <0.001 | |
| Spinal Cord | DSC | 0.83 (0.81, 0.84) | 0.53 (0.52, 0.55) | <0.001 |
| HD (mm) | 27.39 (22.23, 33.35) | 196.68 (185.58, 208.11) | <0.001 | |
| HD95 (mm) | 10.48 (8.07, 13.21) | 93.85 (88.26, 99.67) | <0.001 |
| Time (s) | Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring (Mean (CI)) | Deep Learning Auto-Contouring (Mean (CI)) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contouring | 153.43 (150.63, 156.08) | 69.53 (68.40, 70.58) | <0.001 |
| Review and Editing | 544.55 (495.02, 612.48) | 352.98 (315.40, 397.92) | <0.001 |
| Total | 697.97 (647.55, 764.92) | 422.51 (385.39, 467.14) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, C.K.C.; Leung, V.W.S.; Hung, R.H.M. Clinical Evaluation of Deep Learning and Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring for Head and Neck Radiation Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11681. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211681
Ng CKC, Leung VWS, Hung RHM. Clinical Evaluation of Deep Learning and Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring for Head and Neck Radiation Therapy. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(22):11681. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211681
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Curtise K. C., Vincent W. S. Leung, and Rico H. M. Hung. 2022. "Clinical Evaluation of Deep Learning and Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring for Head and Neck Radiation Therapy" Applied Sciences 12, no. 22: 11681. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211681
APA StyleNg, C. K. C., Leung, V. W. S., & Hung, R. H. M. (2022). Clinical Evaluation of Deep Learning and Atlas-Based Auto-Contouring for Head and Neck Radiation Therapy. Applied Sciences, 12(22), 11681. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211681






