Geological Distribution of the Miocene Carbonate Platform in the Xisha Sea Area of the South China Sea, and Its Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
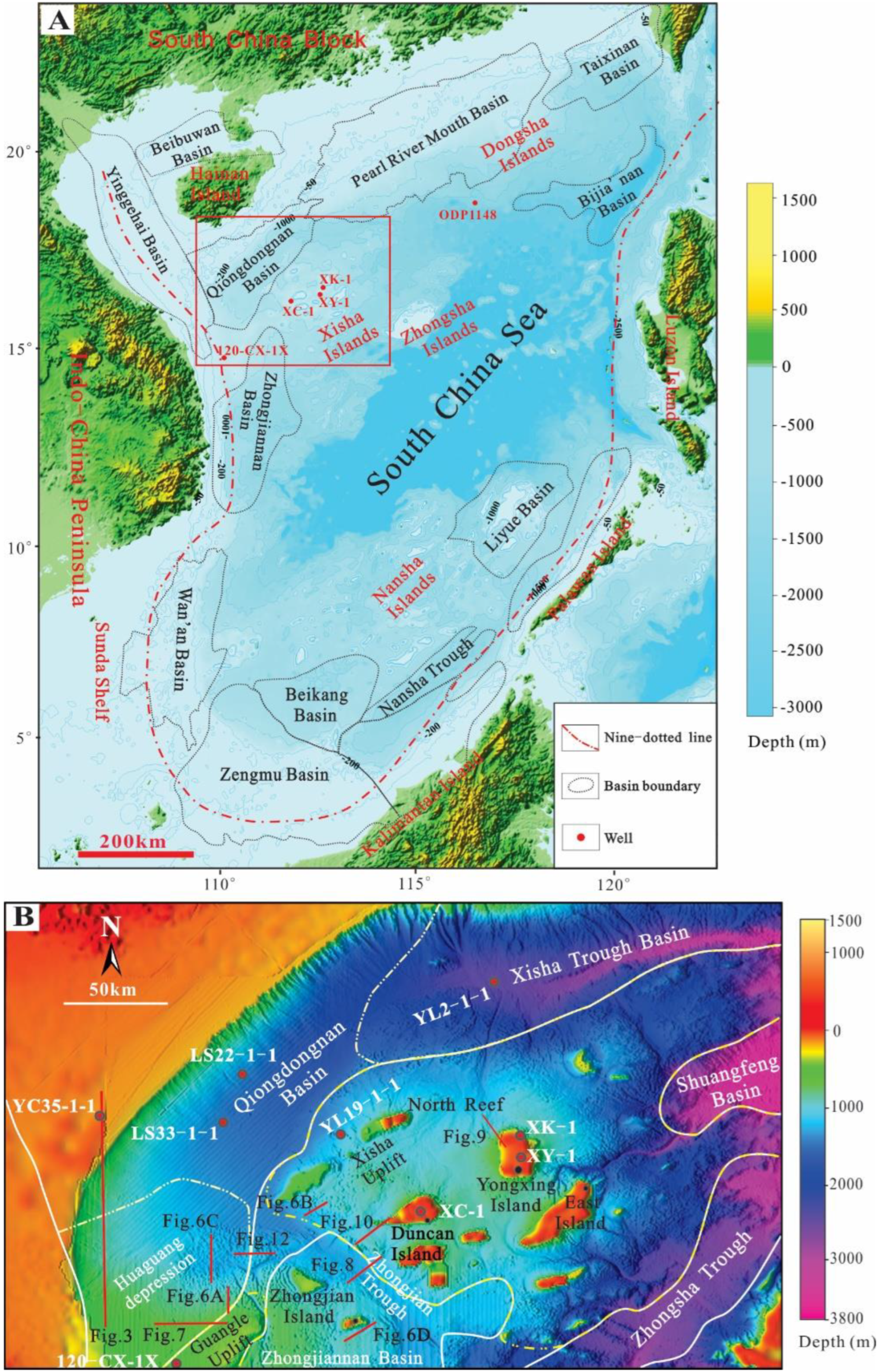
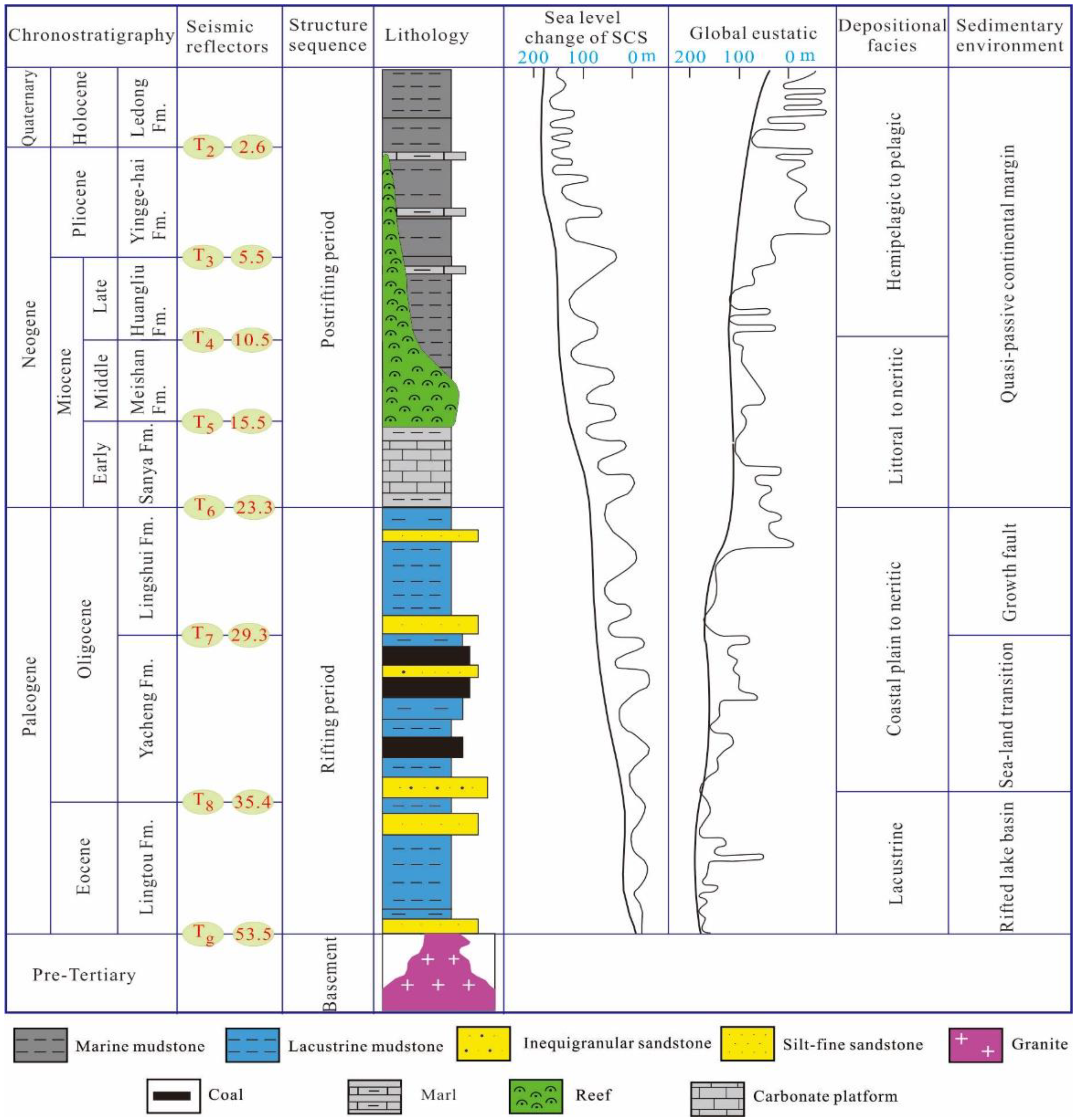
2. Geological Settings
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
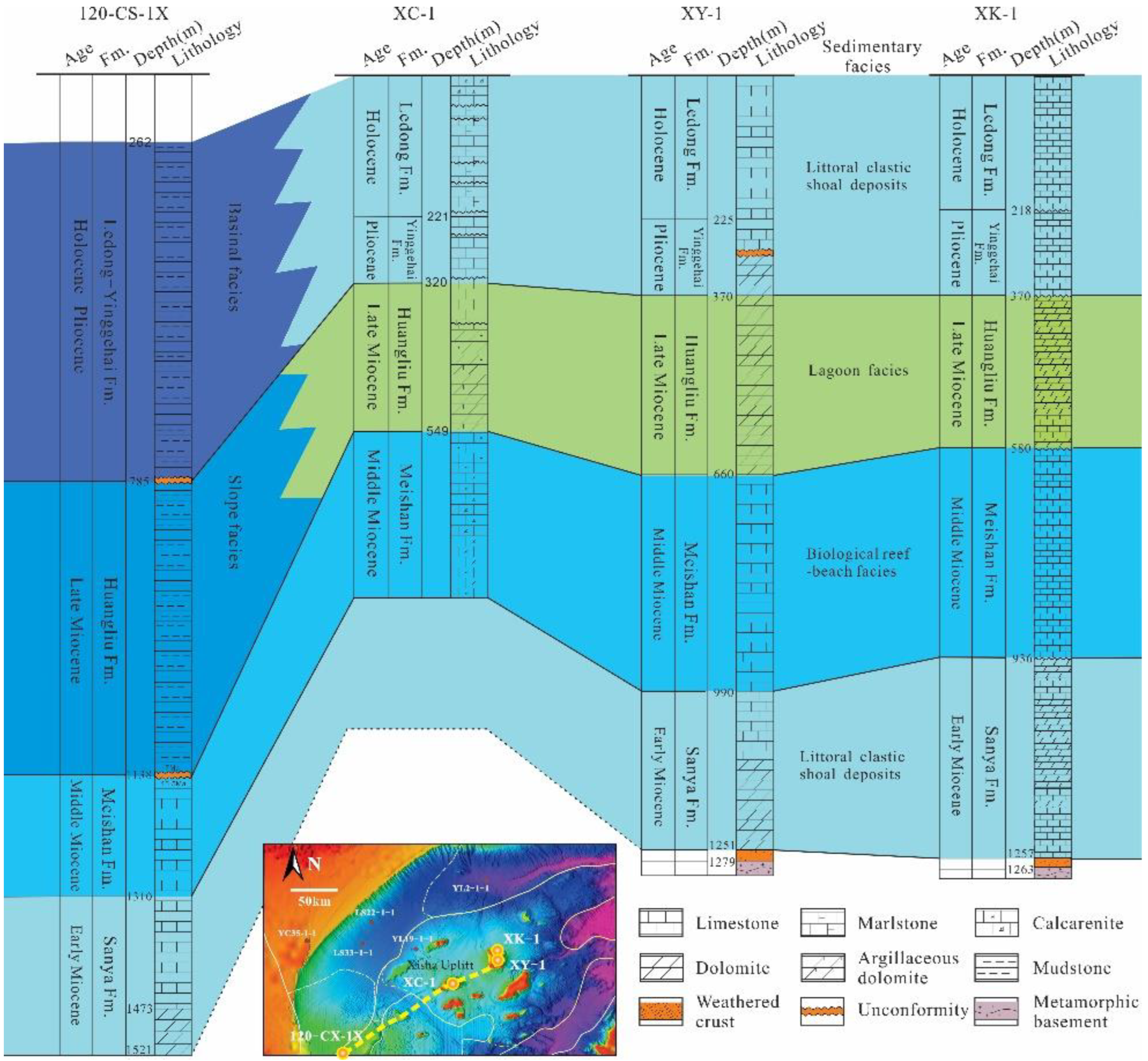
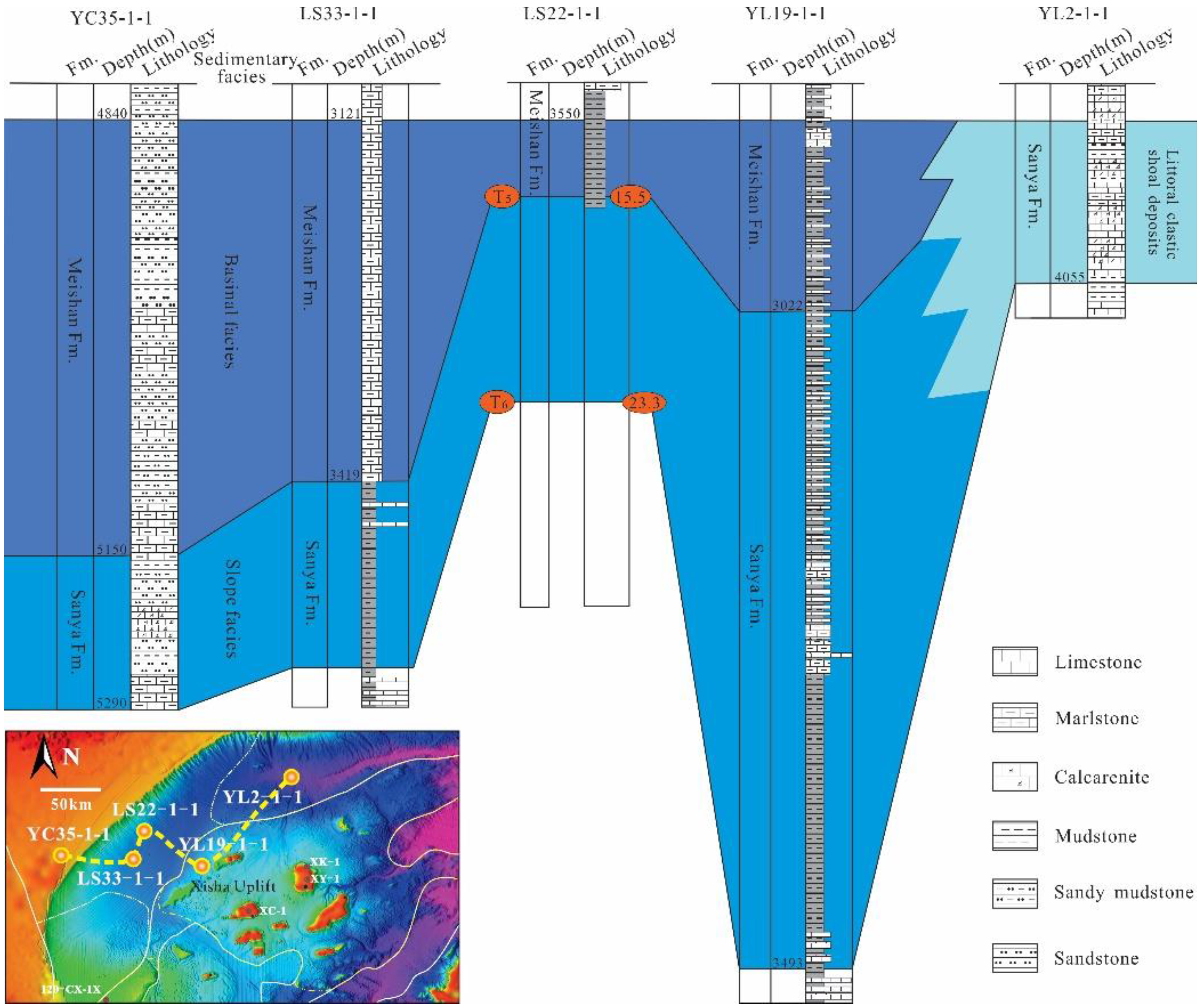
4.1. Sedimentary Characteristics from Drilling Wells
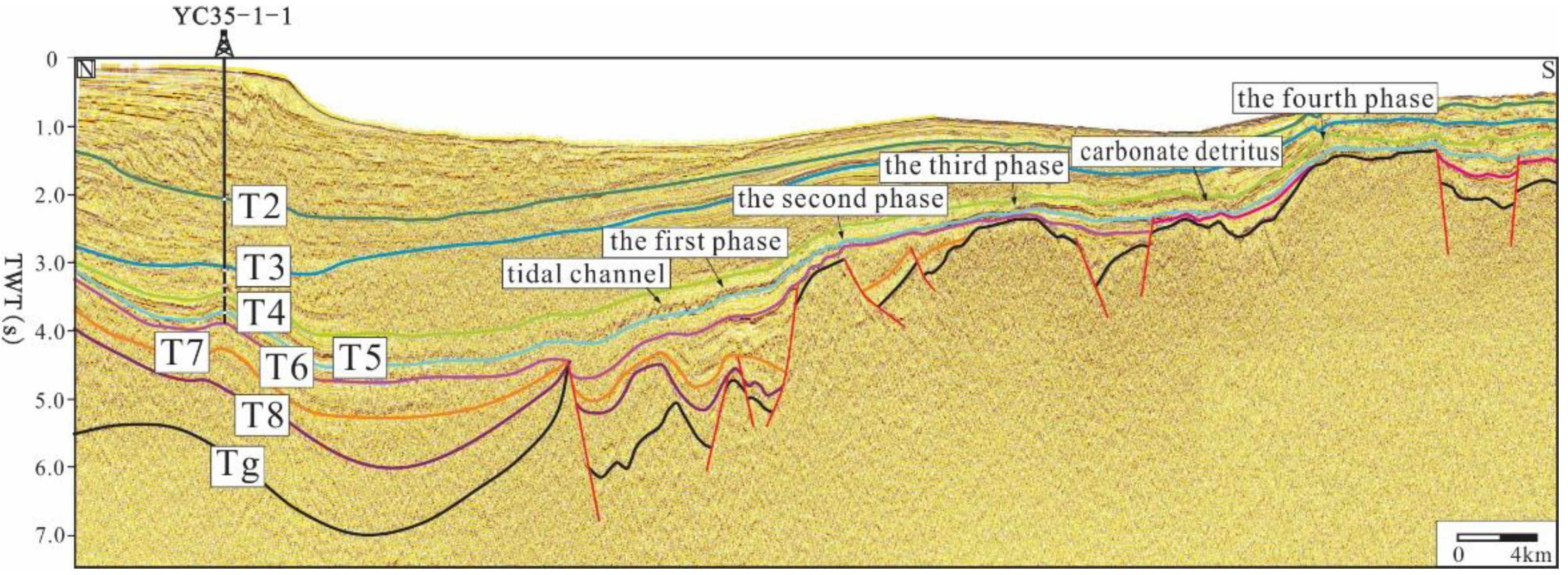
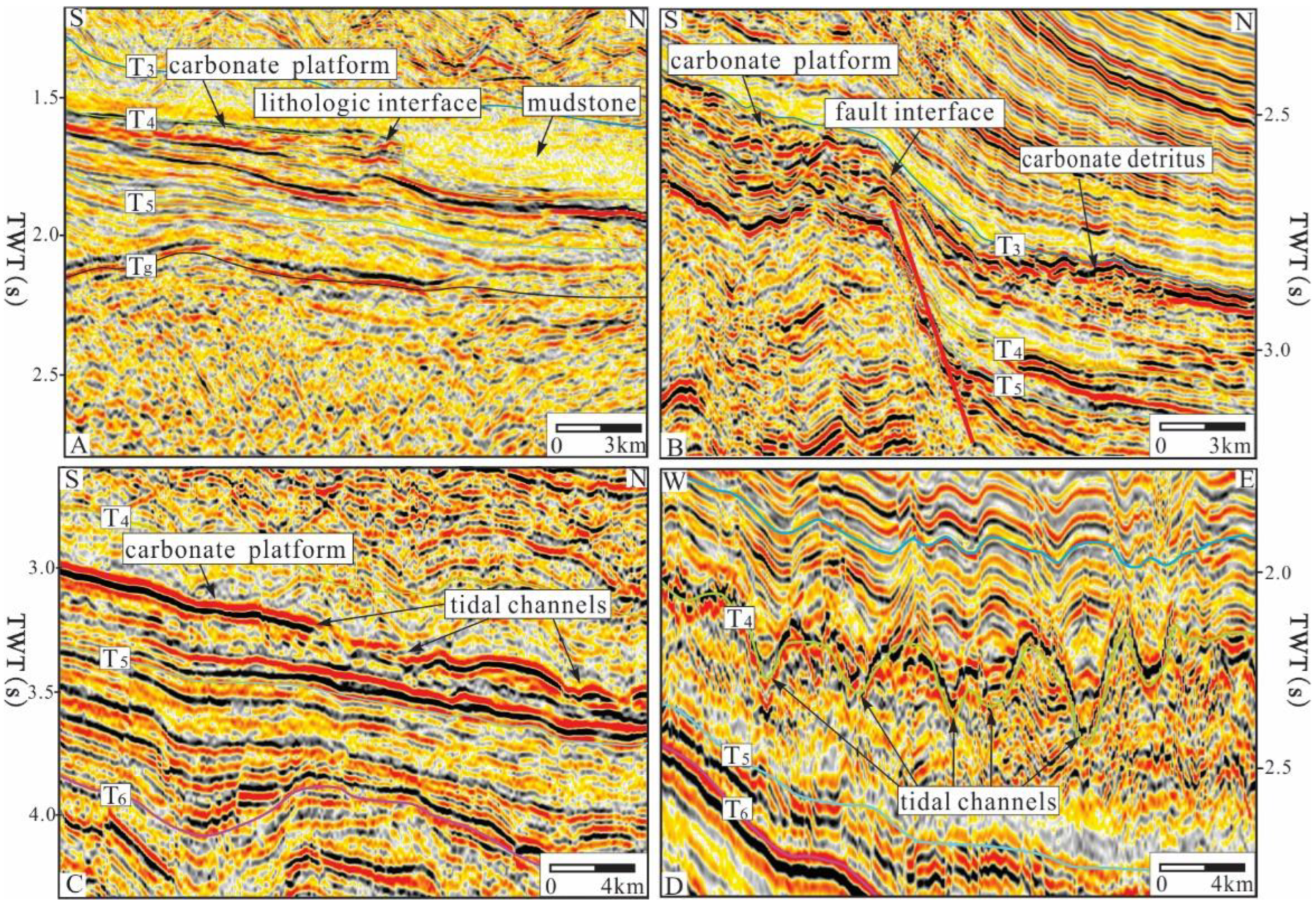
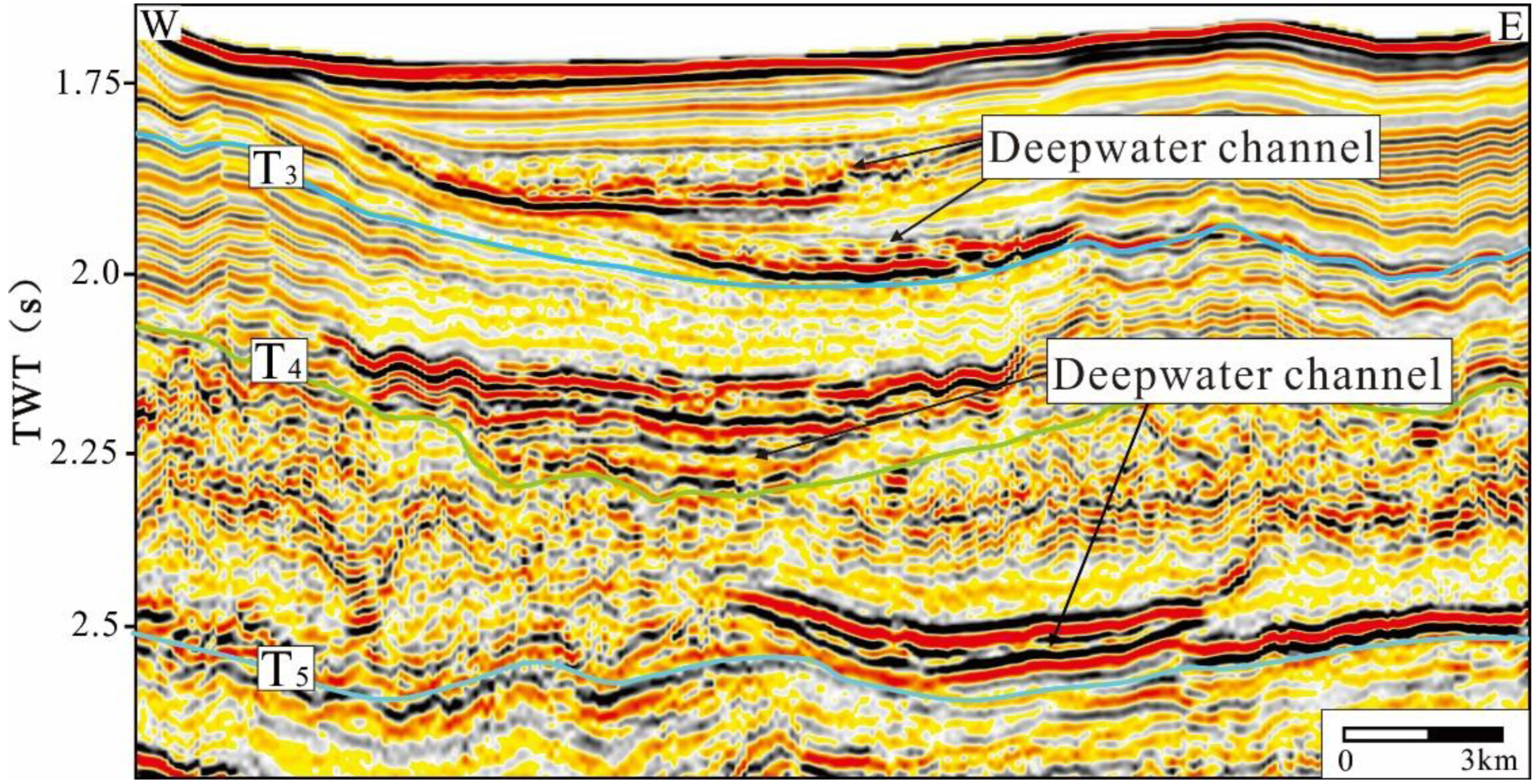
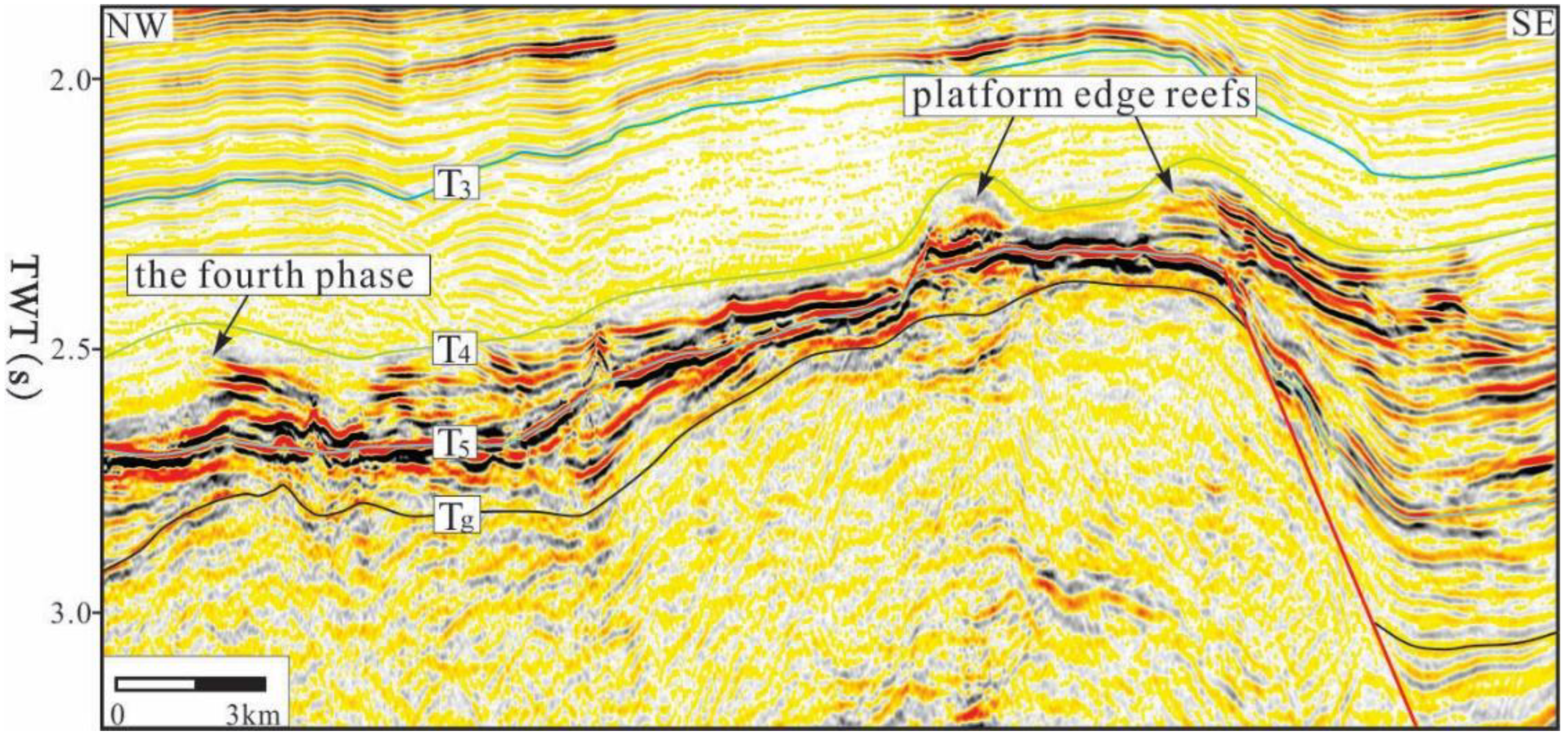
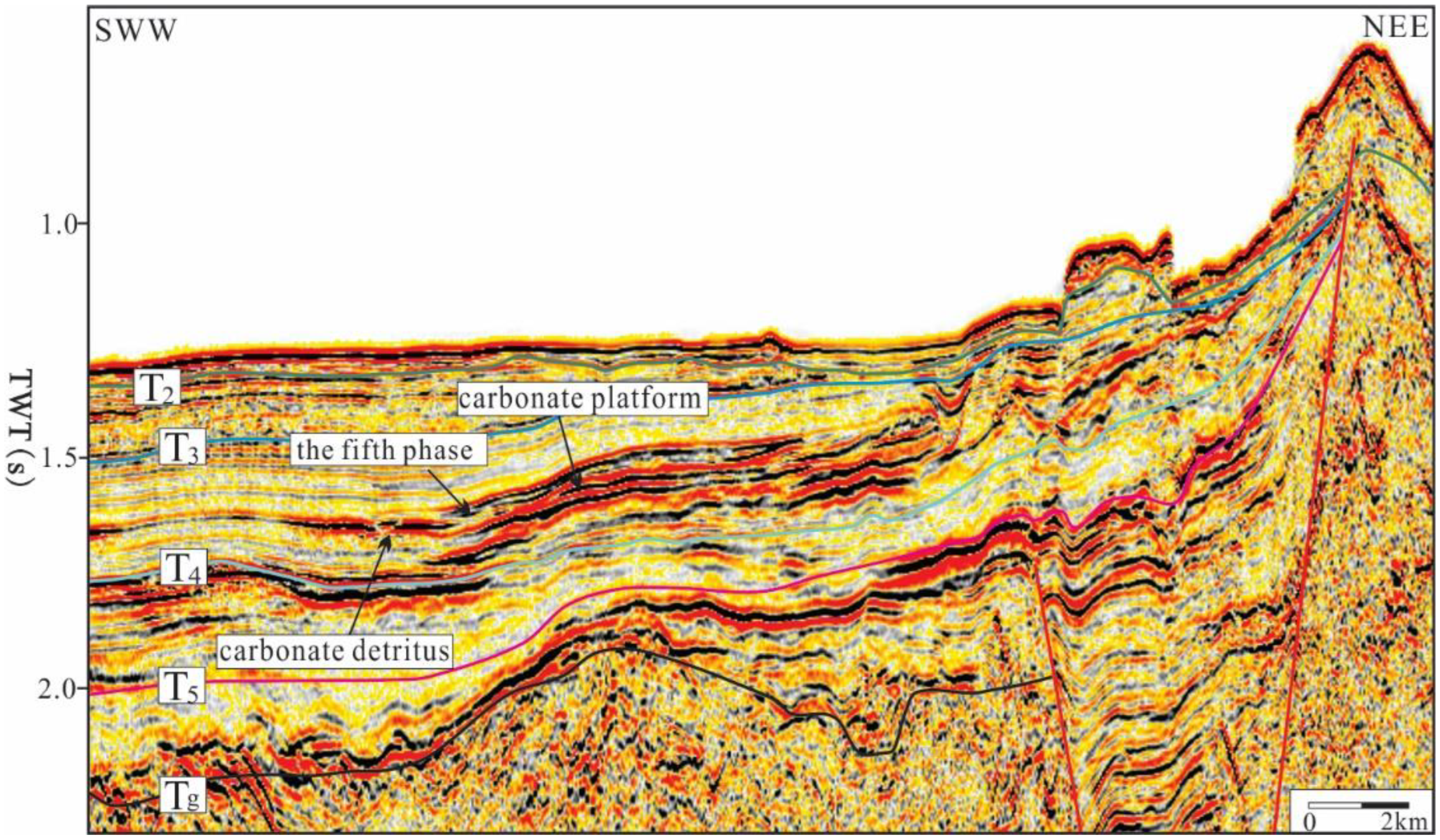
4.2. Morphological Characteristics from Seismic Data
5. Discussion
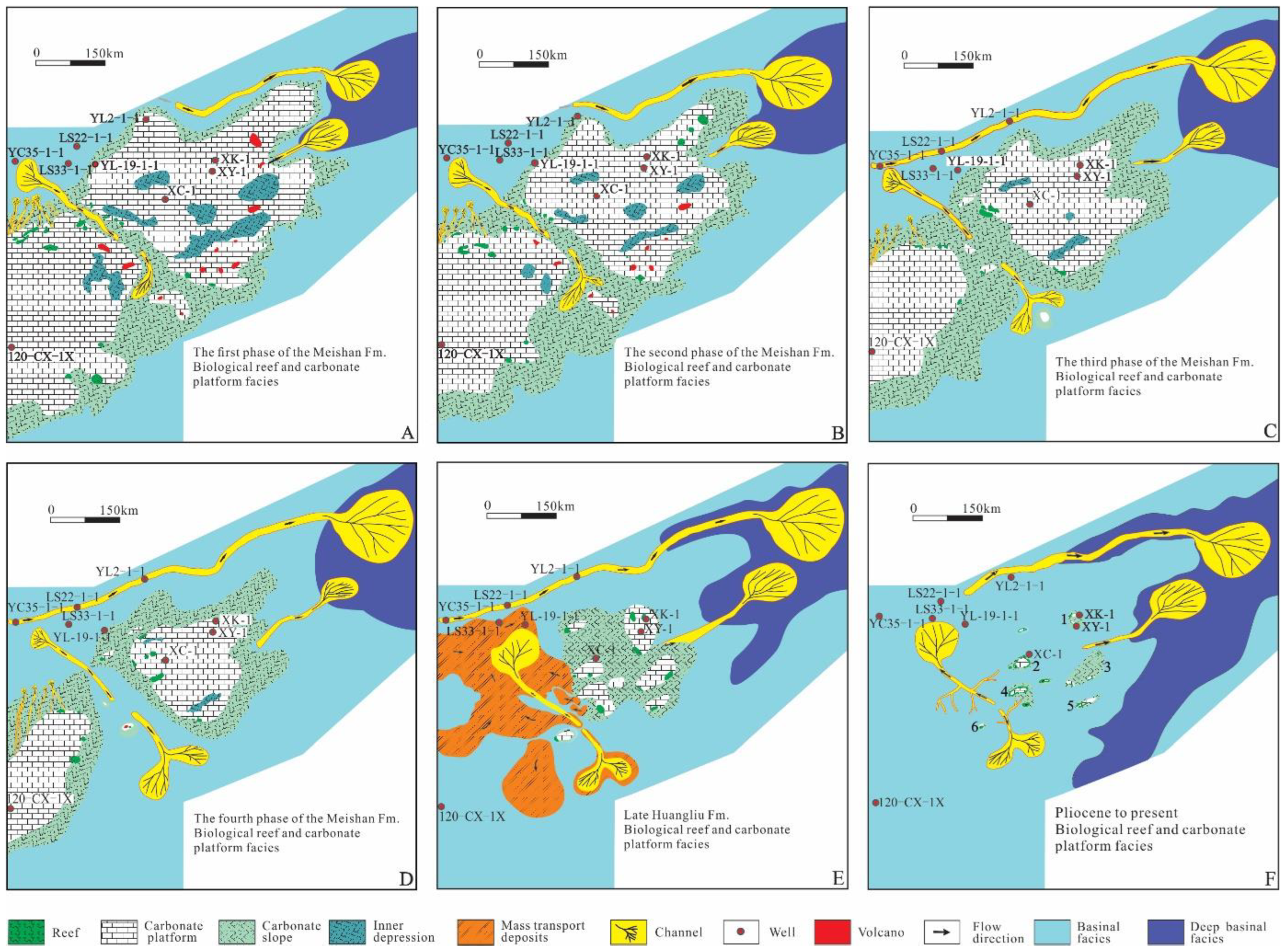
5.1. Distribution of the Carbonate Platform
5.1.1. The Bloom Stage
5.1.2. The Recession Stage
5.1.3. The Submerged Stage
5.1.4. Present
5.2. Significance of Hydrocarbon Exploration
5.2.1. Physical Properties of the Reservoir Rock
5.2.2. Regional Source Rock
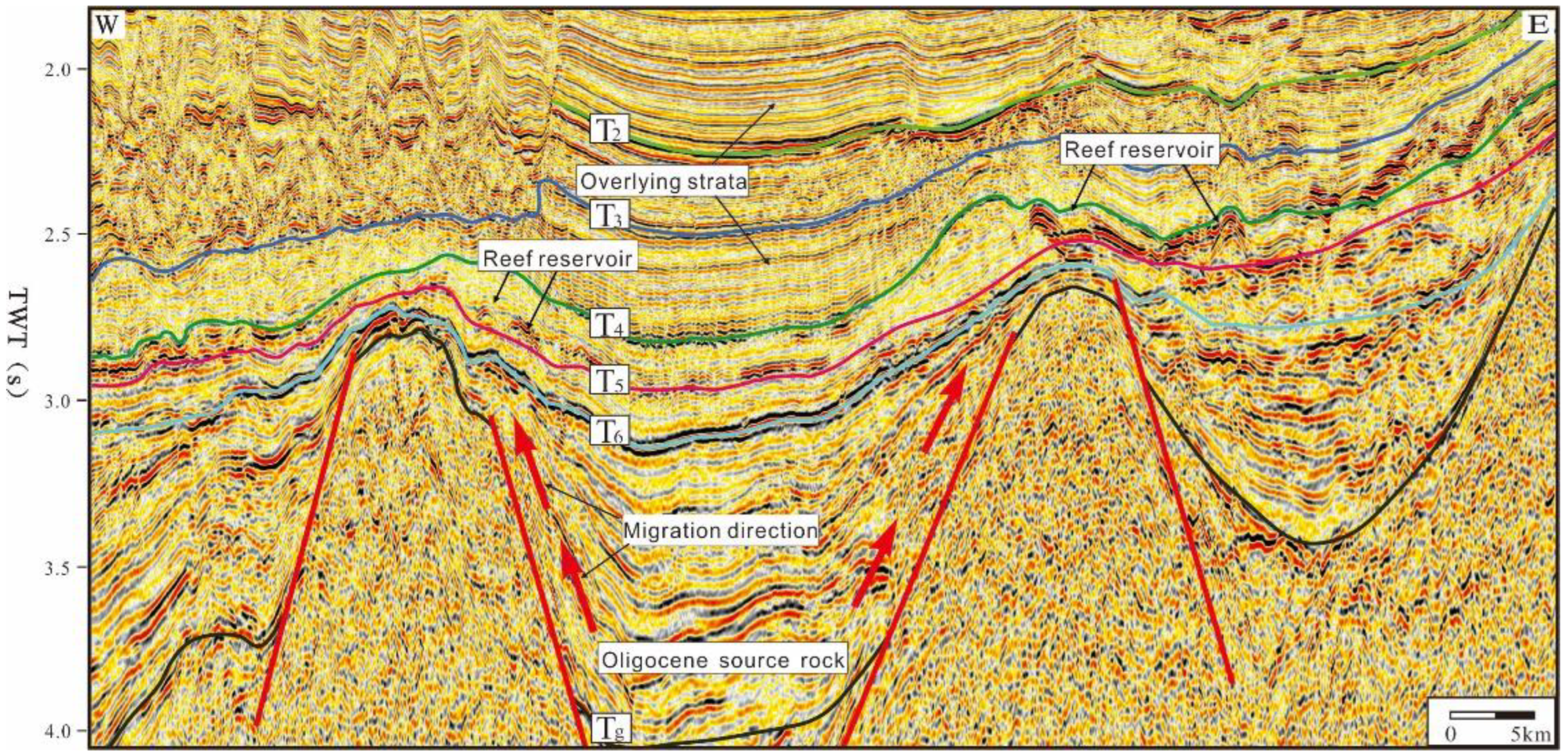
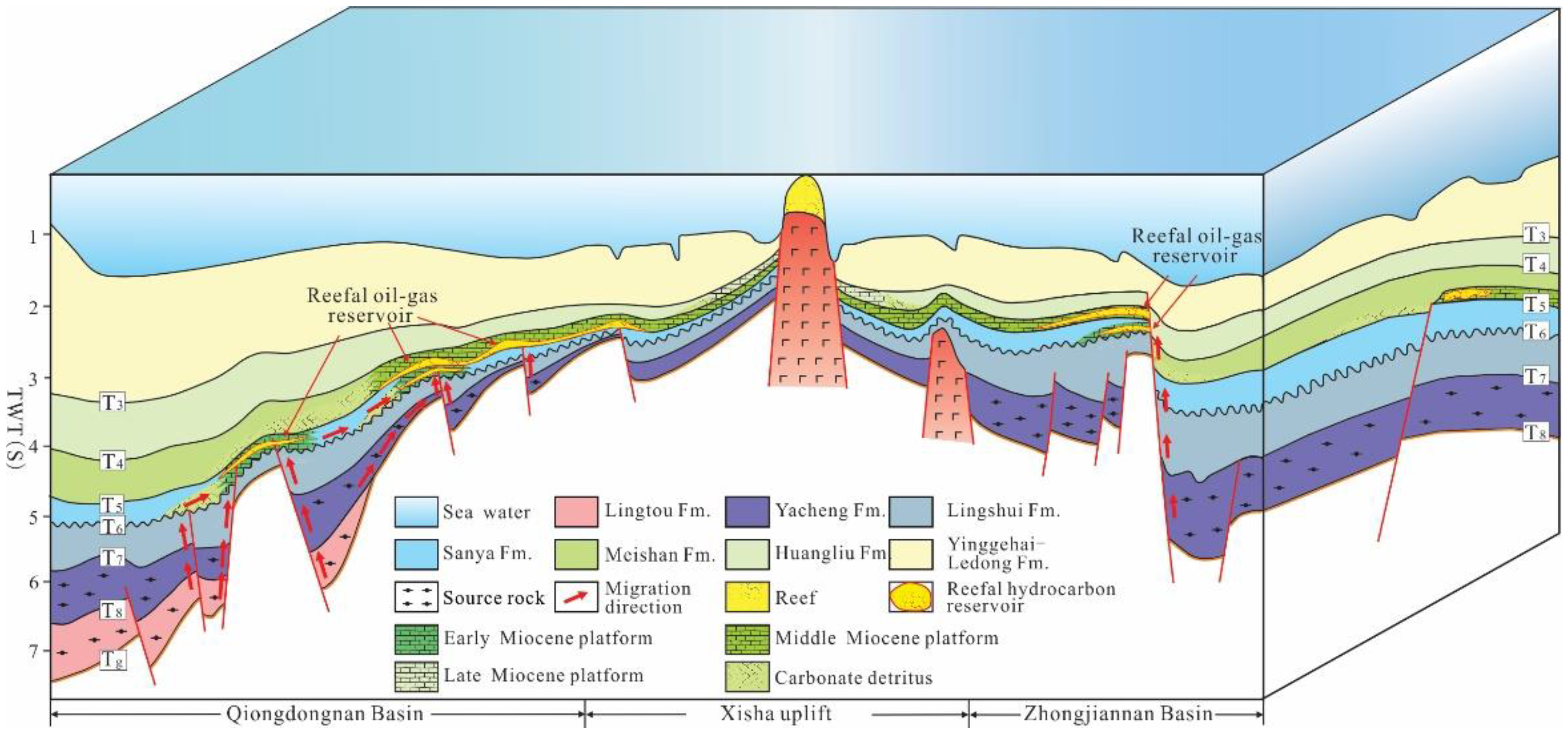
5.2.3. Migration System and Capping Layer
5.2.4. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Potential
5.2.5. Favorable Exploration Zones
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Three identification marks of the boundaries of the carbonate platforms in the Xisha waters have been established: lithological mutation interfaces, fault interfaces, and tidal channels. Among them, the lithological mutation interfaces constitute the lithological mutations of the strongly reflecting carbonate rock and the weakly reflecting mudstone, the fault interfaces are mostly the interfaces between faults and steep cliffs, and the tidal channels are on the gentle slopes of the platform and facilitate exchange between the platform and the sea. For the passage, the cross-section of the seismic section is shown as a “V”-shaped undercut.
- (2)
- The Miocene carbonate platform in the Xisha sea area is divided into six phases and three evolution stages. In the early Middle Miocene, the carbonate platform was fully developed and large in scale. The biological reefs were mainly distributed on the steep slopes from the western to the southwestern edge of the platform. In the Late Miocene, the carbonate platform began to decline and mainly developed in the Xisha Uplift. After the Late Miocene, the platform entered the submerged stage. The platform was located on the periphery of the islands and reefs above the Xisha Uplift, represented by the Dongdao and Yongxing Islands. Since the Pliocene, the platform’s scale has further decreased, and atolls that grow vertically are the main platforms, which remain on the periphery of the islands and reefs.
- (3)
- Based on the analysis of the development characteristics of carbonate reservoirs and oil and gas accumulation factors in the study area, it is proposed that the Miocene carbonate platform in the Xisha sea area has a typical accumulation model of “lower generation, upper reservoir and upper cap”. The hydrocarbon source rock, migration path, and other oil- and gas-related geological conditions indicate that the Huaguang Sag in the Qiongdongnan Basin and the northern Zhongjiannan Basin are two favorable exploration zones for carbonate rocks.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michel, J.; Laugié, M.; Pohl, A.; Lanteaume, C.; Masse, J.-P.; Donnadieu, Y.; Borgomano, J. Marine carbonate factories: A global model of carbonate platform distribution. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 108, 1773–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, Y.; Faisal, M.A.; Biswas, A.; Ali, S.H.; Imran, Q.S.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Ehsan, M. Seismic expression of Miocene carbonate platform and reservoir characterization through geophysical approach: Application in central Luconia, offshore Malaysia. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 11, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Qin, Y.; Wan, X. Sedimentary dynamics in the distal margin around isolated carbonate platforms of the northern South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 884921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khain, V.E.; Polyakova, I.D. Oil and gas potential of deep-and ultradeep-water zones of continental margins. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2004, 39, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, H. Types of organic reef and exploration direction in Zhujiang Formation of Dongsha uplift. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X. Forming Condition of Late-Cenozoic Reef Facies Carbonate Rocks in Xisha Sea Area and Their Oil and Gas Exploration Potential. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Lü, F.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, S. Distribution and model of reef and carbonate platforms in the south deepwater sag of Qiongdongnan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2009, 20, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Gu, M.; Lu, Y.; Dong, D.; Zhao, H. Seismic reflection characteristics and depositional model of carbonate platforms in Xisha sea area. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2010, 32, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Lü, F.; Dong, D.; Sun, Q.; Lu, Y.; Gu, M. Seismic characteristics and development of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northern margin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 770–783. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lü, F.; Lüdmann, T.; Fulthorpe, C.; Wang, B. Architecture, development and geological control of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northwestern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2014, 350, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Ding, W.; Franke, D.; Yao, Y.; Shi, H.; Pang, X.; Cao, Y.; Lin, J.; Kulhanek, D.K. Seismic stratigraphy of the central South China Sea basin and implications for neotectonics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1377–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, F.; Borgomano, J.; Montaggioni, L. Development patterns and controlling factors of Tertiary carbonate buildups: Insights from high-resolution 3D seismic and well data in the Malampaya gas field (Offshore Palawan, Philippines). Sediment. Geol. 2005, 175, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, G. Seismic interpretation of reef carbonate reservoir and hydrocarbon implication in the deepwater Area of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W. Nature Gas Geology in the North Continent Margin Basin of South China Sea; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Mi, L.; Qu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Shengbiao, H. Petroleum geology of deep-water areas in offshore China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, F.; Wu, Y.; He, X.; Wang, B. Early prediction on source rocks of the Oligocene Yacheng Formation in deepwater area of Huagang depression, Qiongdongnan basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 805–816. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, S.; Lü, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y. The evolution model of Later Cenozoic carbonate platform in Xisha Sea area and its geological control. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2014, 34, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Bin, X. Development and controlling factors of Neogene reefs in Xisha sea area. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2016, 38, 787–795. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Xia, B. Paleogeomorphology of Early Middle Miocene in the Xisha sea area and its control factors. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2016, 36, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.G.; Kominz, M.A.; Browning, J.V.; Wright, J.D.; Mountain, G.S.; Katz, M.E.; Sugarman, P.J.; Cramer, B.S.; Christie-Blick, N.; Pekar, S.F. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change. Science 2005, 310, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fyhn, M.B.W.; Boldreel, L.O.; Nielsen, L.H.; Giang, T.C.; Nga, L.H.; Hong, N.T.M.; Nguyen, N.D.; Abatzis, I. Carbonate platform growth and demise offshore Central Vietnam: Effects of Early Miocene transgression and subsequent onshore uplift. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 76, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, D.; Huang, K.; You, L.; Duan, X.; Li, S. Microscopic features and genesis for Miocene to Pliocene dolomite in well Xike-1, Xisha Islands. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2015, 40, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q. The Sedimentary Research about Reef Carbonatite in Xisha Islands Waters. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China, 2010; 170p. [Google Scholar]
- Zampetti, V.; Schlager, W.; van Konijnenburg, J.-H.; Everts, A.-J. Architecture and growth history of a Miocene carbonate platform from 3D seismic reflection data; Luconia province, offshore Sarawak, Malaysia. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Carbonate reservoir characteristics and its prediction of Dongsha massif. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2011, 33, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L. The evolution and main controlling factors of reef and carbonate platform in Wan’an Basin. Earth Sci. 2016, 41, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, H.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J. Seismic Response Characteristics and Identification of Miocene Carbonate Rocks in Dongsha Uplift of Pearl River Month Basin. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2011, 33, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, P.M.; Purkis, S.J.; Ellis, J. Analyzing spatial patterns in modern carbonate sand bodies from Great Bahama Bank. J. Sediment. Res. 2011, 81, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, S.; Dong, D. Cenozoic magmatism in the northern continental margin of the South China Sea: Evidence from seismic profiles. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2016, 37, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Qin, Z.; Spence, G.; Lü, F. Seismic characteristics of the Huaguang mass transport deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Implications for regional tectonic activity. Mar. Geol. 2013, 346, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; You, L. Sedimentology of Carbonate Bioherm Reservoir in Well Xike-1, South China Sea-Reservoir Characteristics and Diagenetic Evolution; China University of Geosciences Press: Wuhan, China, 2016; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Yan, W.; Huang, L. Evolution and Controlling Factors of the Reef and Carbonate Platform in Wan’an Basin, South China Sea. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Yuan, S.; Wu, S.; Zhong, C. Double provenance depositional model and exploration prospect in the deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2008, 35, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, G.; Mi, L.; Wu, S. Reservoir type and sedimentary evolution in the continental margin deepwater area of the northern South China Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2007, 28, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.H.; Watkins, J.S. Seismic sequence stratigraphy and hydrocarbon potential of the Phu Khanh Basin, offshore central Vietnam, South China Sea. AAPG Bull. 1998, 82, 1711–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Fyhn, M.B.W.; Boldreel, L.O.; Nielsen, L.H. Geological development of the Central and South Vietnamese margin: Implications for the establishment of the South China Sea, Indochinese escape tectonics and Cenozoic volcanism. Tectonophysics 2009, 478, 184–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Pan, S.; Jing, Z.; Ma, Q.; Gan, H.; Zhao, J.-X. Sedimentary architecture and provenance analysis of a sublacustrine fan system in a half-graben rift depression of the South China Sea. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 409, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Carter, A.; Hoang, L.V.; Fox, M.; Pham, S.N.; Vinh, H.B. Evolution of the continental margin of south to central Vietnam and its relationship to opening of the South China Sea (East Vietnam Sea). Tectonics 2022, 41, e2021TC006971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Mi, L.; Wu, S.; Tao, W.; He, S.; Lü, J. Deepwater area-the new prospecting targets of northern continental margin of South China Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2007, 28, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Yan, W.; Liu, S.; Cai, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhong, K.; Pei, J.; Sun, B. The tectonic evolution of the Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern margin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 77, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, G.; Hou, G.; Zhong, K.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Characteristics of migration system of paleogene Lingshui Formation in the deep water area in Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 138–148. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Yan, W.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Geological Distribution of the Miocene Carbonate Platform in the Xisha Sea Area of the South China Sea, and Its Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211831
Yang Z, Zhang G, Wu S, Zhu Y, Wu C, Zhang L, Liu S, Yan W, Sun M, Zhang Y, et al. Geological Distribution of the Miocene Carbonate Platform in the Xisha Sea Area of the South China Sea, and Its Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(22):11831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211831
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhen, Guangxue Zhang, Shiguo Wu, Youhua Zhu, Cong Wu, Li Zhang, Songfeng Liu, Wei Yan, Ming Sun, Yaoming Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Geological Distribution of the Miocene Carbonate Platform in the Xisha Sea Area of the South China Sea, and Its Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration" Applied Sciences 12, no. 22: 11831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211831
APA StyleYang, Z., Zhang, G., Wu, S., Zhu, Y., Wu, C., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Yan, W., Sun, M., Zhang, Y., Du, X., & Xu, C. (2022). Geological Distribution of the Miocene Carbonate Platform in the Xisha Sea Area of the South China Sea, and Its Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration. Applied Sciences, 12(22), 11831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211831





