Dual-Mode Control Scheme to Improve Light Load Efficiency for Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converters Using Single-Phase-Shift Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
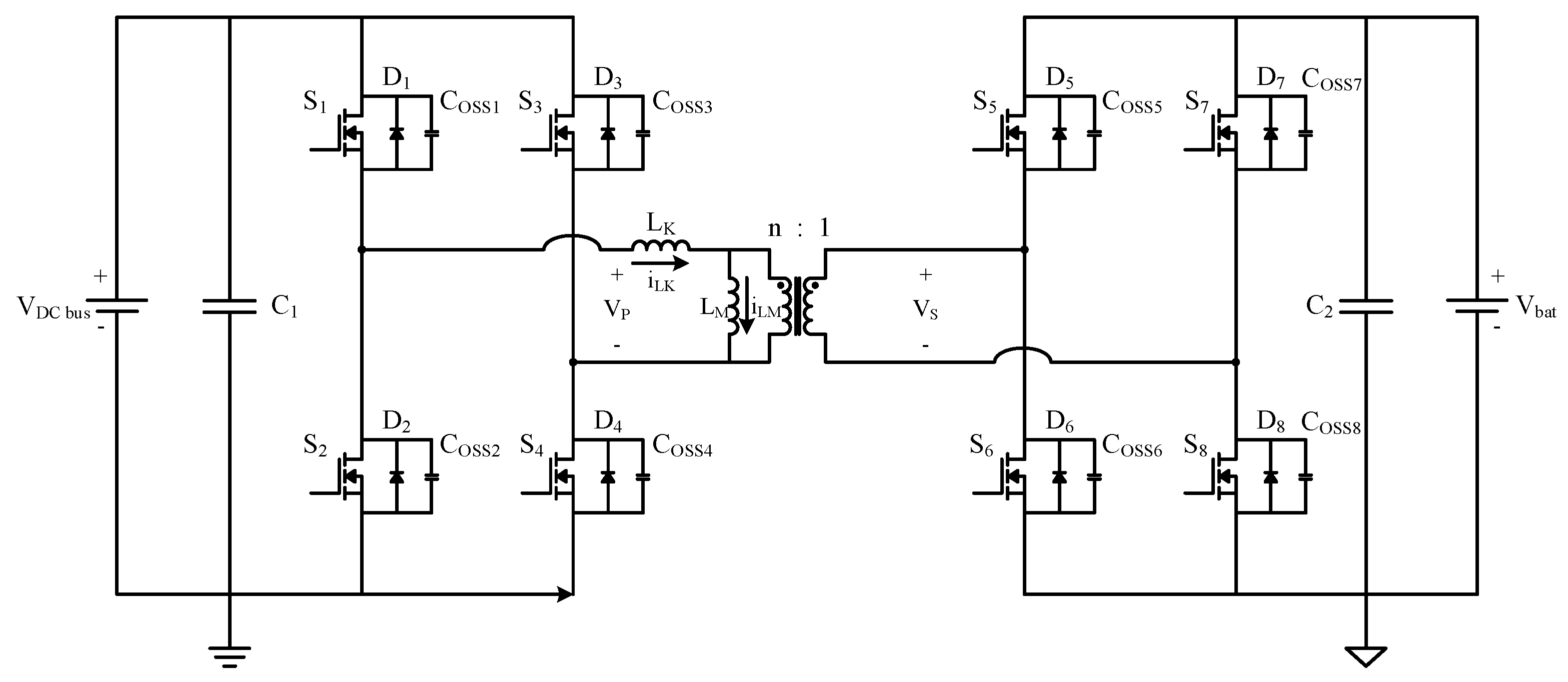
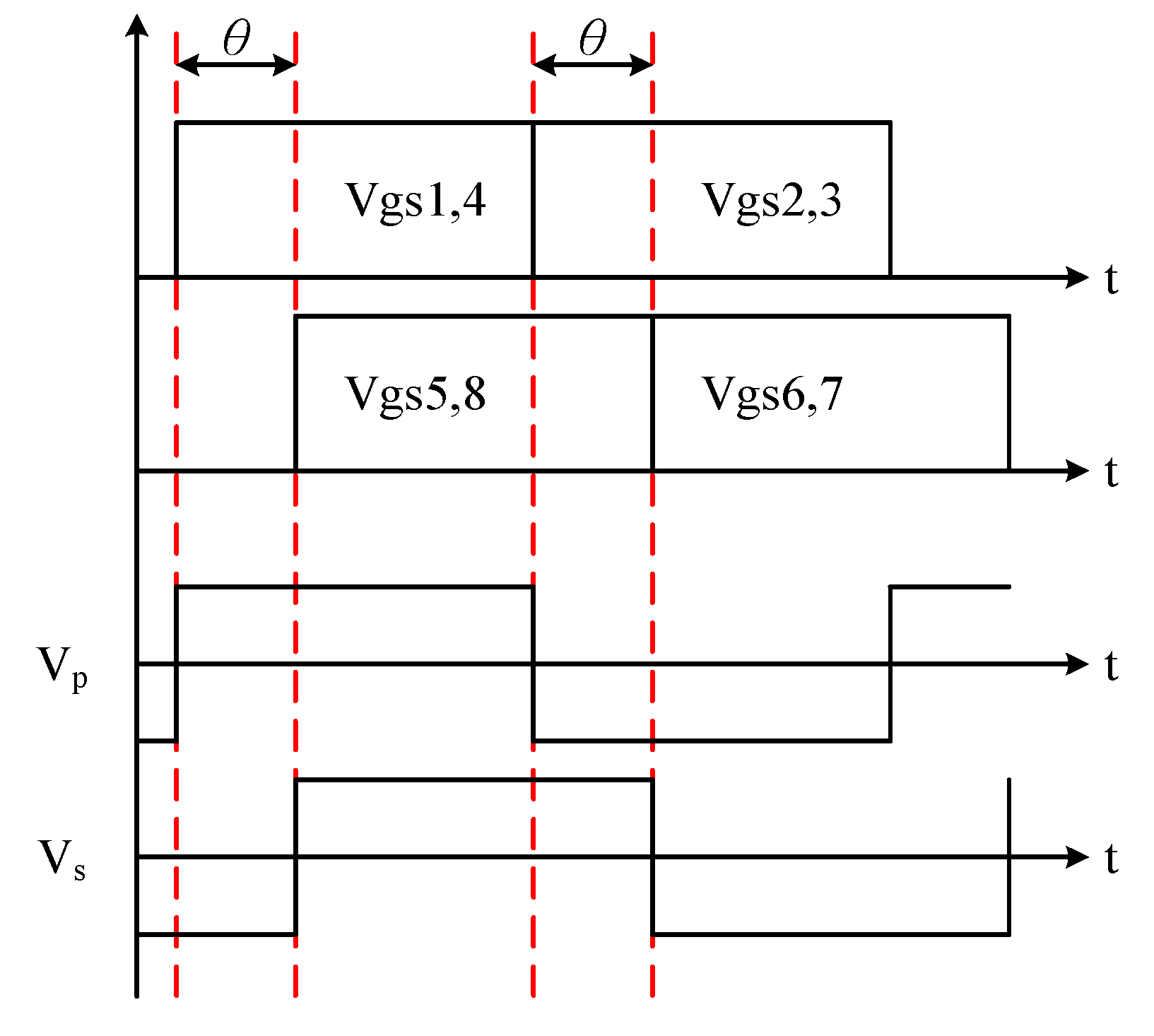
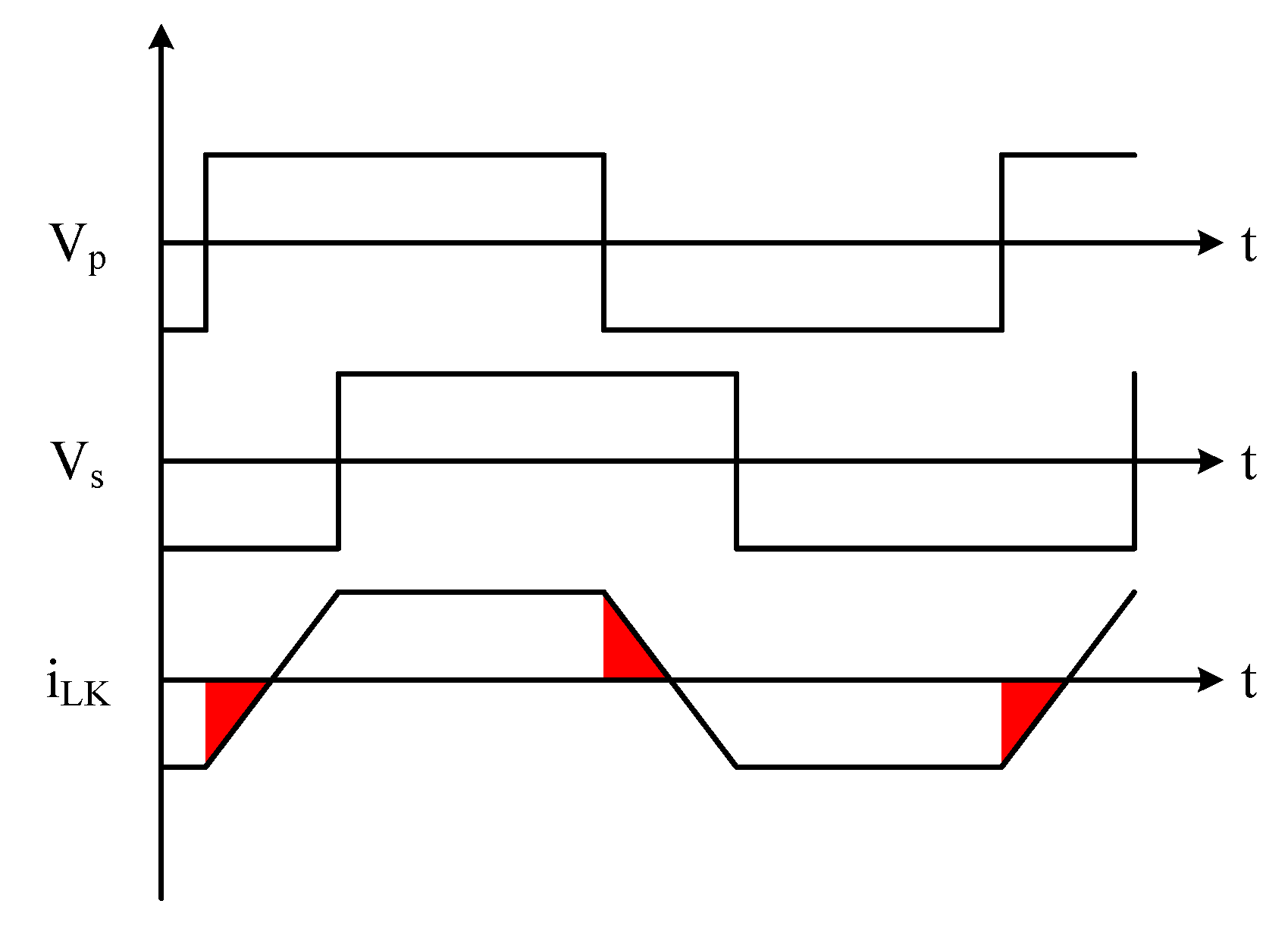
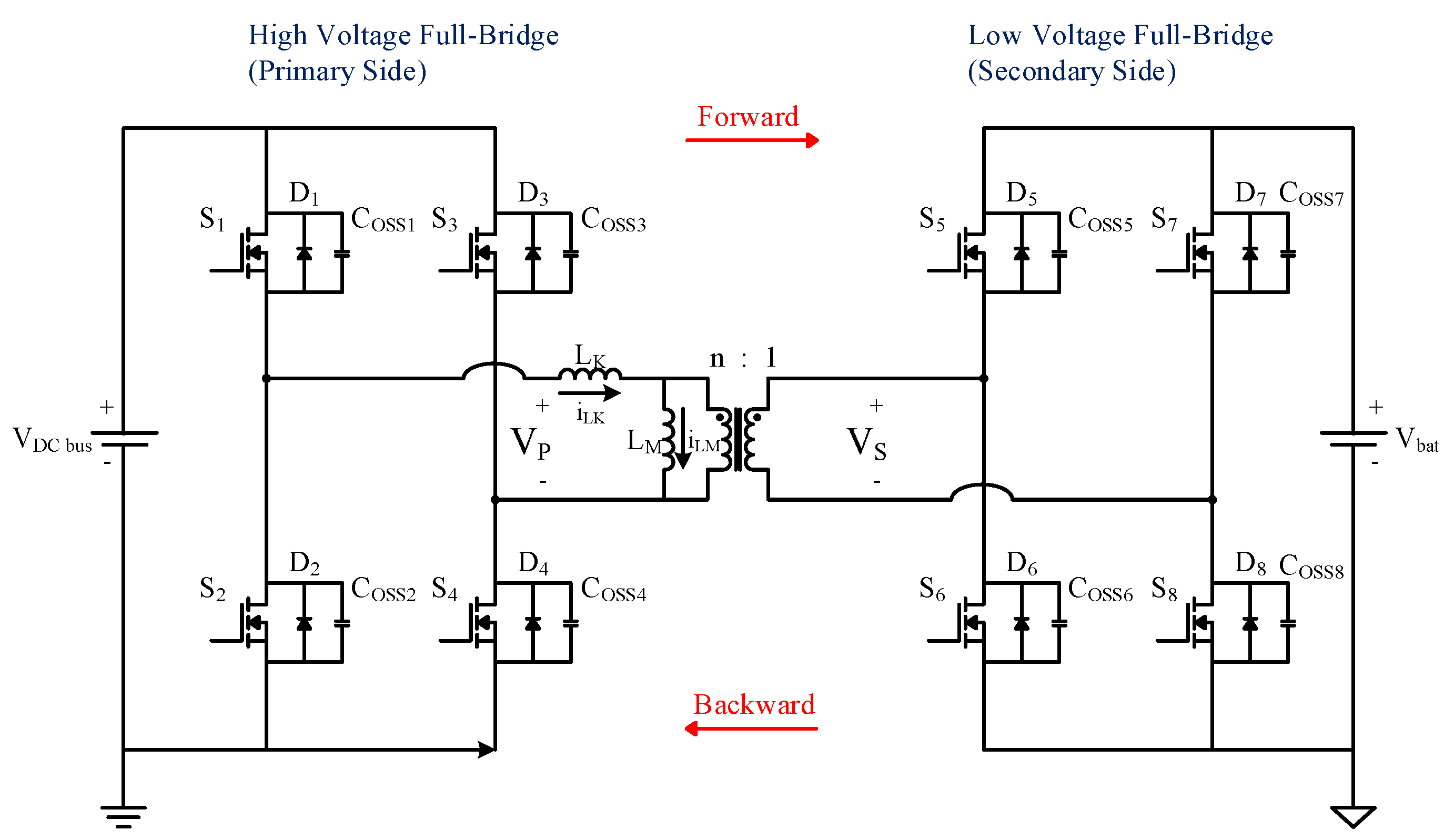
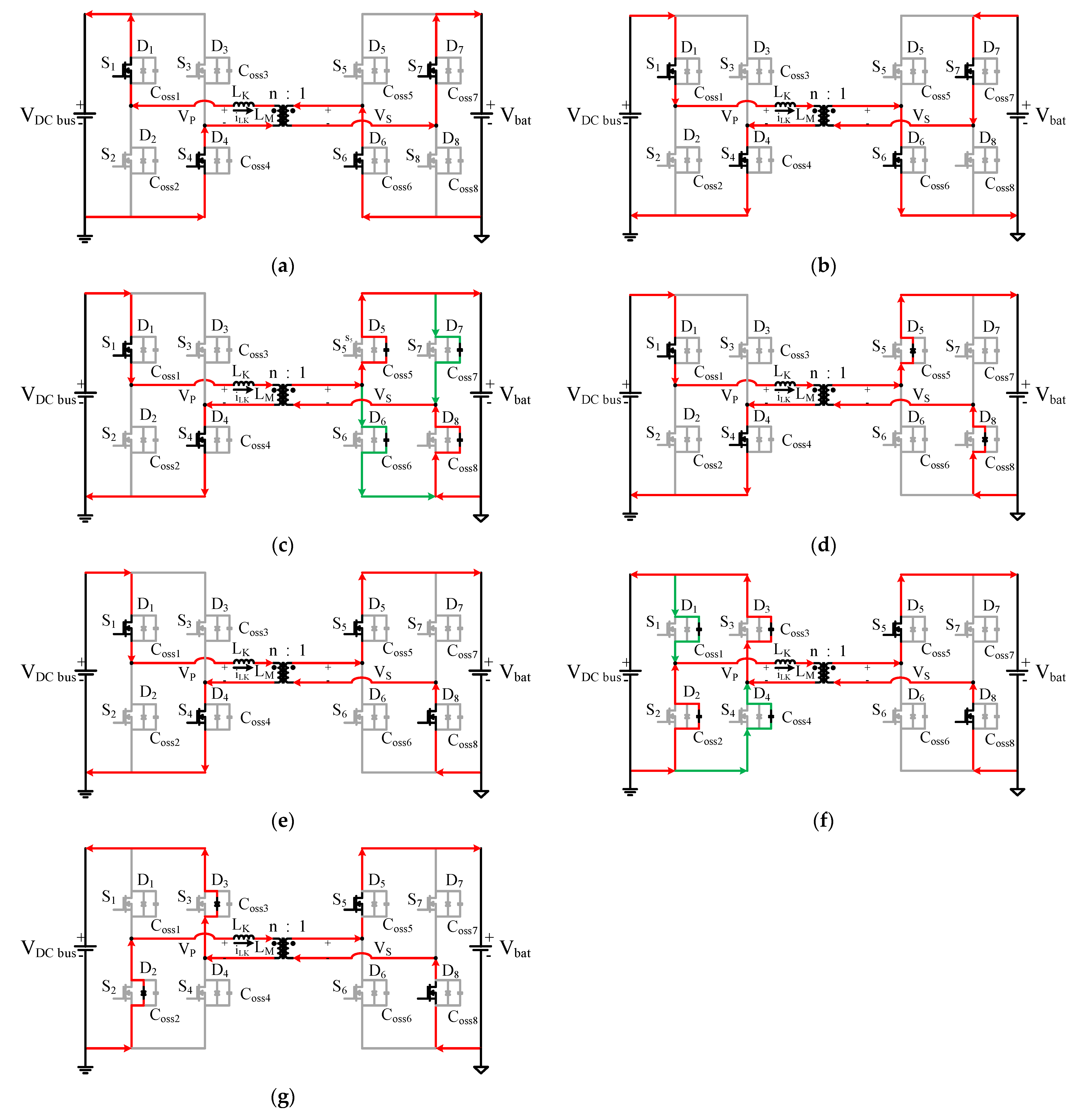
2. Operating Principle of the Proposed Dual-Mode Control Strategy for the DAB Converter
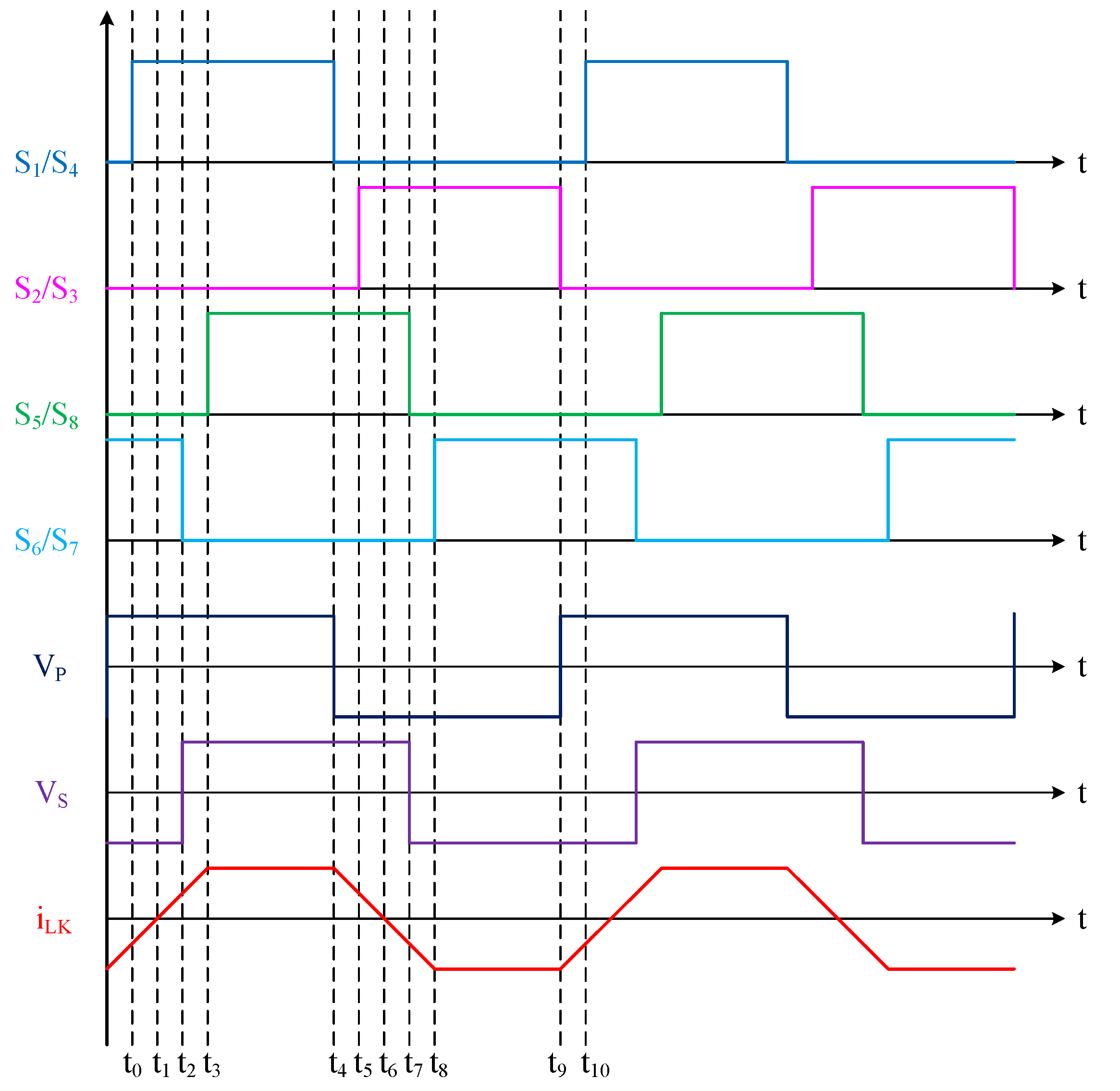
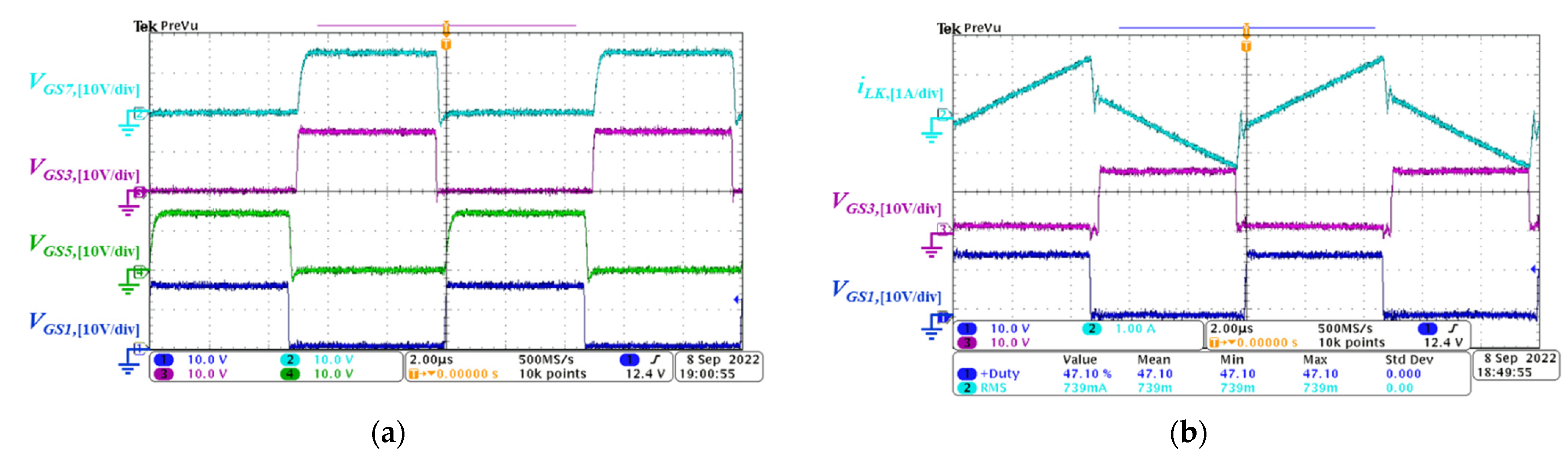
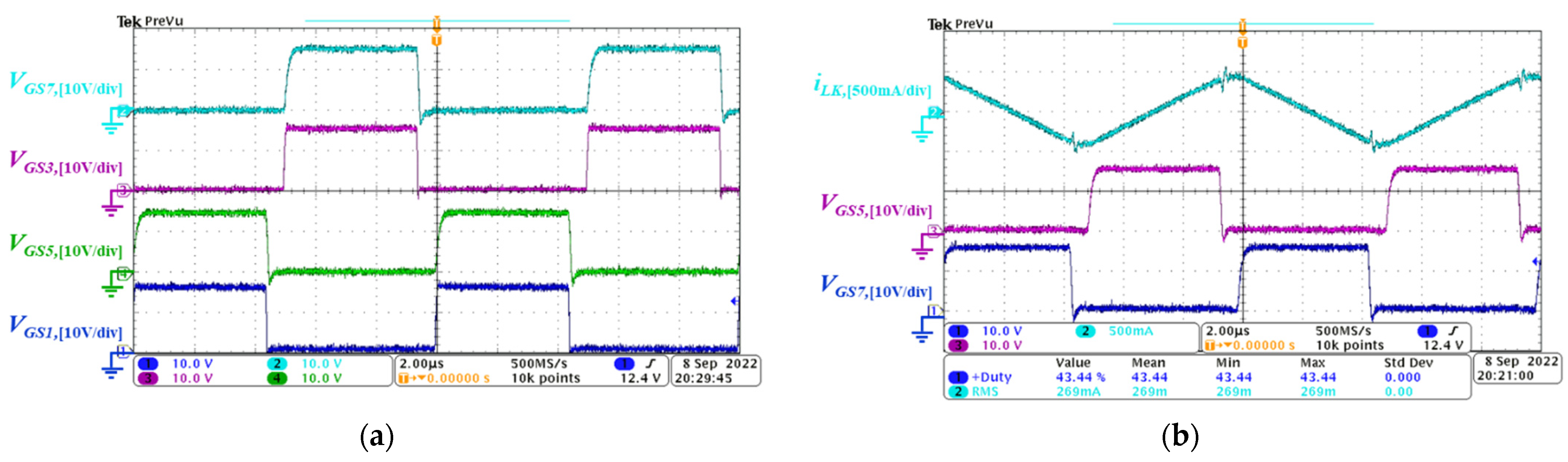
2.1. Light Load
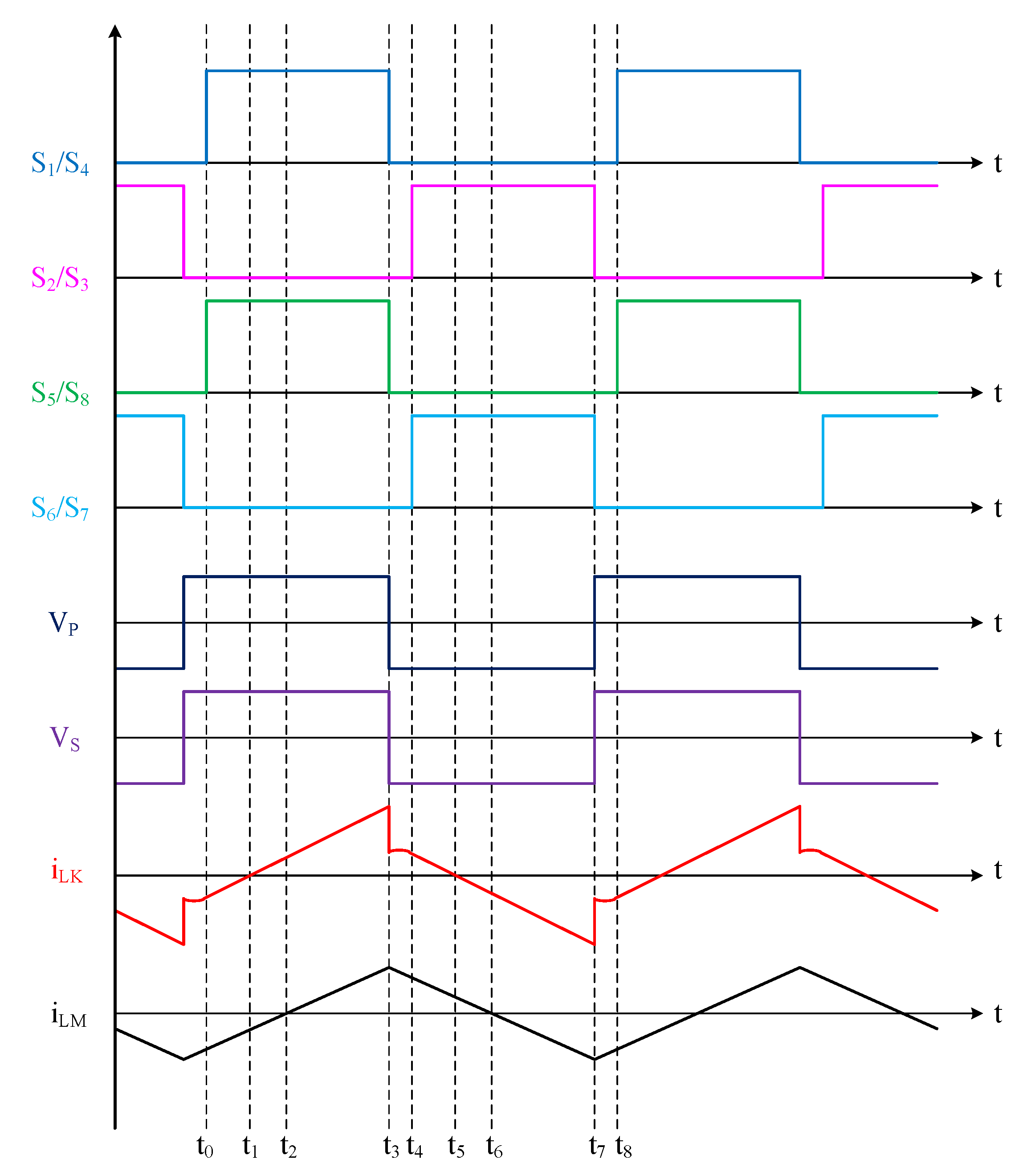
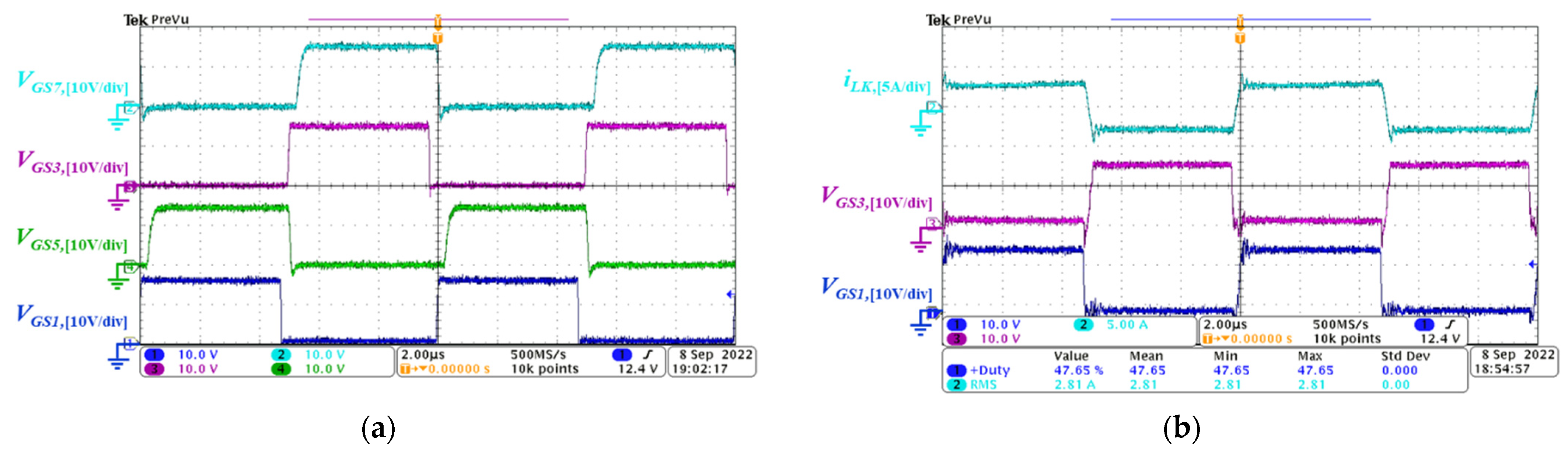
2.2. Medium-to-Full Load
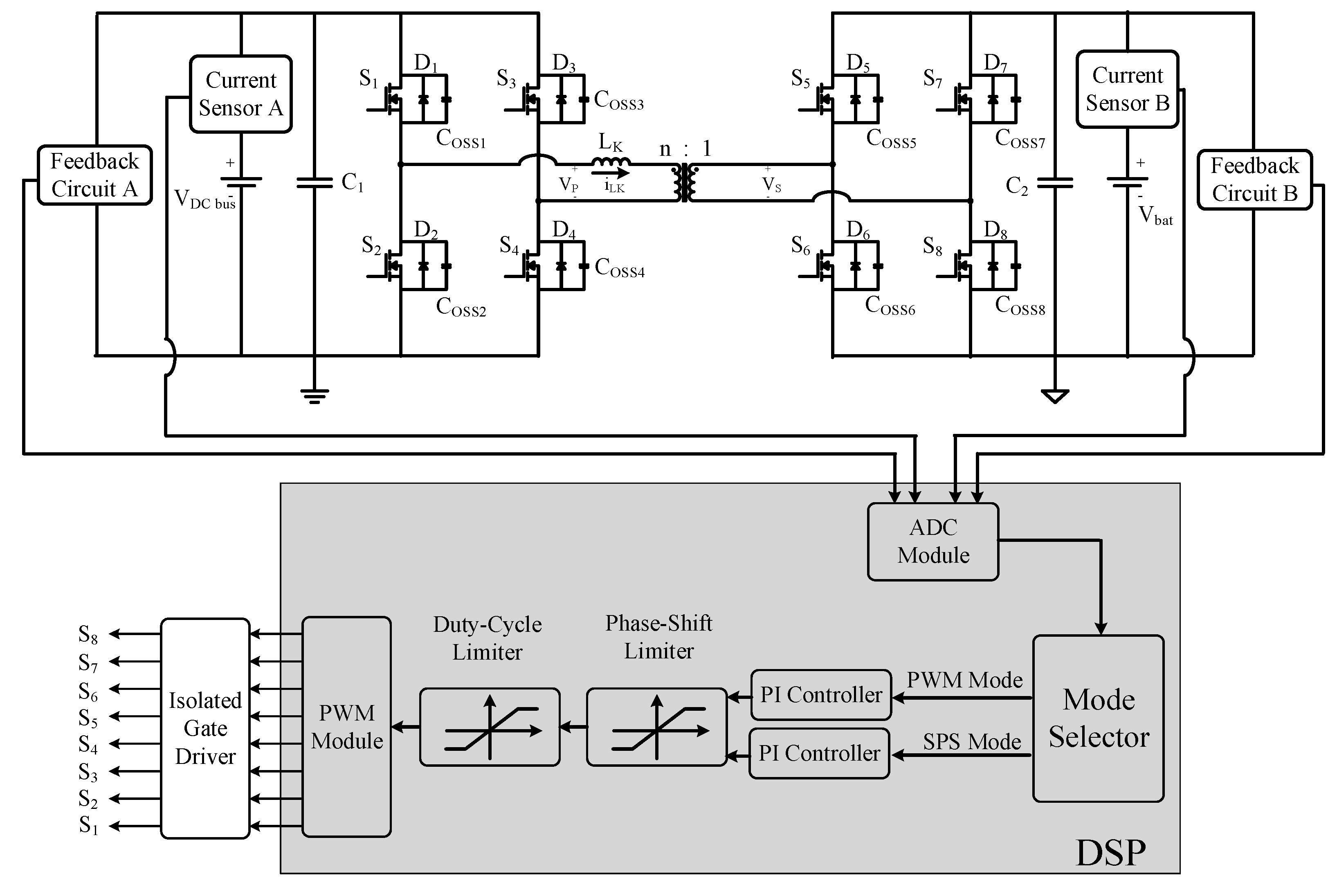
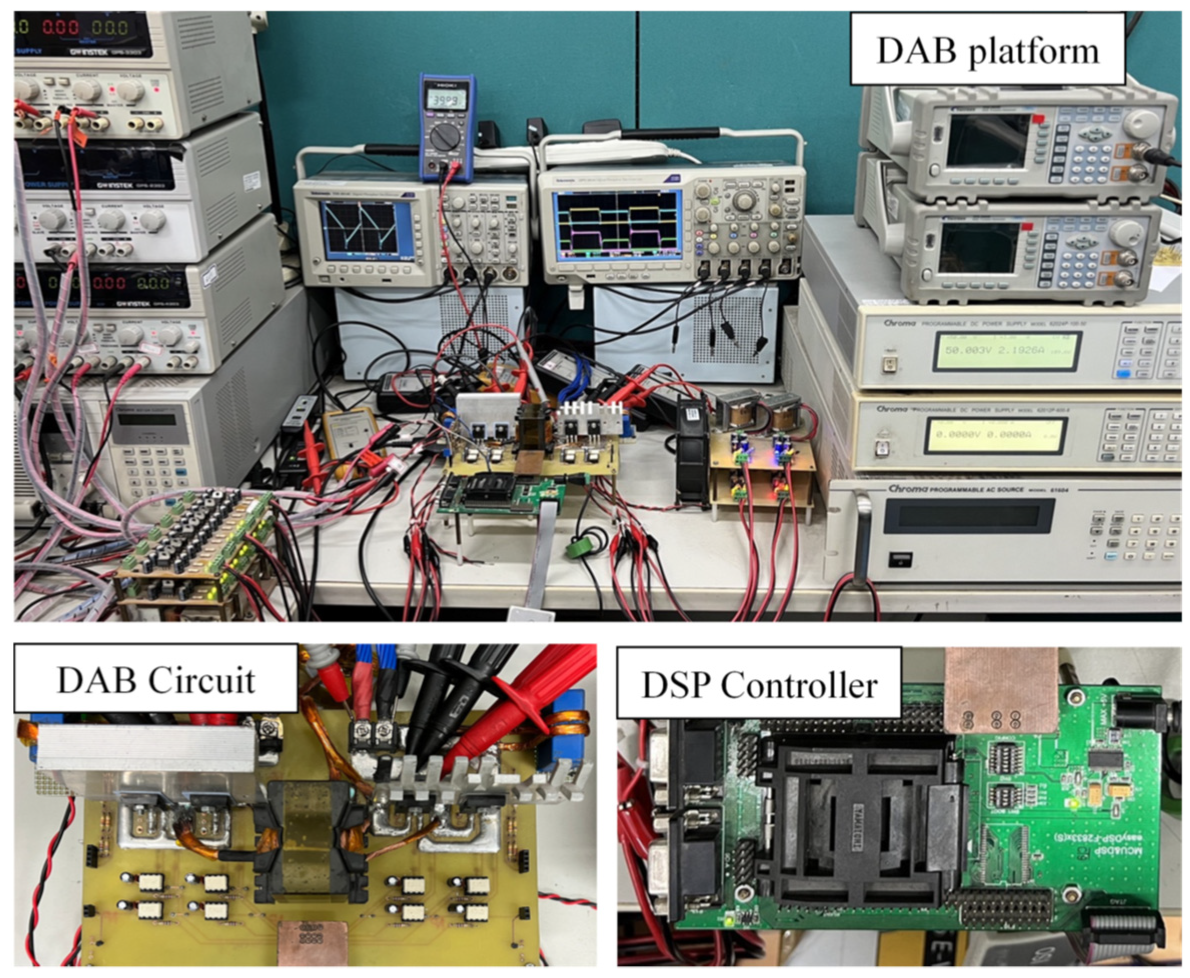
3. Design of the DAB Converter Prototype
3.1. Transformer Selection
3.2. Inductor Selection
3.3. Output Capacitor Selection
4. Power Loss Model of the DAB Converter
4.1. Power Switch Losses
4.2. Transformer Losses
4.3. Inductor Losses
4.4. Total Power Losses
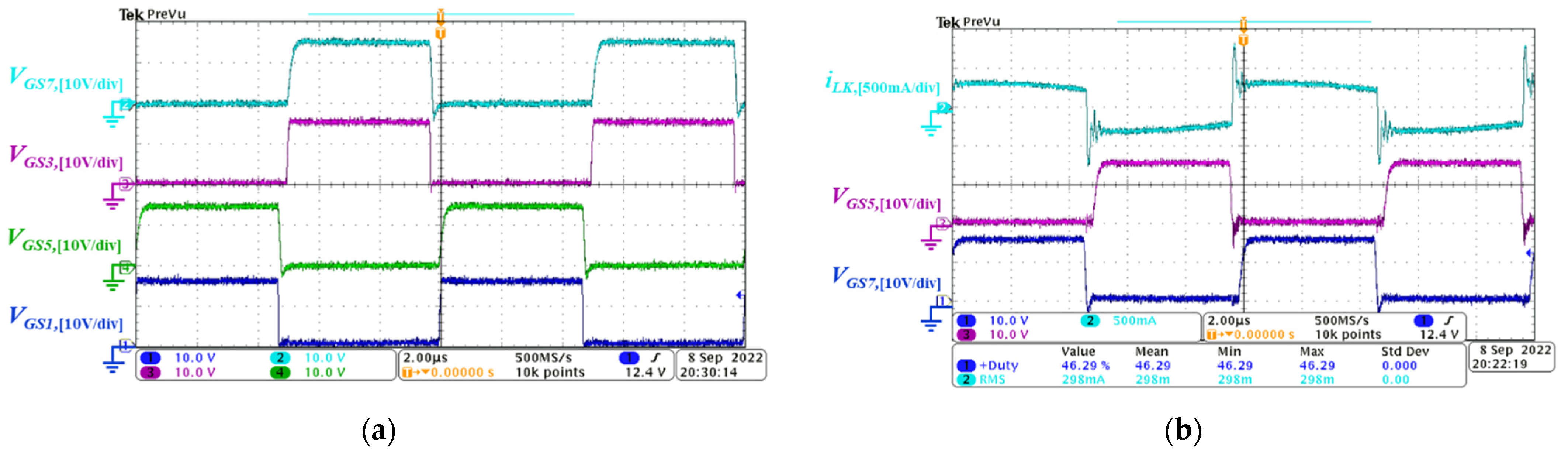
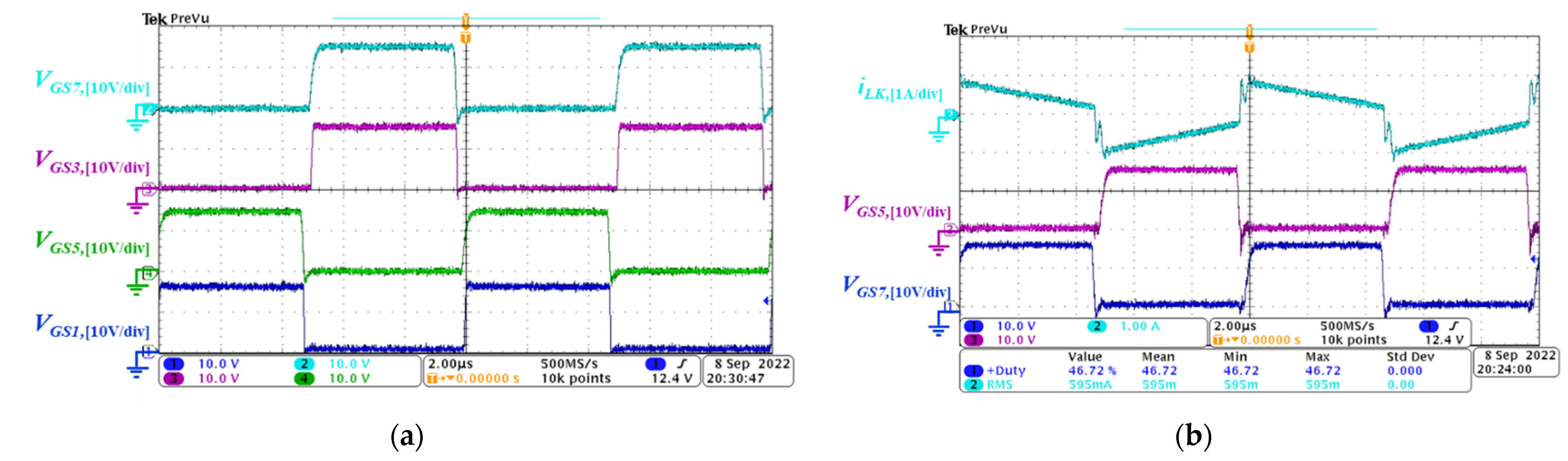
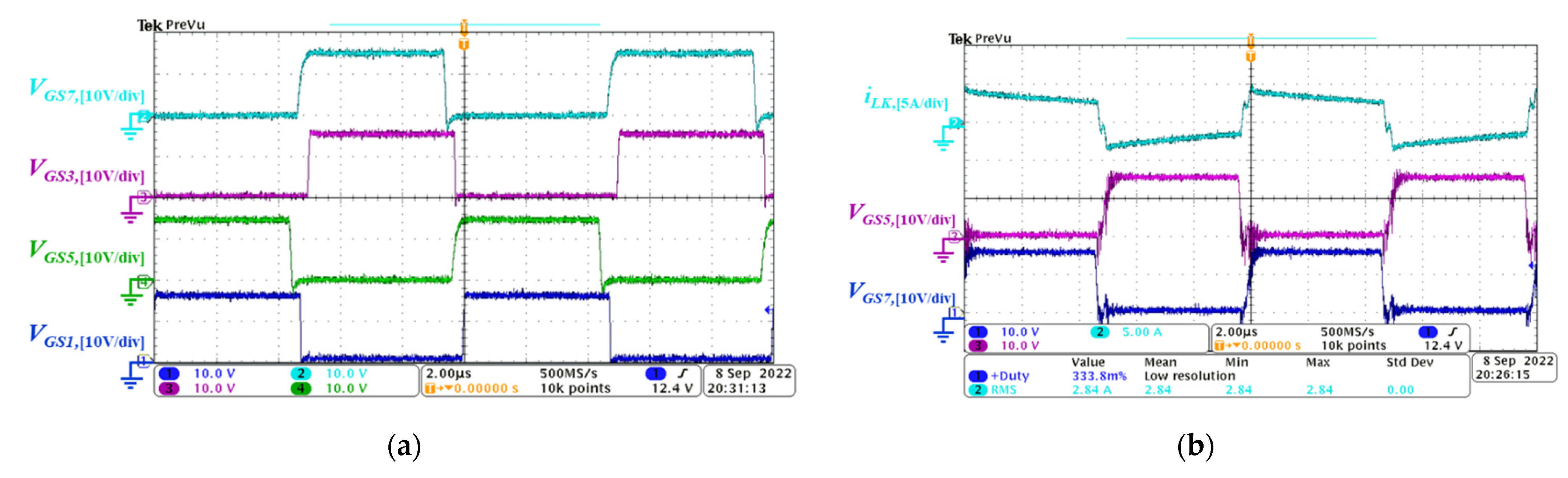
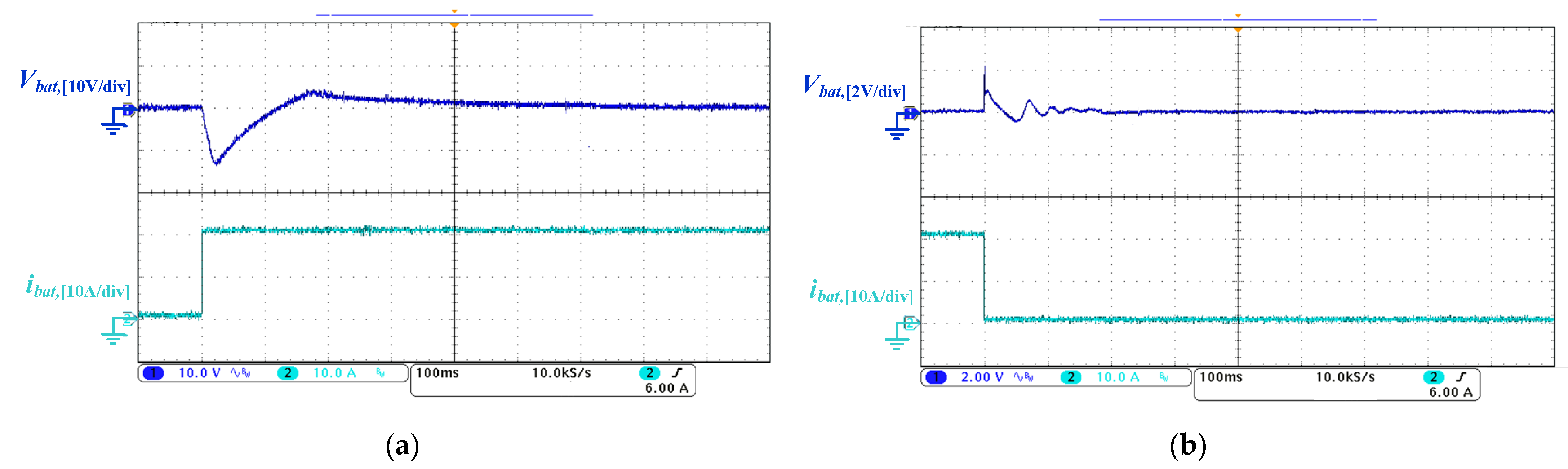
5. Experimental Results
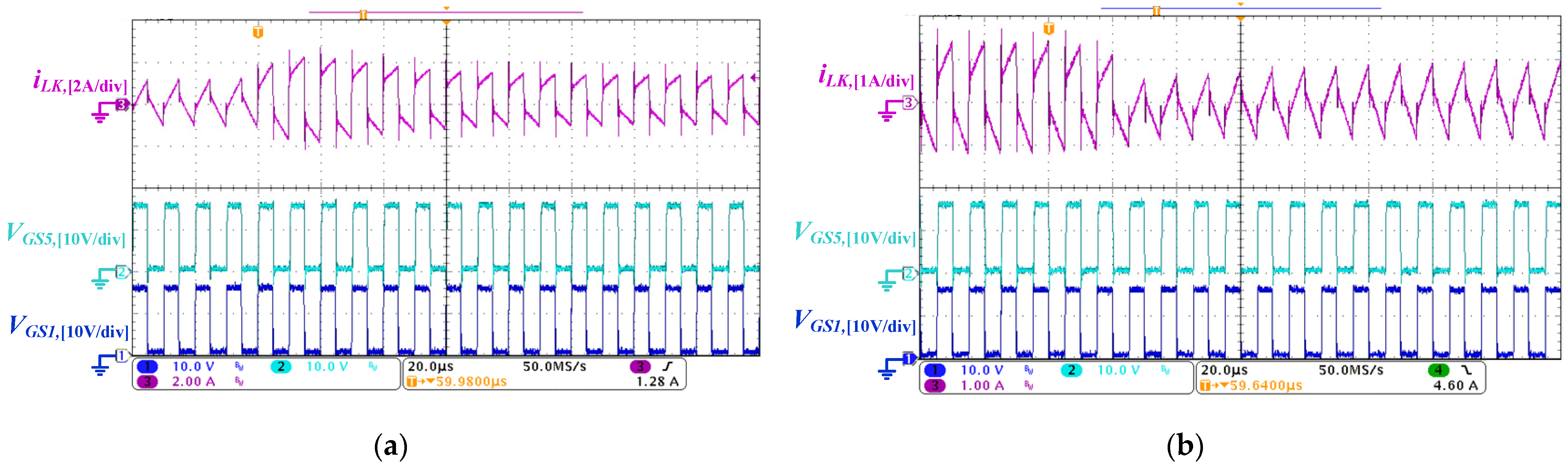
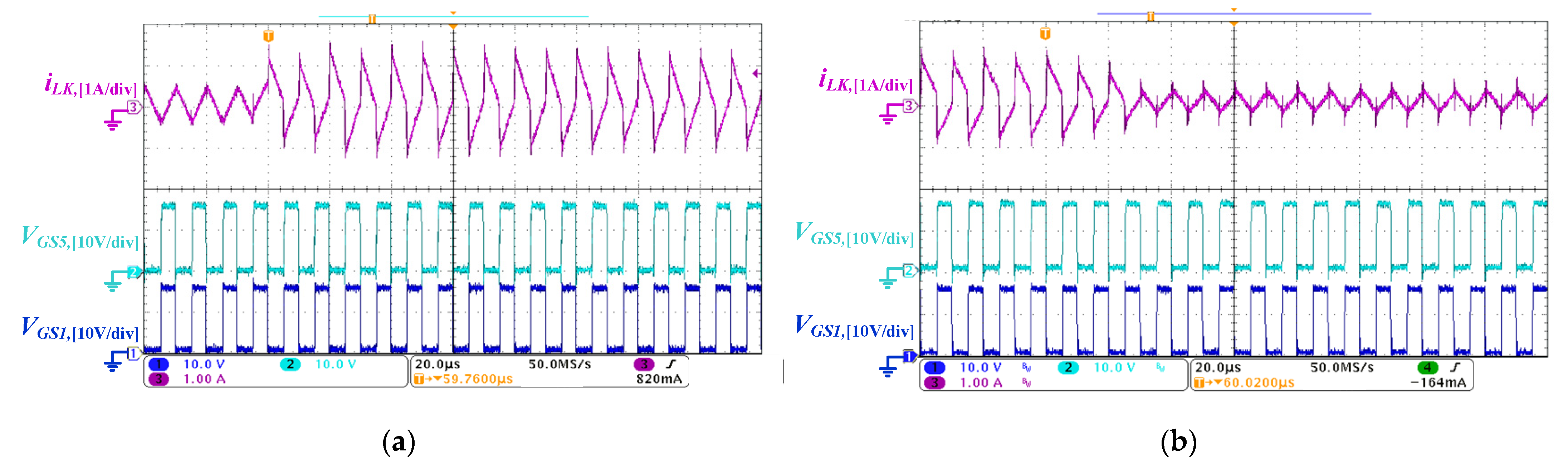
5.1. Forward Power Conversion Mode
5.2. Backward Power Conversion Mode
5.3. Load Transient Testing for the Proposed DAB Converter
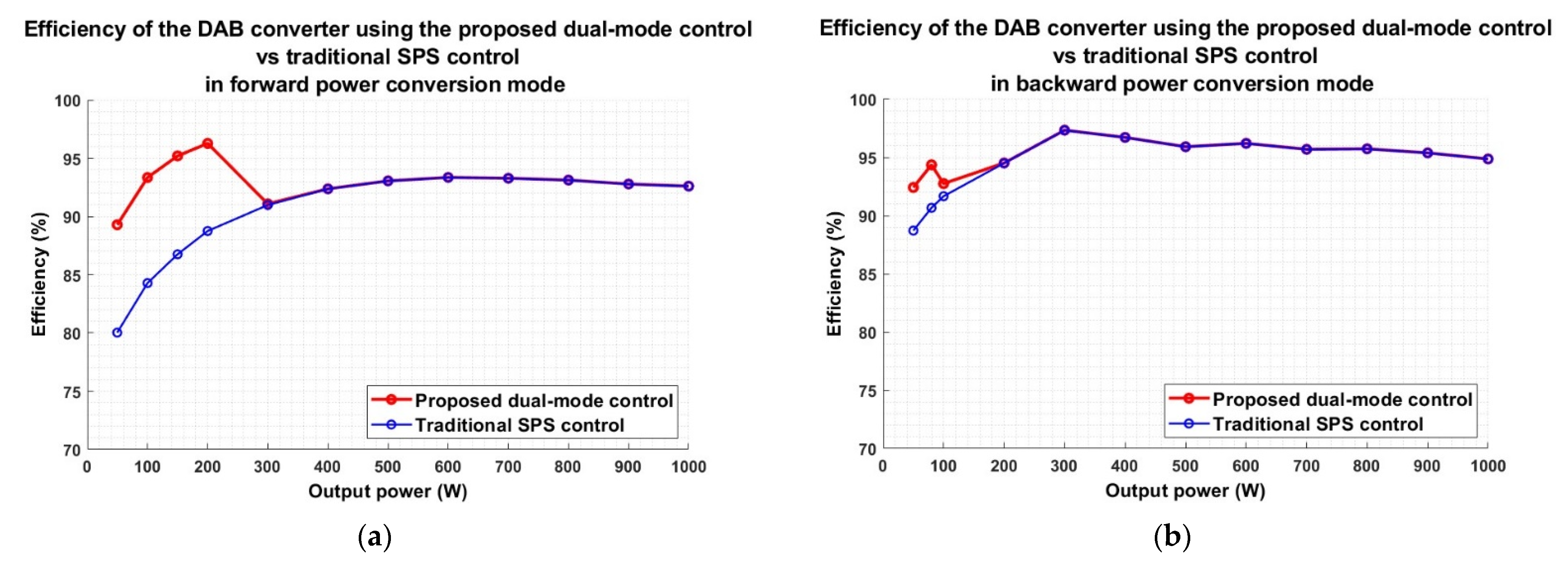
5.4. Efficiency Comparison Curve
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Research and Innovation; European SmartGrids Technology Platform. European SmartGrids Technology Platform: Vision and strategy for Europe’s Electricity Networks of the Future; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Can, E. A new multi-level inverter with reverse connected dual dc to dc converter at simulation. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2022, 42, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costinett, D.; Maksimovic, D.; Zane, R. Design and control for high efficiency in high step-down dual active bridge converters operating at high switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 3931–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Doncker, R.W.; Divan, D.M.; Kheraluwala, M.H. A three-phase soft-switched high-power-density DC/DC converter for high-power applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Akagi, H. A bidirectional isolated DC–DC converter as a core circuit of the next-generation medium-voltage power conversion system. IEEE Trans. Power 2007, 22, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigerwald, R.L.; De Doncker, R.W.; Kheraluwala, H. A comparison of high-power DC-DC soft-switched converter topologies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1996, 32, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenke, R.; Mura, F.; De Doncker, R.W. Comparison of non-resonant and super-resonant dual-active ZVS-operated high-power DC-DC converters. In Proceedings of the 2009 13th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 8–10 September 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Xu, M.; Sun, J.; Lee, F.C. A family of high power density unregulated bus converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krismer, F.; Kolar, J.W. Accurate power loss model derivation of a high-current dual active bridge converter for an automotive application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wen, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G.; Ma, J. Minimum-backflow-power scheme of DAB-based solid-state transformer with extended-phase-shift control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 3483–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Fully ZVS, minimum RMS current operation of the dual-active half-bridge converter using closed-loop three-degree-of-freedom control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10188–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-H.; Cheng, H.-L.; Chan, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-D.; Chang, Y.-N. Design of an Isolated Bidirectional Symmetric Resonant Converter. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, F. A new dual-bridge series resonant DC–DC converter with dual tank. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 3884–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TDK. Mn-Zn Ferrite Cores for Switching Power Supplies PQ Series. Available online: https://product.tdk.com/system/files/dam/doc/product/ferrite/ferrite/ferrite-core/catalog/ferrite_mz_sw_pq_en.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Pressman, A. Switching Power Supply Design; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Design Guide: TIDA-010054 Bidirectional, Dual Active Bridge Reference Design for Level 3 Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. 2019. Available online: https://www.ti.com/document-viewer/lit/html/TIDUES0C/GUID-714D036F-89AA-4176-B535-67496BDA93E6#TITLE-TIDUES0ID-7516C1F1-8B53-4F6E-D989-7869B3181718 (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Gladish, J.; Semiconductor, F. MOSFET Selection to Minimize Losses in Low-Output-Voltage DC-DC Converters Fairchild Semiconductor Power Seminar 2008–2009. Available online: https://nanopdf.com/download/mosfet-selection-to-minimize-losses-in-low-output_pdf (accessed on 29 September 2022).





| Item | Proposed | Ref. [10] | Ref. [12] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topology | DAB | DAB | SRDAB |
| Control strategy | Dual-mode PWM-SPS | MEPS | PFM |
| Transformer type | Conventional transformer | Solid-state transformer | Conventional transformer |
| Prototype power rating | 1 kW | 200 W | 1 kW |
| Switching frequency | 100 kHz | 20 kHz | 70–150 kHz |
| Maximum efficiency | 97.30% | pprox. 90.00% | 94.60% |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Primary voltage, VDcbus | 400 V |
| Secondary voltage, Vbat | 50 V |
| Maximum output power, Po,max | 1 kW |
| Maximum power, PMax | 4.5 kW |
| Switching frequency, fsw | 100 kHz |
| Maximum phase-shift, Dmax | 0.2 |
| Voltage ripple, ΔVDcbus, ΔVbat | <5% |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Primary voltage, VDcbus | 400 V |
| Secondary voltage, Vbat | 50 V |
| Transformer turns ratio, n | 24:3 |
| Maximum output power, Po,max | 1 kW |
| Switching frequency, fsw | 100 kHz |
| Maximum phase-shift, Dmax | 0.2 |
| Magnetizing inductance, LM | 1.2 mH |
| Leakage inductance, LK | 57 µH |
| High-voltage side capacitor, C1 | 100 µF |
| Low-voltage side capacitor, C2 | 360 µF |
| Load Condition | Proposed | Ref. [10] | Ref. [12] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light load (10% of power rating) | 93.34% | n/a | approx. 86% |
| Medium load (50% of power rating) | 93.04% | approx. 88% | approx. 92% |
| Full load (100% of power rating) | 92.59% | approx. 90% | 93.25% |
| Item | Model No. | Parameter | Power Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pri. (S1~S4) | SCT3080ALGC11 | RDS(ON) = 80 mΩ; Ciss = 571 pF; Crss = 19 pF | 1.769 W |
| Sec. (S5~S8) | IRFP4321PBF | RDS(ON) = 12 mΩ; Ciss = 4460 pF; Crss = 82 pF | 2.385 W |
| Transformer | PC95PQ50/50Z-12 | PCV(Tr) = 39,810 W/m3; Ve(Tr) = 37.2 × 10−6 m3; RCopper(Pri) = 3.35 Ω; RCopper(Sec) = 0.0155 Ω | 1.499 W |
| Inductor | CM467125 | PCV(In) = 40 × 103 W/m3; Ve(In) = 21.373 × 10−6 m3; RCopper(In) = 0.2554 Ω | 0.813 W |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, T.N.T.; Chang, W.-Y.; Wang, J.-M. Dual-Mode Control Scheme to Improve Light Load Efficiency for Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converters Using Single-Phase-Shift Control. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12356. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312356
Tran TNT, Chang W-Y, Wang J-M. Dual-Mode Control Scheme to Improve Light Load Efficiency for Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converters Using Single-Phase-Shift Control. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(23):12356. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312356
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Thanh Nhat Trung, Wen-Yan Chang, and Jian-Min Wang. 2022. "Dual-Mode Control Scheme to Improve Light Load Efficiency for Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converters Using Single-Phase-Shift Control" Applied Sciences 12, no. 23: 12356. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312356
APA StyleTran, T. N. T., Chang, W.-Y., & Wang, J.-M. (2022). Dual-Mode Control Scheme to Improve Light Load Efficiency for Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converters Using Single-Phase-Shift Control. Applied Sciences, 12(23), 12356. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312356






