Effect of Process Parameters on Distortions Based on the Quantitative Model in the SLM Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Numerical Method
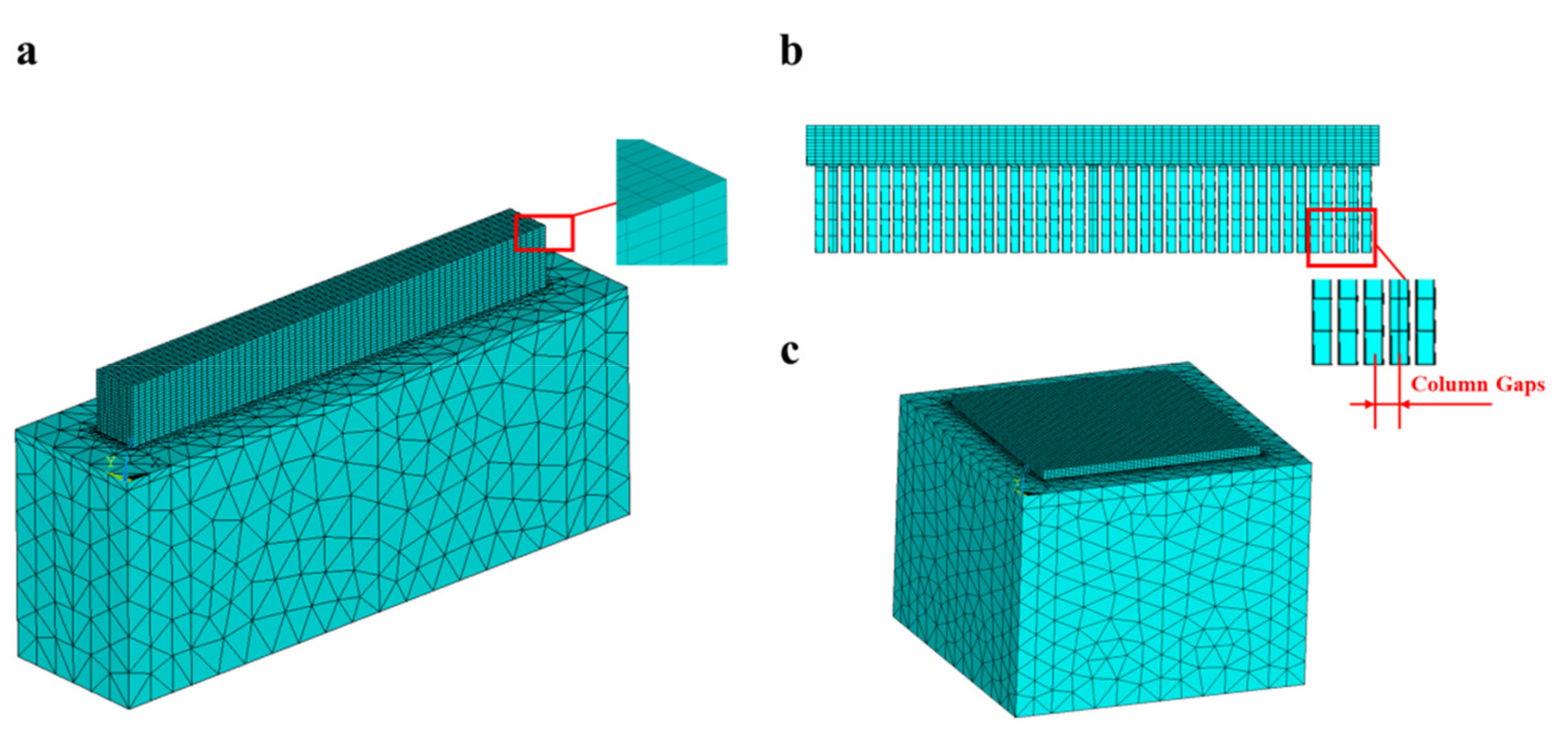
2.3. Simulation Details
3. Results
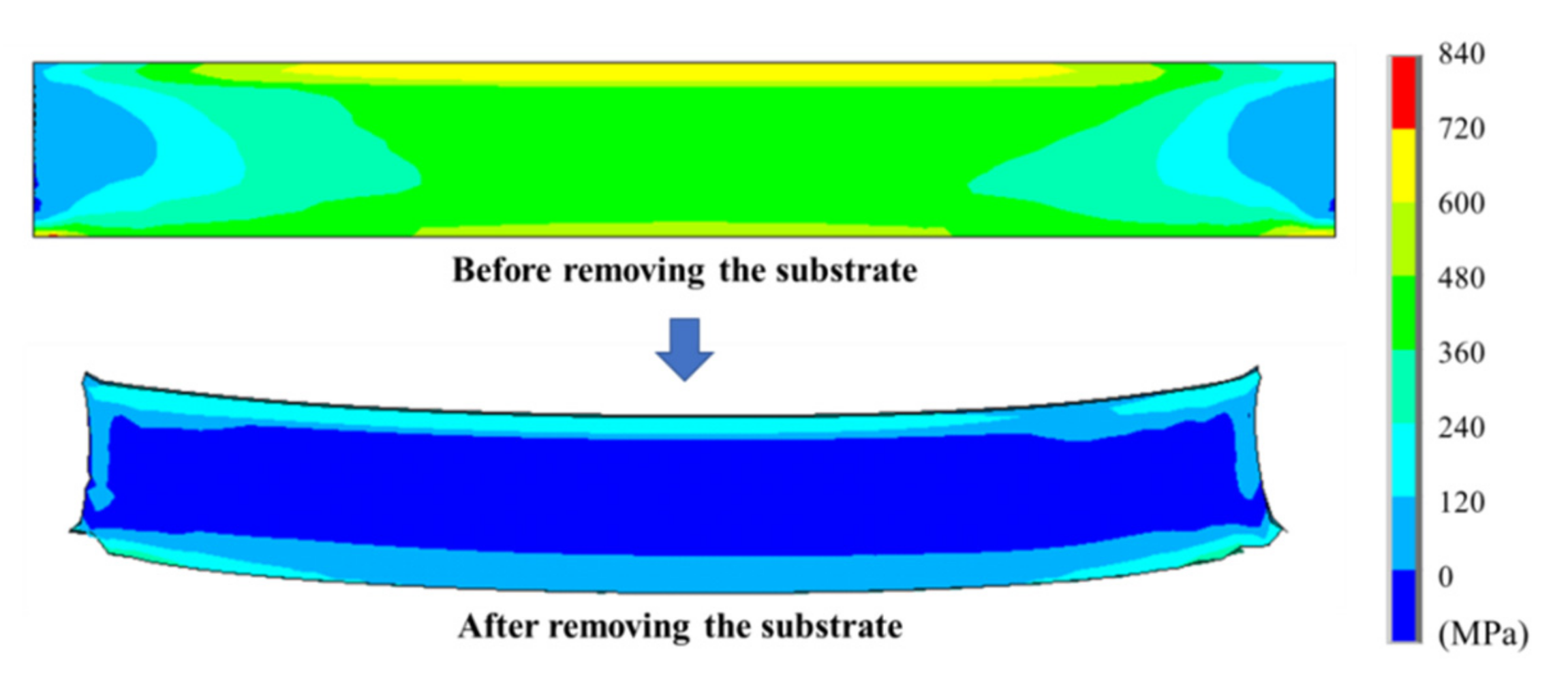
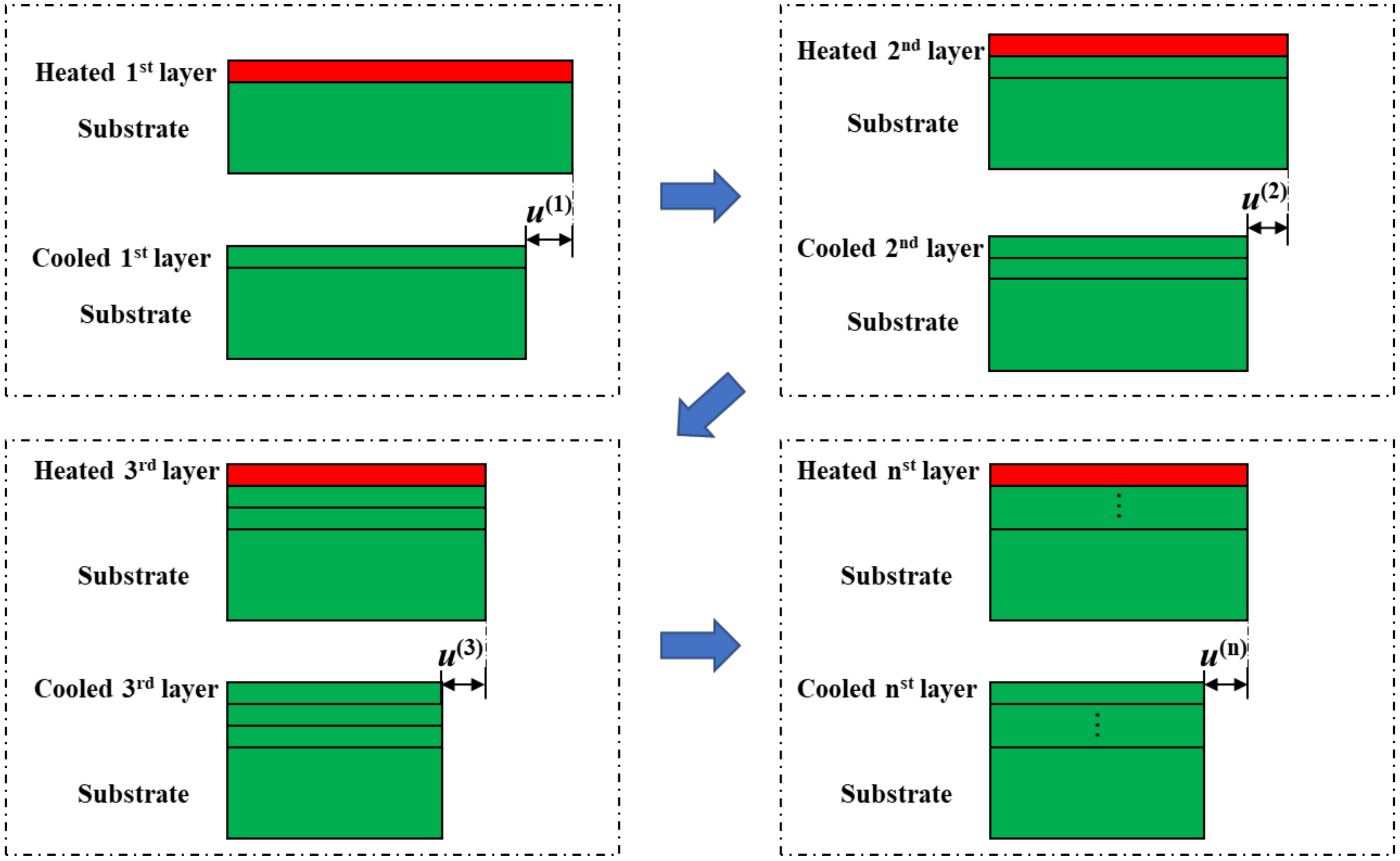
3.1. Mechanism of Distortion
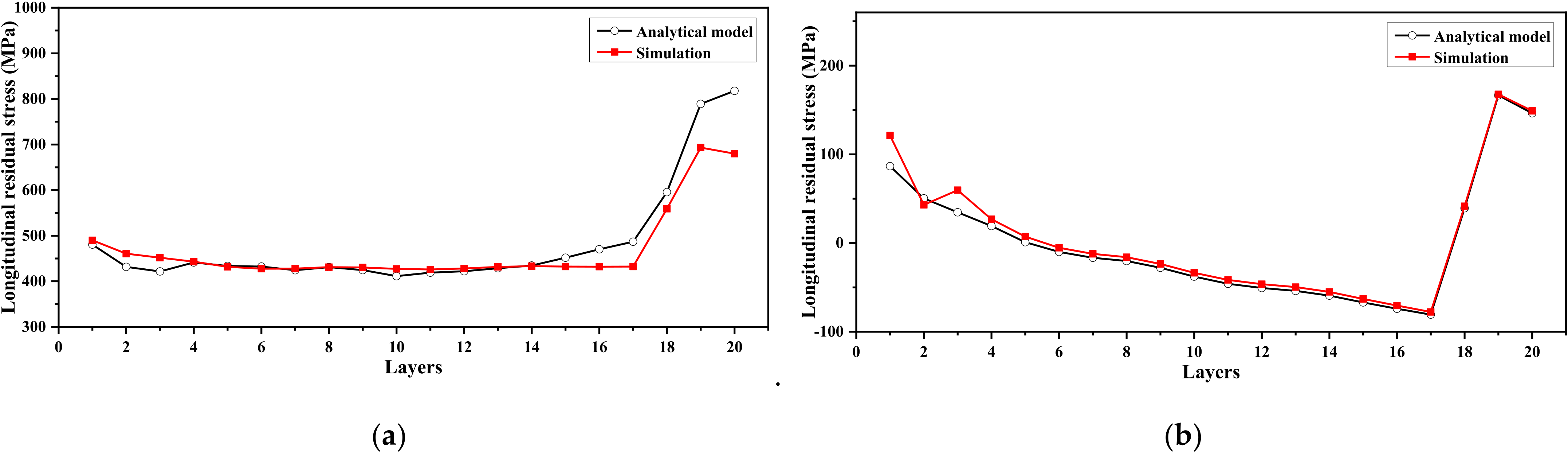
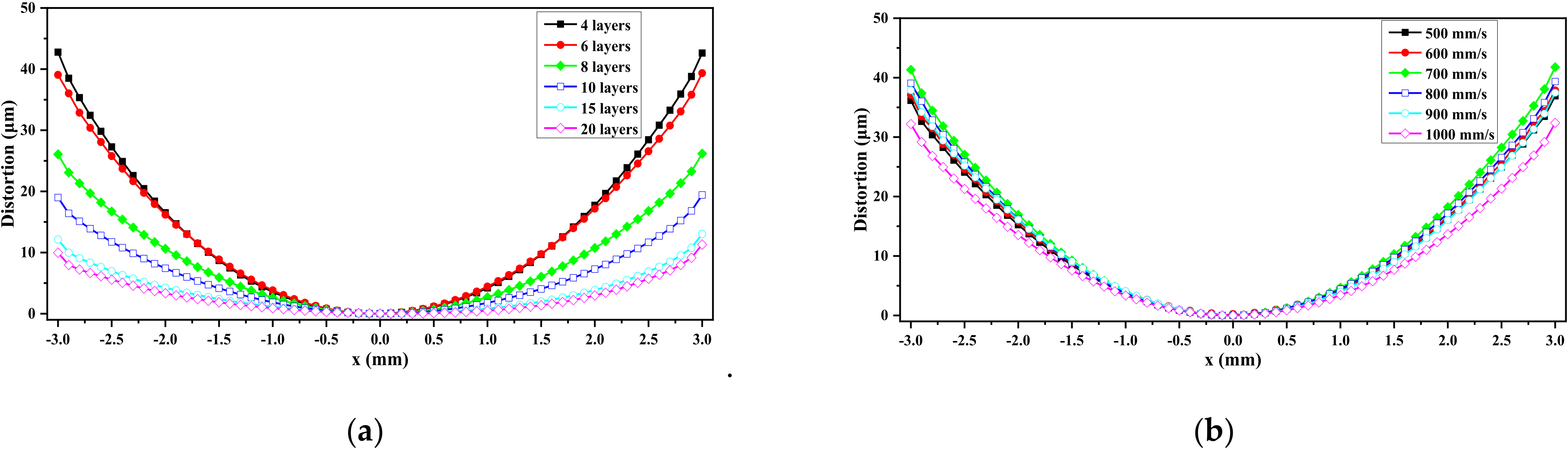
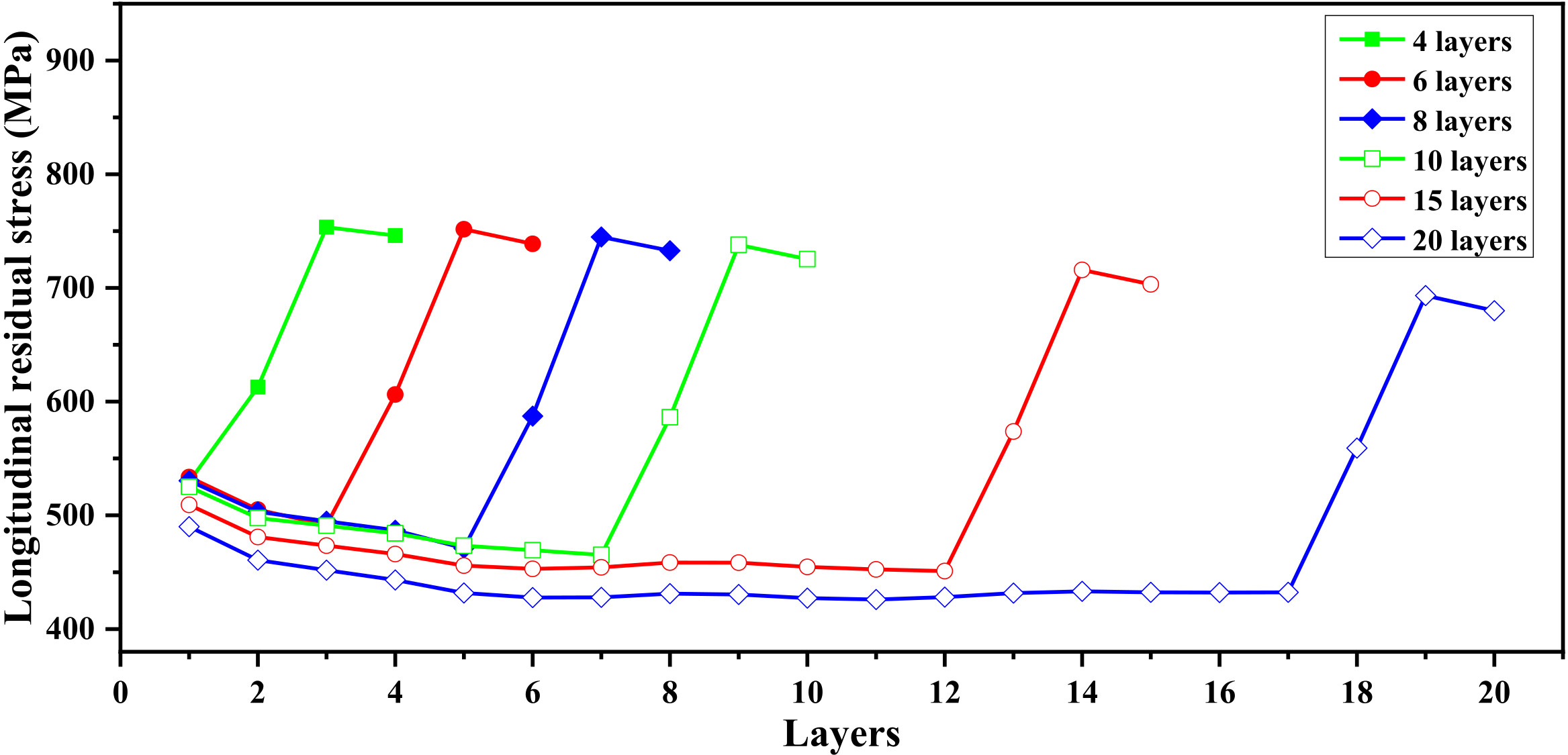
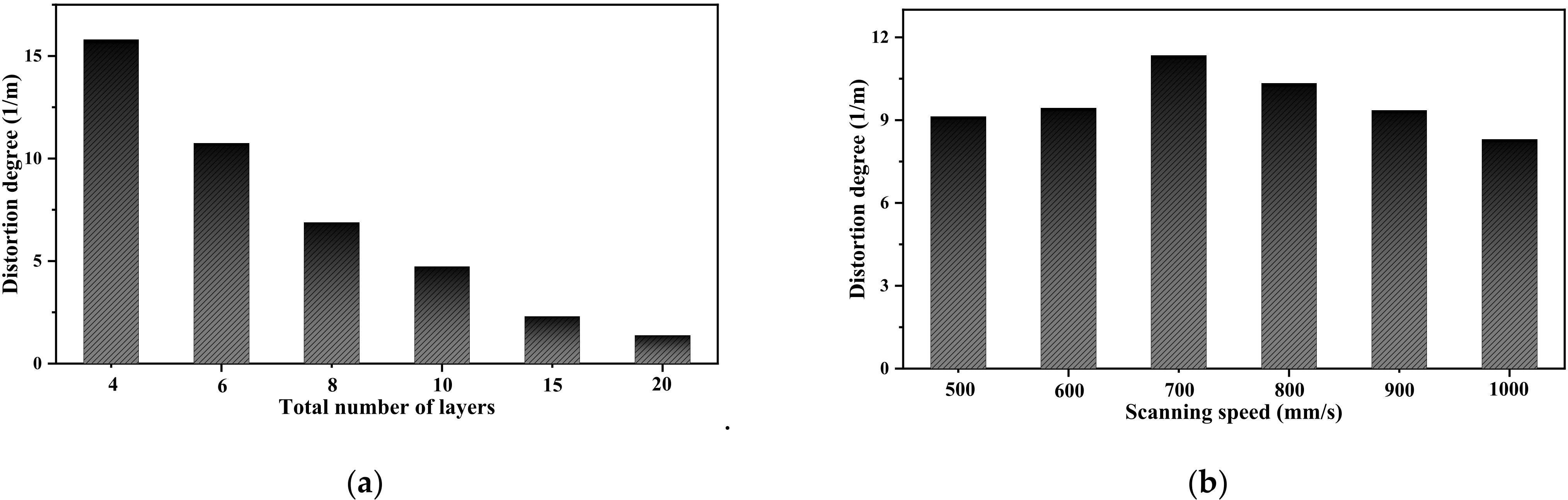
3.2. Number of Layers and Scanning Speed
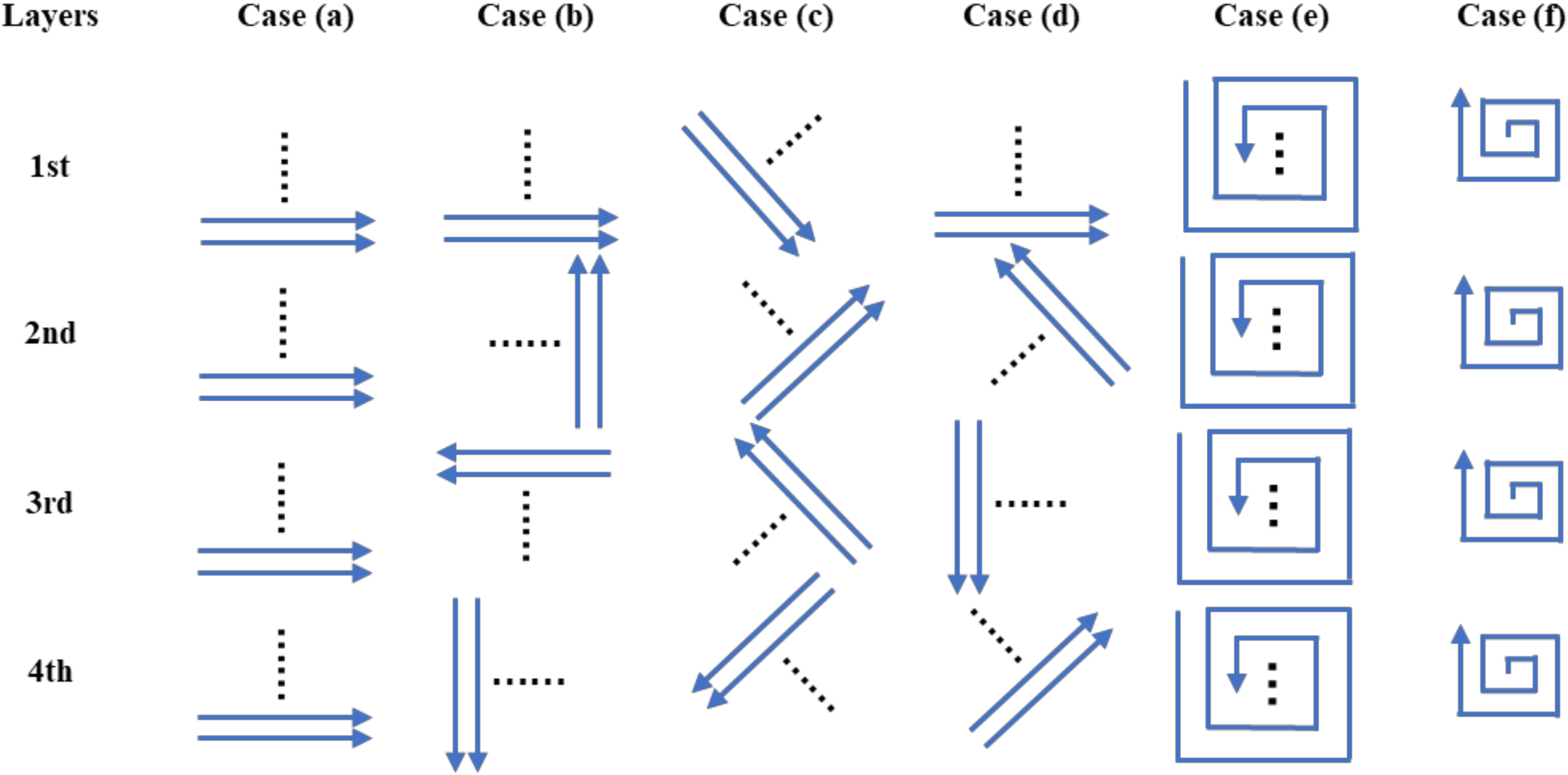
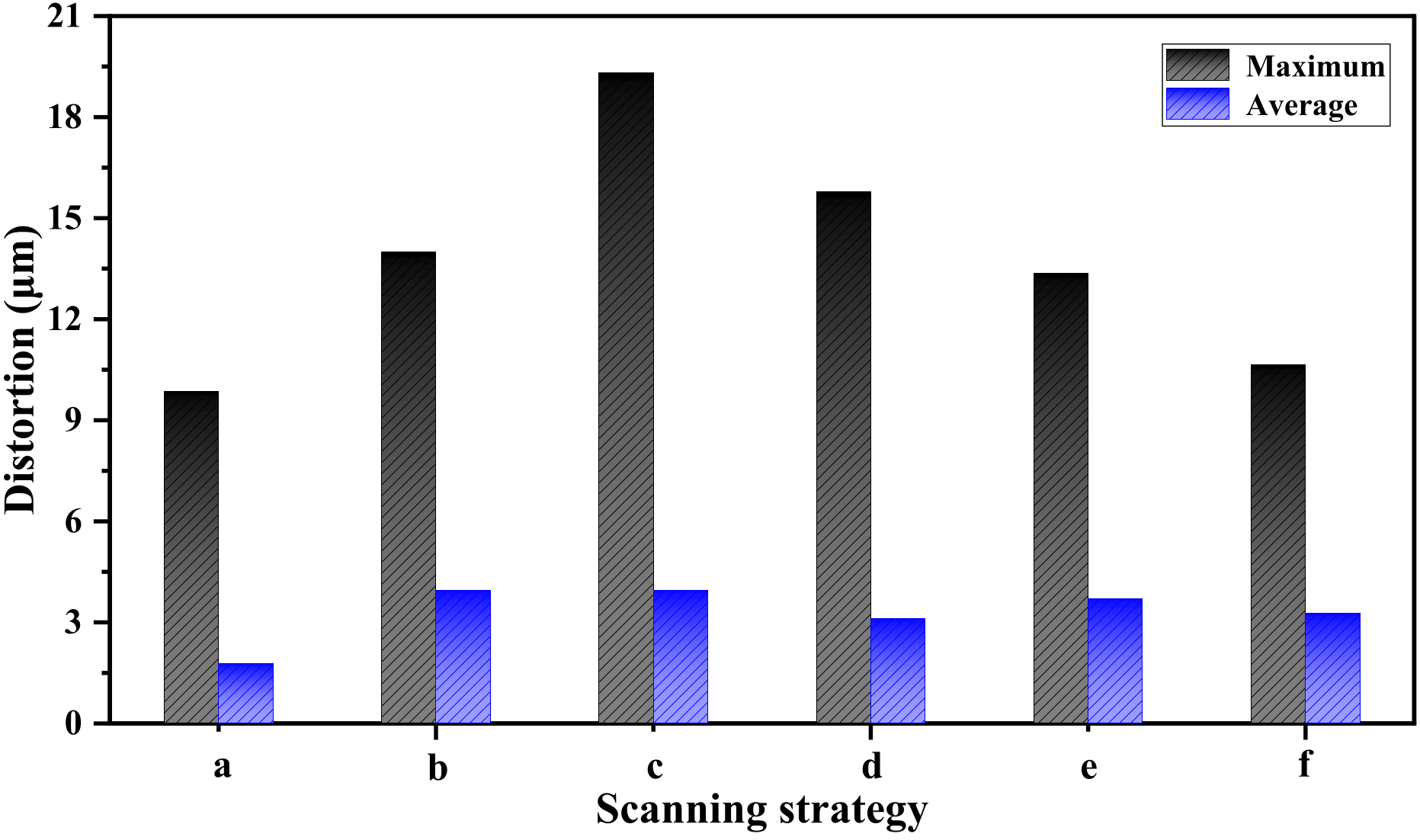
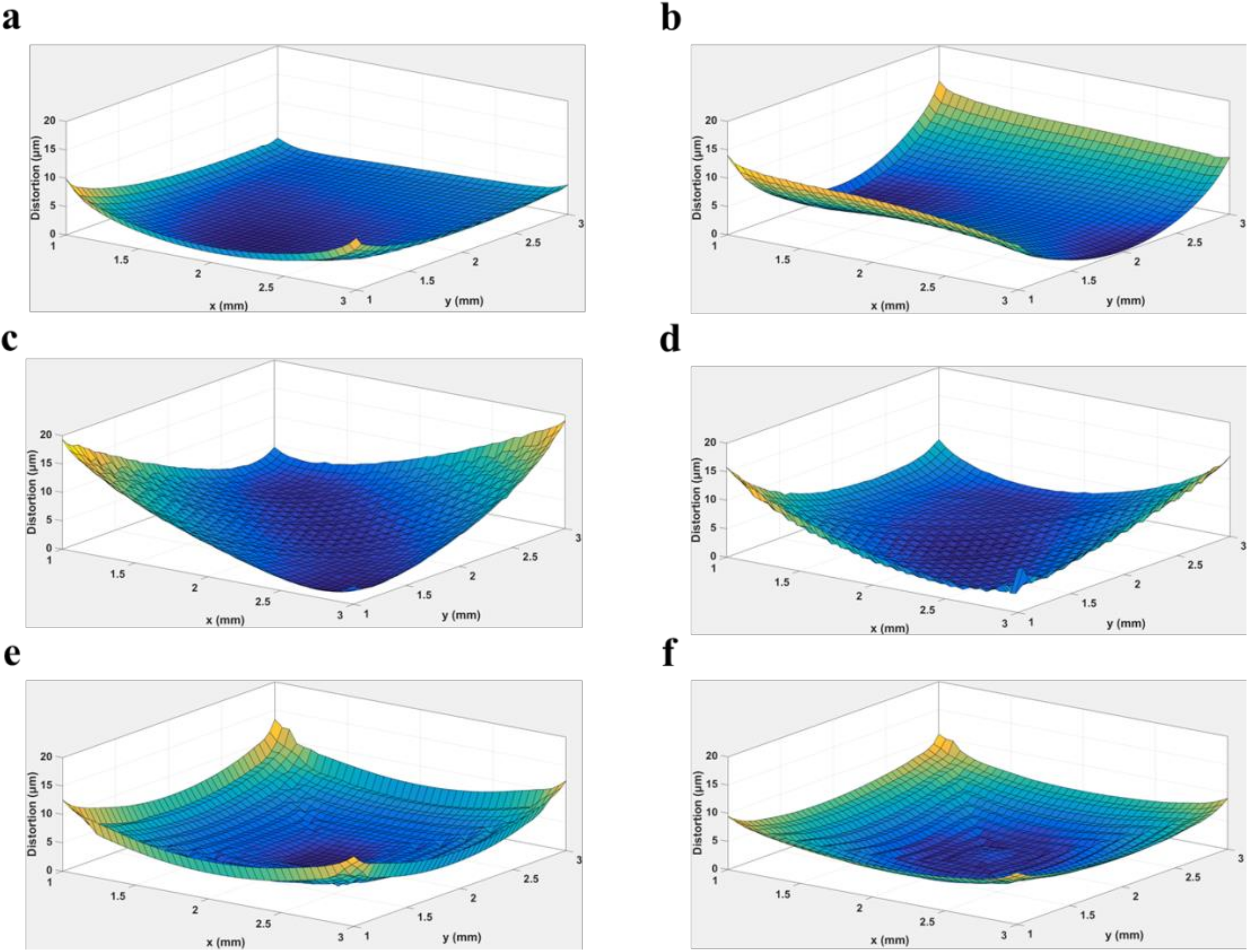
3.3. Stiffness of Support Structures and Scanning Strategy
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, X.; Waddell, C.; Hamilton, C.; Xiao, H. Quality Prediction and Control in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing via Novel Machine Learning Framework. Micromachines 2022, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xiao, H. Autonomous robotic feature-based freeform fabrication approach. Materials 2022, 15, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Wang, D.-W.; Song, L.-J.; Mukhtar, A.; Huang, D.-N.; Yang, C.; Yan, M. Effect of heat treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb intermetallic fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 817, 141352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-L.; Pan, W.-T.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.-H.; Shu, D.; Zhang, L.; Dong, A.-P.; Sun, B.-D. Microstructures and mechanical properties of GTD222 superalloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 807, 140668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-Z.; Wang, H.-X.; Feng, W.-W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Ma, S.-Y.; Wei, J. The crack and pore formation mechanism of Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 91, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-S.; Liu, E.-W.; Du, Y.-L.; Liu, T.-T.; Liao, W.-H. Cracking mechanism and a novel strategy to eliminate cracks in TiAl alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. Scr. Mater. 2021, 204, 114151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.-J.; Gao, S.; Lan, L.; He, B. Effect of Rescanning Strategy on Residual Stress and Distortion of Two Alloys Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6493–6501. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.-Q.; Lv, F.; Liang, H.-X.; Shen, L.-D.; Tian, Z.-J.; Zhao, J.-F.; Song, Y.-D.; Shuai, C.-J. Towards a comprehensive understanding of distortion in additive manufacturing based on assumption of constraining force. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2021, 16, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.P.; Froyen, L.; Van Vaerenbergh, J.; Mercelis, P.; Rombouts, M.; Lauwers, B. Selective laser melting of iron-based powder. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 149, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkoohi, E.; Dobbs, J.R.; Liang, S.Y. Analytical mechanics modeling of in-process thermal stress distribution in metal additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promoppatum, P.; Yao, S.-C. Influence of scanning length and energy input on residual stress reduction in metal additive manufacturing: Numerical and experimental studies. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 49, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.-Q.; Sievers, D.E.; Garmestani, H.; Liang, S.Y. Analytical Thermal Modeling of Metal Additive Manufacturing by Heat Sink Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, D.-Q.; Zhao, J.-F.; Liang, H.-X.; Tian, Z.-J.; Shen, L.-D.; Xiao, M.; Ahsan, M.N.; Wang, C.-J. Assumption of Constraining Force to Explain Distortion in Laser Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2018, 11, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.-F.; Fang, X.-Y.; Guo, Y.-B. Efficient predictive model of part distortion and residual stress in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, S.M.; Nasr, M.N.A.; El Gamal, H.A. Finite element modelling for part distortion calculation in selective laser melting. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 58, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afazov, S.; Denmark, W.A.D.; Toralles, B.L.; Holloway, A.; Yaghi, A. Distortion prediction and compensation in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Feih, S.; Zhai, W.; Sun, C.-N.; Li, F.; Maiti, R.; Wei, J.; Yang, Y.-Z.; Oancea, V.; Brandt, L.R.; et al. Advances in additive manufacturing process simulation: Residual stresses and distortion predictions in complex metallic components. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler, M.; Graf, B.; Rethmeier, M. In-situ distortions in LMD additive manufacturing walls can be measured with digital image correlation and predicted using numerical simulations. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 20, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugwagwa, L.; Yadroitsev, I.; Matope, S. Effect of Process Parameters on Residual Stresses, Distortions, and Porosity in Selective Laser Melting of Maraging Steel 300. Metals 2019, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Finite element simulation and experimental validation of distortion and cracking failure phenomena in direct metal laser sintering fabricated component. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 16, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Shen, L.-D.; Wang, X.; Tian, Z.-J.; Xu, G.-J.; Xie, D.-Q.; Liang, H.-X. Stress and deformation evaluation of the subarea scanning effect in direct laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Gharghouri, M.A.; Nash, P. Finite-element analysis and experimental validation of thermal residual stress and distortion in electron beam additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V build plates. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 237, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Xiao, H.-B.; Ye, F.-P.; Li, Z.-C.; Tang, W.-Z.; Zhu, F.; Chen, C.-T.; Zhu, C. Numerical analysis of the effect of the scan strategy on the residual stress in the multi-laser selective laser melting. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-C.; Chen, L.-Y. A Review on Biomedical Titanium Alloys: Recent Progress and Prospect. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1801215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Shen, S.-N.; Xie, H.-M.; Shi, W.-X.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Shen, B.-N.; Chen, L.-W.; Xiao, B.; et al. Evolution of molten pool during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 055302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Wildman, R.D. Understanding the effect of laser scan strategy on residual stress in selective laser melting through thermo-mechanical simulation. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, B.; Shrestha, S.; Chou, K. Stress and deformation evaluations of scanning strategy effect in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 240–251. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-P.; Yin, J.; Zhu, H.-H.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, X.-Y. Effect of overlap rate and pattern on residual stress in selective laser melting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 145, 103433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Property (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Latent heat ΔH (J·kg−1) | 2.86 × 105 |
| Density ρ (kg·m−3) | |
| Specific heat cp (J·kg−1·K−1) | |
| Thermal conductivity kλ (W·m−1·K−1) | |
| Viscosity μ (N·m−1·s−1) | exp(−1.6 + 5346/T) × 10−3 |
| Temperature (K) | Thermal Expansion Coefficientαth (1/K) | Elastic Modulus E (GPa) | Yield Stress σy (MPa) | Plastic Tangent Modulus Hp (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 296 | 8.78 | 125 | 1000 | 0.7 |
| 366 | 9.83 | 110 | 630 | 2.2 |
| 477 | 10 | 100 | 630 | 2.2 |
| 589 | 10.7 | 100 | 525 | 2.2 |
| 700 | 11.1 | 80 | 500 | 1.9 |
| 811 | 11.2 | 74 | 446 | 1.9 |
| 922 | 11.7 | 55 | 300 | 1.9 |
| 1033 | 12.2 | 27 | 45 | 2 |
| 1144 | 12.3 | 20 | 25 | 2 |
| 1366 | 12.4 | 5 | 5 | 2 |
| 1923 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Parameters (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Layer thickness h (μm) | 40 |
| Porosity ϕ | 0.48 |
| Laser power P (W) | 200 |
| Laser radius r0 (μm) | 75 |
| Hatch space dh (μm) | 100 |
| Scanning speed v (mm/s) | 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000 |
| Dwelling time between layers td (s) | 8 |
| Ambient temperature T∞ (K) | 300 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, S.; Pang, L.; Xu, C.; Xiao, X. Effect of Process Parameters on Distortions Based on the Quantitative Model in the SLM Process. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031567
Zou S, Pang L, Xu C, Xiao X. Effect of Process Parameters on Distortions Based on the Quantitative Model in the SLM Process. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031567
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Sheng, Libao Pang, Chang Xu, and Xinyi Xiao. 2022. "Effect of Process Parameters on Distortions Based on the Quantitative Model in the SLM Process" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031567
APA StyleZou, S., Pang, L., Xu, C., & Xiao, X. (2022). Effect of Process Parameters on Distortions Based on the Quantitative Model in the SLM Process. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031567







