Abstract
Pharmaceutical product quality is of vital importance for patient safety. Impurities and potential degradation products can cause changes in chemistry, pharmacological and toxicological properties by having a significant impact on product quality and safety. Stress-testing (forced degradation) studies of pharmaceutical preparations became necessary to assure degradation mechanisms and potential degradation products. Consequently, it is crucial to understand the nature of possible degradation products. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is a powerful vibrational spectroscopic technique that can provide valuable information about changes in a molecular structure with its intrinsic finger-print property. In this study, a forced degradation study was conducted on pemetrexed (PMT), an antifolate chemotherapy drug, in order to identify its likely chemical degradation products. The degradation mechanism of PMT was investigated under various experimental conditions; basic (0.1 M NaOH), acidic (0.1 M HCl), and oxidative (3% H2O2 v/v). We used silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) of average size 60 nm as SERS substrates. The study shows that SERS can be a fast and reliable technique to study the stability and possible degradation mechanisms of drugs under several different conditions.
1. Introduction
Drug safety and effectiveness are important concerns due to potential adverse effects through their degradation products on patient health and the environment [1,2]. Investigation of possible molecular changes in a drug molecule over time without interference from excipients, impurities, and degradation products (DPs) is required [3]. Excipients used to prepare the pharmaceutical form of a drug and/or inappropriate environmental conditions can also promote the degradation of a drug substance [2]. For instance, primary and secondary amines can react with carbohydrates to form glycosylamines. Many of the reported drug–excipient reactions involve hydrolysis, oxidation, or a specific interaction of drugs with reactive impurities in excipients [2,4]. The impurities and potential DPs may cause changes in chemistry, and the pharmacological and toxicological properties of drugs having significant impact on product quality and safety [5,6]. Furthermore, the degradation molecules and their concentration levels have a vital importance not only for a patient’s safety but also other living things exposed to the molecules via environmental factors such as soil, water, vegetables, and fruits [1]. It should be noted that even if concentrations found in the environment are at generally low levels, medicinal products are developed to be highly potent substances, and thus concentration levels on their own are not the precise indication of the associated risks [1,7]. The risk factors are associated with the nature of a substance such as degradability, toxicity of a compound, exposure duration, toxicity of metabolites, and physicochemical properties. For these reasons, forced degradation (stress-testing) studies of pharmaceutical preparations became necessary to assure degradation mechanisms and potential DPs [8,9,10]. The authorities such as FDA and ICH guide stability tests to figure out the quality of a drug substance and drug product. According to the regulatory guidelines, the stress factors must include acid and base hydrolysis, oxidation, thermal degradation, photolysis, and freeze–thaw cycles and shear [11,12].
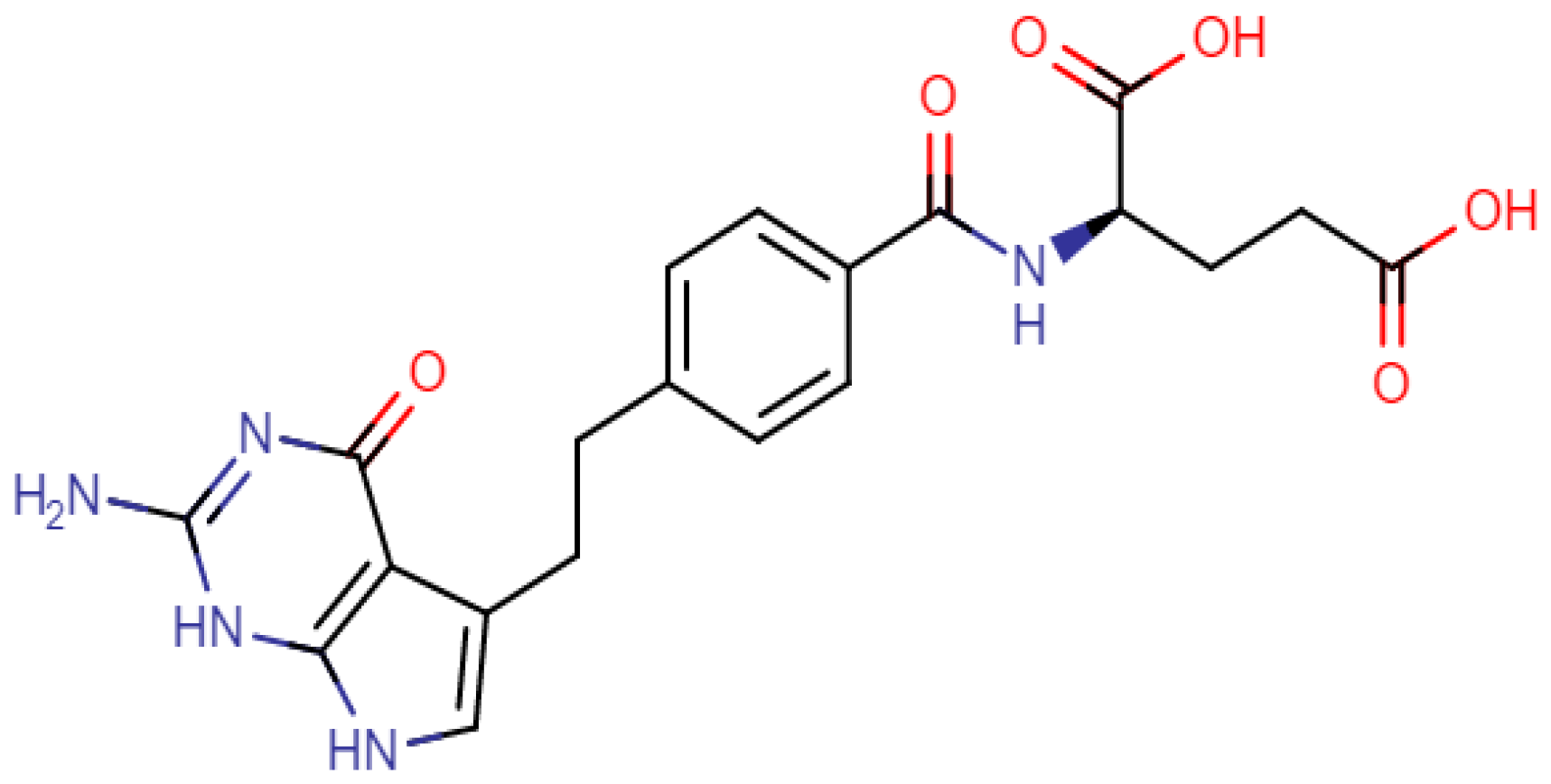
In this study, the degradation behavior of pemetrexed (PMT), a structure shown in Figure 1, is investigated under stress conditions such as oxidative and hydrolytic stress following ICH guidelines [11]. PMT is an antifolate chemotherapy drug which is first-line treatment for patients with advanced non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer. PMT applies its effect by disrupting folate-dependent metabolic processes essential for cell transcription [13]. It acts by inhibiting thymidylate synthase, dihydrofolate reductase, and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyl transferase enzymes used in purine and pyrimidine synthesis [14]. PMT prevents formation of DNA and RNA, which are required for the growth and survival of both normal and cancerous cells. The degradation profiles of PMT using stability-indicating methods stated by guidelines are also reported in the literature on high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and HPLC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. In most of these studies, the decrease in the concentration of the parent and increase in DPs are monitored under stress conditions. In a few studies, DPs were investigated after their isolation using preparative chromatography, and characterized by mass spectroscopy and NMR techniques for confirmation [18,23]. Additionally, some of the studies of PMT and its metabolites in biological fluids have been conducted using LC/MS methods [24,25,26,27].
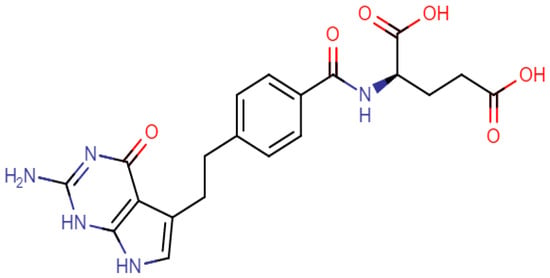
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of PMT.
Jansen et al. [18] and Warner et al. [15] identified several PMT DPs through oxidation and hydrolysis using HPLC and NMR. First, the DPs were separated in a reversed-phase preparative HPLC method, then they were identified with NMR. In another study, Respaud et al. also identified only two potential DPs, des-glutamate and glutamic acid [19]. In their study, they employed a HPLC instrument equipped with an ultraviolet and evaporative light-scattering detector to determine the DPs of PMT. More recently, a new HPLC method for PMT degradation was developed and validated as per ICH guidelines using a design of experiments methodology equipped with Box–Behnken design by Narenderan et al. [23]. As seen in all reported studies, in spite of the fact that HPLC is the most used technique to investigate the degradation and stability of drugs, it is not possible to perform the analysis in a single HPLC method. For this reason, mass spectroscopy is heavily used to complement HPLC for the characterization of degradation products. However, the MS-based techniques are expensive, time-consuming, and requires highly trained personnel. As an alternative, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) has been gaining attention for drug analysis in recent years [28,29,30].
SERS has received growing interest in variety of areas due to its inherent merits such as high sensitivity down to a single molecule, intrinsic finger-printing property, and multiplexing features due to the narrow spectral bands. These features make SERS one of the most powerful techniques for non-destructive, in situ, in vitro and in vivo analysis of chemical and biological substances. A noble, gold or silver, metal nanostructured surface is essential to achieve strong SERS activity. Although both noble metal surfaces are routinely used, AgNPs are preferred in some cases due to their higher SERS activity [31]. When colloidal metal nanoparticles are used as SERS substrates, the analyte of interest is simply mixed with the colloidal suspension and spotted on a suitable surface [32].
This study is the continuation of our effort to investigate the potential of SERS for the drug degradation profiles [28]. In our previous study, we monitored the degradation behavior of tofacitinib and methotrexate under hydrolytic, oxidative and thermal conditions using mesoporous Si@AgNPs as SERS substrate. We found that drug molecules and naked AgNPs surfaces might interact in the presence of HCl or H2O2, and AgNP surfaces can result in undesired reactions due to their high chemical reaction [33]. We aimed the study at understanding the effects of naked AgNPs on PMT degradation with NaOH, HCl and H2O2 exposure up to 48 h. This study will be first of its kind to date.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) Synthesis and Characterization
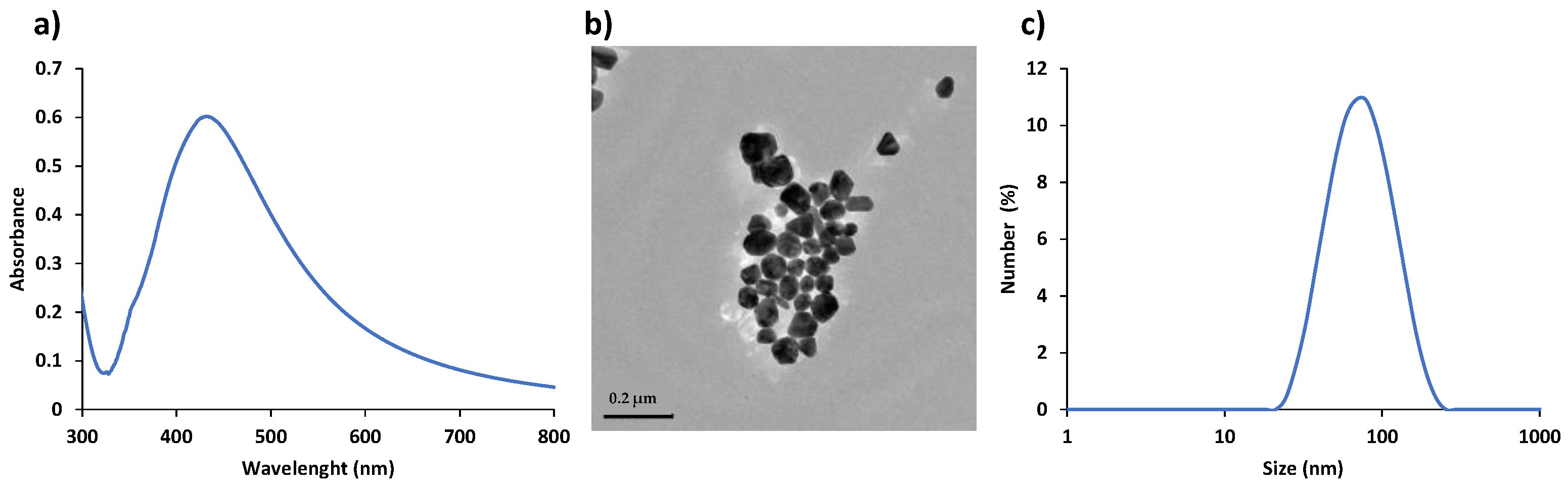
All glass was cleaned with aqua regia (nitric acid:hydrocloric acid, 3:1 (v/v)) to remove any impurities present on the glass surface. AgNPs were synthesized by the Lee-Meisel method [28]. The concentration of the AgNPs suspension was labelled as ‘‘1X’’ as synthesized. The initial suspension was concentrated 32 times by centrifugation and removal of the supernatant, and labeled as “32X”, which was used as the SERS substrate. Figure 2 shows the characterization of AgNPs colloidal suspension using Ultraviolet–visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The colloidal suspension of AgNPs has a maximum absorbance at 430 nm as seen in Figure 2a. Figure 2b, c show a representative TEM and DLS plot with an average hydrodynamic size of 60 nm of AgNPs, respectively.
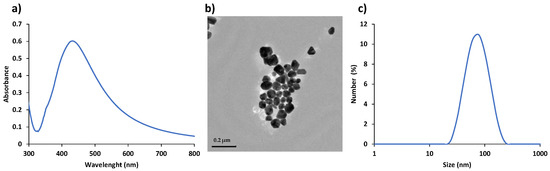
Figure 2.
UV-vis spectrum (a), TEM image (Scale bar: 0.2 μm) (b), and DLS plot showing hydrodynamic size distribution (c) of AgNPs.
2.2. Forced Degradation Conditions
The main stock solutions of PMT prepared at 25 μgmL−1 was protected from light exposure and stored at 4 °C. The forced degradation conditions include hydrolytic conditions of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH), acidic 0.1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl), and oxidative conditions of 3% v/v hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) based on ICH recommendations [12,13,28,34]. The basic and acidic degradation of PMT were performed by mixing 1 mL of PMT stock solution with 2 mL 0.1 M NaOH and 0.1 M HCl at room temperature for 6, 12, 24, 30 and 48 h. For the oxidative stress, 1 mL of PMT stock solution was treated with 2 mL of 3% (v/v) H2O2 at room temperature for the same exposure times in hydrolytic degradation. Each sample measurement was repeated three times, and from each droplet, 30 spectra were collected and averaged.
2.3. SERS Studies
The drug solutions were first exposed to basic, acidic and oxidative conditions at increasing durations from 6 to 48 h. Then, an aliquot from each of these solutions was mixed with AgNPs suspension. From this mixture, 1 μL volume was placed onto a CaF2 slide and allowed to dry. All measurements were performed by using a Renishaw InVia Reflex Raman Microscopy System (Renishaw plc., New Mills, Wotton-under-Edge Gloucestershire, Kingswood, UK). An 830 nm laser was used to acquire the SERS spectra. The collection time for each SERS measurement was 10 s and a total of 10 spectra from different aggregates on the droplet area were collected. We attempted to identify both the degradation rate and mechanisms.
3. Results and Discussion
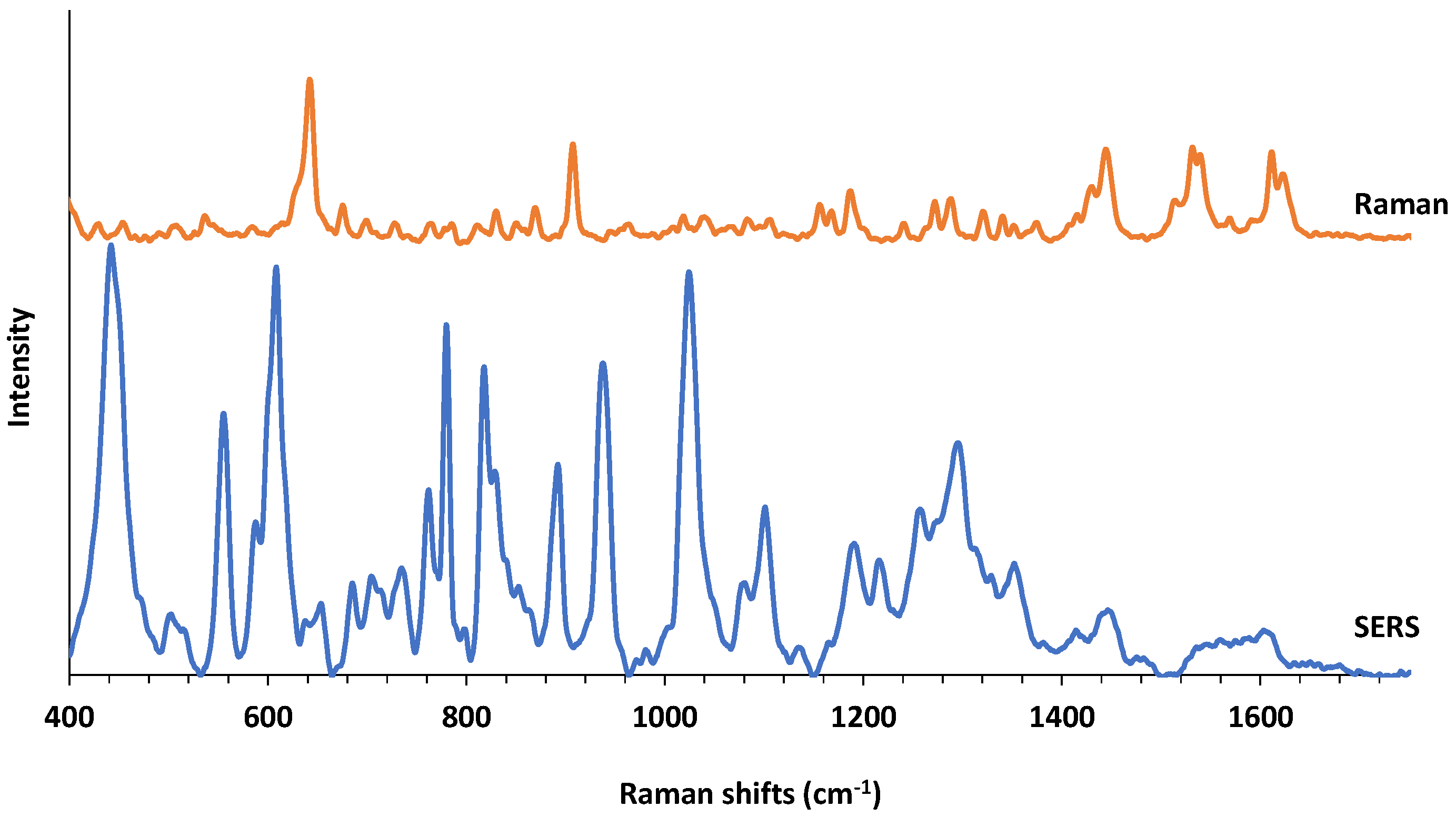
Raman and SERS spectra of a molecule can be very different depending on the nature of the interaction of a molecule with the substrate surface. In order to give an idea to the reader, we provide a comparison of average intensity-normalized and baseline-corrected Raman and SERS spectra of PMT in Figure 3. In an interesting study, AuNPs-PMT conjugates were synthesized and characterized with the aim of utilizing AuNPs as drug carriers [35]. In that study, both Raman and SERS spectra of PMT were reported. Although the experimental conditions for both Raman and SERS spectral acquisitions are different, it is important to mention this study as spectral reference point. A bulk Raman spectrum of PMT is also provided in Figure S1. As expected, many new spectral bands on SERS spectra appears and there is almost no spectral overlap between two spectra indicating a high affinity of PMT to the AgNPs surface. Table S1 shows the tentative SERS band assignments for PMT and as it degrades under several experimental conditions based on the previous studies [20,24,36,37].
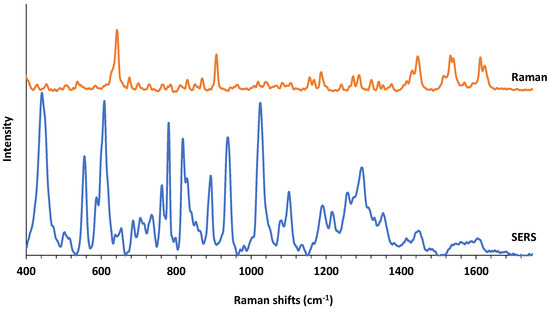
Figure 3.
Comparison of Raman and SERS spectra of PMT.
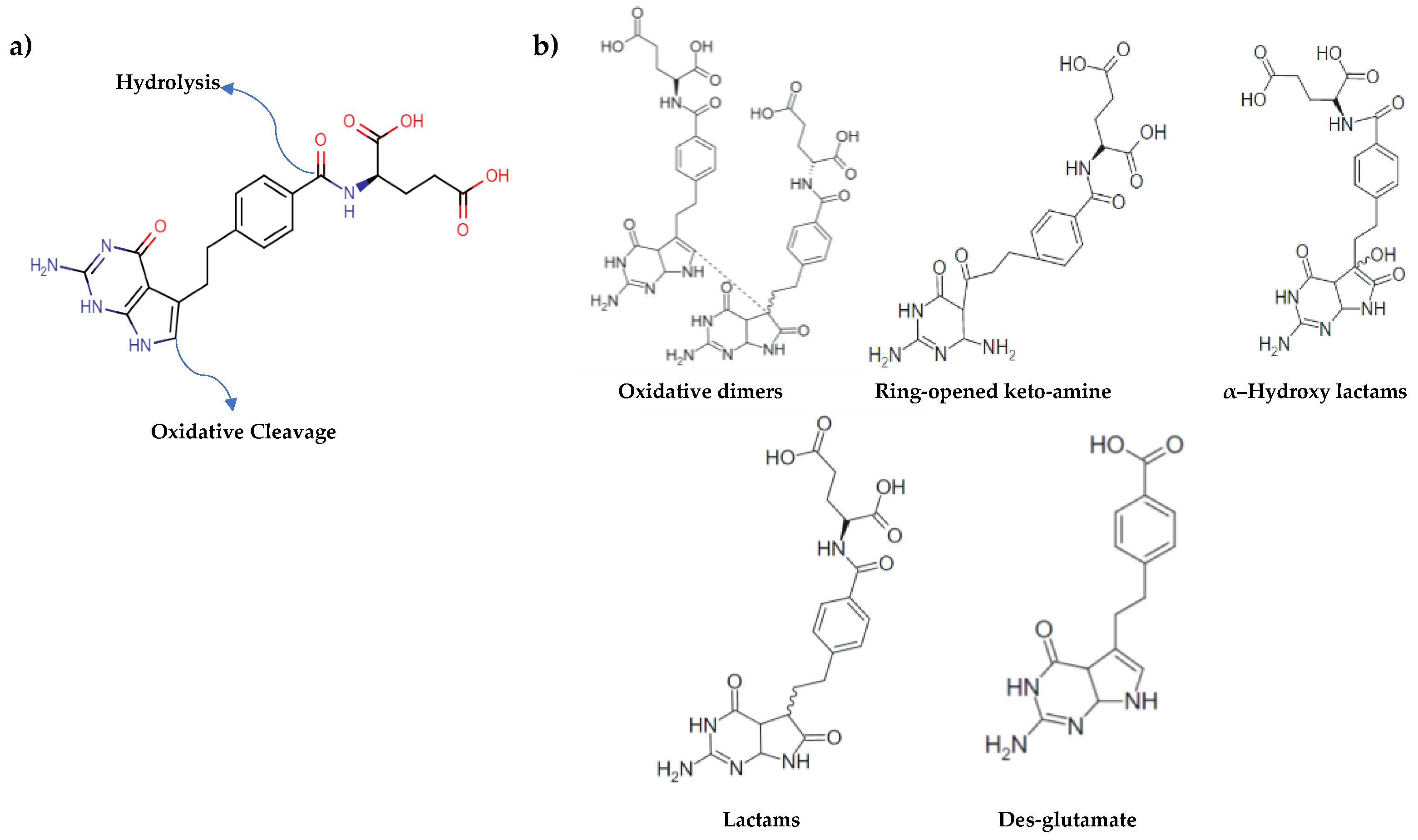
The forced degradation studies indicated that the PMT substance degrades in solution via two main degradation pathways, hydrolysis of the amide linkage at low pH, and oxidation of the five-member ring of the pyrrolopyrimidine moiety [15,19,23]. Figure 4a shows the two principal reactive sites for the PMT molecule, where chemistry can take place. Figure 4b shows the main potential DPs of PMT, oxidative dimers, ring-opened keto-amine, lactams, des-glutamate and α–hydroxy lactams. This information is important to be able interpret the spectral changes under stress conditions. The other aim is to investigate how stress conditions affect the SERS activity of AgNPs after exposing them with PMT and degradants following the forced degradation conditions.
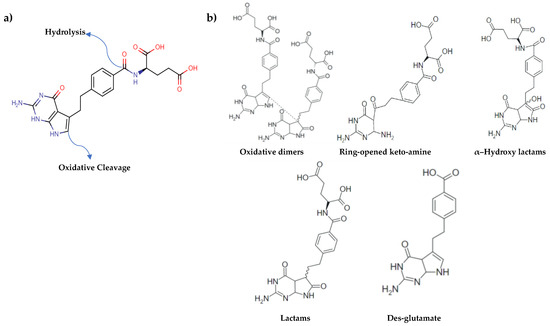
Figure 4.
(a) Possible degradation sites in PMT structure. It degrades via oxidation of its five-member ring of pyrrolopyrimidine moiety through water loss and its rearrangement, and/or hydrolysis of amide bond as shown above, (b) potential degradation products (DPs) of PMT under NaOH, HCl and H2O2 exposures.
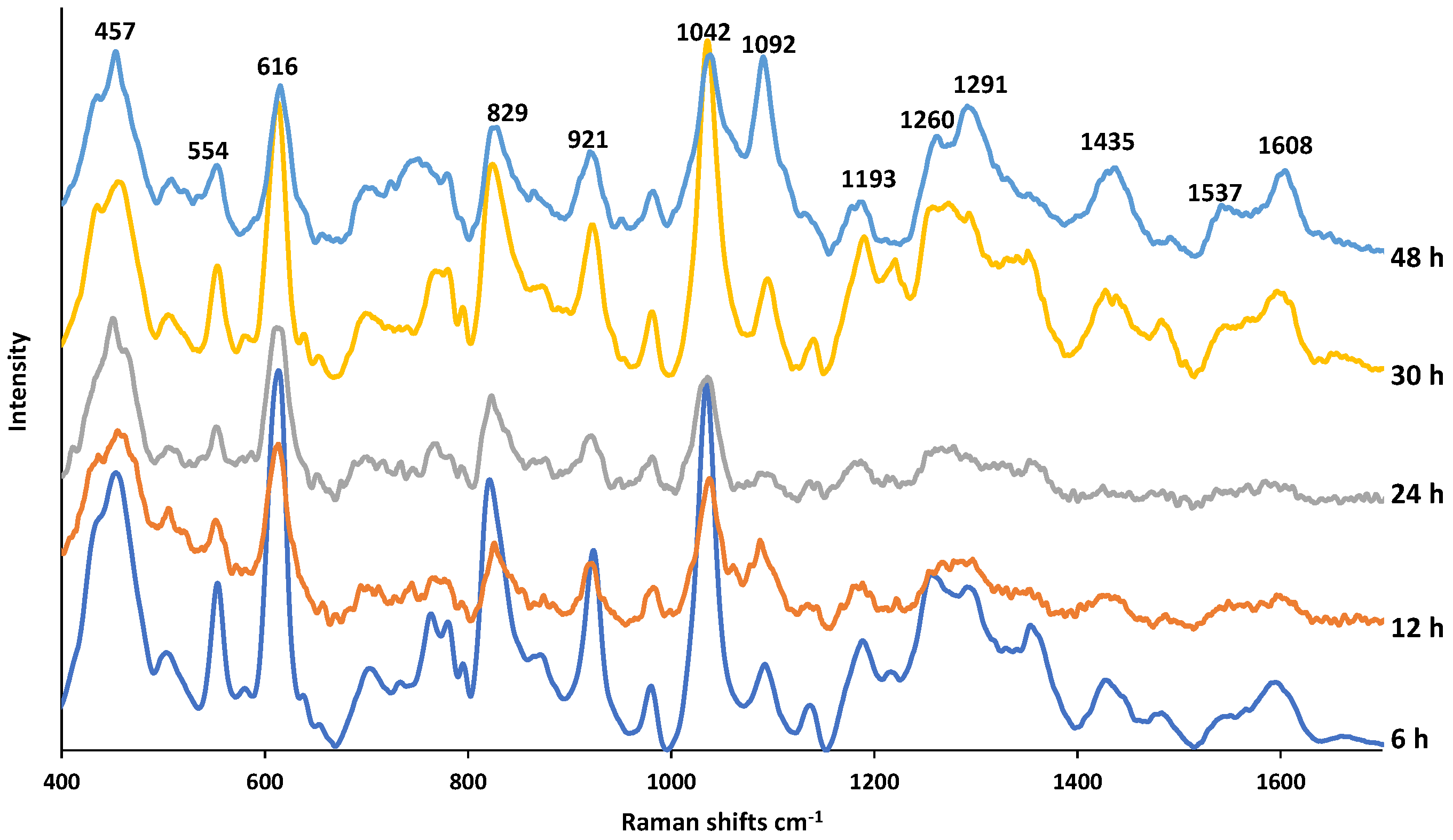
Figure 5 shows the SERS spectra of PMT exposed to NaOH at increasing times. The drug and the NaOH concentrations remain the same but the exposure times increase. An aliquot from the solution during incubation was taken and mixed with the AgNPs colloidal suspension. As seen, the spectral pattern remains almost the same with increasing NaOH exposure time but several changes in relative band intensities are apparent indicating the concentration changes of the molecular structures originating from their parent compound. In Table S1, the assignment of each band observed on the SERS spectra is provided. It was reported that the DPs in basic conditions are the oxidative dimer, ring-opened keto-amine, and α–hydroxy lactams [18]. According to the study conducted by Jansen et al., 4.2% of PMT exposed 24 h to NaOH was degraded. In our previous study employing mesoporous silica-coated AgNPs as SERS substrates, we also reached the conclusion that NaOH does not cause a destructive effect on AgNPs [28]. From the consistent spectral patterns at increasing exposure times, it is clear that NaOH is compatible with AgNPs and they do not lose their SERS effect and the observed spectral changes is the result of possible mild degradation of PMT.
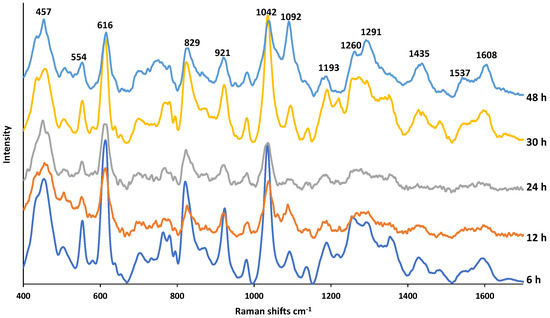
Figure 5.
SERS spectra of PMT exposed to 0.1 M NaOH for a duration of 6–48 h.
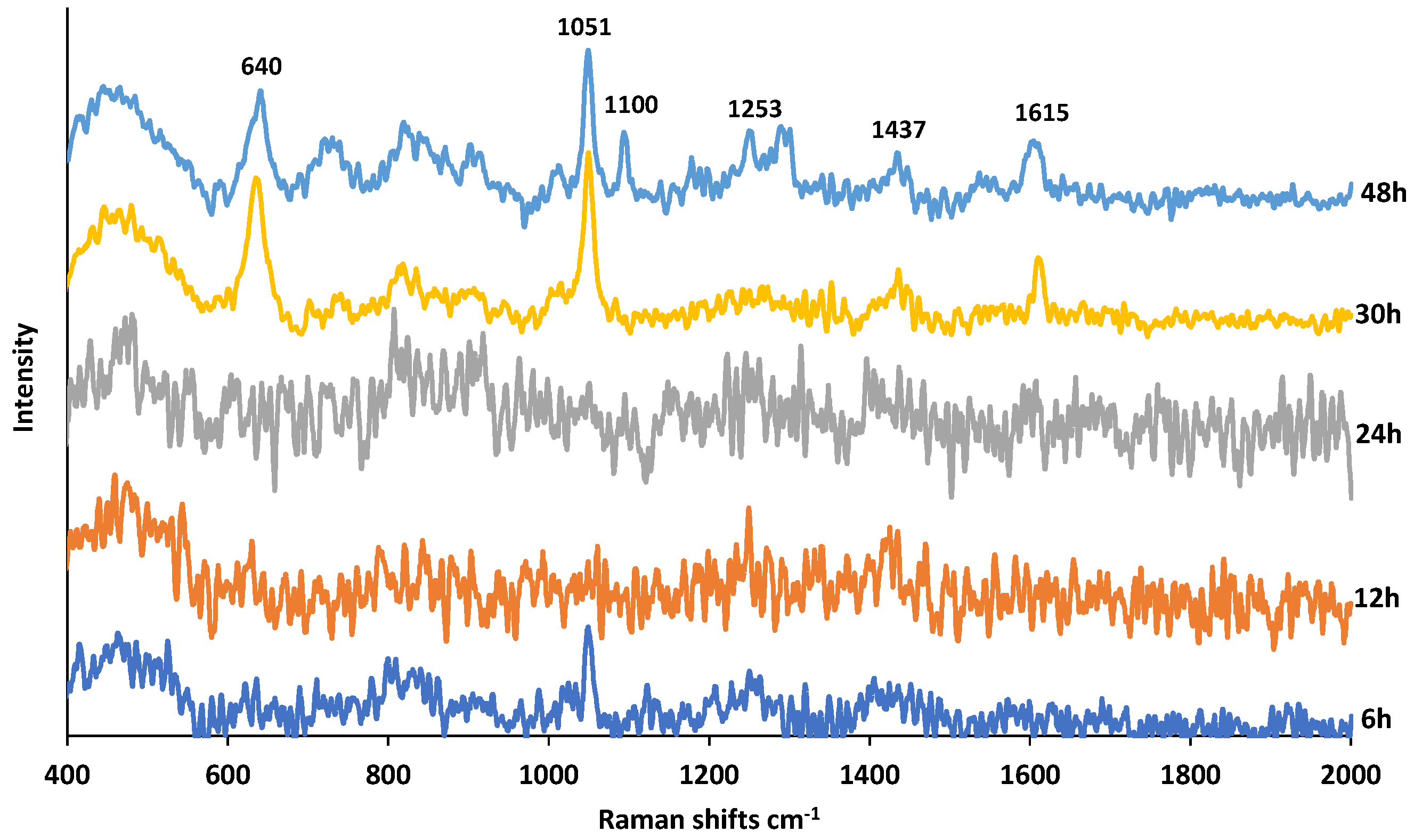
Figure 6 shows the SERS spectra of PMT exposed to HCl at increasing times. The DPs in acidic medium are reported to be an oxidative dimer, ring-opened ketoamine, des-glutamate, and lactams [15,18,20]. When PMT was exposed to HCl for 3 h, 15.32% of PMT degraded [20]. As seen in Figure 6, at shorter exposure times, SERS spectra are quite noisy and do not provide much molecular information. After 30 h exposure, new bands start to appear at 640, 1051, 1100, 1253, 1437, 1615 cm−1 that can be assigned HCH bending, CH in plane bending, NH2 rocking, CH2 symmetric deformation and scissoring of NH2, respectively [28,35]. There could be one reason for this observation, the loss of SERS activity of AgNPs as a result of undesired reactions with HCl during the first 24 h. Once all HCl is consumed, the SERS activity of AgNPs continues to be intact upon mixing reaction mixture with the AgNPs colloidal suspension at 30 and 48 h. Thus, as seen, several bands appear at 30 h, and more bands at 48 h.
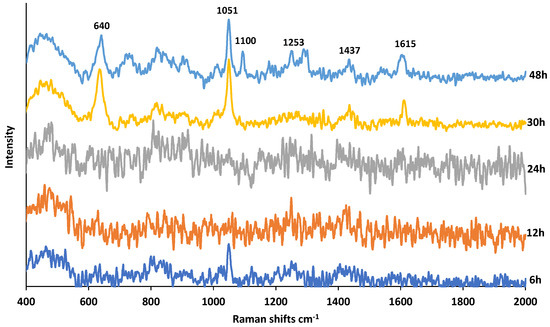
Figure 6.
SERS spectra of PMT exposed to 0.1 M HCl for a duration of 6–48 h.
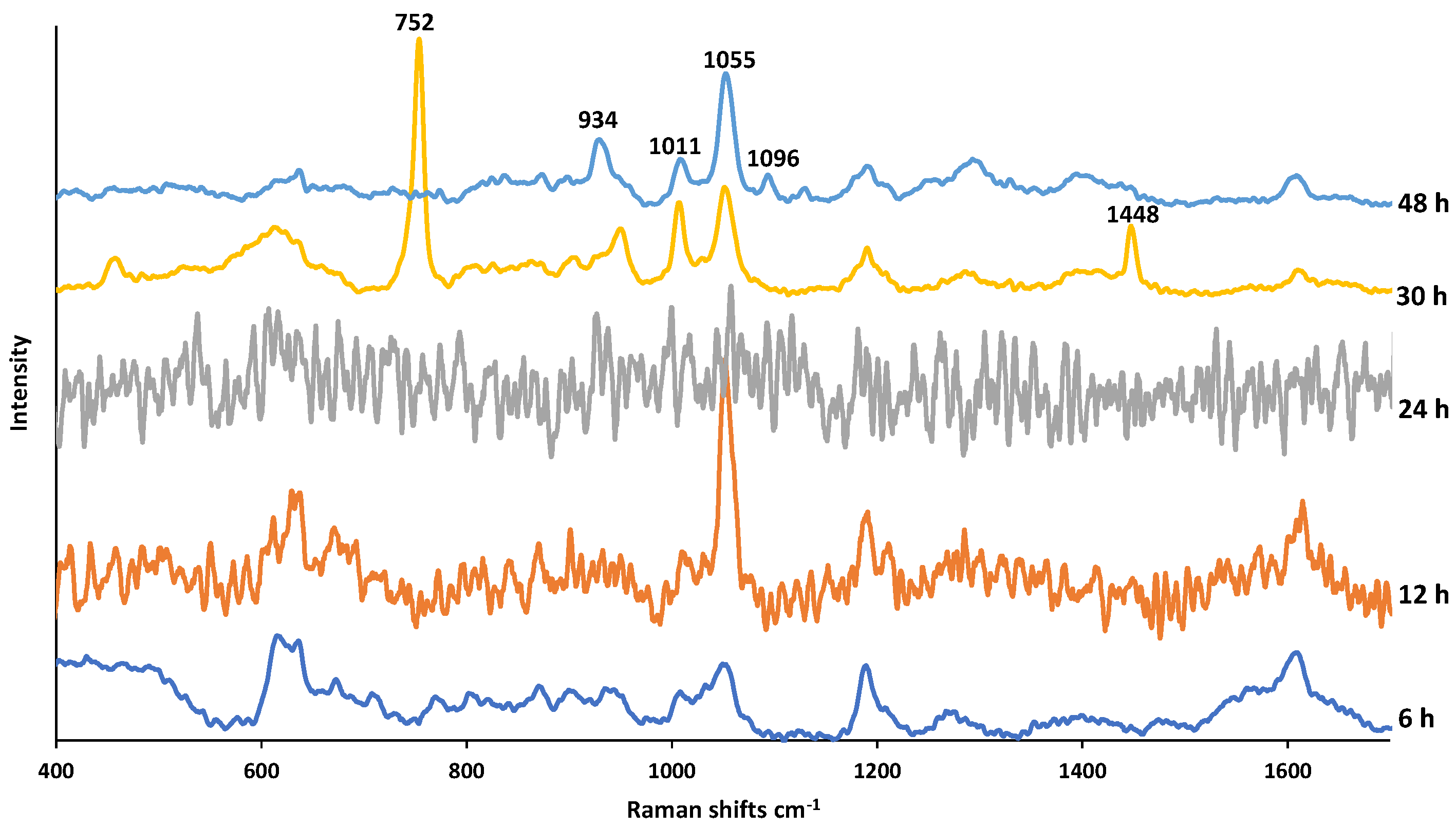
Figure 7 shows the SERS spectra of PMT exposed to H2O2 for increasing durations. According to the PMT degradations studies, PMT is not stable as it is exposed to H2O2 [14,17,18,19]. PMT was degraded by H2O2 as it is an oxidizing agent and the exposure generates DPs such as oxidative dimers and lactams [18,20]. Galla et al. reported that when PMT was exposed to 3% H2O2 for 30 min, 17.15% of PMT degraded [20]. As in Figure 7, it was only possible to obtain a meaningful SERS spectrum after 30 h exposure time. This could be due to the undecomposed H2O2 at earlier exposure times (24, 12, and 6 h), which can cause dissolution of AgNPs, and a result the loss of the SERS activity. The new bands appeared at increased exposure times (30 and 48 h) at 752, 953, 1011, 1055, 1448 cm−1 can be assigned to pyrimidine ring breathing, C=O stretching, hydrogen bonds of pyrimidine-water, CH in plane bending, and H2C=CH-CH3 symmetric deformation, respectively [28,35]. On the other hand, after 48 h exposure, while both bands at 752 and 1448 cm−1 disappeared, a new band occurred at 1096 cm−1. This can be explained with oxidation of carbon atoms in CO, CN or CH bonds.
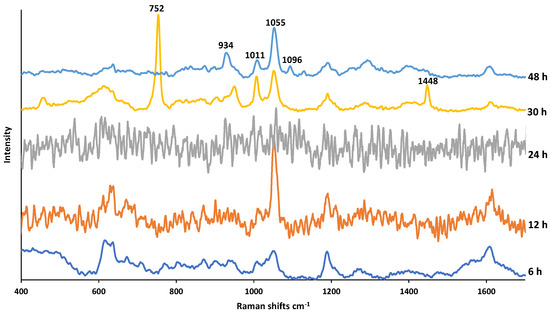
Figure 7.
SERS spectra of PMT exposed to 3% H2O2 for a duration of 6–48 h.
Since the same concentration of HCl and H2O2 is used for all exposure times, at increasing exposure times, the HCl and H2O2 left in the drug and degradation product mixture react with the AgNPs mixed with this causing the loss of SERS activity. This could be due to dissolution of AgNPs into its ions or precipitation of AgNPs as result of change in surface charge. When the spectra of PMT exposed to HCl and H2O2 from 30 to 48 h are compared, the same bands at 1051, 1100, 1437 cm−1 (Table S1) with little shifts are observed. This explains that the oxidative dimer and lactams are the DPs of PMT for both conditions.
4. Conclusions
This SERS study indicates that the degradation of PMT with NaOH exposure is a much milder process than the H2O2 case since almost no SERS bands are observed with the exposure to H2O2 at shorter exposure times. Even 6 h of H2O2 exposure results in complete degradation or all DPs being below the detection limit of the technique. This study shows that the drug was not stable under the basic, oxidative conditions, and showed varying degrees of degradation depending on exposure time at ambient temperature. The NaOH exposure caused much milder degradation of the drug as clearly observed from the SERS spectra. Although HPLC and LC–MS analyses need to obtain a complete picture of the degradation profile of an API under various stress conditions, SERS can provide useful insights into possible degradation mechanisms. Although, as demonstrated in this study, SERS can used to study the autoxidation, molecular fragmentation, dimerization and polymerization of drugs under different conditions in an aqueous solution, the possible interactions of the agents used with the SERS substrates should be realized.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12041807/s1, Figure S1: Raman spectrum of PMT; Table S1: Tentative SERS band assignments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, data curation, writing, review and editing, visualization: H.Y. and M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Lockwood, S.; Saïdi, N.; Morgan, V.A. Options for a Strategic Approach to Pharmaceuticals in the Environment Task 1 Report—Revised Version; INERIS (French National Institute for Industrial Environment and Risks); LSE (The London School of Economics and Political Science); Milieu Ltd.; European Commission-DG ENV: Tokyo, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bryn, S.R.; Xu, W.; Newman, A. Chemical reactivity in solid-state pharmaceuticals: Formulation implications. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2001, 48, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, W.H.; Fachi, M.M.; Cerqueira, L.B.; Campos, M.L.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Trindade, A.C.L.B.; Reason, I.J.M.; Pontarolo, R. Stability Indicating Method for Determination of Benznidazole and Its Degradation Products in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M.; Thakur, A.B.; Ghoshal, R.N.; Fakes, M.G.; Ranadive, S.A.; Morris, K.R.; Varia, S.A. Selection of solid dosage form composition through drug-excipient compatibility testing. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsante, K.M.; Huynh-Ba, K.C.; Baertschi, S.; Reed, R.A.; Landis, M.S.; Furness, S.; Olsen, B.; Mowery, M.; Russo, K.; Iser, R.; et al. Recent Trends in Product Development and Regulatory Issues on Impurities in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) and Drug Products. Part 2: Safety Considerations of Impurities in Pharmaceutical Products and Surveying the Impurity Landscape. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2013, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.R.D.O.; Homem-De-Mello, M.; Silveira, D.; Simeoni, L.A. Advice on Degradation Products in Pharmaceuticals: A Toxicological Evaluation. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2014, 68, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgal, S.; Toni, A.; Lockwood, S.; Salès, K.; Backhaus, T. Study on the Environmental Risks of Medicinal Products; Final Report; Executive Agency for Health and Consumers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013; pp. 1–310. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, A.H.; Salgado, H.R.N. Stability Study and Degradation Kinetics of Ceftazidime in Pharmaceutical Preparations Advances in Analytical Chemistry. Adv. Anal. Chem. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Larat, V.; Feltham, C. Raman Spectroscopy of Pharmaceutical Ingredients Under Humidity Controlled Atmosphere. HORIBA scientific. Application Note, Pharmaceutical RA61. Available online: https://static.horiba.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Yilmaz, H. Forced Degradation Studies to Assess the Stability of a Janus Kinase Inhibitor Using RPLC Method. Suleyman Demirel Univ. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2021, 25, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- ICH. Impurities in New Drug Products; IFPMA: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- ICH. Final Guidance on Stability Testing of Biotechnological/ Biological Products Availability; International Conference on Harmonization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, M.; White, R.M.; Booth, B.P.; Wang, Y.C.; Ham, D.Y.L.; Liang, C.Y.; Rahman, A.; Gobburu, J.V.S.; Li, N.; Sridhara, R.; et al. Pemetrexed in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 982–992. [Google Scholar]
- Joerger, M.; Omlin, A.; Cerny, T.; Fruh, M. The Role of Pemetrexed in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Special Focus on Pharmacology and Mechanism of Action. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, A.; Piraner, I.; Weimer, H.; White, K. Development of a purity control strategy for pemetrexed disodium and validation of associated analytical methodology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 105, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, G.; Suryanarayana, M.V.; Jadhav, M.J.; Ravikumar, M.; Someswararao, N.; Acharyulu, P.V.R. A Stability-Indicating LC Assay Method for Pemetrexed Disodium. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Trissel, L.A. Physical Instability of Frozen Pemetrexed Solutions in PVC Bags. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006, 40, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, P.J.; Smith, W.K.; Baertschi, S.W.; Dorman, D.E.; Kemp, C.A.; McCune, K.A. Determination of the degradation chemistry of the antitumor agent pemetrexed disodium. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3256–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Respaud, R.; Tournamille, J.F.; Croix, C.; Laborie, H.; Elfakir, C.; Viaud-Massuard, M.C. Development of an ion-pairing reversed-phase liquid chromatography method using a double detection analysis (UV and evaporative light scattering detection to monitor the stability of Alimta®-pemetrexed preparations: Identification and quantification of l-glutamic acid as a potential degradation product. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- Galla, V.K.; Archana, V.; Jinka, R. A new rapid Stability indicating RP-PDA-UPLC method for the estimation of Assay of Pemetrexed disodium-An anti-Lung cancer drug from lyophilized parenteral formulation. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hemchand, S.; Babu, R.R.C.; Annapurna, M.M. A new validated stability-indicating gradient RP-HPLC method for the determination of pemetrexed disodium and its process related substances. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 588–610. [Google Scholar]
- Adyanth, M.N.M.K.; Ravi, T.C.K.W.P. Determination of related substances in pemetrexed disodium (Form-IV) in bulk drug samples by HPLC. Pharm. Technol. 2014, 38. Available online: https://www.pharmtech.com/view/determination-related-substances-pemetrexed-disodium-form-iv-bulk-drug-samples-hplc (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Narenderan, S.T.; Ramesh, J.; Babu, B.; Meyyanathan, S.N.A. stability-indicating LC–MS/MS method optimization for Pemetrexed through design of experiments: Identification and characterization of major oxidative degradation product. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 183, 113150. [Google Scholar]
- Meesters, R.J.W.; Cornelissen, R.; van Klaveren, R.J.; de Jonge, R.; Boer, E.D.; Lindemans, J.; Luider, T.M. A new ultrafast and high-throughput mass spectrometric approach for the therapeutic drug monitoring of the multitargeted anti-folate pemetrexed in plasma from lung cancer patients. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rivory, L.P.; Clarke, S.J.; Boyer, M.; Bishop, J.F. Highly sensitive analysis of the antifolate pemetrexed sodium: A new cancer agent in human plasma and urine by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Bio. Med. Sci. Appl. 2001, 765, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobin-Dubigeon, C.; Amiand, M.B.; Herrenknecht, C.; Bard, J.M. Development and validation of an improved liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the determination of pemetrexed in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 2451–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmer, E.W.J.; Teulen, M.J.A.; Boosman, R.J.; Rouw, N.; Burgers, J.A.; Heine, R. Highly sensitive quantification of pemetrexed in human plasma using UPLC-MS/MS to support micro dosing studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5277. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, H.; Cobandede, Z.; Yilmaz, D.; Cinkilic, A.; Culha, M.; Demiralay, E.C. Monitoring forced degradation of drugs using silica coated AgNPs with surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Talanta 2020, 214, 120828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zahry, M.R.; Lendl, B. Structure elucidation and degradation kinetic study of Ofloxacin using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy, Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 193, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zahry, M.R.; Refaat, I.H.; Mohamed, H.A.; Rosenberg, E.; Lendl, B. Utility of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for elucidation and simultaneous determination of some penicillins and penicilloic acid using hydroxylamine silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 144, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, Y.; Tana, Z.; Liu, J. Coffee-ring effect-based simultaneous SERS substrate fabrication and analyte enrichment for trace analysis. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, E.; Culha, M. Influence of droplet drying configuration on surface-enhanced Raman scattering performance. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17829–17836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, Y.-J. High chemical reactivity of silver nanoparticles toward hydrochloric acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline, I.H.T. Stability testing of new drug substances and products. Q1A R2 Curr. Step 2003, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Stolarczyk, E.U.; Stolarczyk, K.; Łaszcz, M.; Kubiszewski, M.; Leś, A.; Michalak, O. Pemetrexed conjugated with gold nanoparticles—Synthesis, characterization and a study of noncovalent interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alula, M.T.; Mengesha, Z.T.; Mwenesongole, E. Advances in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for analysis of pharmaceuticals: A review. Vib. Spectrosc. 2018, 98, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztas, D.Y.; Altunbek, M.; Uzunoğlu, D.; Yılmaz, H.; Çetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Çulha, M. Tracing size and surface chemistry dependent endosomal uptake of gold nanoparticles using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 2019, 35, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).