Food Allergies: Immunosensors and Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Milk Allergy
2.1. Standard Approaches for Analyses of Dairy Allergens
2.2. Immunosensor
2.3. Management
3. Peanut Allergy
3.1. Immunosensor
3.2. Management
4. Tree Nut Allergy
4.1. Immunosensor
4.2. Management
5. Shellfish Allergy
5.1. Immunosensor
5.2. Management
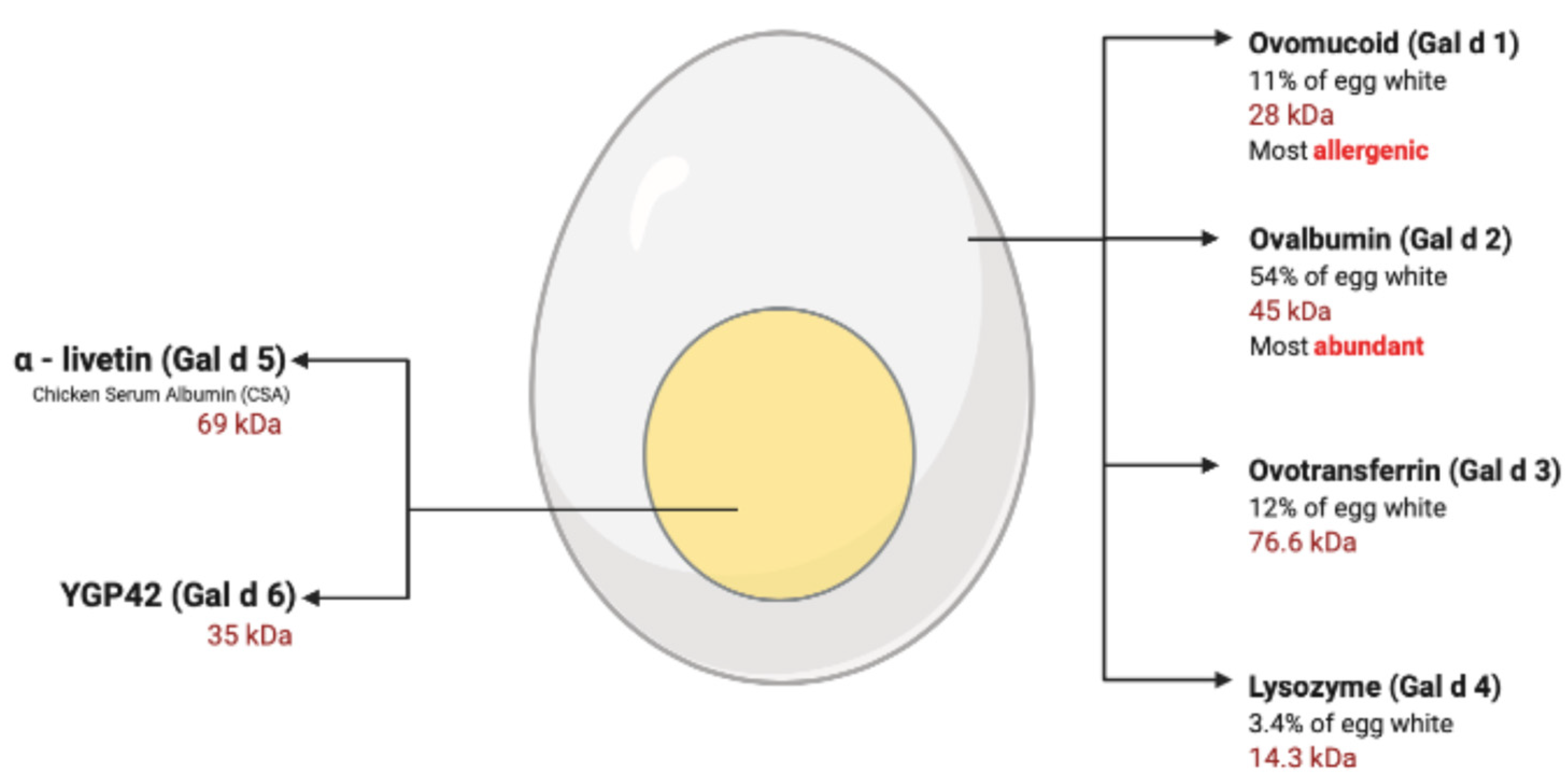
6. Egg Allergy
6.1. Immunosensor
6.2. Management
7. Wheat Allergy
7.1. Immunosensor
7.2. Management
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross, G.M.S.; Bremer, M.G.E.G.; Nielen, M.W.F. Consumer-friendly food allergen detection: Moving towards smartphone-based immunoassays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5353–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashley, J.; Shukor, Y.; D’Aurelio, R.; Trinh, L.; Rodgers, T.L.; Temblay, J.; Pleasants, M.; Tothill, I.E. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for α-Casein Detection Using Surface Plasmon Resonance as a Milk Allergen Sensor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prado, M.; Ortea, I.; Vial, S.; Rivas, J.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velázquez, J. Advanced DNA- and Protein-Based Methods for the Detection and Investigation of Food Allergens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2511–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Kong, J.; Chen, Q. A hybridization chain reaction coupled with gold nanoparticles for allergen gene detection in peanut, soybean and sesame DNAs. Analyst 2019, 144, 3886–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boushell, V.; Pang, S.; He, L. Aptamer-Based SERS Detection of Lysozyme on a Food-Handling Surface. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Fu, L. Quantification of shellfish major allergen tropomyosin by SPR biosensor with gold patterned Biochips. Food Control 2020, 107, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, P.; Pi, F.; Ji, J.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Sun, X. A novel mast cell co-culture microfluidic chip for the electrochemical evaluation of food allergen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.S.; Warren, C.M.; Smith, B.M.; Jiang, J.; Blumenstock, J.A.; Davis, M.M.; Schleimer, R.P.; Nadeau, K.C. Prevalence and Severity of Food Allergies Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e185630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Arribas, L.N.; Benito-Peña, E.; Hurtado-Sánchez, M.d.C.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Biosensing based on nanoparticles for food allergens detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, R.C.; Barroso, M.F.; González-García, M.B.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. New Trends in Food Allergens Detection: Toward Biosensing Strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Chen, Y.; Ge, Y. Simultaneous detection of eight food allergens using optical thin-film biosensor chips. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6889–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S.; Warrier, M.R.; Springston, E.E.; Smith, B.M. The Prevalence of Childhood Food Allergy in the United States. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, AB33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafen, J.J.S.; Newberry, S.J.; Riedl, M.A.; Bravata, D.M.; Maglione, M.; Suttorp, M.J.; Sundaram, V.; Paig, N.M.; Towfigh, A.; Hulley, B.J.; et al. Diagnosing and Managing Common Food Allergies A Systematic Review. JAMA 2015, 303, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, A.A.; Morais, S.; Maquieira, Á. Simultaneous determination of four food allergens using compact disc immunoassaying technology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; Monaci, L.; Visconti, A. Advances in biosensor development based on integrating nanotechnology and applied to food-allergen management. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 47, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmatov, U.; Venderbosch, I.; Devereux, G.; Simon, F.E.R.; Sheikh, A. Allergen-specific oral immunotherapy for peanut allergy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 9, CD009014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan, A.; Oh, J.H.; Park, M.K.; Kim, S.W.; Park, C.; Lee, J. Assessment of peanut allergen Ara h1 in processed foods using a SWCNTs-based nanobiosensor. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Ji, J.; An, L.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tang, L. Mast cell-based electrochemical biosensor for quantification of the major shrimp allergen Pen a 1 (tropomyosin). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Montiel, V.R.V.; Serafín, V.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Cutting-Edge Advances in Electrochemical Affinity Biosensing at Different Molecular Level of Emerging Food Allergens and Adulterants. Biosensors 2020, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, G.M.; Khuda, S.E.; Parker, C.H.; Eischeid, A.C.; Pereira, M. Detection of allergen markers in food: Analytical methods. In Food Safety: Innovative Analytical Tools for Safety Assessment; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 65–121. ISBN 9781119160588. [Google Scholar]
- Nehra, M.; Lettieri, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Kumar, S. Nano-Biosensing Platforms for Detection of Cow’s Milk Allergens: An Overview. Sensors 2020, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashley, J.; D’Aurelio, R.; Piekarska, M.; Temblay, J.; Pleasants, M.; Trinh, L.; Rodgers, T.L.; Tothill, I.E. Development of a β-Lactoglobulin sensor based on SPR for milk allergens detection. Biosensors 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, T.R.; Chen, W.T.; Liao, H.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Yen, H.C.; Liao, T.W.; Wen, C.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, D.Y. Improving Hydrogen Evolution Activity of Earth-Abundant Cobalt-Doped Iron Pyrite Catalysts by Surface Modification with Phosphide. Small 2017, 13, 1603356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalik, C.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Alimansur, M.; Jazidie, A.; Nuh, M.; Chang, C.C.; Wang, D.Y.; Kuo, T.R. High UV-VIS-NIR light-induced antibacterial activity by heterostructured TiO2-FeS2 nanocomposites. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8911–8920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.R.; Liao, H.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Wei, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Lin, J.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Wen, C.Y.; et al. Correction: Extended visible to near-infrared harvesting of earth-abundant FeS2-TiO2 heterostructures for highly active photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutalik, C.; Wang, D.Y.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Jazidie, A.; Yougbare, S.; Kuo, T.R. Light-activated heterostructured nanomaterials for antibacterial applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yougbaré, S.; Mutalik, C.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Kristanto, H.; Jazidie, A.; Nuh, M.; Cheng, T.M.; Kuo, T.R. Nanomaterials for the Photothermal Killing of Bacteria. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Kuo, T.R.; Su, H.J.; Lai, W.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, D.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, C.C. Fluorescence-guided probes of aptamer-targeted gold nanoparticles with computed tomography imaging accesses for in vivo tumor resection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yougbare, S.; Chang, T.K.; Tan, S.H.; Kuo, J.C.; Hsu, P.H.; Su, C.Y.; Kuo, T.R. Antimicrobial gold nanoclusters: Recent developments and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, T.K.; Cheng, T.M.; Chu, H.L.; Tan, S.H.; Kuo, J.C.; Hsu, P.H.; Su, C.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Lee, C.M.; Kuo, T.R. Metabolic Mechanism Investigation of Antibacterial Active Cysteine-Conjugated Gold Nanoclusters in Escherichia coli. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15479–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, C.; Breiteneder, H. Peanut allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liang, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, H.; et al. A proteomic analysis of peanut seed at different stages of underground development to understand the changes of seed proteins. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilu, K.W.; Friend, S.A.; Vallanadu, V.; Brown, A.M.; Hollingsworth, L.R.; Bevan, D.R. Molecular evolution of genes encoding allergen proteins in the peanuts genus Arachis: Structural and functional implications. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, H.E. The Economic Impact of Peanut Allergies. Am. J. Manag. Care 2018, 24, S428–S433. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, S.; Li, J.; Chang, S.; Maleki, S.J. Quantitative and kinetic analyses of peanut allergens as affected by food processing. Food Chem. X 2019, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaparkhe, M.B.; Lee, T.H.; Tan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Kim, C.; Rainville, L.K.; Lemke, C.; Compton, R.O.; Robertson, J.; et al. Comparative and evolutionary analysis of major peanut allergen gene families. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 2468–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Y.; Dreskin, S.C. Redefining the major peanut allergens. Immunol. Res. 2013, 55, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleber-Janke, T.; Crameri, R.; Appenzeller, U.; Schlaak, M.; Becker, W.M. Selective cloning of peanut allergens, including profilin and 2S albumins, by phage display technology. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 119, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulis, M.; Chen, X.; Lew, J.; Wang, Q.; Patel, O.P.; Zhuang, Y. The 2S albumin allergens of Arachis hypogaea, Ara h 2 and Ara h 6, are the major elicitors of anaphylaxis and can effectively desensitize peanut-allergic mice. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cai, Q.; Chen, Q. Thermal processing effects on peanut allergen Ara h 2 allergenicity in mice and its antigenic epitope structure. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aremu, M.O.; Olonisakin, A.; Bako, D.A.; Madu, P.C. Compositional studies and physicochemical characteristics of cashew nut (Anarcadium occidentale) flour. Pak. J. Nutr. 2006, 5, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aremu, M.O.; Ogunlade, I.; Olonisakin, A. Fatty acid and amino acid composition of protein concentrate from cashew nut (Anarcadium occidentale) grown in Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Pak. J. Nutr. 2007, 6, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, E.; Galvin, K.; O’Connor, T.; Maguire, A.; O’Brien, N. Fatty acid profile, tocopherol, squalene and phytosterol content of brazil, pecan, pine, pistachio and cashew nuts. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 57, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiteneder, H.; Radauer, C. A classification of plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radauer, C.; Bublin, M.; Wagner, S.; Mari, A.; Breiteneder, H. Allergens are distributed into few protein families and possess a restricted number of biochemical functions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, P.G.J.; Potts, J.; Kummeling, I.; Mills, E.N.C.; Clausen, M.; Dubakiene, R.; Barreales, L. The prevalence and distribution of food sensitization in European adults. Allergy 2014, 69, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archila, L.D.; Chow, I.-T.; McGinty, J.W.; Renand, A.; Jeong, D.; Robinson, D.; Farrington, M.L.; Kwok, W.W. Ana o 1 and Ana o 2 cashew allergens share cross-reactive CD4+ T-cell epitopes with other tree nuts. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastiaan-Net, S.; Pina-Pérez, M.C.; Dekkers, B.J.W.; Westphal, A.H.; America, A.H.P.; Ariëns, R.M.C.; de Jong, N.W.; Wichers, H.J.; Mes, J.J. Identification and in silico bioinformatics analysis of PR10 proteins in cashew nut. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1581–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. 2), S116–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, J.F.; Pascual, C.; Burks, A.W.; Helm, R.M.; Esteban, M.M. Frequency of food allergy in a pediatric population from Spain. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 1995, 6, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, T.; Sicherer, S. Current perspectives on tree nut allergy: A review. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Furlong, T.J.; Muñoz-Furlong, A.; Burks, A.W.; Sampson, H.A. A voluntary registry for peanut and tree nut allergy: Characteristics of the first 5149 registrants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rukmini, A. Alergi Kacang tanah: Mekanisme, pengujian dan pengendaliannya. J. Ilm. Padma Sri. Kreshna 2009, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dubiela, P.; Kabasser, S.; Smargiasso, N.; Geiselhart, S.; Bublin, M.; Hafner, C.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K. Jug r 6 is the allergenic vicilin present in walnut responsible for IgE cross-reactivities to other tree nuts and seeds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nugraha, R.; Kamath, S.D.; Johnston, E.; Karnaneedi, S.; Ruethers, T.; Lopata, A.L. Conservation Analysis of B-Cell Allergen Epitopes to Predict Clinical Cross-Reactivity Between Shellfish and Inhalant Invertebrate Allergens. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarupalee, T.; Chatchatee, P.; Komolpis, K.; Suratannon, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Yingchutrakul, Y.; Yimchuen, W.; Butta, P.; Jacquet, A.; Palaga, T. Detecting Allergens From Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon That Can Bind and Cross-link IgE by ELISA, Western Blot, and a Humanized Rat Basophilic Leukemia Reporter Cell Line RS-ATL8. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, W.S.; Yuen, A.W.T.; Wai, C.Y.Y.; Leung, N.Y.H.; Chu, K.H.; Leung, P.S.C. Diagnosis of fish and shellfish allergies. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Kong, D.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Li, H. IgE and IgG4 responses to shrimp allergen tropomyosin and its epitopes in patients from coastal areas of northern China. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramovitch, J.B.; Kamath, S.; Varese, N.; Zubrinich, C.; Lopata, A.L.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Rolland, J.M. IgE Reactivity of Blue Swimmer Crab (Portunus pelagicus) Tropomyosin, Por p 1, and Other Allergens; Cross-Reactivity with Black Tiger Prawn and Effects of Heating. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramovitch, J.B.; Lopata, A.L.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Rolland, J.M. Effect of thermal processing on T cell reactivity of shellfish allergens—Discordance with IgE reactivity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rona, R.J.; Keil, T.; Summers, C.; Gislason, D.; Zuidmeer, L.; Sodergren, E.; Madsen, C. The prevalence of food allergy: A meta-analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei-Liang Tan, J.; Valerio, C.; Barnes, E.H.; Turner, P.J.; Van Asperen, P.A.; Kakakios, A.M.; Campbell, D.E. A randomized trial of egg introduction from 4 months of age in infants at risk for egg allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1621–1628.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savage, J.H.; Matsui, E.C.; Skripak, J.M.; Wood, R.A. The natural history of egg allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.D.; Peters, R.L.; Koplin, J.J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Gurrin, L.C.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Martino, D.J.; Neeland, M.; Tang, M.L.K.; Allen, K.J. Egg allergen specific IgE diversity predicts resolution of egg allergy in the population cohort HealthNuts. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 74, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.L.; Koplin, J.J.; Gurrin, L.C.; Dharmage, S.C.; Wake, M.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Tang, M.L.K.; Lowe, A.J.; Matheson, M.; Dwyer, T.; et al. The prevalence of food allergy and other allergic diseases in early childhood in a population-based study: HealthNuts age 4-year follow-up. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 145–153.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, D.J.; Metcalfe, J.; Makrides, M.; Gold, M.S.; Quinn, P.; West, C.E.; Loh, R.; Prescott, S.L. Early regular egg exposure in infants with eczema: A randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 387–392.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Maat-Bleeker, F.; van Dijk, A.G.; Berrens, L. Allergy to egg yolk possibly induced by sensitization to bird serum antigens. Ann. Allergy 1985, 54, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanapala, P.; Silva, C.; Doran, T.; Suphioglu, C. Cracking the egg: An insight into egg hypersensitivity. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anet, J.; Back, J.F.; Baker, R.S.; Barnett, D.; Burley, R.W.; Howden, M.E. Allergens in the white and yolk of hen’s egg. A study of IgE binding by egg proteins. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1985, 77, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.B. Allergy and allergic diseases. First of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotti, L.L.; Lutter, C.K.; Bunn, D.A.; Stewart, C.P. Eggs: The uncracked potential for improving maternal and young child nutrition among the world’s poor. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, R.L.; Dharmage, S.C.; Gurrin, L.C.; Koplin, J.J.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Lowe, A.J.; Tang, M.L.K.; Tey, D.; Robinson, M.; Hill, D.; et al. The natural history and clinical predictors of egg allergy in the first 2 years of life: A prospective, population-based cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 485–491.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemon-Mulé, H.; Sampson, H.A.; Sicherer, S.H.; Shreffler, W.G.; Noone, S.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A. Immunologic changes in children with egg allergy ingesting extensively heated egg. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.B. Allergy and Allergic Diseases; Blackwell Science: Malden, MA, USA, 1997; ISBN 9780865428676. [Google Scholar]
- Steinman, R.M. The Dendritic Cell System. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 271–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.G.; Jenkins, M.K. Co-stimulatory functions of antigen-presenting cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 99, S62–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabs, F.; Plum, M.; Laursen, N.S.; Jensen, R.K.; Mølgaard, B.; Miehe, M.; Mandolesi, M.; Rauber, M.M.; Pfützner, W.; Jakob, T.; et al. Trapping IgE in a closed conformation by mimicking CD23 binding prevents and disrupts FcϵRI interaction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, J.M.L. Diarrhoea due to allergy to egg: Is there a role for specific IgG? Allergol. Immunopathol. 2014, 42, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansotegui, I.J.; Melioli, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Gómez, R.M.; Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Ebisawa, M.; Luengo, O.; Caraballo, L.; Passalacqua, G.; Poulsen, L.K.; et al. A WAO—ARIA—GA2LEN consensus document on molecular-based allergy diagnosis (PAMD@): Update 2020. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloom, B.; Cohen, R.A.; Freeman, G. Summary health statistics for U.S. children: National health interview survey, 2010. Vital Health Stat. 10 2011, 250, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau, J.; Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 1998, 392, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipet, A.; Botturi, K.; Pinot, D.; Vervloet, D.; Magnan, A. Allergen-specific immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis and asthma. Mechanisms and proof of efficacy. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kay, A.B.; Bousquet, J.; Holt, P.G.; Kaplan, A.P. Allergy and Allergic Diseases, 2 Volumes, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; 2184p, ISBN 9781405157209. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, H.; Sicherer, S.H. Food-induced anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis Princ. Pract. 2013, 32, 83–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volcheck, G.W. Clinical Allergy: Diagnosis and Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2009; 491p. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, R.A. New horizons in allergen immunotherapy. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 1711–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Calderón, R.; Gonzalo-Garijo, M.; Lamilla-Yerga, A.; Mangas-Santos, R.; Moreno-Gastón, I. Recurrent angioedema due to lysozyme allergy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 17, 264–266. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, E.; Eggleston, P. Immunotherapy for Allergic Disease. In Pediatric Allergy: Principles and Practice; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016; pp. 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Juhász, A.; Belova, T.; Florides, C.G.; Maulis, C.; Fischer, I.; Gell, G.; Birinyi, Z.; Ong, J.; Keeble-Gagnère, G.; Maharajan, A.; et al. Genome mapping of seed-borne allergens and immunoresponsive proteins in wheat. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pahr, S.; Selb, R.; Weber, M.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Hofer, G.; Dordić, A.; Keller, W.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Giavi, S.; Mäkelä, M.; et al. Biochemical, biophysical and IgE-epitope characterization of the wheat food allergen, Tri a 37. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigerio, J.; Pellesi, R.; Mezzasalma, V.; De Mattia, F.; Galimberti, A.; Lambertini, F.; Suman, M.; Zanardi, S.; Leporati, A.; Labra, M. Development of a DNA barcoding-like approach to detect mustard allergens in wheat flours. Genes 2019, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.S.; Dyer, A.A.; Jain, N.; Greenhawt, M.J. Childhood Food Allergies: Current Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaharu, U. Genome Analysis in Brassica with Special Reference to the Experimental Formation of B. Napus and Peculiar Mode of Fertilization. Jpn. J. Bot. 1935, 7, 389–452. [Google Scholar]
- Kalunke, R.M.; Tundo, S.; Sestili, F.; Camerlengo, F.; Lafiandra, D.; Lupi, R.; Larré, C.; Denery-Papini, S.; Islam, S.; Ma, W.; et al. Reduction of Allergenic Potential in Bread Wheat RNAi Transgenic Lines Silenced for CM3, CM16 and 0.28 ATI Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krisnawati, D.I.; Alimansur, M.; Atmojo, D.S.; Rahmawati, E.Q.; Rahayu, D.; Susilowati, E.; Kuo, T.-R. Food Allergies: Immunosensors and Management. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052393
Krisnawati DI, Alimansur M, Atmojo DS, Rahmawati EQ, Rahayu D, Susilowati E, Kuo T-R. Food Allergies: Immunosensors and Management. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052393
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrisnawati, Dyah Ika, Moh Alimansur, Didik Susetiyanto Atmojo, Elfi Quyumi Rahmawati, Dwi Rahayu, Erna Susilowati, and Tsung-Rong Kuo. 2022. "Food Allergies: Immunosensors and Management" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052393
APA StyleKrisnawati, D. I., Alimansur, M., Atmojo, D. S., Rahmawati, E. Q., Rahayu, D., Susilowati, E., & Kuo, T.-R. (2022). Food Allergies: Immunosensors and Management. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052393







