An Adaptive Operational Modal Analysis under Non-White Noise Excitation Using Hybrid Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Operational Modal Analysis
2.2. CNN
2.3. GRU
3. The Proposed Method and Simulation Verification
3.1. Dataset Process
3.2. The Proposed Method
3.3. Modal Training and Results
4. Experimental Verification
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Conventional OMA Methods
4.3. Model Training and Results
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- According to the comparison of the training and test results of the same dataset with different network structures, it shows that the hybrid neural network is optimal.
- (2)
- A total of 11 beams with different qualities are numerically simulated. The training time and convergence speed of the response data with different SNRs are the same, and the test results of the first beam are the same, showing that the anti-noise ability of the proposed method is strong. In addition, the effectiveness of the method is proved by comparing with the finite element solution, analytical solution, and the test results of the first beam.
- (3)
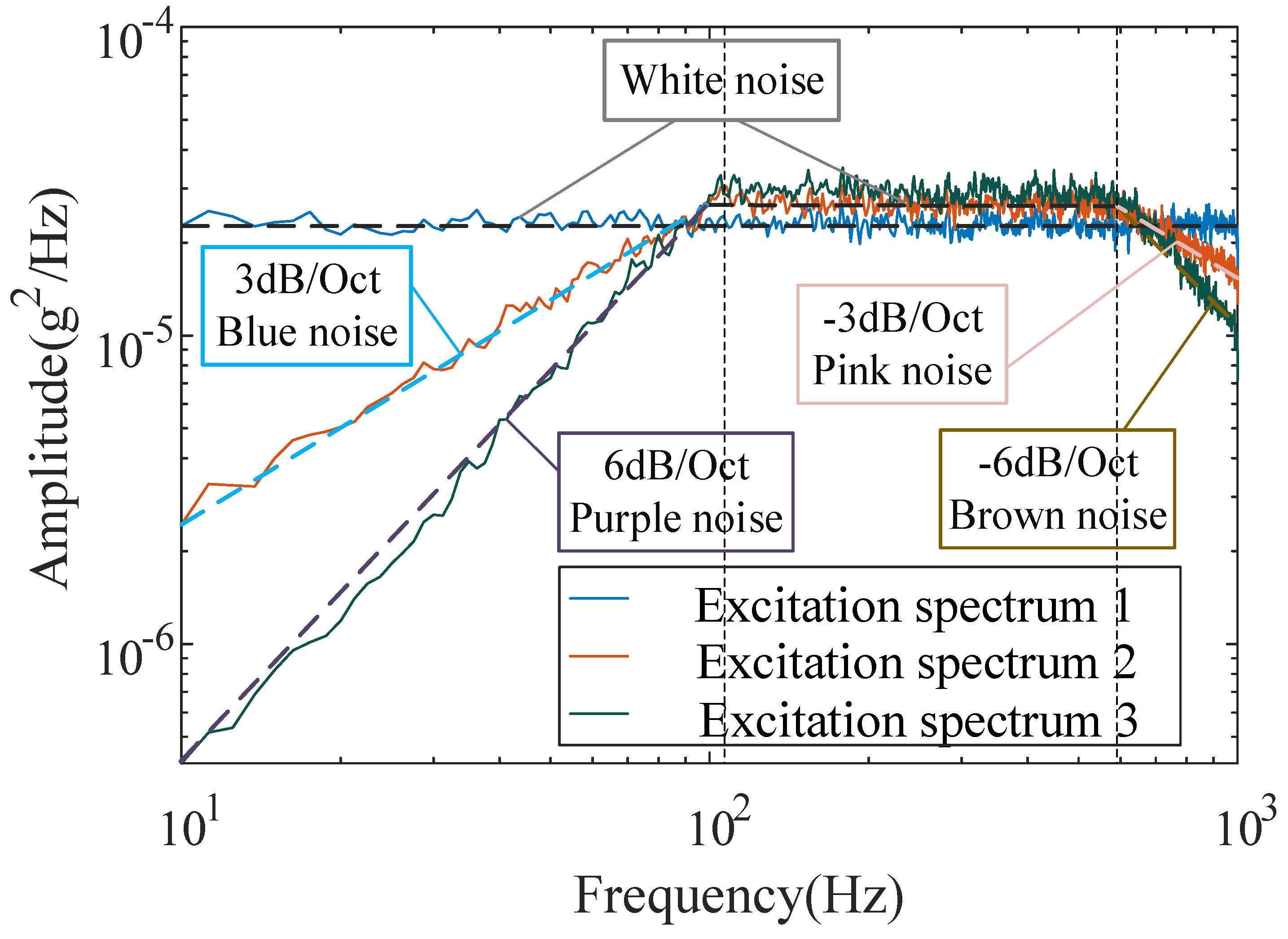
- The conventional OMA methods are used to identify the modal parameters of the beam. There are false modes and mode leakage when identifying the modal parameters of the response under non-white noise excitation (excitation spectrum 2 and excitation spectrum 3). Taking the analysis results as a reference, the results of different methods for identifying the response under non-white noise excitation are compared. It is found that the proposed method has no modal leakage and the highest identification accuracy. Therefore, the proposed method is not limited by the excitation type and is more suitable for the actual ambient excitation.
- (4)
- The results of the proposed method for identifying the rudder surface under different noise excitations are consistent, which shows that the anti-noise ability of the method is strong. Compared with the analysis results, the identification errors of the first four modal frequencies are all less than 0.2%, so the identification accuracy of the proposed method is high.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, X.; Man, J.; Wang, H. Structural vibration monitoring and operational modal analysis of offshore wind turbine structure. Ocean Eng. 2018, 150, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.C.; Alamdari, M.M.; Ye, X.W. Fast operational modal analysis of a single-tower cable-stayed bridge by a Bayesian method. Measurement 2021, 174, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioldi, F.; Rizzi, E. Earthquake-induced structural response output-only identification by two different operational modal analysis techniques. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yan, W.J.; Ren, W.X. Application of transmissibility measurements to operational modal analysis of railway, highway, and pedestrian cable-stayed bridges. Measurement 2019, 148, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Mirdamadi, H.R.; Ziaei, R.S. Operational modal analysis and fatigue life estimation of a chisel plow arm under soil-induced random excitations. Measurement 2018, 116, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Chen, D.M.; Zhu, W.D. Operational modal analysis using lifted continuously scanning laser doppler vibrometer measurements and its application to baseline-free structural damage identification. J. Vib. Control 2019, 25, 1341–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez-Borjas, J.J.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Camarena-Martinez, D. Nonlinear mode decomposition-based methodology for modal parameters identification of civil structures using ambient vibrations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitner, M.; Sirohi, J.; Tinney, C.E. Modal parameter estimation of a reduced-scale rocket nozzle using blind source separation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 095401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, R.; Zhang, L.; Andersen, P. Modal identification from ambient responses using frequency domain decomposition. In Proceedings of the IMAC 18: Proceedings of the International Modal Analysis Conference (IMAC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 7–10 February 2000; pp. 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Auweraer, H.; Guillaume, P.; Verboven, P. Application of a fast-stabilizing frequency domain parameter estimation method. J. Dyn. Syst. 2001, 123, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, A.; Drozdowska, M.; Szafrański, M. Material Parameters Identification of Historic Lighthouse Based on Operational Modal Analysis. Materials 2020, 13, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.T.; Lynch, J.P. Market-based frequency domain decomposition for automated mode shape estimation in wireless sensor network. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2010, 17, 808–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozer, E.; Purasinghe, R.; Feng, M.Q. Multi-output modal identification of landmark suspension bridges with distributed smartphone data: Golden Gate Bridge. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, S.; Brincker, R. Robust Multi-dataset Identification with Frequency Domain Decomposition. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 508, 116207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nita, G.M.; Mahgoub, M.A.; Sharyatpanahi, S.G.; Cretu, N.C.; El-Fouly, T.M. Higher order statistical frequency domain decomposition for operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 84, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, R.; Ventura, C.E.; Andersen, P. Damping estimation by frequency domain decomposition. In Proceedings of the International Modal Analysis Conference 19: A Conference on Structural Dynamics, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 5–8 February 2001; Volume 1, pp. 698–703. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.M.; Wang, T.; Tamura, Y. A frequency-spatial domain decomposition (FSDD) method for operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2010, 24, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M. Modal parameters identification of bridge by improved stochastic subspace identification method with Grubbs criterion. Meas. Control 2021, 54, 002029402199383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.H.; Thomas, M.; Lakis, A.A. Operational modal analysis by updating autoregressive model. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonekemper, L.; Wiemann, M.; Kraemer, P. Automated set-up parameter estimation and result evaluation for SSI-Cov-OMA. Vibroeng. Procedia 2020, 34, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Hua, X.G.; Chen, Z.Q. AMD-Based Random Decrement Technique for Modal Identification of Structures with Close Modes. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 31, 04018057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Yang, Q.S. Applicability of random decrement technique in extracting aerodynamic damping of crosswind-excited tall buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppanen, J.M.; Turunen, J.; Koivisto, M. Modal Analysis of Power Systems through Natural Excitation Technique. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.Y.; Xin, K.G.; Spencer, B. Decentralized NExT/ERA and RDT/ERA system identification in wireless smart sensor net-works. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 204, 4946–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonge, F.; Ippolito, F.; Raimondi, F.M. System identification via optimised wavelet-based neural networks. IEEE Proc.-Control Theory Appl. 2003, 150, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, P.F.; Palazotto, A.N. HHT-based nonlinear signal processing method for parametric and non-parametric identification of dynamical systems. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2008, 50, 1619–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, K.; Wang, Z.; Maalej, M. Adaptive magnitude spectrum algorithm for Hilbert–Huang transform based frequency identi-fication. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, E. System identification methods for (operational) modal analysis: Review and comparison. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2012, 19, 51–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Chen, H.; Vandepitte, D.; Luo, A.Z. Multi-exciter stationary non-Gaussian random vibration test with time domain randomization. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 122, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Mja, B.; Yc, C.; Hs, B. A method to distinguish harmonic frequencies and remove the harmonic effect in operational modal analysis of rotating structures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 161, 107928. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.-H.; Wang, P.; Chao, K.-M.; Etlin, H.-C.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Lai, Y.-H. Wind Power Forecasting with Deep Learning Networks: Time-Series Forecasting. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lei, Y.G.; Li, N.P.; Yan, T.; Li, N. Machinery health indicator construction based on convolutional neural networks considering trend burr. Neurocomputing 2018, 292, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Lei, Y.G.; Lu, N.; Xing, S. Deep normalized convolutional neural network for imbalanced fault classification of machinery and its understanding via visualization. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 110, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoyu, Y.; Shubhendu, K.S.; Mostafa, T.; Nikta, A.; Yang, Y.; Amin, M.; Rai, R. CNN-LSTM deep learning architecture for computer vision-based modal frequency detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106885. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.H.; Chen, H.; Guan, C. Random convolutional neural network structure: An intelligent health monitoring scheme for diesel engines. Measurement 2021, 171, 108786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Pi, D.C.; Xie, L.Q.; Luo, Y. Multiscale attentional residual neural network framework for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. Measurement 2021, 177, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.T.; Yan, C.L.; Chen, C.H.; Yang, Z.J.; Tian, H.L.; Wang, S.Y. Light neural network with fewer parameters based on CNN for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Measurement 2021, 181, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.L.; Wang, H.M. Robust output feedback stabilization for uncertain discrete-time stochastic neural networks with time-varying delay. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 51, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merainani, B.; Boualem, C.; Rahmoune, D.; Ould-Bouamama, B. A novel gearbox fault feature extraction and classification using Hilbert empirical wavelet transform, singular value decomposition, and SOM neural network. J. Vib. Control 2017, 24, 2512–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sato, T.; Iai, S.; Hutchinson, T. A pattern recognition technique for structural identification using observed vibration signals: Linear case studies. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, L.; Betti, M.; Biagini, P. Neural network based modal identification of structural systems through output-only measurement. Comput. Struct. 2014, 138, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Huang, X.; Song, M.L.; LaFave, J.M. Automatic identification of modal parameters for structures based on an uncertainty diagram and a convolutional neural network. Structures 2020, 28, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinto, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 2, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F.A. Learning to Forget: Continual Prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Han, T.; Gao, Z.; Lee, C.H. A review of impinging jets during rocket launching. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2019, 109, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowski, J.; Wylomanska, A.; Zimroz, R. Two-Stage Data Driven Filtering for Local Damage Detection in Presence of Time Varying Signal to Noise Ratio. Vib. Eng. Technol. Mach. 2015, 23, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.-F.; Xing, Y.-D. Lenet-5 convolution neural network with mish activation function and fixed memory step gradient descent method. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing, Chengdu, China, 13–15 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.Y.; Li, S.B.; Bai, Q.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.; Miao, Y. Review of Image Classification Algorithms Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 13, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, K.J.; Robertson, J.E. Prediction of space shuttle fluctuating pressure environments, including rocket plume effects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1973, 19730021153. [Google Scholar]
- Casper, K.M.; Beresh, S.J.; Henfling, J.F.; Spillers, R.W.; Pruett, B.; Schneider, S.P. Hypersonic wind-tunnel measurements of boundary-layer transition on a slender cone. AIAA J. 2016, 54, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Layer | Parameters | Activation Function |
|---|---|---|
| Conv1 (C1) | kernel size = 64; stride = 1; padding = 2; input channels = 1; output channels = 16 | Mish |
| Max pooling1 (P1) | data kernel size = 2; stride = 2 | - |
| GRU (G2) | hidden size = 256; layers = 2 | tanh |
| Fully connected layer3 (FC3) | Inputdim = Size(YG); Outputdim = Size (Output) | PReLU |
| Physical Parameters | Experimental Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic Modulus (Pa) | Mass Density (kg/m3) | Spectral Lines | Analysis Frequency Band (Hz) | Sampling Frequency (Hz) | Sampling Length (s) | Test Time (s) |
| 7.1 × 1010 | 2770 | 800 | 1000 | 2560 | 0.8 | 400 |
| Methods | The Proposed Method | PP | EFDD | FSDD | SSI-COV | SSI-DATA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation spectrum 1 (%) | 1st | 0 | 7.63 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 8.73 | 3.56 |
| 2nd | 0 | −1.84 | −1.36 | −0.41 | −1.26 | 4.41 | |
| 3rd | 0 | −0.06 | −0.35 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 0.68 | |
| 4th | −0.21 | 0.18 | 0.58 | −0.17 | 0.23 | 0.50 | |
| 5th | 0 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.08 | −1.27 | |
| Excitation spectrum 2 (%) | 1st | 0 | −1.05 | 0.06 | 3.56 | - | - |
| 2nd | 0 | 0.82 | −0.08 | 0.31 | 0.69 | 7.11 | |
| 3rd | 0 | 0.94 | 0.46 | 1.14 | 0.62 | 1.09 | |
| 4th | −0.21 | 0.21 | 0.18 | −0.065 | 0.036 | 0 | |
| 5th | 0 | 0.37 | −0.88 | 1.53 | −0.14 | −0.52 | |
| Excitation spectrum 3 (%) | 1st | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2nd | 0 | 1.39 | −0.08 | 0.21 | −2.84 | 10.2 | |
| 3rd | 0 | 1.72 | 0.87 | 1.69 | 1.06 | 1.51 | |
| 4th | −0.21 | 1.26 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.21 | |
| 5th | 0 | 0.37 | 1.01 | 2.02 | −0.05 | −0.37 | |
| Excitations | The Proposed Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | |
| Excitation spectrum 1 (%) | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.049 | −0.049 |
| Excitation spectra 2 and 3 (%) | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.049 | −0.049 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, R.; He, X.; Ren, S. An Adaptive Operational Modal Analysis under Non-White Noise Excitation Using Hybrid Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052471
Qin M, Chen H, Zheng R, He X, Ren S. An Adaptive Operational Modal Analysis under Non-White Noise Excitation Using Hybrid Neural Networks. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052471
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Min, Huaihai Chen, Ronghui Zheng, Xudong He, and Siyu Ren. 2022. "An Adaptive Operational Modal Analysis under Non-White Noise Excitation Using Hybrid Neural Networks" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052471
APA StyleQin, M., Chen, H., Zheng, R., He, X., & Ren, S. (2022). An Adaptive Operational Modal Analysis under Non-White Noise Excitation Using Hybrid Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052471






