Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications
Abstract
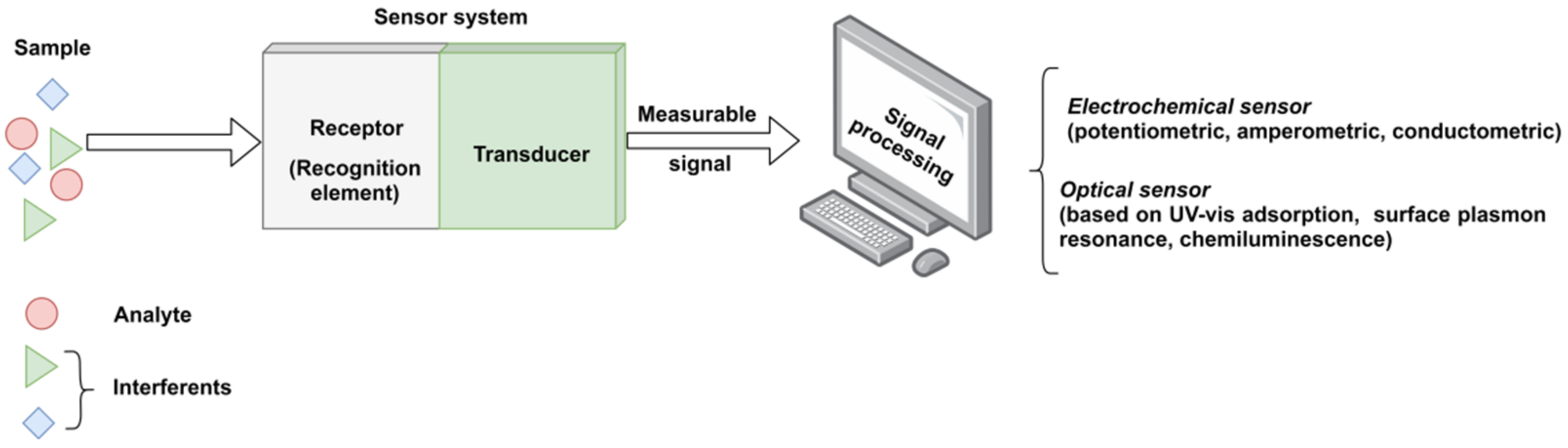
:1. Introduction
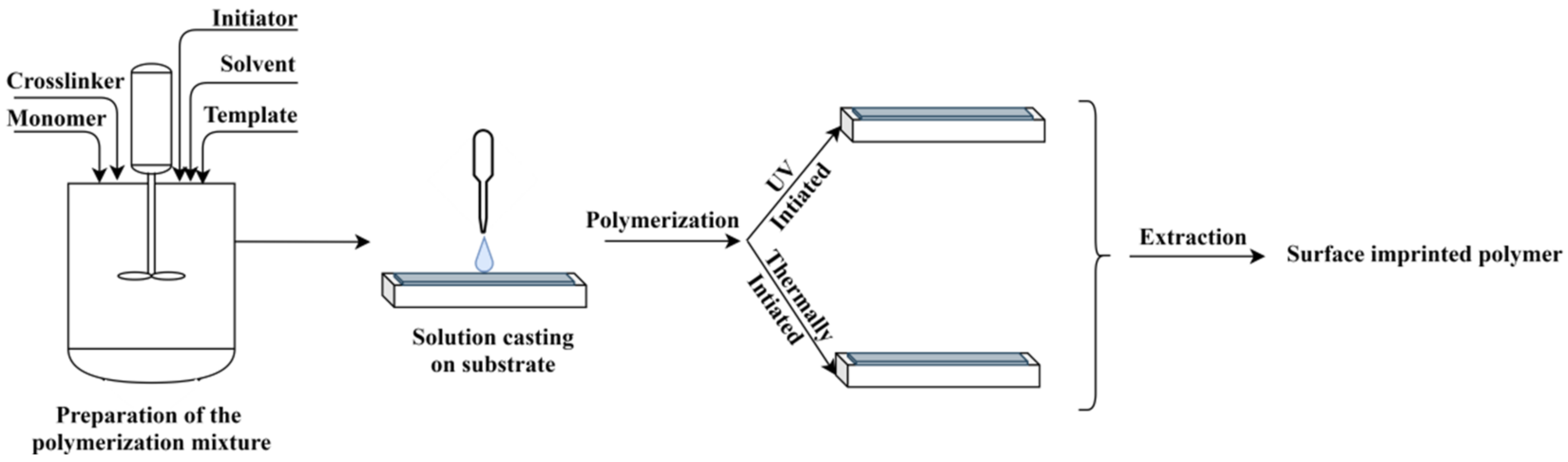
2. Molecular Imprinting by Surface Polymerization
3. Molecular Imprinting by Electropolymerization
4. Molecular Imprinting Using MIP Particles Embedded in Pastes or Inks
| Synthesis Method | Receptor | Support | Analyte | Characterization Method(s) | LOD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drop coating | MIP film | SPCE 1 | Sertraline | CV 2 and DPV 3 | 1.99 × 10−9 M | [117] |
| Coating | MIP film | Paper-based device | 8-hydroxy-20-deoxyguanosine and 3-nitrotyrosine | CV and SWV 4 | 1.38 × 10−8 M and 2.7 × 10−9 M | [118] |
| Dropcasting | MIP film | SPCE | Bisphenol A | CV and HPLC 5 | 6.0 × 10−11 M | [119] |
| Dropcasting | Membrane | Chromatography paper used as electrode | Bisphenol A | Potentiometric detection | 1.5 × 10−7 M | [120] |
| Spincoating | MIP Membrane | GCE 6 | Phenylephrine | DPV and HPLC | - | [124] |
| Spincoating | MIP film | Au electrode quartz crystal | Chloramphenicol | Oscillation frequency | 7 × 10−8 µg·mL−1 | [125] |
| Spincoating | MIP film | Quartz plates | 1-hydroxypyrene | CV | 3.353 × 10−10 M | [126] |
| Dropping | Film | SPCE | Trazosin | CV, DPV and EIS 7 | 3.0 × 10−7 M | [129] |
| Dropcasting | Film | GCE | Diphenylamine | DPV | 5.0 × 10−8 M | [130] |
| Functionalization of carbon black paste electrode | Layer | Functionalized Carbon black | Imazethapyr | DPV | 3.0 × 10−8 M | [131] |
5. Molecular Imprinting by Sol–Gel Derived Techniques
6. Molecular Imprinting by Phase-Inversion
| Synthesis Method | Receptor | Support | Analyte | Characterization Method(s) | LOD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casting | MIP film | Ti/TiO2 electrode | Bisphenol A | Amperometric measurements | 1.3 × 10−9 M | [173] |
| Casting | Hybrid MIP membrane | Glass support | Citrinin | Batch binding, HPLC 1 | 0.5 ng·g−1 | [182] |
| Casting | MIP Membrane | Conductive graphite | Trimethoprim | Potentiometric measurements | 4.01 × 10− 7 M | [184] |
| Casting | MIP Membrane | Conductive graphite | Enrofloxacin | Potentiometric measurements | 0.9 µg·mL−1 | [185] |
| Dropwise | MIP Film | Screen-printed gold electrode | Regenerating Protein 1B | CV 2 | 0.1 pg·mL−1 | [186] |
| 3D-Imprinting | MIP Membrane | Polyvinylidene fluoride/carbon black membrane | Non-woven (Polyester-17153) and 5000 mesh fabric | Morpho-structural, CV | / | [187] |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plata, M.R.; Contento, A.M.; Ríos, A. State-of-the-Art of (Bio)Chemical Sensor Developments in Analytical Spanish Groups. Sensors 2010, 10, 2511–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Cisneros, C.S.; Ibáñez-García, N.; Valdés, F.; Alonso, J. LTCC microflow analyzers with monolithic integration of thermal control. Sens. Actuators A 2007, 138, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, J.; Alegret, S.; Valle, M. Flow-injection electronic tongue based on potentiometric sensors for the determination of nitrate in the presence of chloride. Sens. Actuators B 2004, 101, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, Z.O.; Uygun, H.D.E.; Ermiş, N.; Canbay, E. Chapter 3—Molecularly Imprinted Sensors—New Sensing Technologies. In Biosensors—Micro and Nanoscale Applications; Intech: London, UK, 2015; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, S.; Sharma, M.K.; Shaik, M.; Das, R.; Rao, V.K. Sensors—A Nanotechnological Approach for the Detection of Organophosphorous Compounds/Pesticides. In The Impact of Pesticides, 1st ed.; AcademyPublish.org: Wyoming, MI, USA, 2012; pp. 391–415. [Google Scholar]
- Boysen, R.I.; Schwarz, L.J.; Nicolau, D.V.; Hearn, M.T.W. Molecularly imprinted polymer membranes and thin films for the separation and sensing of biomacromolecules. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 314–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, W.J.; Yang, S.H.; Ali, F. Molecular imprinted polymers for separation science: A review of reviews. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ge, Y.; Piletsky, S.A.; Lunec, J. Molecularly Imprinted Sensors: Overview and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers as antibody and receptor mimics for assays, sensors and drug discovery. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xua, S.; Li, J. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: Current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheyen, E.; Schillemans, J.P.; Van Wijk, M.; Demeniex, M.-A.; Hennink, W.E.; Van Nostrum, C.F. Challenges for the effective molecular imprinting of proteins. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3008–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, T.; Deng, Q.; Fang, G.; Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, S. Molecularly imprinted upconversion nanoparticles for highly selective and sensitive sensing of Cytochrome C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretjakov, A.; Syritski, V.; Reut, J.; Boroznjak, R.; Öpik, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer film interfaced with Surface Acoustic Wave technology as a sensing platform for label-free protein detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 902, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, A.M.; Zaharia, A.; Paruch, L.; Perrin, F.X.; Sarbu, A.; Olaru, A.G.; Paruch, A.M.; Iordache, T.V. Highly efficient materials working in tandem against pathogenic bacteria in wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešić, M.P.; Todorov, M.D.; Becskereki, G.; Horvai, G.; Verbić, T.Ž.; Tóth, B. A novel method of molecular imprinting applied to the template cholesterol. Talanta 2020, 217, 121075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular Imprinting Techniques Used for the Preparation of Biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wu, F.; Au, C.; Tao, Q.; Pi, M.; Zhang, W. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer by suspension polymerization for selective extraction of p-hydroxybenzoic acid from water. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 46984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Han, X.; Peng, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer via Emulsion Polymerization for Application in Solanesol Separation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardeshi, S.; Singh, S.K. Precipitation polymerization: A versatile tool for preparing molecularly imprinted polymer beads for chromatography applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23525–23536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branger, C.; Meouche, W.; Margaillan, A. Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, D.S.; Kofinas, P. Molecular imprinting of peptides and proteins in aqueous media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L. Synthesis of dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents for solid phase extraction of aminoglycosides antibiotics from environmental water samples. Talanta 2020, 208, 120385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Urraca, J.L.; Benito-Pena, E.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Martins, S.A.; Orellana, G.; Sellergren, B. Molecularly imprinted polymers as biomimetic receptors for fluorescence-based optical sensors. In Proceedings of the Third European Workshop on Optical Fibre Sensors (SPIE), Naples, Italy, 2 July 2007; Volume 6619. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.S.; Dabrowski, M.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Surface development of molecularly imprinted polymer films to enhance sensing signals. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthoff, E.L.; Bright, F.V. Molecularly templated materials in chemical sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 594, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, R.; Mei, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole nanonecklaces for detection of herbicide through molecular recognition-amplifying current response. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 702, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Poma, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A. MIP sensors—The electrochemical approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo- Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-López, M.C.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, S.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Electrochemical sensing with electrodes modified with molecularly imprinted polymer films. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Diaz, G.; Antuna-Jimenez, D.; Blanco- López, M.C.; Lobo- Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. New materials for analytical biomimetic assays based on affinity and catalytic receptors prepared by molecular imprinting. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 33, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S.; Spivak, D.A. Molecular Imprinting in Monolayer Surfaces. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, P.; Ziaee, M.; Abdouss, M.; Farazin, A.; Mizaikoff, B. Biomacromolecule template-based molecularly imprinted polymers with an emphasis on their synthesis strategies: A review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 1124–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; He, X.-W.; Yuan, X.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Molecularly imprinted beads with double thermosensitive gates for selective recognition of proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Turner, A.P. Too large to fit? Recent developments in macromolecular imprinting. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Y.; Tan, T.; Svec, F. Molecular imprinting of proteins in polymers attached to the surface of nanomaterials for selective recognition of biomacromolecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillberg, A.; Tabrizian, M. Biomolecule imprinting: Developments in mimicking dynamic natural recognition systems. IRBM 2008, 29, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Shi, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Men, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers by the surface imprinting technique. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; D’Agostino, G.; Pesavento, M.; Zenia, L. High selectivity and sensitivity sensor based on MIP and SPR intapered plastic optical fibers for the detection of l-nicotine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 529–53638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont, A.-S.; Jaeger, S.; Knopp, D.; Niessner, R.; Gauglitz, G.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymer films for reflectometric interference spectroscopic sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3267–327239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wei, M.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, H. High-sensitive imprinted membranes based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering for selective detection of antibiotics in water. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Noronha, J.P.C.; Sales, M.G.F. Electrochemical biosensor based on biomimetic material for myoglobin detection. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 107, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M.; Hu, X.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on polypyrrole/dopamine@graphene incorporated with surface molecularly imprinted polymers thin film for recognition of olaquindox. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 132, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical sensor for quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 353, 131160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-T.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Epitope molecularly imprinted polymer coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor for the determination of human serum albumin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 879–88656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, R.I.; Li, S.; Chowdhury, J.; Schwarz, L.J.; Hearn, M.T.W. Selectivity optimisation of biomimetic molecularly imprinted polymer thin films. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 97, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhai, X.; Deng, Q.; Yuan, S.; Cao, M.; Wang, S. Preparation and Evaluation of Lysozyme Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film on the Surface of Multi-wall Carbon Nanotubes. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Molecular Imprinting: Principles and Applications of Micro- and Nano-Structured Polymers, 1st ed.; Pan Stanford Publishing Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2012; pp. 87–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Recent Advances in Macromolecularly Imprinted Polymers by Controlled Radical Polymerization Techniques. Mol. Imprinting 2015, 3, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Roy, E.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Nano-iniferter based imprinted sensor for ultra-trace level detection of prostate-specific antigen in both men and women. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.R.; Qin, L.; Jia, M.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y. Novel surface modified molecularly imprinted membrane prepared with iniferter for permselective separation of lysozyme. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Q.Q.; Qu, F.; Liu, Z.J.; Dai, R.J.; Zhang, Y.K. Superparamagnetic lysozyme surface-imprinted polymer prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization and its application for protein separation. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; Sellergren, B. Thin molecularly imprinted polymer films via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Armutcu, C.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer film based plasmonic sensors for detection of ochratoxin A in dried fig. Polym. Bull. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, F.; Li, K.; Liu, H. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film Grafted from Porous Silica for Selective Recognition of Testosterone. Anal. Lett. 2006, 39, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Singh, M. Water-compatible surface imprinting of ‘baclofen’ on silica surface for selective recognition and detection in aqueous solution. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 3019–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhoseini, F.; Langille, E.A.; Azizi, A.; Bottaro, C.S. Thin film molecularly imprinted polymer (TF-MIP), a selective and single-use extraction device for high-throughput analysis of biological samples. Analyst 2021, 146, 3157–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.D.; Jamieson, O.; Crapnell, R.D.; Rurack, K.; Soares, T.C.C.; Mecozzi, F.; Laude, A.; Gruber, J.; Novakovica, K.; Peeters, M. Dual detection of nafcillin using a molecularly imprinted polymer-based platform coupled to thermal and fluorescence read-out. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 5105–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati, N.; Blel, N.; Lattach, Y.; Ktari, N.; Zerrouki, C. Chemical and Biological Sensors from Conducting and Semiconducting Polymers. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Inzelt, G. Conducting Polymers—A New Area in Electrochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Heinze, J.; Frontana-Uribe, B.A.; Ludwigs, S. Electrochemistry of conducting polymers-persistent models and new concepts. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4724–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-cando, A.; Rendon-Enriquez, I.; Tausch, M.; Scherf, S. Thin functional polymer films by electropolymerization. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaz, U.; Ashraf, S.M. Conductive Polymer Composite and Blends: Recent Trends. In Nanostructured Polymer Blends; Thomas, S., Shanks, R., Sarathchandran, C., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 509–538. [Google Scholar]
- De Leon, A.; Advincula, R.C. Chapter 11—Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control Conducting Polymers with Superhydrophobic Effects as Anticorrosion Coating. In Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control; Tiwari, A., Rawlins Hihara, L.H., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 409–430. [Google Scholar]
- Gvozdenović, M.M.; Jugović, B.Z.; Stevanović, J.S.; Grgur, B.N. Electrochemical synthesis of electroconducting polymers. Chem. Ind. 2014, 68, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, G.G.; Tsekouras, G.; Wang, C. Chapter 11—Inherently conducting polymers via electropolymerization for energy conversion and storage. In Electropolymerization: Concepts, Materials and Applications; Cosnier, S., Karyakin, A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, S.; Yang, Y. Spectral characteristics of polyaniline nanostructures synthesized by using cyclic voltammetry at different scan rates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 11558–11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Miura, N. Large-area network of polyaniline nanowires prepared by potentiostatic deposition process. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuna-Jimenez, S.; Diaz-Diaz, G.; Blanco-Lopez, M.C.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tunon-Blanco, P. Chapter 1—Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors: Past, present, and future. In Molecularly Imprinted Sensors: Overview and Applications; Li, S., Ge, Y., Piletsky, S.A., Lunec, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, O.S.; Bedwell, T.S.; Esen, C.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Molecularly imprinted polymers in electrochemical and optical sensors. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z. Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Jesny, S.; Kumar, K.G. A voltammetric sensor for acetaminophen based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted poly(o-aminophenol) modified gold electrode. Talanta 2018, 179, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.R.; Bacchu, M.S.; Daizy, M.; Tarafder, C.; Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, M.Z.H. A highly poly-arginine based MIP as an electrochemical sensor for selective detection of dimetridazole. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1121, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Ciocan, V.; Opik, A.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensor for electrochemical detection of erythromycin. Talanta 2020, 209, 120502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrini, M.; Florea, A.; Cristea, C.; Sandulescu, R.; Vocanson, F.; Errachid, A.; Bouchikhi, B.; El Bari, N.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Development of a novel sensitive molecularly imprinted polymer sensor based on electropolymerization of a microporous-metal-organic framework for tetracycline detection in honey. Food Control 2016, 59, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Zamani, M.; Ardaki, M.S. Rapid electrochemical synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers on functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective recognition of sunset yellow in food samples. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 243, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Gan, T.; Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, K. Electrochemical sensor based on electropolymerized dopamine molecularly imprinted film for tetrabromobisphenol A. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 826, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, B.C. Novel electrochemical sensing platform based on integration of molecularly imprinted polymer with Au@Ag hollow nanoshell for determination of resveratrol. Talanta 2019, 196, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for atrazine detection by electropolymerization of o-phenylenediamine. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 56534–56540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motia, S.; Tudor, I.A.; Popescu, R.M.; Bouchikhi, B.; Bari, N. Development of a novel electrochemical sensor based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer for selective detection of sodium lauryl sulfate in environmental waters and cosmetic products. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 823, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguro, I.; Pacheco, J.G.; Delerue-Matos, C. Low cost, easy to prepare and disposable electrochemical molecularly imprinted sensor for diclofenac detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kan, X. Conductive imprinted electrochemical sensor for epinephrine sensitive detection and double recognition. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 836, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Pacheco, J.G.; Rebelo, P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor prepared on a screen-printed carbon electrode for naloxone detection. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 243, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaabani, N.; Chan, N.W.C.; Lee, W.E.; Jemere, A.B. Electrochemical determination of naloxone using molecularly imprinted poly(para-phenylenediamine) sensor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 137508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.A.S.; Mounssef, B., Jr.; Carvalho, F.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Braga, A.A.C.; Aldous, L.; Goncalves, L.M.; Quinaz, M.B. Methylone screening with electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer on screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 316, 128133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. A surface plasmon resonance-based optical fiber probe fabricated with electropolymerized molecular imprinting film for melamine detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regasa, M.B.; Soreta, T.R.; Femi, O.E.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Kumar, S. Molecularly imprinted polyaniline molecular receptor-based chemical sensor for electrochemical determination of melamine. J. Mol. Recognit. 2020, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Zalpour, N. Selective detection of Asulam with in-situ dopamine electropolymerization based electrochemical MIP sensor. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 169, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Geng, X.; Liu, Y.; Long, H.; Du, J. A novel electrochemical sensor based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of luteolin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 842, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, J.; Hong, S.; She, Y.; EI-Aty, A.M.A.; He, Y.; Yhu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Fabrication of a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor based in electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer hybrid nanocomposites for the detection of 4-nanylphenol in packaged milk samples. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 559, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu-Scheers, E.; Bouden, S.; Grillot, C.; Bicolle, J.; Warmont, F.; Bertagna, V.; Cagnon, B.; Vautrin-Ul, C. Trace anthracene electrochemical detection based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, R.A.; Lobato, A.; Mounssef, B., Jr.; Tasic, N.; Braga, A.A.; Maldaner, A.O.; Aldous, L.; Paixao, T.R.L.C.; Goncalves, L.M. Electroanalytical profiling of cocaine samples by means of an electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer using benzocaine as the template molecule. Analyst 2021, 146, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, A.E.; Abd-Ellatief, M.R. Molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine electrochemical sensor for entacapone. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.N. Carbon paste electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1958, 30, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švancara, I.; Kalcher, K. Carbon Paste Electrodes, Electrochemistry of Carbon Electrodes, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 379–423. [Google Scholar]
- Materon, E.M.; Wong, A.; Gomes, L.M.; Ibañez-Redí, G.; Joshi, N., Jr.; Oliveira, N.O.; Faria, R.C. Combining 3D printing and screen-printing in miniaturized, disposable sensors with carbon paste electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 5633–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, W.T.; Putra, B.R.; Fauzi, A.; Ramadhanti, D.; Rohaeti, E.; Heryanto, R. A Brief Review on Fabrication of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode: Materials and Techniques. Indo. J. Chem. Res. 2021, 8, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, T.; Shrivas, K.; Dewangan, K.; Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, N.K.; Deb, M.K.; Pervez, S. Design and development of conductive nanomaterials for electrochemical sensors: A modern approach. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 24, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ahmadi, M.; Fargas, G.; Perinka, N.; Reguera, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Llanes, L.; Jiménez-Piqué, E. Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks: From Synthesis and Ink Formulation to Their Use in Printing Technologies. Metals 2022, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, J.S.; Orzari, L.O.; Silva-Neto, H.A.; Neiva de Ataíde, V.; Mendes, L.F.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Janegitz, B.C. Different approaches for fabrication of low-cost electrochemical sensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 32, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S. Electrochemistry of Carbon Electrodes, Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Jewell, E.; Philip, B.; Greenwood, P. Improved Manufacturing Performance of Screen Printed Carbon Electrodes through Material Formulation. Biosensors 2016, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, J.P.; Wring, S.A. Recent developments in the design and application of screen-printed electrochemical sensors for biomedical, environmental, and industrial analyses. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R. Electrochemical Characterization of Commercial and Home-Made Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 2021–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreotti, I.A.D.A.; Orzari, L.O.; Camargo, J.R.; Faria, R.C.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F.; Gatti, A.; Janegitz, B.C. Disposable and flexible electrochemical sensor made by recyclable material and low cost conductive ink. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 840, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, E.; Michailidis, N. Printable conductive inks used for the fabrication of electronics: An overview. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 502009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, B.; Jewell, E.; Worsley, D. The impact of solvent characteristics on performance and process stability of printed carbon resistive materials. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.; He, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Derby, B. Water-based highly conductive graphene inks for fully printed humidity sensors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 455304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, C.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted thin film surfaces in sensing: Chances and challenges. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 161, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.R.; Silva, T.A.; Rivas, G.A.; Janegitz, B.C. Novel eco-friendly water-based conductive ink for the preparation of disposable screen-printed electrodes for sensing and biosensing applications. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 409, 139968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilă, A.M.; Iordache, T.V.; Sârbu, A.; Ciurlică, A.L.; Zaharia, A.; Chiriac, A.L.; Sandu, T.; Stoica, E.B.; Apostol, S. Sensitive Hybrid Films Molecularly Imprinted with Thiodiglycol Coating Screen Printed Carbon Electrodes, and Process for Manufacturing them. Ro. Patent RO135012A2, 28 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, A.; Ojani, R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Raoof, J. Direct voltammetric determination of carbendazim by utilizing a nanosized imprinted polymer/MWCNTs-modified electrode. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R.R.; Lakshmanakumar, M.; Jayalatha, J.B.B.A.; Rajan, K.S.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Fabrication of screen-printed electrodes: Opportunitiesand challenges. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 8951–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervini, P.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Strategies for preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers modified electrodes and their application in electroanalysis: A review. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrokhavar, R.; Motaharian, A.; Hosseini, M.R.M.; Mohammadsadegh, S. Screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) modified by molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) nanoparticles and graphene nanosheets for determination of sertraline antidepressant drug. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nontawong, N.; Ngaosri, P.; Chunta, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Amatatongchai, M. Smart sensor for assessment of oxidative/nitrative stress biomarkers using a dual-imprinted electrochemical paper-based analytical device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1191, 339363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, E.V.; Branger, C.; Bikanga, R.; Florea, A.M.; Istamboulie, G.; Calas-Blanchard, C.; Noguer, T.; Sarbu, A.; Brisset, H. Detectionof Bisphenol A in aqueous medium by screen printed carbon electrodes incorporating electrochemical molecularly imprintedpolymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, A.H.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Liang, R. A paper-based potentiometric sensing platform based on molecularly imprinted nanobeads for determination of bisphenol A. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, A.H.; Cetó, X.; Del Valle, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers—Towards electrochemical sensors and electronic tongues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6117–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, B.E.; Gavrila, A.-M.; Sarbu, A.; Iovu, H.; Brisset, H.; Miron, A.; Iordache, T.-V. Uncovering the behavior of screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with polymers molecularly imprinted with lipopolysaccharide. Electrochem. Commun. 2021, 124, 106965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Srivastava, S.; Tiwari, K.; Sharma, P.S. Ascorbic acid sensor basedon molecularly imprinted polymer-modified hanging mercury drop electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 29, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuduan, Y.; Youwen, T.; Weipeng, Z.; Zhaof, H. An electrochemical sensor forphenylephrine based on molecular imprinting. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Ebarvia, B.S.; Ubando, I.E.; Sevilla, F.B., III. Biomimetic piezoelectric quartz crystal sensor with chloramphenicol-imprinted polymer sensing layer. Talanta 2015, 144, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.-H.; Lee, C.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, Y.-D.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, H. An electrochemical nanofilm sensor for determination of 1-hydroxypyrene using molecularly imprinted receptors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mutio, D.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Gotiandia, A.; Larrauri, I.; Goicolea, M.A.; Barrio, R.J. Controlled grafting of molecularly imprinted films on gold microelectrodes using a self-assembled thiol iniferter. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 279, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.J.; Shin, Y.J.; Shin, J.S. Cholesterol recognition system by molecular imprinting on self-assembled monolayer. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 559, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Jalilian, Z.; Nezhadali, A. A novel electrochemical sensor based on electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid determination of trazosin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. An Electrochemical Sensor for Diphenylamine Detection Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with 1,4-Butanediyl-3,3′-bis-l-vinylimidazolium Dihexafluorophosphate Ionic Liquid as Cross-Linker. Polymers 2018, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelis, P.N.; Casarin, J.; Júnior, A.C.G.; Rocha, L.R.; Prete, M.C.; Tarley, C.R.T. Development of a Novel Molecularly Imprinted Polyvinylimidazole/Functionalized Carbon Black Nanocomposite-based Paste Electrode for Electrochemical Sensing of Imazethapyr in Rice Samples. Electroanalysis 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Santos, D.M.; Montes, A.; Sanchez-Coronilla, A.; Navas, J. Sol-gel applications for consolidating stones: An example for prosect-based learning in a physical chemistry lab. J. Chem. Educ. 2014, 91, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, R.B. Hybrid sol-gel coatings for corrosion mitigation: A critical review. Polymers 2020, 12, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landau, M.V. Chapter 2.3.4—Sol-gel process. In Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; Ertl, G., Knözinger, H., Schüth, F., Weitkamp, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 119–159. [Google Scholar]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Zchnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol-gel’ as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montilla, F.; Cotarelo, M.A.; Morallon, E. Hybrid sol-gel-conducting polymer synthesised by electrochemical insertion: Tailoring the capacitance of polyaniline. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 19, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.H.; Bierwagen, G.P. Sol–gel coatings on metals for corrosion protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 64, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanghadikolaei, A.; Ansary, J.; Ghoreishi, R. Sol-gel process applications: A mini-review. Proc. Nat. Res. Soc. 2018, 2, 02008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Gao, Y.-L.; Wang, P.-P.; Shang, H.; Pan, S.-Y.; Li, X.-J. Sol-gel molecularly imprinted polymer for selective solid phase microextraction of organophosphorus pesticides. Talanta 2013, 115, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Mishra, S.B. Sol-gel derived organic-inorganic hybrid materials: Synthesis, characterization and applications. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, A.-M.; Radu, I.C.; Stroescu, H.; Zaharia, A.; Stoica, E.-B.; Ciurlica, A.-L.; Iordache, T.-V.; Sârbu, A. Role of Functional Monomers upon the Properties of Bisphenol a Molecularly Imprinted Silica Films. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, A.; Iordache, T.V.; Florea, A.-M.; Georgescu, E.-B.; Apostol, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Films with Drugs and Process for Their Obtaining. Ro. Patent RO133363B1, 29 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrila, A.-M.; Iordache, T.V.; Lazau, C.; Rotariu, T.; Cernica, I.; Stroescu, H.; Stoica, M.; Orha, C.; Bandas, C.E.; Sarbu, A. Biomimetic Sensitive Elements for 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene Tested on Multi-Layered Sensors. Coatings 2020, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mujahid, A.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Dickert, F.L. Chemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted sol-gel materials. Materials 2010, 3, 2196–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.-H. Chapter 13—Molecularly imprinted sol-gel sensors. In Molecularly Imprinted Sensors; Songjun, L., Ge, L., Piletsky, S.A., Lunec, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 303–337. [Google Scholar]
- Guney, S.; Cebeci, F.C. Selective electrochemical sensor for theophylline based on an electrode modified with imprinted sol-gel film immobilized on carbon nanoparticle layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengamra, M.; Grayaa-Jaoued, N.; Khlifi-Riani, A.; Chehimi, M.M.; Kalfat, R. Highly selective molecularly imprinted sol-gel membrane grafted to gold for the detection of melamine. Silicon 2019, 11, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Opik, A.; Furchner, A.; Syritski, V. Hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer for amoxicillin detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, B.; Hayashi, K. Development of molecular imprinted sol-gel LSPR sensor for detection of volatile cis-jasmone in plant. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, G.D.; Sonato, A.; Gazzola, E.; Ruffato, G.; Brusa, S.; Romanato, F. SPR Enhanced molecular imprinted sol-gel film: A promising tool for gas-phase TNT detection. Mater. Lett. 2016, 162, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.M.; Miguel, E.M.; Dos Silva, J.S.; Da Silva, C.B.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Kubota, L.T.; Gonzaga, F.B.; Santos, W.J.R.; Lima, P.L. Application of a nanostructured platform and imprinted sol-gel film for determination of chlorogenic acid in food samples. Talanta 2018, 156–157, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Bai, H.; Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Cao, Q. Electrochemical sensor for detection of europium based on poly-catechol and ion-imprinted sol-gel film modified screen-printed electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 824, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Shan, X.; Chen, Z. Derivative chiral copper(II) complexes as template of an electrochemical molecular imprinting sol-gel sensor for enantiorecognition of aspartic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2019, 1072, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized carbon nanotubes for highly selective removal of aristolochic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1602, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Wan, F.; Ni, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, J. Electrochemical sensor for detection of trichlorfon based on molecularly imprinted sol-gel films modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2012, 22, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Long, C.; Wei, S.; Sun, Y. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted film for high sensitivity detection of clenbuterol prepared using sol-gel method. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, T.; Lu, X.; Kan, X. Imprinted sol-gel electrochemical sensor for melamine direct recognition and detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 713, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, N.; Chan, N.W.C.; Jemere, A.B. A molecularly imprinted sol-gel electrochemical sensor for naloxone determination. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavipanah, I.; Alipour, E.; Deiminiat, B.; Rounaghi, G.H. A novel electrochemical imprinted sensor for ultrasensitive detection of the psychoactive substance “Mephedrone”. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Y.; Hong, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ning, B.; Gao, Z. Ultrasensitive sensing of diethylstilbestrol based on AuNPs/MWCNTs-CS composites coupling with sol-gel molecularly imprinted polymer as a recognition element of an electrochemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiminiat, B.; Rounaghi, G.H. Fabrication of a new electrochemical imprinted sensor for determination of ketamine based on modified polytyramine/sol-gel/f-\MWCNTs@AuNPs nanocomposite/pencil graphireelectreode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, C.; Drioli, E.; Guzzo, L.; Donato, L. Bio-Mimetic Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Membranes. Sensors 2014, 14, 13863–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedborg, E.; Winquist, F.; Lundstrom, I.; Andersson, L.I.; Mosbach, K. Some studies of molecularly imprinted polymer membranes in combination with field-effect devices. Sens. Actuators A 1993, 37–38, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprinting of theophylline in acrylonitrile–acrylic acid copolymer membrane. Chem. Lett. 1995, 10, 927–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew-Krotz, J.; Shea, K.J. Imprinted polymer membranes for the selective transport of targeted neutral molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8154–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M. Molecularly imprinted polymeric membranes. Bioseparation 2001, 10, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Fukaya, T.; Abe, M.; Fujii, N. Phase inversion molecular imprinting by using template copolymers for high substrate recognition. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2866–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, E.-B.G.; Gavrila, A.-M.F.; Iordache, T.-V.; Sarbu, A.; Iovu, H.; Sandu, T.; Brisset, H. Molecularly imprinted membranes obtained via wet phase inversion for ephedrine retention. UPB Sci. Bull. 2020, 82, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Brisbane, C.; McCluskey, A.; Bowyer, M.; Holdsworth, C.I. Molecularly imprinted films of acrylonitrile/methyl methacrylate/acrylic acid terpolymers: Influence of methyl methacrylate in the binding performance of l-ephedrine imprinted films. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 2872–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Murawaki, Y.; Reddy, P.S.; Abe, M.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprinting of caffeine and its recognition assay by quartz-crystal microbalance. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, X.; Peng, H.; Fu, L.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Simultaneous phase-inversion and imprinting based sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of bisphenol A. Talanta 2018, 176, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.-M.; Sârbu, A.; Iordache, T.-V.; Zaharia, A.; Radu, A.-L.; Apostol, S.; Iancu, S.; Duldner, M.; Lazau, C.; Hubca, G. TNT-molecularly imprinted membranes via phase inversion method. In Proceedings of the Greener and Safer Energetic and Ballistic Systems Conference, Bucharest, Romania, 10–23 May 2015; pp. 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, N.W.; Holmes, N.; Brisbane, C.; McGeachie, A.B.; Bowyer, M.C.; McCluskey, A.; Holdswortha, C.I. Effect of template on the formation of phase-inversed molecularly imprinted polymer thin films: An assessment. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3663–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Phase Inversion Technique-Based Polyamide Films and Their Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, M.; Marin, L.; Cozan, V.; Bruma, M. Aromatic polysulfones used in sensor applications. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2009, 22, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Barbani, N.; Rosellini, E.; Donati, M.; Costantino, P.; Cristallini, C.; Ciardelli, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers by phase inversion technique for the selective recognition of saccharides of biomedical interest in aqueous solutions. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udrea, I.; Sarbu, A.; Stefan, V.I.; Beda, M.; Nechifor, G.; Sarbu, L.; Radu, L.; Neata, M. Covalent immobilization of enzymes on molecularly imprinted polymers for biosensors. In Proceedings of the Conference CEEX, Brasov, Romania, 22–24 October 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Udrea, I.; Sarbu, A.; Radu, G.L.; Nechifor, G.; Bradu, C.; Nicoleta, M.; Beda, M.; Sarbu, L.; Diaconu, M. Molecularly imprinted membranes with covalently immobilized enzymes for biosensors. In Proceedings of the Conference CEEX, Brasov, Romania, 24–26 October 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, E.; Khajavian, M.; Sahebjamee, N.; Mahmoudi, M.; Drioli, E.; Matsuura, T. Advances in nanocomposite and nanostructured chitosan membrane adsorbents for environmental remediation: A review. Desalination 2022, 527, 115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, R.; Zheng, X.; Youn, H.; Chen, Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted CS membrane for recognizing naringin in aqueous media. Polym. Bull. 2011, 66, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, D.; Barbani, N.; Cristallini, C.; Giusti, P.; Ciardelli, G. Molecularly imprinted membranes for an improved recognition of biomolecules in aqueous medium. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.P.; Saad, B.; Nakajima, L.; Kobayashi, T. Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Membranes for the Determination of Citrinin in Rice. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, T.S.C.R.; Almeida, S.A.A.; Guerreiro, J.R.L.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M.; Sales, M.G.F. Trimethoprim-selective electrodes with molecularly imprinted polymers acting as ionophores and potentiometric transduction on graphite solid-contact. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamel, A.H.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Rebelo, T.S.C.R.; Sales, M.G.F. Molecularly-imprinted materials for potentiometric transduction: Application to the antibiotic enrofloxacin. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 2107–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurcevic, S.; Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Liao, C.-L.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T.; Lin, H.-Y. Polymers imprinted with three REG1B peptides for electrochemical determination of Regenerating Protein 1B, a urinary biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, N.A.; Zaliman, S.Q.; Leo, C.P.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S.; Poh, P.E. 3D imprinted superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/carbon black membrane for membrane distillation with electrochemical cleaning evaluation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, L.; Ding, Y.; Cusano, A.; Fan, J.A.; Hu, Q.; Wang, K.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. Waveguide-Based Fluorescent Immunosensor for the Simultaneous Detection of Carbofuran and 3-Hydroxy-Carbofuran. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, L.; Memon, A.G.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H. Waveguide-Based Fluorescent Immunosensor for the Simultaneous Detection of Carbofuran and 3-Hydroxy-Carbofuran. Biosensors 2020, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shan, D.; Zhou, X.; Shi, H.; Song, B.; Falke, F.; Leinse, A.; Heideman, R. TriPleX™ waveguide-based fluorescence biosensor for multichannel environmental contaminants detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Synthesis Method | Receptor | Support | Analyte | Characterization Method(s) | LOD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spincoating | MIP film MIP nanoparticles | Glass | Atrazine | RIfS 1 measurements. | >1.7 ppm | [40] |
| Precipitation polymerization/polymer casting | MIP layer | SERS substrate 2 | Enrofloxacin hydrochloride | Raman | 10−7 mol·L−1 | [41] |
| Casting | MIP membrane | Screen-printed gold electrode | Myoglobin | EIS 3 SWV 4 | 2.25 µg·mL−1 | [42] |
| Grafting polymerization synchronized with crosslinking/imprinting | MIP film | GCE 5 | Olaquindox | CV 6, DPV 7, EIS | 7.5 nmol L−1 | [43] |
| Covalent imprinting/drop casting | MIP film | Au-TFME 8 | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 | CV, SWV | 4.8 pg·mL−1 | [44] |
| Dropcasting | MIP membrane | QCM 9 crystal chip | Human serum albumin | Langmuir, Freundlich, Langmuir–Freundlich isotherm | 0.026 μg mL−1 | [45] |
| Synthesis Method | Receptor | Support | Analyte | Electrochemical Characterization Method(s) | LOD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV 1 | MIP film | Au electrode 2 | Acetaminophen | CV, EIS 3 and SWV 4 | 2.3 ×10−9 M | [72] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE 5 | Dimetridazole | DPV 6 | 10−10 M | [73] |
| Potentiostatic conditions | MIP film | Au electrode | Erythromycin | DPV | 1 × 10−10 M | [74] |
| CV | MIP film | Au electrode | Tetracycline | LSV 7 | 2.2 × 10−16 M | [75] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE | Sunset yellow | CV | 5 × 10−9 M | [76] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE | Tetra-bromo-bisphenol A | DPV | 2.7 × 10−10 M | [77] |
| CV | MIP film | Modified ITO 8 electrode | Resveratrol | CV and EIS | 7.1 × 10−12 M | [78] |
| CV | MIP film | Au electrode | Atrazine | CV and DPV | 1 × 10−9 M | [79] |
| CV | MIP film | Au electrode | Sodium lauryl sulfate | CV, DPV and EIS | 1.8 × 10−10 g/L | [80] |
| CV | MIP film | SPCE 9 | Diclofenac | DPV | 2 × 10−7 M | [81] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE | Epinephrine | CV and DPV | 7.6 × 10−8 M | [82] |
| CV | MIP film | Modified SPCE | Naloxone | DPV | 2 × 10−7 M | [83] |
| CV | MIP film | Modified SPCE | Naloxone | DPV | 1.6 × 10−7 M | [84] |
| CV | MIP film | Screen-printed gold electrode | Methylone | SWV | 1.1 × 10−6 M | [85] |
| CV | MIP film | Cr/Au film | Melamine | Resonance Wavelength Modulation | 5.1 × 10−12 M | [86] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE | Melamine | CV and SWV | 4.47 × 10−10 M | [87] |
| CV | MIP film | Modified GCE | Asulam | CV, DPV and EIS | 1.7 × 10−13 M | [88] |
| CV | MIP film | ITO electrode | Luteolin | DPV | 2.4 × 10−8 M | [89] |
| CV | MIP film | Modified electrode based on graphene and HAuCl4 | 4-nonylphenol | CV and DPV | 0.01 ng·mL−1 | [90] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE | Anthracene | SWV | 1.2 × 10−8 M | [91] |
| CV | MIP film | SPCE | Cocaine | SWV and EIS | 2.9 × 10−9 M | [92] |
| CV | MIP film | GCE | Entacapone | EIS and DPV | 5 × 10−8 M | [93] |
| Deposition Method | Receptor | Support | Analyte | Characterization Method(s) | LOD | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol–gel method | Spin coating | MIP film | Modified GCE 1 | Theophylline | CV 2 and DPASV 3 | 1.4 × 10−9 M | [146] |
| Immersion | MIP film | Modified Au 4 electrode | Melamine | CV and SWV 5 | 0.4 × 10−9 M | [147] | |
| Spin coating | MIP film | Au surface of SPR device | Amoxicillin | SPR 6 and CV | 7.3 × 10−11 M | [148] | |
| Spin coating | MIP film | Au modified glass substrate | Cis-jasmone | FT-IR 7, LSPR 8 | 3.5 ppm | [149] | |
| Spin coating | MIP film | SPR substrate | Trinitrotoluene | SPR | 0.26 ppb | [150] | |
| Immersion | MIP film | Modified GCE | Chlorogenic acid | DPV 9 | 3.2 × 10−8 M | [151] | |
| Dripping | MIP film | SPE 10 | Europium | CV, EIS 11, DPV | 1 × 10−7 M | [152] | |
| Dripping | MIP film | GCE | Aspartic acid | SWSV 12 | 1.77 × 10−6 M | [153] | |
| Coating | MIP film | MCNTs 13 | Aristolochic acid | Adsorption experiments | 0.034 µg/mg | [154] | |
| Immersion | MIP film | GCE | Trichlorfon | EIS and CV | 2.8 × 10−9 g/mL | [155] | |
| Hybrid sol–gel method | Electrochemical | MIP film | Au electrode | Clenbuterol | DPV | 3.1 × 10−8 M | [156] |
| Electrochemical | MIP film | GCE | Melamine | DPV | 6.8 × 10−8 M | [157] | |
| Electrochemical | MIP film | Modified ITO 14 electrode | Naloxone | CV and DPV | 2 × 10−8 M | [158] | |
| Electrochemical | MIP film | GCE | Mephedrone | SWV | 8 × 10−10 M | [159] | |
| Electrochemical | MIP film | Modified GCE | Diethylstilbestrol | DPV | 24.3 fg/mL | [160] | |
| Electrochemical | MIP film | Pencil graphite electrode | Ketamine | EIS and SWV | 7 × 10−10 M | [161] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavrilă, A.-M.; Stoica, E.-B.; Iordache, T.-V.; Sârbu, A. Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063080
Gavrilă A-M, Stoica E-B, Iordache T-V, Sârbu A. Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(6):3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063080
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavrilă, Ana-Mihaela, Elena-Bianca Stoica, Tanţa-Verona Iordache, and Andrei Sârbu. 2022. "Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications" Applied Sciences 12, no. 6: 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063080
APA StyleGavrilă, A.-M., Stoica, E.-B., Iordache, T.-V., & Sârbu, A. (2022). Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications. Applied Sciences, 12(6), 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063080









