Abstract
The advanced development of deep learning methods has recently made significant improvements in medical image segmentation. Encoder–decoder networks, such as U-Net, have addressed some of the challenges in medical image segmentation with an outstanding performance, which has promoted them to be the most dominating deep learning architecture in this domain. Despite their outstanding performance, we argue that they still lack some aspects. First, there is incompatibility in U-Net’s skip connection between the encoder and decoder features due to the semantic gap between low-processed encoder features and highly processed decoder features, which adversely affects the final prediction. Second, it lacks capturing multi-scale context information and ignores the contribution of all semantic information through the segmentation process. Therefore, we propose a model named MDA-Unet, a novel multi-scale deep learning segmentation model. MDA-Unet improves upon U-Net and enhances its performance in segmenting medical images with variability in the shape and size of the region of interest. The model is integrated with a multi-scale spatial attention module, where spatial attention maps are derived from a hybrid hierarchical dilated convolution module that captures multi-scale context information. To ease the training process and reduce the gradient vanishing problem, residual blocks are deployed instead of the basic U-net blocks. Through a channel attention mechanism, the high-level decoder features are used to guide the low-level encoder features to promote the selection of meaningful context information, thus ensuring effective fusion. We evaluated our model on 2 different datasets: a lung dataset of 2628 axial CT images and an echocardiographic dataset of 2000 images, each with its own challenges. Our model has achieved a significant gain in performance with a slight increase in the number of trainable parameters in comparison with the basic U-Net model, providing a dice score of 98.3% on the lung dataset and 96.7% on the echocardiographic dataset, where the basic U-Net has achieved 94.2% on the lung dataset and 93.9% on the echocardiographic dataset.
1. Introduction
Image segmentation is the process of clustering homogeneous pixels to highlight regions of interest. In the medical domain, it is one of the most critical and challenging tasks [1]. The segmentation of an object in medical images is essential for providing clinical measures, diagnosing various diseases, and following up with disease progression [2]. In clinical practice, manual segmentation is still applied to medical images. Clinicians are primarily interested in segmenting a region of interest by distinguishing some interesting areas in the image, such as lung regions, COVID-19 infection regions, left ventricle regions, etc. Using the segmented region, physicians can calculate some features that are needed for diagnosis [3]. However, manual segmentation tasks are very tedious, time-consuming, and prone to intra- and interobserver variability. Thus, an automated and accurate segmentation is mandatory for improving clinical workflow and supporting quick decision making for patient treatment.
However, providing an automated segmentation model is still challenging for the following reasons: (1) The limited amount of annotated medical datasets mislead the understanding of whether a model performs better or over-fits under the limited amount of dataset; (2) medical datasets require image processing tasks that require prior knowledge to help direct the learning-based model; (3) the challenging nature of medical images with fuzzy boundaries, motion artifacts, intensity dissimilarity, and variability in the shape and size of the region of interest; and (4) the model’s generalizability, where a trained model fails on a new dataset due to the different equipment used for the same medical modality and the various image-acquisition protocols. These challenges have made the automated segmentation problem remain an attractive area of research.
In this paper, in parallel to appreciating the capabilities of U-Net, we argue that its architecture may lack some criteria which limit its efficiency in segmenting challenging medical datasets across different modalities with variability in the shape and size of the region of interest. Consequently, based on recent advancements in deep computer vision, we propose a multi-scale dilated attention segmentation model named MDA-Unet. The model leverages its strength from U-Net architecture and various network modules, which consider network depth, multi-scale feature extraction, and distinguishable features through attention mechanisms. The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
- Based on potential scopes of improvement, we propose a multi-scale deep learning segmentation model with a slight increase in the number of trainable parameters in comparison with the basic U-Net model.
- We increase the network depth by utilizing residual blocks instead of the basic U-Net blocks, which deepens the network using identity shortcut connections. Those connections help propagate the low fine details, ease the training process, and reduce the gradient vanishing problem.
- We propose a multi-scale spatial attention module, which further enhances the capability of the spatial attention mechanism to emphasize multi-scale spatial features driven from feature maps captured using a hybrid hierarchical dilated convolution module, which additionally overcomes the gridding artifacts problem induced by increasing the receptive field using dilated convolution.
- Through a channel attention mechanism, we use the high-level decoder features to guide and enhance the low-level encoder features, thus improving the encoder–decoder concatenation process.
- We evaluate our model on two different public datasets with different modalities and show significant improvement over U-Net and its variants.
2. Related Work
Most of the improvements in biomedical image segmentation are based on the U-Net model; this is due to the efficiency and simplicity of its architecture. However, it still has some drawback that limits its capabilities. Recently, some extension networks have been proposed to enhance its performance on medical image. For example, Zhou et al. [4] proposed U-Net++, which has provided good results for segmenting polyps, liver, brain tumor, and cell nuclei from different modalities. The structure of U-Net++ is composed of encoder and decoder sub-networks connected through nested and dense skip connections to aggregate multi-scale features [5]. Despite its superior performance, the main drawback in U-Net++ is that it involves complex and heavy computations for a large number of intermediate convolution operations. Moreover, Humin et al. [6] introduced the U-Net3+ architecture, which is a full-scale connected U-Net with deep supervision making maximum use of the feature maps in full scales. The model was trained on liver CT images and surpassed state-of-the-art methods; however, this superior performance is accompanied by a large number of trainable parameters in comparison with the basic U-Net model.
In addition, Tarek et al. [7] have introduced R2U-Net, which improves upon U-Net by embedding recurrent residual convolution blocks to train the network deeper. However, their model holds a large number of parameters (almost double U-Net) and is liable to over-fit when trained on a small sample of medical images. Another variant of U-net was proposed by Changlu et al. [8], which integrates a convolutional DropBlocks to suppress less informative features and alleviate the over-fitting problem. Their model has outperformed the basic U-Net model (with and without dropout) on retinal vessel images. However, despite the simplicity of their model, it still lacks capturing multi-scale information. Finally, Amer et al. [9] proposed a left ventricle segmentation model based on U-Net, named ResDUnet. In their model, the feature map at each layer is simultaneously passed through residual blocks and dilated convolution; they aimed at enlarging the receptive field at each layer to capture global context information using a fixed sized dilation rate at each layer, which is still insufficient to extract multi-scale features from each layer.
Attention mechanisms have led to a new research direction for medical image segmentation. These mechanisms leverage global information to highlight informative features and suppress less informative ones. This is performed through aggregating spatial features to focus on ‘where’ exactly a region of interest is, using a spatial attention mechanism, or aggregating channel features which focus on ‘what’ are the meaningful features to represent. In both cases, they suppress unrelated features, increase the feature representation power, and boost the network performance [10].
Accordingly, several studies focused on developing attention mechanisms to further promote the feature’s representation power. Hu et al. [11] proposed a model based on a squeeze and excitation unit which investigates the interdependencies among various channels from a convolution output. This unit performs global average pooling to emphasize useful channels and suppress useless ones. Their model has outperformed other models in ILSVRC 2017 for image classification. In addition, Woo et al. [12] proposed an interesting attention mechanism, called convolution block attention module (CBAM), a self-attention mechanism that aggregates spatial and channel information for efficient feature refinement. Later on, they proposed a bottleneck attention module (BAM) [13], which proposed integrating dilated convolution into the spatial attention mechanism to facilitate constructing an effective spatial map. Moreover, other attention mechanisms were proposed in [14,15].
For medical image segmentation models based on attention mechanisms, Oktay et al. [16] proposed Attention U-Net for segmenting computed tomographic (CT) abdominal images. They proposed a spatial attention gate (AG) and integrated it into the U-Net skip connections. Their model was efficient in locating objects and has outperformed the basic U-Net model. However, it still lacks the consideration of high-level semantics since their attention mechanism focuses only on shallow encoder features. In addition, it disregards capturing multi-scale features, which are highly effective in segmenting medical objects with variability in size and shape.
Moreover, Changlu Guo et al. [17] has integrated a spatial attention mechanism in the U-Net bottleneck to extract informative features which improved the network performance in segmenting vessels from retinal fundus images. Looking from another perspective, Guofeng et al. [18] developed a channel-attention network based on U-Net to segment esophagus and esophageal cancer lesions from CT images. Their model provided promising results by filtering out less informative features and highlighting important ones. Most recently, although few studies [12,19,20,21] have proposed to utilize both attention aspects. However, according to the literature, the idea of developing a multi-scale feature attention module was never addressed. In addition, the fusion strategy and the location of both attention mechanisms is still uncertain.
Multiscale semantic information plays a crucial role in achieving a high performance for a segmentation network. Earlier methods usually use pooling operations or increase the kernel size to a provide larger receptive field of an output neuron. However, increasing the kernel size requires many computations and increases the model complexity [22]. In addition, increasing the number of pooling layers provide a reduced feature map size, which potentially leads to loss of useful spatial information and poses challenges to upsample the segmentation output back to its original resolution. On the other hand, if the segmentation results are achieved at the larger resolution from the earlier layers, we will not be able to make use of the higher-level semantics for better understanding [23].
Therefore, to capture multi-scale information, dilated convolution have been utilized in the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module developed in DeeplabV3 [24], which is inspired by spatial pyramid pooling (PSP) [25]. The ASPP module effectively increases the receptive field by using different dilation rates in parallel, which is beneficial in capturing objects and image contexts at multiple scales. However, for some applications, to achieve a large enough receptive field, the ASPP has to employ a very large dilation rate (i.e., d ≥ 25). This increased dilation rate causes discontinuity in computation because the neighboring units in the output are computed from separate units in the input, which causes inconsistency in small local details and less modeling power [26]. Moreover, the ASPP module brings high computation cost because it demands the input feature maps to have a large number of channels (i.e., 2048) [27]. Inspired from ASPP, DenseASPP [28] was proposed, which integrates wider contextual information with increasing the dilation rate layer by layer. However, in addition to holding much computation cost, a major drawback in this method is the inattentiveness to local fine details, since it models contextual information from high-level features only, without paying attention to recovering the semantic details of the input.
The above-mentioned methods show that U-Net is the most widely used model in medical image segmentation. They also highlight how attention mechanisms and multi-scale feature extraction methods efficiently boost the segmentation performance. Therefore, our model is based on the U-Net architecture integrated with a channel attention mechanism and a multi-scale spatial attention mechanism to learn multi-scale discriminative features, which enhances the network segmentation performance across medical images with different modalities and variability in the shape and size of the region of interest.
3. Proposed Model
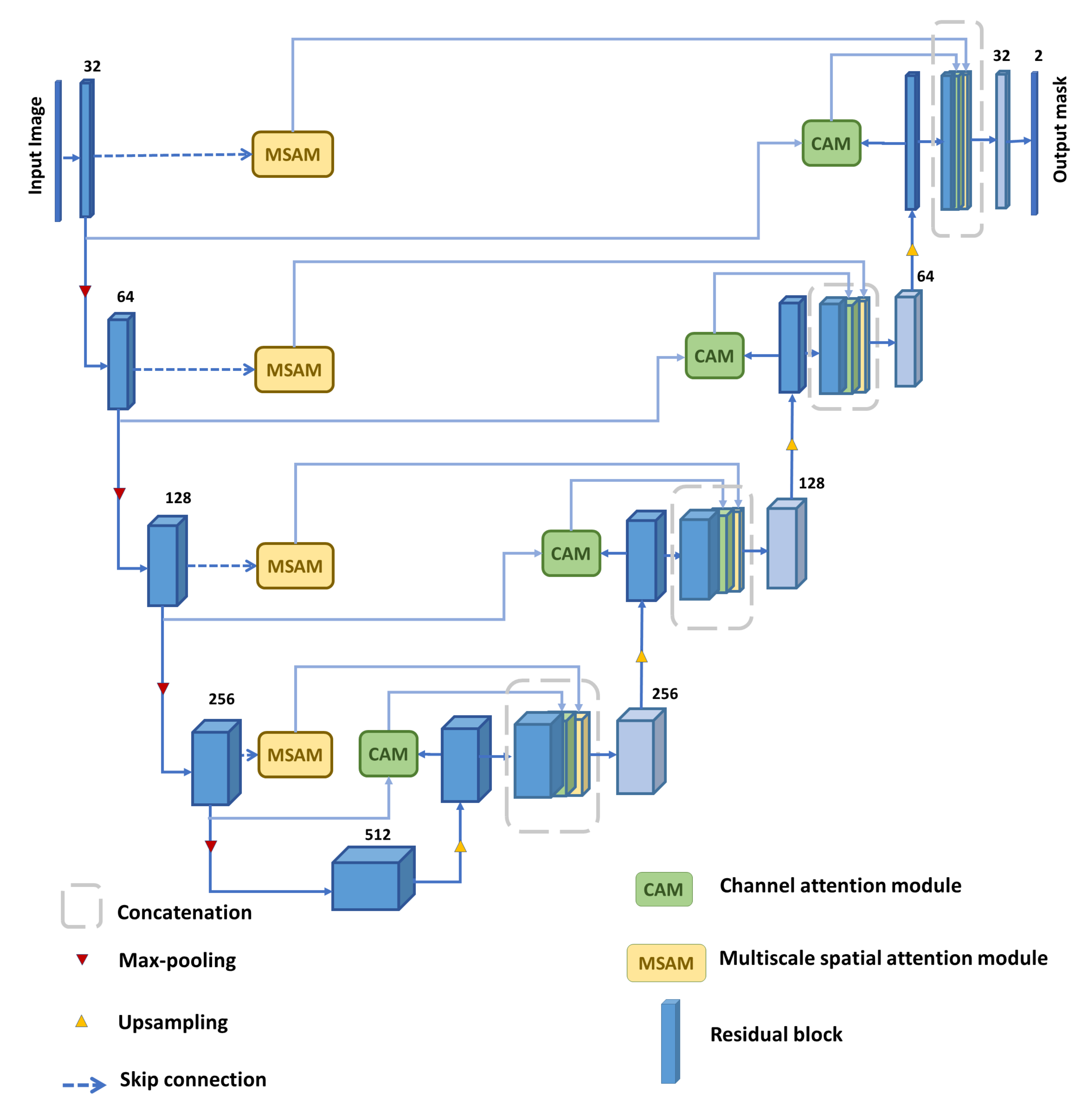
In this section, we describe the design and functionality of each module utilized in the proposed MDA-Unet model, depicted in Figure 1. Afterwards, a series of ablation experiments are demonstrated to examine different design choices and variations in the parameters in each integrated module.
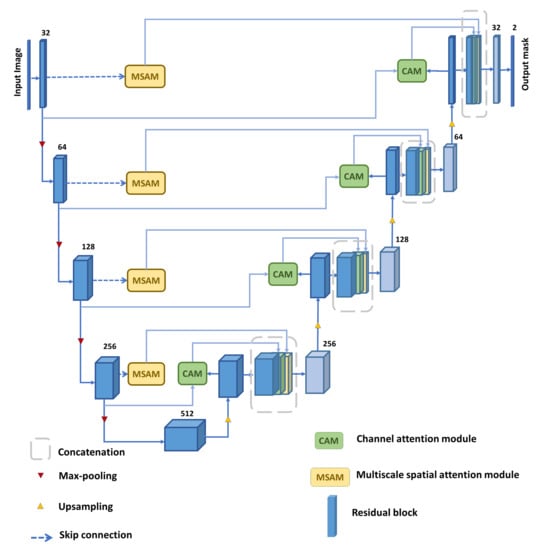
Figure 1.
Overview of our proposed Multi-scale dilated attention model (MDA-Unet).
3.1. Residual Block
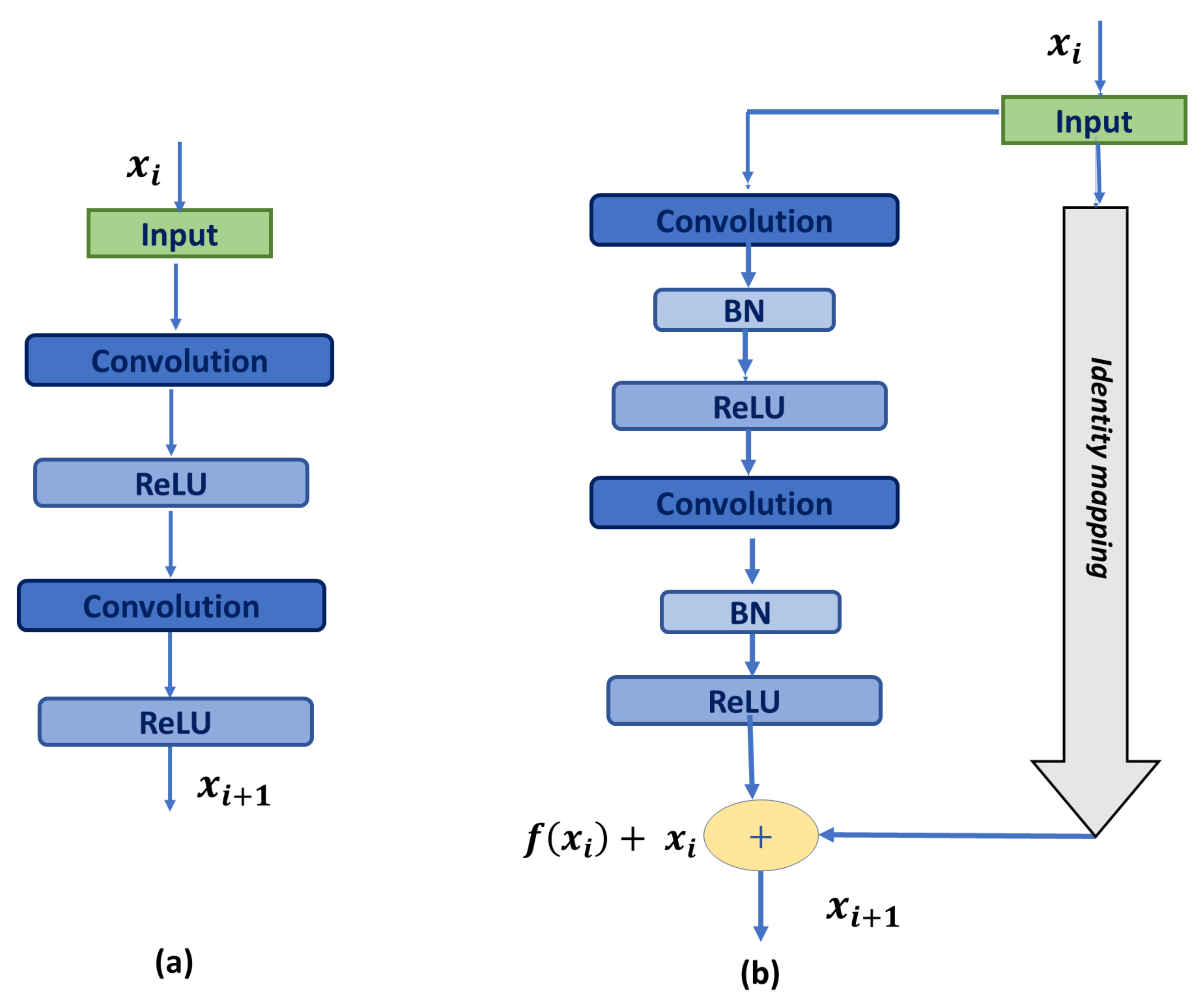
The current U-Net architecture has only a few layers. However, it can be substantially deeper to provide better performance [29]. Though adding more layers sometimes increases the network performance, it enlarges the number of parameters, leading to redundant computation and increasing the problem of gradient vanishing during training. Gradient vanishing is the decrease in the learning rate with forward propagation due to the presence of too many hidden layers, which degrades the network’s performance [30]. To mitigate this problem, Hu et al. [27] introduced residual blocks that share the same idea of concatenating the input (identity short-cut) and propagating the low fine details. This enhances the network performance without the need for going deeper or deploying a pre-trained network.
Thus, residual blocks are confirmed to provide deeper networks and reduce the gradient vanishing problem. Moreover, residual connections make the model learning easier as they learn a function with reference to the input feature map, instead of an referenced function [27]. Accordingly, we replace the basic U-Net blocks shown in Figure 2a with residual blocks proposed in [27], shown in Figure 2b, where each block is constituted of two 3 × 3 convolution layers, followed by batch normalization and a ReLU activation function. The input (identity-shortcut) is passed through 1 × 1 convolution, followed by batch normalization, and added with the output using element-wise summation.
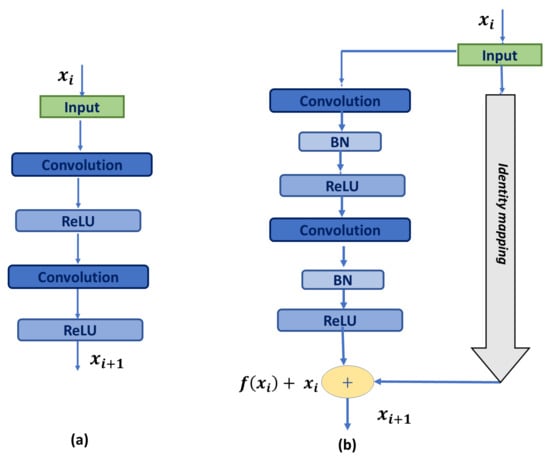
Figure 2.
Building blocks: (a) U-Net basic building block; (b) Residual block. ‘+’ represents element-wise addition.
Each residual unit is defined as [27]:
where and are the input and output of the i-th residual unit, respectively; is the residual function; is the activation function; and is an identity-mapping function. is the weight vector of the feature map at the i-th residual unit.
3.2. Multi-Scale Spatial Attention Module (MSAM)
Spatial attention modules hold a few additional parameters that focus on ‘where’ an informative part is. They are lightweight models which enhance important spatial features and suppress less important ones, thereby improving the network’s interpretability and reducing the computation complexity [12]. They produce refined features by inferring an attention map along the features’ spatial dimension and multiplying it with the input features.
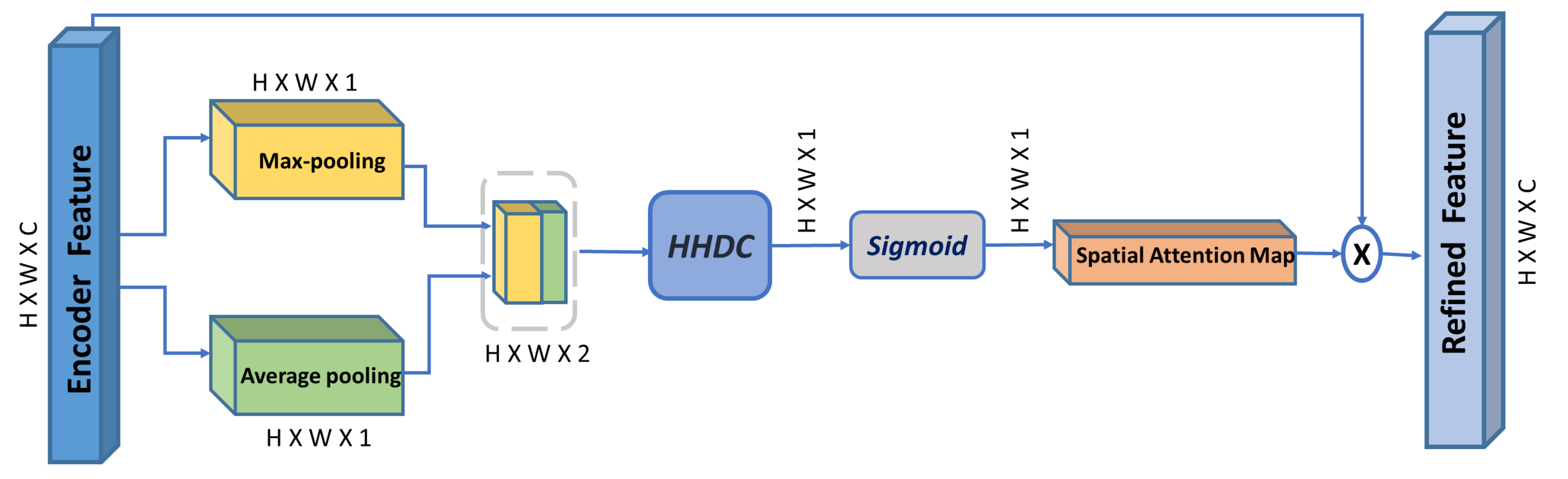
According to [13], using dilated convolution facilitates constructing a more effective spatial map and allows an exponential expansion of the receptive field, which enables the spatial attention module to seamlessly aggregate enriched contextual information. In this regard, we propose our multi-scale spatial attention module (MSAM), illustrated in Figure 3. It aggregates spatial features from different spatial locations derived by a hybrid hierarchical dilated convolution module (HHDC). This module further enhances the effectiveness of the spatial attention map in localizing objects at different scales (explained in details in Section 4).
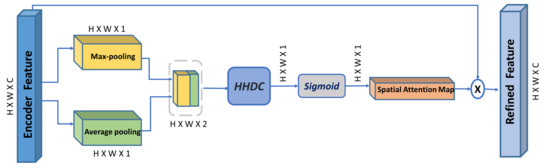
Figure 3.
Overview of our proposed Multi-scale spatial attention module (MSAM). HHDC is the proposed Hybrid Hierarchical Dilated Convolution module. ‘×’ is element-wise multiplication.
Given the encoder feature map as input, MSAM infers a 2D multi-scale spatial attention map , and the produced refined feature is:
To compute the multi-scale spatial attention map, average-pooling and max-pooling are simultaneously applied to the input encoder features along the channel axis to produce two different spatial context descriptors: and . Then, both feature descriptors are concatenated and passed to the HHDC module, followed by a sigmoid function to obtain the final multi-scale 2D spatial attention map. Afterward, the input encoder feature is then multiplied with the multi-scale 2D spatial attention map to obtain the final refined encoder feature. The spatial attention map is computed as follows:
where denotes the sigmoid function, and HHDC denotes the Hybrid hierarchical dilated convolution with multiple dilation rates (i.e., 1, 2, and 3).
The functionality of the average-pooling operation is to give feedback on all points from each feature map during the gradient backpropagation, while the max-pooling operation gives feedback only where the response is greatest in the feature map in the backpropagation process [31]; thus, both operations effectively highlight informative regions.
Previous attention modules, such as CBAM [12] and BAM [13], increase the receptive field by applying either a 7 × 7 convolution or 2 consecutive dilated convolution operations, respectively. We argue that using a large-sized kernel as in CBAM emphasizes the attention on large-scale features, discarding small ones. In addition, a gridding artifact problem may occur in BAM due to the consecutive use of two dilated convolutions with the same dilation rate. According to [32], using consecutive dilation rates with a common factor makes the convolution kernel too sparse to cover any local information, missing the details of very small objects in the image.
In contrast, we leverage multi-scale information by forwarding the concatenated features to the HHDC module, which encodes effective multi-scale spatial features to emphasize important spatial information from different receptive fields. It is worth mentioning that the MSAM is integrated along with the skip connection for the following two reasons: (1) Since the low-level encoder features mainly focus on extracting spatial details, providing rich detail information such as contour and edges, the MSAM would thus further contribute to highlighting key areas at multiple spatial locations and restrain irrelevant areas and (2) to alleviate the inherent semantic gap between encoder and decoder features because directly stacking those features together provides inconsistency in the model prediction. For instance, features learned at low-level layers with minimal processing (before max-pooling operation) are concatenated with features at high-level layers with much more processing (after the last deconvolution layer) [33]. Thus, the spatial attention module is integrated to add convolution operations that account for more processing, thereby decreasing the semantic gap for effectual fusion between features.
3.3. Hybrid Hierarchical Dilated Convolution Module (HHDC)
The encoder path progressively reduces the resolution of the input feature map, which misses the details of small objects that are even hard to recover with skip connections, reducing the prediction produced by each unit. Since contextual information is critical in disambiguating local cues [34], then the reduction in the receptive field is an undesirable price to pay for the segmentation of the objects. In addition, the segmentation task is challenging when the object is very small or when the background dominates the image and suppresses the object’s signal [35]. Therefore, dilated convolution is beneficial in enlarging the receptive field to compensate for the reduction in feature maps induced by the max-pooling operation applied along the encoder path of the U-Net.
Dilated convolution [36] is a special form of standard convolution in which the alignment of kernel weights is expanded by a dilation rate which broadens the field of view of the filters. Thereby, using the dilation rate, we can adjust the filter’s field of view to capture multi-scale context information. For example, in dilated convolution, the receptive field of a 3 × 3 dilated convolution with a dilation rate of 3 resembles the receptive field of a standard 5 × 5 convolution. So, dilated convolution increases the receptive field at no additional computation since only n × n pixels participate in the convolution operation.
Dilated convolution is applied over a two-dimensional feature map x, where for each location i on the output y and kernel size k, a filter w is applied as defined in [36]:
where the dilation rate d is equivalent to the stride with which the input signal is sampled. This process resembles convolving the input x with the up-sampled filters produced by inserting (d-1) zeroes between two consecutive filter values along each spatial dimension.
Despite the efficiency of dilated convolution in increasing the receptive field, the segmentation mask generated by simply one dilation rate throughout the whole model still does not cover all semantic strengths. In addition, progressively increasing the dilation rate fails to capture small local features [37] and introduces unwanted checkboard or gridding artifacts problems. This gridding artifact problem occurs when a feature map has higher-frequency content than the sampling rate of the dilated convolution. This problem results in the inconsistency of local information and hampers the performance of the model [35]. In this regard, Chen et al. [24] proposed parallelized dilated convolution module with different dilation rates, called the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP). They added it as a decoder module to effectively recover detailed object boundaries. However, the ASPP module learns many parameters and has high memory requirements.
In addition, Yu et al. [35] stacked different dilated convolutions to learn contextual representation from the larger receptive field and keep a high spatial resolution until the final segmentation layer. Their model has provided outstanding performance in comparison to other segmentation models. Still, it also has a high memory requirement since it avoids any feature downsampling all the way through the final output. A similar strategy was suggested in [32,38]. So, the past few models integrated dilated convolution either in a parallelized or a stacked way. However, Sachin et al. [39] introduced the efficient spatial pyramid module (ESP), where all of the dilated convolution branches are calculated in parallel, and the branch with the largest dilation rate determines the receptive field. Thus, all of the neurons in each branch share the same field of view, which is still insufficient for scale variation. However, they have concluded that the hierarchical addition of dilated convolutions overcomes the gridding artifacts problem.
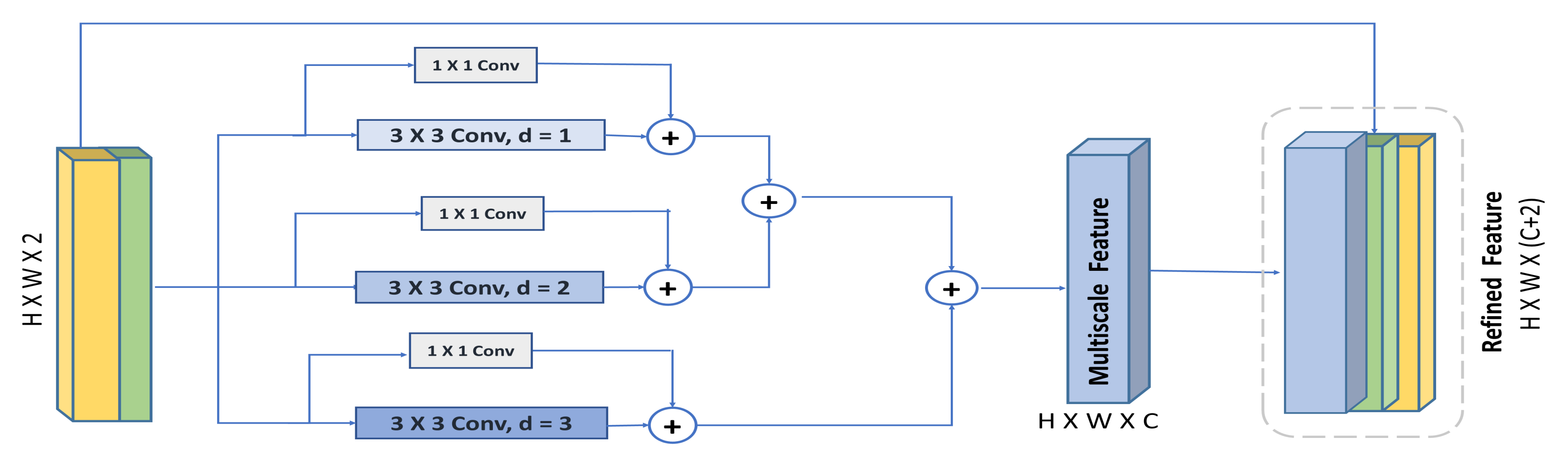
Therefore, inspired by concluded observations in [39], we propose the HHDC module, illustrated in Figure 4. The figure shows the concatenated feature descriptors (max-pooled feature descriptor and average-pooled feature descriptor) being decomposed into multiple residual dilated convolution with different dilation rates. To retain the hierarchical dependencies in multi-scale context well, the feature maps with high dilation rates are aggregated first, then those with a smaller dilation rate are aggregated next. Then, the output is concatenated with the input feature. The residual connections in each dilated convolution block is used to speed up the network convergence, facilitate training, and help the flow of low fine details, which might be scattered by increasing the dilation rate [27]. In addition, according to [39], the hierarchical addition of dilated convolution obtains larger receptive field and involves more pixels in the computation of the feature maps. Finally, the residual connections and small dilation rates are effective in capturing small regions of interest, while the large dilation rates with high-level context and wider visual cues are beneficial in recognizing large-scale objects. Thereby, the whole module is added to provide a multi-scale feature extraction to localize objects at various spatial locations.
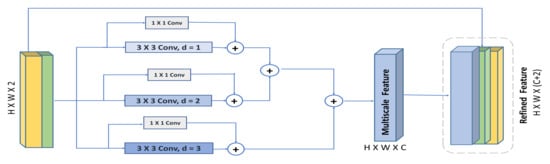
Figure 4.
Overview of our proposed Hybrid Hierarchical Dilated Convolution module (HHDC).
3.4. Channel Attention Module (CAM)
Channel attention modules hold a small number of additional parameters which learn ‘what’ is the meaningful representation of a given feature without additional supervision. They capture the explicit relationship between channels in the convolutional layers through a contextual gating mechanism, assigning a weight (i.e., channel attention) to each channel in the feature map [40].
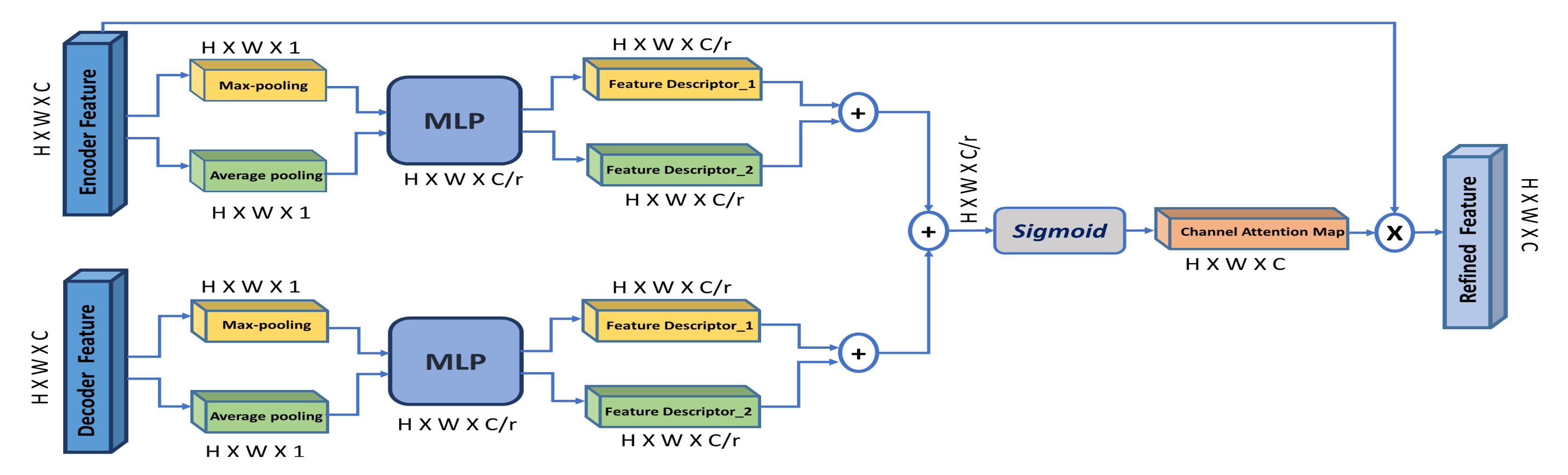
The channel attention module is inspired from [12], shown in Figure 5. However, different from [12], our channel-attention module is applied on both encoder and decoder features simultaneously. According to [15], low-level encoder features contain poor semantic information, while high-level decoder features contain rich semantic information. In addition, the decoder features can provide global context as guidance of low-level features to select meaningful context information, which promotes the model’s performance to detect small objects and focus on detailed information.
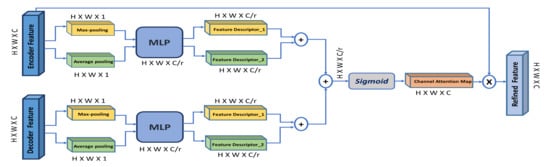
Figure 5.
Overview of the channel attention module (CAM). ‘MLP’ is a multi-layer perceptron and ‘r’ is the reduction ratio.
So, we aggregate information along the spatial dimension of the encoder and decoder features using max-pooling and average-pooling to generate two feature descriptors: () and (), which denote average-pooled features and max-pooled features, respectively. To capture the correlation across multiple channels, both features are forwarded to a shared multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to produce the channel attention map . This MLP here is two fully connected layers and one hidden layer. To reduce parameter overhead, the hidden activation layer is set to (), where r is the reduction ratio.
For both encoder and decoder features, the output of the MLP is combined using element-wise summation. Afterwards, the generated squeezed channel attention map for the encoder () and the decoder () are combined using element-wise summation, and then a sigmoid function is applied to produce the final channel attention map (). This map is multiplied with the input encoder feature to produce the refined encoder feature with enhanced contextual information, which is later concatenated with the corresponding decoder features along the skip connection. The final refined encoder feature is computed as:
The channel attention map is computed as follows:
Channel attention map is computed using using max-pooling and average-pooling, since together they both learn the extent of the target object and distinctive object features to infer fine channel-wise attention map [12].
4. Materials and Evaluation Metrics
In this section, we first provide a brief description of the dataset used to evaluate the performance of the proposed model. Then, we discuss the implementation details, followed by a description of the evaluation measures used in our study.
4.1. Dataset
To evaluate the effectiveness of our model, we used two publicly available datasets. The first dataset is for the segmentation of the left ventricle (LV) from echocardiographic images, introduced in [41]. It contains 2D echocardiographic images for 500 patients. For each patient, 2D apical four-chamber and two-chamber view sequences are captured and annotated by qualified clinicians. Those two frames are typically used by clinicians to assess the cardiac functionality of the heart. The total number of images is 2000, each with an average resolution of 500 × 600. The second dataset is for the segmentation of lung regions from 2628 axial CT images introduced in [42], with a resolution of 512 × 512. Left and right lung regions are annotated by qualified clinicians. Both datasets were intensity normalized between 0 and 1 and resized to 256 × 256 for computation limitation.
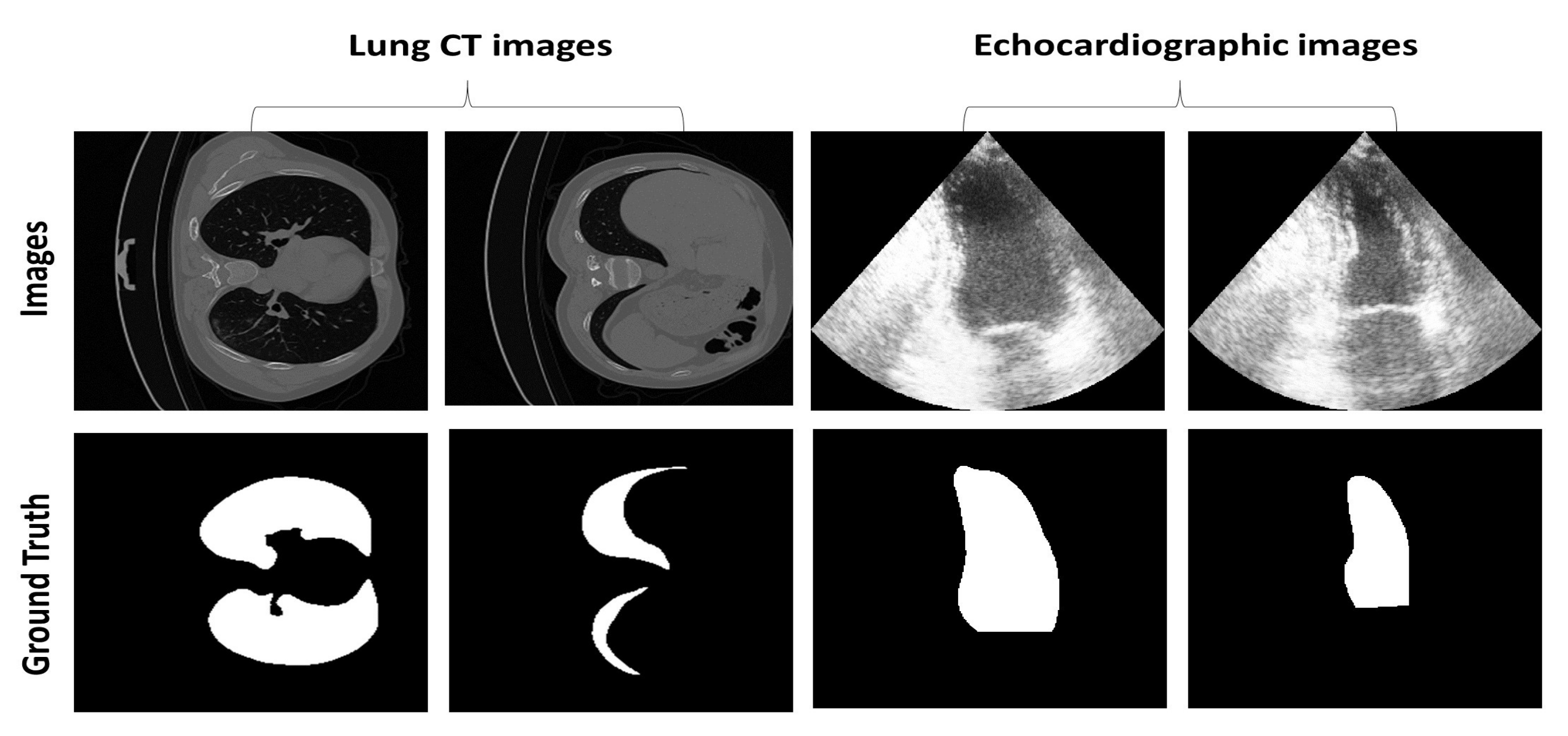
Figure 6 shows an example of the two different frames from echocardiographic images annotated by the clinician at the end-diastolic phase (relaxation state) and end-systolic phase (contraction state). It also shows two lung regions segmented by the clinician at different respiration stages during examination. The figure illustrates the variability in the size and shape of the region of interest for both datasets and the challenging nature of echocardiographic images with blurred boundaries and poorly visible LV regions.
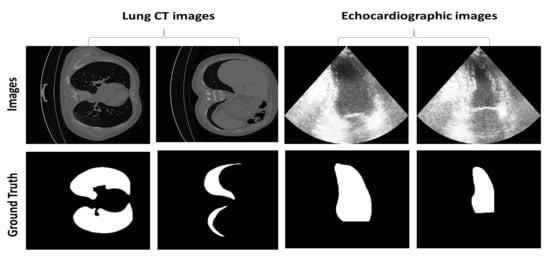
Figure 6.
Example of images and their ground truth image containing the segmentation mask from the two datasets.
4.2. Implementation Details
We implemented our model in Python environment with keras 2.3.1 and Tensorflow 2.0. The model is trained with Adam optimizer at a learning rate of 0.0001 and early stopped if the validation loss does not decrease for 5 consecutive epochs. Dice loss is used as the network’s objective function. Both datasets were split into 70% for training, 20% for validation, and 10% for testing, where each set holds different patients. At the end of the training procedure, we used the network weights of the epoch with the lowest validation loss to evaluate images in the test set. The model is trained from scratch without any transfer learning or the use of data augmentation for fair evaluation. However, to avoid over-fitting, the dropout technique [43] is applied with ratio of 50%, which reduces computation yet provides regularization to the network.
Our model is built upon the standard U-Net architecture, with four blocks in the encoder and decoder path and a bottleneck layer that holds the compressed spatial information. The number of filters in both paths is 32, 64, and 128, and that for the bottleneck is 512. At the end of the network, a 1 × 1 convolution is applied, followed by a sigmoid function to generate the final segmentation mask. The dilation rates for the HHDC module are set to 1, 2, and 3 at the upper 2 layers (with a large feature map and a large semantic gap between encoder–decoder features). In comparison, the dilation rate at the last 2 layers is set to 1 and 2 (for the small feature maps and the reduced semantic gap between encoder–decoder features). Finally, to minimize parameter overhead, the reduction ratio in the channel attention module is set to 8.
4.3. Evaluation Measures
For evaluating our model, we used three statistical evaluation measures: Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) [44], Jaccard index (JI) [45], and F-score (F) [46]. DSC is the spatial overlap index and reproducibility validation index, defined as:
F-score is the test’s accuracy, calculated from the precision and recall, defined as:
JI is the intersection over union and is defined as:
where TP, TN, FP, and FN are the true positive, true negative, the false positive, and the false negative values (i.e., the positive regions which were not detected by the model), respectively. The higher the value of the above indices, the better the performance.
5. Evaluation Results and Discussion
In this section, we first compared the performance of our model with three relevant segmentation models. Then, we conducted several experiments to investigate the effectiveness of each utilized module and study the impact of different parameter tunings.
5.1. Comparison with Other Segmentation Models
We evaluated the performance of the proposed model against three segmentation models, such as U-Net [47], ResDUnet [9], Attention U-Net [14], and U-Net3+ [6]. The ResDUnet model proposed by Amer et al. [9] was trained on the same dataset used here (LV dataset). To keep the number of parameters compared to our model, we implemented all models with a five blocks along the encoder and decoder. Experimental results were performed using two different classes of medical images, echocardiographic images for the left ventricle segmentation and CT images for lung segmentation.
Table 1 shows the number of trainable parameters, the training time, and the segmentation performance of our proposed model (on the test set) in comparison with U-Net, ResDUnet, Attention U-Net, and U-Net3+. The results were demonstrated in percentage ratio for better readability. If we look at the DSC measure for the lung CT images, it can be observed that our model outperformed the basic U-Net, ResDUnet, Attention U-Net, and U-Net3+ model by 4.1%, 2.5%, 1.8%, and 0.4%, respectively. For the LV images, our model has outperformed the basic U-Net model, ResDUnet, Attention U-Net, and U-Net3++ model by 2.8%, 1.6%, 1.1%, and 0.6%, respectively. In comparison with Attention U-Net and U-Net3+, our model has slightly increased the performance but significantly reduced the number of trainable parameters and training time.

Table 1.
Statistical evaluation and trainable parameters for our model in comparison with other segmentation models. Training time is demonstrated in hours.
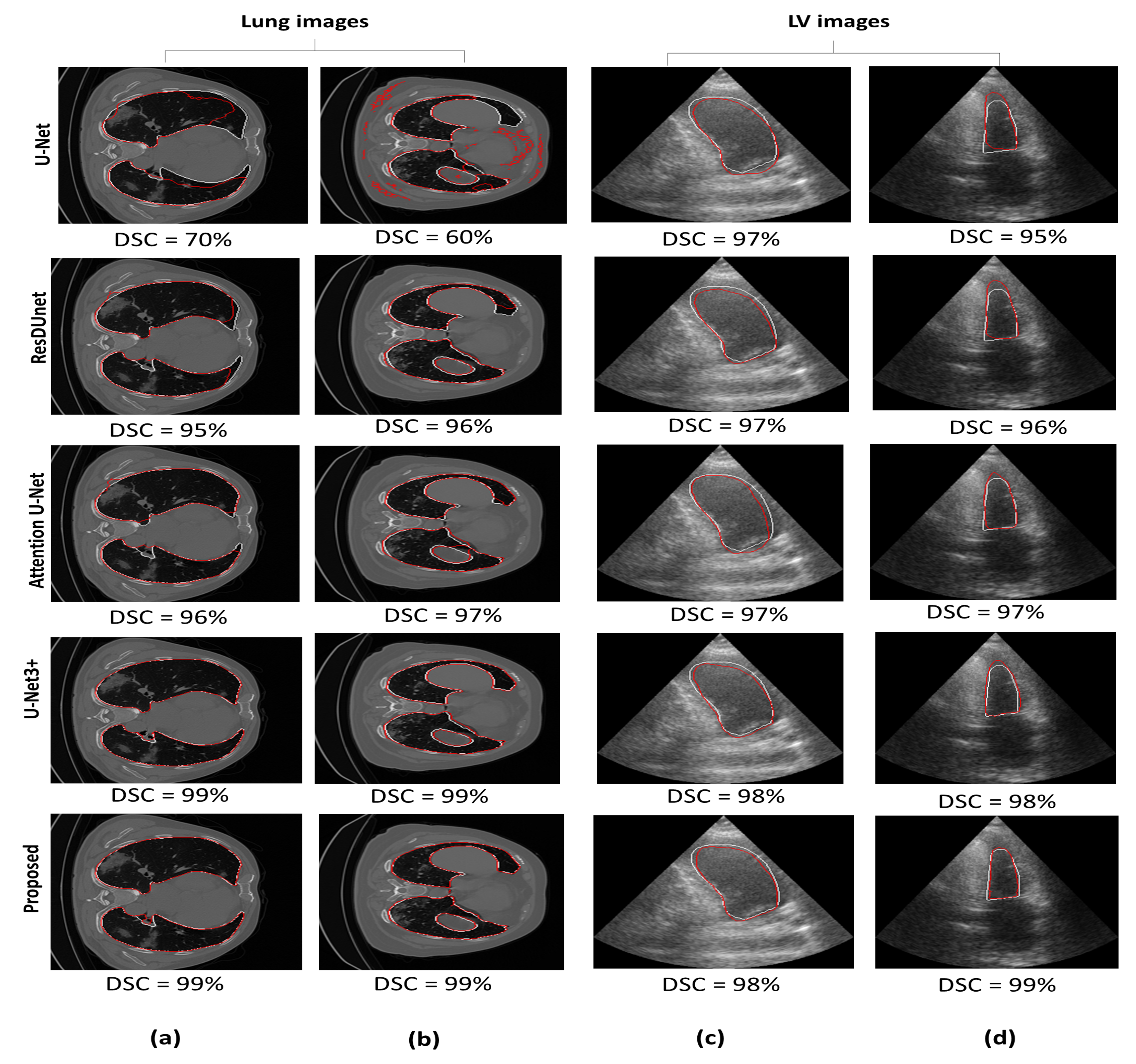
Figure 7 illustrates a qualitative comparison between the proposed model and the other segmentation models. For the lung CT images, the U-Net model tends to under-segment the lung region (Figure 7a) or provide too many false positives (Figure 7b). For the same two images, Attention U-Net is observed to slightly outperform ResDUnet (Figure 7a); however, it partitioned the connected lung region into two parts (Figure 7b). In comparison with U-Net3+, our model has provided comparable performance. For both lung images, the proposed model shows the best performance with no false positives and accurate delineation, especially at the difficult deformed parts of the lung region (i.e., near the Trachea).
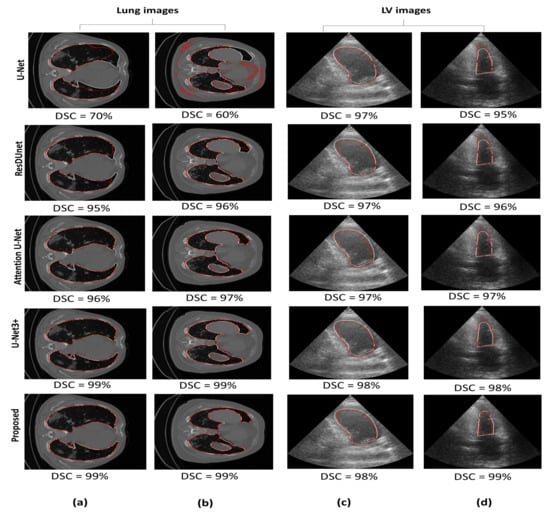
Figure 7.
Segmentation performance for U-Net, ResDUnet, Attention U-Net, U-Net3+, and our proposed MDA-Unet model. White contour represents the ground truth delineation. Red contours represent the predicted delineation. (a,b) are the lung CT images. (c,d) are the left ventricle images.
For LV images, seen in Figure 7c,d, the three models, U-Net, ResDUnet, and attention U-Net show comparable delineation. However, for both frames, it can be observed that our model has significantly outperformed the basic U-Net model, providing a more uniform and accurate delineation, and has also improved the delineation in comparison with Attention U-Net and ResDUnet, especially seen in the more challenging frame: the end-systolic frame (Figure 7d). U-Net3+ and our model have provided comparable delineation; however, our model has also outperformed in the delineation of the end-systolic frame: the upper boundary of the left ventricle (i.e., near the apex).
Generally, the outperformance of our model in comparison with ResDUnet could be explained by the multi-scale context aggregation induced by utilizing different dilation rates in the HHDC at each layer. In contrast, ResDUnet focused on enlarging the receptive field using a fixed dilation rate at each layer. Using one single-scale context may not represent the hierarchical dependencies between an object and its surrounding and might be insufficient in contributing all semantic information. In addition, the improvement over Attention U-Net could be explained by integrating the multi-scale spatial attention module, which enhanced representing the features at different locations. Moreover, Attention U-Net emphasizes spatial information from shallow encoder features. In contrast, our model incorporates the channel attention module with both encoder and decoder features to increase the contextual information of the low-level encoder features. In addition, despite the comparable performance with U-Net3+, still the credit goes to the proposed model in reducing the model complexity. Finally, it is worth mentioning that our proposed model has increased the number of trainable parameters by 0.9% in comparison with the basic U-Net model, which could be negligible when compared to performance gain.
5.2. Ablation Experiments
In this subsection, we evaluate the design choices of the integrated modules and their influence on the overall performance. First, we show the effectiveness of adding the MSAM and CAM module. Second, we illustrate the significance of the proposed HHDC module integrated into the spatial attention mechanism, as a comparison with the spatial attention module proposed in CBAM [12] and BAM [13]. Third, we study the model performance for different reduction ratios used in the channel attention module. Finally, we compare the performance of different dilation rates used in the HHDC module. For all experiments, we used the lung dataset for training and testing and the DSC measure for assessing the performance.
5.2.1. Adding Attention Modules
We examined the segmentation performance by adding the MSAM and the CAM modules to the basic U-Net model. From the segmentation results shown in Table 2, it is observed that adding the CAM module has increased the model performance by 1.4%. This increase in performance is due to two reasons: (1) highlighting meaningful features in the image by capturing explicit relationships between channels and (2) seizing useful contextual information from the high-level decoder to enhance the low-level encoder features. Thus, ensuring an effectual fusion between both features. On the other hand, the model performance got boosted by 2.9% when the MSAM is added. This boost in performance is due to aggregating spatial features from different spatial locations derived by the HHDC module, which is integrated into each MSAM module. In addition, both attention modules helped in reducing the semantic gap between encoder and decoder features, thus reducing the inconsistency between the concatenated features. Finally, it is observed that adding both attention modules has increased the model performance with a slight increase in the trainable parameters.

Table 2.
Segmentation results after adding each attention module separately and then combining them.
5.2.2. Adding Hierarchical Hybrid Dilated Convolution Module
We evaluated the effectiveness of adding the HHDC module into the spatial attention mechanism as a comparison with the spatial attention modules used in CBAM [12] and BAM [13]. To recall, the spatial attention module in CBAM increased the contextual information using convolution with a kernel size of 7 × 7. In contrast, the spatial attention module in BAM used two consecutive dilated convolutions with a fixed dilation rate (d = 4) and a kernel size of 3 × 3.
Table 3 shows an increase in performance by 0.9% and 2.1% when using CBAM’s and BAM’s spatial attention modules, respectively. However, integrating the HHDC module has boosted the performance by 3%. Compared with CBAM, the superior performance is explained by considering various semantic information produced by the different receptive fields, while the superior performance in comparison with BAM is due to the hierarchical addition of the multiple receptive fields, which covers multi-scale features and overcomes the gridding problem. BAM enlarges the receptive field using two consecutive dilated convolutions with a fixed dilation rate, which increases the possibility of the gridding artifacts problem [32].

Table 3.
Comparing segmentation performance and trainable parameters using different spatial attention modules.
5.2.3. Changing the Reduction Ratio
We studied the model performance for different values of the reduction ratio used in CAM module. As discussed in Section 3.4, this reduction ratio is used to reduce the network parameters. In Table 4, we notice that the model performance is somehow robust for the reduction ratios of 4, 8, and 16. However, a significant drop is seen when using a reduction ratio of 32. This drop is due to the increased reduction in the number of channels, which might have suppressed useful image features. So, based on the results illustrated, we chose a reduction ratio of 8, since it achieved a fair balance between the segmentation accuracy and the model capacity.

Table 4.
Segmentation results and trainable parameters for different values of the reduction ratio.
5.2.4. Changing the Dilation Rate
We investigated the model performance by changing the dilation rate in the HHDC module. As mentioned in Section 4, this dilation rate is responsible for enlarging the receptive field to integrate more global context information.
From Table 5, we observe a performance drop when using a dilation rate of (1,2), which means that both dilation rates are insufficient in covering all semantic content in the image. This observation goes with the understanding in [13] which states that increasing the receptive field enables the spatial attention module to aggregate more contextual information. A drop in performance is seen when using a dilation rate of (1,2,5). This could be explained by the gridding artifact problem that might have occurred when we increased the receptive field in comparison with the size of the feature map. Therefore, we chose a dilation rate of (1,2,3), as this combination seems to cover most of the semantic information in the image. It is also worth noting that the number of trainable parameters is the same for dilation rates of (1,2,3) and (1,2,5) because increasing the receptive field does not include any increase in trainable parameters. However, fewer parameters were seen when using dilation rates of (1,2) since it involves less number of convolution operations.

Table 5.
Segmentation results and trainable parameters for different values of the dilation rate.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a novel deep learning model (MDA-Unet). The model leverages various computer vision modules to enhance the capability of U-Net model in capturing multi-scale information. In principle, we replaced the basic U-Net blocks with alternative residual blocks to provide a deeper model, ease the training process, and reduce the gradient vanishing problem.
We integrated the spatial mechanism with a hybrid hierarchical dilated module, which has the following advantages: (1) It is constituted of different dilation rates to provide different receptive fields which captures multi-scale context information, where the small receptive field is needed to capture small objects and the large receptive field is beneficial for capturing large scale objects, and (2) it provides a dense region of interest prediction, compensating for the loss of semantic information induced by max-pooling operation. Furthermore, we precisely integrated the multi-scale spatial attention module into the skip connections to alleviate the disparity between encoder–decoder features and further highlight key areas at multiple scales and restrain irrelevant areas. Moreover, to enhance the encoder–decoder feature concatenation, we used the decoder features to guide the selection of low-level features. This is achieved by passing both encoder and decoder features to a channel attention mechanism and adding their channel attention map, which is multiplied by encoder features (coming from skip connection) to produce refined encoder features before concatenating with the corresponding decoder features.
Incorporating these modifications, our module has overshadowed U-Net and its variants, ResDUnet, Attention U-Net, and U-Net3+ on two different medical datasets, lung CT and echocardiographic dataset. Both datasets have variability in the shape and size of the region of interest, where echocardiographic images were more challenging with a fuzzy boundary of the region of interest. However, our model has significantly improved manual segmentation with a minimal increase in trainable parameters on both datasets. Therefore, we believe that MDA-Unet has a great potential in helping physicians during their examination and improving the clinical workflow.
In the future, it might be helpful to provide a more sparse and denser receptive field in HHDC. This can be achieved by incorporating a large convolution kernel in parallel with dilated convolution. In addition, we wish to address the model performance for multiple trainings to analyze the interobserver variability. Furthermore, coupling the model with post-processing techniques, such as CRF as RNN, might help capture edge details accurately. Moreover, we further wish to define an appropriate search space to indicate which hyperparameters need to be optimized for effective performance on other medical images, such as MRI and mammogram images. Finally, we are interested in assessing the performance of the proposed modules across other state-of-the-art segmentation models, such as TransUnet, since the proposed modules can be used as plug-and-play modules for any CNN-based model.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and X.Y.; methodology, A.A. and X.Y.; software, A.A.; validation, A.A., X.Y. and T.L.; formal analysis, A.A.; investigation, A.A.; resources, A.A. and X.Y.; data curation, A.A., X.Y. and T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, X.Y. and T.L.; visualization, A.A.; supervision, X.Y. and T.L.; project administration, X.Y. and T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These can be found at (http://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/, accessed on 26 October 2021) and (http://camus.creatis.insa-lyon.fr/challenge/#, accessed on 15 October 2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McGuinness, K.; O’connor, N.E. A comparative evaluation of interactive segmentation algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, S.; Doyle, S.; Agner, S.; Madabhushi, A.; Feldman, M.; Tomaszewski, J. Automated gland and nuclei segmentation for grading of prostate and breast cancer histopathology. In Proceedings of the 2008 5th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Paris, France, 14–17 May 2008; pp. 284–287. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhi, R.; Jafari, M.; Kasaei, S.; Keshavarzian, P. Benign and malignant breast tumors classification based on region growing and CNN segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.W.; Wu, J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Pei, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W. SD-UNet: A structured dropout U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Athens, Greece, 28–30 October 2019; pp. 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, A.; Ye, X.; Janan, F. ResDUnet: A Deep Learning based Left Ventricle Segmentation Method for Echocardiography. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 159755–159763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Ye, N. Learning cascade attention for fine-grained image classification. Neural Netw. 2020, 122, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Yi, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Fan, C. Sa-unet: Spatial attention u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 1236–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, J. Channel-attention U-Net: Channel attention mechanism for semantic segmentation of esophagus and esophageal cancer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122798–122810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, J.; Fang, W.; Deng, S. SCAU-Net: Spatial-Channel Attention U-Net for Gland Segmentation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariyani, Y.S.; Eom, H.; Park, C. DA-Capnet: Dual Attention Deep Learning Based on U-Net for Nailfold Capillary Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 10543–10553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Dense dilated network with probability regularized walk for vessel detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ran, S.; Ding, J.; Liu, B.; Ge, X.; Ma, G. Multi-U-Net: Residual Module under Multisensory Field and Attention Mechanism Based Optimized U-Net for VHR Image Semantic Segmentation. Sensors 2021, 21, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. Denseaspp for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3684–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y. Deep residual learning for image steganalysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10437–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Kim, J.; Kumar, A.; Fulham, M.; Feng, D. Stacked fully convolutional networks with multi-channel learning: Application to medical image segmentation. Vis. Comput. 2017, 33, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Du, A.; Orgun, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z. Tumor attention networks: Better feature selection, better tumor segmentation. Neural Netw. 2021, 140, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Cottrell, G. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, A.; Ye, X.; Janan, F. Residual Dilated U-Net for the Segmentation of COVID-19 Infection From CT Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 462–470. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, A.; Ye, X.; Zolgharni, M.; Janan, F. ResDUnet: Residual dilated UNet for left ventricle segmentation from echocardiographic images. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 2019–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V.; Funkhouser, T. Dilated residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Mercan, E.; Bartlett, J.; Weaver, D.; Elmore, J.; Shapiro, L. Learning to segment breast biopsy whole slide images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 663–672. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnet: Efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 552–568. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; Wei, J.; Sun, B.; Su, S.; Zuo, Z.; Wu, P. ASCU-Net: Attention Gate, Spatial and Channel Attention U-Net for Skin Lesion Segmentation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, S.; Smistad, E.; Pedrosa, J.; Østvik, A.; Cervenansky, F.; Espinosa, F.; Espeland, T.; Berg, E.A.R.; Jodoin, P.M.; Grenier, T.; et al. Deep learning for segmentation using an open large-scale dataset in 2D echocardiography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- COVID-19—Medical Segmentation. Available online: http://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/ (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Pellicer, J.; Zamora-Martínez, F.; España-Boquera, S.; Castro-Bleda, M.J. F-measure as the error function to train neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Tenerife, Spain, 12–14 June 2013; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).