A Numerical Aerodynamic Analysis on the Effect of Rear Underbody Diffusers on Road Cars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
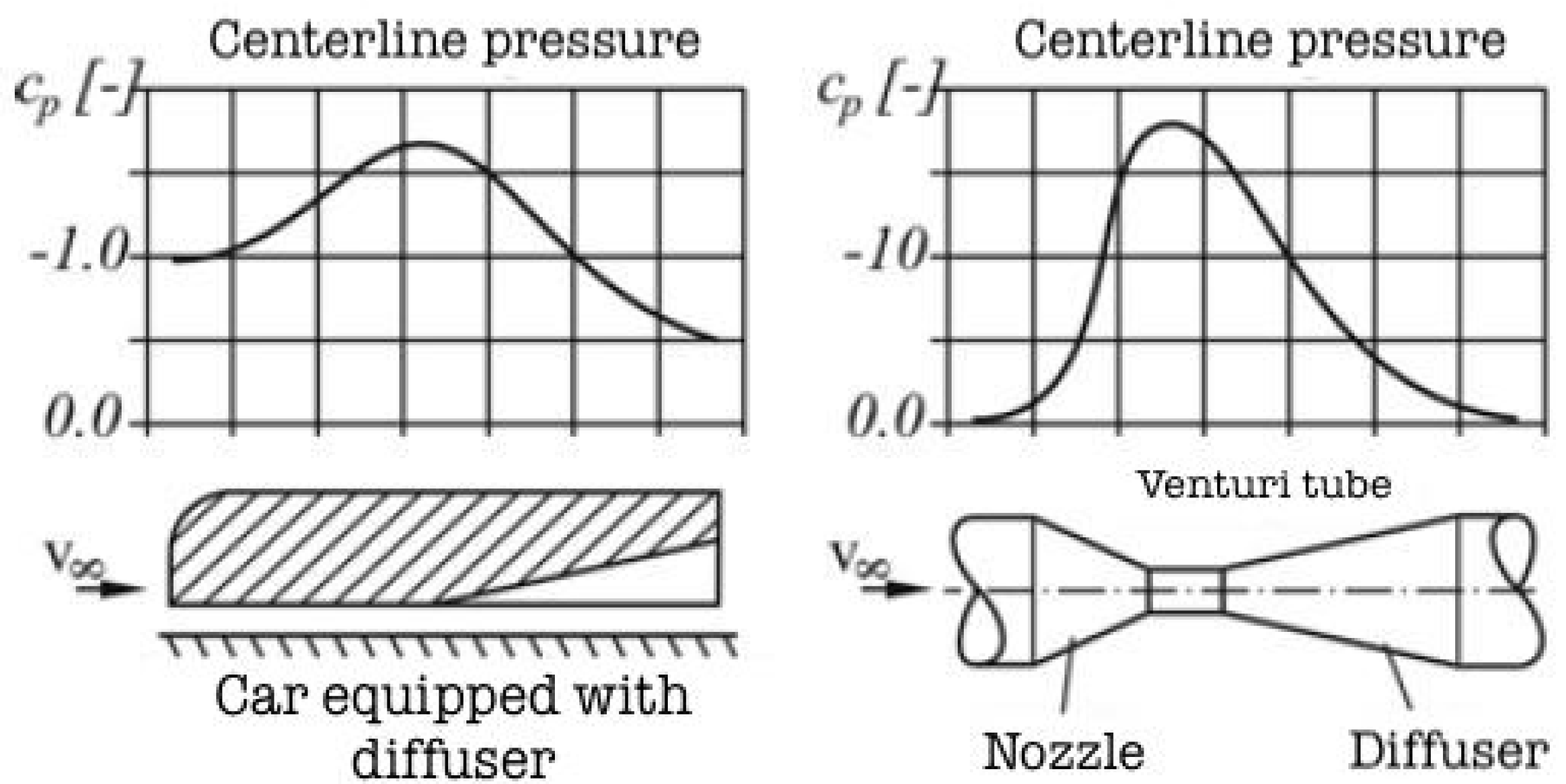
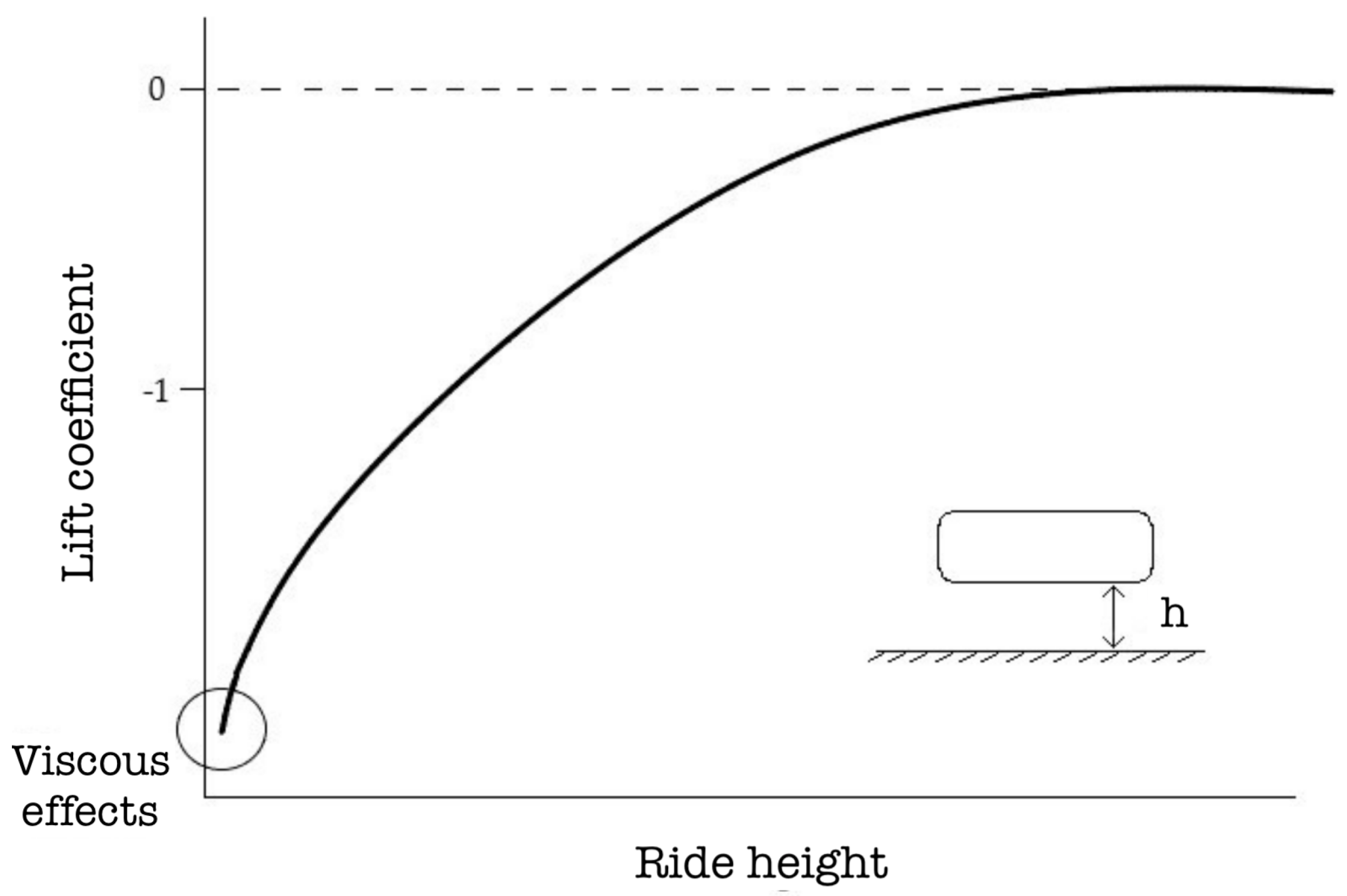
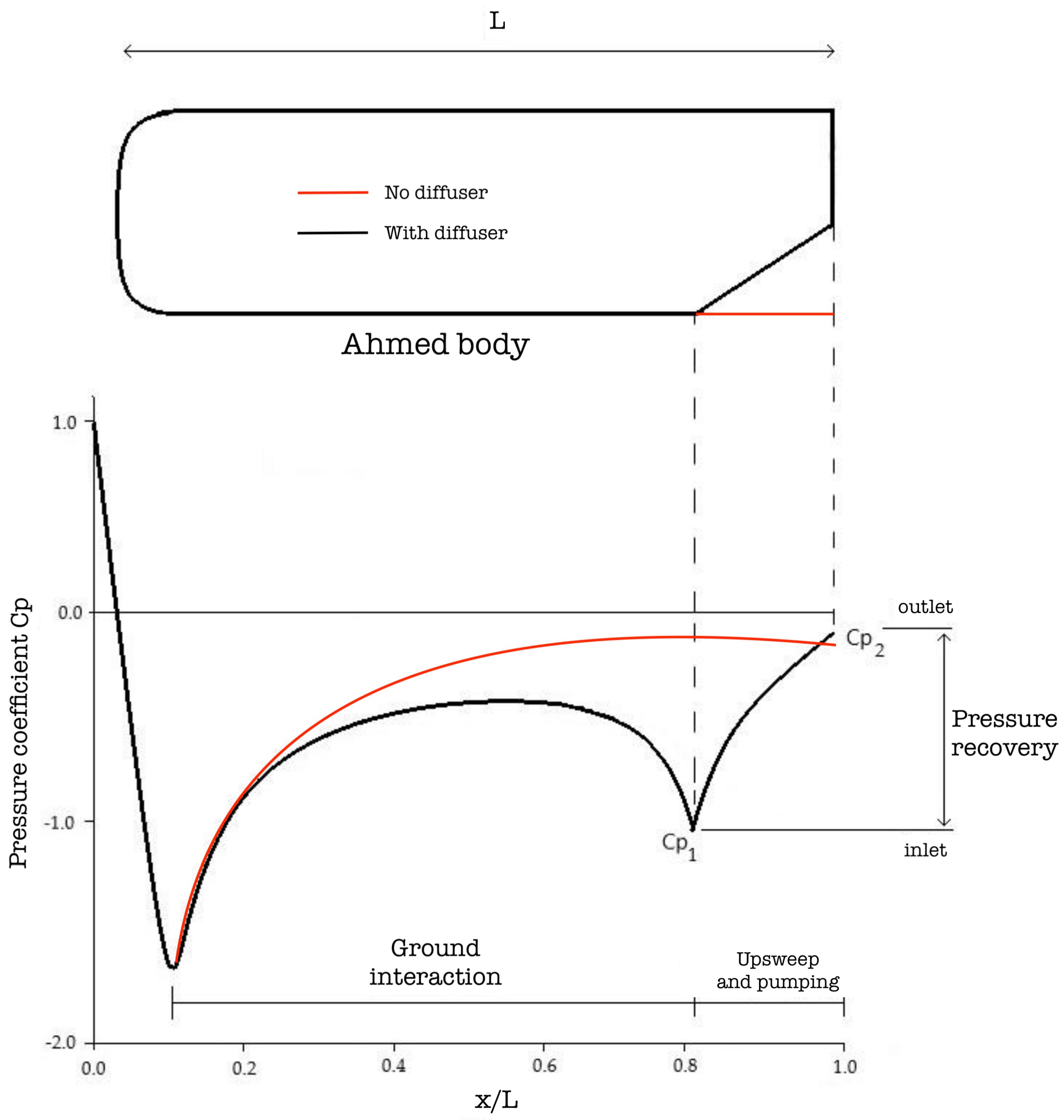
1.1. Literature Review and Diffusers’ Fundamental Theory
1.2. Aim of the Work and Justification
2. Materials and Methods
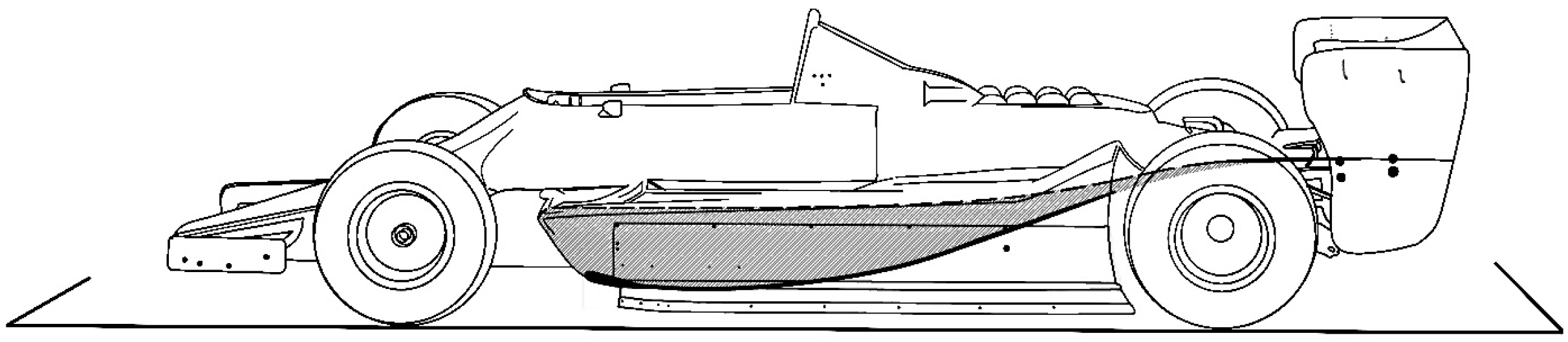
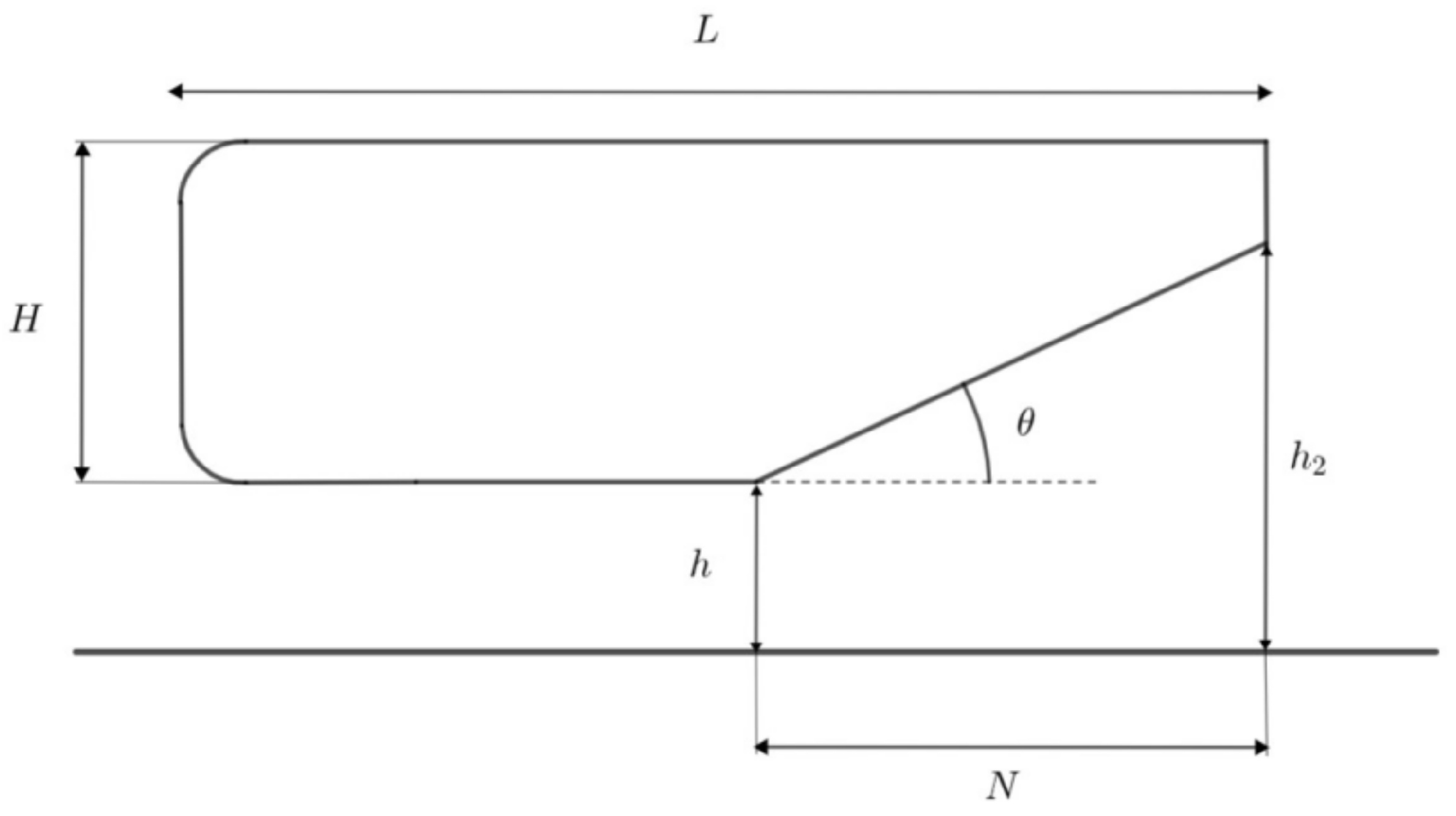
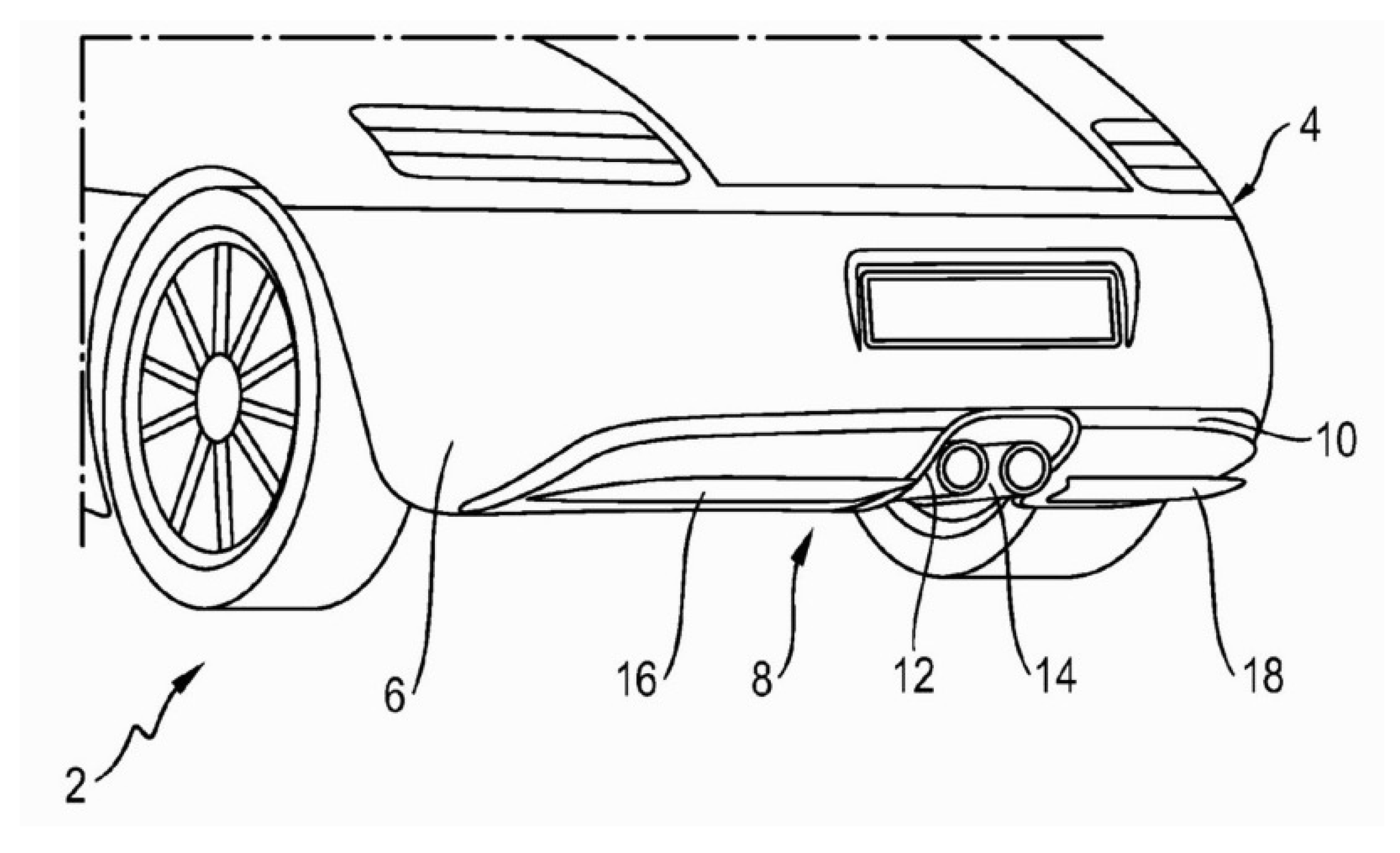
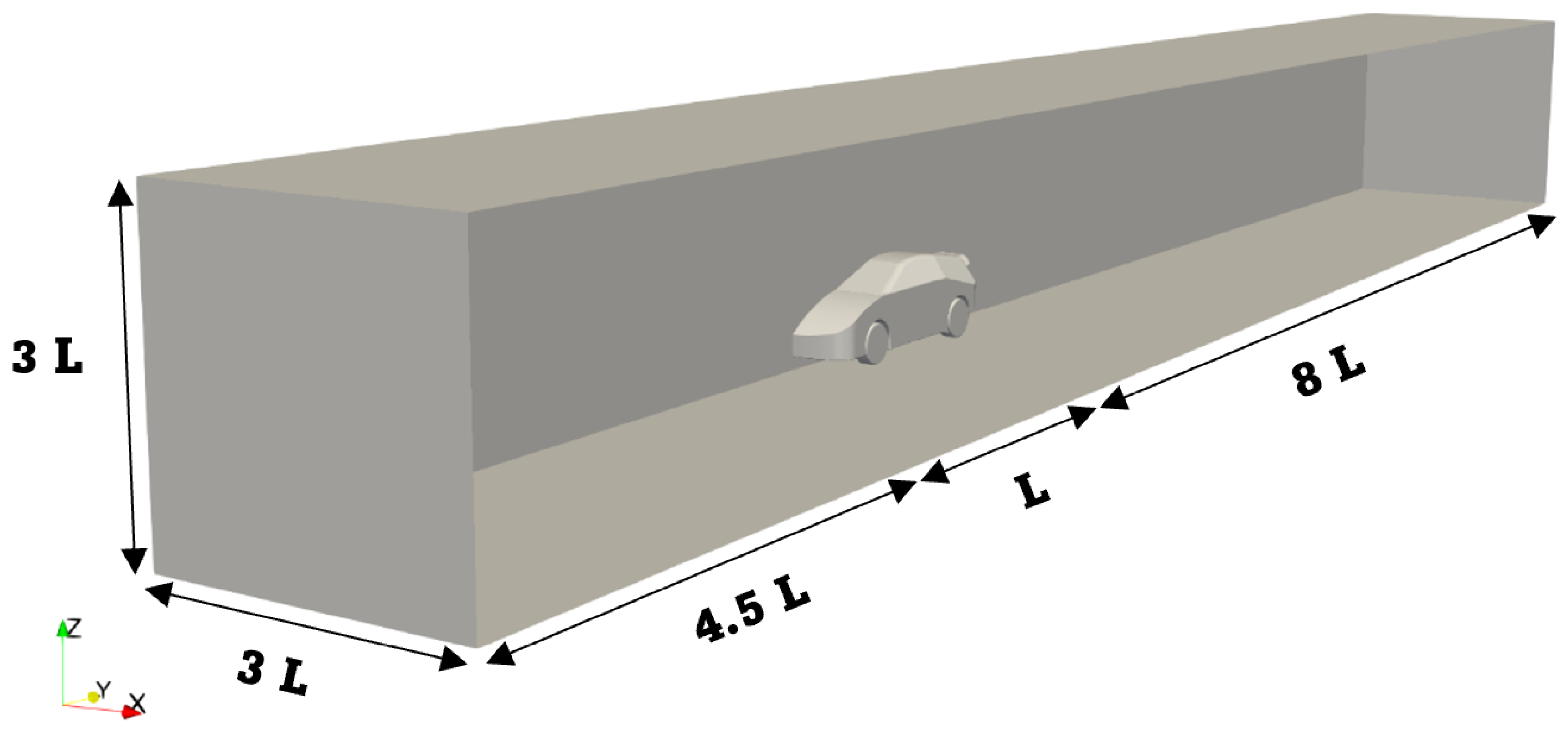
2.1. Geometry
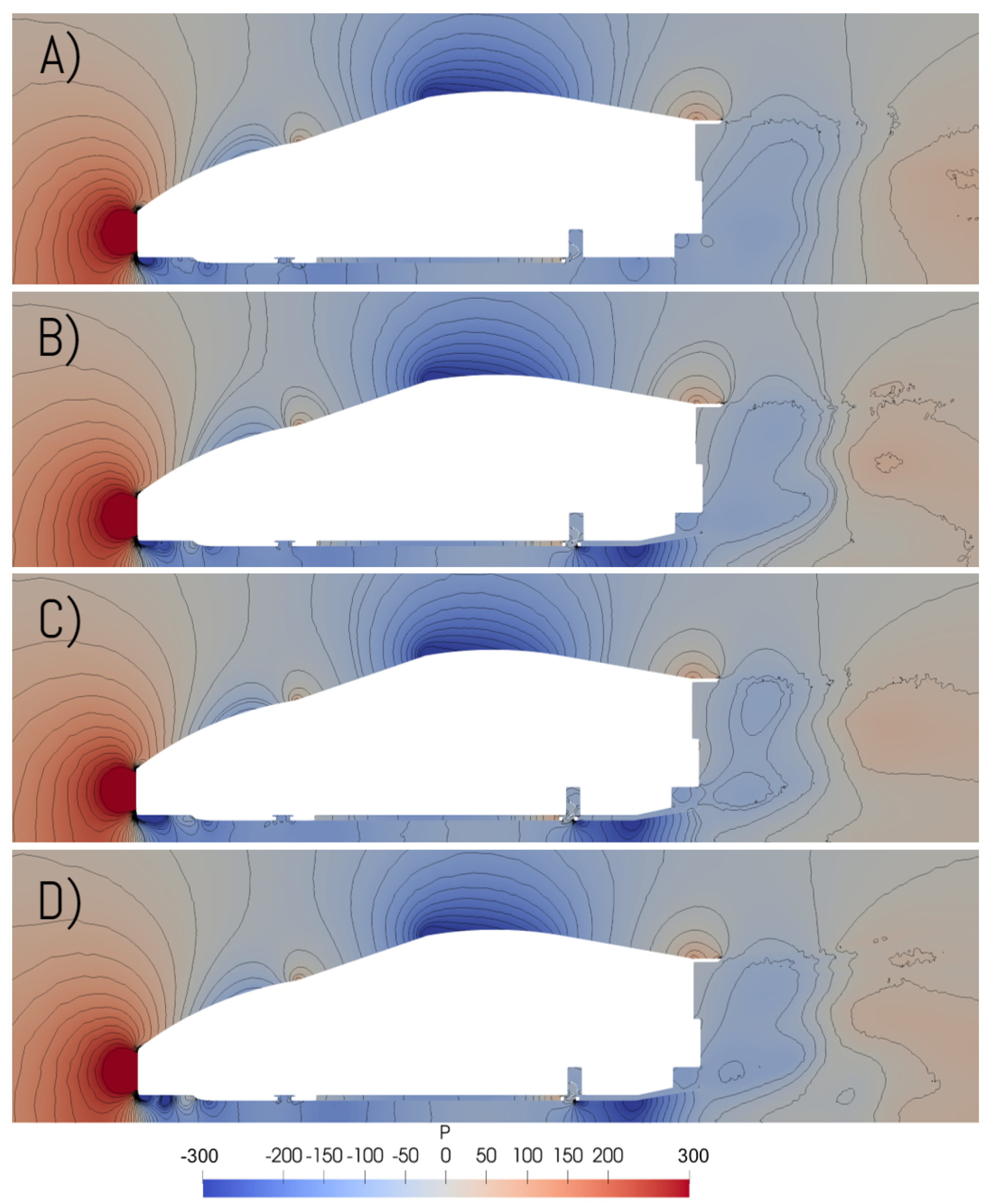
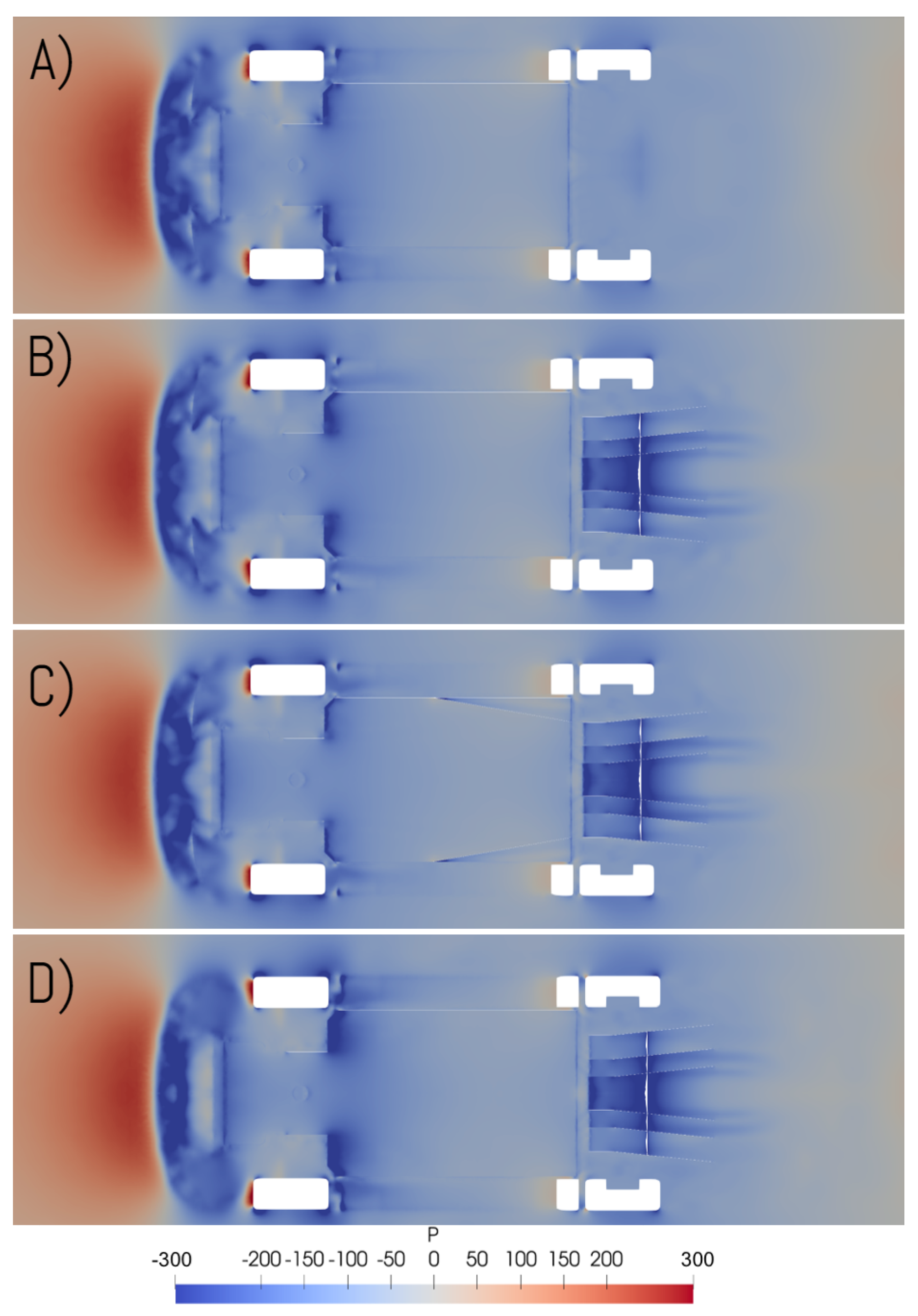
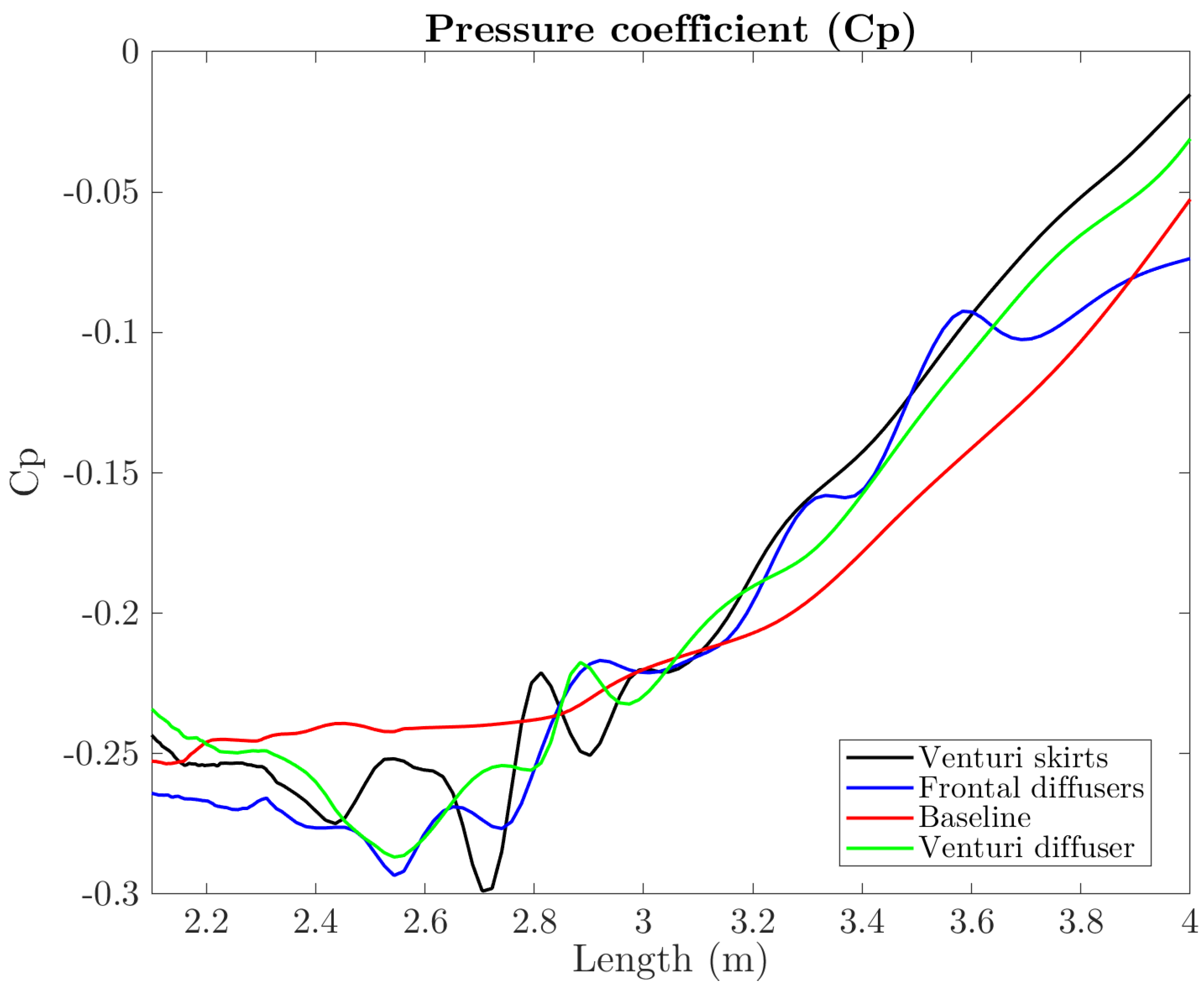
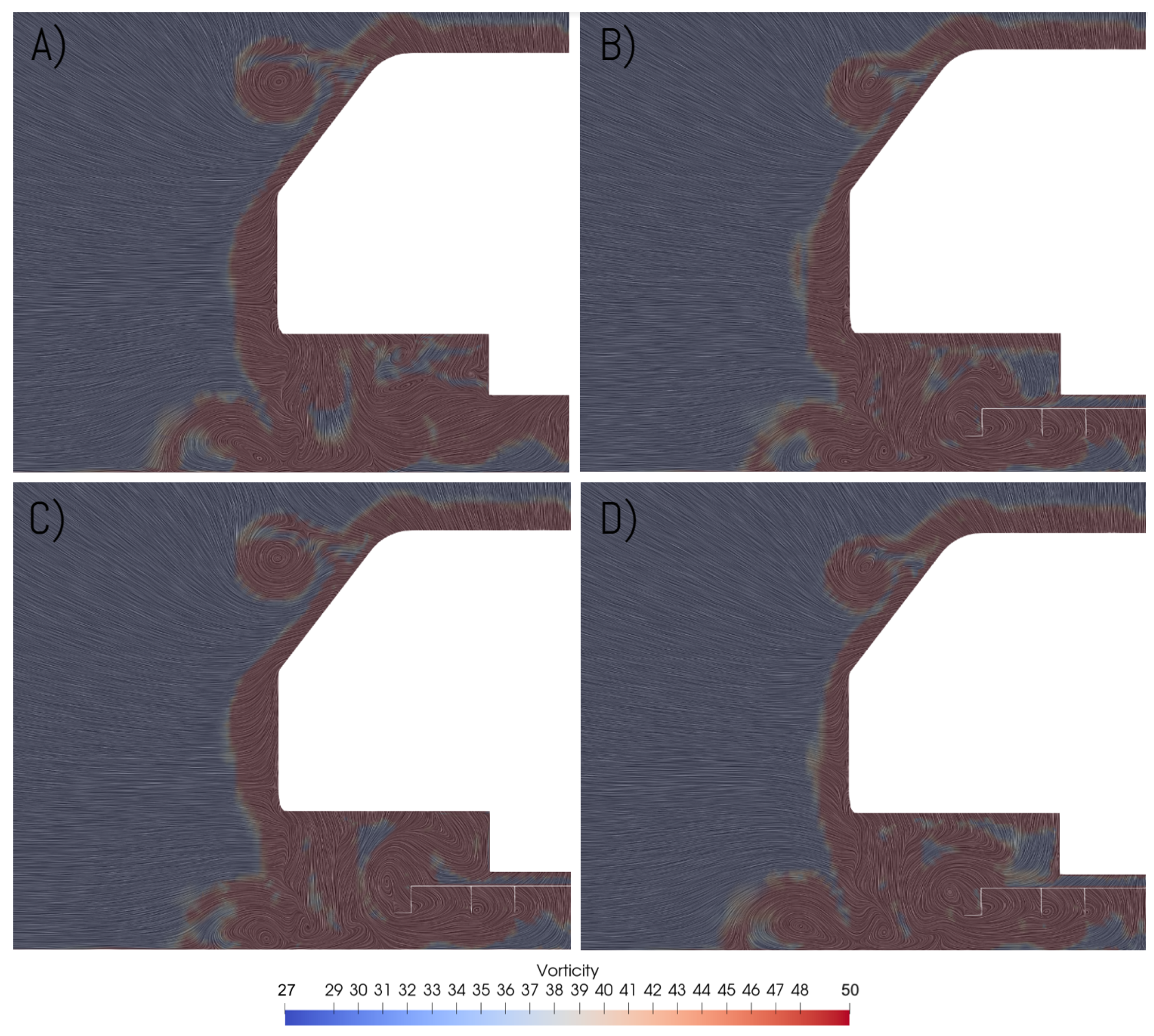
- Venturi diffuser: uses a 7 angle diffuser on the rear of the baseline model.
- Venturi skirts: uses the Venturi diffuser configuration with the addition of diagonal sealing skirts on the underbody to channelise and guide the flow towards the diffuser area.
- Venturi frontal diffuser: again, uses the Venturi diffuser configuration, along with two small frontal diffuser sections in front of the region of the tires.
2.2. Solver
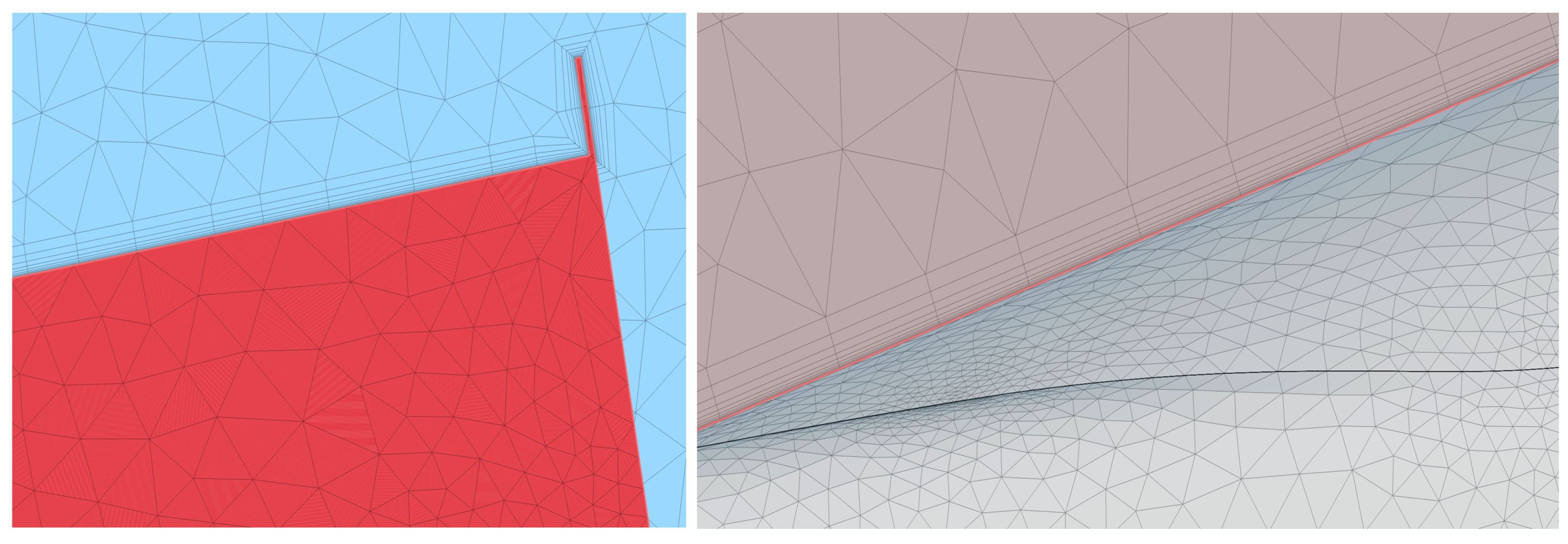
2.3. Domain and Mesh
2.4. Boundary and Initial Conditions
- Inlet velocity at 25 m/s, a value that can be easily justified in a wind tunnel experiment (for possible future validation purposes).
- Pressure outlet at atmospheric pressure.
- Ground velocity at 25 m/s.
- Symmetry plane (only half of the car was simulated).
- Slip condition on the remaining sidewall and the upper surface.
- Rotating wall at both front and rear wheels (87 rad/s).
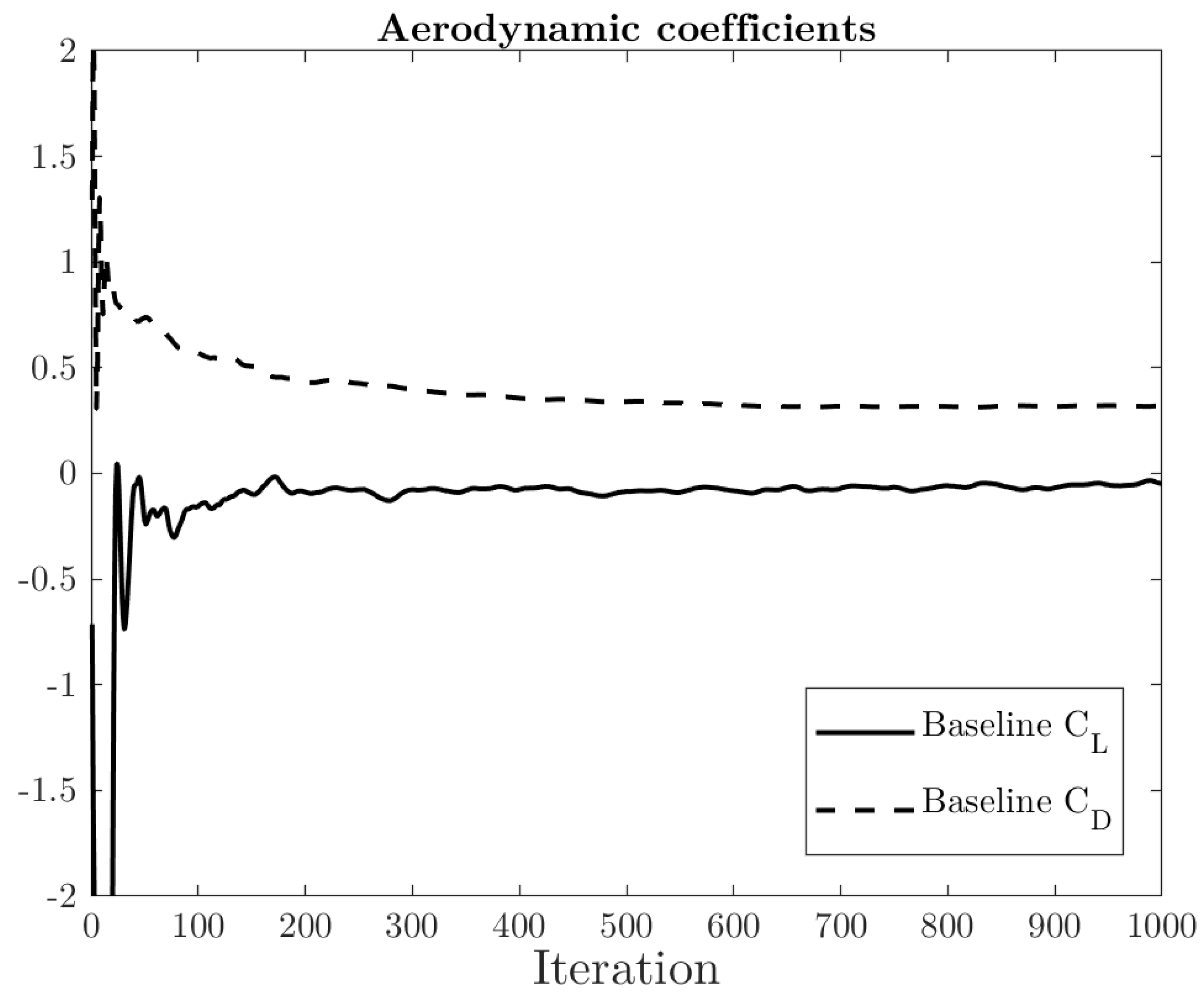
2.5. Simulation Performance
3. Results and Discussion
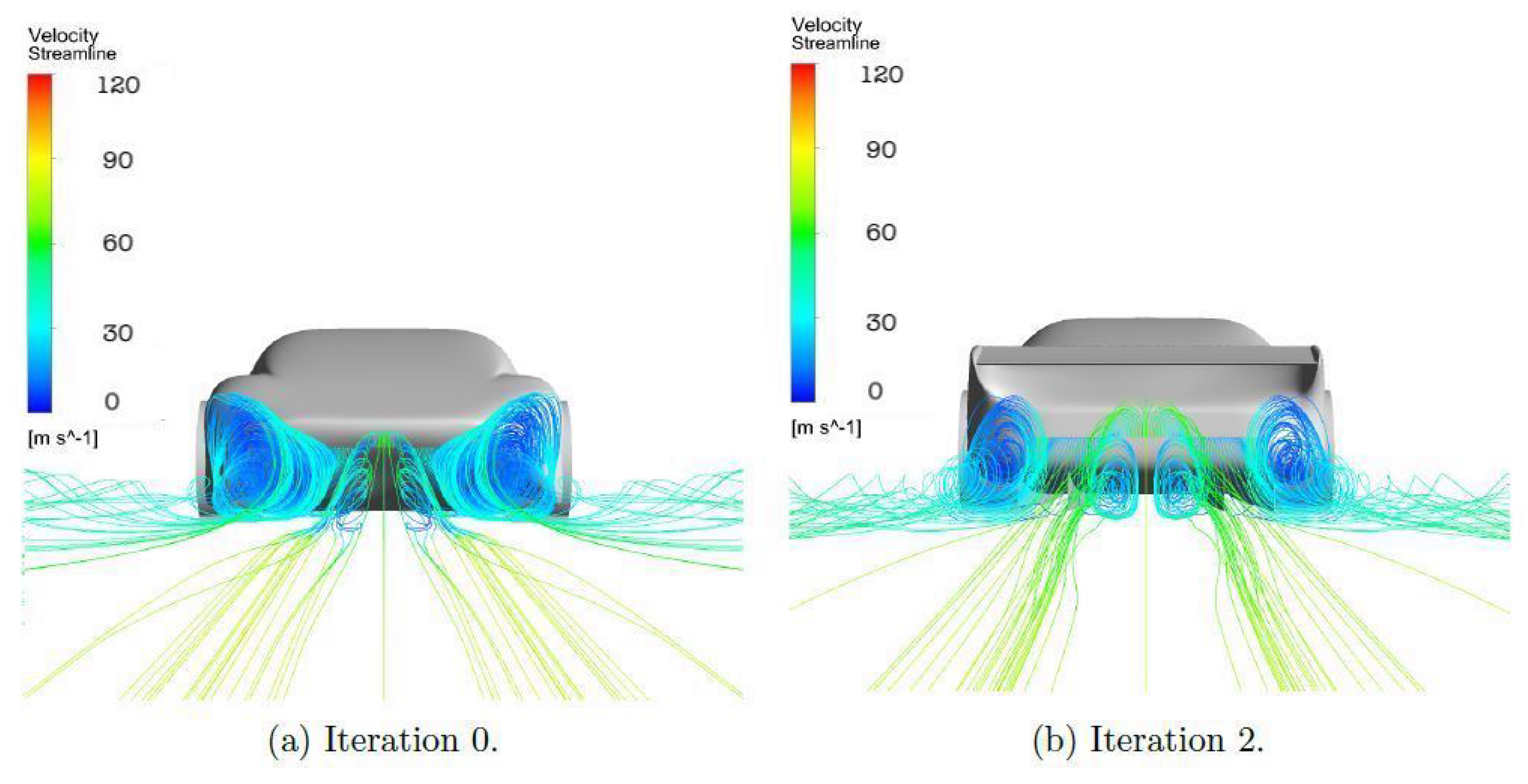
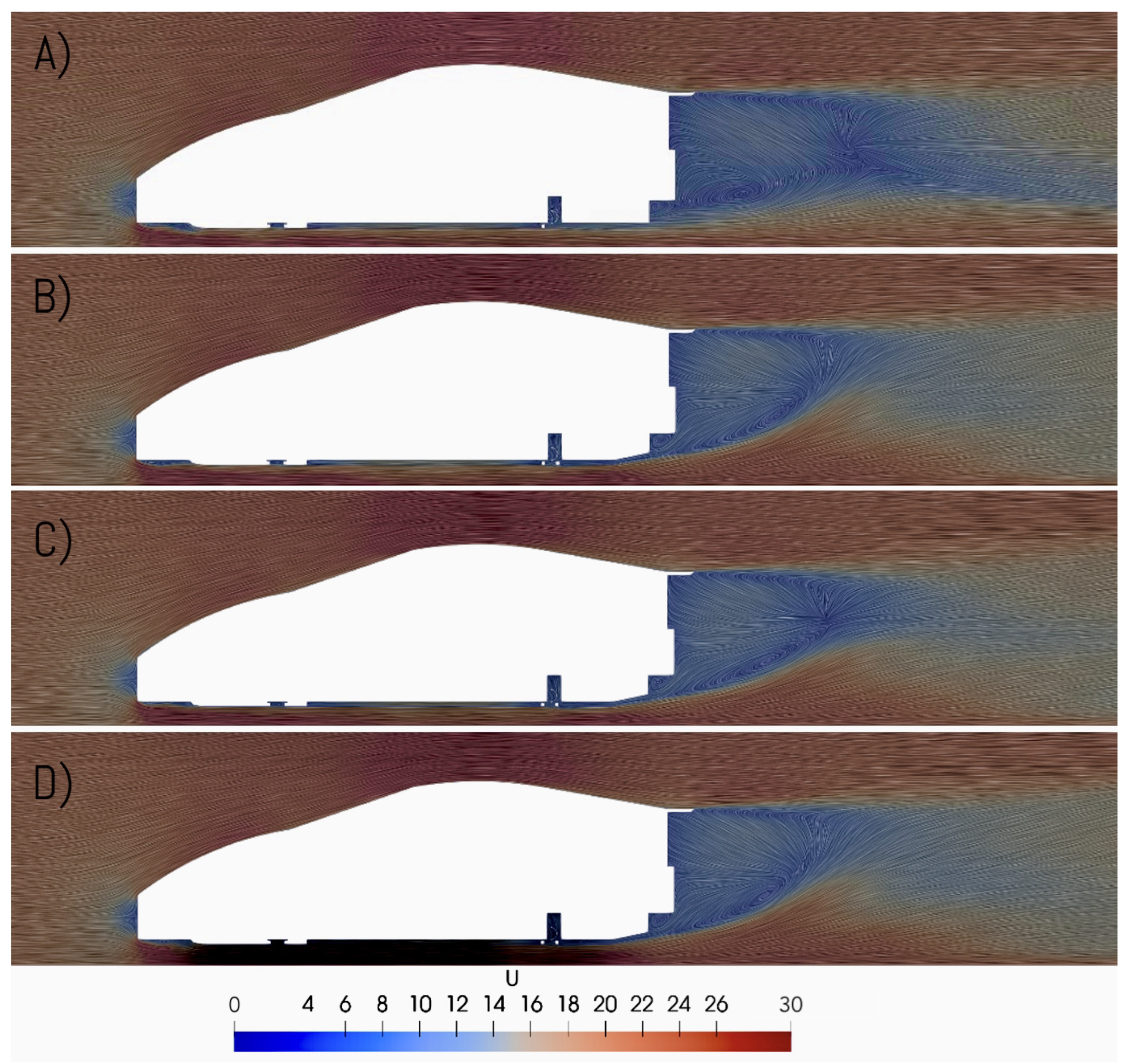
3.1. Velocity Distribution
3.2. Pressure Distribution
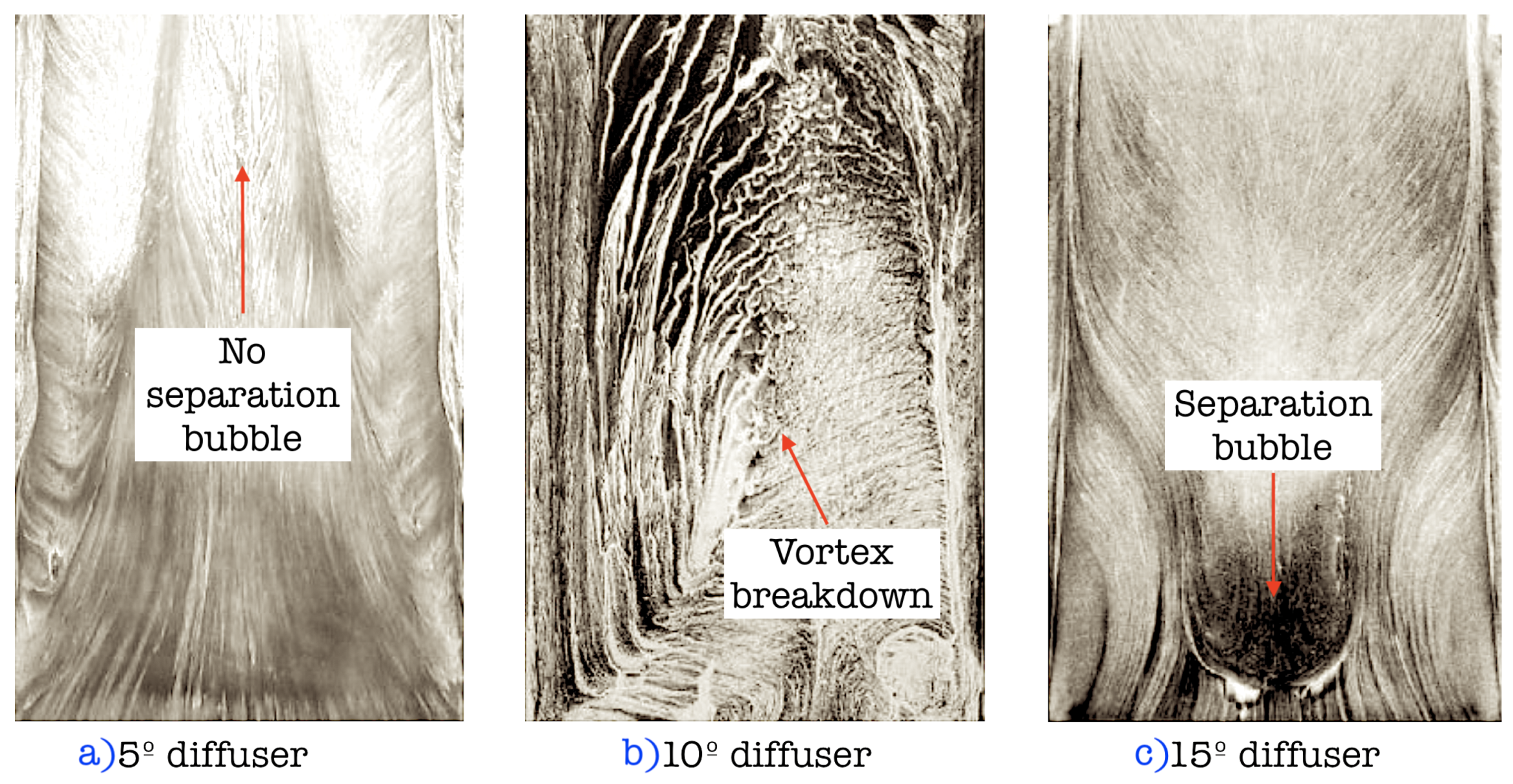
3.3. Vorticity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| FVM | Finite Volume Method |
| GAMG | Geometric Algebraic Multi Grid |
| GCI | Grid Convergence Index |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| L | Vehicle length [m] |
| Reference parameter [] | |
| l | Turbulent length scale [m] |
| I | Turbulent intensity [%] |
| Re | Reynolds Number |
| Cp | Pressure coefficient |
| Fluid density [kg/] | |
| Fluid velocity [m/s] | |
| Dynamic viscosity [kg/m·s] | |
| S | Reference Surface [] |
| Lift coefficient | |
| Drag coefficient | |
| E | Aerodynamic Efficiency |
References
- Katz, J. Aerodynamics of race cars. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2006, 38, 27–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hucho, W.; Sovran, G. Aerodynamics of road vehicles. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1993, 25, 485–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.; Sherwin, C.; Passmore, M.; Le Good, G. Aerodynamic drag of a compact SUV as measured on-road and in the wind tunnel. SAE Trans. 2002, 111, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Alkan, B. Aerodynamic Analysis of Rear Diffusers for a Passenger Car Using CFD. engrXiv 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, K.R.; Bertenyi, T.; Dutil, G.; Syms, J.; Sovran, G. The aerodynamic performance of automotive underbody diffusers. SAE Trans. 1998, 107, 150–179. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, J. Race Car Aerodynamics: Designing for Speed; R. Bentley: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ehirim, O.; Knowles, K.; Saddington, A. A review of ground-effect diffuser aerodynamics. J. Fluids Eng. 2019, 141, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcar, L.; Toet, W.; Gamez-Montero, P.J. Study of the Effect of Vertical Airfoil Endplates on Diffusers in Vehicle Aerodynamics. Designs 2021, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huminic, A.; Huminic, G. Computational Study Of Curved Underbody Diffusers. E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sci. 2019, 128, 10002. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Ramm, G.; Faltin, G. Some salient features of the time-averaged ground vehicle wake. SAE Trans. 1984, 93, 473–503. [Google Scholar]
- Hucho, W.H. Aerodynamics of Road Vehicles: From Fluid Mechanics to Vehicle Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gilliéron, P.; Kourta, A. Aerodynamic drag reduction by vertical splitter plates. Exp. Fluids 2010, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, J.F.; Aider, J.L. Drag and lift reduction of a 3D bluff body using flaps. Exp. Fluids 2008, 44, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Jeong, S.; Obayashi, S. Drag reduction of a pickup truck by a rear downward flap. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2011, 12, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Toet, W.; Zerihan, J. Ground effect aerodynamics of race cars. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senior, A.E.; Zhang, X. The force and pressure of a diffuser-equipped bluff body in ground effect. J. Fluids Eng. 2001, 123, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.S.; Kang, S.O.; Jun, S.O.; Park, H.I.; Kee, J.D.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.H. Aerodynamic design optimization of rear body shapes of a sedan for drag reduction. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, F.; Assi, G.R.; Sherwin, S.J.; Meneghini, J.R.; Doorly, D.J. An investigation on the effect of rear underbody diffusers over the flow around automotive bluff bodies. Imp. Coll. Lond. 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Haris, M.N.; Sapit, A.; Mohamed, N.H.N. Study of Airflow Due to Rear Diffuser of Supercar. J. Complex Flow 2020, 2, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, K.R.; Syms, J.; Sovran, G. Selecting automotive diffusers to maximise underbody downforce. SAE Trans. 2000, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Sharma, S. An investigation on the aerodynamics of a symmetrical airfoil in ground effect. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2005, 29, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, T.A. Numerical Investigation on Aerodynamic Effects of Vanes and Flaps on Automotive Underbody Diffusers; Technical Report, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arun Saha, D.D. Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power Contemporary Research; Springer: Mumbai, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stefano Discetti, A.I. Experimental Aerodynamics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Toet, W. William Toet Explains Air Ducts; Kimberley Media Group: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chandavari, V.; Palekar, S. Diffuser angle control to avoid flow separation. Int. J. Tech. Res. Appl. 2014, 2, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Numerical Analysis of Underbody Diffusers with Different Angles and Channels; Technical Report, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huminic, A.; Huminic, G. Aerodynamics of curved underbody diffusers using CFD. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 205, 104300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.T.; Shimada, T.; Sinditskii, V.P.; Calabro, M. Chemical Rocket Propulsion: A Comprehensive Survey of Energetic Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, J. The influence of a vehicle underbody on aerodynamics of a simple car shapes with an underfloor diffuser. In Proceedings of the Vehicle Aerodynamics, R. Ae. S. Conference, Loughborough, UK, 18–19 July 1994; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, P.; Amandolese, X.; Aider, J.L. Drag reduction on the 25 slant angle Ahmed reference body using pulsed jets. Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.O.; Jun, S.O.; Park, H.i.; Song, K.S.; Kee, J.D.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.H. Actively translating a rear diffuser device for the aerodynamic drag reduction of a passenger car. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authority, M. Porsche patents active rear diffuser. Mot. Auth. 2017, 12, 042017. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.B. Race Car Aerodynamic Design and Optimization via CFD and the Discrete Adjoint Method. Master’s Thesis, Aalborg Univeristy Esbjerg, Esbjerg, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huminic, A.; Huminic, G.; Soica, A. Study of aerodynamics for a simplified car model with the underbody shaped as a Venturi nozzle. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2012, 58, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huminic, A.; Huminic, G. Aerodynamic study of a generic car model with wheels and underbody diffuser. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2017, 18, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhrmann, A.; Zhang, X. Influence of diffuser angle on a bluff body in ground effect. J. Fluids Eng. 2003, 125, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asif Ahmed, A.M. CFD analysis of diffuser in a car for downforce generation. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Parthasarathy, M.; Aravind, L.; Narayanan, R.S.; Vegesh, B.; Nelson, D.S. Design and analysis of a rear diffuser in a sedan car. Mater. Today Proc. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, P.; Foias, C. Navier–Stokes Equations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, A.; Castilla, R. Aerodynamic Study of the Wake Effects on a Formula 1 Car. Energies 2020, 13, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eymard, R.; Gallouët, T.; Herbin, R. Finite volume methods. Handb. Numer. Anal. 2000, 7, 713–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R.; Kuntz, M.; Langtry, R. Ten years of industrial experience with the SST turbulence model. Turbul. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 4, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Broniszewski, J.; Piechna, J. A fully coupled analysis of unsteady aerodynamics impact on vehicle dynamics during braking. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2019, 13, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I. Procedure for Estimation and Reporting of Uncertainty Due to Discretization in CFD Applications. J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130, 078001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NASA. Examining Spatial Grid Convergence. NASA Gov. 2021, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, D.; Correia, J.; Silva, A. The Influence of Front Wing Pressure Distribution on Wheel Wake Aerodynamics of a F1 Car. Energies 2021, 14, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J. Eddy dynamics and kinematics of convective turbulence. In Buoyant Convection in Geophysical Flows; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 41–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jermann, C.; Pujals, G.; Meliga, P.; Serre, E.; Gallaire, F. Characterization of the streamwise vortices and near-wake dynamics in the turbulent flow around the 25° Ahmed body based on SPIV. In Proceedings of the 3rd GDR Symposium «Flow Separation Control», Ecole Centrale de Lille, Marbella, Spain, 7–8 September 2013. [Google Scholar]






| Mesh Parameters | = |
|---|---|
| 1.500 | |
| 1.500 | |
| 0.320 | |
| 0.310 | |
| 0.282 | |
| p | 2.08 |
| 1.218% | |
| 2.928% | |
| 1.032 |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Free stream velocity | 25 m/s |
| Fluid density () | 1.225 kg/m3 |
| Turbulent Intensity (I) | 0.150% |
| Turbulent length scale (l) | 0.172 m |
| Reynolds Number (Re) |
| Baseline | Venturi Diff. | Venturi Skirts | Venturi Front. Diff. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.047 | −0.573 | −0.887 | −0.773 | |
| 0.320 | 0.325 | 0.324 | 0.332 | |
| E | −0.146 | −1.763 | −2.737 | −2.323 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guerrero, A.; Castilla, R.; Eid, G. A Numerical Aerodynamic Analysis on the Effect of Rear Underbody Diffusers on Road Cars. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083763
Guerrero A, Castilla R, Eid G. A Numerical Aerodynamic Analysis on the Effect of Rear Underbody Diffusers on Road Cars. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(8):3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083763
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuerrero, Alex, Robert Castilla, and Giorgio Eid. 2022. "A Numerical Aerodynamic Analysis on the Effect of Rear Underbody Diffusers on Road Cars" Applied Sciences 12, no. 8: 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083763
APA StyleGuerrero, A., Castilla, R., & Eid, G. (2022). A Numerical Aerodynamic Analysis on the Effect of Rear Underbody Diffusers on Road Cars. Applied Sciences, 12(8), 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083763







