Abstract
The pandemic of COVID-19 has caused millions of infections, which has led to a great loss all over the world, socially and economically. Due to the false-negative rate and the time-consuming characteristic of the Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) tests, diagnosing based on X-ray images and Computed Tomography (CT) images has been widely adopted to confirm positive COVID-19 RT-PCR tests. Since the very beginning of the pandemic, researchers in the artificial intelligence area have proposed a large number of automatic diagnosing models, hoping to assist radiologists and improve the diagnosing accuracy. However, after two years of development, there are still few models that can actually be applied in real-world scenarios. Numerous problems have emerged in the research of the automated diagnosis of COVID-19. In this paper, we present a systematic review of these diagnosing models. A total of 179 proposed models are involved. First, we compare the medical image modalities (CT or X-ray) for COVID-19 diagnosis from both the clinical perspective and the artificial intelligence perspective. Then, we classify existing methods into two types—image-level diagnosis (i.e., classification-based methods) and pixel-level diagnosis (i.e., segmentation-based models). For both types of methods, we define universal model pipelines and analyze the techniques that have been applied in each step of the pipeline in detail. In addition, we also review some commonly adopted public COVID-19 datasets. More importantly, we present an in-depth discussion of the existing automated diagnosis models and note a total of three significant problems: biased model performance evaluation; inappropriate implementation details; and a low reproducibility, reliability and explainability. For each point, we give corresponding recommendations on how we can avoid making the same mistakes and let AI perform better in the next pandemic.
1. Introduction
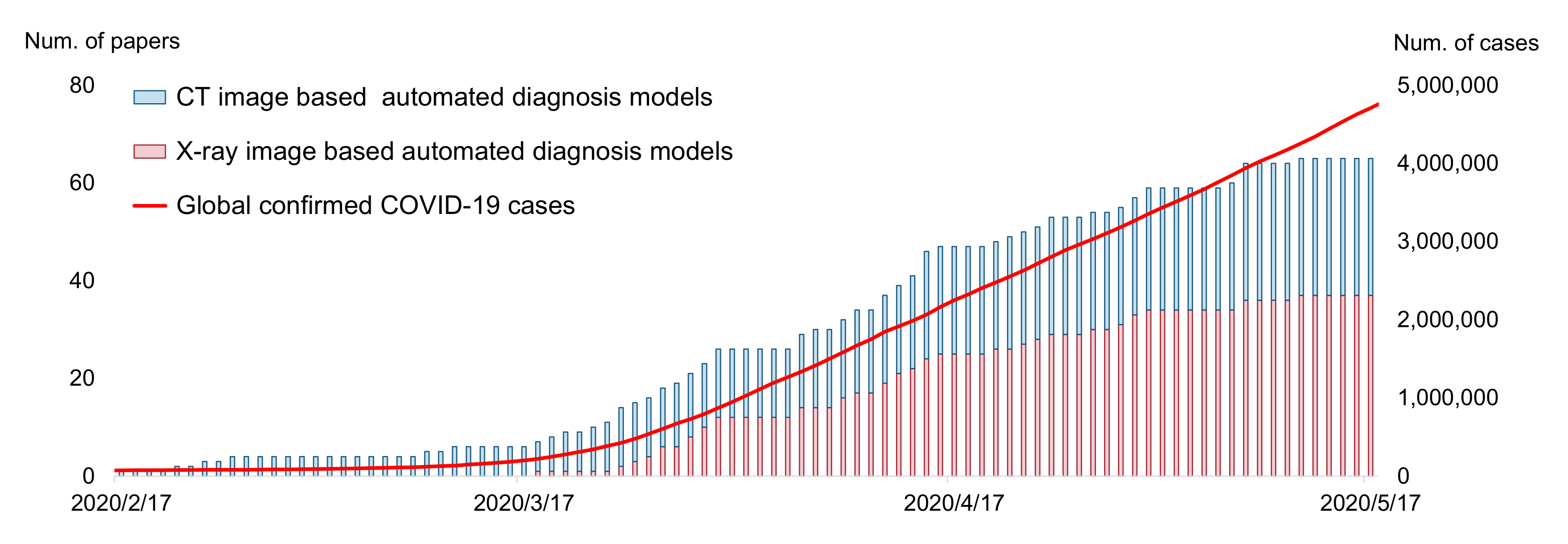
The SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic began in the spring of 2020. In the battle between humans and the novel coronavirus, medical professionals and scientists contributed a large amount. At the same time, a popular reaction from other research communities, including the AI community, is “how can we help?”. In practice, the diagnosis of COVID-19 can be based on two methods: the Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) test and radiography imaging (X-ray or CT scan). Current AI technologies can hardly help with RT-PCR tests, but they can assist the radiography imaging-based diagnosis of COVID-19 from a computer vision perspective. In the virus-stricken area, radiologists have a heavy burden on analyzing massive scanning images, so automated diagnosis models have great potential value in supporting medical decisions. The AI community responded very quickly to this point. The first automated diagnosis model (from Wang et al. [1]) was posted on MedRXiv on 17 February 2020, when the total number of confirmed cases was only around 64,000 (current global confirmed cases: more than 400,000,000 (data retrieved from https://covid19.who.int, accessed on 11 February 2022)), nearly a month before the World Health Organization (WHO) announced COVID-19 as a global pandemic (12 March 2020). As shown in Figure 1, following the work of Wang et al. [1], a large number of researchers dived into this field, making the automated diagnosis of COVID-19 become a noticeable research hotspot in the AI community. Meanwhile, an unprecedented amount of papers have been presented. As of this writing, there are more than 1320 manuscripts on arXiv (Google Scholar search: COVID-19 [“CT” OR “X-ray”] [“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR “artificial intelligence”] site:arxiv.org) and 535 manuscripts on medRXiv (Google Scholar search: COVID-19 [“CT” OR “X-ray”] [“machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR “artificial intelligence”] site:medrxiv.org). As shown in Table 1, at least 13 special issues on this topic have been held by various journals. Moreover, there are more than 20 review or survey papers [2] that have been presented to the best of our knowledge.
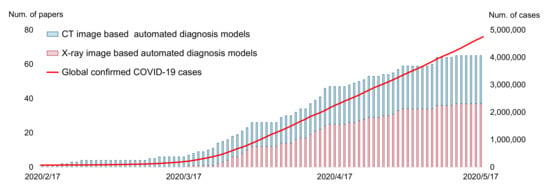
Figure 1.
Accumulated count of automated COVID-19 diagnosing models during the 3 months after the first model was proposed (17 February to 17 May 2021). The data are obtained according to the initial submission date on arXiv/medRXiv.

Table 1.
The special issues that have been held by various journals during 2020–2022. All links are accessed on 5 March 2022.
The research on the automated diagnosis of COVID-19 is highly interdisciplinary. A good study should be qualified with both clinical standards and AI standards. From the clinical perspective, the model should avoid making mistakes such as improper data collection, data prepossessing and data augmentations. From the AI perspective, the models should have rigorous experiment design, enough robustness and a good generalization ability. However, unfortunately, while there are thousands of studies that appeared in these two years, very few of them are qualified from both sides. On 27 March 2020, a group from Europe presented an early review of the diagnosis models [3,4]. Among hundreds of covered studies, they found that “all models were rated at high or unclear risk of bias” according to the result obtained from PROBAST [5] (a prediction model risk of bias assessment tool). On 13 November 2020, Summers [6] described AI for COVID-19 imaging as “A Hammer in Search of a Nail”. He called for moving beyond studies that repeatedly show that AI can detect COVID-19. Reliable diagnosis models that can meet real-world clinical requirements are more urgently needed. However, this need was not met by subsequent studies. On 15 March 2021, a group from the UK [7] published an article pointing out that “our review finds that none of the models identified are of potential clinical use due to methodological flaws and/or underlying biases”. Later, a review paper [8] noted that “The vast majority of manuscripts were found to be deficient regarding potential use in clinical practice”.
The problems of the research on the automated diagnosis of COVID-19 are not limited to an insufficient application value. A group from the University of Cambridge reviewed studies of AI models for COVID-19 diagnosis and found an “apparent deterioration in standards of research” [9]. Hryniewska et al. [10] listed numerous mistakes that were made during the research of the automated diagnosis of COVID-19. Cruz et al. [11] analyzed public COVID-19 datasets and found that most of them had significant problems that would lead to a high risk of model bias.
Review and survey papers are also important. A good review can help researchers to quickly understand the current status and background of the research field, reducing the risk of conducting repetitive work. In June 2020, we contributed a conference paper [12] that reviews the automated diagnosis model of COVID-19. In that paper, we pointed out that the literature coverage of existing reviews is insufficient, as demonstrated in Table 2. Meanwhile, they lack proper organization, a comparison of performance and an in-depth analysis of shortcomings. Specifically, in several reviews, diagnosing models are divided into CT-based models and X-ray-based models, but CT-based models and X-ray-based models share many similarities in preprocessing, feature extraction, classification and evaluation. Many early reviews contain repetitive restatements summarizing previous papers, failing to provide their own insights and new perspectives and failing to point out clear directions in how AI will be used in practical medicine in the future. These points are partially confirmed by a recent paper [2] that systematically analyzes the methodological quality of COVID-19 review papers.

Table 2.
Summarizing existing review or survey papers related to automated diagnosis of COVID-19.
Therefore, based on our previous conference paper, we aim to present a systematic review for the 2-year (2020–2022) development of the medical imaging-based automated diagnosis of COVID-19 in this paper. We classify existing methods into two types—classification and segmentation—then define universal model pipelines and analyze the techniques that have been used in each step. We also review the existing public datasets. More importantly, we summarize the problems that emerged in the research on this field, and provide some comments and suggestions on how AI can perform better in the next pandemic. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. We first discuss the input modalities of automated diagnosis models in Section 2. In Section 3 and Section 4, we, respectively, present a systematic review of existing methods and datasets. Section 5 discusses the limitation of existing methods and present corresponding recommendations, and Section 6 concludes this paper.
2. Input Modalities: CT or X-ray
2.1. Clinical Perspective
An early study (March 2020) pointed out that fever, cough, myalgia, fatigue, expectoration, and dyspnea are the main clinical symptoms of COVID-19 patients [24]. These symptoms can be used to diagnose COVID-19. However, later research shows that many infected patients (estimated as at around 20%) can be asymptomatic, and that those asymptomatic patients play an important role in the transmission of COVID-19 [25,26,27]. Real-time RT-PCR has proven to be a much more effective way to diagnose COVID-19, but it still has the risk of false-negative and false-positive results [28].
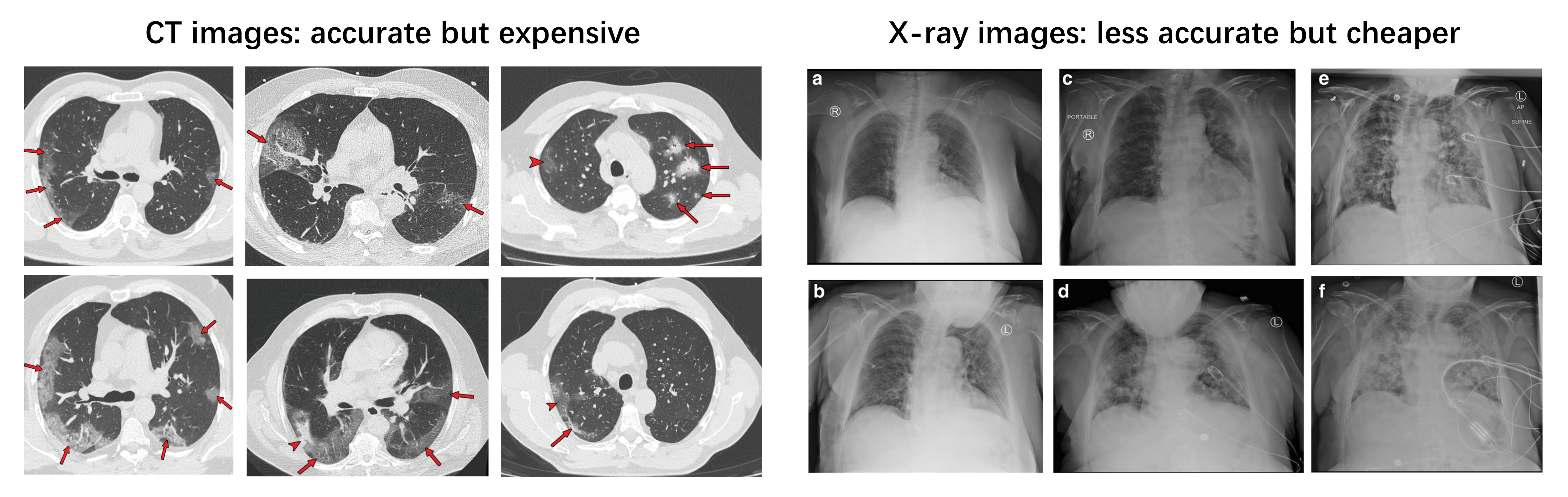
To solve this issue, medical imaging (CT or X-ray)-based diagnoses can be used as a complementary method to correct false-negative RT-PCR tests. In February 2020, a group from China [29] found that some patients with positive chest CT findings may present with negative results of RT-PCR tests for COVID-19. CT patterns of COVID-19 includes Ground-Glass Opacities (GGO), vascular enlargement, bilateral abnormalities, lower lobe involvement and posterior predilection [30]. Fang et al. [31] reported that the sensitivity of CT-based diagnosis was greater than that of RT-PCR (98% vs. 71%). Meanwhile, chest X-ray imaging has also proven to be an effective tool for diagnosing COVID-19 [32]. Cozzi et al. [33] showed that there are several commonly observed features in chest X-ray images, including lung consolidations, GGO, nodules and reticular–nodular opacities. Rousan et al. [32] showed that nearly half of COVID-19 patients have abnormal chest X-ray findings, and that GGO in lower lobes is the most common finding. Some typical examples of COVID-19 CT and X-ray features can be found in Figure 2.
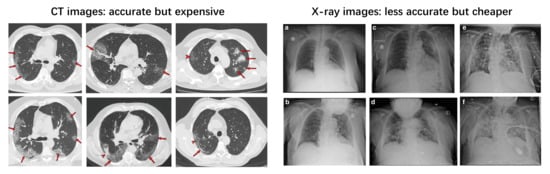
Figure 2.
Typical CT (left) [30] and chest X-ray (right) [32] images of COVID-19-infected patients. The right subfigure a–f represents different cases, please refer to [32] for more details.
At present, a (repeated) RT-PCR test is the most commonly adopted COVID-19 diagnosing approach due to its scalability and relatively high sensitivity. Medical imaging-based diagnosis is used as a complementary method to the RT-PCR test. Comparing CT and X-ray-based diagnoses, a CT-based diagnoses are much more accurate (and even better than RT-PCR) but much more expensive, whereas X-ray-based diagnoses are less accurate but less expensive [34,35,36].
2.2. Artificial Intelligence Perspective
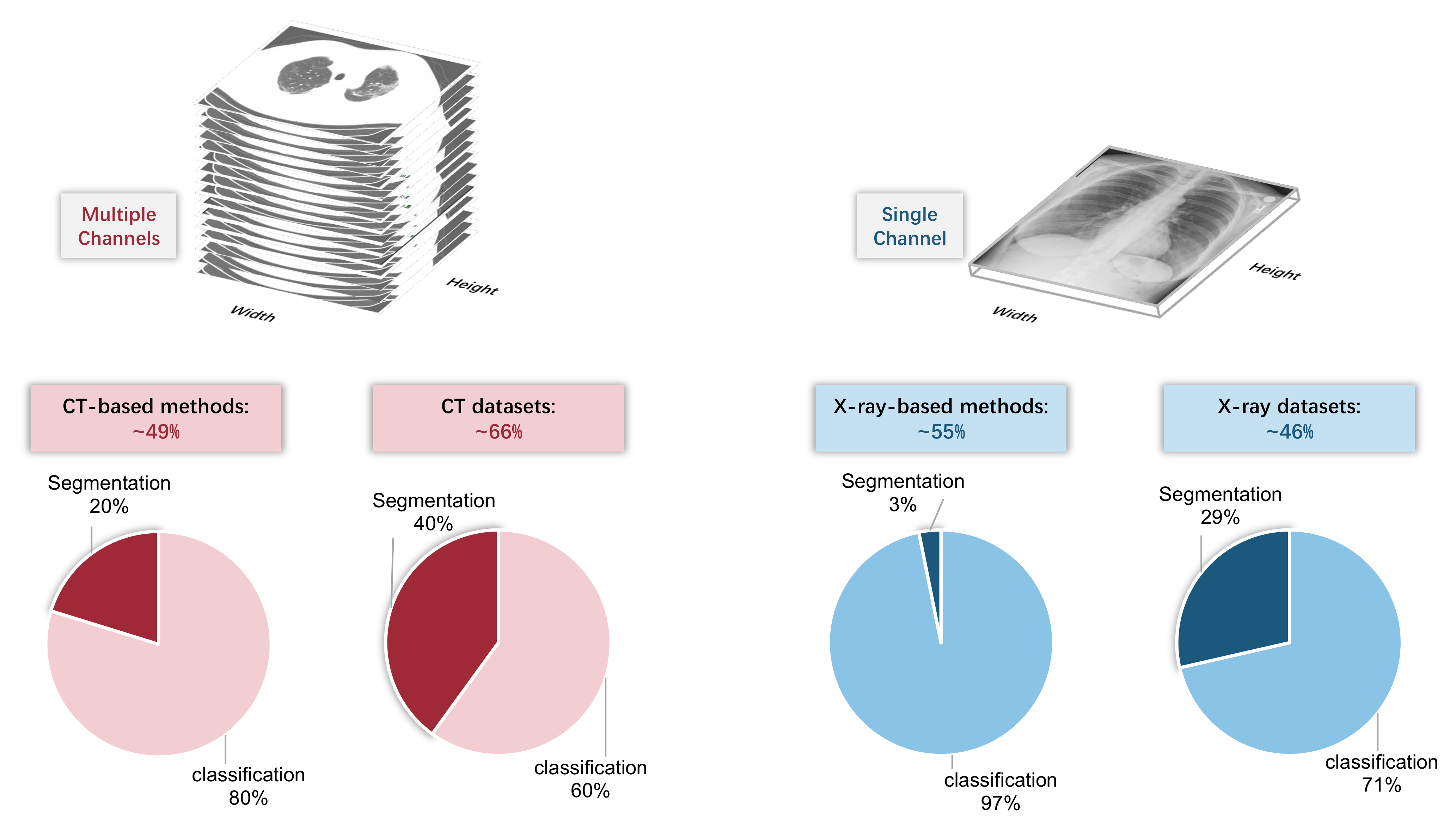
From the perspective of using artificial intelligence algorithms, the most significant difference between CT and X-ray images is the input shape. As shown in Figure 3, a CT image contains a series of slices; therefore, the input has multiple channels. However, there are also some methods that ignore the multiple channels and treat each slice independently, leading to the loss of spatial contextual information. Comparatively, X-ray images only have a single channel.
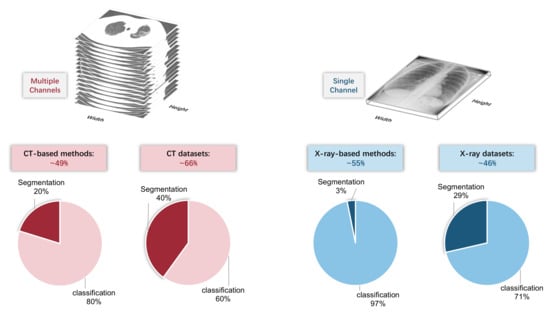
Figure 3.
Top: CT image contains multiple channels, whereas X-ray image only has a single channel. Bottom: the proportion of CT/X-ray-based methods and datasets.
Despite the difference in data dimension, there are not many other differences between CT and X-ray images from the artificial intelligence perspective, since most existing methods do not utilize any explicit domain knowledge. Therefore, the number of CT-based methods and X-ray based methods are approximately equal (49% vs. 53 (some methods are compatible with both CT and X-ray images)) among the covered papers in this review. However, we found that, among CT-based and X-ray based methods, the proportion of classification methods and segmentation methods is different. CT-based segmentation methods account for 20%, whereas X-ray-based segmentation methods account for only 3%. The reason might be the difficulty of the X-ray-based segmentation task. Meanwhile, it can also be partially explained by the imbalance in the dataset type: the proportion of the CT-based segmentation dataset is more than that of the X-ray-based segmentation dataset (40% vs. 29%).
3. Automated Diagnosis of COVID-19
Current automated diagnosis methods of COVID-19 can be divided into two categories: image-level diagnosis and pixel-level diagnosis. Image-level diagnosis refers to the methods that predict the label (e.g., COVID-19/normal) from a given medical image. Pixel-level diagnosis can further provide the location of the lesion via predicting a segmentation mask. Since most image-level and pixel-level methods are based on different neural network architecture (i.e., image classification network, such as ResNet [37], and image segmentation network, such as U-Net [38]), we will review each type of method separately in this section. Image-level diagnosis methods will be firstly introduced in Section 3.1, whereas pixel level methods will be presented in Section 3.2.
3.1. Image-Level Diagnosis: Classification-Based Models
3.1.1. Overview
To give a formal definition of the image-level diagnosis of COVID-19, suppose we have a dataset with N samples, where and are the ith input image and the class label of the corresponding image. Our goal is to learn a function f, which is usually a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) [39], to predict the label from a given image accurately. In other words, the results of classification can be written as and we expect a low prediction error for each i.
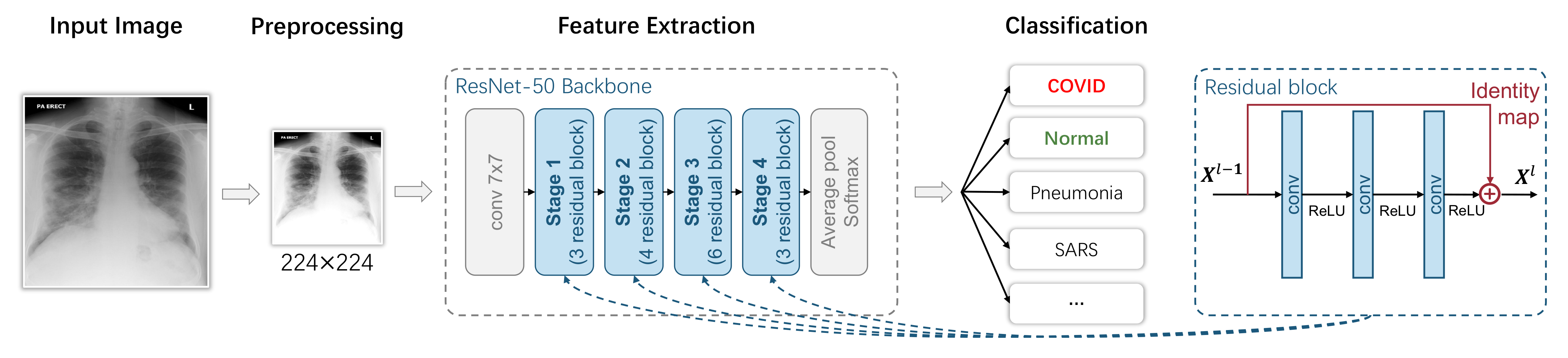
This formulation is adopted by most researchers. Here, we first define a commonly adopted pipeline that consists of several steps, then introduce techniques that have been used in each step in the following sections (Section 3.1.2, Section 3.1.3, Section 3.1.4, Section 3.1.5). As shown in Figure 4, this pipeline is a combination of the following steps: first, the lung scanning images (CT or X-ray) are preprocessed by data augmentation or lung segmentation; then, the feature vectors are extracted by Convolution Neural Networks (CNN) or other feature extractors. The classifier predicts the label that corresponds to the input image.
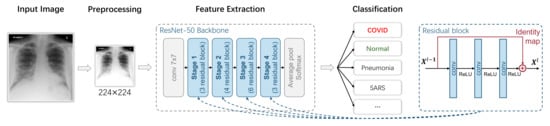
Figure 4.
A typical ResNet-classification-based image-level COVID-19 diagnosis model.
In Figure 4, we use a ResNet-50 as the feature extraction backbone, which is adopted by most researchers according to our statistics in Section 3.1.3. The ResNet-50 backbone can be divided into four stages, and each of them has three, four, six and three blocks. The detailed structure of a block is shown on the right side of Figure 4. It is an important method to ensure that deep learning does not degenerate with the increasing number of network layers.
3.1.2. Preprocessing
In the existing literature, researchers mainly used three types of preprocessing methods: data augmentation, image equalization and lung segmentation. Data augmentation can enlarge the dataset and prevent overfitting, equalization improves the image quality and lung segmentation can preserve the region of interest (ROI) only and avoid the undesired interference from areas out of the lung.
To avoid overfitting and solve the problem of data imbalance, data augmentations are the most adopted method in the preprocessing stage. Rotating, flipping, scaling, cropping and brightness and contrast adjusting [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] are the simplest and most common data augmentation methods. For simplicity, in Table 3, we summarize basic transformation-based data augmentation methods used by COVID-19 diagnosing models. We also summarize the total number of papers that adopt each type of data augmentation in the last row of Table 3. It can be seen that rotating and filling and scaling or cropping are the most widely adopted techniques. However, their augmentation strength is limited. For example, in the comparative experiment of Mizuho et al. [55], the conventional data augmentation method improved the diagnosing performance by only 4%. Therefore, researchers proposed applying other advanced data augmentation methods. To balance the imbalanced data, Rahul Kumar et al. [56] proposed the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE). Mehmet et al. [52] performed Zero-phase Component Analysis (ZCA whitening) to remove redundant information in input scanning images. Nour et al. [57] and Arvan et al. [58] used the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN [59] and Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (CGAN [60]), respectively, to generate virtual samples for data augmentation. Generative models can significantly increase the dataset size, but the quality of the generated sample is difficult to guarantee. The purpose of data augmentation is to prevent overfitting by increasing the variation, but, in these virtual sample methods, the discriminant lesion patterns might be lost or distorted if the model increases the variation too much.

Table 3.
Basic transformation-based data augmentation methods. The last row summarizes the total number of papers that adopt the corresponding approach.
In addition to the issue of insufficient data or imbalanced data, there are also large image variations that are caused by different types of scanners. As shown in Figure 5, we can observe significant image variation across different CT scanners. To solve this issue, Md et al. [95] and Oh et al. [96] performed histogram equalization on the images. However, histogram equalization has the potential harm of affecting image details or bringing unexpected noise. Md et al. [95] eliminated the noise by introducing a Perona–Malik Filter (PMF) [97], whereas some other researchers [93,94,98,99] solved the problem by proposing the Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE).

Figure 5.
Significant variation among CT images caused by different scanners.
Lung segmentation aims to preserve only the lung area. This is motivated by prior domain knowledge: COVID-19 is a type of viral pneumonia, and the evidence of infection cannot lie outside of the lung. Lung segmentation can be conducted by using pretrained lung segmentation models. Importantly, we note that, though segmentation models are used and segmentation masks are predicted in this step, it has a fundamental difference to the pixel-level diagnosis model. Lung segmentation is independent of identifying COVID-19. It only requires identifying the lung area. Differently, pixel-level diagnosis needs to locate the exact area of the COVID-19 lesion.
3.1.3. Feature Extraction
As previously demonstrated in Section 2 and shown in Figure 2, scanning images of COVID-19 has certain characteristic manifestations, such as Ground-Glass Opacity (GGO) and a crazy-paving pattern distributed in a certain zone of lungs [16]. Feature extraction detects those discriminative lesion patterns. Most COVID-19 diagnosing models adopted the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for feature extraction, and most of them used existing network structures, such as ResNet [37], GoogLeNet [100], DenseNet [101], VGG [102], MobileNet [103], SqueezeNet [104], AlexNet [105], Capsule [106], etc. We summarized some popular CNN structures that have been used by COVID-19 diagnosing models in Table 4.

Table 4.
CNNs used By COVID-19 diagnosing models.
Some researchers also proposed automatic network structure designing methods to identify the best network structure for lung feature extraction. Wang et al. [155] used a generative synthesis approach to identify the optimal network architecture. Dalia et al. [46] applied a Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA) to determine the best network architecture hyperparameters. Sivaramakrishnan et al. [137] developed an iteratively pruning strategy to identify the optimal network structure. The model ensemble can also promote the overall performance. Lawrence et al. [118] and Umut et al. [45] performed a model ensemble by voting and feature fusion. Md et al. [95] applied Softmax Class Posterior Averaging (SCPA) and Prediction Maximization (PM) for the model ensemble, and Rodolfo et al. [156] combined seven traditional feature extraction models with Inception-v3 to obtain better results. Mahesh et al. [145] assembled different CNNs using a stacked generalization approach [115] to further improve the model performance. These models assumed that different sub-models learn nonlinear discriminative features and semantic image representation from images of different levels. Therefore, the combined model will be more robust and accurate.
In the beginning, trying existing CNNs is fast and convenient. However, these networks are designed for general image classification tasks, such as the ImageNet challenge. Radiologists diagnose COVID-19 by finding distinguishing local patterns. Some researchers design local methods to extract more discriminative features. For example, Umut et al. [45] and Oh et al. [96] used the local patches to train the CNN feature extractor. To analyze local textural features, Chirag Goel et al. [157] proposed the Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM). However, lung infectious areas may vary significantly in size, and the local methods with a fixed patch size are unable to extract features of the target with the larger size. Hu et al. [158] proposed multi-scale learning to overcome such deficiencies. The network aggregated features from different layers to make the final decision. Similarly, Ying et al. [108] and Tan et al. [108] integrated ResNet or DenseNet with the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) [159], which is a pyramidal hierarchy network structure for multi-scale feature extraction. In addition, the lesion of COVID-19 in the lung is a 3D object, and slice-wise contextual information in CT images would be lost by a conventional 2D feature extractor. Therefore, Zheng et al. [41], Xi et al. [151], Wang et al. [61] and Chih-Chung Hsu et al.[78] proposed CNN structures with 3D convolution units to detect COVID-19 to solve this defect. Han et al. [160] proposed an Attention-based Deep 3D Multiple Instance Learning (AD3D-MIL) algorithm that can predict the infection according to multiple CT slices. Compared to conventional 2D methods that predict the infection according to a single CT slice, 3D methods can make the diagnosis more accurate. In addition, some researchers also proposed some methods for the post-processing of the extracted features. For example, [151] used PCA to find the most influential features, and Jin et al [154] used the ReliefF algorithm to rank the extracted features.
In practice, radiologists also need to consider information such as epidemiology and clinical manifestations for diagnosis. Therefore, some methods also combine auxiliary external information with visual features to improve the model. Wang et al. [161] combine clinical features, including age, sex and co-morbidity, with CNN features. Similarly, since the infected area usually lies near the edge of the lung, Xu et al. additionally provided the distance-from-edge information [107] of the local patch to the network. Shi et al. [162] and Sun et al. [163] calculated human-designed features, including using the volume, infection lesion number, histogram distribution, surface area and radionics information.
3.1.4. Classification
Classification is used to present a diagnosing prediction (such as COVID-19/non-COVID-19) according to the extracted feature. Most existing COVID-19 diagnosing models use CNN as the feature extractor, and most of them use softmax as the classifier. Some researchers proposed improvements based on the CNN-softmax scheme. For example, Wang et al. [1] combined softmax, decision tree and Adaboost algorithms, and Zhang et al. [113] simultaneously performed softmax loss-based classification and contrastive loss-based anomaly detection to make the final decision. However, these deep models are black-box and usually need large-scale training sets. In the literature of [45,109,164], researchers developed non-end-to-end models and took the Support Vector Machine (SVM) as the classifier. Comparative experiments of classification algorithms, including SVM, logistic regression, k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN), Multi-Layer Perception (MLP), decision tree, AdaBoost, random forest, LightGBM [165], and bagging classifier have been carried out in [119,156,162,163]. Among them, classifiers in [119,156] are for visual feature classification, whereas classifiers in [162,163] are for hand-crafted clinical feature classification, in which, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) [166] and deep forest [167] algorithms were used for feature selection.
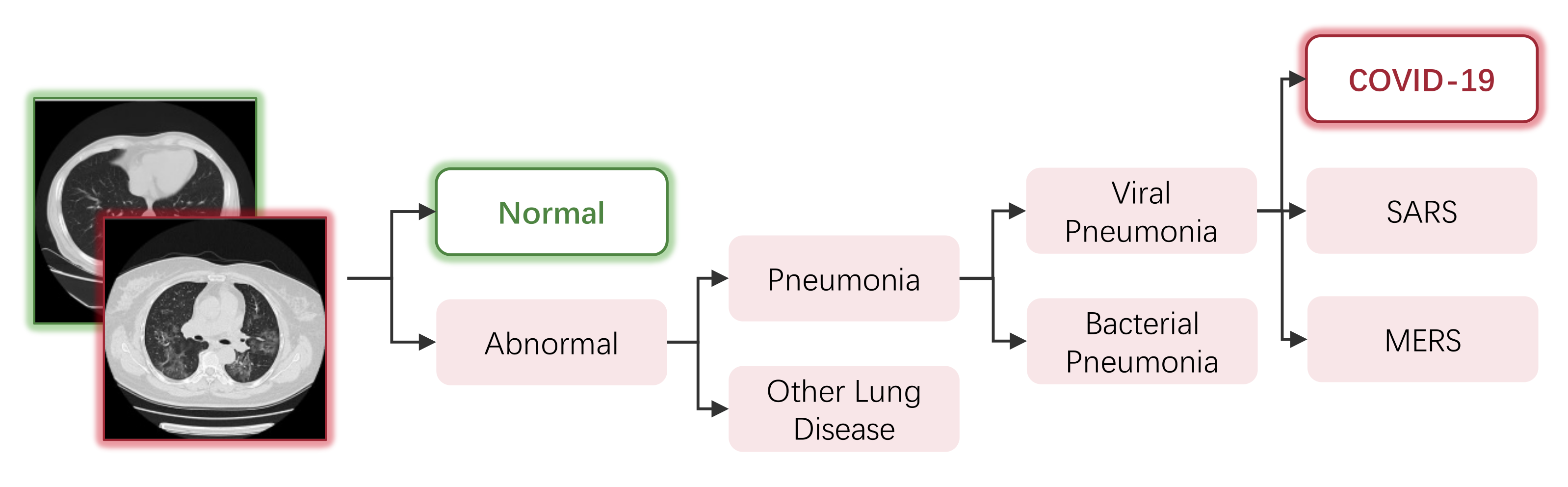
A straightforward way of modeling the COVID-19 diagnosing task into a classification task is through binary classifying the scanning images into a COVID-19 class and normal class; this is adopted by many models [40,41,45,47,49,50,53,54,58,62,65,67,83,110,111,112,113,119,126,138,143,148,150,152,164,168,169,170,171,172,173]. However, in practice, test images of other types of abnormal lungs can be misclassified as COVID-19. As shown in Figure 6, diagnosing COVID-19 is a fine-grained task. Lung diseases that belong to the same subclass share similar patterns in scanning images, and have a chance to be misclassified. Researchers overcome the problem of misclassification mainly through two approaches: multi-class classification and multi-step classification.
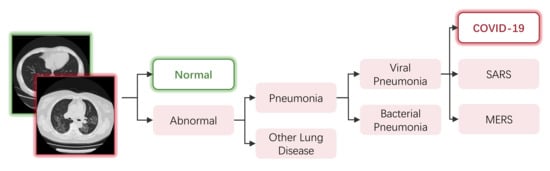
Figure 6.
An example of the hierarchical relationships of different lung diseases.
For multi-class classification, some researchers added other pneumonia categories in addition to the binary classification tasks, such as viral pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) and non-COVID-19 pneumonia. As summarized in Table 5, the classification tasks of COVID-19/normal/viral pneumonia/bacterial pneumonia [44,48,52,74,93,95,114,116,118,122,124,133,155,174,175,176] and COVID-19/non-COVID-19 pneumonia [41,57,66,69,76,79,84,86,94,110,134,135,142,149,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184] are the most popular setting. Some models also take into account other types of lung diseases, including ARDS [46,109], tuberculosis [95,96,185], lung cancer [42,161], pneumocystis, streptococcus, varicella [156], fevers and upper respiratory tract symptoms [117] and Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) caused by other viruses [61].

Table 5.
Classes involved in multi-class classification models. VP: viral pneumonia; BP: bacterial pneumonia; CAP: community-acquired pneumonia; NCP: non-COVID-19 pneumonia.
However, methods of multi-class classification rely heavily on datasets. Meanwhile, the model cannot learn the hierarchical relationships between categories. Multi-step hierarchical classification is used to help the models learn such hierarchical relationships. For example, Eduardo et al. [75] and Yeh et al. [140] trained two binary classifiers: one for normal/pneumonia classification and one for further COVID-19/non-COVID-19 classification. Lv et al. [98] firstly classified the screening image into normal/bacterial pneumonia/viral pneumonia, and then performed the COVID-19/non-COVID-19 classification. Wang et al. [61] optimized the classifier by minimizing a three-task objective function: one for normal/COVID-19 + ILD classification (detection task), one for COVID-19/ILD classification (binary classification task) and one for normal/COVID-19/ILD classification (combined three-category classification task). The above methods manually set up the hierarchical relationships for the models, while Rodolfo et al. [156] proposed automatically learning a decision tree using the state-of-the-art Clus-HMC framework. They also comparatively tested multi-class classification and automatic multi-step classification (hierarchical classification), and they reached the conclusion that the multi-step classification could be a feasible approach to improving the COVID-19 recognition performance.
3.1.5. Evaluation
Researchers evaluated their proposed models with several metrics in experiments. The most used metrics are accuracy and the Area Under Curve (AUC). Accuracy is the ratio of correctly classified samples. AUC is the area under the ROC curve, which is the graph of the function between the true positive rate and false positive rate. The average accuracy and AUC of diagnosing models based on X-ray scanning are 94.76% and 96.94, and the average accuracy and AUC of CT scanning-based models are 90.13% and 94.76. Theoretically, 3D CT scanning contains more information than 2D X-ray scanning, and CT scanning can also avoid the occlusion of ribs compared with X-ray scanning. However, X-ray scanning-based models achieve better performance. We consider the reason for this to be that the large size of X-ray training sets helps these models, whereas CT scanning is relatively more difficult to collect. The average training set size of X-ray-based models is 4185, and the average size of CT-based models is only 1417.
Although the performance of existing models is relatively high (average accuracy of 93.59% and average AUC of 95.75), the size of the test set is worth noting; in some models, the test set only has a few COVID-19 samples. The average COVID-19/total ratio of test sets is 0.274:1, which is highly imbalanced (the ratio of training sets is 0.3:1, which is also imbalanced). In Table 4, we also color the table cells according to the number of samples in the training and testing dataset (green and red are, respectively, corresponding to higher and lower than the average, and the saturation is correlated with the difference from the average). Some researchers reproduced the experiment with different datasets, but achieved a significantly lower performance compared to the originally reported performance [192]. The reason for this might be due to the model overfitting and the lack of appropriate control of patients and ground truth labels. Moreover, models in Table 4 are evaluated in different datasets, and most of them are private datasets of combined datasets. We think a proper benchmark test set is vital for further research of this area. Experiments on the same benchmark test set can also benefit the hospitals’ selection of diagnosing models. In addition, how to combine the accuracy, AUC and other evaluation criteria, such as the precision, recall and time complexity, in order to choose the best model for practical applications is still an open question [193].
3.2. Pixel-Level Diagnosis: Segmentation-Based Models
3.2.1. Overview
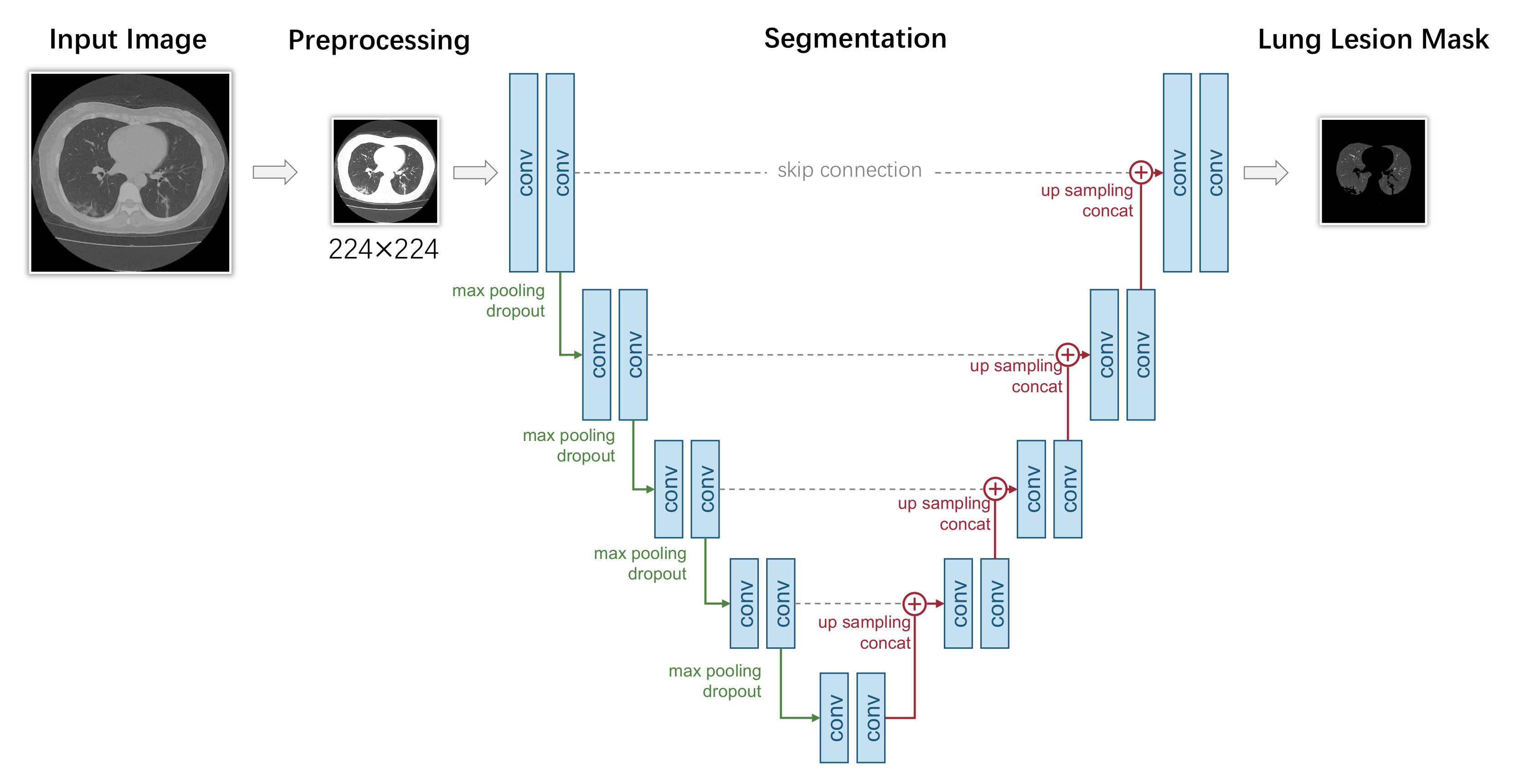
The pixel-level diagnosis of COVID-19 can be formalized as follows: suppose we have a dataset with N samples, where and are the ith input scanning image (CT/X-ray) and the corresponding binary lung lesion annotation. For each pixel of , zero represents the background, whereas one represents a lung lesion instance. The goal here is to learn a function f that predicts from accurately. Similar to classification-based models, the lung lesion detection can be written as , and we expect a low prediction error for each i.
We present a typical segmentation-based COVID-19 diagnosis model in Figure 7. This model uses a U-Net for segmentation, which mainly consists of two parts: an encoder network and a decoder network. The encoder network has four downsample stages with convolution and pooling layers that analyze the contextual pixel information in the image to obtain the semantic feature. In each stage, the input tensor first goes through two convolutional layers with ReLU activation. The output of convolutional layers is max-pooled with a kernel size of , therefore reducing the spatial resolution by a half. Let denote the two convolutional layers, and let represent the max-pooling layer. The L is the total number of stages. The output feature maps of each stage of the encoder E can be formulated as follows:
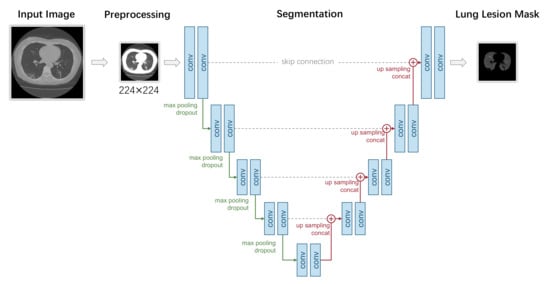
Figure 7.
A typical UNet-segmentation-based pixel-level COVID-19 diagnosis model.
The decoder network consists of four upsample stages. It recovers the same resolution of the given input image. In each stage, a skip connection is built with the corresponding stage in the encoder. The output tensor of the former stage of the decoder is upsampled and concatenated along the channel axis with the output tensor of the same stage of the encoder. The upsampling is performed by conducting nearest interpolation. Then, two convolutions with ReLU activation and the same padding is applied. Let denote the upsampling operation and let the ⊕ represent the concatenate operation; the output tensor of each stage of the decoder D can be formulated as follows:
3.2.2. Preprocessing
Similar to classification-based models, the following preprocessing methods are used during preprocessing: data augmentation and lung segmentation.
Data augmentation, such as random clipping, left-right and up-down flipping, mirroring operation, rotation, scaling, etc. [71,107,123,194], is of vital importance to train the neural network to achieve a high generalizability. In addition to these simple and common methods, Bo et al. [42] used a cubic interpolation approach for image normalization. Chen et al. [194] minimized the influence of various random noises (e.g., words) on the segmentation. To deal with the imbalanced distribution of the sizes of the infection regions between COVID-19 and CAP, Xi et al. [123] developed a dual-sampling strategy to mitigate the imbalanced learning.
As classification-based models, lung segmentation can reduce the interference from the area out of the lung and therefore boost the model performance. Chen et al. [168] trained UNet++ to extract valid areas in CT images. Md et al. [47] employed an inception residual recurrent convolutional neural network with a Transfer Learning (TL) approach for COVID-19 detection and NABLA-N network model for segmenting the regions infected by COVID-19. Shuo et al. [161] used a fully automatic DL model (DenseNet121-FPN) to segment lung areas in the chest CT image. However, they found that some inflammatory tissues attaching to the lung wall may be excluded falsely by the model. In addition, there are also many other lung segmentation methods, such as: VB-Net [123], U-Net [195], ANN [71], FCN-8s, V-Net and 3D U-Net++ [42]. Among them, VB-Net replaces the conventional convolutional layers in the up and down blocks with bottlenecks, and achieves good and efficient segmentation results. U-Net is a fully convolutional network that uses skip connection to fuse the information of multi-resolution layers. V-net uses a volumetric and fully convolutional neural network to achieve three-dimensional image segmentation.
3.2.3. Segmentation
There are two different segmentation tasks in COVID-19 diagnosis models: lung region segmentation and lung lesion segmentation. Lung region segmentation is used to separate the whole lung region from the background, and lung lesion segmentation is used to distinguish the lesion region from other lung regions. The first lung region segmentation is usually performed as a preprocessing step. Here, we only focus on the methods that have been used in lung lesion segmentation.
The V-Net-based segmentation model VNET-IR-RPN17 [107] was trained for pulmonary tuberculosis purposes; it was verified to be good enough to separate candidate patches from viral pneumonia. Md et al. [47] employed an inception residual recurrent convolutional neural network with a transfer learning approach for COVID-19 detection and NABLA-N network model for segmenting the regions infected by COVID-19. Chen et al. [194] used the aggregated residual transformations to learn a robust and expressive feature representation and applied the soft attention mechanism to achieve the automated segmentation of multiple COVID-19 infection regions. Wu et al. [196] trained a JCS system, which includes a segmentation branch that is trained with accurately annotated CT images, performing fine-grained lesion segmentation. Fan et al. [197] proposed a novel COVID-19 Lung Infection Segmentation Deep Network (Inf-Net) that can automatically identify infected regions from chest CT slices. Xi et al. [123] proposed a novel online attention module with a 3D Convolutional Network (CNN) to focus on the infection regions in the lungs when making decisions of diagnoses. Rohit Lokwani et al. [195] built a 2D segmentation model using the U-Net architecture, which gives the output by marking out the region of infection. Gao et al. [198] developed a Dual-branch Combination Network (DCN) for COVID-19 diagnoses that can simultaneously achieve individual-level classification and lesion segmentation. Yang et al. [199] proposed federated semi-supervised learning for COVID region segmentation in 3D chest CT. The framework is designed to leverage unlabeled data for federated learning.
3.2.4. Evaluation
The most commonly used evaluation metrics of the models related to segmentation are the accuracy and Area Under Curve (AUC). The average accuracy and AUC of diagnosing models based on X-ray scanning are 98.74% and 99, and the average accuracy and AUC of CT scanning-based models are 91.68% and 95.37. In fact, compared with X-ray, CT can more deeply examine the lesions in a certain position of an organ. However, here, the models based on X-ray scanning achieve a better performance. We think that there are a couple of reasons for this phenomenon, which are as followed. First, COVID-19 diagnosing models based on segmentation are far fewer than COVID-19 diagnosing models based on classification, and there are fewer models based on X-ray scanning, which makes the result relatively singular. Second, X-ray images are easier to collect than CT images. The average training set size of X-ray-based models is much larger than that of CT-based models, where the former is 3843 and the latter is only 2723.
The performance of existing models related to segmentation is relatively high (average accuracy of 92.97% and average AUC of 95.89). In addition, in the models we have collected, the average COVID-19 images of test sets are 507, and the average total images of test sets are 829, where the average COVID-19/total ratio of test sets is 0.611:1. This ratio is still relatively balanced. Only when the ratio is more balanced can we train a more optimized model. Among them, by comparing MiniSeg with state-of-the-art image segmentation methods, Qiu et al. [200] proved that MiniSeg not only achieves the best performance but also has a high efficiency, where MiniSeg has an accuracy of 99.15%. Wang et al. [42] proposed a “3D Unet++—ResNet-50” combined model, which achieved the best Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.991 among four combined models mentioned in the text. In addition to the accuracy and AUC, sensitivity and specificity are also good evaluation metrics. Sensitivity/specificity measured the fraction of positives/negatives that were correctly identified as positive/negative, so sensitivity/specificity was also known as the true positive/negative rate.
4. Datasets
Having sufficient and high-quality annotated training data is important for the design, implementation and evaluation of COVID-19 diagnosis models. In this section, we discuss existing datasets of COVID-19 scanning images. Table 6 and Table 7 provide overviews of ten classification datasets and five segmentation datasets, respectively, including the size, scanning type, number of COVID-19 samples and total samples, data annotations and other categories besides COVID-19.

Table 6.
Summary of COVID-19 image classification datasets.

Table 7.
Summary of COVID-19 image segmentation datasets.
4.1. Classification Datasets
- SARS-CoV-2 CT-scan Dataset [201]. These data have been collected from real patients in hospitals from Sao Paulo, Brazil. The aim of this dataset is to encourage the research and development of artificial intelligent methods that are able to identify if a person is infected by SARS-CoV-2 through the analysis of his/her CT scans. There are 2482 images in total, including gender information;
- COVID-CT-Dataset [202]. The COVID-CT-Dataset is a radiologist-confirmed CT image dataset. The images are collected from 760 COVID-19-related preprint PDFs in medRxiv and bioRxiv. The labels are decided according to the associated figure captions, while other information, such as age and gender, are also extracted;
- COVID-CT Dataset [63]. This dataset contains the full original CT scans of 377 persons, including other information, such as age and sex. It was gathered from Negin radiology located in Sari, Iran, between 5 March and 23 April 2020. There are 15,589 and 48,260 CT scan images belonging to 95 COVID-19 and 282 normal persons, respectively. The format of the exported radiology images was a 16-bit grayscale DICOM format with a 512 × 512 pixels resolution;
- CT Scans for COVID-19 Classification [203]. Data were collected from two hospitals: Union Hospital (HUST-UH) and Liyuan hospital (HUST-LH). There are a total of 39,370 CT images, and they are in a JPG format with a resolution of 512 × 512;
- Large COVID-19 CT Scan Slice Dataset [204]. The CT images in this dataset are collected from seven public datasets, which include COVID-CT-Dataset, COVID-CT-MD, Covid-Chestxray-Dataset, MosMedData, COVID-19 CT Lung and Infection Segmentation Dataset, COVID-CTset and COVID-19 CT Segmentation Dataset. There are 17,104 images in total, and all of the CAP images are from the dataset of Afshar et al., in which, 25 cases were previously annotated and their radiologist annotated the remaining 35 volumes. The images are in PNG format with a resolution of 512 × 512. The dataset also contains information such as gender, age and country;
- COVIDx Dataset [155]. The COVIDx Dataset is a combined dataset. The X-ray images in the COVIDx Dataset are collected from more than five different data repositories, which include COVID-19 Image Data Collection, COVID-19 Chest X-ray Dataset Initiative, ActualMed COVID-19 Chest X-ray Dataset Initiative, RSNA Pneumonia Detection Challenge dataset and COVID-19 radiography database; therefore, there are 30,882 images in the dataset. However, the COVIDx Dataset is also a highly imbalanced dataset: the positive samples account for only less than 3% of all samples;
- COVID-19 Radiography Database [43]. The COVID-19 Radiography Database is the winner of the COVID-19 Dataset Award of Kaggle. A team of researchers from Qatar University, Doha, Qatar, and the University of Dhaka, Bangladesh, along with their collaborators from Pakistan and Malaysia in collaboration with medical doctors, has created this dataset. The images are mainly collected from the Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology (SIRM) COVID-19 DATABASE and other databases and publications. All of the images are X-ray images, and in PNG format with a resolution of 299 × 299;
- COVID-19 Detection X-ray Dataset [205]. The 5073 X-ray images are collected from Github user ieee8023 for COVID-19 X-rays and Paul Mooney for Pneumonia Dataset. All images are in JPEG format;
- Augmented COVID-19 X-ray Images Dataset [206]. The Augmented COVID-19 X-ray Images Dataset is modified from two datasets, including Covid-Chestxray-Dataset and Chest-Xray-Pneumonia. There are a total of 3532 X-ray images in PNG format. The images are augmented by basic augmentation methods, such as rotating, flipping, scaling and cropping;
- Covid-Chestxray-Dataset [207]. Data were largely compiled from public databases on websites such as Radiopaedia.org, the Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology2 and the Hannover Medical School. Both X-ray and CT images are involved in the COVID-19 X-ray Images Dataset, where 930 images in total are in JPG format. However, 43 of 45 CT images are COVID-19-positive. The imbalance makes it unsuitable to be used alone. This dataset not only consists of the lung bounding box, but is also annotated with other information, such as sex, age, location, survival, etc.
4.2. Segmentation Datasets
- COVID-19 CT Lung and Infection Segmentation Dataset [208]. The CT images in this dataset are collected from five public datasets, which include StructSeg 2019, NSCLC, MSD Lung Tumor, COVID-19-CT-Seg and MosMed. This dataset contains 20 labeled COVID-19 CT scans. Left lung, right lung and infections are labeled by two radiologists and verified by an experienced radiologist;
- COVID-19 CT Segmentation Dataset [209]. 110 axial CT images from 60 patients with COVID-19 are in this dataset, which is segmented by a radiologist. Three types of objects, including ground-glass, consolidation and pleural effusion, are annotated. Ground-glass opacities are in blue, consolidation is in yellow and pleural effusion is in green. The images are in JPG format, while other information, such as age and sex, are also extracted. This dataset is suitable for the training of both the classification model and detection model;
- MOSMEDDATA [210]. A total of 1110 CT images were provided by municipal hospitals in Moscow, Russia. A small subset of studies (n = 50) has been annotated by the experts of the Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Health Care Department. During the annotation, for every given image, ground-glass opacifications and regions of consolidation were selected as positive (white) pixels on the corresponding binary pixel mask. This dataset also includes other information, such as age and gender;
- COVIDGR Dataset [211]. COVIDGR Dataset is a balanced X-ray dataset that covered all levels of severity of illness, from normal with positive RT-PCR, mild and moderate to severe. Data were collected from an expert radiologist team of the Hospital Universitario San Cecilio, and there are 852 X-ray images in total;
- BIMCV COVID-19+ [212]. BIMCV COVID-19+ is a 389.27 GB annotated dataset that consists of both X-ray and CT images. Data were collected from public sources, including COVID-CT-Dataset, COVID-19 dataset and COVID-19 RADIOGRAPHY DATABASE. Data were also collected from some private datasets. There are 23,527 images in total, 23 of which were annotated by a team of expert radiologists. Two types of objects, including ground-glass and consolidation, are annotated. Ground-glass opacities are in green, and consolidation is in purple. Images are stored at a high resolution and entities are localized with anatomical labels in a Medical Imaging Data Structure (MIDS) format. The dataset also contains other information, such as sex, age, diagnostics, survival, etc.
5. Discussion
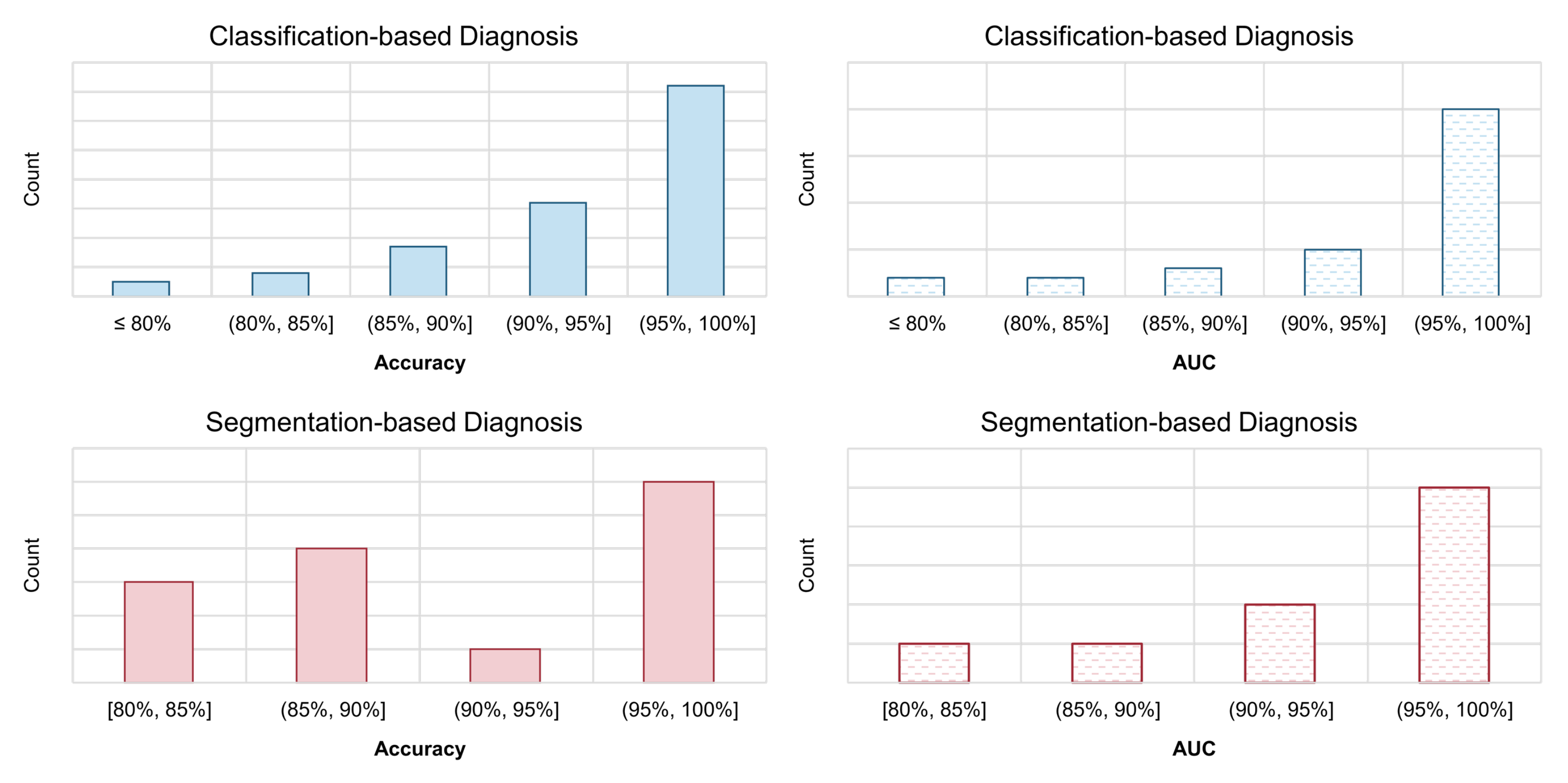
Existing automated COVID-19 diagnosis methods have reported extraordinary performances. To demonstrate this point, we show histograms of these reported model performances in Figure 8. For the two types of the most commonly used evaluation metrics, the accuracy and AUC, we calculate the proportion of them falling within each interval. The histograms are obtained independently for classification-based models and segmentation models. As we can see, the performance reported by most models lies in the range of (95%, 100%], regardless of the type of model (classification or segmentation) and the used metrics (accuracy or AUC). Such a performance surpasses that of human radiologist professionals by a large range. However, after the two-year development in this field, there are still very few models that can be actually applied in the real-world clinical scenario. From this perspective, the academic research of COVID-19 automated diagnosis is not satisfying enough in this COVID-19 pandemic. So, what went wrong? In this section, we summarize the problems that have appeared during the research of applying AI to the automated diagnosis of COVID-19. We hope that if there is a need for emergent AI research and application in the future again, by avoiding these problems, the AI community can perform better next time.
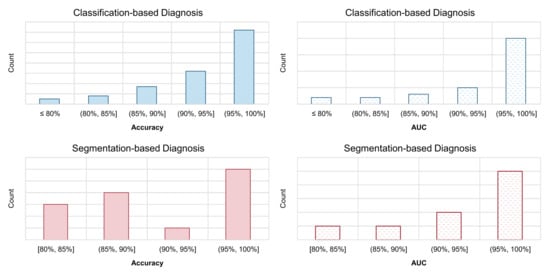
Figure 8.
Histograms of the reported performance of automated diagnosis models for COVID-19. We calculate the proportion of the reported model accuracy and AUC metrics that falls within each interval. The model with very high claimed performance (e.g., >95%) accounts for a high proportion.
5.1. Biased Model Performance Evaluation
We think that the major problem of COVID-19 diagnosis model-related research is the lack of benchmarks. There is not a well-recognized benchmark testing set (e.g., something like ImageNet [213] for image classification, MS-COCO [214] for object detection and Cityscapes [215] for semantic segmentation) that can be used to compare COVID-19 diagnosis models. As a result, different papers used different datasets, making their results not fully comparable. In addition, this problem leads to the appearance of many papers that benchmark existing deep models on different datasets repeatedly. Most importantly, this creates difficulties for researchers in assessing the effectiveness of numerous newly proposed methods.
- Recommendation: Well-recognized institutions should establish benchmarks (using baseline models and a high-quality dataset and releasing reproducible codes) as soon as possible.
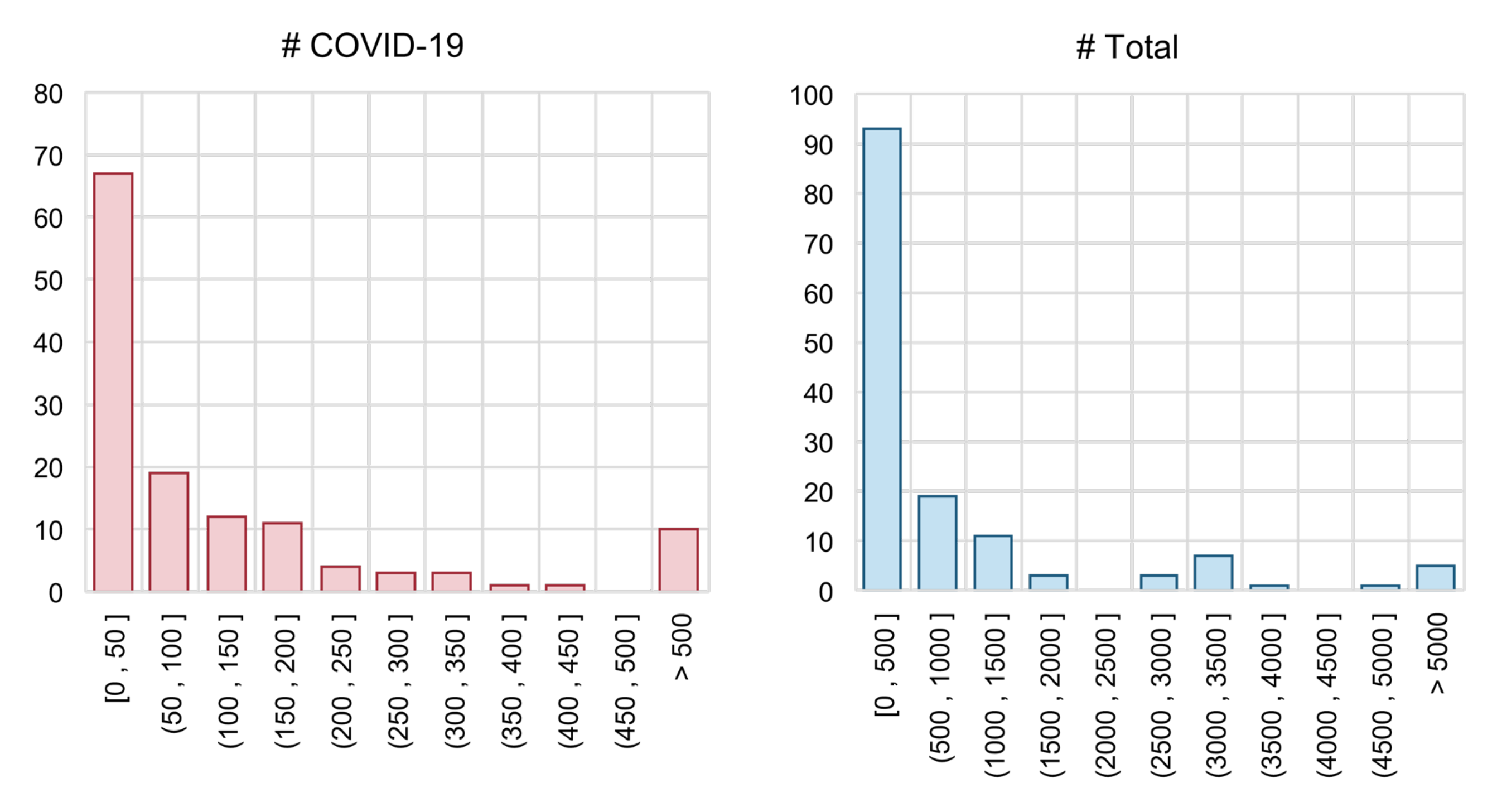
In addition to the problem of lacking a benchmark, each individual performance evaluation report is not fully reliable. Many papers used no validation set (which means that the authors directly tune the hyperparameters on the test set), leading to the problem of data leakage. Moreover, in many studies, the testing set is too small. As in Figure 9, we show the distributions of sample numbers (COVID-19 samples vs. total samples) in the testing set of COVID-19 diagnosis models. For papers that did not explicitly declare the size of the training and test set, we calculate them with the corresponding train–test split ratio. Unfortunately, most studies used a very small testing set: the number of COVID-19 samples of more than 50% studies is smaller than 50. There are even several methods that used fewer than 10 COVID-19 samples to evaluate their methods [111,116,153]. We think this is one of the core reasons for the production of over-optimistic reports.
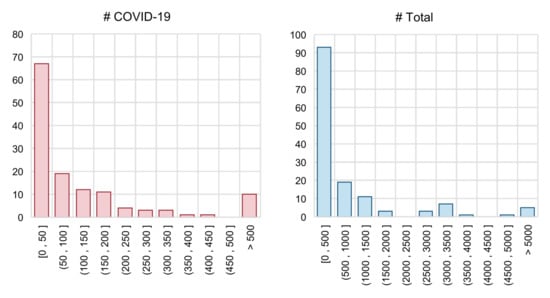
Figure 9.
Histograms of the testing set size. “# COVID-19” = number of samples labelled as COVID-19 positive; “# Total” = total number of sample.
- Recommendation: The testing set should not be used for validation. In addition, the testing set should be sufficiently large; otherwise, it cannot give an accurate estimation of the model performance.
In spite of the scale of COVID-19 diagnosis datasets, their quality is also problematic to some extend. For data acquisition, several datasets are a combination of different datasets, which would lead to potential data leakage and the production of an over-optimistic estimation of the model performance. Some datasets are collected from the figures in the PDF file of published papers, whereas some datasets convert the original DICOM file format into PNG or JPG format. Both of them would lead to a decrease in image quality [9]. Moreover, in many datasets, different classes of samples are collected from different sources, which would lead to a high risk of model bias [11].
- Recommendation: When making a new dataset public, researchers should guarantee its quality and provide as much detailed information as possible.
5.2. Inappropriate Implementation Details
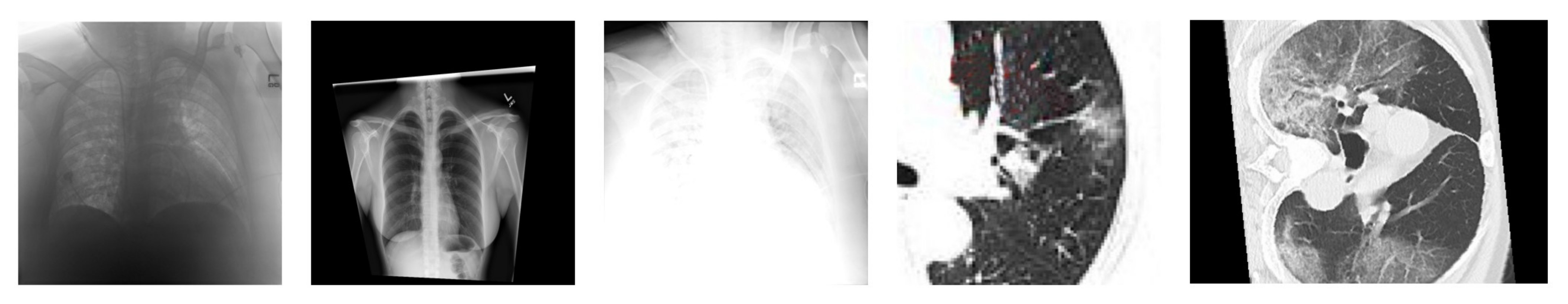
The major issue in the research of the automated diagnosis of COVID-19 is the lack of data, especially in the early stage (e.g., first several month). In addition, many COVID-19 datasets are also highly imbalanced. The most popular solution to such an issue is performing data augmentation. However, as shown in Figure 10, some data augmentation techniques that work well for images of general objects are too aggressive for medical images. In addition, several studies tried to apply GAN-based data augmentation. Modern GANs have achieved impressive performances in generating realistic general images (e.g., objects, faces, etc.), but this does not mean that they naturally become perfect choices for generating COVID-19 images. Moreover, there are few theoretical guarantees about the effectiveness of GAN-based data augmentation in medical images. Many open questions need in-depth investigation.
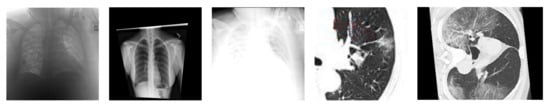
Figure 10.
Some data augmentation techniques that work well for images of general objects are too aggressive for medical images.
- Recommendation: When solving the problem of lacking training data with data augmentation, the ’safety’ of selected data augmentation techniques should be considered.
Another typical solution to the lack of a massive amount of training data is transfer learning. Among existing works, 34 models adopted the transfer learning scheme. They pretrained the CNN on a larger image dataset (mostly on ImageNet), then fine-tuned the model with X-ray or CT scanning images. However, ImageNet contains images of general objects, which make the convolution filters learn some patterns that will not appear in scanning images. Instead, transferring the model that was pretrained on the lung cancer dataset [161] or conventional pneumonia dataset [140] can lead to a better performance.
- Recommendation: When solving the problem of lacking training data with transfer learning, it is better to select the pretraining dataset carefully, or consider using domain adaptation algorithms [169,216].
5.3. Low Reproducibility, Reliability and Explainability
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant progress in the last decade. Open-source deep learning frameworks and public implementations of state-of-the-art methods make the deep learning model able to be easily accessed by the community. If newly designed deep neural network architectures, loss functions and pretrained model weights for COVID-19 diagnosis can be conveniently utilized, then the technical barrier can be lowered and the research cycle can be accelerated. Unfortunately, among our covered 179 studies, only 48 of them provide an official implementation (i.e., 26%). This poses difficulties when researchers came to this field and tried to establish some baselines for comparison.
- Recommendation: If possible, upload clean codes accompanying the posted papers. Prepare easy-to-follow documents that describe how to re-implement the proposed method.
If no official code is released, researchers can also reimplement the proposed methods according to the paper. Unfortunately, a proportion of papers have the problem of missing important implementation details, such as a detailed data preprocessing procedure, neural network architectures, hyperparameter settings, the learning rate, batchsize, number of total epochs, etc. Without these details, other researchers would face a great difficulty in reimplementing and performing a fair comparison. Moreover, readers and reviewers cannot identify the potential mistakes without these details.
- Recommendation: authors should provide sufficient technical details of their proposed methods in order to guarantee the reproducibility.
In existing classification-based methods, Class Activation Mapping (CAM) and Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) [217] are adopted by many researchers [40,50,87,95,96,98,110,113,114,115,117,120,137,139,140,155,158,160,169,218] to output heatmaps for explaining the final result and present an intuitive understanding of which area the model is focusing on. Ideally, these heatmaps can provide radiologists with more useful information and further help them. However, we found that most papers only present the output heatmaps, but provide no analysis about them. We think that one possible reason for this is that they lack radiologist experts to analyze the correctness of the heatmaps. As already illustrated in [9], working as a multidisciplinary team and respect of the opinions of clinicians are important in automated COVID-19 diagnosis research. If this is not conducted, some AI researchers could fail to realize the mistakes that were made by the model according to the heatmaps [10].
- Recommendation: Work as a multidisciplinary team. Opinions from domain experts are valuable for evaluating the correctness of AI models.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we review 179 medical imaging-based automatic diagnosis models of COVID-19. We first discuss the two types of input modalities and compare their differences from both a clinical perspective and artificial intelligence perspective. Them, we divide existing methods into classification-based models and segmentation-based models. Universal pipelines are defined for both of them. For each step in the pipeline, we review and analyze the adopted techniques in detail. Furthermore, a total of 10 COVID-19 datasets for classification-based models and a total of 5 datasets for segmentation models are reviewed. Finally, we summarize three significant problems that emerged in the research of the automated diagnosis of COVID-19: a biased model performance evaluation; inappropriate implementation details; and a low reproducibility, reliability and explainability. We hope that, based on our provided corresponding recommendations, AI can play a better role next time.
Funding
This work was partially funded by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under grant No. BK20191298, Research Fund from Science and Technology on Underwater Vehicle Technology Laboratory (2021JCJQ-SYSJJ-LB06905), Water Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province under grant No. 2021072.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wang, S.; Kang, B.; Ma, J.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, M.; Guo, J.; Cai, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. A deep learning algorithm using CT images to screen for Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6096–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemioło, P.; Storman, D.; Orzechowski, P. A Call For Better Methodological Quality Of Reviews On Using Artificial Intelligence For COVID-19 Detection In Medical Imaging—An Umbrella Systematic Review. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, L.; van Calster, B.; Bonten, M.J.; Collins, G.S.; Debray, T.P.A.; de Vos, M.; Haller, M.C.; Heinze, G.; Moons, K.G.M.; Riley, R.D.; et al. Systematic review and critical appraisal of prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 infection. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, L.; van Calster, B.; Bonten, M.J.; Collins, G.S.; Debray, T.P.A.; de Vos, M.; Haller, M.C.; Heinze, G.; Moons, K.G.M.; Riley, R.D.; et al. Prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of covid-19: Systematic review and critical appraisal. BMJ 2020, 369, m1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Wolff, R.; Riley, R.D.; Whiting, P.F.; Westwood, M.E.; Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Kleijnen, J.; Mallett, S. PROBAST: A Tool to Assess Risk of Bias and Applicability of Prediction Model Studies: Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, W1–W33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Summers, R.M. Artificial Intelligence of COVID-19 Imaging: A Hammer in Search of a Nail. Radiology 2020, 298, E162–E164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Driggs, D.; Thorpe, M.; Gilbey, J.D.; Yeung, M.; Ursprung, S.; Avilés-Rivero, A.I.; Etmann, C.; McCague, C.; Beer, L.; et al. Common pitfalls and recommendations for using machine learning to detect and prognosticate for COVID-19 using chest radiographs and CT scans. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Beymer, D.J.; Rajan, D.; Coy, A.; Mukherjee, V.V.; Manica, M.; Prasanna, P.; Ballah, D.; Guindy, M.; Shaham, D.; et al. On the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging of COVID-19. medRxiv 2020, 2, 10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driggs, D.; Selby, I.; Roberts, M.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Rudd, J.H.F.; Yang, G.; Babar, J.L.; Sala, E.; Schönlieb, C.B. Machine Learning for COVID-19 Diagnosis and Prognostication: Lessons for Amplifying the Signal While Reducing the Noise. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e210011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewska, W.; Bombinski, P.; Szatkowski, P.; Tomaszewska, P.; Przelaskowski, A.; Biecek, P. Checklist for responsible deep learning modeling of medical images based on COVID-19 detection studies. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 118, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, B.G.S.; Bossa, M.N.; Sölter, J.; Husch, A.D. Public Covid-19 X-ray datasets and their impact on model bias—A systematic review of a significant problem. medRxiv 2021, 74, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ji, S.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. A Review of Automated Diagnosis of COVID-19 Based on Scanning Images. In Proceedings of the ICRAI 2020: 6th International Conference on Robotics and Artificial Intelligence, Singapore, 20–22 November 2020; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.; Luccioni, A.S.; Pham, K.H.; Lam, C.S.N.; Luengo-Oroz, M.A. Mapping the landscape of Artificial Intelligence applications against COVID-19. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2020, 69, 807–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T. Artificial Intelligence in the Battle against Coronavirus (COVID-19): A Survey and Future Research Directions. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.07343. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, M.; Rehman, H.; Naït-Ali, A. Detection of Covid-19 From Chest X-ray Images Using Artificial Intelligence: An Early Review. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05436. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Tang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Gong, L.; Lu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liao, H.; Chen, F.; Yang, F.; et al. The Role of Imaging in the Detection and Management of COVID-19: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 14, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Bansal, A. Novel coronavirus (COVID-19) diagnosis using computer vision and artificial intelligence techniques: A review. Multim. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 19931–19946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Inan, T.T.; Rafi, S.; Akter, S.S.; Sarker, I.H.; Islam, A.K.M.N. A Survey on the Use of AI and ML for Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.07449. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, C.; Lacki, M.; Sainsbury, B.; Henry, J.; Filippov, M.; Rossa, C. Sonographic Diagnosis of COVID-19: A Review of Image Processing for Lung Ultrasound. Front. Big Data 2021, 4, 612561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, G. Survey of the Detection and Classification of Pulmonary Lesions via CT and X-ray. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15442. [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi, S.; Ejmalian, A.; Moghaddam, M.E.; Abin, A.A.; Frangi, A.F.; Mohammadi, M.; Rad, H.S. Medical imaging and computational image analysis in COVID-19 diagnosis: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, W.; Narin, A. Deep neural networks for COVID-19 detection and diagnosis using images and acoustic-based techniques: A recent review. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 15345–15362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, M.R.H.; Bharati, S.; Podder, P. Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: A review. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.14910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, T.; qing Wang, Y.; ping Wang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Huang, T.B.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.P. COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Egli-Gany, D.; Counotte, M.J.; Hossmann, S.; Imeri, H.; Ipekci, A.M.; Salanti, G.; Low, N. Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Medicine 2020, 17, e1003346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byambasuren, O.; Cardona, M.; Bell, K.J.L.; Clark, J.; McLaws, M.L.; Glasziou, P.P. Estimating the extent of asymptomatic COVID-19 and its potential for community transmission: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Off. J. Assoc. Med. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Can. 2020, 5, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, A.M.; Lancaster, J. Asymptomatic transmission of covid-19. BMJ 2020, 371, m4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahamtan, A.; Ardebili, A. Real-time RT-PCR in COVID-19 detection: Issues affecting the results. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, C.; Wang, F.; jing Liu, J. Chest CT for Typical 2019-nCoV Pneumonia: Relationship to Negative RT-PCR Testing. Radiology 2020, 296, 1315–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwee, T.C.; Kwee, R.M. Chest CT in COVID-19: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Lin, M.; Ying, L.; Pang, P.; Ji, W.B. Sensitivity of Chest CT for COVID-19: Comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020, 296, E115–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousan, L.A.; Elobeid, E.; Karrar, M.; Khader, Y.S. Chest X-ray findings and temporal lung changes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzi, D.; Albanesi, M.; Cavigli, E.; Moroni, C.; Bindi, A.; Luvarà, S.; Lucarini, S.; Busoni, S.; Mazzoni, L.N.; Miele, V. Chest X-ray in new Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: Findings and correlation with clinical outcome. Radiol. Medica 2020, 125, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhama, K.; Khan, S.; Tiwari, R.; Sircar, S.; Bhat, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, K.P.; Chaicumpa, W.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019—COVID-19. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00028-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, F.; Saatchi, M.; Zadeh, S.S.T.; Aghamir, Z.S.; Shabestari, A.N.; Reis, L.O.; Aghamir, S.M.K. A meta-analysis of accuracy and sensitivity of chest CT and RT-PCR in COVID-19 diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borakati, A.; Perera, A.; Johnson, J.; Sood, T. Diagnostic accuracy of X-ray versus CT in COVID-19: A propensity-matched database study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of Convolutional Neural Networks: Analysis, Applications, and Prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozes, O.; Frid-Adar, M.; Greenspan, H.; Browning, P.D.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W.B.; Bernheim, A.; Siegel, E. Rapid AI Development Cycle for the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic: Initial Results for Automated Detection & Patient Monitoring using Deep Learning CT Image Analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.05037. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Deng, X.; Fu, Q.; feng Zhou, Q.; Feng, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Deep Learning-based Detection for COVID-19 from Chest CT using Weak Label. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Luo, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, W.; Hou, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; et al. AI-assisted CT imaging analysis for COVID-19 screening: Building and deploying a medical AI system in four weeks. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al-Emadi, N.; et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, P.; Heidarian, S.; Naderkhani, F.; Oikonomou, A.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Mohammadi, A. COVID-CAPS: A capsule network-based framework for identification of COVID-19 cases from X-ray images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkaya, U.; Öztürk, S.; Barstugan, M. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Classification using Deep Features Fusion and Ranking Technique. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03698. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, D.; Hassanien, A.E.; Ella, H.A. GSA-DenseNet121-COVID-19: A Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 Disease based on Gravitational Search Optimization Algorithm. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05084. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M.S.; Nasrin, M.S.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. COVID_MTNet: COVID-19 Detection with Multi-Task Deep Learning Approaches. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03747. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Kafieh, R.; Sonka, M.; Yazdani, S.; Soufi, G.J. Deep-COVID: Predicting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 65, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsinelli, M.; Cinque, L.; Placidi, G. A light CNN for detecting COVID-19 from CT scans of the chest. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 140, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, B.D.; Jaskolski, C.; Zhong, C.; Asmani, H. Intra-model Variability in COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.02167. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaç, M.; Ahishali, M.; Degerli, A.; Kiranyaz, S.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Gabbouj, M. Convolutional Sparse Support Estimator-Based COVID-19 Recognition From X-ray Images. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Jeon, S.; Lee, S.; Managuli, R.; Kim, C. Multi-Channel Transfer Learning of Chest X-ray Images for Screening of COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.05576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, L.; Zhou, T.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y. Momentum contrastive learning for few-shot COVID-19 diagnosis from chest CT images. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 113, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M.; Noguchi, S.; Matsuo, H.; Murakami, T. Automatic classification between COVID-19 pneumonia, non-COVID-19 pneumonia, and the healthy on chest X-ray image: Combination of data augmentation methods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Arora, R.; Bansal, V.; Sahayasheela, V.J.; Buckchash, H.; Imran, J.; Narayanan, N.; Pandian, G.N.; Raman, B. Accurate Prediction of COVID-19 using Chest X-ray Images through Deep Feature Learning model with SMOTE and Machine Learning Classifiers. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, N.E.M.; Taha, M.H.N.; Hassanien, A.E.; Elghamrawy, S.M. Detection of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Associated Pneumonia based on Generative Adversarial Networks and a Fine-Tuned Deep Transfer Learning Model using Chest X-ray Dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.01184. [Google Scholar]
- Mobiny, A.; Cicalese, P.A.; Zare, S.; Yuan, P.; Abavisani, M.; Wu, C.C.; Ahuja, J.; de Groot, P.M.; Nguyen, H.V. Radiologist-Level COVID-19 Detection Using CT Scans with Detail-Oriented Capsule Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.07407. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Bao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Lu, H.; Luo, H.; Xiang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Qian, D. Prior-Attention Residual Learning for More Discriminative COVID-19 Screening in CT Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, A.M.; Şengür, A. Deep learning approaches for COVID-19 detection based on chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 164, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A.; Sakhaei, S.M. A fully automated deep learning-based network for detecting COVID-19 from a new and large lung CT scan dataset. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.K.A.; Cömert, Z.; Polat, K. A Novel Medical Diagnosis model for COVID-19 infection detection based on Deep Features and Bayesian Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Gianchandani, N.; Singh, D.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M. Classification of the COVID-19 infected patients using DenseNet201 based deep transfer learning. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 5682–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifani, P.; Shalbaf, A.; Vafaeezadeh, M. Automated detection of COVID-19 using ensemble of transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network based on CT scans. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 16, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglione, E.; Barbano, C.A.; Berzovini, C.; Calandri, M.; Grangetto, M. Unveiling COVID-19 from CHEST X-ray with Deep Learning: A Hurdles Race with Small Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakanis, S.; Leontidis, G. Lightweight deep learning models for detecting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 130, 104181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaudt, D.; Kloth, C.; Spaete, C.; Hinteregger, A.; Beer, M.; von Schwerin, R. Improving COVID-19 CXR Detection with Synthetic Data Augmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.07529. [Google Scholar]
- Trinh, Q.H.; Nguyen, M.L. Custom Deep Neural Network for 3D Covid Chest CT-scan Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.01456. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, M.F.; Unlersen, M.F.; Sabanci, K.; Durdu, A. CNN-based transfer learning–BiLSTM network: A novel approach for COVID-19 infection detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 98, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, A.; Kontopoulos, I.; Tserpes, K. COVID-19 detection from chest X-ray images using Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Xu, X.; Zheng, T.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Cui, X. DenseCapsNet: Detection of COVID-19 from X-ray images using a capsule neural network✩. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Khan, M.U.G.; Javed, K. Deep learning model for distinguishing novel coronavirus from other chest related infections in X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, E.; Silva, P.; Silva, R.; Silva, L.; Guimarães, J.; Miozzo, G.; Menotti, D. Towards an effective and efficient deep learning model for COVID-19 patterns detection in X-ray images. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; shan Zhang, Y.; Xing, E.P.; Xie, P. Sample-Efficient Deep Learning for COVID-19 Diagnosis Based on CT Scans. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chen, G.L.; Wu, M.H. Visual Transformer with Statistical Test for COVID-19 Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.05334. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. 3D RegNet: Deep Learning Model for COVID-19 Diagnosis on Chest CT Image. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.04055. [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.P.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention Gated Networks: Learning to Leverage Salient Regions in Medical Images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monshi, M.M.A.; Poon, J.; Chung, Y.Y.; Monshi, F.M. CovidXrayNet: Optimizing data augmentation and CNN hyperparameters for improved COVID-19 detection from CXR. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y. Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Diagnose COVID-19 From Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.09695. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, S.R.; Nayak, D.R.; Sinha, U.; Arora, V.; Pachori, R.B. Application of deep learning techniques for detection of COVID-19 cases using chest X-ray images: A comprehensive study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 64, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Kanafi, A.R.; Acharya, U.R.; Khadem, N.; Mohammadi, A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguolo, G.; Nanni, L. A critic evaluation of methods for COVID-19 automatic detection from X-ray images. Int. J. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, P.; Dai, L.; Yang, Y.; Xie, P.; Tan, Y.X.; Du, J.; Shan, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhong, Q.; et al. Assisting Scalable Diagnosis Automatically via CT Images in the Combat against COVID-19. medRxiv 2020, 11, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Distinguishes COVID-19 from Community Acquired Pneumonia on Chest CT. Radiology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atitallah, S.B.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W.; Gh’ezala, H.B. Randomly initialized convolutional neural network for the recognition of COVID-19 using X-ray images. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 32, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, A.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Ren, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.; Buch, V.; Neumark, N.; Bizzo, B.C.; Tak, W.Y.; et al. Deep metric learning-based image retrieval system for chest radiograph and its clinical applications in COVID-19. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, M.; Pisov, M.; Shevtsov, A.; Shirokikh, B.; Kurmukov, A.; Blokhin, I.A.; Chernina, V.Y.; Solovev, A.V.; Gombolevskiy, V.A.; Morozov, S.P.; et al. CT-Based COVID-19 triage: Deep multitask learning improves joint identification and severity quantification. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 71, 102054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyar, A.; Modzelewski, R.; Li, H.; Ruan, S. Multi-task deep learning based CT imaging analysis for COVID-19 pneumonia: Classification and segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammulle, H.; Fernando, T.; Sridharan, S.; Denman, S.; Fookes, C. Multi-Slice Net: A Novel Light Weight Framework for COVID-19 Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Systems (ICAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–13 August 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Sobeih, T.; Han, L.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.C.; Lechareas, S.; Tridente, A.; Chen, H.; White, S. CXR-Net: An Encoder-Decoder-Encoder Multitask Deep Neural Network for Explainable and Accurate Diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia with Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.10813. [Google Scholar]
- Henna, S.; Reji, A.P. A Data Augmented Approach to Transfer Learning for Covid-19 Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.02870. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.R.; Döhmen, T.; Rebholz-Schuhmann, D.; Decker, S.; Cochez, M.; Beyan, O. DeepCOVIDExplainer: Explainable COVID-19 Predictions Based on Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.04582. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Ye, J.C. Deep Learning COVID-19 Features on CXR Using Limited Training Data Sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalaveni, V.; Rajalakshmi, R.; Narayanankutty, K.A. Image Denoising Using Variations of Perona-Malik Model with Different Edge Stopping Functions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 58, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, D.; Qi, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y. A cascade network for Detecting COVID-19 using chest X-rays. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.01468. [Google Scholar]
- Siddhartha, M.; Santra, A. COVIDLite: A depth-wise separable deep neural network with white balance and CLAHE for detection of COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13873. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.E.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Han, S.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <1MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2012, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, S.; Frosst, N.; Hinton, G.E. Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.09829. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Ma, C.; Du, P.; Li, X.; Lv, S.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Su, J.; Lang, G.; et al. Deep Learning System to Screen Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.09334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Jie, Y.; Wang, R.; Chong, Y.; et al. Deep learning Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT images. medRxiv 2020, 18, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethy, P.K.; Behera, S.K.; Ratha, P.K.; Biswas, P. Detection of coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) based on Deep Features and Support Vector Machine. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Chen, W.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, J.; Shi, H.; Feng, J. Development and Evaluation of an AI System for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemdan, E.E.D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. COVIDX-Net: A Framework of Deep Learning Classifiers to Diagnose COVID-19 in X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, C.; Xia, Y. COVID-19 Screening on Chest X-ray Images Using Deep Learning based Anomaly Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12338. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, B.; Tucker, A. Estimating Uncertainty and Interpretability in Deep Learning for Coronavirus (COVID-19) Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10769. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.; Yi, S.L.; Zeng, Y.L.; Ye, F.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Ren, Y.D.; Luo, L.; Pan, J.S.; Zhang, Q. Deep Learning-Based Recognizing COVID-19 and other Common Infectious Diseases of the Lung by Chest CT Scan Images. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, M.; Hafeez, A. COVID-ResNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Screening of COVID19 from Radiographs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.14395. [Google Scholar]
- Gozes, O.; Frid-Adar, M.; Sagie, N.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W.; Greenspan, H. Coronavirus Detection and Analysis on Chest CT with Deep Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02640. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L.O.; Paul, R.; Goldgof, D.B.; Goldgof, G.M. Finding Covid-19 from Chest X-rays using Deep Learning on a Small Dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02060. [Google Scholar]
- Kassani, S.H.; Kassani, P.H.; Wesolowski, M.J.; Schneider, K.A.; Deters, R. Automatic Detection of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in X-ray and CT Images: A Machine Learning Based Approach. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punn, N.S.; Agarwal, S. Automated diagnosis of COVID-19 with limited posteroanterior chest X-ray images using fine-tuned deep neural networks. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 2689–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A New Modified Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting COVID-19 from X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08052. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Han, Z.; Wei, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hong, Y.; Cong, J. Robust Screening of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray via Discriminative Cost-Sensitive Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12592. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, X.; Huo, J.; Xia, L.; Shan, F.; Liu, J.; Mo, Z.; Yan, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, Q.; Song, B.; et al. Dual-Sampling Attention Network for Diagnosis of COVID-19 From Community Acquired Pneumonia. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Saad, F.; Sarasaen, C.; Ghosh, S.; Khatun, R.; Radeva, P.; Rose, G.; Stober, S.; Speck, O.; Nürnberger, A. Exploration of Interpretability Techniques for Deep COVID-19 Classification using Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.02570. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, A.; Saeedi, M.; Maghsoudi, A. A Novel and Reliable Deep Learning Web-Based Tool to Detect COVID-19 Infection from Chest CT-Scan. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.14419. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsi, A.; Asgharnezhad, H.; Jokandan, S.S.; Khosravi, A.; Kebria, P.M.; Nahavandi, D.; Nahavandi, S.; Srinivasan, D. An Uncertainty-Aware Transfer Learning-Based Framework for COVID-19 Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lu, H.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, S.; qiang Huo, B.; Dong, Y. The ensemble deep learning model for novel COVID-19 on CT images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 98, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hui, H.; Niu, M.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; He, B.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Tian, J.; et al. Deep learning-based multi-view fusion model for screening 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia: A multicentre study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 128, 109041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horry, M.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Paul, M.; Ulhaq, A.; Pradhan, B.; Saha, M.; Shukla, N. X-ray Image based COVID-19 Detection using Pre-trained Deep Learning Models. 2020. Available online: https://engrxiv.org/index.php/engrxiv/preprint/view/937 (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Bukhari, S.U.K.; Bukhari, S.U.K.; Syed, A.; Shah, S.S.H. The diagnostic evaluation of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for the assessment of chest X-ray of patients infected with COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutounet-Cartan, P.G.B. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Diagnose COVID-19 and other Pneumonia Diseases from Posteroanterior Chest X-rays. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00845. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemi, N.; Shoeibi, A.; Khodatars, M.; Heras, J.; Rahimi, A.; Zare, A.; Pachori, R.B.; Górriz, J.M. Automatic Diagnosis of COVID-19 from CT Images using CycleGAN and Transfer Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.11949. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiser, F.A.; da Costa, C.A.; de Oliveira Ramos, G.; Bohn, H.C.; dos Santos, I.H.F.; da Rosa Righi, R. Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Networks for COVID-19 Classification on Chest X-rays. In Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, T. COVID19 Diagnosis using AutoML from 3D CT scans. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Virtual Conference, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Arsenos, A.; Soukissian, L.; Kollias, S.D. MIA-COV19D: COVID-19 Detection through 3-D Chest CT Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Virtual Conference, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Bessiana, T. Covid-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing Transfer Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajaraman, S.; Siegelman, J.; Alderson, P.O.; Folio, L.S.; Folio, L.R.; Antani, S.K. Iteratively Pruned Deep Learning Ensembles for COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-rays. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115041–115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonz’alez, G.; Bustos, A.; Salinas, J.M.; de la Iglesia-Vayá, M.; Galant, J.; Cano-Espinosa, C.; Barber, X.; Orozco-Beltr’an, D.; Cazorla, M.; Pertusa, A. UMLS-ChestNet: A deep convolutional neural network for radiological findings, differential diagnoses and localizations of COVID-19 in chest X-rays. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.05274. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, D. COVID-MobileXpert: On-Device COVID-19 Screening using Snapshots of Chest X-ray. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03042. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.F.; Cheng, H.T.; Wei, A.; Liu, K.C.; Ko, M.C.; Kuo, P.C.; Chen, R.J.; Lee, P.C.; Chuang, J.H.; Chen, C.M.; et al. A Cascaded Learning Strategy for Robust COVID-19 Pneumonia Chest X-ray Screening. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12786. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Guo, H. Data Augmentation and CNN Classification For Automatic COVID-19 Diagnosis From CT-Scan Images On Small Dataset. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07148. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Qian, Y.; Gao, A. COVID-VIT: Classification of COVID-19 from CT chest images based on vision transformer models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.01682. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiri, H.; Alavi, S.A. A novel framework based on deep learning and ANOVA feature selection method for diagnosis of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.06340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, M.; Mirniaharikandehei, S.; Khuzani, A.Z.; Danala, G.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, B. Improving the performance of CNN to predict the likelihood of COVID-19 using chest X-ray images with preprocessing algorithms. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2020, 144, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gour, M.; Jain, S. Stacked Convolutional Neural Network for Diagnosis of COVID-19 Disease from X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13817. [Google Scholar]
- Brunese, L.; Mercaldo, F.; Reginelli, A.; Santone, A. Explainable Deep Learning for Pulmonary Disease and Coronavirus COVID-19 Detection from X-rays. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Keniya, R.; Shridharani, A.; Punjabi, M.; Shah, J.; Mehendale, N.D. Diagnosis of COVID-19 using CT scan images and deep learning techniques. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, S.; Mangalagiri, J.; Galita, J.; Morris, M.; Saboury, B.; Yesha, Y.; Yesha, Y.; Nguyen, P.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Chapman, D. CCS-GAN: COVID-19 CT-scan classification with very few positive training images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.01605. [Google Scholar]
- Teli, M.N. TeliNet: Classifying CT scan images for COVID-19 diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Virtual Conference, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Aznaouridis, S.; Tzani, M. Extracting Possibly Representative COVID-19 Biomarkers from X-ray Images with Deep Learning Approach and Image Data Related to Pulmonary Diseases. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2020, 40, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghdid, H.S.; Asaad, A.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; Sadiq, A.S.; Khan, M.K. Diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia from X-ray and CT images using deep learning and transfer learning algorithms. In Multimodal Image Exploitation and Learning 2021; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Loey, M.; Smarandache, F.; Khalifa, N.E.M. Within the Lack of Chest COVID-19 X-ray Dataset: A Novel Detection Model Based on GAN and Deep Transfer Learning. Symmetry 2020, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, W.; Dong, S.; Dong, C.; Ye, X. Hybrid ensemble model for differential diagnosis between COVID-19 and common viral pneumonia by chest X-ray radiograph. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 131, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.M.; Bertolini, D.; Teixeira, L.O.; Silla, C.N., Jr.; Costa, Y.M.G. COVID-19 identification in chest X-ray images on flat and hierarchical classification scenarios. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 194, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, C.; Kumar, A.; Dubey, S.; Srivastava, V. Efficient Deep Network Architecture for COVID-19 Detection Using Computed Tomography Images. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Gao, Y.; Niu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, X.; Wang, M.; Fang, E.F.; Menpes-Smith, W.; Xia, J.; et al. Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for COVID-19 Infection Detection and Classification From CT Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118869–118883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.B.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S.J. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Wei, B.; Hong, Y.; Li, T.; Cong, J.; Zhu, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, W. Accurate Screening of COVID-19 Using Attention-Based Deep 3D Multiple Instance Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2584–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zha, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Niu, M.; Wang, M.; Qiu, X.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; et al. A Fully Automatic Deep Learning System for COVID-19 Diagnostic and Prognostic Analysis. medRxiv 2020, 56, 2000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Xia, L.; Shan, F.; Wu, D.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Y.; Sui, H.; Shen, D. Large-Scale Screening of COVID-19 from Community Acquired Pneumonia using Infection Size-Aware Classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09860. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Mo, Z.; Yan, F.; Xia, L.; Shan, F.; Ding, Z.; Song, B.; Gao, W.; Shao, W.; Shi, F.; et al. Adaptive Feature Selection Guided Deep Forest for COVID-19 Classification With Chest CT. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.E.; Mahdy, L.N.; Ezzat, K.A.; Elmousalami, H.H.; Ella, H.A. Automatic X-ray COVID-19 Lung Image Classification System based on Multi-Level Thresholding and Support Vector Machine. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. NIPS. 2017. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2017/file/6449f44a102fde848669bdd9eb6b76fa-Paper.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Feng, J. Deep Forest: Towards An Alternative to Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08835. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; lian Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Gong, D.; lin Zhao, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zheng, B.; et al. Deep learning-based model for detecting 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia on high-resolution computed tomography: A prospective study. medRxiv 2020, 10, 19196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Niu, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, P.; Yao, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Tan, M. COVID-DA: Deep Domain Adaptation from Typical Pneumonia to COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.01577. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, X.; Lee, H.C.; Diao, K.; Huang, M.; Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Ma, Y.; Robson, P.M.; Chung, M.S.; et al. Artificial intelligence–enabled rapid diagnosis of patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo e Sousa, A.; Reis, F.; Zerbini, R.; Comba, J.L.D.; Falcão, A.X. CNN Filter Learning from Drawn Markers for the Detection of Suggestive Signs of COVID-19 in CT Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 31 October–4 November 2021; pp. 3169–3172. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.R.; Budka, M. An Automated Approach for Timely Diagnosis and Prognosis of Coronavirus Disease. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.G.; Ye, S. Recognition of COVID-19 Disease Utilizing X-ray Imaging of the Chest Using CNN. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering (iCCECE), Southend, UK, 16–17 August 2021; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.K.; Alam, M.A.; Elahi, M.T.E.; Roy, S.; Wahid, S.R. CVR-Net: A deep convolutional neural network for coronavirus recognition from chest radiography images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.11993. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Fattah, S.A. CovXNet: A multi-dilation convolutional neural network for automatic COVID-19 and other pneumonia detection from chest X-ray images with transferable multi-receptive feature optimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathari, S. Automatic Detection of COVID-19 and Pneumonia from Chest X-ray using Deep Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.09384. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Jing, B.; Wang, Z. SODA: Detecting Covid-19 in Chest X-rays with Semi-supervised Open Set Domain Adaptation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, M.; Esfahanian, P.; Movahed, S.M.S.; Gorgin, S.; Rahmati, D.; Kiani, A.; Nadji, S.A.; Haseli, S.; Hoseinyazdi, M.; Roshandel, J.; et al. ai-corona: Radiologist-Assistant Deep Learning Framework for COVID-19 Diagnosis in Chest CT Scans. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Kumar, V.; Vaishali; Kaur, M. Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, H.; Ghosh, S.; Dhar, A.; Obaidullah, S.M.; Santosh, K.C.; Roy, K. Shallow Convolutional Neural Network for COVID-19 Outbreak Screening Using Chest X-rays. Cogn. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barstugan, M.; Ozkaya, U.; Şaban, Ö. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Classification using CT Images by Machine Learning Methods. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2003.09424. [Google Scholar]
- Morani, K.; Ünay, D. Deep Learning Based Automated COVID-19 Classification from Computed Tomography Images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.11191. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Liu, J. A 3D CNN Network with BERT For Automatic COVID-19 Diagnosis From CT-Scan Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S. A hybrid deep learning framework for Covid-19 detection via 3D Chest CT Images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03904. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Santosh, K.C.; Pal, U. Truncated inception net: COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest X-rays. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonchuk, J.; Prescott, B.; Melanchthon, P.; Singh, R. COVID-19 Pneumonia and Influenza Pneumonia Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.07102. [Google Scholar]
- Ucar, F.; Korkmaz, D. COVIDiagnosis-Net: Deep Bayes-SqueezeNet based diagnosis of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from X-ray images. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Vandenhirtz, J.; Nagy, J.B.; Bacsa, D.; Riley, M. Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-rays using Deep Learning: Comparing COGNEX VisionPro Deep Learning 1.0 Software with Open Source Convolutional Neural Networks. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343414434_Detection_of_COVID-19_from_Chest_X-rays_using_Deep_Learning_Comparing_COGNEX_VisionPro_Deep_Learning_10_Software_with_Open_Source_Convolutional_Neural_Networks (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Miron, R.; Moisii, C.; Dinu, S.A.; Breaban, M. COVID Detection in Chest CTs: Improving the Baseline on COV19-CT-DB. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.04808. [Google Scholar]
- Elghamrawy, S.M.; ell Hassanien, A. Diagnosis and Prediction Model for COVID19 Patients Response to Treatment based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Whale Optimization Algorithm Using CT Images. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Xia, L.; Yan, F.; Wan, Z.; Shi, F.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Wu, D.; Sui, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) With Structured Latent Multi-View Representation Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2606–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Sinha, P.; Purkayastha, S.; Mashhaditafreshi, N.; Tariq, A.; Jeong, J.J.; Trivedi, H.; Gichoya, J.W. Was there COVID-19 back in 2012? Challenge for AI in Diagnosis with Similar Indications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13262. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Abdulkareem, K.H.; Al-Waisy, A.S.; Mostafa, S.A.; Al-Fahdawi, S.; Dinar, A.M.; Alhakami, W.; Baz, A.; Al-Mhiqani, M.N.; Alhakami, H.; et al. Benchmarking Methodology for Selection of Optimal COVID-19 Diagnostic Model Based on Entropy and TOPSIS Methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 99115–99131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y. Residual Attention U-Net for Automated Multi-Class Segmentation of COVID-19 Chest CT Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05645. [Google Scholar]
- Lokwani, R.; Gaikwad, A.; Kulkarni, V.; Pant, A.; Kharat, A. Automated Detection of COVID-19 from CT Scans Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Mei, J.; Xu, J.; Fan, D.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, M. JCS: An Explainable COVID-19 Diagnosis System by Joint Classification and Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3113–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Zhou, T.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.B.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Inf-Net: Automatic COVID-19 Lung Infection Segmentation from CT Scans. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.14133. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.; Su, J.; biao Jiang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Feng, Z.; Shen, H.; Rong, P.; Xu, X.; Qin, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Dual-branch combination network (DCN): Towards accurate diagnosis and lesion segmentation of COVID-19 using CT images. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 67, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Myronenko, A.; Roth, H.R.; Harmon, S.A.; Xu, S.; Turkbey, B.; Turkbey, E.B.; Wang, X.; et al. Federated semi-supervised learning for COVID region segmentation in chest CT using multi-national data from China, Italy, Japan. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J. MiniSeg: An Extremely Minimum Network for Efficient COVID-19 Segmentation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 35, 4846–4854. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, E.A.; Angelov, P.P.; Biaso, S.; Froes, M.H.; Abe, D.K. SARS-CoV-2 CT-scan dataset:A large dataset of real patients CT scans for SARS-CoV-2 identification. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Xie, P. COVID-CT-Dataset: A CT Scan Dataset about COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, W.; Lei, S.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.H.; Geng, Z.; et al. iCTCF: An integrative resource of chest computed tomography images and clinical features of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Res. Square 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maftouni, M.; Law, A.C.C.; Shen, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ayoobi Yazdi, N.; Kong, Z. A Robust Ensemble-Deep Learning Model for COVID-19 Diagnosis based on an Integrated CT Scan Images Database. In IIE Annual Conference; Ayoobi Yazdi, N.; Institute of Industrial and Systems Engineers (IISE): Norcross, Georgia, 2021; pp. 632–637. [Google Scholar]
- Covid-19-Detection-X-ray-Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/darshan1504/covid19-detection-xray-dataset (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Alqudah, A.M. Augmented COVID-19 X-ray Images Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/2fxz4px6d8/4 (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L. COVID-19 Image Data Collection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11597. [Google Scholar]
- COVID-19 CT Lung and Infection Segmentation Dataset. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3757476 (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- COVID-19 CT Segmentation Dataset. 2020. Available online: http://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/ (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Morozov, S.P.; Andreychenko, A.E.; Pavlov, N.A.; Vladzymyrskyy, A.V.; Ledikhova, N.V.; Gombolevsky, V.A.; Blokhin, I.A.; Gelezhe, P.B.; Gonchar, A.V.; Chernina, V.Y. MosMedData: Chest CT Scans with COVID-19 Related Findings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.06465. [Google Scholar]
- Tabik, S.; G’omez-R’ios, A.; Mart’in-Rodr’iguez, J.L.; Sevillano-Garc’ia, I.; Rey-Area, M.; Charte, D.; Guirado, E.; Su’arez, J.L.; Luengo, J.; Valero-Gonz’alez, M.A.; et al. COVIDGR Dataset and COVID-SDNet Methodology for Predicting COVID-19 Based on Chest X-ray Images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Iglesia-Vayá, M.; Saborit, J.M.; Montell, J.A.; Pertusa, A.; Bustos, A.; Cazorla, M.; Galant, J.; Barber, X.; Orozco-Beltrán, D.; García-García, F.; et al. BIMCV COVID-19+: A large annotated dataset of RX and CT images from COVID-19 patients. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.01174. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2009), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.J.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2014—13th European Conference, Proceedings, Part V. Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D.J., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 8693, pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep Visual Domain Adaptation: A Survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Cogswell, M.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Why did you say that? arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.07450. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Mitra, S.; Saha, N. Deep Learning for Screening COVID-19 using Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10507. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).